Please wait
00001008852025FYfalse66.6733.33http://fasb.org/us-gaap/2025#FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberhttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2025#FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberhttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2025#FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberhttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2025#FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberhttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2025#FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberhttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2025#FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberhttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2025#PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAndFinanceLeaseRightOfUseAssetAfterAccumulatedDepreciationAndAmortizationhttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2025#PropertyPlantAndEquipmentAndFinanceLeaseRightOfUseAssetAfterAccumulatedDepreciationAndAmortizationhttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2025#AccountsPayableAndAccruedLiabilitiesCurrenthttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2025#AccountsPayableAndAccruedLiabilitiesCurrenthttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2025#LongTermDebtAndCapitalLeaseObligationsCurrenthttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2025#LongTermDebtAndCapitalLeaseObligationsCurrenthttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2025#LongTermDebtAndCapitalLeaseObligationshttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2025#LongTermDebtAndCapitalLeaseObligationshttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2025#AccountsPayableAndAccruedLiabilitiesCurrent http://fasb.org/us-gaap/2025#OtherLiabilitiesNoncurrenthttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2025#AccountsPayableAndAccruedLiabilitiesCurrent http://fasb.org/us-gaap/2025#OtherLiabilitiesNoncurrenthttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2025#AccountsPayableAndAccruedLiabilitiesCurrent http://fasb.org/us-gaap/2025#OtherLiabilitiesNoncurrenthttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2025#AccountsPayableAndAccruedLiabilitiesCurrenthttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2025#AccountsPayableAndAccruedLiabilitiesCurrenthttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2025#AccountsPayableAndAccruedLiabilitiesCurrent377iso4217:USDxbrli:sharesiso4217:USDxbrli:sharesutr:miunp:segmentxbrli:pureunp:asset_classunp:siteunp:state00001008852025-01-012025-12-3100001008852025-06-3000001008852026-01-300000100885us-gaap:CargoAndFreightMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885us-gaap:CargoAndFreightMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885us-gaap:CargoAndFreightMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885us-gaap:ProductAndServiceOtherMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885us-gaap:ProductAndServiceOtherMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885us-gaap:ProductAndServiceOtherMember2023-01-012023-12-3100001008852024-01-012024-12-3100001008852023-01-012023-12-3100001008852025-12-3100001008852024-12-3100001008852023-12-3100001008852022-12-310000100885stpr:CA2025-01-012025-12-310000100885us-gaap:StateAndLocalTaxJurisdictionOtherMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885us-gaap:StateAndLocalTaxJurisdictionOtherMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885us-gaap:StateAndLocalTaxJurisdictionOtherMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885us-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-12-310000100885us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2022-12-310000100885us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2022-12-310000100885us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2022-12-310000100885us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2022-12-310000100885us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885us-gaap:CommonStockMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885us-gaap:CommonStockMember2023-12-310000100885us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2023-12-310000100885us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2023-12-310000100885us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2023-12-310000100885us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2023-12-310000100885us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885us-gaap:CommonStockMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885us-gaap:CommonStockMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885us-gaap:CommonStockMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885us-gaap:CommonStockMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2025-12-310000100885country:MX2025-01-012025-12-310000100885country:MX2024-01-012024-12-310000100885country:MX2023-01-012023-12-310000100885unp:BulkMemberunp:ReportableSegmentMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885unp:BulkMemberunp:ReportableSegmentMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885unp:BulkMemberunp:ReportableSegmentMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885unp:IndustrialMemberunp:ReportableSegmentMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885unp:IndustrialMemberunp:ReportableSegmentMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885unp:IndustrialMemberunp:ReportableSegmentMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885unp:PremiumMemberunp:ReportableSegmentMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885unp:PremiumMemberunp:ReportableSegmentMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885unp:PremiumMemberunp:ReportableSegmentMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885us-gaap:CargoAndFreightMemberunp:ReportableSegmentMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885us-gaap:CargoAndFreightMemberunp:ReportableSegmentMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885us-gaap:CargoAndFreightMemberunp:ReportableSegmentMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885unp:OtherSubsidiaryRevenuesMemberunp:ReportableSegmentMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885unp:OtherSubsidiaryRevenuesMemberunp:ReportableSegmentMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885unp:OtherSubsidiaryRevenuesMemberunp:ReportableSegmentMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885unp:AccessorialRevenuesMemberunp:ReportableSegmentMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885unp:AccessorialRevenuesMemberunp:ReportableSegmentMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885unp:AccessorialRevenuesMemberunp:ReportableSegmentMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885unp:OtherMiscellaneousProductAndServiceRevenuesMemberunp:ReportableSegmentMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885unp:OtherMiscellaneousProductAndServiceRevenuesMemberunp:ReportableSegmentMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885unp:OtherMiscellaneousProductAndServiceRevenuesMemberunp:ReportableSegmentMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885unp:ReportableSegmentMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885unp:ReportableSegmentMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885unp:ReportableSegmentMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885unp:UnionPacificCorporation2000DirectorsPlanMember2000-04-300000100885unp:UnionPacificCorporation2000DirectorsPlanMember2025-12-310000100885unp:UnionPacificCorporation2013StockIncentivePlanMember2013-05-310000100885unp:UnionPacificCorporation2013StockIncentivePlanMember2025-12-310000100885unp:UnionPacificCorporation2021StockIncentivePlanMember2021-05-310000100885unp:UnionPacificCorporation2021StockIncentivePlanMember2025-12-310000100885unp:UnionPacificCorporation2021EmployeeStockPurchasePlanMember2021-05-310000100885unp:UnionPacificCorporation2021EmployeeStockPurchasePlanMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885unp:RetentionAwardsMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885unp:RetentionAwardsMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885unp:RetentionAwardsMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2025-12-310000100885unp:RetentionAwardsMember2024-12-310000100885unp:RetentionAwardsMember2025-12-310000100885unp:PerformanceStockUnitAwardsMember2025-02-012025-02-280000100885unp:PerformanceStockUnitAwardsMember2024-12-310000100885unp:PerformanceStockUnitAwardsMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885unp:PerformanceStockUnitAwardsMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2025-06-092025-06-090000100885us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2025-06-102025-06-100000100885us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2025-12-310000100885unp:PerformanceStockUnitAwardsMemberus-gaap:ShareBasedCompensationAwardTrancheOneMember2025-02-012025-02-280000100885unp:PerformanceStockUnitAwardsMemberus-gaap:ShareBasedCompensationAwardTrancheTwoMember2025-02-012025-02-280000100885us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2023-12-310000100885us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885us-gaap:QualifiedPlanMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885us-gaap:NonqualifiedPlanMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885us-gaap:QualifiedPlanMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885us-gaap:NonqualifiedPlanMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembersrt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembersrt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembersrt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanDebtSecurityMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembersrt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanDebtSecurityMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanDebtSecurityMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanDebtSecurityMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembersrt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanRealEstateMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembersrt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanRealEstateMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanRealEstateMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanRealEstateMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2024-12-310000100885srt:ScenarioForecastMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2026-01-012026-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:USTreasuryAndGovernmentMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:USTreasuryAndGovernmentMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:USTreasuryAndGovernmentMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:USTreasuryAndGovernmentMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:CorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:CorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:CorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:CorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesCommonStockMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesCommonStockMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesCommonStockMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesCommonStockMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel12And3Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberunp:VentureCapitalAndBuyoutPartnershipsMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:RealEstateFundsMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberunp:CollectiveTrustAndOtherFundsMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberunp:DefinedBenefitPlanOtherAssetsLiabilitiesMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:USTreasuryAndGovernmentMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:USTreasuryAndGovernmentMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:USTreasuryAndGovernmentMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:USTreasuryAndGovernmentMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:CorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:CorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:CorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:CorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesCommonStockMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesCommonStockMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesCommonStockMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesCommonStockMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel12And3Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberunp:VentureCapitalAndBuyoutPartnershipsMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:RealEstateFundsMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberunp:CollectiveTrustAndOtherFundsMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberunp:DefinedBenefitPlanOtherAssetsLiabilitiesMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885unp:FourZeroOneThriftPlanBefore2018Member2025-01-012025-12-310000100885unp:FourZeroOneThriftPlan2018BeyondMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885us-gaap:CollectiveBargainingArrangementOtherMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885us-gaap:CollectiveBargainingArrangementOtherMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885us-gaap:CollectiveBargainingArrangementOtherMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885unp:RealEstateTransactionMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885unp:RealEstateTransactionMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885stpr:KS2025-01-012025-12-310000100885unp:LouisianaAndArkansasMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885unp:NebraskaLowaKansasAndArkansasMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885us-gaap:AccumulatedDefinedBenefitPlansAdjustmentMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:AccumulatedTranslationAdjustmentMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:AccumulatedGainLossNetCashFlowHedgeParentMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:AccumulatedDefinedBenefitPlansAdjustmentMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885us-gaap:AccumulatedTranslationAdjustmentMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885us-gaap:AccumulatedGainLossNetCashFlowHedgeParentMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885us-gaap:AccumulatedDefinedBenefitPlansAdjustmentMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:AccumulatedTranslationAdjustmentMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:AccumulatedGainLossNetCashFlowHedgeParentMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:AccumulatedDefinedBenefitPlansAdjustmentMember2023-12-310000100885us-gaap:AccumulatedTranslationAdjustmentMember2023-12-310000100885us-gaap:AccumulatedGainLossNetCashFlowHedgeParentMember2023-12-310000100885us-gaap:AccumulatedDefinedBenefitPlansAdjustmentMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885us-gaap:AccumulatedTranslationAdjustmentMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885us-gaap:AccumulatedGainLossNetCashFlowHedgeParentMember2024-01-012024-12-3100001008852025-07-2800001008852025-07-282025-07-2800001008852025-07-270000100885us-gaap:AssetBackedSecuritiesSecuritizedLoansAndReceivablesMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885us-gaap:AssetBackedSecuritiesSecuritizedLoansAndReceivablesMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885us-gaap:AssetBackedSecuritiesSecuritizedLoansAndReceivablesMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885us-gaap:LandMember2025-12-310000100885unp:RoadrailAndOtherTrackMaterialMember2025-12-310000100885unp:RoadTiesMember2025-12-310000100885unp:RoadBallastMember2025-12-310000100885unp:RoadOtherMember2025-12-310000100885unp:RoadMember2025-12-310000100885unp:EquipmentLocomotivesMember2025-12-310000100885unp:EquipmentFreightCarsMember2025-12-310000100885unp:EquipmentWorkEquipmentAndOtherMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:EquipmentMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:TechnologyEquipmentMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:ConstructionInProgressMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:LandMember2024-12-310000100885unp:RoadrailAndOtherTrackMaterialMember2024-12-310000100885unp:RoadTiesMember2024-12-310000100885unp:RoadBallastMember2024-12-310000100885unp:RoadOtherMember2024-12-310000100885unp:RoadMember2024-12-310000100885unp:EquipmentLocomotivesMember2024-12-310000100885unp:EquipmentFreightCarsMember2024-12-310000100885unp:EquipmentWorkEquipmentAndOtherMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:EquipmentMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:TechnologyEquipmentMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:ConstructionInProgressMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:OtherExpenseMemberunp:ChassisAssetsMember2024-04-012024-06-300000100885us-gaap:RailroadTransportationEquipmentMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885unp:RailroadTransportationTrackAssetsMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2024-12-310000100885srt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:NotesPayableToBanksMember2025-12-310000100885srt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:NotesPayableToBanksMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:NotesPayableToBanksMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:NotesPayableToBanksMember2024-12-310000100885srt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:EquipmentTrustCertificateMember2025-12-310000100885srt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:EquipmentTrustCertificateMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:EquipmentTrustCertificateMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:EquipmentTrustCertificateMember2024-12-310000100885srt:MinimumMemberunp:FinanceLeaseMember2025-12-310000100885srt:MaximumMemberunp:FinanceLeaseMember2025-12-310000100885unp:FinanceLeaseMember2025-12-310000100885unp:FinanceLeaseMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:EquipmentTrustCertificateMemberunp:RailroadAssetsEquipmentMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:EquipmentTrustCertificateMemberunp:RailroadAssetsEquipmentMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2024-12-310000100885unp:UnsecuredNotesDueFebruary202035Memberus-gaap:UnsecuredDebtMember2025-02-130000100885unp:UnsecuredNotesDueDecember12054Memberus-gaap:UnsecuredDebtMember2025-02-130000100885us-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2025-12-310000100885us-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2024-12-310000100885us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityNotPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2025-12-310000100885srt:MinimumMemberunp:PersonalInjuryMember2025-12-310000100885srt:MaximumMemberunp:PersonalInjuryMember2025-12-310000100885unp:PersonalInjuryMember2024-12-310000100885unp:PersonalInjuryMember2023-12-310000100885unp:PersonalInjuryMember2022-12-310000100885unp:PersonalInjuryMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885unp:PersonalInjuryMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885unp:PersonalInjuryMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885unp:PersonalInjuryMember2025-12-3100001008852025-04-0100001008852025-04-012025-12-3100001008852022-04-0100001008852022-04-012025-03-3100001008852025-01-012025-03-3100001008852024-01-012024-03-3100001008852025-04-012025-06-3000001008852024-04-012024-06-3000001008852025-07-012025-09-3000001008852024-07-012024-09-3000001008852025-10-012025-12-3100001008852024-10-012024-12-310000100885unp:A2025AcceleratedShareRepurchaseMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885unp:A2025AcceleratedShareRepurchaseMember2025-01-012025-03-310000100885unp:A2025AcceleratedShareRepurchaseMember2025-04-012025-06-300000100885unp:A2025AcceleratedShareRepurchaseMember2025-02-182025-02-180000100885unp:TTXCompanyMemberunp:UPRRMember2025-12-310000100885unp:TTXCompanyMemberunp:UPRRMember2024-12-310000100885unp:UPRRMemberus-gaap:EquityMethodInvesteeMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885unp:UPRRMemberus-gaap:EquityMethodInvesteeMember2024-01-012024-12-310000100885unp:UPRRMemberus-gaap:EquityMethodInvesteeMember2023-01-012023-12-310000100885unp:UPRRMemberus-gaap:EquityMethodInvesteeMember2025-12-310000100885unp:UPRRMemberus-gaap:EquityMethodInvesteeMember2024-12-310000100885unp:NorfolkSouthernMember2025-07-280000100885srt:ScenarioForecastMemberunp:NorfolkSouthernMember2027-01-012027-03-310000100885srt:ScenarioForecastMemberunp:NorfolkSouthernMember2027-03-310000100885srt:ScenarioForecastMember2027-03-310000100885unp:PurchasedServicesAndMaterialsMemberunp:NorfolkSouthernMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885unp:OtherAcquisitionRelatedCostsMemberunp:NorfolkSouthernMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885unp:NorfolkSouthernMember2025-01-012025-12-310000100885unp:NorfolkSouthernMember2025-12-310000100885unp:NorfolkSouthernMember2025-07-280000100885unp:EricG.GehringerMember2025-10-012025-12-310000100885unp:EricG.GehringerMember2025-12-31
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One)
☒ ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2025
OR
☐ TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the transition period from __________ to ____________
Commission File Number 1-6075
UNION PACIFIC CORPORATION
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| | | | | | | | |
| Utah | | 13-2626465 |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
| | | | | |
1400 Douglas Street, Omaha, Nebraska | 68179 |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (402) 544-5000
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| | | | | | | | |
| Title of each Class | Trading Symbol | Name of each exchange on which registered |
| Common Stock (Par Value $2.50 per share) | UNP | New York Stock Exchange |
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
☑ Yes ☐ No
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act.
☐ Yes ☑ No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. ☑ Yes ☐ No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). ☑ Yes ☐ No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Large Accelerated Filer | ☑ | Accelerated Filer | ☐ | Non-Accelerated Filer | ☐ |
| Smaller Reporting Company | ☐ | Emerging Growth Company | ☐ | | |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act.
☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. ☑
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant’s executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). ☐Yes ☑ No
As of June 30, 2025, the aggregate market value of the registrant’s Common Stock held by non-affiliates (using the New York Stock Exchange closing price) was $136.1 billion.
The number of shares outstanding of the registrant’s Common Stock as of January 30, 2026, was 593,391,460.
Documents Incorporated by Reference – Portions of the registrant’s definitive Proxy Statement for the Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held on May 14, 2026, are incorporated by reference into Part III of this report. The registrant’s Proxy Statement will be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year that this report relates pursuant to Regulation 14A.
UNION PACIFIC CORPORATION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
February 6, 2026
Fellow Shareholders:
The Union Pacific team continued to build on ‘what’s possible’ in 2025, and we delivered best-ever full year results across safety, service, and operating performance while growing our volumes. These results demonstrate that we are committed to our strategy – Safety, Service, and Operational Excellence leads to Growth – and understand what we need to do to set the Company up for future success. We know success can be measured in many ways, but to us it’s about serving our customers, communities, and employees while driving value to our owners.
In 2025, we reported an 8% increase in earnings per share versus 2024. Total volume increased 1% versus 2024, driven by coal, industrial chemicals and plastics, grain and grain products, and rock shipments, partially offset by weaker demand for automotive and energy and specialized markets shipments. We achieved an operating ratio of 59.8%, a 10-basis point improvement versus 2024. This improvement is the result of the entire team’s commitment to building a safer, more consistent and cost-efficient network, so we can grow with our customers.
Safety is the foundation of everything we do. Our unwavering commitment is for every employee to go home safe, every day. In 2025, we meaningfully improved our personal injury and derailment rates and reported the best safety results in Company history. Additionally, our employee safety results were the best in the industry. These outcomes demonstrate the effectiveness of continued investments in training, safety programs, infrastructure, and technology. Though we are proud of our improvements, we will not waiver on our goal to be the best in safety for our employees and the communities we serve.
Service is what we sold our customers. Our full year operating metrics demonstrate we’ve built a solid foundation, as freight car velocity improved 8% and intermodal and manifest Service Performance Index (SPI) improved 9 and 11 points to 99% and 100%, respectively. We also invested $3.5 billion in capital to harden our infrastructure, modernize older locomotives, grow our business, improve service, and embed new technologies into our processes. We will benefit long-term from our investments in the Kansas City, Inland Empire, and Lathrop intermodal terminals; Texas Gulf Coast manifest terminals; and Pacific Northwest and Southwest main lines; while also modernizing transportation planning systems and providing our customers expanded visibility and self-service tools.
Operational Excellence is about operating efficiently and productively. We drive value with our available resources but also maintain a buffer so our service is resilient, managing the inevitable ups and downs that come with weather, fluctuating volumes, and securing growth. We effectively responded to shifts in business mix throughout 2025 as we handled elevated international intermodal shipments in the first half of the year coupled with strong bulk shipments throughout the year. As customer demand changed and international intermodal volumes declined in the second half of the year, we effectively modified our resources to match demand while improving our service performance. We managed our costs by operating a very efficient network, removing car handlings, and reducing dwell. Our performance in workforce productivity, locomotive productivity, terminal dwell, train length, and fuel consumption was at best-ever levels in 2025.
The execution of our strategy led to Growth in 2025. Operating revenues grew 1% driven by strong core pricing and higher volume, which more than offset business mix, lower fuel surcharge revenues, and reduced other revenues. Excluding the impact of fuel, our freight revenues grew 3%. We remain agile and maintain a buffer of resources, positioning us to respond quickly to demand and win with our customers.
As we start the year in 2026, it’s clear the Union Pacific team is consistently delivering at the highest levels across Safety, Service, and Operational Excellence. Our priority is to continue to improve and run a great railroad. We also have a historic opportunity with Norfolk Southern to create America’s first transcontinental railroad. As we work toward regulatory approval, we are focused on maintaining a strong financial position so we can continue to grow for many years to come.
Thank you for your ownership of Union Pacific.
Chief Executive Officer
DIRECTORS AND SENIOR MANAGEMENT
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| BOARD OF DIRECTORS | | | | |
| | | | |
David B. Dillon Former Chairman and CEO - The Kroger Company Board Committees: Audit; Corporate Governance, Nominating, and Sustainability Sheri H. Edison Former Executive Vice President and General Counsel - Amcor plc Board Committees: Compensation and Talent; Corporate Governance, Nominating, and Sustainability (Chair) Teresa M. Finley Former Chief Marketing and Business Services Officer - United Parcel Service, Inc. Board Committees: Audit; Compensation and Talent
Deborah C. Hopkins Former Chief Executive Officer - Citi Ventures and Former Chief Innovation Officer - Citi Board Committees: Compensation and Talent; Finance (Chair) | | Jane H. Lute Strategic Advisor - SICPA, North America Board Committees: Audit (Chair); Corporate Governance, Nominating, and Sustainability Michael R. McCarthy Chairman - Union Pacific Corporation and Union Pacific Railroad Company; Chairman - McCarthy Group, LLC; and Chairman - Bridges Trust Company Board Committees: Corporate Governance, Nominating, and Sustainability; Finance Doyle R. Simons Former President and CEO - Weyerhaeuser Company Board Committees: Compensation and Talent (Chair); Corporate Governance, Nominating, and Sustainability
John K. Tien, Jr. Former Deputy Secretary - U.S. Department of Homeland Security Board Committees: Audit; Finance | | V. James Vena Chief Executive Officer - Union Pacific Corporation and Union Pacific Railroad Company John P. Wiehoff Former Chairman, President, and CEO - C.H. Robinson Worldwide, Inc. Board Committees: Audit; Compensation and Talent W Anthony Will Former President and CEO - CF Industries Holdings, Inc. Board Committees: Audit; Finance Christopher J. Williams Chairman - Siebert Williams Shank & Co. Board Committees: Corporate Governance, Nominating, and Sustainability; Finance |
| | | | |
| SENIOR MANAGEMENT | | | | |
| | | | |
V. James Vena Chief Executive Officer Christina B. Conlin Executive Vice President, Chief Legal Officer, and Corporate Secretary Chris C. Fairchild Vice President - Tax Eric J. Gehringer Executive Vice President - Operations Rebecca B. Gregory Vice President and Chief of Staff | | Jennifer L. Hamann Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer Rahul Jalali Executive Vice President and Chief Information Officer Michael V. Miller Vice President and Treasurer Joshua K. Perkes Senior Vice President and Chief Human Resources Officer | | Carrie J. Powers Vice President, Controller, and Chief Accounting Officer Kenny G. Rocker Executive Vice President - Marketing and Sales
|
| | | | |
PART I
Item 1. Business
GENERAL
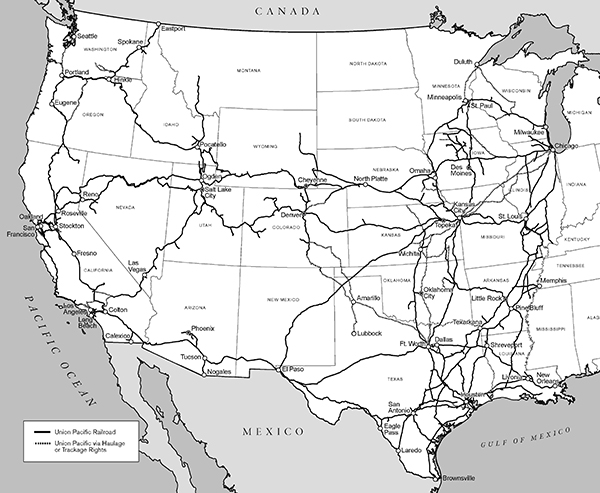
Union Pacific Railroad Company is the principal operating company of Union Pacific Corporation. One of America's most recognized companies, Union Pacific Railroad Company connects 23 states in the western two-thirds of the country by rail, providing a critical link in the global supply chain. The Railroad’s diversified business mix includes Bulk, Industrial, and Premium. Union Pacific serves many of the fastest-growing U.S. population centers, operates from all major West Coast and Gulf Coast ports to Eastern gateways, connects with Canada's rail systems, and is the only railroad serving all six major Mexico gateways. Union Pacific provides value to customers by delivering products in a safe, reliable, fuel-efficient, and environmentally responsible manner.
Union Pacific Corporation was incorporated in Utah in 1969 and maintains its principal executive offices at 1400 Douglas Street, Omaha, NE 68179. The telephone number at that address is (402) 544-5000. The common stock of Union Pacific Corporation is listed on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) under the symbol “UNP”.
For purposes of this report, unless the context otherwise requires, all references herein to "Union Pacific", “UPC”, “Corporation”, “Company”, “we”, “us”, and “our” shall mean Union Pacific Corporation and its subsidiaries, including Union Pacific Railroad Company, which we separately refer to as “UPRR” or the “Railroad”.
STRATEGY
Safety, Service, and Operational Excellence supports the Company's long-term initiative to Grow its freight volumes. Together as a team, the Company will focus on achieving the best safety record in the industry, being known for superior service, grounded in operational excellence, which, in turn, drives growth.
Safety is paramount and, as our first area of focus, sets the foundation for achieving the Company's objectives. The mindset and culture are built around a personal commitment by all employees to prioritize safety so everyone goes home safely.
Service is all about delivering what we sold our customers. We work with our customers to understand the service they need to win in their markets and then drive how we win together. We commit to these service levels and do it with excellence.
Operational Excellence is about operating efficiently and productively. We will drive value with our available resources but also maintain a buffer so our service is resilient, managing the inevitable ups and downs that come with weather, fluctuating volumes, and securing growth.
Growth is the outcome of executing our strategy to be the industry leader in both safety and service resulting in improved margins and greater cash generation, creating long term enterprise value. The expected outcome of successfully executing our strategy will be an industry leading operating ratio and return on invested capital.
As we work to transform our railroad, our core values continue to guide us. Our passion for performance will help us win; our high ethical standards ensure we win in a way that supports all of our stakeholders; and our teamwork ensures we win together.
OPERATIONS
The Railroad, along with its subsidiaries and rail affiliates, is our one reportable operating segment. Although we provide and analyze revenues by commodity group, we treat the financial results of the Railroad as one segment due to the integrated nature of our rail network. Additional information regarding our business and operations, including revenues, financial information and data, and other information regarding environmental matters, is presented in Risk Factors, Item 1A; Legal Proceedings, Item 3; Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations, Item 7; and the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8.
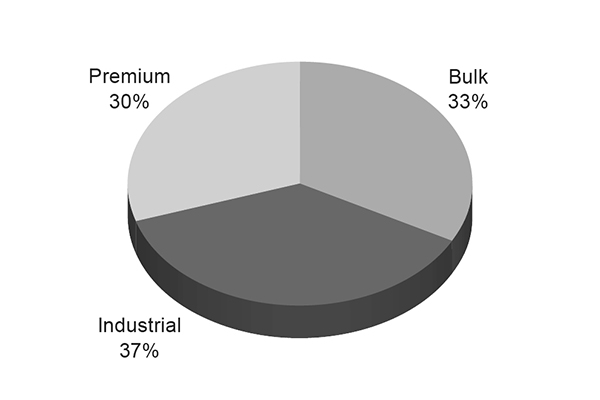
Operations – UPRR is a Class I railroad operating in the U.S. We have 32,889 route miles, connecting Pacific Coast and Gulf Coast ports with the Midwest and Eastern U.S. gateways and providing several corridors to key Mexican and Canadian gateways. We serve the western two-thirds of the country and maintain coordinated schedules with other rail carriers to move freight to and from the Atlantic Coast, the Pacific Coast, the Southeast, the Southwest, Canada, and Mexico. Export and import traffic moves through Gulf Coast, Pacific Coast, and East Coast ports and across the Mexican and Canadian borders. In 2025, we generated freight revenues totaling $23.2 billion from the following three commodity groups:
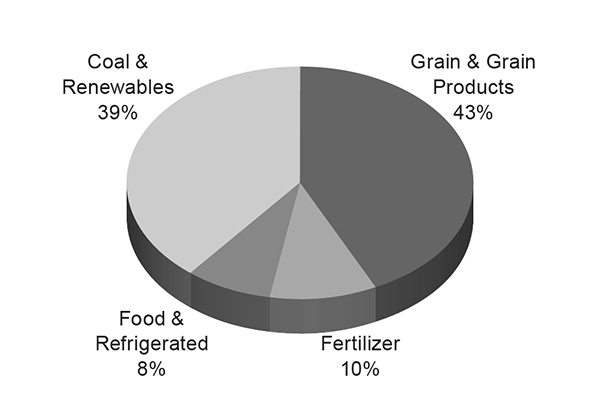
Bulk – The Company's Bulk shipments consist of grain and grain products, fertilizer, food and refrigerated, and coal and renewables. In 2025, this group generated 33% of our freight revenues. We access most major grain markets, connecting the Midwest and Western U.S. producing areas to export terminals in the Pacific Northwest and Gulf Coast ports as well as Mexico. We also serve significant domestic markets, including grain processors, animal feeders, ethanol, and renewable biofuel producers in the Midwest and West. Fertilizer movements originate in the Gulf Coast region, Midwest, Western U.S., and Canada (through interline access) for delivery to major agricultural users in those areas as well as abroad. The Railroad’s network supports the transportation of coal shipments to independent and regulated power companies and industrial facilities throughout the U.S. Through interchange gateways and ports, UPRR’s reach extends to Eastern U.S. utilities as well as to Mexico and other international destinations. Coal traffic originating in the Powder River Basin (PRB) area of Wyoming is the largest portion of the Railroad’s coal business.
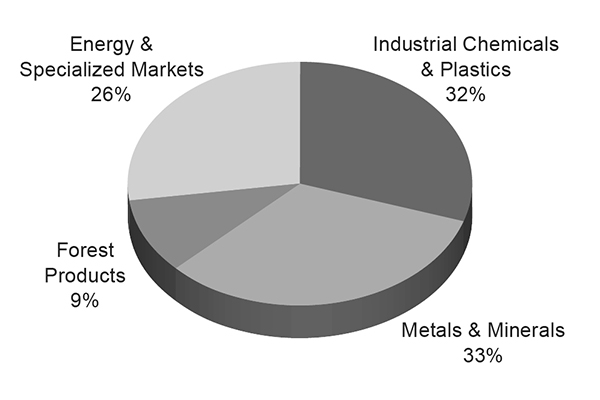
Industrial – Our extensive network facilitates the movement of numerous commodities between thousands of origin and destination points throughout North America. The Industrial group consists of several categories, including construction, industrial chemicals, plastics, forest products, specialized products (primarily waste, salt, and roofing), metals and ores, petroleum, liquid petroleum gases (LPG), soda ash, and sand. Transportation of these products accounted for 37% of our freight revenues in 2025. Commercial, residential, and governmental infrastructure investments drive shipments of steel, aggregates, cement, and wood products. Industrial and light manufacturing plants receive steel, nonferrous materials, minerals, and other raw materials.
The industrial chemicals market consists of a vast number of chemical compounds that support the manufacturing of more complex chemicals. Plastics shipments support automotive, housing, and the durable and disposable consumer goods markets. Forest product shipments include lumber and paper commodities. Lumber shipments originate primarily in the Pacific Northwest or Western Canada and move throughout the U.S. for use in new home construction and repairs and remodeling. Paper shipments primarily support packaging needs. Oil and gas drilling generates demand for raw steel, finished pipe, stone, and drilling fluid commodities. The Company’s petroleum and LPG shipments are primarily impacted by refinery utilization rates, regional crude pricing differentials, pipeline capacity, and the use of asphalt for road programs. Soda ash originates in southwestern Wyoming and California, destined for chemical and glass producing markets in North America and abroad.
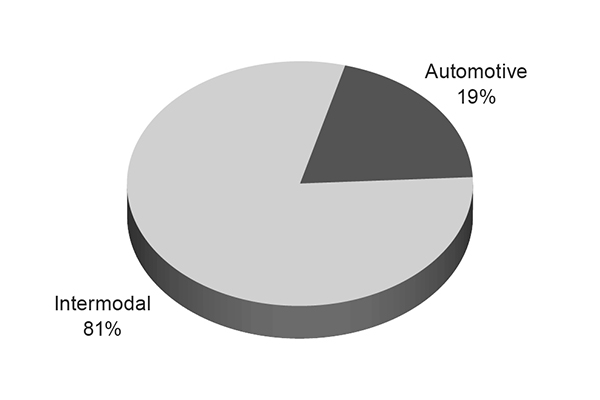
Premium – In 2025, Premium shipments generated 30% of Union Pacific’s total freight revenues. Premium includes finished automobiles, automotive parts, and merchandise in intermodal containers, both domestic and international. International business consists of import and export traffic moving in 20 or 40-foot shipping containers, that mainly pass through West Coast ports, destined for one of the Company's many inland intermodal terminals. Domestic business includes container and trailer traffic picked up and delivered within North America for intermodal marketing companies (primarily shipper agents and logistics companies) as well as truckload carriers.
We are the largest automotive carrier west of the Mississippi River and operate or access more than 40 vehicle distribution centers. The Railroad’s extensive franchise accesses six vehicle assembly plants and connects to West Coast ports, all six major Mexico gateways, and the Port of Houston to accommodate both import and export shipments. In addition to transporting finished vehicles, the Company provides expedited handling of automotive parts in both boxcars and intermodal containers destined for Mexico, the U.S., and Canada.
Seasonality – Some of the commodities we carry have peak shipping seasons, reflecting either or both the nature of the commodity (such as certain agricultural and food products that have specific growing and harvesting seasons) and the demand cycle for the commodity (such as intermodal traffic that generally peaks during the third quarter to meet back-to-school and holiday-related demand for consumer goods during the fourth quarter). The peak shipping seasons for these commodities can vary considerably each year depending upon various factors, including the strength of domestic and international economies and currencies; consumer demand; the strength of harvests, which can be adversely affected by severe weather; market prices for agricultural products; and supply chain disruptions.
Proud & engaged workforce – Our employees are central to our strategy of Safety, Service, and Operational Excellence leading to Growth, and investing in our workforce is key to our success.
Our people: Our award-winning, multigenerational workforce includes talented people from all walks of life, in many stages of life. Made up of management and craft professionals, we are focused on attracting, retaining, and developing talent across our entire system. We employed an average of 29,287 employees during 2025.
Union Pacific works with 13 major rail unions, representing approximately 83% of our workforce. Pursuant to the Railway Labor Act (RLA), a federal statute enacted in 1926, our collective bargaining agreements are subject to modification every five years. Existing agreements remain in effect until new agreements are ratified or until the RLA procedures are exhausted. The RLA is designed to bring the railroads and unions to agreement without disruptions to rail transportation. We have concluded the majority of our local negotiations, which began on January 1, 2025, related to years 2025-2029. There are two negotiations ongoing at one of our subsidiaries.
Our culture: At Union Pacific, The How Matters – high ethical standards guide the decisions we make and action we take to protect our employees, communities, and customers. Our passion for performance drives our safety, customer experience, and financial results while we work as a team to create opportunity for all.
Safety is central to everything we do at Union Pacific. Together, we are committed to cultivating a safety-focused culture, so our employees return home safely every day. To achieve this, our employees identify risks, initiate action to mitigate those risks, and have the courage to care to keep each other safe.
Our success is measured by our personal injury rate (the number of reportable injuries for every 200,000 employee-hours worked) and our derailment incident rate (the number of reportable derailment incidents per million train miles). Reportable personal injuries are defined as on duty incidents or occupational illnesses that result in employees losing time away from work, modifying or restricting their normal duties, or receiving any medical treatment above and beyond first aid. Reportable derailment incidents are defined as any occurrence where a wheel of a locomotive or rail car falls off the track and causes damage to track, equipment, or structures above the Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) reporting threshold, regardless of ownership ($12,400 for 2025 and $12,600 for 2026). Personal injuries and derailment incidents that meet reportable criteria are reported to the FRA.
Our 2025 personal injury rate of 0.68 improved 24%, and our derailment incident rate of 1.75 improved 19% versus 2024. (See further discussion in Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations, Item 7, of this report.)
Union Pacific is committed to creating an environment where people can be their best, personally and professionally. We believe that a supportive culture increases employee engagement, improves morale, and allows qualified employees to succeed and contribute to Union Pacific's success. All of this supports our safety strategy and improves the quality of decision-making, problem-solving, and strategic thinking.
The employee journey: From recruitment to retirement and milestones in between, we are relentlessly focused on supporting and engaging employees throughout their Union Pacific journey. We view it as imperative to invest in our employees with meaningful benefit offerings, developmental experiences, and career opportunities.
The process begins with recruitment, where we strive to attract the most talented employees to join our team. Then, we focus on training and development, which includes courses and programs designed to help our employees grow into new roles and/or learn a new skill in their current role so that we can retain our workforce over time.
Providing competitive compensation and meaningful benefits is key to attracting and retaining talented employees. Union Pacific is committed to continuously reviewing its compensation programs and comprehensive benefits programs to promote programs that are fair and competitive. Both are key to enhancing the value of working for Union Pacific and demonstrating the Company’s commitment to the health and wealth of employees during their career. Benefits vary based on the applicable collective bargaining agreement or an employee’s management status. The final stage of the employee journey is a fulfilling retirement, which is enabled during their Union Pacific career through our compensation and benefit programs, particularly contributions to 401(k) plans and the employee stock purchase plan (ESPP).
Our Board of Directors evaluates our non-union compensation plans and reviews recommendations from the Compensation and Talent Committee, while collective bargaining agreements govern compensation for our union employees. The median annual compensation for all employees employed as of December 31, 2025, was $107,889 (excluding the CEO).
Talent is critical - our ability to recruit and retain employees is directly tied to our railroad’s success, as proven by our 2025 retention rate of 89%, our robust benefit offerings, and work environment that creates meaningful family-supporting careers. We are focused on effectively managing workforce levels to the demands of the business and improving quality of life for our employees.
Railroad security – Our security efforts consist of a wide variety of measures, including employee training, engagement with our customers, training of emergency responders, and partnerships with numerous federal, state, and local government agencies. While federal law requires us to protect the confidentiality of our security plans designed to safeguard against terrorism and other security incidents, the following provides a general overview of our security initiatives.
UPRR security measures – We maintain a comprehensive security plan designed to both deter and respond to any potential or actual threats as they arise. The plan includes four levels of alert status, each with its own set of countermeasures. We employ our own police force, consisting of commissioned and highly-trained officers. The police are certified state law enforcement officers with investigative and arrest powers. The Union Pacific Police Department has achieved accreditation under the Commission on Accreditation for Law Enforcement Agencies, Inc. (CALEA) for complying with the highest law enforcement standards. Our employees undergo recurrent security and preparedness training as well as federally mandated hazardous materials and security training. We regularly review the sufficiency of our employee training programs. We maintain the capability to move critical operations to back-up facilities in different locations.
We operate an emergency response management center 24 hours a day. The center receives reports of emergencies, dangerous or potentially dangerous conditions, and other safety and security issues from our employees, the public, law enforcement, and other government officials. In cooperation with government officials, we monitor both threats and public events, and, as necessary, we may alter rail traffic flow at times of concern to minimize risk to communities and our operations. We comply with the hazardous materials routing rules and other requirements imposed by federal law. We design our operating plan to expedite the movement of Rail Security Sensitive Materials (RSSM), a subset of particularly hazardous materials, to minimize the time rail cars remain idle at yards and terminals located in or near major population centers. Additionally, in compliance with Transportation Security Administration (TSA) regulations, we deployed information systems and instructed employees in tracking and documenting the handoff of RSSM with customers and interchange partners.
We established a number of our own innovative safety and security-oriented initiatives ranging from various investments in technology to The Officer on Train program, which provides local law enforcement officers with the opportunity to ride with train crews to enhance their understanding of railroad operations and risks. Our staff of information security professionals continually assess cybersecurity risks and implement mitigation programs that evolve with the changing technology threat environment. To date, we have not experienced any material disruption of our operations due to a cyber threat or incident directed at us.
Cooperation with federal, state, and local government agencies – We work closely on physical and cybersecurity initiatives with government agencies, including the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT); the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI); the Department of Homeland Security (DHS), along with its Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), and the TSA; as well as local police departments, fire departments, and other first responders.
In compliance with TSA regulations established in 2022, we designated a Cybersecurity Coordinator to oversee our cybersecurity initiatives and report required incidents to the CISA. We communicated our Cybersecurity Incident Response Plan and conducted a Cybersecurity Vulnerability Assessment to identify potential risks. Our Cybersecurity Implementation Plan outlines the specific actions taken to meet the TSA prevention, detection, and response requirements. Additionally, an ongoing assessment program has been implemented to proactively and regularly evaluate the effectiveness of our cybersecurity program to identify and mitigate emerging risks. These efforts have been validated by the TSA, confirming our adherence to their standards.
In conjunction with the Association of American Railroads (AAR), we sponsor Ask Rail, a mobile application that provides first responders with secure links to electronic information, including commodity and emergency response information required by emergency personnel to respond to accidents and other situations. We also participate in the National Joint Terrorism Task Force, a multi-agency effort established by the U.S. Department of Justice and the FBI to combat and prevent terrorism.
We work with the Coast Guard, U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP), and the Military Transport Management Command, which monitor shipments entering the UPRR rail network at U.S. border crossings and ports. We were the first railroad in the U.S. to be named a partner in CBP’s Customs-Trade Partnership Against Terrorism, a partnership designed to develop, enhance, and maintain effective security processes throughout the global supply chain.
Cooperation with customers and trade associations – Through TransCAER (Transportation Community Awareness and Emergency Response), we work with the AAR, the American Chemistry Council, the American Petroleum Institute, and other chemical trade groups to provide communities with preparedness tools, including the training of emergency responders. In cooperation with the FRA and other interested groups, we are also working to develop additional improvements to tank car design that will further limit the risk of releases of hazardous materials.
Sustainable future – Union Pacific believes it is important that we act as environmental stewards, reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and supporting the transition to a more sustainable future. While we work to further reduce our environmental footprint, it is important to note that railroads are already one of the most fuel-efficient means of transportation. Freight rail leads other forms of surface transportation when it comes to minimizing GHG emissions, and we expect rail will continue to play a critical role in mitigating and abating the impacts of climate change. According to the AAR, moving freight by rail instead of truck reduces GHG emissions as freight railroads are, on average, three to four times more fuel efficient than trucks. Therefore, converting freight transportation from truck to rail typically results in an immediate reduction in our customers' scope 3 GHG emissions.
Competition – see “We Face Competition from Other Railroads and Other Transportation Providers” in the Risk Factors in Item 1A of this report.
Key suppliers – see “We Are Dependent on Certain Key Suppliers of Locomotives and Rail” in the Risk Factors in Item 1A of this report.
Available information – Our Internet website is www.up.com. We make available free of charge on our website (under the “Investors” caption link) our Annual Reports on Form 10-K; our Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q; our current reports on Form 8-K; our proxy statements; Forms 3, 4, and 5, filed on behalf of our directors and certain executive officers; and amendments to such reports filed or furnished pursuant to the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the Exchange Act). We provide these reports and statements as soon as reasonably practicable after such material is electronically filed with, or furnished to, the SEC. We also make available on our website previously filed SEC reports and exhibits via a link to EDGAR on the SEC’s Internet site at www.sec.gov. Additionally, our corporate governance materials, including By-Laws, Board Committee charters, governance guidelines and policies, and codes of conduct and ethics for directors, officers, and employees are available on our website. From time to time, the corporate governance materials on our website may be updated as necessary to comply with rules issued by the SEC and the NYSE or as desirable to promote the effective and efficient governance of our Company. Any security holder wishing to receive, without charge, a copy of any of our SEC filings or corporate governance materials should send a written request to: Secretary, Union Pacific Corporation, 1400 Douglas Street, Omaha, NE 68179.
References to our website address, in this report, including references in Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations, Item 7, are provided as a convenience and do not constitute, and should not be deemed, an incorporation by reference of the information contained on, or available through, the website. Therefore, such information should not be considered part of this report.
GOVERNMENTAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL REGULATION
Governmental regulation – Our operations are subject to a variety of federal, state, and local regulations, generally applicable to all businesses. (See also the discussion of certain regulatory proceedings in Legal Proceedings, Item 3.)
The operations of the Railroad are subject to the regulations of the FRA and other federal and state agencies as well as the regulatory jurisdiction of the Surface Transportation Board (STB). The STB has jurisdiction over rates charged on certain regulated rail traffic; common carrier service of regulated traffic; freight car compensation; transfer, extension, or abandonment of rail lines; and acquisition of control of rail common carriers (see Note 20 to the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8, for information regarding the pending acquisition of Norfolk Southern). The STB is reviewing proposed rulemaking in various areas, including reciprocal switching and commodity exemptions. The STB also continues to explore changes to the methodology for determining railroad revenue adequacy, the possible uses of revenue adequacy in regulating railroad rates, and ways to regulate service, including by use of emergency service orders. The STB posts quarterly reports on rate reasonableness cases, maintains a database on service complaints, and has the authority to initiate investigations, among other things.
The DOT, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, the Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration, and the DHS, along with other federal agencies, have jurisdiction over certain aspects of safety, movement of hazardous materials and hazardous waste, emissions requirements, and equipment standards. Additionally, various state and local agencies have jurisdiction over disposal of hazardous waste and seek to regulate movement of hazardous materials in ways not preempted by federal law.
Environmental regulation – We are subject to extensive federal and state environmental statutes and regulations pertaining to public health and the environment. The statutes and regulations are administered and monitored by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and by various state environmental agencies, such as the California Air Resources Board (CARB) and the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ), among others. The primary laws affecting our operations are the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act, regulating the management and disposal of solid and hazardous wastes; the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act, regulating the cleanup of contaminated properties; the Clean Air Act, regulating air emissions; and the Clean Water Act, regulating wastewater discharges.
Information concerning environmental claims and contingencies and estimated remediation costs is set forth in Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations - Critical Accounting Estimates - Environmental, Item 7, and Note 17 to the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8.
Item 1A. Risk Factors
The following discussion addresses significant factors, events, and uncertainties that make an investment in our securities risky and provides important information for the understanding of our “forward-looking statements,” which are discussed immediately preceding Item 7A of this Form 10-K and elsewhere. The risk factors set forth in this Item 1A should be read in conjunction with the rest of the information included in this report, including Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations, Item 7, and Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8.
We urge you to consider carefully the factors described below and the risks that they present for our operations as well as the risks addressed in other reports and materials that we file with the SEC and the other information included or incorporated by reference in this Form 10-K. When the factors, events, and contingencies described below or elsewhere in this Form 10-K materialize, our business, reputation, financial condition, results of operations, cash flows, or prospects can be materially adversely affected. In such case, the trading price of our common stock could decline, and you could lose part or all of your investment. The disclosures in this section reflect our beliefs and opinions as to factors that could materially and adversely affect us in the future. References to past events are provided by way of example only and are not intended to be a complete listing or a representation as to whether or not such factors have occurred in the past or their likelihood of occurring in the future. Additional risks and uncertainties not currently known to us or that we currently deem immaterial may also materially adversely affect our business, reputation, financial condition, results of operations, cash flows, and prospects.
Strategic and operational risks
We must manage fluctuating demand for our services and network capacity – Significant reductions in demand for rail services with respect to one or more commodities or changes in consumer preferences that affect the businesses of our customers can lead to increased costs associated with resizing our operations, including higher unit operating costs and costs for the storage of locomotives, rail cars, and other equipment; workforce adjustments; and other related activities, which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity. If there is significant demand for our services that exceeds the designed capacity of our network or shifts in traffic flow that are contrary to the designed capacity of our network, we can experience challenges, including congestion and reduced velocity, that could compromise the level of service we provide to our customers. This level of demand also can compound the impact of weather and weather-related events on our operations and velocity. We cannot be sure that our efforts to improve our transportation plan, add capacity, improve operations at our yards and other facilities, and improve our ability to address surges in demand for any reason by carrying a resource buffer will fully or adequately address any service shortcomings resulting from demand exceeding our planned capacity. From time to time we also experience other operational or service challenges related to network capacity, dramatic and unplanned fluctuations in our customers’ demand for rail service with respect to one or more commodities or operating regions, or other events that could negatively impact our operational efficiency, any or all of which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity.
We transport hazardous materials – We transport certain hazardous materials and other materials, including crude oil, ethanol, and toxic inhalation hazard (TIH) materials, such as chlorine, that pose certain risks in the event of a release or combustion. Additionally, U.S. laws impose common carrier obligations on railroads that require us to transport certain hazardous materials regardless of risk or potential exposure to loss. An accident or other incident on our network, at our facilities, or at the facilities of our customers involving the release or combustion of hazardous materials can involve significant costs and claims for personal injury, property damage, and environmental penalties and remediation in excess of our insurance coverage for these risks, which could harm our reputation or have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity.
The ability to update or maintain technology could adversely affect our operations – We rely on information technology in all aspects of our business, including technology systems operated by us (whether created by us or purchased), under control of third parties, and open-source software. If we do not have sufficient capital or do not deploy sufficient capital in a timely manner to acquire, develop, or implement new technology or maintain or upgrade current systems, such as Positive Train Control (PTC), NetControl, or the latest version of our transportation control systems, we may suffer a rail service outage or competitive disadvantage within the rail industry and with companies providing other modes of transportation service, which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity.
We are subject to cybersecurity risks – We rely on information technology in all aspects of our business, including technology systems operated by us (whether created by us or purchased), under control of third parties, and open-source software. We have experienced and will likely continue to experience varying degrees of cyber incidents in the normal course of business. There can be no assurance that the resources we devote to protect our technology systems and proprietary data or the systems we have designed to identify, prevent, or limit the effects of cyber incidents will be sufficient to prevent or detect such incidents, or to avoid a material adverse impact on our systems after such incidents do occur. Furthermore, due to the rising numbers and increasing sophistication of cyber-attacks, an increasingly complex information technology supply chain, and the nature of zero-day exploits, we may be unable to anticipate or implement adequate measures to prevent a security breach, including by ransomware or as a result of human error or other cyber-attack methods, from materially affecting our systems or the systems of third-parties upon which we rely. The rapid evolution and increased availability of artificial intelligence may intensify cybersecurity risks by making cyber-attacks more sophisticated and cybersecurity incidents more difficult to detect, contain, and mitigate. A cyber incident that results in significant service interruption; safety failure; other operational difficulties; unauthorized access to (or the loss of access to) competitively sensitive, confidential, or other critical data or systems; loss of customers; financial losses; regulatory fines; reputational harm; or misuse or corruption of critical data and proprietary information, could have a material adverse impact on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity. We may experience security breaches that could remain undetected for an extended period and, therefore, have a greater impact on us. Additionally, we may be exposed to increased cybersecurity risk because we are a component of the critical U.S. infrastructure.
Severe weather and natural events could result in significant business interruptions and expenditures – As a railroad with a vast network, we are exposed to severe weather conditions and other natural phenomena, including earthquakes, hurricanes, fires, floods, mudslides or landslides, extreme temperatures, avalanches, and significant precipitation, and climate change may cause or contribute to the severity or frequency of such weather conditions. Line outages and other interruptions caused by these conditions have in the past and could in the future adversely affect parts or all of our rail network, potentially negatively affecting revenues, costs, and liabilities, despite efforts we undertake to plan for these events. Our revenues can also be adversely affected by severe weather that causes damage and disruptions to our customers. These impacts caused by severe weather or other natural phenomena could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity.
A significant portion of our revenues involves transportation of commodities to and from international markets – Although revenues from our operations are attributable to transportation services provided in the U.S., a significant portion of our revenues involves the transportation of commodities to and from international markets, including Mexico, Canada, and Southeast Asia, by various carriers and, at times, various modes of transportation. Significant and sustained interruptions of trade with Mexico, Canada, or countries in Southeast Asia, including China, could adversely affect customers and other entities that, directly or indirectly, purchase or rely on rail transportation services in the U.S. as part of their operations, and any such interruptions, including international armed conflicts, such as the Russia-Ukraine and Israel-Hamas wars, could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity. Any one or more of the following could cause a significant and sustained interruption of trade with Mexico, Canada, or countries in Southeast Asia: (a) a deterioration of security for international trade and businesses; (b) the adverse impact of new laws, rules, and regulations or the interpretation or enforcement of laws, rules, and regulations by government entities, courts, or regulatory bodies, including the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) or other international trade agreements; (c) actions of taxing authorities that affect our customers doing business in or with foreign countries; (d) any significant adverse economic developments, such as extended periods of high inflation, material disruptions in the banking sector or in the capital markets of these foreign countries, and significant changes in the valuation of the currencies of these foreign countries that could materially affect the cost or value of imports or exports; (e) shifts in patterns of international trade, including as a result of changes to international trade agreements or policies, that adversely affect import and export markets; (f) a material reduction in foreign direct investment in these countries; and (g) public health crises, including the outbreak of pandemic or contagious disease, such as the coronavirus and its variant strains (COVID). Changes to trade policy both U.S. and foreign, including imposition of tariffs on imports, could cause demand for shipping from international markets to decrease, and if the declines are significant enough, it could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity.
We are dependent on certain key suppliers of locomotives and rail – Due to the capital-intensive nature and sophistication of locomotive equipment, parts, and maintenance, potential new suppliers face high barriers to entry. Therefore, if any of our two domestic suppliers of locomotives discontinues manufacturing locomotives, supplying parts, or providing maintenance for any reason, including bankruptcy or insolvency or the inability to manufacture locomotives that meet efficiency or regulatory emissions standards, we could experience significant cost increases and reduced availability of the locomotives that are necessary for our operations. Additionally, we utilize a limited number of steel producers that meet our rail specifications. Rail is critical to our operations for rail replacement programs, maintenance, and for adding additional network capacity, new rail and storage yards, and expansions of existing facilities. This industry similarly has high barriers to entry, and if there is any significant consolidations or mergers in this industry, or one of these suppliers discontinues operations for any reason, including bankruptcy or insolvency, we could experience both significant cost increases for rail purchases and difficulty obtaining sufficient rail for maintenance and other projects. Changes to trade agreements or policies that result in increased tariffs on goods imported into the United States could also result in significant cost increases for rail purchases and difficulty obtaining sufficient rail.
Workforce risks
Strikes or work stoppages could adversely affect our operations – The U.S. Class I railroads are party to collective bargaining agreements with various labor unions. The majority of our employees belong to labor unions and are subject to these agreements. Disputes over the terms of these or future agreements or the terms of such agreements, or our potential inability to negotiate acceptable contracts with these unions or the renegotiation of them or their term can lead to, among other things, strikes, work stoppages, slowdowns, or lockouts, any or all of which could compromise our service reliability or cause a significant disruption of our operations, and could increase our costs for wages, health care, and other benefits, which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity. Labor disputes, work stoppages, slowdowns, or lockouts at loading/unloading facilities, ports, or other transport access points, or by employees of our customers or our suppliers, could compromise our service reliability and have a material adverse impact on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity.
The availability of qualified personnel could adversely affect our operations – Changes in demographics, training requirements, and pandemic illnesses or restrictions could negatively affect the availability of qualified personnel for us, our customers, and throughout the supply chain. Our ability to quickly react to other factors that affect our ability to attract and retain employees may be restricted due to limited flexibility to make unilateral changes to collective bargaining agreements, which cover the majority of our workforce. Unpredictable increases in demand for rail services and a lack of network fluidity may exacerbate our risks related to having insufficient qualified personnel, which could have a negative impact on our operational efficiency and otherwise have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity.
Legal and regulatory risks
We are subject to significant governmental regulation – We are subject to governmental regulation by a significant number of federal, state, and local authorities covering a variety of health, safety, labor, employment, environmental, economic (as discussed below), tax, social, and other matters. Many laws and regulations require us to obtain and maintain various licenses, permits, and other authorizations, and we cannot guarantee that we will continue to be able to do so. Our failure to comply with applicable laws and regulations could have a material adverse effect on us as a result of litigation or proceedings by private parties, governments, or regulators, including and in addition to those described in Note 17 to the Consolidated Financial Statements entitled "Commitments and Contingencies." Governments or regulators may change the legislative or regulatory frameworks that we operate in without providing us any recourse to address any adverse effects on our business, including, without limitation, regulatory determinations or rules regarding dispute resolution, increasing the amount of our traffic subject to common carrier regulation, business relationships with other railroads, use of embargoes, calculation of our cost of capital or other inputs relevant to computing our revenue adequacy, the prices we charge, changes in tax rates, enactment of new tax laws or tariffs, and revision in tax regulations. Significant legislative activity in Congress or regulatory activity by other government branches or agencies, such as the STB, could expand regulation of railroad operations and pricing for rail services, which could reduce the viability of capital spending on our rail network, facilities, and equipment, and increase our costs for purchased goods and services. Such legislative or regulatory activity, or recent tariff activity imposed in the U.S. and retaliatory tariffs implemented in other countries, could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity. During fiscal year 2025, new tariffs were imposed in the U.S. for imports from a broad range of countries and materials. Several countries also implemented or proposed retaliatory tariffs on imports from the U.S., as well as other barriers to trade. Incremental import tariffs adversely affected demand for our services and increased our costs for purchased goods and services during fiscal year 2025 and may continue to do so in 2026. In addition, retaliatory tariffs by regions outside the U.S., currently in effect or adopted in the future, may impact demand for our services and our costs for purchased goods and services.
We may be subject to various claims and lawsuits that could result in significant expenditures – As a railroad with operations in densely populated urban areas and a vast rail network, we are exposed to the potential for various claims and litigation related to labor and employment, personal injury, property damage, environmental liability, and other matters. Any material changes to litigation trends or a catastrophic rail accident or series of accidents involving any or all of property damage, personal injury, and environmental liability that exceed our insurance coverage for such risks could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity. In addition, some of these matters could impact the cost of obtaining, or availability in general, of insurance coverage meant to cover these types of risks.
We are subject to significant environmental laws and regulations – Due to the nature of the railroad business, our operations are subject to extensive federal, state, and local environmental laws and regulations concerning, among other things, emissions to the air; discharges to waters; handling, storage, transportation, and disposal of waste and other materials; and hazardous material or petroleum releases. We generate and transport hazardous and non-hazardous waste in our operations. Environmental liability can extend to previously owned or operated properties, leased properties, properties owned by third parties, as well as properties we currently own. Environmental liabilities also have arisen and may arise from claims asserted by adjacent landowners or other third parties in toxic tort litigation. We have been and may be subject to allegations or findings that we have violated, or are strictly liable under, these laws or regulations. We currently have certain obligations at existing sites for investigation, remediation, and monitoring, and we likely will have obligations at other sites in the future. We believe we maintain adequate estimated liabilities for these obligations, but fluctuations of potential costs affect our estimates based on our experience and, as necessary, the advice and assistance of our consultants. However, actual costs may vary from our estimates due to a variety of factors, including changes to environmental laws or interpretations of such laws, technological changes affecting investigations and remediation, the participation and financial viability of other parties responsible for any such liability, and the corrective action or change to corrective actions required to remediate any existing or future sites. We could incur significant costs as a result of any of the foregoing, and we may be required to incur significant expenses to investigate and remediate known, unknown, or future environmental contamination, which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity.
Macroeconomic and industry risks
We face competition from other railroads and other transportation providers – We face competition from other railroads, motor carriers, ships, barges, and pipelines. Our main railroad competitor is Burlington Northern Santa Fe LLC. Its primary subsidiary, BNSF Railway Company (BNSF), operates parallel routes in many of our main traffic corridors. In addition, we operate in corridors served by other railroads and motor carriers. Motor carrier competition exists in all three of our commodity groups. Because of the proximity of our routes to major inland and Gulf Coast waterways, barges can be particularly competitive, especially for grain and bulk commodities in certain areas where we operate. In addition to price competition, we face competition with respect to transit times, quality, and reliability of service from motor carriers and other railroads. Motor carriers in particular generally have an advantage over railroads with respect to transit times and timeliness of service. Additionally, we must build or acquire and maintain our rail system, while trucks, barges, and maritime operators are able to use public rights-of-way maintained by public entities. Any of the following could also affect the competitiveness of our transportation services for some or all of our commodities, which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity: (a) improvements or expenditures materially increasing the quality or reducing the costs of these alternative modes of transportation, such as autonomous or more fuel efficient trucks, (b) legislation that eliminates or significantly increases the existing size or weight limitations applied to motor carriers, or (c) legislation or regulatory changes that impose operating restrictions or requirements on railroads or that adversely affect the profitability of some or all railroad traffic. Many movements face product or geographic competition where our customers can use different products (e.g., natural gas instead of coal, sorghum instead of corn) or commodities from different locations (e.g., grain from states or countries that we do not serve, crude oil from different regions). Sourcing different commodities or different locations allows shippers to substitute different carriers, and such competition may reduce our volumes or constrain prices. Additionally, any future consolidation of the rail industry could result in increased competition among industry participants.
We may be affected by climate change and market or regulatory responses to climate change – Climate change, including the impact of global warming and transition risks involving policy, legal risks, and market risks, could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity on both a long-term and near-term basis. Restrictions, caps, taxes, or other controls on emissions of greenhouse gases (GHGs), including diesel exhaust, could significantly increase our operating costs. Restrictions on emissions could also affect our customers that (a) use commodities that we carry to produce energy, (b) use significant amounts of energy in producing or delivering the commodities we carry, or (c) manufacture or produce goods that consume significant amounts of energy or burn fossil fuels, including chemical producers, farmers and food producers, and automakers and other manufacturers. Significant cost increases, government regulation, or changes of consumer preferences for goods or services relating to alternative sources of energy, emissions reductions, and GHG emissions can materially affect the markets for the commodities we carry and demand for our services, which in turn could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity. Government incentives encouraging the use of alternative sources of energy, including modifications or elimination of such incentives, also can affect certain of our customers and the markets for certain of the commodities we carry in a manner that could unpredictably alter our traffic patterns or reduce demand.
Compliance with laws or regulations related to climate change, along with defending and resolving legal claims and other litigation, could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity. Climate change may cause severe weather conditions and other natural phenomena, including earthquakes, hurricanes, fires, floods, mudslides or landslides, extreme temperatures, avalanches, and significant precipitation. Severe weather conditions and other natural phenomena has in the past and could in the future cause line outages and other interruptions to our infrastructure. Any of these factors, individually or in operation with one or more of the other factors, or other unpredictable impacts of climate change could reduce the amount of traffic we handle and have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity.
Our efforts to achieve emission reduction targets or aspirations could significantly increase our operational costs and capital expenditures. In addition, stakeholder expectations regarding some of these matters may be evolving and there may be differing views among stakeholders, which could harm our reputation or increase our costs. Our ability to meet such targets or aspirations can depend on significant technological advancements, including, for example, suitable alternative fuels and zero-emissions locomotives, and when such technological advancements will take place, if at all, and whether they will be readily available on commercially reasonable terms is currently unknown. There can be no assurances we will achieve our emission reduction targets or aspirations, or that the associated costs will not be higher than expected, or that the regulatory landscape will not have a negative impact on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity. Government mandates may lead to the premature adoption of unproven and unreliable technology, which could negatively affect operational reliability, customer service, and supply chain continuity.
Our business, financial condition, and results of operations have been adversely affected, and in the future, could be materially adversely affected by pandemics or other public health crises – Pandemics, epidemics, and other outbreaks of disease can have significant and widespread impacts. As we saw during the peaks of the COVID pandemic, outbreaks of disease can cause a global slowdown of economic activity (including the decrease in demand for a broad variety of goods), disruptions in global supply chains, and significant volatility and disruption of financial markets, resulting further in adverse effects on workforces, customers, and regional and local economies. The impact of pandemics or public health crises on our results of operations and financial condition will depend on numerous evolving factors, including, but not limited to: governmental, business, and individuals’ actions taken in response to a global pandemic or other public health crises (including restrictions on travel and transport, workforce pressures, social distancing, and shelter-in-place orders); the effect of a pandemic or other public health crises on economic activity and actions taken in response; the effect on our customers and their demand for our services; the effect of a pandemic or other public health crises on the credit-worthiness of our customers; national or global supply chain challenges or disruptions; facility closures; commodity cost volatility; general macroeconomic uncertainty in key global markets and financial market volatility; global economic conditions and levels of economic growth; and the pace of recovery as the pandemic subsides as well as response to a potential reoccurrence. Further, a pandemic or other public health crises, and the volatile regional and global economic conditions stemming from such an event, could also precipitate and aggravate the other risk factors that we identify, which could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations (including revenues and profitability), and/or stock price. Additionally, a pandemic or other public health crises also may affect our operating and financial results in a manner that is not presently known to us or that we currently do not consider to present significant risks to our operations.
Financial risks
We are affected by fluctuating fuel prices – Fuel costs constitute a significant portion of our transportation expenses. Diesel fuel prices can be subject to dramatic fluctuations, and significant price increases could have a material adverse effect on our operating results. Although we currently are able to recover a significant amount of our fuel expenses from our customers through revenues from fuel surcharges, we cannot be certain that we will always be able to mitigate rising or elevated fuel costs through our fuel surcharges. Additionally, future market conditions or legislative or regulatory activities could adversely affect our ability to apply fuel surcharges or adequately recover increased fuel costs through fuel surcharges. As fuel prices fluctuate, our fuel surcharge programs trail such fluctuations in fuel prices by approximately two months and are from time-to-time a significant source of quarter-over-quarter and year-over-year volatility, particularly in periods of rapidly changing prices. International, political, and economic factors, events and conditions, including international armed conflicts such as the Russia-Ukraine and Israel-Hamas wars, and other geopolitical tensions in the Middle East and elsewhere, affect the volatility of fuel prices and supplies. Weather can also affect fuel supplies and limit domestic refining capacity. A severe shortage of, or disruption to, domestic fuel supplies could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity. Alternatively, lower fuel prices could have a negative impact on certain commodities we transport, such as coal and domestic drilling-related shipments, which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity.
We rely on capital markets – Due to the significant capital expenditures required to operate and maintain a safe and efficient railroad, we rely on the capital markets to provide some of our capital requirements. We utilize long-term debt instruments, bank financing, and commercial paper, and we pledge certain amount of our receivables as collateral for credit. Significant instability or disruptions of the capital markets, including, among other things, elevated interest rates in the credit markets and/or changes in interest rates, or deterioration of our financial condition due to internal or external factors could restrict or prohibit our access to, and significantly increase the cost of, commercial paper and other financing sources, including bank credit facilities and the issuance of long-term debt, including corporate bonds, and could also have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity. A significant deterioration of our financial condition could result in a reduction of our credit rating to below investment grade, which could restrict us from utilizing our current receivables securitization facility (Receivables Facility). These developments also could limit our access to external sources of capital and significantly increase the costs of short and long-term debt financing, which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity.
Pending acquisition risks
The mergers are subject to conditions, some or all of which may not be satisfied or completed on a timely basis, if at all. Failure to complete the mergers could have material adverse effects on our business — On July 28, 2025, the Company, Norfolk Southern, Ruby Merger Sub 1 Corporation, and Ruby Merger Sub 2 LLC, entered into an agreement and plan of merger (the merger agreement). The completion of the mergers (as defined in the merger agreement) is subject to a number of conditions, including, among others, the receipt of the requisite regulatory approvals, which make the completion of the mergers and timing thereof uncertain. Also, either the Company or Norfolk Southern may terminate the merger agreement if the mergers have not been consummated by January 28, 2028, which is referred to as the end date (subject to an automatic extension in certain circumstances), except that this right to terminate the merger agreement will not be available to any party whose failure to perform any obligation under the merger agreement has been the primary cause of the failure of the mergers to be consummated on or before that date.
If the mergers are not completed, our ongoing business may be materially adversely affected and, without realizing any of the benefits of having completed the mergers, we will be subject to a number of risks, including the following:
•the market price of our common stock could decline;
•we could owe substantial termination fees to Norfolk Southern under certain circumstances;
•time, resources, and costs committed by our management team to matters relating to the mergers could otherwise have been devoted to pursuing other beneficial opportunities;
•we may experience negative reactions from the financial markets or from customers, suppliers, employees, labor unions, or other business partners; and
•we will be required to pay our respective costs relating to the mergers, such as legal, accounting, and printing fees, whether or not the mergers are completed.
In addition, if the mergers are not completed, we could be subject to litigation related to any failure to complete the mergers or related to any enforcement proceeding commenced against us to perform our obligations under the merger agreement, and whether or not any such litigation has any merit, the cost of defending such litigation may be significant. The materialization of any of these risks could adversely impact our ongoing business.
Similarly, delays in the completion of the mergers could, among other things, result in additional transaction costs, loss of revenues, or other negative effects associated with uncertainty about completion of the mergers.
The merger agreement contains provisions that limit our ability to pursue alternatives to the mergers, and, in specified circumstances, could require us to pay substantial termination fees to Norfolk Southern — The merger agreement contains certain provisions that restrict our ability to initiate, solicit, knowingly encourage, or, subject to certain exceptions, engage in discussions or negotiations with respect to, or approve or recommend, any alternative proposal.
In some circumstances, upon termination of the merger agreement in connection with an alternative proposal, we may be required to pay a termination fee of $2.5 billion to Norfolk Southern.
These provisions could discourage a potential acquiror of us or alternative merger partner that might have an interest in acquiring all or a significant portion of the Company or pursuing an alternative acquisition transaction with us from considering or proposing such a transaction, even if it were prepared to pay consideration with a higher per-share value than the per-share value proposed to be realized in the mergers. In particular, a termination fee, if applicable, could result in a potential acquiror of us or alternative merger partner proposing to pay a lower price to our shareholders than it might otherwise have proposed to pay absent such a fee.
If the merger agreement is terminated in accordance with its terms, and we or Norfolk Southern seek another business combination, we may not be able to negotiate a transaction with another party on terms comparable to, or better than, the terms of the merger agreement.
The mergers are subject to the receipt of the requisite regulatory approvals, which requisite regulatory approvals may never be obtained, therefore preventing completion of the mergers. In addition, in granting such approvals, regulatory authorities may impose conditions that could have a significant adverse effect on the Company, Norfolk Southern, or the combined company and the expected benefits of the mergers therefore preventing completion of the mergers — Before the mergers may be completed, the requisite regulatory approvals must have been obtained, including the approval, authorization, or exemption by the U.S. Surface Transportation Board (STB) of the mergers and other transactions contemplated by the merger agreement within the jurisdiction of the STB. The terms and conditions of the approvals that are granted may impose requirements, concessions, limitations, or costs or place restrictions on the conduct of the combined company’s business. Subject to the terms and conditions of the merger agreement, the Company and Norfolk Southern have each agreed to use their reasonable best efforts to take, or cause to be taken, all actions, and to do, or cause to be done, and to assist and cooperate with each other in doing, all things necessary, proper, or advisable to cause the conditions to closing set forth in the merger agreement to be satisfied and to consummate and make effective the mergers and the other transactions contemplated by the merger agreement prior to the end date, except that we are not required to take, or commit to take, or agree to or accept any “materially burdensome regulatory condition” (as defined in the merger agreement). For purposes of the foregoing, “reasonable best efforts” includes, among others, (i) proposing, negotiating, committing to, and effecting, by consent decree, hold separate order, or otherwise, the sale, divestiture, license, hold separate, or disposition of any and all of the share capital or other equity interest, assets, products, or businesses of the Company or of Norfolk Southern and its subsidiaries and (ii) otherwise taking or committing to take any actions that after the first effective time (as defined in the merger agreement) would limit our freedom of action with respect to, or our ability to retain, or otherwise agreeing to any restriction, requirement, or limitation with respect to our assets, products, or businesses, in each case as may be required in order to avoid the entry of, or to effect the dissolution of, any injunction, temporary restraining order, or other order that would otherwise have the effect of preventing or delaying the closing. The STB and other regulatory and governmental authorities may impose requirements, concessions, and other conditions on the granting of such approvals. If such regulatory and governmental authorities seek to impose such requirements, concessions, or conditions, lengthy negotiations may ensue among such authorities, the Company and Norfolk Southern. Such requirements, concessions, and conditions and the process of obtaining regulatory approvals could have the effect of delaying completion of the mergers and such requirements, concessions, and conditions may not be identified or satisfied for an extended period of time. Such requirements, concessions and conditions may also impose additional costs or limitations on the combined company following the completion of the mergers and the parties have agreed to accept such requirements, concessions, and conditions, even if significant, subject to the agreed-upon materially burdensome regulatory condition limitation in favor of us. These requirements, concessions, and conditions may therefore reduce the anticipated benefits of the mergers, including synergies, which could also have a significant adverse effect on the combined company’s business and cash flows and results of operations, and we cannot predict what, if any, requirements, concessions, and conditions may be required by regulatory or governmental authorities whose approvals are required. The requisite regulatory approvals may not be obtained at all, may not be obtained in a timely fashion, and may contain conditions on the completion of the mergers. In January 2026, the STB announced its finding that the major merger application filed by the Company and Norfolk Southern was incomplete, as a result of which the STB rejected the application without prejudice. The decision does not result in the dismissal of the mergers, and the Company is permitted to file a revised application, which will commence a new review by the STB for completeness. If we experience further delays as a result of the STB’s review process or we are unable to obtain other
regulatory approvals on a timely basis, any such delays may increase our costs and reduce the anticipated benefits of the mergers, which could also have a significant adverse effect on the combined company’s business.
In addition, under existing law, our railroad competitors and customers, Norfolk Southern’s railroad competitors and customers, and other interested parties may intervene to oppose the STB application or seek protective conditions in the event approval by the STB is granted, which might affect the decision of the STB, delay the approval process, or reduce the anticipated benefits of the mergers. Furthermore, if the STB does not provide final approval or imposes conditions on its approval in a final order, and the Company and Norfolk Southern decide to appeal such final order from the STB, any such appeal might not be resolved for a substantial period of time after the entry of such order by the STB.
The Company and Norfolk Southern are each subject to business uncertainties and contractual restrictions while the mergers are pending, which could adversely affect both our business and operations and the combined company’s business and operations — In connection with the pendency of the mergers, some customers, suppliers, and other persons with whom the Company or Norfolk Southern has a business relationship have or may delay or defer certain business decisions or terminate, change, or renegotiate their relationships with us or Norfolk Southern, as the case may be, as a result of the mergers, which could negatively affect our or Norfolk Southern’s respective revenues, earnings, and cash flows, as well as the market price of our common stock, regardless of whether the mergers are completed.
Under the terms of the merger agreement, each of the Company and Norfolk Southern is subject to certain restrictions on the conduct of its business prior to completing the first merger (as defined in the merger agreement), which may adversely affect its ability to execute certain of its business strategies, including, in the case of Norfolk Southern, the ability in certain cases to enter into or amend contracts, acquire or dispose of assets, incur indebtedness, incur capital expenditures, settle litigation, amend organizational documents, declare dividends, enter new business lines, and invest in third parties. Such limitations could adversely affect each party’s businesses and operations prior to the completion of the mergers.
Each of the risks described above may be exacerbated by delays or other adverse developments with respect to the completion of the mergers.
Uncertainties associated with the mergers may cause a loss of management personnel and other key employees, and the Company and Norfolk Southern may have difficulty attracting and motivating management personnel and other key employees, and combining cultures between the two companies could be challenging, which could adversely affect the future business and operations of the combined company — The Company and Norfolk Southern are dependent on the experience and industry knowledge of their respective management personnel and other key employees to execute their business plans. The combined company’s success after the completion of the mergers will depend in part upon our ability, and Norfolk Southern’s ability, to attract, motivate, and retain key management personnel and other key employees as well as develop a singular culture framed in the strategy of Safety, Service, and Operational Excellence. Prior to completion of the mergers, our current and prospective employees, and Norfolk Southern’s current and prospective employees, may experience uncertainty about their roles within the combined company following the completion of the mergers, which may have an adverse effect on our ability, and Norfolk Southern’s ability, to attract, motivate, or retain management personnel and other key employees. In addition, no assurance can be given that the combined company will be able to attract, motivate, or retain management personnel and other key employees of the Company and Norfolk Southern to the same extent that the Company and Norfolk Southern have previously been able to attract or retain employees.
We may and have been a target of securities class action and derivative lawsuits that could result in substantial costs and may delay or prevent the mergers from being completed, whether or not such lawsuits have any merit — Securities class action lawsuits and derivative lawsuits are often brought against public companies that have entered into merger agreements. Even if the lawsuits are without merit, defending against or otherwise resolving these claims can result in substantial costs and divert management time and resources. An adverse judgment could result in monetary damages, which could have a negative impact on our liquidity and financial condition. Additionally, if a plaintiff is successful in obtaining an injunction prohibiting completion of the mergers, then that injunction may delay or prevent the mergers from being completed, or from being completed within the expected timeframe, which may adversely affect our business, financial position, and results of operation.
Completion of the mergers may trigger change in control or other provisions in certain agreements to which Norfolk Southern or its subsidiaries are a party, which may have an adverse impact on the combined company’s business and results of operations — The completion of the mergers may trigger change in control and other provisions in certain agreements to which Norfolk Southern or its subsidiaries are a party. If the Company and Norfolk Southern are unable to negotiate waivers of those provisions, the counterparties may exercise their rights and remedies under the agreements, potentially terminating the agreements or seeking monetary damages. Even if the Company and Norfolk Southern are able to negotiate waivers, the counterparties may require a fee for such waivers or seek to renegotiate the agreements on terms less favorable to Norfolk Southern or the combined company. Any of the foregoing or similar developments may have an adverse impact on the combined company’s business and results of operations.
The combined company may be unable to successfully integrate the businesses of the Company and Norfolk Southern and realize the anticipated benefits of the mergers — The success of the mergers will depend, in part, on the combined company’s ability to successfully combine the businesses of the Company and Norfolk Southern, which currently operate as independent public companies, and realize the anticipated benefits, including synergies, cost savings, innovation, and operational efficiencies, from the combination. If the combined company is unable to achieve these objectives within the anticipated time frame, or at all, the anticipated benefits may not be realized fully, or at all, or may take longer to realize than expected and the value of its common stock may be harmed. Additionally, as a result of the mergers, rating agencies may take negative actions against the combined company’s credit ratings, which may increase the combined company’s financing costs, including in connection with any financing of the mergers.
The mergers involve the integration of Norfolk Southern’s business with our existing business, which is a complex, costly, and time-consuming process. Neither the Company nor Norfolk Southern have previously completed a transaction comparable in size or scope to the mergers. The integration of the two (2) companies may result in material challenges, including, without limitation:
•the diversion of management’s attention from ongoing business concerns and performance shortfalls at one or both of the companies as a result of the devotion of management’s attention to the mergers;
•managing a larger combined company;
•creating, implementing, and executing a unified business strategy, and operational, financial, and managerial control with respect to the combined entity;
•the inherent risk and complexity of integrating railroad operations, including operating, information technology, safety, and managerial systems and processes, particularly on a large scale, in the context of ongoing business operations and customer commitments;
•maintaining employee morale and attracting, motivating, and retaining management personnel and other key employees;
•the possibility of faulty assumptions underlying expectations regarding the integration process;
•retaining existing business and operational relationships and attracting new business and operational relationships;
•consolidating corporate and administrative infrastructures and eliminating duplicative operations and inconsistencies in standards, controls, procedures, and policies;
•coordinating geographically separate organizations;
•unanticipated changes in federal or state laws or regulations or international trade agreements, including additional regulatory scrutiny or additional regulatory requirements as a result of the transaction or the size, scope, and complexity of the combined company’s business operations; and
•unforeseen expenses or delays associated with the mergers.
Many of these factors will be outside of the combined company’s control and any one of them could result in delays, increased costs, decreases in the amount of expected revenues, and diversion of management’s time and energy, which could materially affect the combined company’s financial position, results of operations, and cash flows.
The Company and Norfolk Southern have operated, and until completion of the mergers will continue to operate, independently. The Company and Norfolk Southern are currently permitted to conduct only limited planning for the integration of the two (2) companies following the mergers and have not yet determined the exact nature of how the businesses and operations of the two (2) companies will be combined after the mergers. The actual integration may result in additional and unforeseen expenses, and the anticipated benefits of the integration plan may not be realized.
The future results of the combined company may be adversely impacted if the combined company does not effectively manage its expanded operations following the completion of the mergers — Following the completion of the mergers, the size of the combined company’s business will be significantly larger than the current size of our business. The combined company’s ability to successfully manage this expanded business will depend, in part, upon management’s ability to design and implement operational, managerial, financial, and strategic initiatives that address not only the integration of two (2) independent stand-alone companies, but also the increased scale and scope of the combined business with its associated increased costs and complexity. There can be no assurances that the combined company will be successful or that it will realize the expected operating efficiencies, cost savings, and other benefits currently anticipated from the mergers.
The combined company is expected to incur substantial expenses related to the completion of the mergers and the integration of the Company and Norfolk Southern — The combined company is expected to incur substantial expenses in connection with the completion of the mergers and the integration of the Company and Norfolk Southern. There are a large number of processes, policies, procedures, operations, technologies, and systems that must be integrated, including purchasing, accounting and finance, sales, payroll, pricing, revenue management, marketing, and benefits. In addition, our business and Norfolk Southern’s business will continue to maintain a presence in Omaha, Nebraska and Atlanta, Georgia, respectively. The substantial majority of these costs will be non-recurring expenses related to the mergers (including any financing of the mergers), facilities, and systems consolidation costs. The combined company may incur additional costs to retain employees and/or maintain employee morale and to attract, motivate, or retain management personnel and other key employees. We will also incur transaction fees and costs related to formulating integration plans for the combined business, and the execution of these plans may lead to additional unanticipated costs. Additionally, as a result of the mergers, rating agencies may take negative actions with regard to the combined company’s credit ratings, which may increase the combined company’s financing costs, including in connection with any financing of the mergers. These incremental transaction and merger-related costs may exceed the savings the combined company expects to achieve from the elimination of duplicative costs and the realization of other efficiencies related to the integration of the businesses, particularly in the near term, and in the event there are material unanticipated costs.
The combined company’s indebtedness may limit its flexibility and increase its borrowing costs — The combined company’s consolidated indebtedness may have the effect of, among other things, increasing borrowing costs. In addition, the amount of cash required to service the indebtedness levels will be greater than the amount of cash flows required to service the indebtedness of the Company or Norfolk Southern individually prior to completion of the mergers. The level of indebtedness could also reduce dividend payments, share repurchases, and other activities and may create competitive disadvantages relative to other companies with lower debt levels. The combined company may be required to raise additional financing for working capital, capital expenditures, acquisitions, or other general corporate purposes. The combined company’s ability to arrange additional financing or refinancing will depend on, among other factors, its financial condition and performance, as well as prevailing market conditions, the terms of third party debt financing incurred in connection with the consummation of the mergers (if any), and other factors beyond its control. There can be no assurance that the combined company will be able to obtain additional financing or arrange refinancing on terms acceptable to it or at all, and any such failure could materially adversely affect its operations and financial condition.
The financing arrangements that the combined company will enter into in connection with the mergers may, under certain circumstances, contain restrictions and limitations that could significantly impact the combined company’s ability to operate its business — We expect to incur significant new indebtedness in connection with the mergers. We also expect that the agreements governing the indebtedness that the combined company will incur in connection with the mergers will contain covenants that, among other things, may, under certain circumstances, place limitations on the dollar amounts paid or other actions we or the combined company can or will be able to take.
In addition, the combined company will likely be required to comply with a leverage covenant as set forth in these agreements.
The combined company’s ability to comply with the leverage covenant in future periods will depend on its ongoing financial and operating performance, which in turn will be subject to economic conditions and to financial, market, and competitive factors, many of which are beyond the combined company’s control. The ability to comply with this covenant in future periods will also depend on the combined company’s ability to successfully implement its overall business strategy and realize the anticipated benefits of the mergers, including synergies, cost savings, innovation, and operational efficiencies.
Various risks, uncertainties, and events beyond the combined company’s control could affect its ability to comply with the covenants contained in its financing agreements. Failure to comply with any of the covenants in its existing or future financing agreements could result in a default under those agreements and under other agreements containing cross-default provisions. A default would permit lenders to accelerate the maturity of the debt under these agreements and to foreclose upon any collateral securing the debt. Under these circumstances, the combined company might not have sufficient funds or other resources to satisfy all of its obligations. In addition, the limitations imposed by financing agreements on the combined company’s ability to incur additional debt and to take other actions might significantly impair its ability to obtain other financing.
General risk factors
We are affected by general economic conditions – Prolonged, severe adverse domestic and global macroeconomic conditions or disruptions of financial and credit markets, including, for example, the cycles of recessionary fears, inflationary pressures, changes in interest rates, and/or related monetary policy actions by governments in response to inflation, may affect the producers and consumers of the commodities we carry and may have a material adverse effect on our access to liquidity, results of operations, and financial condition.
We may be affected by acts of terrorism, war, or risk of war – Our rail lines, facilities, and equipment, including rail cars carrying hazardous materials, could be direct targets or indirect casualties of terrorist attacks. Terrorist attacks, or other similar events, any government response thereto, and war or risk of war may adversely affect our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity. In addition, insurance premiums for some or all of our current coverages could increase dramatically, or certain coverages may not be available to us in the future. Also, in the event of a national crisis or emergency, one or more government entities could take actions (such as via the U.S. Defense Production Act or the International Emergency Economic Powers Act) that could diminish our rights or economic opportunities with respect to the transportation services we offer.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
None.
Item 1C. Cybersecurity
Risk management and strategy
The Company is subject to cybersecurity threats that could have a material adverse impact on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity. See also our discussion in the Risk Factors in Item 1A of this report. As a component of our Company-wide enterprise risk management framework, we implemented a cybersecurity program whose objective is to assess, identify, and manage risks from cybersecurity threats that may result in adverse effects on the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the electronic information systems that we own. We regularly perform internal security assessments, engage third-party consultants to conduct external security assessments, and participate in, conduct, and/or administer exercises, drills, and recovery tests as part of this program. We also maintain training programs and policies and procedures designed to safeguard employee handling and use of data, internet usage, controlled access measures, and physical protections. We consult with industry groups, monitor threat intelligence reports, and communicate with various government agencies in an effort to stay up-to-date on changes in the cybersecurity threat landscape. This program, in addition to addressing our own information systems, is also designed to oversee, identify, and reduce the potential impact of a security incident at a third-party service provider or that otherwise impacts third-party technology and systems we use.
Internal cybersecurity team
The Company’s internal information security organization (Internal Cybersecurity Team), led by our Executive Vice President and Chief Information Officer (CIO) as well as the Assistant Vice President and Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), is responsible for coordinating all aspects of the Company’s electronic information security systems, including prevention, detection, mitigation, and remediation of cybersecurity incidents, as well as implementing, monitoring, and maintaining our enterprise-wide security strategy, standards, architecture, policies, and processes. Our CIO reports directly to our Chief Executive Officer, our CISO reports to our CIO, and reporting to our CISO are our Deputy Chief Information Security Officer (Deputy CISO) and other experienced information security personnel responsible for various parts of our business. In addition to our internal cybersecurity capabilities, we also periodically engage assessors, consultants, auditors, and other third parties to assist with assessing, identifying, and managing cybersecurity risks. When the Company learns of a cybersecurity incident at a third-party service provider, the Company’s respective department contacts maintain communication with the third-party service provider and communicate any cybersecurity incidents to the CISO.
Security policy and requirements
As part of the Company’s Crisis Management Plan, the Company's cybersecurity Incident Response Plan (the IRP) provides a framework for responding to cybersecurity incidents. The IRP sets out a coordinated approach to discovering, investigating, containing, tracking, mitigating, and remediating cybersecurity incidents, including a framework for elevating and reporting findings and keeping senior management and other key stakeholders informed and involved, based on assessments regarding the scope or significance of incidents. The IRP applies to the Company’s extended computing environment, including electronic information resources that are owned or used by the Company and are routinely relied on to support our operations. Additionally, in 2025, certain management employees participated in a tabletop exercise to simulate a response to a cybersecurity incident, and the teams incorporated the findings of this exercise into our Business Sustainment Plans
The Internal Cybersecurity Team has robust processes and redundancies in place designed with the objective of deterring, detecting, mitigating, and responding to potential cybersecurity threats, which includes a vulnerability assessment, prioritization, and remediation program. The Internal Cybersecurity Team also performs regular system penetration testing to validate our security controls and assess our infrastructure and applications. All management employees take mandatory security awareness training on the Company’s data security policies and procedures, which is supplemented by Company-wide testing initiatives, including periodic phishing tests.
Our information security program is designed to align our defenses and resources to identify, assess, and address more likely and more damaging cyber events, to provide support for our organizational mission and operational objectives, and to position us to deter, detect, mitigate, and respond to a wide variety of potential attacks in a timely fashion. Our information security program employs quantitative and qualitative approaches to evaluate the effectiveness of controls and assess the resiliency of critical computing resources. This data is combined with knowledge of common attack techniques to assess the likelihood of components being compromised and assess potential financial implications under different scenarios. The results are used to help identify potentially material risks and provide insights which are taken into account when prioritizing our security initiatives.
Material cybersecurity risks, threats, and incidents
Due to the evolving nature of cybersecurity threats, it has and will continue to be difficult to prevent, detect, mitigate, and remediate cybersecurity incidents. While we are not aware of having experienced any material effects or reasonably likely material effects on our Company, its business strategy, results of operations, or financial condition resulting from cybersecurity threats or incidents to date, as a critical infrastructure provider, we may be a target of well-funded and sophisticated adverse actors. There can be no guarantee that we will not be the subject of future risks or incidents that have such an effect, or that we are not currently the subject of an undetected risk or incident that may have such an effect.
We also rely on information technology and third-party vendors to support our operations, including our secure processing of personal, confidential, sensitive, proprietary, and other types of information. Despite ongoing efforts to continue improvement of our and our vendors’ ability to protect against cyber incidents, we may not be able to protect all of the information systems we use. Incidents may lead to reputational harm, revenue and client loss, legal actions, or statutory penalties, among other consequences. For a more detailed discussion of these risks, see our discussion in the Risk Factors in Item 1A of this report.
Governance
The Board of Directors has delegated primary oversight of the Company’s cybersecurity risk to the Audit Committee, which receives updates on cybersecurity risks, risk mitigation initiatives, and incidents at Audit Committee meetings from the CIO, CISO, and other members of management, as needed. When making decisions regarding director appointments and committee assignments, the Board of Directors takes into consideration the cybersecurity experience of directors and director candidates and strives to maintain cybersecurity expertise on the Board of Directors and Audit Committee. We have protocols by which certain cybersecurity incidents are reported to the Audit Committee and Board of Directors.
At the management level, our CIO, CISO, and Deputy CISO, each of whom has extensive cybersecurity knowledge and skills gained from over 29 years, 30 years, and 21 years of relevant work experience, respectively, head the Internal Cybersecurity Team that is responsible for implementing and maintaining cybersecurity and data protection practices across our business, with our CIO reporting directly to our Chief Executive Officer. Our CISO and Deputy CISO receive reports on cybersecurity threats from a number of experienced information security professionals for various parts of our business on an ongoing basis and, in conjunction with other management personnel, regularly consult on risk management measures implemented by the Company to identify and mitigate data protection and cybersecurity risks.
In addition, our Risk and Compliance Committee (RCC) is responsible for oversight and support of the Company’s Enterprise Risk Management and Compliance and Ethics programs and is comprised of the Executive Leadership Team, the Vice President Law and Chief Compliance Officer (Compliance Officer), and the Assistant Vice President - Accounting who has responsibilities for Enterprise Risk Management. The RCC also created a subcommittee, the Enterprise Risk Management Committee (ERMC), who is charged with continually monitoring, evaluating, and managing enterprise risks. The ERMC includes the Compliance Officer, General Auditor, Vice President and Chief Safety Officer, CISO, Vice President - Strategy and Corporate Development, Assistant Vice President - Accounting, and Assistant Vice President - HDC and Network Operations. The RCC and ERMC both meet throughout the year and receive periodic updates on cybersecurity from the CISO.
Item 2. Properties
We employ a variety of assets in the management and operation of our rail business. Our rail network covers 23 states in the western two-thirds of the U.S.
TRACK
Our rail network includes 32,889 route miles. We own 26,294 miles and operate on the remainder pursuant to trackage rights or leases. The following table describes track miles:
| | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, | 2025 | 2024 |
| Route | 32,889 | 32,880 |
| Other main line | 7,148 | 7,116 |
| Passing lines and turnouts | 3,526 | 3,526 |
| Switching and classification yard lines | 8,851 | 8,850 |
| Total miles | 52,414 | 52,372 |
HEADQUARTERS BUILDING
We own our headquarters building in Omaha, Nebraska. The facility has 1.2 million square feet of space that can accommodate approximately 4,000 employees.
HARRIMAN DISPATCHING CENTER
The Harriman Dispatching Center (HDC), located in Omaha, Nebraska, is our primary dispatching facility. It is linked to regional dispatching and locomotive management facilities at various locations along our network. HDC employees coordinate movement of locomotives and trains; manage traffic, train crews, as well as engineering and signal requirements for safe repair and maintenance, on our network; and coordinate interchanges with other railroads. Generally, around 600 employees work on-site in the facility. In the event of a disruption of operations at HDC due to a cyber-attack, flooding or severe weather, pandemic outbreak, or other event, we maintain the capability to conduct critical operations at back-up facilities in different locations.
RAIL FACILITIES
In addition to our track structure, we operate numerous facilities, including terminals for intermodal and other freight; rail yards for building trains (classification yards), switching, storage-in-transit (the temporary storage of customer goods in rail cars prior to shipment), and other activities; offices to administer and manage our operations; dispatching centers to direct traffic on our rail network; crew on duty locations for train crews along our network; and shops and other facilities for fueling, maintenance, and repair of locomotives and repair and maintenance of rail cars and other equipment. The following table includes the major yards and terminals on our system:
| | | | | |
| Major classification yards | Major intermodal terminals |
| North Little Rock, Arkansas | Global 4 (Chicago), Illinois |
| Englewood (Houston), Texas | Global 2 (Chicago), Illinois |
| Gateway Yard (St. Louis), Illinois | East Los Angeles, California |
| Livonia, Louisiana | Mesquite (Dallas), Texas |
| Fort Worth, Texas | ICTF (Los Angeles), California |
| North Platte East, Nebraska | Lathrop, California |
| North Platte West, Nebraska | Marion (Memphis), Arkansas |
| Roseville, California | Port Laredo, Texas |
| Settegast (Houston), Texas | Settegast (Houston), Texas |
RAIL EQUIPMENT
Our equipment includes owned and leased locomotives and rail cars; heavy maintenance equipment and machinery; other equipment and tools in our shops, offices, and facilities; and vehicles for maintenance, transportation of crews, and other activities. As of December 31, 2025, we owned or leased the following units of equipment:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Locomotives | Owned | Leased | Total | Average
age (yrs.) |
| Multiple purpose | 6,228 | 605 | 6,833 | 26.1 |
| Switching | 120 | - | 120 | 45.6 |
| Other | 11 | - | 11 | 50.8 |
| Total locomotives | 6,359 | 605 | 6,964 | N/A |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Freight cars | Owned | Leased | Total | Average
age (yrs.) |
| Covered hoppers | 16,205 | 7,129 | 23,334 | 20.8 |
| Open hoppers | 4,254 | 519 | 4,773 | 38.2 |
| Gondolas | 6,130 | 3,666 | 9,796 | 23.3 |
| Boxcars | 3,534 | 4,772 | 8,306 | 26.3 |
| Refrigerated cars | 2,270 | 791 | 3,061 | 18.6 |
| Flat cars | 1,594 | 2,629 | 4,223 | 32.0 |
| Other | - | 297 | 297 | 36.9 |
| Total freight cars | 33,987 | 19,803 | 53,790 | N/A |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Highway revenue equipment | Owned | Leased | Total | Average
age (yrs.) |
| Containers | 45,678 | 128 | 45,806 | 14.0 |
| Chassis | 4,297 | 613 | 4,910 | 11.6 |
| Total highway revenue equipment | 49,975 | 741 | 50,716 | N/A |
We continuously assess our need for equipment to run an efficient and reliable network. Many factors cause us to adjust the size of our active fleets, including changes in carload volumes, weather events, seasonality, customer preferences, and operational efficiency initiatives. As some of these factors are difficult to assess or can change rapidly, we maintain a buffer to remain agile. Without the buffer, our ability to react quickly is hindered as equipment suppliers are limited and lead times to acquire equipment are long and may be in excess of a year. We believe our locomotive and freight car fleets are appropriately sized to meet our current and future business requirements. These fleets serve as the most reliable and efficient equipment to facilitate growth without additional acquisitions. Locomotive and freight car in service utilization percentages for the year ended December 31, 2025, were 68% and 76%, respectively.
CAPITAL EXPENDITURES
Our rail network requires significant annual capital investments for replacement, improvement, and expansion. These investments enhance safety, support the transportation needs of our customers, improve our operational efficiency, and support emission reduction initiatives. Additionally, we add new equipment to our fleet to replace older equipment and to support growth and customer demand.
2025 Capital program – During 2025, our capital program totaled approximately $3.5 billion. (See the cash capital investments table in Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations - Liquidity and Capital Resources, Item 7, of this report.)
2026 Capital plan – In 2026, we expect our capital plan to be approximately $3.3 billion. (See further discussion of our 2026 capital plan in Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations - Liquidity and Capital Resources, Item 7, of this report.)
OTHER
Equipment encumbrances – See Note 14 and 16 to the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8.
Environmental matters – Certain of our properties are subject to federal, state, and local laws and regulations governing the protection of the environment. (See discussion within this report of environmental issues in Business - Governmental and Environmental Regulation, Item 1; Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations - Critical Accounting Estimates - Environmental, Item 7; and Note 17 to the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8.)
Item 3. Legal Proceedings
From time to time, we are involved in legal proceedings, claims, and litigation that occur in connection with our business. We routinely assess our liabilities and contingencies in connection with these matters based upon the latest available information and, when necessary, we seek input from our third-party advisors when making these assessments. Consistent with SEC rules and requirements, we describe below material pending legal proceedings (other than ordinary routine litigation incidental to our business), material proceedings known to be contemplated by governmental authorities, other proceedings arising under federal, state, or local environmental laws and regulations (including governmental proceedings involving potential fines, penalties, or other monetary sanctions in excess of $1,000,000), and such other pending matters that we may determine to be appropriate. See also Note 17 to the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8.
ENVIRONMENTAL MATTERS
We receive notices from the EPA and state environmental agencies alleging that we are or may be liable under federal or state environmental laws for remediation costs at various sites throughout the U.S., including sites on the Superfund National Priorities List or state superfund lists. We cannot predict the ultimate impact of these proceedings and suits because of the number of potentially responsible parties involved, the degree of contamination by various wastes, the scarcity and quality of volumetric data related to many of the sites, and the speculative nature of remediation costs.
Information concerning environmental claims and contingencies and estimated remediation costs is set forth in this report in Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations - Critical Accounting Estimates - Environmental, Item 7, and Note 17 to the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8.
OTHER MATTERS
Antitrust litigation – As we reported in our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2007, 20 rail shippers (many of whom were represented by the same law firms) filed virtually identical antitrust lawsuits in various federal district courts against us and four other Class I railroads in the U.S. Currently, UPRR and three other Class I railroads are the named defendants in the lawsuits. The original plaintiff filed the first of these claims in the U.S. District Court in New Jersey on May 14, 2007. These suits alleged that the named railroads engaged in price-fixing by establishing common fuel surcharges for certain rail traffic.
On August 16, 2019, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit (D.C. Circuit) affirmed the decision of U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia (U.S. District Court) denying class certification (the Certification Denial). Only five plaintiffs remain in this multidistrict litigation (MDL I) originally filed in 2007. The MDL I claims previously were proceeding on a consolidated basis in the U.S. District of Columbia District Court before the Honorable Paul L. Friedman. In 2024, they were transferred to the Honorable Beryl A. Howell.
Since the Certification Denial, approximately 106 lawsuits by individual shippers are pending in federal court based on claims essentially identical to those alleged in MDL I. The Judicial Panel on Multidistrict Litigation consolidated these suits for pretrial proceedings in the U.S. District Court before the Honorable Beryl A. Howell (MDL II).
As we reported in our Current Report on Form 8-K, filed on June 10, 2011, Oxbow Carbon & Minerals LLC and related entities (Oxbow) filed a complaint against UPRR in the U.S. District Court on June 7, 2011. In 2019, Oxbow dismissed certain claims and the claims that remain are the same as the Plaintiffs’ claims in MDL I. Oxbow's claims previously were proceeding in the U.S. District of Columbia District Court before the Honorable Pail L. Friedman. In 2024, Oxbow's case was transferred to the Honorable Beryl A. Howell
As we reported in our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2025, on June 24, 2025, Judge Howell granted all defendant railroads summary judgment and directed the closure of the cases. Plaintiffs have appealed Judge Howell's decision to the U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit.
We continue to deny the allegations that our fuel surcharge programs violate the antitrust laws or any other laws. We believe that these lawsuits are without merit, and we will vigorously defend our actions, including on appeal. Therefore, we currently believe that these matters will not have a material adverse effect on any of our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable.
Information About Our Executive Officers and Principal Executive Officers of Our Subsidiaries
The Board of Directors typically elects and designates our executive officers on an annual basis at the board meeting held in conjunction with the Annual Meeting of Shareholders, and they hold office until their successors are elected. Executive officers also may be elected and designated throughout the year, as the Board of Directors considers appropriate. There are no family relationships among the officers, nor is there any arrangement or understanding between any officer and any other person pursuant to officer selection. The following table sets forth certain information current as of February 6, 2026, relating to the executive officers of UPC and the Railroad.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Name | Position | Age | Business
experience during
past five years |
| V. James Vena | Chief Executive Officer | 67 | [1] |
| Jennifer L. Hamann | Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer | 58 | Current Position |
| Christina B. Conlin | Executive Vice President, Chief Legal Officer, and Corporate Secretary | 53 | [2] |
| Eric J. Gehringer | Executive Vice President - Operations | 46 | Current Position |
| Rahul Jalali | Executive Vice President and Chief Information Officer | 52 | [3] |
| Carrie J. Powers | Vice President, Controller, and Chief Accounting Officer | 55 | [4] |
| Kenny G. Rocker | Executive Vice President - Marketing and Sales | 54 | Current Position |
| | | |
[1]Mr. Vena was elected Chief Executive Officer effective August 14, 2023. He previously served as a Senior Advisor to the Chairman (January 2021 - June 2021) and Chief Operating Officer (January 2019 - December 2020).
[2]Ms. Conlin was elected Executive Vice President, Chief Legal Officer, and Corporate Secretary effective July 16, 2025. She most recently served as Senior Vice President, Chief Legal Officer, and Corporate Secretary (April 2025 – July 2025), Senior Vice President and Deputy General Counsel (December 2024 – April 2025). She was previously Chief Risk Officer and Regulatory Affairs Assistant General Counsel of Good Year Tire & Rubber Company (July 2022 – December 2024), and a Partner at Baker McKenzie (October 2016 – July 2022).
[3]Mr. Jalali was elected Executive Vice President and Chief Information Officer effective June 1, 2023. Mr. Jalali most recently served as Senior Vice President and Chief Information Officer (November 2020 - May 2023).
[4]Ms. Powers was elected Vice President, Controller, and Chief Accounting Officer effective May 8, 2025. Ms. Powers previously served as Assistant Vice President - Financial Reporting (March 2019 - May 2025).
PART II
Item 5. Market for the Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters, and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Our common stock is traded on the NYSE under the symbol “UNP”.
At January 30, 2026, there were 593,391,460 shares of common stock outstanding and 25,761 common shareholders of record. On that date, the closing price of the common stock on the NYSE was $235.10. We paid dividends to our common shareholders during each of the past 126 years.
Comparison over one- and three-year periods – The following table presents the cumulative total shareholder returns, assuming reinvestment of dividends, over one- and three-year periods for the Corporation (UNP), a peer group index (comprised of CSX Corporation and Norfolk Southern Corporation), the Dow Jones Transportation Index (DJ Trans), and the Standard & Poor’s 500 Stock Index (S&P 500).
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Period | UNP | Peer Group | DJ Trans | S&P 500 |
| 1 Year (2025) | 3.8 | % | 19.8 | % | 10.9 | % | 17.9 | % |
| 3 Year (2023 - 2025) | 19.7 | % | 23.7 | % | 35.6 | % | 86.0 | % |
Five-year performance comparison – The following graph provides an indicator of cumulative total shareholder returns for the Corporation as compared to the peer group index (described above), the DJ Trans, and the S&P 500. The graph assumes that $100 was invested in the common stock of Union Pacific Corporation and each index on December 31, 2020, and that all dividends were reinvested. The information below is historical in nature and is not necessarily indicative of future performance.
Purchases of equity securities – During 2025, we repurchased 11,951,818 shares of our common stock at an average price of $234.15. The following table presents common stock repurchases during each month for the fourth quarter of 2025:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Period | Total number of
shares purchased [a] | Average price
paid per share | Total number of shares
purchased as part of a
publicly announced plan
or program [b] | Maximum number of
shares remaining
under the plan or
program [c] |
| Oct. 1 through Oct. 31 | 330 | | $ | 229.80 | | - | | 93,888,442 | |
| Nov. 1 through Nov. 30 | 401 | | 224.63 | | - | | 93,888,442 | |
| Dec. 1 through Dec. 31 | - | | - | | - | | 93,888,442 | |
| Total | 731 | | $ | 226.96 | | - | | N/A |
[a]Total number of shares purchased during the quarter includes approximately 731 shares delivered or attested to UPC by employees to pay stock option exercise prices and satisfy tax withholding obligations for stock option exercises or vesting of retention awards.
[b]As part of the pending acquisition of Norfolk Southern described in Note 20 to the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8, we paused our share repurchase program.
[c]Effective April 1, 2025, our Board of Directors authorized the repurchase of up to 100 million shares of our common stock by March 31, 2028. These repurchases may be made on the open market or through other transactions. Our management has sole discretion with respect to determining the timing and amount of these transactions.
Item 6. [Reserved]
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The following discussion should be read in conjunction with the Consolidated Financial Statements and applicable notes to the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8, and other information in this report, including Risk Factors set forth in Item 1A and Critical Accounting Estimates and Cautionary Information at the end of this Item 7. The following section generally discusses 2025 and 2024 items and year-to-year comparisons between 2025 and 2024. Discussions of 2023 items and year-to-year comparisons between 2024 and 2023 that are not included in this Form 10-K can be found in “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” in Part II, Item 7, of the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2024.
The Railroad, along with its subsidiaries and rail affiliates, is our one reportable operating segment. Although we provide and analyze revenues by commodity group, we treat the financial results of the Railroad as one segment due to the integrated nature of our rail network.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
2025 Results
•Safety – Building on the foundation and commitment to our safety culture, 2025 furthered our progress towards world-class safety. With a focus on four central pillars – Injury Prevention, Leverage Technology, Situational Awareness Testing, and Peer-to-Peer Engagement, we are cultivating a safety-focused mindset so all of our employees return home safely each day.
Injury Prevention efforts focus on specific, critical tasks where any form of non-compliance can result in a serious injury. Training is vital to teach our employees how to safely execute those critical tasks in order to reduce the risk of injury or derailment.
By Leveraging Technology, we seek to eliminate or automate activities with the most risk. Over 7,000 wayside detectors monitor freight cars and locomotives in real time, generating 72 million data points daily to proactively identify and mitigate risks. We are building safer trains with our proprietary Physics Train Builder technology, which allows us to evaluate train and route characteristics to enable proactive intervention by our Operating Practices Command Center to prevent derailments. We utilize our autonomous geometry car fleet to inspect 500,000 miles of track annually. This technology and the data it provides enable us to direct investments and resources in the right place, helping to significantly reduce track-caused derailments over the last 10 years.
Situational Awareness Testing (a program we call COMMIT) is our program that observes, tests, and coaches our employees to promote understanding and compliance with our work rules. COMMIT goes beyond traditional classroom learning, with an emphasis on in-the-field training with employees actively running the railroad.
Peer-to-Peer Engagement drives employee ownership through engagement with our safety programs. Our culture embodies a personal commitment to do our jobs with a passion for safety so everyone goes home safe. Employees are encouraged to speak up if they see unsafe behaviors.
The focus on these four pillars continues to drive improvement, resulting in our best-ever personal injury and derailment incident rate annual safety results. Compared to 2024, our personal injury rate (the number of reportable injuries for every 200,000 employee-hours worked) of 0.68 decreased 24% and our derailment incident rate (the number of reportable derailment incidents per million train miles) of 1.75 improved 19%.
•Service – Bolstered by sequentially improving freight car velocity and terminal dwell, our network remained fluid throughout 2025 as we achieved best-ever results for many of our operating metrics. For the year ended December 31, 2025, freight car velocity increased to 225 daily miles per car, an improvement of 8%, while terminal dwell declined 8% during the same period compared to 2024. Both service performance index measures improved to essentially three-year performance bests as we achieved intermodal service performance of 99% and manifest service performance of 100% for the full year 2025.
•Operational Excellence – We effectively adapted to shifts in business traffic mix throughout 2025 as we handled elevated international intermodal shipments in the first half of the year coupled with strong bulk shipments throughout the year. As customer demand changed, we efficiently modified our resources to match demand while improving our service performance.
•Financial results – Core pricing gains, strong productivity, and 1% volume growth positively impacted our financial results and offset the impact of inflation, negative business mix, and acquisition-related costs. Operating income of $9.8 billion increased 1% from 2024, and our operating ratio improved 10 basis points to 59.8% in 2025. Net income of $7.1 billion translated into earnings of $11.98 per diluted share, improving 8% from the prior year.
We generated $9.3 billion of cash provided by operating activities, yielded free cash flow of $2.3 billion after reductions of $3.8 billion for cash used in investing activities and $3.2 billion in dividends paid. Cash provided by operating activities was positively impacted by $0.3 billion due to the enactment of H.R.1 and the reinstatement of 100% bonus depreciation.
Free cash flow is defined as cash provided by operating activities less cash used in investing activities and dividends paid. Free cash flow is not considered a financial measure under GAAP by SEC Regulation G and Item 10 of SEC Regulation S-K and may not be defined and calculated by other companies in the same manner. We believe free cash flow is important to management and investors in evaluating our financial performance and measures our ability to generate cash without additional external financing. Free cash flow should be considered in addition to, rather than as a substitute for, cash provided by operating activities. The following table reconciles cash provided by operating activities (GAAP measure) to free cash flow (non-GAAP measure):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Cash provided by operating activities | $ | 9,290 | | $ | 9,346 | | $ | 8,379 | |
| Cash used in investing activities | (3,762) | | (3,325) | | (3,667) | |
| Dividends paid | (3,236) | | (3,213) | | (3,173) | |
| Free cash flow | $ | 2,292 | | $ | 2,808 | | $ | 1,539 | |
2026 Outlook
•Safety – We are committed to our goal of world-class safety and are continuously identifying areas in which we can enhance safety. In 2026, our focus remains on our four pillars of safety. Critical safety tasks will be reinforced. Training to engage both new and experienced employees is fundamental to our success. We will continue using a comprehensive safety management approach utilizing technology, hazard identification and risk assessments, employee engagement, training, quality control, and targeted capital investments. In addition, we will continue to collect and utilize data with the goal of identifying and mitigating exposure to risk, detect rail defects, improve or close grade crossings, and educate the public and law enforcement agencies about crossing safety through a combination of our own programs (including risk assessment strategies), industry programs, and local community activities across the network. Our culture is ingrained with a safety-first mindset, critical to our success, both operationally and financially, and our focus will not deviate in 2026.
•Service – We are committed to delivering the service we sold to our customers. As we meet with customers to agree on their specific needs and outcomes, we will continue to measure ourselves against the best service we provided them over the last three years and use that as a guide for meeting their expectations. We will engage with customers by being the first to act on new opportunities, investing to grow, and finding innovative solutions to win together.
•Operational Excellence – To provide our customers with the service we sold, we must run a fluid network. Network fluidity enables us to effectively utilize all our resources and provides the capacity to respond in an ever-changing environment. Terminal dwell and freight car velocity are key indicators of that fluidity. We will continue to transform our railroad using technology and automation to further improve our service product, improve resource utilization, and lower our overall cost structure.
•Business volumes – We expect macroeconomic uncertainties to persist in 2026, and those uncertainties could have a material impact on our 2026 financial and operating results. 2026 industrial production is forecasted to be essentially flat with 2025, coupled with reduced expectations for housing starts and light vehicle sales. Lower international intermodal business, largely due to the resumption of historical trade patterns, is expected to negatively impact volumes. However, higher coal demand, from elevated natural gas prices and increased coal-fired electricity production, is expected to positively impact volumes. In addition, other factors, such as geopolitical instability or changes in trade policies that may affect economic activity and demand for rail transportation; natural gas prices, weather conditions, and demand for other energy sources may impact the coal market; crude oil prices and spreads may drive demand for petroleum products and drilling materials; available truck capacity could impact our intermodal business; and international trade agreements could promote or hinder trade. Fuel prices may continue to fluctuate in the current economic environment. As prices fluctuate, there will be a timing impact on earnings, as our fuel surcharge programs trail increases or decreases in fuel prices by approximately two months. Regardless of macroeconomic or other external factors, we remain focused on operating a safe, fluid, and efficient rail network while delivering the service we sold our customers and capitalizing on new business opportunities.
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Operating revenues
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 | % Change 2025 v 2024 | % Change 2024 v 2023 |
| Freight revenues | $ | 23,220 | | $ | 22,811 | | $ | 22,571 | | 2 | % | 1 | % |
| Other subsidiary revenues | 718 | | 788 | | 872 | | (9) | | (10) | |
| Accessorial revenues | 475 | | 554 | | 584 | | (14) | | (5) | |
| Other | 97 | | 97 | | 92 | | - | | 5 | |
| Total | $ | 24,510 | | $ | 24,250 | | $ | 24,119 | | 1 | % | 1 | % |
We generate freight revenues by transporting products from our three commodity groups. Freight revenues vary with volumes (carloads) and average revenue per car (ARC). Changes in price, traffic mix, and fuel surcharges drive ARC. Customer incentives, which are primarily provided for shipping to/from specific locations or based on cumulative volumes, are recorded as a reduction to operating revenues. Customer incentives that include variable consideration based on cumulative volumes are estimated using the expected value method, which is based on available historical, current, and forecasted volumes, and recognized as the related performance obligation is satisfied. We recognize freight revenues over time as shipments move from origin to destination. The allocation of revenues between reporting periods is based on the relative transit time in each reporting period with expenses recognized as incurred.
Other subsidiary revenues (primarily logistics and commuter rail operations) are generally recognized over time as shipments move from origin to destination. The allocation of revenues between reporting periods is based on the relative transit time in each reporting period with expenses recognized as incurred. Accessorial revenues are recognized at a point in time as performance obligations are satisfied.
Freight revenues of $23.2 billion increased 2% from 2024 driven by core pricing gains and a 1% increase in volumes, partially offset by traffic mix (for example, a relative increase in coal and rock shipments, which have a lower ARC, combined with a decline in lumber shipments, which have a higher ARC) and lower fuel surcharge revenues. Volume increases were primarily driven by coal, grain and grain products, industrial chemicals and plastics, and rock shipments, partially offset by weaker demand for automotive and energy and specialized markets shipments.
Our fuel surcharge programs generated freight revenues of $2.3 billion and $2.6 billion in 2025 and 2024, respectively. Fuel surcharge revenues in 2025 decreased $218 million due to lower fuel prices and the lag impact of fluctuating fuel prices (it can generally take up to two months for changing fuel prices to affect fuel surcharge recoveries), partially offset by higher volumes.
In 2025, other subsidiary revenues decreased compared to 2024 due to the transfer of our commuter operations to Metra. Accessorial revenues decreased in 2025 compared to 2024 as a result of lower intermodal container revenues due to an intermodal equipment sale and a one-time contract settlement, both of which occurred in 2024, partially offset by higher intermodal accessorial revenues.
The following tables summarize the year-over-year changes in freight revenues, revenue carloads, and ARC by commodity type:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Freight revenues Millions | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 | % Change 2025 v 2024 | % Change 2024 v 2023 |
| Grain & grain products | $ | 3,926 | | $ | 3,828 | | $ | 3,644 | | 3 | % | 5 | % |
| Fertilizer | 856 | | 811 | | 757 | | 6 | | 7 | |
| Food & refrigerated | 1,018 | | 1,085 | | 1,041 | | (6) | | 4 | |
| Coal & renewables | 1,786 | | 1,483 | | 1,916 | | 20 | | (23) | |
| Bulk | 7,586 | | 7,207 | | 7,358 | | 5 | | (2) | |
| Industrial chemicals & plastics | 2,512 | | 2,345 | | 2,176 | | 7 | | 8 | |
| Metals & minerals | 2,193 | | 2,081 | | 2,194 | | 5 | | (5) | |
| Forest products | 1,290 | | 1,326 | | 1,347 | | (3) | | (2) | |
| Energy & specialized markets | 2,609 | | 2,688 | | 2,521 | | (3) | | 7 | |
| Industrial | 8,604 | | 8,440 | | 8,238 | | 2 | | 2 | |
| Automotive | 2,398 | | 2,452 | | 2,421 | | (2) | | 1 | |
| Intermodal | 4,632 | | 4,712 | | 4,554 | | (2) | | 3 | |
| Premium | 7,030 | | 7,164 | | 6,975 | | (2) | | 3 | |
| Total | $ | 23,220 | | $ | 22,811 | | $ | 22,571 | | 2 | % | 1 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Revenue carloads Thousands | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 | % Change 2025 v 2024 | % Change 2024 v 2023 |
| Grain & grain products | 880 | | 850 | | 798 | | 4 | % | 7 | % |
| Fertilizer | 216 | | 213 | | 191 | | 1 | | 12 | |
| Food & refrigerated | 163 | | 177 | | 175 | | (8) | | 1 | |
| Coal & renewables | 797 | | 702 | | 867 | | 14 | | (19) | |
| Bulk | 2,056 | | 1,942 | | 2,031 | | 6 | | (4) | |
| Industrial chemicals & plastics | 704 | | 672 | | 645 | | 5 | | 4 | |
| Metals & minerals | 747 | | 719 | | 793 | | 4 | | (9) | |
| Forest products | 203 | | 213 | | 213 | | (5) | | - | |
| Energy & specialized markets | 587 | | 607 | | 582 | | (3) | | 4 | |
| Industrial | 2,241 | | 2,211 | | 2,233 | | 1 | | (1) | |
| Automotive | 793 | | 824 | | 820 | | (4) | | - | |
| Intermodal [a] | 3,357 | | 3,357 | | 3,028 | | - | | 11 | |
| Premium | 4,150 | | 4,181 | | 3,848 | | (1) | | 9 | |
| Total | 8,447 | | 8,334 | | 8,112 | | 1 | % | 3 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Average revenue per car | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 | % Change 2025 v 2024 | % Change 2024 v 2023 |
| Grain & grain products | $ | 4,461 | | $ | 4,505 | | $ | 4,567 | | (1) | % | (1) | % |
| Fertilizer | 3,970 | | 3,809 | | 3,962 | | 4 | | (4) | |
| Food & refrigerated | 6,233 | | 6,104 | | 5,929 | | 2 | | 3 | |
| Coal & renewables | 2,241 | | 2,113 | | 2,211 | | 6 | | (4) | |
| Bulk | 3,690 | | 3,710 | | 3,623 | | (1) | | 2 | |
| Industrial chemicals & plastics | 3,568 | | 3,493 | | 3,374 | | 2 | | 4 | |
| Metals & minerals | 2,935 | | 2,893 | | 2,765 | | 1 | | 5 | |
| Forest products | 6,369 | | 6,229 | | 6,310 | | 2 | | (1) | |
| Energy & specialized markets | 4,446 | | 4,426 | | 4,335 | | - | | 2 | |
| Industrial | 3,840 | | 3,818 | | 3,689 | | 1 | | 3 | |
| Automotive | 3,024 | | 2,976 | | 2,955 | | 2 | | 1 | |
| Intermodal [a] | 1,380 | | 1,404 | | 1,504 | | (2) | | (7) | |
| Premium | 1,694 | | 1,714 | | 1,813 | | (1) | | (5) | |
| Average | $ | 2,749 | | $ | 2,737 | | $ | 2,782 | | - | % | (2) | % |
[a]For intermodal shipments, each container or trailer equals one carload.
Bulk – Bulk includes shipments of grain and grain products, fertilizer, food and refrigerated, and coal and renewables. Freight revenues from bulk shipments increased in 2025 compared to 2024 due to 6% higher volumes and core pricing gains, partially offset by negative mix, from increased coal shipments, and lower fuel surcharge revenues. Bulk volume growth compared to 2024 was driven by increased use of coal in electricity generation due to higher natural gas prices coupled with business wins, in addition to, strength in export grain to Mexico and soybean crush production. These volume gains were partially offset by reduced food and beverage shipments.
Industrial – Industrial includes shipments of industrial chemicals and plastics, metals and minerals, forest products, and energy and specialized markets. Freight revenues from industrial shipments increased in 2025 versus 2024 due to core pricing gains and higher volumes, partially offset by a negative mix of traffic, from increased rock and lower lumber shipments, and lower fuel surcharge revenues. Volumes increased 1% compared to 2024 due to stronger demand for rock, plastics, and industrial chemicals shipments partially offset by lower iron ore (as a result of tariff uncertainties), petroleum, and lumber carloads.
Premium – Premium includes shipments of finished automobiles, automotive parts, and merchandise in intermodal containers, both domestic and international. Freight revenues from premium shipments decreased in 2025 driven by lower fuel surcharge revenues, negative business mix from reduced automotive shipments, and lower volumes, partially offset by core pricing gains. The heavy demand from increased U.S. West Coast imports continued into the first half of 2025 due to uncertainty related to trade policies, resulting in first half international intermodal volumes up 17%. Traffic shifted back to historical trade patterns in the second half of 2025 and international intermodal volumes decreased 24% compared to the second half of 2024, resulting in 6% lower international intermodal volumes for 2025. Strong domestic intermodal volumes helped to offset the decline in international shipments as a result of business development wins. Automotive shipments were down 4% year-over-year due to tariff uncertainties in the first half of 2025 and reduced manufacturer production from softer consumer demand.
2025 Bulk Carloads
2025 Industrial Carloads
2025 Premium Carloads
Mexico business – Freight revenues from each of our commodity groups includes revenues from shipments to and from Mexico, which equated to $2.9 billion in 2025, down 1% compared to 2024, driven by a 2% reduction in ARC partially offset by 2% higher volumes. Compared to 2024, intermodal and grain and grain products volumes increased and were partially offset by lower auto parts and finished vehicle shipments.
Operating expenses
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 | % Change 2025 v 2024 | % Change 2024 v 2023 |
| Compensation and benefits | $ | 4,897 | | $ | 4,899 | | $ | 4,818 | | - | % | 2 | % |
| Purchased services and materials | 2,626 | | 2,520 | | 2,616 | | 4 | | (4) | |
| Depreciation | 2,465 | | 2,398 | | 2,318 | | 3 | | 3 | |
| Fuel | 2,390 | | 2,474 | | 2,891 | | (3) | | (14) | |
| Equipment and other rents | 912 | | 920 | | 947 | | (1) | | (3) | |
| Other | 1,374 | | 1,326 | | 1,447 | | 4 | | (8) | |
| Total | $ | 14,664 | | $ | 14,537 | | $ | 15,037 | | 1 | % | (3) | % |
Operating expenses increased $127 million, or 1%, in 2025 compared to 2024 driven by inflation, volume-related costs, acquisition-related expenses, and higher depreciation, partially offset by productivity and lower fuel prices. In addition, the year-over-year comparison was negatively impacted by a gain on the sale of intermodal equipment in 2024 and higher crew staffing agreement ratification charges in 2025 as we reached agreements in both years.
Compensation and benefits – Compensation and benefits include wages, payroll taxes, health and welfare costs, pension costs, and incentive costs. In 2025, expenses were essentially flat compared to 2024 due to wage inflation, increased volumes, higher incentive compensation, and increased crew needs associated with labor agreements, partially offset by 3% lower employee levels. Active train, engine, and yard (TE&Y) force levels decreased 3% in 2025 on 1% increased carloads due to improved network fluidity.
Purchased services and materials – Expense for purchased services and materials includes the costs of services purchased from outside contractors and other service providers (including equipment maintenance and contract expenses incurred by our subsidiaries for external transportation services); materials used to maintain the Railroad’s lines, structures, and equipment; costs of operating facilities jointly used by UPRR and other railroads; transportation and lodging for train crew employees; trucking and contracting costs for intermodal containers; leased automobile maintenance expenses; and tools and supplies. Purchased services and materials increased 4% in 2025 compared to 2024 driven by inflation (including tariff-related material expenses), acquisition-related expenses, and higher locomotive maintenance expense was partially offset by productivity and lower expenses incurred by our subsidiaries. The comparison was also negatively impacted by a favorable contract settlement in 2024.
Fuel – Fuel includes locomotive fuel and gasoline for highway and non-highway vehicles and heavy equipment. Fuel expense decreased compared to 2024 due to a 6% decrease in locomotive diesel fuel prices, declining from an average of $2.64 per gallon (including taxes and transportation costs) in 2024 to $2.49 per gallon in 2025, resulting in a $138 million decrease in expense (excluding any impact from increased volumes year-over-year) and a 1% improvement to the fuel consumption rate in 2024 (computed as gallons of fuel consumed divided by gross ton-miles). Gross-ton miles increased 3% in 2025 and partially offset the impact of lower fuel prices and improved fuel consumption rate.
Depreciation – The majority of depreciation relates to road property, including rail, ties, ballast, and other track material. Depreciation expense was up 3% in 2025 compared to 2024 due to a higher depreciable asset base.
Equipment and other rents – Equipment and other rents expense primarily includes rental expense that the Railroad pays for freight cars owned by other railroads or private companies; freight car, intermodal, and locomotive leases; and office and other rent expenses, offset by equity income from certain equity method investments. Equipment and other rents expense decreased 1% compared to 2024 due to lower operating equipment lease expense, which included favorable contract settlements in 2025, and reduced car hire expense as favorable haul length and improved cycle times partially offset inflation and costs associated with increased demand in commodities utilizing freight cars owned by others. Higher other rental expense and lower equity income partially offset the favorable expense drivers.
Other – Other expenses include property taxes; freight, equipment, and property damage; utilities; insurance; personal injury; environmental; employee travel; telephone and cellular; computer software; bad debt; and other general expenses. Other expenses increased 4% in 2025 compared to 2024 driven by the negative comparison from a 2024 gain on the sale of intermodal equipment, in addition to, higher personal injury costs, and property taxes, partially offset by lower environmental and freight loss and damage casualty costs.
Non-operating items
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 | % Change 2025 v 2024 | % Change 2024 v 2023 |
| Other income, net | $ | 629 | | $ | 350 | | $ | 491 | | 80 | % | (29) | % |
| Interest expense | (1,309) | | (1,269) | | (1,340) | | 3 | | (5) | |
| Income tax expense | $ | (2,028) | | $ | (2,047) | | $ | (1,854) | | (1) | % | 10 | % |
Other income, net – Other income increased $279 million in 2025 compared to 2024 driven by $295 million in higher real estate income, including $250 million in industrial park land sales. The higher real estate income was partially offset by interest received in 2024 from the IRS on refund claims. See Note 6 to the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8, for additional detail.
Interest expense – Interest expense increased 3% in 2025 compared to 2024 due to an increased weighted-average debt level of $32.1 billion in 2025 from $31.6 billion in 2024. In addition, the effective interest rate of 4.1% in 2025 increased from 4.0% in 2024.
Income tax expense – Income tax expense decreased in 2025 compared to 2024. While pre-tax income was higher in 2025, the increase was more than offset by a $115 million reduction in deferred tax expense resulting from newly enacted Kansas legislation, along with the favorable impact of purchased tax credits during the year. In 2024, the states of Louisiana and Arkansas enacted legislation to reduce their corporate income tax rates for future years resulting in a $34 million reduction of our deferred tax expense. Our effective tax rates for 2025 and 2024 were 22.1% and 23.3%, respectively.
OTHER OPERATING/PERFORMANCE AND FINANCIAL STATISTICS
We report a number of key performance measures weekly to the STB. We provide these on our website at https://investor.unionpacific.com/key-performance-metrics.
Operating/performance statistics
Management continuously monitors these key operating metrics to evaluate our operational efficiency in striving to deliver the service product we sold to our customers.
Railroad performance measures are included in the table below:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2025 | 2024 | 2023 | % Change 2025 v 2024 | % Change 2024 v 2023 |
| Gross ton-miles (GTMs) (billions) | 873.6 | 847.4 | 837.5 | 3 | % | 1 | % |
| Revenue ton-miles (billions) | 426.9 | 409.7 | 413.3 | 4 | | (1) | |
| Freight car velocity (daily miles per car) | 225 | 208 | 204 | 8 | | 2 | |
| Average train speed (miles per hour) [a] | 24.3 | 23.6 | 24.2 | 3 | | (2) | |
| Average terminal dwell time (hours) [a] | 20.9 | 22.6 | 23.4 | (8) | | (3) | |
| Locomotive productivity (GTMs per horsepower day) | 139 | 135 | 129 | 3 | | 5 | |
| Train length (feet) | 9,678 | 9,469 | 9,356 | 2 | | 1 | |
| Intermodal service performance index (%) | 99 | | 90 | | 88 | | 9 | pts | 2 | pts |
| Manifest service performance index (%) | 100 | | 89 | | 85 | | 11 | pts | 4 | pts |
| Workforce productivity (car miles per employee) | 1,132 | 1,062 | 1,000 | 7 | | 6 | |
| Total employees (average) | 29,287 | 30,336 | 31,490 | (3) | | (4) | |
| Operating ratio (%) | 59.8 | | 59.9 | | 62.3 | | (0.1) | pts | (2.4) | pts |
[a]As reported to the STB.
Gross and revenue ton-miles – Gross ton-miles are calculated by multiplying the weight of loaded and empty freight cars by the number of miles hauled. Revenue ton-miles are calculated by multiplying the weight of freight by the number of tariff miles. In 2025, gross ton-miles increased 3% and revenue ton-miles increased 4% on 1% higher carloadings year-over-year. Changes in commodity mix drove the year-over-year variances between gross ton-miles, revenue ton-miles, and carloads due to higher coal shipments, which are heavier.
Freight car velocity – Freight car velocity measures the average daily miles per car on our network. The two key drivers of this metric are the speed of the train between terminals (average train speed) and the time a rail car spends at the terminals (average terminal dwell time). Compared to 2024, freight car velocity increased 8% driven by record terminal dwell, which also improved 8%, and 3% higher average train speeds.
Locomotive productivity – Locomotive productivity is gross ton-miles per average daily locomotive horsepower. Locomotive productivity improved 3% in 2025 compared to 2024 driven by improved network fluidity and asset utilization.
Train length – Train length is the average maximum train length on a route measured in feet. Our train length increased 2% compared to 2024 due to train length improvement initiatives and increases in coal train length, coinciding with increased shipments.
Service performance index (SPI) – SPI is a ratio of the service customers are currently receiving relative to the best monthly performance over the last three years. Measuring our performance relative to a historical benchmark demonstrates our focus on continuously improving service for our customers, and we believe it is a better indicator of service performance than the previously disclosed trip plan compliance. SPI does not replace the service commitments we have contractually agreed to with a small number of customers. SPI is calculated for intermodal and manifest products. Intermodal SPI improved 9 points as we adjusted to shifting international intermodal customer demand during 2025. Manifest SPI improved 11 points in 2025 compared to 2024 while handling more volume.
Workforce productivity – Workforce productivity is average daily car miles per employee. Workforce productivity improved 7% in 2025 as average daily car miles increased 3% while employees decreased 3% compared to 2024. We adequately aligned our active TE&Y workforce to support carload demand while maintaining an adequate training pipeline to provide a capacity buffer to enable responsiveness in an ever-changing demand and operating environment.
Operating ratio – Operating ratio is our operating expenses reflected as a percentage of operating revenues. Our operating ratio of 59.8% improved 0.1 points compared to 2024 driven by core pricing gains and productivity initiatives, partially offset by the impact of negative business mix, inflation, and acquisition-related expenses. In addition, operating ratio year-over-year comparison was negatively impacted by 2024 contract settlements, a 2024 gain on the sale of intermodal equipment, and higher labor agreement ratification charges in 2025.
Return on average common shareholders’ equity
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions, except percentages | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Net income | $ | 7,138 | | $ | 6,747 | | $ | 6,379 | |
| Average equity | $ | 17,679 | | $ | 15,839 | | $ | 13,476 | |
| Return on average common shareholders' equity | 40.4 | % | 42.6 | % | 47.3 | % |
Return on invested capital as adjusted (ROIC)
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions, except percentages | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Net income | $ | 7,138 | | $ | 6,747 | | $ | 6,379 | |
| Interest expense | 1,309 | | 1,269 | | 1,340 | |
| Interest on average operating lease liabilities | 46 | | 55 | | 58 | |
| Taxes on interest | (299) | | (308) | | (315) | |
| Net operating profit after taxes as adjusted | $ | 8,194 | | $ | 7,763 | | $ | 7,462 | |
| Average equity | $ | 17,679 | | $ | 15,839 | | $ | 13,476 | |
| Average debt | 31,503 | | 31,886 | | 32,953 | |
| Average operating lease liabilities | 1,140 | | 1,436 | | 1,616 | |
| Average invested capital as adjusted | $ | 50,322 | | $ | 49,161 | | $ | 48,045 | |
| Return on invested capital as adjusted | 16.3 | % | 15.8 | % | 15.5 | % |
ROIC is considered a non-GAAP financial measure by SEC Regulation G and Item 10 of SEC Regulation S-K and may not be defined and calculated by other companies in the same manner. We believe this measure is important to management and investors in evaluating the efficiency and effectiveness of our long-term capital investments. In addition, we currently use ROIC as a performance criterion in determining certain elements of equity compensation for our executives. ROIC should be considered in addition to, rather than as a substitute for, other information provided in accordance with GAAP. The most comparable GAAP measure is return on average common shareholders’ equity. The tables above provide a reconciliation from return on average common shareholders’ equity to ROIC. At December 31, 2025, 2024, and 2023, the incremental borrowing rate on operating leases was 4.0%, 3.8%, and 3.6%, respectively.
Debt / net income
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions, except ratios | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Debt | $ | 31,814 | | $ | 31,192 | | $ | 32,579 | |
| Net income | $ | 7,138 | | $ | 6,747 | | $ | 6,379 | |
| Debt / net income | 4.5 | 4.6 | 5.1 |
Adjusted debt / adjusted EBITDA
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions, except ratios | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Net income | $ | 7,138 | | $ | 6,747 | | $ | 6,379 | |
| Add: | | | |
| Income tax expense | 2,028 | | 2,047 | | 1,854 | |
| Depreciation | 2,465 | | 2,398 | | 2,318 | |
| Interest expense | 1,309 | | 1,269 | | 1,340 | |
| EBITDA | $ | 12,940 | | $ | 12,461 | | $ | 11,891 | |
| Adjustments: | | | |
| Other income, net | (629) | | (350) | | (491) | |
| Interest on operating lease liabilities [1] | 40 | | 48 | | 58 | |
| Adjusted EBITDA (a) | $ | 12,351 | | $ | 12,159 | | $ | 11,458 | |
| Debt | $ | 31,814 | | $ | 31,192 | | $ | 32,579 | |
| Operating lease liabilities | 1,008 | | 1,271 | | 1,600 | |
| Adjusted debt (b) | $ | 32,822 | | $ | 32,463 | | $ | 34,179 | |
| Adjusted debt / adjusted EBITDA (b/a) | 2.7 | 2.7 | 3.0 |
[1]Represents the hypothetical interest expense we would incur (using the incremental borrowing rate) if the property under our operating leases were owned or accounted for as finance leases.
Adjusted debt (total debt plus operating lease liabilities plus after-tax unfunded pension and OPEB (other post-retirement benefit obligations) to adjusted EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, amortization, and adjustments for other income and interest on present value of operating leases) is considered a non-GAAP financial measure by SEC Regulation G and Item 10 of SEC Regulation S-K and may not be defined and calculated by other companies in the same manner. We believe this measure is important to management and investors in evaluating the Company’s ability to sustain given debt levels (including leases) with the cash generated from operations. In addition, a comparable measure is used by rating agencies when reviewing the Company’s credit rating. Adjusted debt to adjusted EBITDA should be considered in addition to, rather than as a substitute for, other information provided in accordance with GAAP. The most comparable GAAP measure is debt to net income ratio. The tables above provide reconciliations from net income to adjusted EBITDA, debt to adjusted debt, and debt to net income to adjusted debt to adjusted EBITDA. At December 31, 2025, 2024, and 2023, the incremental borrowing rate on operating leases was 4.0%, 3.8%, and 3.6%, respectively. Pension and OPEB were funded at December 31, 2025, 2024, and 2023.
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
We are continually evaluating our financial condition and liquidity. We analyze a wide range of economic scenarios and the impact on our ability to generate cash. These analyses inform our liquidity plans and activities outlined below and indicate we have sufficient borrowing capacity to sustain an extended period of lower volumes.
At both December 31, 2025 and 2024, we had a working capital deficit due to upcoming debt maturities. It is not unusual for us to have a working capital deficit, and we believe it is not an indication of a lack of liquidity. We generate strong cash from operations and also maintain adequate resources, including our credit facility and, when necessary, access the capital markets to meet foreseeable cash requirements.
During 2025, we generated $9.3 billion of cash provided by operating activities, paid down $1.4 billion of long-term debt, paid $3.2 billion in dividends, and repurchased shares totaling $2.7 billion. We also announced the pending acquisition of Norfolk Southern described in Note 20 to the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8, and paused our share repurchase program. We have been, and we expect to continue to be, in compliance with our debt covenants.
Our principal sources of liquidity include cash and cash equivalents, our Receivables Facility, our revolving credit facility, as well as, the availability of commercial paper and other sources of financing through the capital markets. On December 31, 2025, we had $1.3 billion of cash and cash equivalents, $250 million of short-term investments, $2.0 billion of committed credit available under our revolving credit facility, and up to $600 million undrawn on the Receivables Facility. As of December 31, 2025, none of the revolving credit facility was drawn, and we did not draw on our revolving credit facility at any time during 2025. Our access to the Receivables Facility may be reduced or restricted if our bond ratings fall to certain levels below investment grade. If our bond rating were to deteriorate, it could have an adverse impact on our liquidity. Access to commercial paper, as well as, other capital market financing is dependent on market conditions. Deterioration of our operating results or financial condition due to internal or external factors could negatively impact our ability to access capital markets as a source of liquidity. Access to liquidity through the capital markets is also dependent on our financial stability. We expect that we will continue to have access to liquidity through any or all of the following sources or activities: (a) increasing the utilization of our Receivables Facility, (b) issuing commercial paper, (c) entering into bank loans, outside of our revolving credit facility, or (iv) issuing bonds or other debt securities to public or private investors based on our assessment of the current condition of the credit markets. The Company’s $2.0 billion revolving credit facility is intended to support the issuance of commercial paper by UPC and also serves as an additional source of liquidity to fund short-term needs. The Company currently does not intend to borrow from this facility.
As described in the notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements and as referenced in the table below, we have contractual obligations that may affect our financial condition. Based on our assessment of the underlying provisions and circumstances of our contractual obligations, other than the risks that we and other similarly situated companies face with respect to the condition of the capital markets (as described in Item 1A of Part II of this report), as of the date of this filing, there is no known trend, demand, commitment, event, or uncertainty that is reasonably likely to occur that would have a material adverse effect on our consolidated results of operations, financial condition, or liquidity. In addition, our commercial obligations, financings, and commitments are customary transactions that are like those of other comparable corporations, particularly within the transportation industry.
The following table identifies material contractual obligations as of December 31, 2025:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Payments due by December 31, |
Millions | Total | 2026 | 2027 | 2028 | 2029 | 2030 | After
2030 |
| Debt [a] | $ | 59,424 | | $ | 2,724 | | $ | 2,455 | | $ | 2,402 | | $ | 2,360 | | $ | 1,816 | | $ | 47,667 | |
| Purchase obligations [b] | 2,537 | | 817 | | 579 | | 434 | | 389 | | 302 | | 16 | |
| Operating leases [c] | 1,125 | | 276 | | 238 | | 191 | | 123 | | 121 | | 176 | |
| Other post-retirement benefits [d] | 355 | | 36 | | 36 | | 36 | | 36 | | 36 | | 175 | |
| Finance lease obligations [e] | 114 | | 42 | | 37 | | 14 | | 21 | | - | | - | |
| Total contractual obligations | $ | 63,555 | | $ | 3,895 | | $ | 3,345 | | $ | 3,077 | | $ | 2,929 | | $ | 2,275 | | $ | 48,034 | |
[a]Excludes finance lease obligations of $105 million as well as unamortized discount and deferred issuance costs of ($1,678) million. Includes an interest component of $26,037 million.
[b]Purchase obligations include locomotive maintenance contracts; purchase commitments for ties, ballast, and rail; and agreements to purchase other goods and services.
[c]Includes leases for locomotives, freight cars, other equipment, and real estate. Includes an interest component of $117 million.
[d]Includes estimated other post-retirement medical payments and payments made under the unfunded pension plan for the next ten years.
[e]Represents total obligations, including an interest component of $9 million.
Cash flows
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Cash provided by operating activities | $ | 9,290 | | $ | 9,346 | | $ | 8,379 | |
| Cash used in investing activities | (3,762) | | (3,325) | | (3,667) | |
| Cash used in financing activities | (5,276) | | (6,067) | | (4,625) | |
| Net change in cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash | $ | 252 | | $ | (46) | | $ | 87 | |
Operating activities
Cash provided by operating activities decreased in 2025 compared to 2024 due to timing of payments to taxing authorities and purchased tax credits.
On July 4, 2025, H.R.1 was enacted that makes key elements of the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act permanent, including provisions for 100% bonus depreciation on qualified property and fully expensing internally developed software, which has and will continue to favorably impact our cash provided by operating activities.
Cash flow conversion is defined as cash provided by operating activities less cash used in capital investments as a ratio of net income. Cash flow conversion rate is not considered a financial measure under GAAP by SEC Regulation G and Item 10 of SEC Regulation S-K and may not be defined and calculated by other companies in the same manner. We believe cash flow conversion rate is important to management and investors in evaluating our financial performance and measures our ability to generate cash without additional external financing. Cash flow conversion rate should be considered in addition to, rather than as a substitute for, cash provided by operating activities. The following table reconciles cash provided by operating activities (GAAP measure) to cash flow conversion rate (non-GAAP measure):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions, except percentages | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Cash provided by operating activities | $ | 9,290 | | $ | 9,346 | | $ | 8,379 | |
| Cash used in capital investments | (3,791) | | (3,452) | | (3,606) | |
| Total (a) | 5,499 | | 5,894 | | 4,773 | |
| Net income (b) | $ | 7,138 | | $ | 6,747 | | $ | 6,379 | |
| Cash flow conversion rate (a/b) | 77 | % | 87 | % | 75 | % |
Investing activities
Cash used in investing activities in 2025 increased compared to 2024 primarily driven by higher capital investments and the purchase of short term investments, partially offset by higher proceeds from real estate sales.
The following table details cash capital investments for the years ended December 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Ties | $ | 523 | | $ | 503 | | $ | 565 | |
| Rail and other track material | 562 | | 493 | | 454 | |
| Ballast | 197 | | 197 | | 194 | |
| Other [a] | 705 | | 740 | | 691 | |
| Total road infrastructure replacements | 1,987 | | 1,933 | | 1,904 | |
| Line expansion and other capacity projects | 258 | | 183 | | 239 | |
| Commercial facilities | 359 | | 317 | | 425 | |
| Total capacity and commercial facilities | 617 | | 500 | | 664 | |
| Locomotives and freight cars [b] | 810 | | 788 | | 728 | |
| Technology and other | 377 | | 231 | | 310 | |
| Total cash capital investments [c] | $ | 3,791 | | $ | 3,452 | | $ | 3,606 | |
[a]Other includes bridges and tunnels, signals, other road assets, and road work equipment.
[b]Locomotives and freight cars include lease buyouts of $311 million, $143 million, and $57 million in 2025, 2024, and 2023, respectively.
[c]Weather-related damages for 2025, 2024, and 2023 are immaterial.
See Note 20 to the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8, for information regarding the pending acquisition of Norfolk Southern.
Capital plan
In 2026, we expect our capital plan to be approximately $3.3 billion. We plan to continue to make investments to support our growth strategy, improve the safety, resiliency, and operational efficiency of the network, harden our infrastructure, and replace older assets, including modernization of our locomotive fleet and acquiring freight cars to support replacement and growth opportunities. In addition, the plan includes investments in growth-related projects to drive more carloads to the network and enhance productivity. This includes terminal investments supporting our manifest network and intermodal ramps to efficiently handle new and existing customers, along with siding investments (extensions and new), and second mainline track projects. The capital plan may be revised if business conditions warrant or if laws or regulations affect our ability to generate sufficient returns on these investments.
Financing activities
Cash used in financing activities decreased in 2025 compared to 2024 driven by an increase of debt issued and a decrease in debt repaid, partially offset by an increase in share repurchases.
See Note 14 to the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8, for a description of all our outstanding financing arrangements and significant new borrowings, Note 18 to the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8, for a description of our share repurchase programs, and Note 20 to the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8, for the pending acquisition of Norfolk Southern.
OTHER MATTERS
Inflation – For capital-intensive companies, inflation significantly increases asset replacement costs for long-lived assets. As a result, assuming that we replace all operating assets at current price levels, depreciation charges (on an inflation-adjusted basis) would be substantially greater than historically reported amounts.
Sensitivity analyses – The sensitivity analyses that follow illustrate the economic effect that hypothetical changes in interest and tax rates could have on our results of operations and financial condition. These hypothetical changes do not consider other factors that could impact actual results.
Interest rates – At both December 31, 2025, and 2024, we did not have variable-rate debt.
Market risk for fixed-rate debt is estimated as the potential increase in fair value resulting from a hypothetical 1% decrease in interest rates as of December 31, 2025, and 2024, and totals an increase of approximately $3.2 billion and $3.0 billion to the fair value of our debt at December 31, 2025, and 2024, respectively. We estimated the fair values of our fixed-rate debt by considering the impact of the hypothetical interest rates on quoted market prices and current borrowing rates.
Tax rates – Our deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured based on current tax law. Future tax legislation, such as a change in the federal corporate tax rate, could have a material impact on our financial condition, results of operations, or liquidity. For example, as of December 31, 2025, a future, permanent 1% increase in our federal income tax rate would increase our deferred tax liability by approximately $550 million. Similarly, a future, permanent 1% decrease in our federal income tax rate would decrease our deferred tax liability by approximately $550 million. As of December 31, 2024, a permanent 1% increase or decrease in our federal income tax rate would have correspondingly increased or decreased our deferred tax liability by approximately $525 million, respectively.
Accounting pronouncements – See Note 3 to the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8.
Asserted and unasserted claims – See Note 17 to the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8.
Indemnities – See Note 17 to the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8.
Pending Acquisition – See Note 20 to the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8, and the Agreement and Plan of Merger dated as of July 28, 2025, by and among the Company, Ruby Merger Sub 1 Corporation, Ruby Merger Sub 2 LLC, and Norfolk Southern, which is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to the Corporation’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated July 29, 2025.
Climate change – Climate change could have an adverse impact on our operations and financial performance (see Risk Factors under Item 1A of this report). We utilize climate scenario analyses to better understand climate-related risks and opportunities the Company may face in the future under a range of potential scenarios. We continue to refine our approach to understand climate-related risks and are taking an iterative approach in our business planning processes as risk factors, solutions, and technology develop. However, we are unable to predict the likelihood, manner, severity, or ultimate financial impact of actual future incidents as climate scenario analysis considers a range of potential outcomes.
We continue to take steps and explore opportunities to reduce our operational impact on the environment, including improving our operational fluidity to increase fuel efficiency, modernizing locomotives for improved reliability and fuel consumption, using renewable fuels, and exploring and testing low- and zero-emissions propulsion technologies. These initiatives are aligned with our strategy of Safety, Service, and Operational Excellence leading to Growth. (See further discussion in "Sustainable Future" in the Operations section in Item 1 of this report.)
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING ESTIMATES
Our Consolidated Financial Statements have been prepared in accordance with GAAP. The preparation of these financial statements requires estimation and judgment that affect the reported amounts of revenues, expenses, assets, and liabilities. We base our estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that we believe are reasonable under the circumstances. The results form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. The following critical accounting estimates are a subset of our significant accounting policies described in Note 2 to the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8. These critical accounting estimates affect significant areas of our financial statements and involve judgment and estimates. If these estimates differ significantly from actual results, the impact on our Consolidated Financial Statements may be material.
Personal injury – See Note 17 to the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8, and "We may be subject to various claims and lawsuits that could result in significant expenditures" in the Risk Factors, Item 1A.
Our personal injury liability is subject to uncertainty due to unasserted claims, timing and outcome of claims, and evolving trends in litigation. There were no material changes to the assumptions used in the latest actuarial analysis.
Our personal injury liability balance and claims activity was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Ending liability balance at December 31 (millions) | $ | 413 | | $ | 379 | | $ | 383 | |
| Open claims, beginning balance | 1,567 | | 1,871 | | 2,036 | |
| New claims | 2,602 | | 2,842 | | 3,008 | |
| Settled or dismissed claims | (2,829) | | (3,146) | | (3,173) | |
| Open claims, ending balance at December 31 | 1,340 | | 1,567 | | 1,871 | |
Environmental costs – See Note 17 to the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8; "We are subject to significant environmental laws and regulations" in the Risk Factors, Item 1A; and Environmental Matters in the Legal Proceedings, Item 3.
Our environmental liability is subject to several factors such as type of remediation, nature and volume of contaminate, number and financial viability of other potentially responsible parties, as well as uncertainty due to unknown alleged contamination, evolving trends in remediation techniques and final remedies, and changes in laws and regulations.
Our environmental liability balance and site activity was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Ending liability balance at December 31 (millions) | $ | 259 | | $ | 268 | | $ | 245 | |
| Open sites, beginning balance | 352 | | 333 | | 353 | |
| New sites | 73 | | 84 | | 74 | |
| Closed sites | (82) | | (65) | | (94) | |
| Open sites, ending balance at December 31 | 343 | | 352 | | 333 | |
Property and depreciation – See Note 11 to the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8.
Assets purchased or constructed throughout the year are capitalized if they meet applicable minimum units of property.
Estimated service lives of depreciable railroad property may vary over time due to changes in physical use, technology, asset strategies, and other factors that will have an impact on the retirement profiles of our assets. We are not aware of any specific factors that are reasonably likely to significantly change the estimated service lives of our assets. Actual use and retirement of our assets may vary from our current estimates, which would impact the amount of depreciation expense recognized in future periods.
Changes in estimated useful lives of our assets due to the results of our depreciation studies could significantly impact future periods’ depreciation expense and have a material impact on our Consolidated Financial Statements. If the estimated useful lives of all depreciable assets were increased by one year, annual depreciation expense would decrease by approximately $81 million. If the estimated useful lives of all depreciable assets were decreased by one year, annual depreciation expense would increase by approximately $76 million. We are projecting an increase in our depreciation expense of approximately 4% in 2026 versus 2025. This is driven by an increase in our projected depreciable asset base.
Pension plans – See Note 5 to the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8.
The critical assumptions used to measure pension obligations and expenses are the discount rates and expected rate of return on pension assets.
We evaluate our critical assumptions at least annually, and selected assumptions are based on the following factors:
•We measure the service cost and interest cost components of our net periodic pension benefit/cost by using individual spot rates matched with separate cash flows for each future year. Discount rates are based on a Mercer yield curve of high-quality corporate bonds (rated AA by a recognized rating agency).
•Expected return on plan assets is based on our asset allocation mix and our historical return, taking into consideration current and expected market conditions.
The following tables present the key assumptions used to measure net periodic pension benefit/cost for 2026 and the estimated impact on 2026 net periodic pension benefit/cost relative to a change in those assumptions:
| | | | | |
| Assumptions | |
| Discount rate for interest on benefit obligations | 4.94 | % |
| Discount rate for service cost | 5.88 | % |
| Discount rate for interest on service cost | 5.64 | % |
| Expected return on plan assets | 5.25 | % |
| | | | | |
Sensitivities Millions | Increase in
pension cost |
| 0.25% decrease in discount rates | $ | - | |
| 0.25% decrease in expected return on plan assets | $ | 12 | |
The following table presents the net periodic pension benefit/cost for the years ended December 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions | Est.
2026 | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Net periodic pension (benefit)/cost | $ | (23) | | $ | (14) | | $ | (3) | | $ | - | |
CAUTIONARY INFORMATION
Certain statements in this report, and statements in other reports or information filed or to be filed with the SEC (as well as information included in oral statements or other written statements made or to be made by us), are, or will be, forward-looking statements as defined by the Securities Act of 1933 and the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. These forward-looking statements and information include, without limitation, statements in the CEO’s letter preceding Part I; statements regarding planned capital expenditures under the caption “2026 Capital Plan” in Item 2 of Part I; and statements and information set forth under the captions “2026 Outlook”; “Liquidity and Capital Resources” in Item 7 of Part II regarding our capital plan, share repurchase programs, contractual obligations, "Pension Benefits", and "Other Matters" in this Item 7 of Part II. Forward-looking statements and information also include any other statements or information in this report (including information incorporated herein by reference) regarding: the merger agreement and the transactions contemplated therein (described in Note 20 to the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8), potential impacts of public health crises, including pandemics, epidemics, and the outbreak of other contagious disease, such as such as the coronavirus and its variant strains (COVID); the Russia-Ukraine and Israel-Hamas wars and other geopolitical tensions in the Middle East and elsewhere, and any impacts on our business operations, financial results, liquidity, and financial position, and on the world economy (including customers, employees, and supply chains), including as a result of fluctuations in volume and carloadings; closing of customer manufacturing, distribution, or production facilities; expectations as to operational or service improvements; expectations as to hiring challenges; availability of employees; expectations regarding the effectiveness of steps taken or to be taken to improve operations, service, infrastructure improvements, and transportation plan modifications (including those discussed in response to increased traffic); expectations as to cost savings, revenue growth, and earnings; the time by which goals, targets, aspirations, or objectives will be achieved; projections, predictions, expectations, estimates, or forecasts as to our business, financial, and operational results, future economic performance, and general economic conditions; proposed new products and services; estimates of costs relating to environmental remediation and restoration; estimates and expectations regarding tax matters; estimates and expectations regarding potential tariffs; potential impacts of H.R. 1, which was enacted on July 4, 2025; expectations that claims, litigation, environmental costs, commitments, contingent liabilities, labor negotiations or agreements, cyber-attacks, or other matters will not have a material adverse effect on our consolidated results of operations, financial condition, or liquidity and any other similar expressions concerning matters that are not historical facts. Forward-looking statements may be identified by their use of forward-looking terminology, such as “believes,” “expects,” “may,” “should,” “would,” “will,” “intends,” “plans,” “estimates,” “anticipates,” “projects,” and similar words, phrases, or expressions.
Forward-looking statements should not be read as a guarantee of future performance, results, or outcomes, and will not necessarily be accurate indications of the times that, or by which, such performance, results or outcomes will be achieved, if ever. Forward-looking statements and information are subject to risks and uncertainties that could cause actual performance or results to differ materially from those expressed in the statements and information. Forward-looking statements and information reflect the good faith consideration by management of currently available information, and may be based on underlying assumptions believed to be reasonable under the circumstances. However, such information and assumptions (and, therefore, such forward-looking statements and information) are or may be subject to variables or unknown or unforeseeable events or circumstances over which management has little or no influence or control, and many of these risks and uncertainties are currently amplified by and may continue to be amplified by, or in the future may be amplified by, among other things, macroeconomic and geopolitical conditions.
The Risk Factors in Item 1A of this report could affect our future results and could cause those results or other outcomes to differ materially from those expressed or implied in any forward-looking statements or information. To the extent circumstances require or we deem it otherwise necessary, we will update or amend these risk factors in a Form 10-Q, Form 8-K, or subsequent Form 10-K. All forward-looking statements are qualified by, and should be read in conjunction with, these Risk Factors.
Forward-looking statements speak only as of the date the statement was made. We assume no obligation to update forward-looking information to reflect actual results, changes in assumptions, or changes in other factors affecting forward-looking information. If we do update one or more forward-looking statements, no inference should be drawn that we will make additional updates with respect thereto or with respect to other forward-looking statements.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk
Information concerning market risk sensitive instruments is set forth under Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations - Other Matters, Item 7.
****************************************
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
| | | | | |
| Index to Consolidated Financial Statements | Page |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Shareholders and the Board of Directors of Union Pacific Corporation
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated statements of financial position of Union Pacific Corporation and Subsidiary Companies (the "Corporation") as of December 31, 2025 and December 31, 2024, the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income, changes in common stockholders' equity, and cash flows, for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2025, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the "financial statements"). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Corporation as of December 31, 2025 and December 31, 2024, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2025, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Corporation's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2025, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and our report dated February 6, 2026, expressed an unqualified opinion on the Corporation's internal control over financial reporting.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Corporation's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Corporation's financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Corporation in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matter
The critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the current-period audit of the financial statements that was communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that (1) relates to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matter below, providing a separate opinion on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which it relates.
Capitalization of Properties — Refer to Notes 2 and 11 to the financial statements
Critical Audit Matter Description
The Corporation’s operations are highly capital intensive and their large network of assets turns over on a continuous basis. Each year, the Corporation develops a capital program for both the replacement of assets and for the acquisition or construction of new assets. In determining whether costs should be capitalized, the Corporation exercises significant judgment in determining whether expenditures meet the applicable minimum units of property criteria and extend the useful life, improve the safety of operations, or improve the operating efficiency of existing assets. The Corporation capitalizes all costs of capital projects necessary to make assets ready for their intended use and because a portion of the Corporation’s assets are self-constructed, management also exercises significant judgment in determining the amount of material, labor, work equipment, and indirect costs that qualify for capitalization. Capitalized costs to Properties, net during 2025 were $3.9 billion.
We identified the capitalization of property during 2025 as a critical audit matter because of the significant judgment exercised by management in determining whether costs meet the criteria for capitalization. This, in turn, required a high degree of auditor judgment when performing audit procedures to evaluate whether the criteria to capitalize costs were met and to evaluate sufficiency of audit evidence to support management’s conclusions.
How the Critical Audit Matter Was Addressed in the Audit
Our procedures related to capitalization of property included the following, among others:
· We tested the effectiveness of controls over the Corporation’s determination of whether costs related to the Corporation’s capital investments should be capitalized or expensed.
· We evaluated the Corporation’s capitalization policy in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
· For a selection of capital projects, we performed the following:
− Obtained the Corporation’s evaluation of each project and determined whether the amount of costs to be capitalized met the criteria for capitalization as outlined within the Corporation’s policy by unit of property.
− Obtained supporting documentation that the project met the applicable minimum units of property criteria and was approved, and evaluated whether the project extended the useful life of an existing asset, improved the safety of operations, or improved the operating efficiency of existing assets.
· For a selection of capitalized costs during the year, we performed the following:
− Evaluated whether the individual cost selected met the criteria for capitalization.
− Evaluated whether the selection was accurately recorded at the appropriate amount based on the evidence obtained.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Omaha, Nebraska
February 6, 2026
We have served as the Corporation's auditor since 1967.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
Union Pacific Corporation and Subsidiary Companies
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions, except per share amounts, for the years ended December 31, | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Operating revenues: | | | |
| Freight revenues | $ | 23,220 | | $ | 22,811 | | $ | 22,571 | |
| Other revenues | 1,290 | | 1,439 | | 1,548 | |
| Total operating revenues | 24,510 | | 24,250 | | 24,119 | |
| Operating expenses: | | | |
| Compensation and benefits | 4,897 | | 4,899 | | 4,818 | |
| Purchased services and materials | 2,626 | | 2,520 | | 2,616 | |
| Depreciation | 2,465 | | 2,398 | | 2,318 | |
| Fuel | 2,390 | | 2,474 | | 2,891 | |
| Equipment and other rents | 912 | | 920 | | 947 | |
| Other | 1,374 | | 1,326 | | 1,447 | |
| Total operating expenses | 14,664 | | 14,537 | | 15,037 | |
| Operating income | 9,846 | | 9,713 | | 9,082 | |
| Other income, net (Note 6) | 629 | | 350 | | 491 | |
| Interest expense | (1,309) | | (1,269) | | (1,340) | |
| Income before income taxes | 9,166 | | 8,794 | | 8,233 | |
| Income tax expense (Note 7) | (2,028) | | (2,047) | | (1,854) | |
| Net income | $ | 7,138 | | $ | 6,747 | | $ | 6,379 | |
| Share and Per Share (Note 8): | | | |
| Earnings per share - basic | $ | 12.00 | | $ | 11.10 | | $ | 10.47 | |
| Earnings per share - diluted | $ | 11.98 | | $ | 11.09 | | $ | 10.45 | |
| Weighted average number of shares - basic | 595.0 | | 607.6 | | 609.2 | |
| Weighted average number of shares - diluted | 595.9 | | 608.6 | | 610.2 | |
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
Union Pacific Corporation and Subsidiary Companies
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions, for the years ended December 31, | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Net income | $ | 7,138 | | $ | 6,747 | | $ | 6,379 | |
| Other comprehensive income/(loss): | | | |
| Defined benefit plans | 71 | | (14) | | (106) | |
| Foreign currency translation | 62 | | (95) | | 58 | |
| Derivative instruments | (1) | | - | | 16 | |
| Total other comprehensive income/(loss) [a] | 132 | | (109) | | (32) | |
| Comprehensive income | $ | 7,270 | | $ | 6,638 | | $ | 6,347 | |
[a]Net of deferred taxes of ($24) million, $6 million, and $31 million during 2025, 2024, and 2023, respectively.
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Financial Statements.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL POSITION
Union Pacific Corporation and Subsidiary Companies
| | | | | | | | |
| Millions, except share and per share amounts as of December 31, | 2025 | 2024 |
| Assets | | |
| Current assets: | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 1,266 | | $ | 1,016 | |
| Short-term investments (Note 13) | 250 | | 20 | |
| Accounts receivable, net (Note 10) | 1,860 | | 1,894 | |
| Materials and supplies | 787 | | 769 | |
| Other current assets | 392 | | 322 | |
| Total current assets | 4,555 | | 4,021 | |
| Investments | 2,885 | | 2,664 | |
| Properties, net (Note 11) | 59,645 | | 58,343 | |
| Operating lease assets (Note 16) | 1,036 | | 1,297 | |
| Other assets | 1,577 | | 1,390 | |
| Total assets | $ | 69,698 | | $ | 67,715 | |
| Liabilities and common shareholders' equity | | |
| Current liabilities: | | |
| Accounts payable and other current liabilities (Note 12) | $ | 3,494 | | $ | 3,829 | |
| Debt due within one year (Note 14) | 1,520 | | 1,425 | |
| Total current liabilities | 5,014 | | 5,254 | |
| Debt due after one year (Note 14) | 30,294 | | 29,767 | |
| Operating lease liabilities (Note 16) | 738 | | 925 | |
| Deferred income taxes (Note 7) | 13,421 | | 13,151 | |
| Other long-term liabilities | 1,764 | | 1,728 | |
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 17) | | |
| Total liabilities | 51,231 | | 50,825 | |
| Common shareholders' equity: | | |
Common shares, $2.50 par value, 1,400,000,000 authorized; 1,113,161,191 and 1,113,018,733 issued; 593,245,884 and 604,241,260 outstanding, respectively | 2,783 | | 2,783 | |
| Paid-in-surplus | 5,589 | | 5,334 | |
| Retained earnings | 69,529 | | 65,628 | |
| Treasury stock | (58,843) | | (56,132) | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income/(loss) (Note 9) | (591) | | (723) | |
| Total common shareholders' equity | 18,467 | | 16,890 | |
| Total liabilities and common shareholders' equity | $ | 69,698 | | $ | 67,715 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Financial Statements.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
Union Pacific Corporation and Subsidiary Companies
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions, for the years ended December 31, | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Operating activities | | | |
| Net income | $ | 7,138 | | $ | 6,747 | | $ | 6,379 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to cash provided by operating activities: | | | |
| Depreciation | 2,465 | | 2,398 | | 2,318 | |
| Deferred and other income taxes | 241 | | 28 | | 117 | |
| Other operating activities, net | (193) | | (13) | | (132) | |
| Changes in current assets and liabilities: | | | |
| Accounts receivable, net | 34 | | 179 | | (177) | |
| Materials and supplies | (18) | | (26) | | (2) | |
| Other current assets | 25 | | (69) | | (38) | |
| Accounts payable and other current liabilities | (196) | | 189 | | (215) | |
| Income and other taxes | (206) | | (87) | | 129 | |
| Cash provided by operating activities | 9,290 | | 9,346 | | 8,379 | |
| Investing activities | | | |
| Capital investments | (3,791) | | (3,452) | | (3,606) | |
| Other investing activities, net | 29 | | 127 | | (61) | |
| Cash used in investing activities | (3,762) | | (3,325) | | (3,667) | |
| Financing activities | | | |
| Dividends paid | (3,236) | | (3,213) | | (3,173) | |
| Share repurchase programs (Note 18) | (2,679) | | (1,505) | | (705) | |
| Debt issued (Note 14) | 1,995 | | 800 | | 1,599 | |
| Debt repaid | (1,428) | | (2,226) | | (2,190) | |
| Other financing activities, net | 72 | | 77 | | (156) | |
| Cash used in financing activities | (5,276) | | (6,067) | | (4,625) | |
| Net change in cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash | 252 | | (46) | | 87 | |
| Cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash at beginning of year | 1,028 | | 1,074 | | 987 | |
| Cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash at end of year | $ | 1,280 | | $ | 1,028 | | $ | 1,074 | |
| Supplemental cash flow information | | | |
| Non-cash investing and financing activities: | | | |
| Capital investments accrued but not yet paid | $ | 131 | | $ | 165 | | $ | 137 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Cash paid during the year for: | | | |
| Federal income taxes, net of refunds | $ | (543) | | $ | (986) | | $ | (1,185) | |
| State income taxes, net of refunds: | | | |
| California | (64) | | * | * |
| | | |
| Other | (257) | | (350) | | (295) | |
| Total state income taxes, net of refunds | (321) | | (350) | | (295) | |
| Foreign income taxes, net of refunds | (13) | | (4) | | (6) | |
| Interest, net of amounts capitalized | $ | (1,311) | | $ | (1,260) | | $ | (1,268) | |
◦Does not meet the 5% threshold for the applicable year.
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Financial Statements.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN COMMON SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY
Union Pacific Corporation and Subsidiary Companies
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions | Common shares | Treasury shares | Common shares | Paid-in- surplus | Retained earnings | Treasury stock | AOCI [a] | Total |
| Balance at January 1, 2023 | 1,112.6 | (500.2) | $ | 2,782 | | $ | 5,080 | | $ | 58,887 | | $ | (54,004) | | $ | (582) | | $ | 12,163 | |
| Net income | | | - | | - | | 6,379 | | - | | - | | 6,379 | |
| Other comprehensive income/(loss) | | | - | | - | | - | | - | | (32) | | (32) | |
| Conversion, stock option exercises, forfeitures, ESPP, and other | 0.3 | 0.5 | - | | 113 | | - | | 50 | | - | | 163 | |
| Share repurchase programs (Note 18) | - | (3.5) | - | | - | | - | | (712) | | - | | (712) | |
Cash dividends declared ($5.20 per share) | - | - | - | | - | | (3,173) | | - | | - | | (3,173) | |
| Balance at December 31, 2023 | 1,112.9 | (503.2) | $ | 2,782 | | $ | 5,193 | | $ | 62,093 | | $ | (54,666) | | $ | (614) | | $ | 14,788 | |
| Net income | | | - | | - | | 6,747 | | - | | - | | 6,747 | |
| Other comprehensive income/(loss) | | | - | | - | | - | | - | | (109) | | (109) | |
| Conversion, stock option exercises, forfeitures, ESPP, and other | 0.1 | 0.7 | 1 | | 141 | | - | | 49 | | - | | 191 | |
| Share repurchase programs (Note 18) | - | (6.3) | - | | - | | - | | (1,515) | | - | | (1,515) | |
Cash dividends declared ($5.28 per share) | - | - | - | | - | | (3,212) | | - | | - | | (3,212) | |
| Balance at December 31, 2024 | 1,113.0 | (508.8) | $ | 2,783 | | $ | 5,334 | | $ | 65,628 | | $ | (56,132) | | $ | (723) | | $ | 16,890 | |
| Net income | | | - | | - | | 7,138 | | - | | - | | 7,138 | |
| Other comprehensive income/(loss) | | | - | | - | | - | | - | | 132 | | 132 | |
| Conversion, stock option exercises, forfeitures, ESPP, and other | 0.2 | 0.8 | - | | 172 | | - | | 66 | | - | | 238 | |
| Share repurchase programs (Note 18) | - | (11.9) | - | | 83 | | - | | (2,777) | | - | | (2,694) | |
Cash dividends declared ($5.44 per share) | - | - | - | | - | | (3,237) | | - | | - | | (3,237) | |
| Balance at December 31, 2025 | 1,113.2 | (519.9) | $ | 2,783 | | $ | 5,589 | | $ | 69,529 | | $ | (58,843) | | $ | (591) | | $ | 18,467 | |
[a]AOCI = Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income/Loss (Note 9)
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Financial Statements.
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Union Pacific Corporation and Subsidiary Companies
For purposes of this report, unless the context otherwise requires, all references herein to "Union Pacific", “Corporation”, “Company”, “UPC”, “we”, “us”, and “our” mean Union Pacific Corporation and its subsidiaries, including Union Pacific Railroad Company, which will be separately referred to herein as “UPRR” or the “Railroad”.
1. Nature of Operations
Operations and segmentation – We are a Class I railroad operating in the U.S. Our network includes 32,889 route miles, connecting Pacific Coast and Gulf Coast ports with the Midwest and Eastern U.S. gateways and providing several corridors to key Mexican and Canadian gateways. We own 26,294 miles and operate on the remainder pursuant to trackage rights or leases. We serve the western two-thirds of the country and maintain coordinated schedules with other rail carriers for the handling of freight to and from the Atlantic Coast, the Pacific Coast, the Southeast, the Southwest, Canada, and Mexico. Export and import traffic is moved through Gulf Coast, Pacific Coast, and East Coast ports and across the Mexican and Canadian borders.
The Railroad, along with its subsidiaries and rail affiliates, is our one reportable operating segment. Although we provide and analyze revenues by commodity group, we treat the financial results of the Railroad as one segment due to the integrated nature of our rail network. The accounting policies of the Railroad segment are the same as those described in Note 2 Significant Accounting Policies.
The Company’s Chief Operating Decision Maker (CODM) is our Chief Executive Officer. The CODM assesses performance for our rail network and decides how to allocate resources based on net income as reported on our Consolidated Statements of Income. The measure of segment assets is reported on our Consolidated Statements of Financial Position as total assets.
Our operating revenues are primarily derived from contracts with customers for the transportation of freight from origin to destination. Although our revenues are principally derived from customers domiciled in the U.S., the ultimate points of origination or destination for some products we transport are outside the U.S. Freight revenues from each of our commodity groups, as described in the table below, includes revenues from shipments to and from Mexico, which amounted to $2.9 billion in 2025, $3.0 billion in 2024, and $2.8 billion in 2023. Our significant segment expenses as monitored by the CODM are shown in the table below. This breakout of revenues and expenses is used by the CODM to monitor and assess the financial performance of our rail network by comparing actual results to prior years and plans.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Bulk | $ | 7,586 | | $ | 7,207 | | $ | 7,358 | |
| Industrial | 8,604 | | 8,440 | | 8,238 | |
| Premium | 7,030 | | 7,164 | | 6,975 | |
| Total freight revenues | $ | 23,220 | | $ | 22,811 | | $ | 22,571 | |
| Other subsidiary revenues | 718 | | 788 | | 872 | |
| Accessorial revenues | 475 | | 554 | | 584 | |
| Other | 97 | | 97 | | 92 | |
| Total operating revenues | $ | 24,510 | | $ | 24,250 | | $ | 24,119 | |
| Operating [a] [c] | 6,816 | | 6,793 | | 6,727 | |
| Administrative [a] [c] | 735 | | 760 | | 763 | |
| Locomotive fuel | 2,335 | | 2,418 | | 2,815 | |
| Acquisition-related (Note 20) | 72 | | - | | - | |
| Other segment items [b] [c] | 2,241 | | 2,168 | | 2,414 | |
| Depreciation | 2,465 | | 2,398 | | 2,318 | |
| Other income, net | (629) | | (350) | | (491) | |
| Interest expense | 1,309 | | 1,269 | | 1,340 | |
| Income tax expense | 2,028 | | 2,047 | | 1,854 | |
| Net income | $ | 7,138 | | $ | 6,747 | | $ | 6,379 | |
[a] Operating and Administrative includes compensation and benefits, purchased services and materials, equipment and other rents, non-locomotive fuel, and other expenses.
[b] Other segment items includes car hire and leases, casualty costs, property taxes, subsidiary expense, and other overhead expense.
[c] Prior periods have been recast to reflect the presentation of the CODM's review in the current year.
Basis of presentation – The Consolidated Financial Statements are presented in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the U.S. (GAAP) as codified in the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) Accounting Standards Codification (ASC).
2. Significant Accounting Policies
Principles of consolidation – The Consolidated Financial Statements include the accounts of Union Pacific Corporation and all of its subsidiaries. Investments in affiliated companies (20% to 50% owned) are accounted for using the equity method of accounting. All intercompany transactions are eliminated. We currently have no less than majority-owned investments that require consolidation under variable interest entity requirements.
Cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash – Cash equivalents consist of investments with original maturities of three months or less. Amounts included in restricted cash represent those required to be set aside by contractual agreement.
The following table provides a reconciliation of cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash reported within the Consolidated Statements of Financial Position that sum to the total of the same such amounts shown on the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 1,266 | | $ | 1,016 | | $ | 1,055 | |
| Restricted cash equivalents in other current assets | 9 | | 4 | | 10 | |
| Restricted cash equivalents in other assets | 5 | | 8 | | 9 | |
| Total cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash equivalents | $ | 1,280 | | $ | 1,028 | | $ | 1,074 | |
Accounts receivable – Accounts receivable includes receivables reduced by an allowance for doubtful accounts. The allowance is based upon historical losses, credit worthiness of customers, and current economic conditions. Receivables not expected to be collected in one year and the associated allowances are classified as other assets in our Consolidated Statements of Financial Position.
Investments – Investments represent our investments in affiliated companies (20% to 50% owned) that are accounted for under the equity method of accounting, and investments in companies (less than 20% owned) accounted for at fair value when there is a readily determined fair value or at cost minus impairment when there are not readily determinable fair values. Our portion of income/loss on equity method investments that are integral to our operations are recorded in operating expenses. Realized and unrealized gains and losses on investments that are not integral to our operations are recorded in other income.
Materials and supplies – Materials and supplies are carried at the lower of average cost or net realizable value.
Property and depreciation – Properties and equipment are carried at cost and are depreciated on a straight-line basis over their estimated service lives, which are measured in years, except for rail in high-density traffic corridors (i.e., all rail lines except for those lines subject to abandonment, yard tracks, and switching tracks), where lives are measured in millions of gross tons per mile of track. We use the group method of depreciation where all items with similar characteristics, use, and expected lives are grouped together in asset classes and are depreciated using composite depreciation rates. The group method of depreciation treats each asset class as a pool of resources, not as singular items. We determine the estimated service lives of depreciable railroad assets by means of depreciation studies. Under the group method of depreciation, no gain or loss is recognized when depreciable property is retired or replaced in the ordinary course of business.
Impairment of long-lived assets – We review long-lived assets, including identifiable intangibles, for impairment when events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. If impairment indicators are present and the estimated future undiscounted cash flows are less than the carrying value of the long-lived assets, the carrying value is reduced to the estimated fair value.
Revenue recognition – Freight revenues are derived from contracts with customers. We account for a contract when it has approval and commitment from both parties, the rights of the parties are identified, payment terms are identified, the contract has commercial substance, and collectability of consideration is probable. Our contracts include private agreements, private rate/letter quotes, public circulars/tariffs, and interline/foreign agreements. The performance obligation in our contracts is typically delivering a specific commodity from a place of origin to a place of destination and our commitment begins with the tendering and acceptance of a freight bill of lading and is satisfied upon delivery at destination. We consider each freight shipment to be a distinct performance obligation.
We recognize freight revenues over time as freight moves from origin to destination. The allocation of revenues between reporting periods is based on the relative transit time in each reporting period with expenses recognized as incurred. Outstanding performance obligations related to freight moves in transit totaled $157 million at December 31, 2025, and $159 million at December 31, 2024, and are expected to be recognized in the following quarter as we satisfy our remaining performance obligations and deliver freight to destination. The transaction price is generally specified in a contract and may be dependent on the commodity, origin/destination, and route. Customer incentives, which are primarily provided for shipping to/from specific locations or based on cumulative volumes, are recorded as a reduction to operating revenues. Customer incentives that include variable consideration based on cumulative volumes are estimated using the expected value method, which is based on available historical, current, and forecasted volumes, and recognized as the related performance obligation is satisfied.
Under typical payment terms, our customers pay us after each performance obligation is satisfied and there are no material contract assets or liabilities associated with our freight revenues. Outstanding freight receivables are presented in our Consolidated Statements of Financial Position as accounts receivable, net.
Freight revenues related to interline transportation services that involve other railroads are reported on a net basis. The portion of the gross amount billed to customers that is remitted by the Company to another party is not reflected as freight revenues.
Other revenues consist primarily of revenues earned by our other subsidiaries (primarily logistics and commuter rail operations) and accessorial revenues. Other subsidiary revenues are generally recognized over time as shipments move from origin to destination. The allocation of revenues between reporting periods is based on the relative transit time in each reporting period with expenses recognized as incurred. Accessorial revenues are recognized at a point in time as performance obligations are satisfied.
Translation of foreign currency – Our portion of the assets and liabilities related to foreign investments are translated into U.S. dollars at the exchange rates in effect at the balance sheet date. Revenues and expenses are translated at the average rates of exchange prevailing during the year. Unrealized gains or losses are reflected within common shareholders’ equity as accumulated other comprehensive income or loss.
Fair value measurements – We use a fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs to valuation techniques used to measure fair value into three broad levels. The level in the fair value hierarchy within which the fair value measurement in its entirety falls is determined based on the lowest level input that is significant to the fair value measurement in its entirety. These levels include:
Level 1: Quoted market prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities.
Level 2: Observable market-based inputs or unobservable inputs that are corroborated by market data.
Level 3: Unobservable inputs that are not corroborated by market data.
We have applied fair value measurements to our short-term investments, certain equity investments, pension plan assets, and short- and long-term debt.
Stock-based compensation – We issue treasury shares to cover stock option exercises, stock unit vestings, and ESPP shares, while new shares are issued when retention shares are granted.
We measure and recognize compensation expense for all stock-based awards made to employees, including stock options and ESPP awards. Compensation expense is based on the fair value of the awards as measured at the grant date and is expensed ratably over the service period of the awards (generally the vesting period). The fair value of retention awards is the closing stock price on the date of grant, the fair value of stock options is determined by using the Black-Scholes option pricing model, and the fair value of ESPP awards is based on the Company contribution match.
Earnings per share – Basic earnings per share are calculated on the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding during each period. Diluted earnings per share include shares issuable upon exercise of outstanding stock options and stock-based awards where the conversion of such instruments would be dilutive.
Income taxes – We account for income taxes by recording taxes payable or refundable for the current year and deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that are reported in different periods for financial reporting and income tax purposes. The majority of our deferred tax assets relate to expenses that already have been recorded for financial reporting purposes but not deducted for tax purposes. The majority of our deferred tax liabilities relate to differences between the tax bases and financial reporting amounts of our land and depreciable property, due to accelerated tax depreciation (including bonus depreciation), revaluation of assets in purchase accounting transactions, and differences in capitalization methods. These expected future tax consequences are measured based on current tax law; the effects of future tax legislation are not anticipated.
When appropriate, we record a valuation allowance against deferred tax assets to reflect that these tax assets may not be realized. In determining whether a valuation allowance is appropriate, we consider whether it is more likely than not that all or some portion of our deferred tax assets will not be realized, based on management’s judgments using available evidence for purposes of estimating whether future taxable income will be sufficient to realize a deferred tax asset.
We recognize tax benefits that are more likely than not to be sustained upon examination by tax authorities. The amount recognized is measured as the largest amount of benefit that is greater than 50 percent likely to be realized upon settlement. A liability for “unrecognized tax benefits” is recorded for any tax benefits claimed in our tax returns that do not meet these recognition and measurement standards.
Leases – We determine if an arrangement is or contains a lease at inception. Operating lease assets and operating lease liabilities are recognized based on the present value of the future minimum lease payments over the lease term at commencement date. When an implicit rate is not available, we use a collateralized incremental borrowing rate for operating leases based on the information available at commencement date, including lease term, in determining the present value of future payments. The operating lease asset also includes any lease payments made and excludes lease incentives and initial direct costs incurred. Our lease terms may include options to extend or terminate the lease when it is reasonably certain that the option will be exercised. Operating leases are included in operating lease assets, accounts payable and other current liabilities, and operating lease liabilities on our Consolidated Statements of Financial Position. Finance leases are included in properties, net, debt due within one year, and debt due after one year on our Consolidated Statements of Financial Position. Operating lease expense is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term and primarily reported in equipment and other rents and financing lease expense is recorded as depreciation and interest expense in our Consolidated Statements of Income.
We have lease agreements with lease and non-lease components, and we have elected to not separate lease and non-lease components for all classes of underlying assets. Leases with an initial term of 12 months or less are not recorded on our Consolidated Statements of Financial Position. Leases with initial terms in excess of 12 months are recorded as operating or financing leases in our Consolidated Statements of Financial Position.
Pension benefits – In order to measure the expense associated with pension benefits, we must make various assumptions including discount rates used to value certain liabilities, expected return on plan assets used to fund these expenses, compensation increases, employee turnover rates, and anticipated mortality rates. The assumptions used by us are based on our historical experience as well as current facts and circumstances. We use an actuarial analysis to measure the expense and liability associated with these benefits.
Personal injury – The cost of injuries to employees and others on our property is charged to expense based on estimates of the ultimate cost and number of incidents each year. We use an actuarial analysis to measure the expense and liability, including unasserted claims. Our personal injury liability is not discounted to present value due to the uncertainty surrounding the timing of future payments. Legal fees and incidental costs are expensed as incurred.
Environmental – When environmental issues have been identified with respect to property currently or formerly owned, leased, or otherwise used in the conduct of our business, we perform, with the assistance of our consultants, environmental assessments on such property. We expense the cost of the assessments as incurred. We accrue the cost of remediation where our obligation is probable and such costs can be reasonably estimated. We do not discount our environmental liabilities when the timing of the anticipated cash payments is not fixed or readily determinable. Legal fees and incidental costs are expensed as incurred.
Use of estimates – The preparation of our Consolidated Financial Statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect certain reported assets and liabilities, the disclosure of certain contingent assets and liabilities as of the date of the Consolidated Financial Statements, as well as the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual future results may differ from such estimates.
3. Accounting Pronouncements
In December 2023, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update No. (ASU) 2023-09, Income Taxes (Topic 740): Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures, which requires business entities to expand their annual disclosures of the effective rate reconciliation and income taxes paid. The ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2024, may be adopted on a prospective or retrospective basis, and early adoption is permitted. The Company adopted this ASU on December 31, 2025, on a retrospective basis. See the Supplemental Cash Flow Information of the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows and Note 7 Income Taxes.
In November 2024, the FASB issued ASU 2024-03, Income Statement - Reporting Comprehensive Income - Expense Disaggregation Disclosures (Subtopic 220-40): Disaggregation of Income Statement Expenses, which requires disclosure of additional information about specific expense categories in the notes to the financial statements. The ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2026, and interim periods within fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2027, may be adopted on a prospective or retrospective basis, and early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the effect that the new guidance will have on our related disclosures.
In July 2025, the FASB issued ASU 2025-05, Financial Instruments - Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses for Accounts Receivable and Contract Assets, which allows a practical expedient that assumes current conditions as of the balance sheet date do not change for the remaining life of the asset. The ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2025, and interim periods within those fiscal years, must be adopted on a prospective basis, and early adoption is permitted. We elected to early adopt ASU 2025-05 on December 31, 2025, which did not have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
In September 2025, the FASB issued ASU 2025-06, Intangibles - Goodwill and Other - Internal-Use Software (Subtopic 350-40): Targeted Improvements to the Accounting for Internal-Use Software, which details the criteria for capitalization of internal-use software costs. The ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2027, and interim periods within those fiscal years, may be adopted on a prospective, modified, or retrospective transition approach, and early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the effect that the new guidance will have on our consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
In December 2025, the FASB issued ASU 2025-10, Government Grants (Topic 832): Accounting for Government Grants Received by Business Entities, which provides recognition, measurement, and presentation authoritative guidance for grants received by a business entity from a government. The ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2028, and interim reporting periods within those fiscal years, may be adopted on a modified prospective, modified retrospective, or retrospective approach, and early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the effect that the new guidance will have on our consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
4. Stock Options and Other Stock Plans
In April 2000, the shareholders approved the Union Pacific Corporation 2000 Directors Plan (Directors Plan) whereby 2,200,000 shares of our common stock were reserved for issuance to our non-employee directors. Under the Directors Plan, each non-employee director, upon his or her initial election to the Board of Directors, received a grant of 4,000 retention shares or retention stock units. In July 2018, the Board of Directors eliminated the retention grant for directors newly elected in 2018 and all future years. As of December 31, 2025, 16,000 restricted shares were outstanding under the Directors Plan.
The Union Pacific Corporation 2013 Stock Incentive Plan (2013 Plan) was approved by shareholders in May 2013. The 2013 Plan reserved 78,000,000 shares of our common stock for issuance, plus any shares subject to awards made under previous plans as of February 28, 2013, that are subsequently cancelled, expired, forfeited, or otherwise not issued under previous plans. Under the 2013 Plan, non-qualified stock options, incentive stock options, retention shares, stock units, and incentive bonus awards may be granted to eligible employees of the Corporation and its subsidiaries. Non-employee directors are not eligible for awards under the 2013 Plan. As of December 31, 2025, 501,049 stock options and no retention shares and stock units were outstanding under the 2013 Plan. We no longer grant any stock options or other stock or unit awards under this plan.
The Union Pacific Corporation 2021 Stock Incentive Plan (2021 Plan) was approved by shareholders in May 2021. The 2021 Plan reserved 23,000,000 shares of our common stock for issuance, plus any shares subject to awards made under previous plans as of December 31, 2022, that are subsequently cancelled, expired, forfeited, or otherwise not issued under previous plans. Under the 2021 Plan, non-qualified stock options, incentive stock options, retention shares, stock units, and incentive bonus awards may be granted to eligible employees of the Corporation and its subsidiaries. Non-employee directors are not eligible for awards under the 2021 Plan. As of December 31, 2025, 1,593,585 stock options and 1,187,093 retention shares were outstanding under the 2021 Plan.
The Union Pacific Corporation 2021 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (2021 ESPP) was approved by shareholders in May 2021. The 2021 ESPP reserved 10,000,000 shares of our common stock for issuance. Under the 2021 ESPP, eligible employees of the Corporation and its subsidiaries may elect to purchase shares with a Company match award. Non-employee directors are not eligible for awards under the 2021 ESPP. As of December 31, 2025, 1,537,960 shares were issued under the 2021 ESPP.
Pursuant to the above plans 29,874,539; 31,063,392; and 31,979,909 shares of our common stock were authorized and available for grant at December 31, 2025, 2024, and 2023, respectively.
Stock-based compensation – We have several stock-based compensation plans where employees receive nonvested stock options, nonvested retention shares, and nonvested stock units. We refer to the nonvested shares and stock units collectively as “retention awards”. Employees may also participate in our ESPP.
Information regarding stock-based compensation expense appears in the table below:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Stock-based compensation, before tax: | | | |
| Stock options | $ | 24 | | $ | 18 | | $ | 16 | |
| Retention awards | 102 | | 77 | | 71 | |
| ESPP | 16 | | 23 | | 20 | |
| Total stock-based compensation, before tax | $ | 142 | | $ | 118 | | $ | 107 | |
| Excess income tax benefits from equity compensation plans | $ | 12 | | $ | 15 | | $ | 11 | |
Stock options – Stock options are granted at the closing price on the date of grant, have 10-year contractual terms, and vest no later than 3 years from the date of grant. At December 31, 2025, outstanding stock options are not subject to performance or market-based vesting conditions.
The table below shows the annual weighted-average assumptions used for Black-Scholes valuation purposes:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted-average assumptions | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Risk-free interest rate | 4.3 | % | 4.2 | % | 3.9 | % |
| Dividend yield | 2.2 | % | 2.1 | % | 2.6 | % |
| Expected life (years) | 4.3 | 4.4 | 4.5 |
| Volatility | 22.4 | % | 28.7 | % | 29.3 | % |
| Weighted-average grant-date fair value of options granted | $ | 48.70 | | $ | 61.75 | | $ | 48.31 | |
The risk-free rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant; the expected dividend yield is calculated as the ratio of dividends paid per share of common stock to the stock price on the date of grant; the expected life is based on historical and expected exercise behavior; and expected volatility is based on the historical volatility of our stock price over the expected life of the stock option.
A summary of stock option activity during 2025 is presented below:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Options (thous.) | Weighted-average exercise price | Weighted-average remaining contractual term (yrs.) | Aggregate intrinsic value (millions) |
| Outstanding at January 1, 2025 | 1,981 | $ | 195.81 | | 5.8 | $ | 74 | |
| Granted | 423 | 243.51 | | N/A | N/A |
| Exercised | (288) | 157.41 | | N/A | N/A |
| Forfeited or expired | (21) | 238.93 | | N/A | N/A |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2025 | 2,095 | $ | 210.29 | | 5.6 | $ | 58 | |
| Vested or expected to vest at December 31, 2025 | 2,074 | $ | 210.03 | | 5.6 | $ | 58 | |
| Options exercisable at December 31, 2025 | 1,400 | $ | 196.12 | | 4.2 | $ | 55 | |
At December 31, 2025, there was $10 million of unrecognized compensation expense related to nonvested stock options, which is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 0.7 years. Additional information regarding stock option exercises appears in the following table:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Intrinsic value of stock options exercised | $ | 26 | | $ | 35 | | $ | 23 | |
| Cash received from option exercises | 51 | | 46 | | 27 | |
| Treasury shares repurchased for employee payroll taxes | (8) | | (8) | | (5) | |
| Income tax benefit realized from option exercises | 4 | | 7 | | 5 | |
| Aggregate grant-date fair value of stock options vested | $ | 16 | | $ | 15 | | $ | 14 | |
Retention awards – Retention awards are granted at no cost to the employee, vest over periods lasting up to 4 years, and have dividends and dividend equivalents paid to participants during the vesting periods.
Changes in our retention awards during 2025 were as follows:
| | | | | | | | |
| Shares (thous.) | Weighted-Average Grant-Date Fair Value |
| Nonvested at January 1, 2025 | 915 | $ | 222.50 | |
| Granted | 229 | 243.48 | |
| Vested | (231) | 205.32 | |
| Forfeited | (35) | 230.34 | |
| Nonvested at December 31, 2025 | 878 | $ | 232.18 | |
At December 31, 2025, there was $50 million of total unrecognized compensation expense related to nonvested retention awards, which is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 0.8 years.
Performance stock unit awards – In February 2025, our Board of Directors approved performance stock unit grants. This plan is based on performance targets for annual return on invested capital (ROIC) and operating income growth (OIG) compared to companies in the S&P 100 Industrials Index plus the Class I railroads. We define ROIC as net operating profit adjusted for interest expense (including interest on average operating lease liabilities) and taxes on interest divided by average invested capital adjusted for average operating lease liabilities.
The February 2025 stock units awarded to executives are subject to continued employment for 37 months, the attainment of certain levels of ROIC, and the relative three-year OIG. We expense two-thirds of the fair value of the units that are probable of being earned based on our forecasted ROIC over the three-year performance period, and with respect to the third year of the plan, we expense the remaining one-third of the fair value subject to the relative three-year OIG. We measure the fair value of performance stock units based upon the closing price of the underlying common stock as of the date of grant. Dividend equivalents are accumulated during the service period and paid to participants only after the units are earned.
Changes in our performance stock unit awards during 2025 were as follows:
| | | | | | | | |
| Shares (thous.) | Weighted-Average Grant-Date Fair Value |
| Nonvested at January 1, 2025 | 607 | $ | 219.08 | |
| Granted | 254 | 243.51 | |
| Vested | (72) | 244.95 | |
| Unearned | (83) | 244.35 | |
| Forfeited | (87) | 219.28 | |
| Nonvested at December 31, 2025 | 619 | $ | 222.68 | |
At December 31, 2025, there was $11 million of total unrecognized compensation expense related to nonvested performance stock unit awards, which is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 1.0 year. This expense is subject to achievement of the performance measures established for the performance stock unit grants.
Employee stock purchase plan – Employee and Company contributions are used to issue treasury shares the month after employee contributions are withheld based on the settlement date closing price. Effective with the June 10, 2025, purchase (for employee services rendered in May 2025), the Company match was changed from 40% to 20% of the amount contributed by the employee up to a maximum employee contribution of 5% of monthly salary (limited to $15,000 annually). We expense the Company contributions in the month the employee services were rendered (i.e., the month the employee contributions were withheld).
5. Retirement Plans
Pension benefits
We provide defined benefit retirement income to eligible non-union employees through qualified and non-qualified (supplemental) pension plans. Qualified and non-qualified pension benefits are based on years of service and the highest compensation during the latest years of employment, with specific reductions made for early retirements. Non-union employees hired on or after January 1, 2018, are no longer eligible for pension benefits, but are eligible for an enhanced 401(k) benefit as described below in other retirement programs.
Funded status
We are required by GAAP to separately recognize the overfunded or underfunded status of our pension plans as an asset or liability. The funded status represents the difference between the projected benefit obligation (PBO) and the fair value of the plan assets. Our non-qualified (supplemental) pension plan is unfunded by design. The PBO of the pension plans is the present value of benefits earned to date by plan participants, including the effect of assumed future compensation increases. Plan assets are measured at fair value. We use a December 31 measurement date for plan assets and obligations for all our retirement plans.
Changes in our PBO and plan assets were as follows for the years ended December 31:
| | | | | | | | |
| Funded status | | |
| Millions | 2025 | 2024 |
| Projected benefit obligation | | |
| Projected benefit obligation at beginning of year | $ | 3,513 | | $ | 3,880 | |
| Service cost | 41 | | 52 | |
| Interest cost | 179 | | 186 | |
| Actuarial loss/(gain) | (41) | | (269) | |
| Gross benefits paid | (417) | | (336) | |
| Projected benefit obligation at end of year | $ | 3,275 | | $ | 3,513 | |
| Plan assets | | |
| Fair value of plan assets at beginning of year | $ | 4,068 | | $ | 4,400 | |
| Actual return/(loss) on plan assets | 294 | | (28) | |
| Non-qualified plan benefit contributions | 33 | | 32 | |
| Gross benefits paid | (417) | | (336) | |
| Fair value of plan assets at end of year | $ | 3,978 | | $ | 4,068 | |
| Funded status at end of year | $ | 703 | | $ | 555 | |
The 2025 actuarial gains were insignificant. Actuarial gains that decrease the 2024 PBO were driven by an increase in discount rates from 5.00% to 5.61%.
Amounts recognized in the statement of financial position as of December 31, 2025 and 2024, consist of:
| | | | | | | | |
| Millions | 2025 | 2024 |
| Noncurrent assets | $ | 1,083 | | $ | 950 | |
| Current liabilities | (32) | | (32) | |
| Noncurrent liabilities | (348) | | (363) | |
| Net amounts recognized at end of year | $ | 703 | | $ | 555 | |
Pre-tax amounts recognized in accumulated other comprehensive income/loss consist of $542 million and $644 million net actuarial loss as of December 31, 2025 and 2024, respectively.
Pre-tax changes recognized in other comprehensive income/loss as of December 31, 2025, 2024, and 2023, were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Net actuarial (loss)/gain | $ | 93 | | $ | (11) | | $ | (159) | |
| Amortization of: | | | |
| Actuarial loss | 8 | | 11 | | 9 | |
| Total | $ | 101 | | $ | - | | $ | (150) | |
Underfunded accumulated benefit obligation – The accumulated benefit obligation (ABO) is the present value of benefits earned to date, assuming no future compensation growth. The underfunded accumulated benefit obligation represents the difference between the ABO and the fair value of plan assets.
The following table discloses only the PBO, ABO, and fair value of plan assets for pension plans where the accumulated benefit obligation is in excess of the fair value of the plan assets as of December 31:
| | | | | | | | |
| Underfunded accumulated benefit obligation | | |
| Millions | 2025 | 2024 |
| Projected benefit obligation | $ | 380 | | $ | 395 | |
| Accumulated benefit obligation | $ | 376 | | $ | 389 | |
| Fair value of plan assets | - | | - | |
| Underfunded accumulated benefit obligation | $ | (376) | | $ | (389) | |
The ABO for all defined benefit pension plans was $3.2 billion and $3.3 billion at December 31, 2025 and 2024, respectively.
Assumptions – The weighted-average actuarial assumptions used to determine benefit obligations at December 31:
| | | | | | | | |
| Percentages | 2025 | 2024 |
| Discount rate | 5.53 | % | 5.61 | % |
| Compensation increase | 3.60 | % | 4.00 | % |
Expense
Pension expense is determined based upon the annual service cost of benefits (the actuarial cost of benefits earned during a period) and the interest cost on those liabilities, less the expected return on plan assets. The expected long-term rate of return on plan assets is applied to a calculated value of plan assets that recognizes changes in fair value over a 5-year period. This practice is intended to reduce year-to-year volatility in pension expense, but it can have the effect of delaying the recognition of differences between actual returns on assets and expected returns based on long-term rate of return assumptions. Differences in actual experience in relation to assumptions are not recognized in net income immediately but are deferred in accumulated other comprehensive income/loss and, if necessary, amortized as pension expense.
The components of our net periodic pension benefit/cost were as follows for the years ended December 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Service cost | $ | 41 | | $ | 52 | | $ | 52 | |
| Interest cost | 179 | | 186 | | 187 | |
| Expected return on plan assets | (242) | | (252) | | (248) | |
| Amortization of actuarial loss | 8 | | 11 | | 9 | |
| Net periodic pension (benefit)/cost | $ | (14) | | $ | (3) | | $ | - | |
Assumptions – The weighted-average actuarial assumptions used to determine expense were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Percentages | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Discount rate for interest on benefit obligations | 5.32 | % | 4.91 | % | 5.14 | % |
| Discount rate for service cost | 5.75 | % | 5.05 | % | 5.19 | % |
| Discount rate for interest on service cost | 5.68 | % | 5.02 | % | 5.21 | % |
| Expected return on plan assets | 5.25 | % | 5.25 | % | 5.25 | % |
| Compensation increase | 3.90 | % | 4.00 | % | 4.10 | % |
We measure the service cost and interest cost components of our net periodic pension benefit/cost by using individual spot discount rates matched with separate cash flows for each future year. The discount rates were based on a yield curve of high-quality corporate bonds. The expected return on plan assets is based on our asset allocation mix and our historical return, taking into account current and expected market conditions.
Cash contributions
The following table details cash contributions, if any, for the qualified and non-qualified (supplemental) pension plans:
| | | | | | | | |
| Millions | Qualified | Non-qualified |
| 2025 | $ | - | | $ | 33 | |
| 2024 | $ | - | | $ | 32 | |
Our policy with respect to funding the qualified pension plans is to fund at least the minimum required by law and not more than the maximum amount deductible for tax purposes.
The non-qualified pension plan is not funded and is not subject to any minimum regulatory funding requirements. Benefit payments for each year represent supplemental pension payments. We anticipate our 2026 supplemental pension payments will be made from cash generated from operations.
Benefit payments
The following table details expected benefit payments for the years 2026 through 2035:
| | | | | |
| Millions | |
| 2026 | $ | 213 | |
| 2027 | 213 | |
| 2028 | 214 | |
| 2029 | 215 | |
| 2030 | 216 | |
| Years 2031 - 2035 | $ | 1,104 | |
Asset allocation strategy
Our pension plan asset allocation at December 31, 2025 and 2024, and target allocation for 2026, are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Target
allocation 2026 | Percentage of plan assets
December 31, |
| 2025 | 2024 |
| Equity securities | 20% to 30% | 23 | % | 24 | % |
| Debt securities | 70% to 80% | 76 | | 75 | |
| Real estate | 0% to 2% | 1 | | 1 | |
| Total | | 100 | % | 100 | % |
The pension plan investments are held in a master trust. The investment strategy for pension plan assets is to maintain a broadly diversified portfolio designed to achieve our target average long-term rate of return of 5.25%. While we believe we can achieve a long-term average rate of return of 5.25%, we cannot be certain that the portfolio will perform to our expectations. Assets are strategically allocated among equity, debt, and other investments in order to achieve a diversification level that reduces fluctuations in investment returns. Asset allocation target ranges for equity, debt, and other portfolios are evaluated at least every three years with the assistance of an independent consulting firm. Actual asset allocations are monitored monthly, and rebalancing actions are executed at least quarterly, as needed.
The weighted average credit rating of the debt portfolio was AA- at both December 31, 2025 and 2024. The debt portfolio is also broadly diversified and invested primarily in U.S. Treasury, mortgage, and corporate securities. The weighted-average maturity of the debt portfolio was 21 years and 22 years at December 31, 2025 and 2024.
The investment of pension plan assets in securities issued by UPC is explicitly prohibited by the plan for both the equity and debt portfolios, other than through index fund holdings.
Fair value measurements
The pension plan assets are valued at fair value. The following is a description of the valuation methodologies used for the investments measured at fair value, including the general classification of such instruments pursuant to the valuation hierarchy.
Federal government securities – Federal Government Securities consist of bills, notes, bonds, and other fixed income securities issued directly by the U.S. Treasury or by government-sponsored enterprises. These assets are valued using a bid evaluation process with bid data provided by independent pricing sources. Federal Government Securities are classified as Level 2 investments.
Bonds and debentures – Bonds and debentures consist of debt securities issued by U.S. and non-U.S. corporations as well as state and local governments. These assets are valued using a bid evaluation process with bid data provided by independent pricing sources. Corporate, state, and municipal bonds and debentures are classified as Level 2 investments.
Corporate stock – This investment category consists of common and preferred stock issued by U.S. and non-U.S. corporations. Most common shares are traded actively on exchanges and price quotes for these shares are readily available. Common stock is classified as a Level 1 investment. Preferred shares included in this category are valued using a bid evaluation process with bid data provided by independent pricing sources. Preferred stock is classified as a Level 2 investment.
Venture capital and buyout partnerships – This investment category is comprised of interests in limited partnerships that invest primarily in privately-held companies. Due to the private nature of the partnership investments, pricing inputs are not readily observable. Asset valuations are developed by the general partners that manage the partnerships. These valuations are based on the application of public market multiples to private company cash flows, market transactions that provide valuation information for comparable companies, and other methods. The fair value recorded by the master trust is calculated using each partnership’s net asset value (NAV).
Real estate funds – The plan’s real estate investments are primarily interests in private real estate investment trusts, partnerships, limited liability companies, and similar structures. Valuations for the holdings in this category are not based on readily observable inputs and are primarily derived from property appraisals. The fair value recorded by the master trust is calculated using the NAV for each investment.
Collective trust and other funds – Collective trust and other funds are comprised of shares or units in commingled funds and limited liability companies that are not publicly traded. The underlying assets in these entities (global stock funds and short-term investment funds) are publicly traded on exchanges and price quotes for the assets held by these funds are readily available. The fair value recorded by the master trust is calculated using NAV for each investment.
As of December 31, 2025, the pension plan assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions | Quoted prices
in active
markets for
identical inputs
(Level 1) | Significant
other
inputs
(Level 2) | Significant
unobservable
inputs
(Level 3) | Total |
| Plan assets at fair value: | | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| Federal government securities | $ | - | | $ | 1,471 | | $ | - | | $ | 1,471 | |
| Bonds and debentures | - | | 1,492 | | - | | 1,492 | |
| Corporate stock | 235 | | 2 | | - | | 237 | |
| Total plan assets at fair value | $ | 235 | | $ | 2,965 | | $ | - | | $ | 3,200 | |
| Plan assets at NAV: | | | | |
| | | | |
| Venture capital and buyout partnerships | | | | 413 | |
| Real estate funds | | | | 20 | |
| Collective trust and other funds | | | | 306 | |
| Total plan assets at NAV | | | | $ | 739 | |
| Other assets/(liabilities) [a] | | | | 39 | |
| Total plan assets | | | | $ | 3,978 | |
As of December 31, 2024, the pension plan assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions | Quoted prices
in active
markets for
identical inputs
(Level 1) | Significant
other
inputs
(Level 2) | Significant
unobservable
inputs
(Level 3) | Total |
| Plan assets at fair value: | | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| Federal government securities | $ | - | | $ | 1,448 | | $ | - | | $ | 1,448 | |
| Bonds and debentures | - | | 1,512 | | - | | 1,512 | |
| Corporate stock | 220 | | 6 | | - | | 226 | |
| Total plan assets at fair value | $ | 220 | | $ | 2,966 | | $ | - | | $ | 3,186 | |
| Plan assets at NAV: | | | | |
| | | | |
| Venture capital and buyout partnerships | | | | 446 | |
| Real estate funds | | | | 26 | |
| Collective trust and other funds | | | | 370 | |
| Total plan assets at NAV | | | | $ | 842 | |
| Other assets/(liabilities) [a] | | | | 40 | |
| Total plan assets | | | | $ | 4,068 | |
[a]Includes accrued receivables, net payables, and pending broker settlements.
The master trust’s investments in limited partnerships and similar structures (used to invest in private equity and real estate) are valued at fair value based on their proportionate share of the partnerships’ fair value as recorded in the limited partnerships’ audited financial statements. The limited partnerships allocate gains, losses, and expenses to the partners based on the ownership percentage as described in the partnership agreements.
Other retirement programs
Other post-retirement benefits – We provide medical benefits for eligible retirees hired before January 1, 2004. These benefits are funded as medical claims are paid. In 2025, we completed a buyout of life insurance benefits for eligible retirees hired before January 1, 2004. OPEB expense is determined based upon the annual service cost of benefits and the interest cost on those liabilities plus amortization of net (gain)/loss amounts offset by amortization of prior service credits recorded in AOCI. Our OPEB liability was $84 million and $104 million at December 31, 2025 and 2024, respectively. The liability is based on discount rate assumptions of 5.42% and 5.53% at December 31, 2025 and 2024, respectively. OPEB net periodic (benefit)/cost was ($2) million in 2025, ($5) million in 2024, and ($7) million in 2023.
401(k)/Thrift plan – For non-union employees hired prior to January 1, 2018, and eligible union employees for whom we make matching contributions, we provide a defined contribution plan (401(k)/thrift plan). We match 50% for each dollar contributed by employees up to the first 6% of compensation contributed. For non-union employees hired on or after January 1, 2018, we match 100% for each dollar, up to the first 6% of compensation contributed, in addition to contributing an annual amount of 3% of the employee’s annual base salary. Our plan contributions were $29 million in 2025, $28 million in 2024, and $27 million in 2023.
Railroad retirement system – All Railroad employees are covered by the Railroad Retirement System (the System). Contributions made to the System are expensed as incurred and amounted to approximately $681 million in 2025, $671 million in 2024, and $711 million in 2023.
Collective bargaining agreements – Under collective bargaining agreements, we participate in multi-employer benefit plans that provide certain post retirement health care and life insurance benefits for eligible union employees. Premiums paid under these plans are expensed as incurred and amounted to $9 million in 2025, $12 million in 2024, and $16 million in 2023.
6. Other Income
Other income included the following for the years ended December 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Real estate income [a] | $ | 558 | | $ | 263 | | $ | 414 | |
| Interest income | 56 | | 52 | | 52 | |
| Net periodic pension benefit/(costs) | 55 | | 55 | | 52 | |
| Non-operating property environmental remediation and restoration | (32) | | (37) | | (37) | |
| Interest from IRS refund claims | - | | 24 | | - | |
| Other | (8) | | (7) | | 10 | |
| Total | $ | 629 | | $ | 350 | | $ | 491 | |
[a]2025 includes $250 million in industrial park land sales. 2023 includes a one-time $107 million transaction.
7. Income Taxes
Components of income tax expense were as follows for the years ended December 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Current tax expense: | | | |
| Federal | 1,460 | | 1,649 | | 1,417 | |
| State | 321 | | 359 | | 314 | |
| Foreign | 6 | | 11 | | 6 | |
| Total current tax expense | 1,787 | | 2,019 | | 1,737 | |
| Deferred and other tax expense/(benefit): | | | |
| Federal | 351 | | 47 | | 219 | |
| State [a] | (114) | | (24) | | (104) | |
| Foreign | 4 | | 5 | | 2 | |
| Total deferred and other tax expense | 241 | | 28 | | 117 | |
| Total income tax expense | $ | 2,028 | | $ | 2,047 | | $ | 1,854 | |
[a]In 2025, Kansas enacted corporate income tax legislation that resulted in a $115 million reduction of our deferred tax expense. In 2024, Louisiana and Arkansas enacted corporate income tax legislation that resulted in a $34 million reduction of our deferred tax expense. In 2023, Nebraska, Iowa, Kansas, and Arkansas enacted corporate income tax legislation that resulted in a $114 million reduction of our deferred tax expense.
For the years ended December 31, reconciliations between statutory and effective tax rates are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions, except percentages | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Federal Taxes | $ | 1,925 | | 21.0 | % | $ | 1,847 | | 21.0 | % | $ | 1,729 | | 21.0 | % |
| State and local income tax, net of federal benefit | 163 | | 1.8 | | 264 | | 3.0 | | 166 | | 2.0 | |
| Foreign tax effects | 10 | | 0.1 | | 16 | | 0.2 | | 8 | | 0.1 | |
| | | | | | |
| Effect of cross-border tax laws | (2) | | - | | 1 | | - | | (2) | | - | |
| Tax credits | (50) | | (0.6) | | (45) | | (0.5) | | (21) | | (0.3) | |
| | | | | | |
| Nontaxable or nondeductible items | (16) | | (0.2) | | (36) | | (0.4) | | (37) | | (0.4) | |
| Changes in unrecognized tax benefits | (2) | | - | | - | | - | | (1) | | - | |
| Other adjustments | - | | - | | - | | - | | 12 | | 0.1 | |
| Effective tax rate | $ | 2,028 | | 22.1 | % | $ | 2,047 | | 23.3 | % | $ | 1,854 | | 22.5 | % |
The state statutory rate, net of federal benefits, was 3.1%, 3.2%, and 3.4% for years ended December 31, 2025, 2024, and 2023, respectively.
UPRR operates in the western two-thirds of the country. The majority of our state taxes are paid in the states where we actively operate. The following states represent over 50% of our state income tax liability, listed in order of magnitude:
| | | | | | | | |
| 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| California | California | California |
| Illinois | Nebraska | Nebraska |
| Nebraska | Illinois | Illinois |
| Kansas | Kansas | Kansas |
| Iowa | Iowa |
Deferred income tax assets/(liabilities) were comprised of the following at December 31:
| | | | | | | | |
| Millions | 2025 | 2024 |
| Deferred income tax liabilities: | | |
| Property | $ | (13,260) | | $ | (13,020) | |
| Operating lease assets | (248) | | (314) | |
| Other | (639) | | (581) | |
| Total deferred income tax liabilities | (14,147) | | (13,915) | |
| Deferred income tax assets: | | |
| Operating lease liabilities | 241 | | 308 | |
| Accrued casualty costs | 184 | | 172 | |
| Accrued wages | 52 | | 51 | |
| Stock compensation | 34 | | 28 | |
| Other | 215 | | 205 | |
| Total deferred income tax assets | 726 | | 764 | |
| Net deferred income tax liability | $ | (13,421) | | $ | (13,151) | |
In 2025 and 2024, there were no valuation allowances against deferred tax assets.
A reconciliation of changes in unrecognized tax benefits liabilities/(assets) from the beginning to the end of the reporting period is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Unrecognized tax benefits at January 1 | $ | 32 | | $ | 30 | | $ | 34 | |
| Refunds from/(payments to) and settlements with taxing authorities | - | | 7 | | - | |
| Decreases for positions taken in prior years | (1) | | (6) | | (1) | |
| Increases/(decreases) for interest and penalties | 1 | | 1 | | - | |
| Lapse of statutes of limitations | (5) | | - | | (4) | |
| Increases for positions taken in current year | - | | - | | 1 | |
| | | |
| Unrecognized tax benefits at December 31 | $ | 27 | | $ | 32 | | $ | 30 | |
We recognize interest and penalties as part of income tax expense. Total accrued liabilities for interest and penalties were $4 million at both December 31, 2025 and 2024, respectively. Total interest and penalties recognized as part of income tax expense/(benefit) were $1 million for both 2025 and 2024 and ($1) million for 2023.
Several state tax authorities are examining our state income tax returns for years 2020 through 2024. With few exceptions, we are no longer subject to state income tax examinations by tax authorities for years before 2020. Additionally, we are no longer subject to U.S. federal income tax examinations by tax authorities for years before 2022.
The portion of our unrecognized tax benefits that relates to permanent changes in tax and interest would reduce our effective tax rate, if recognized. The remaining unrecognized tax benefits relate to tax positions for which only the timing of the benefit is uncertain. The unrecognized tax benefits that would reduce our effective tax rate are $27 million for 2025, $32 million for 2024, and $30 million for 2023.
8. Earnings Per Share
The following table provides a reconciliation between basic and diluted earnings per share for the years ended December 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions, except per share amounts | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Net income | $ | 7,138 | | $ | 6,747 | | $ | 6,379 | |
| Weighted-average number of shares outstanding: | | | |
| Basic | 595.0 | | 607.6 | | 609.2 | |
| Dilutive effect of stock options | 0.3 | | 0.4 | | 0.4 | |
| Dilutive effect of retention awards | 0.6 | | 0.6 | | 0.6 | |
| Diluted | 595.9 | | 608.6 | | 610.2 | |
| Earnings per share - basic | $ | 12.00 | | $ | 11.10 | | $ | 10.47 | |
| Earnings per share - diluted | $ | 11.98 | | $ | 11.09 | | $ | 10.45 | |
Diluted earnings per share was computed using the treasury stock method for both stock options and retention awards. Common stock options totaling 1.0 million, 0.6 million, and 0.9 million for 2025, 2024, and 2023, respectively, were excluded from the computation of diluted earnings per share because the exercise prices of these stock options exceeded the average market price of our common stock for the respective periods, and the effect of their inclusion would be anti-dilutive.
9. Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income/Loss
Reclassifications out of accumulated other comprehensive income/loss were as follows (net of tax):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions | Defined benefit plans | Foreign currency translation | Derivative instruments [a] | Total |
| Balance at January 1, 2025 | $ | (498) | | $ | (241) | | $ | 16 | | $ | (723) | |
| Other comprehensive income/(loss) before reclassifications | 2 | | 62 | | - | | 64 | |
| Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income/(loss) [b] | 69 | | - | | (1) | | 68 | |
Net year-to-date other comprehensive income/(loss), net of taxes of ($24) million | 71 | | 62 | | (1) | | 132 | |
| Balance at December 31, 2025 | $ | (427) | | $ | (179) | | $ | 15 | | $ | (591) | |
| | | | |
| Balance at January 1, 2024 | $ | (484) | | $ | (146) | | $ | 16 | | $ | (614) | |
| Other comprehensive income/(loss) before reclassifications | 2 | | (95) | | - | | (93) | |
| Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income/(loss) [b] | (16) | | - | | - | | (16) | |
Net year-to-date other comprehensive income/(loss), net of taxes of $6 million | (14) | | (95) | | - | | (109) | |
| Balance at December 31, 2024 | $ | (498) | | $ | (241) | | $ | 16 | | $ | (723) | |
[a]Related to interest rate swaps from equity method investments.
[b]The defined benefit plans accumulated other comprehensive income/loss reclassification components are 1) prior service cost/credit and 2) net actuarial loss, which are both included in the computation of net periodic pension benefit/cost. See Note 5 Retirement Plans for additional details.
10. Accounts Receivable
Accounts receivable include freight and other receivables reduced by an allowance for doubtful accounts. At December 31, 2025 and 2024, our accounts receivable were reduced by $4 million and $6 million, respectively. Receivables not expected to be collected in one year and the associated allowances are classified as other assets in our Consolidated Statements of Financial Position. At December 31, 2025 and 2024, receivables classified as other assets were reduced by allowances of $64 million and $69 million, respectively.
Receivables securitization facility – On July 28, 2025, the Railroad completed the renewal of the receivables securitization facility (the Receivables Facility). The new $600 million, 3-year facility replaces the prior $800 million facility and will mature in July 2028. Under the Receivables Facility, the Railroad sells most of its eligible third-party receivables to Union Pacific Receivables, Inc. (UPRI), a consolidated, wholly-owned, bankruptcy-remote subsidiary that may subsequently transfer, without recourse, an undivided interest in accounts receivable to investors. The investors have no recourse to the Railroad’s other assets except for customary warranty and indemnity claims. Creditors of the Railroad do not have recourse to the assets of UPRI.
The amount recorded under the Receivables Facility was $0 at both December 31, 2025 and 2024. During the year ended December 31, 2025, we issued $0 and repaid $0 under the Receivables Facility. The Receivables Facility was supported by $1.5 billion and $1.6 billion of accounts receivable as collateral at December 31, 2025 and 2024, respectively, which, as a retained interest, is included in accounts receivable, net in our Consolidated Statements of Financial Position.
The outstanding amount the Railroad maintains under the Receivables Facility may fluctuate based on current cash needs. The maximum allowed under the Receivables Facility is $600 million with availability directly impacted by eligible receivables, business volumes, and credit risks, including receivables payment quality measures such as default and dilution ratios. If default or dilution ratios increase one percent, the allowable outstanding amount under the Receivables Facility would not materially change.
The costs of the Receivables Facility include interest, which will vary based on prevailing benchmark and commercial paper rates, program fees paid to participating banks, commercial paper issuance costs, and fees of participating banks for unused commitment availability. The costs of the Receivables Facility are included in interest expense and were $3 million, $8 million, and $9 million for 2025, 2024, and 2023, respectively.
11. Properties
The following tables list the major categories of property and equipment as well as the weighted-average estimated useful life for each category (in years):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions, except estimated useful life | Cost | Accumulated
depreciation | Net book
value | Estimated
useful life |
| As of December 31, 2025 |
| Land | $ | 5,471 | | N/A | $ | 5,471 | | N/A |
| Road: | | | | |
| Rail and other track material | 19,747 | | $ | 7,936 | | 11,811 | | 45 |
| Ties | 12,779 | | 4,305 | | 8,474 | | 34 |
| Ballast | 6,646 | | 2,309 | | 4,337 | | 34 |
| Other roadway [a] | 24,610 | | 6,080 | | 18,530 | | 47 |
| Total road | 63,782 | | 20,630 | | 43,152 | | N/A |
| Equipment: | | | | |
| Locomotives | 9,926 | | 3,813 | | 6,113 | | 18 |
| Freight cars | 3,080 | | 1,107 | | 1,973 | | 23 |
| Work equipment and other | 1,318 | | 540 | | 778 | | 17 |
| Total equipment | 14,324 | | 5,460 | | 8,864 | | N/A |
| Technology and other | 1,414 | | 669 | | 745 | | 12 |
| Construction in progress | 1,413 | | - | | 1,413 | | N/A |
| Total | $ | 86,404 | | $ | 26,759 | | $ | 59,645 | | N/A |
[a]Other roadway includes grading, bridges and tunnels, signals, buildings, and other road assets.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions, except estimated useful life | Cost | Accumulated
depreciation | Net book
value | Estimated
useful life |
| As of December 31, 2024 |
| Land | $ | 5,441 | | N/A | $ | 5,441 | | N/A |
| Road: | | | | |
| Rail and other track material | 19,283 | | $ | 7,642 | | 11,641 | | 46 |
| Ties | 12,358 | | 4,109 | | 8,249 | | 34 |
| Ballast | 6,495 | | 2,182 | | 4,313 | | 34 |
| Other roadway [a] | 23,913 | | 5,681 | | 18,232 | | 47 |
| Total road | 62,049 | | 19,614 | | 42,435 | | N/A |
| Equipment: | | | | |
| Locomotives | 9,517 | | 3,724 | | 5,793 | | 18 |
| Freight cars | 3,011 | | 1,037 | | 1,974 | | 22 |
| Work equipment and other [b] | 1,222 | | 482 | | 740 | | 17 |
| Total equipment | 13,750 | | 5,243 | | 8,507 | | N/A |
| Technology and other | 1,431 | | 640 | | 791 | | 12 |
| Construction in progress | 1,169 | | - | | 1,169 | | N/A |
| Total | $ | 83,840 | | $ | 25,497 | | $ | 58,343 | | N/A |
[a]Other roadway includes grading, bridges and tunnels, signals, buildings, and other road assets.
[b]For retirements of depreciable railroad properties that do not occur in the normal course of business, a gain or loss may be recognized if the retirement meets each of the following three conditions: (a) is unusual, (b) is material in amount to the asset class, and (c) varies significantly from the retirement profile identified through our depreciation studies. In the second quarter of 2024, we sold a large portion of an intermodal equipment asset class resulting in a $46 million gain recognized in other expense in our Consolidated Statements of Income.
Property and depreciation – Our railroad operations are highly capital-intensive, and our large base of homogeneous, network-type assets turns over on a continuous basis. Each year we develop a capital program for the replacement of assets and for the acquisition or construction of assets that enable us to enhance our operations or provide new service offerings to customers. We currently have more than 60 depreciable asset classes, and we may increase or decrease the number of asset classes due to changes in technology, asset strategies, or other factors.
We determine the estimated service lives of depreciable railroad assets by means of depreciation studies. We perform depreciation studies at least every 3 years for equipment and every 6 years for track assets (i.e., rail and other track material, ties, and ballast) and other road property. Our depreciation studies take into account the following factors:
•Statistical analysis of historical patterns of use and retirements of each of our asset classes,
•Evaluation of any expected changes in current operations and the outlook for continued use of the assets,
•Evaluation of technological advances and changes to maintenance practices, and
•Expected salvage to be received upon retirement.
For rail in high-density traffic corridors, we measure estimated service lives in millions of gross tons per mile of track. It has been our experience that the lives of rail in high-density traffic corridors are closely correlated to usage (i.e., the amount of weight carried over the rail). The service lives also vary based on rail weight, rail condition (e.g., new or secondhand), and rail type (e.g., straight or curve). Our depreciation studies for rail in high-density traffic corridors consider each of these factors in determining the estimated service lives. For rail in high-density traffic corridors, we calculate depreciation rates annually by dividing the number of gross ton-miles carried over the rail (i.e., the weight of loaded and empty freight cars, locomotives, and maintenance of way equipment transported over the rail) by the estimated service lives of the rail measured in millions of gross tons per mile. For all other depreciable assets, we compute depreciation based on the estimated service lives of our assets as determined from the analysis of our depreciation studies. Changes in the estimated service lives of our assets and their related depreciation rates are implemented prospectively.
Under the group method of depreciation, the historical cost (net of salvage) of depreciable property that is retired or replaced in the ordinary course of business is charged to accumulated depreciation and no gain or loss is recognized. The historical cost of certain track assets is estimated by multiplying the current replacement cost of track assets by a historical index factor derived from (a) inflation indices published by the Bureau of Labor Statistics and (b) the estimated useful lives of the assets as determined by our depreciation studies. The indices were selected because they closely correlate with the major costs of the properties comprising the applicable track asset classes. Because of the number of estimates inherent in the depreciation and retirement processes and because it is impossible to precisely estimate each of these variables until a group of property is completely retired, we continually monitor the estimated service lives of our assets and the accumulated depreciation associated with each asset class to ensure our depreciation rates are appropriate. In addition, we determine if the recorded amount of accumulated depreciation is deficient (or in excess) of the amount indicated by our depreciation studies. Any deficiency (or excess) is amortized as a component of depreciation expense over the remaining service lives of the applicable classes of assets.
For retirements of depreciable railroad properties that do not occur in the normal course of business, a gain or loss may be recognized if the retirement meets each of the following three conditions: (a) is unusual, (b) is material in amount to the asset class, and (c) varies significantly from the retirement profile identified through our depreciation studies. A gain or loss is recognized in other income when we sell land or dispose of assets that are not part of our railroad operations.
No gains or losses were recognized due to the retirement of depreciable railroad properties in 2025 or 2023. In 2024, we sold a large portion of an intermodal equipment asset class resulting in a gain recognized in other expense in our Consolidated Statements of Income.
We review construction in progress assets that have not yet been placed into service, for impairment when events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of a long-lived asset or assets may not be recoverable. If impairment indicators are present and the estimated future undiscounted cash flows are less than the carrying value of construction in progress assets when grouped with other assets and liabilities at the lowest level where identifiable cash flows are largely independent, the carrying value is reduced to the estimated fair value.
When we purchase an asset, we capitalize all costs necessary to make the asset ready for its intended use. However, many of our assets are self-constructed. A large portion of our capital expenditures is for replacement of existing track assets and other road properties, which is typically performed by our employees, and for track line expansion and other capacity projects. Costs that are directly attributable to capital projects (including overhead costs) are capitalized. Direct costs that are capitalized as part of self-constructed assets include material, labor, and work equipment. Indirect costs are capitalized if they clearly relate to the construction of the asset.
Costs incurred that extend the useful life of an asset, improve the safety of our operations, or improve operating efficiency are capitalized, while normal repairs and maintenance are expensed as incurred. Total expense for repairs and maintenance incurred was approximately $2.3 billion for 2025, $2.3 billion for 2024, and $2.5 billion for 2023.
Assets held under finance leases are recorded at the lower of the net present value of the minimum lease payments or the fair value of the leased asset at the inception of the lease. Amortization expense is computed using the straight-line method over the shorter of the estimated useful lives of the assets or the period of the related lease.
12. Accounts Payable and Other Current Liabilities
| | | | | | | | |
| Millions | Dec. 31,
2025 | Dec. 31,
2024 |
| Accounts payable | $ | 804 | | $ | 847 | |
| Compensation-related accruals | 642 | | 618 | |
| Income and other taxes payable | 491 | | 605 | |
| Interest payable | 375 | | 372 | |
| Accrued casualty costs | 278 | | 319 | |
| Current operating lease liabilities (Note 16) | 270 | | 346 | |
| Equipment rents payable | 102 | | 109 | |
| Other | 532 | | 613 | |
| Total accounts payable and other current liabilities | $ | 3,494 | | $ | 3,829 | |
13. Financial Instruments
Short-term investments – All of the Company’s short-term investments consist of time deposits and government agency securities. These investments are considered Level 2 investments and are valued at amortized cost, which approximates fair value. As of December 31, 2025 and 2024, the Company had $250 million and $20 million of short-term investments, respectively. All short-term investments have a maturity of three to twelve months from the date of purchase and are classified as held-to-maturity.
Fair value of financial instruments – The fair value of our short- and long-term debt was estimated using a market value price model, which utilizes applicable U.S. Treasury rates along with current market quotes on comparable debt securities. All of the inputs used to determine the fair market value of the Corporation’s long-term debt are Level 2 inputs and obtained from an independent source. At December 31, 2025, the fair value of total debt was $26.5 billion, approximately $5.3 billion less than the carrying value. At December 31, 2024, the fair value of total debt was $25.3 billion, approximately $5.9 billion less than the carrying value. The fair value of the Corporation’s debt is a measure of its current value under present market conditions. The fair value of our cash equivalents approximates their carrying value due to the short-term maturities of these instruments.
14. Debt
Total debt as of December 31, 2025 and 2024, is summarized below:
| | | | | | | | |
| Millions | 2025 | 2024 |
Notes and debentures, 2.3% to 7.2% due through February 14, 2072 | $ | 32,694 | | $ | 32,044 | |
Equipment obligations, 2.6% to 6.2% due through January 2, 2031 [a] | 693 | | 732 | |
Finance leases, 3.1% to 6.8% due through August 21, 2029 | 105 | | 109 | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| Unamortized discount and deferred issuance costs | (1,678) | | (1,693) | |
| Total debt | 31,814 | | 31,192 | |
| Less: current portion | (1,520) | | (1,425) | |
| Total long-term debt | $ | 30,294 | | $ | 29,767 | |
[a]Equipment obligations are secured by an interest in certain railroad equipment with a carrying value of approximately $0.8 billion at both December 31, 2025 and 2024.
Debt maturities – The following table presents aggregate debt maturities as of December 31, 2025, excluding market value adjustments:
| | | | | |
| Millions | |
| 2026 | $ | 1,521 | |
| 2027 | 1,291 | |
| 2028 | 1,239 | |
| 2029 | 1,276 | |
| 2030 | 753 | |
| Thereafter | 27,412 | |
| Total principal | 33,492 | |
| Unamortized discount and deferred issuance costs | (1,678) | |
| Total debt | $ | 31,814 | |
Credit facilities – At December 31, 2025, we had $2.0 billion of credit available under our revolving credit facility (the Facility), which is designated for general corporate purposes and supports the issuance of commercial paper. During 2025, we issued $0 and repaid $0 through the Facility. As of both December 31, 2025 and 2024, we had $0 outstanding with the Facility. Commitment fees and interest rates payable under the Facility are similar to fees and rates available to comparably rated, investment-grade borrowers. The Facility allows for borrowings at floating rates based on Term Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR), plus a spread, depending upon credit ratings for our senior unsecured debt. The Facility, set to expire May 20, 2027, requires UPC to maintain an adjusted debt-to-EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization) coverage ratio.
The definition of debt used for purposes of calculating the adjusted debt-to-EBITDA coverage ratio includes, among other things, certain credit arrangements, finance leases, guarantees, unfunded and vested pension benefits under Title IV of Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 (ERISA), and unamortized debt discount and deferred debt issuance costs. At December 31, 2025, the Company was in compliance with the adjusted debt-to-EBITDA coverage ratio, which allows us to carry up to $47.7 billion of debt (as defined in the Facility), and we had $33.5 billion of debt (as defined in the Facility) outstanding at that date. The Facility does not include any other financial restrictions, credit rating triggers (other than rating-dependent pricing), or any other provision that could require us to post collateral. The Facility also includes a $150 million cross-default provision and a change-of-control provision.
During 2025, we issued $0 and repaid $0 of commercial paper. As of both December 31, 2025 and 2024, we had $0 of commercial paper outstanding. Our revolving credit facility supports our outstanding commercial paper balances, and, unless we change the terms of our commercial paper program, our aggregate issuance of commercial paper will not exceed the amount of borrowings available under the Facility.
Shelf registration statement and significant new borrowings – We filed an automatic shelf registration statement with the SEC that became effective on February 13, 2024. On July 28, 2025, the Board of Directors authorized the issuance of up to $20.0 billion of debt securities, replacing the prior authorization from 2024, which had $7.0 billion of authority remaining. Under our shelf registration, we may issue, from time to time, any combination of debt securities, preferred stock, common stock, or warrants for debt securities or preferred stock in one or more offerings.
During the year ended December 31, 2025, we issued the following unsecured, fixed-rate debt securities under our shelf registration:
| | | | | | | | |
| Date | | Description of securities |
| February 13, 2025 | | $1.00 billion of 5.100% Notes due February 20, 2035 |
| | $1.00 billion of 5.600% Notes due December 1, 2054 |
We used the net proceeds from the offerings for general corporate purposes, including the repurchase of common stock pursuant to our share repurchase programs. These debt securities include change-of-control provisions. At December 31, 2025, we had remaining authority from the Board of Directors to issue up to $20.0 billion of debt securities under our shelf registration.
Receivables securitization facility – As of both December 31, 2025 and 2024, we recorded $0 of borrowings under our Receivables Facility as secured debt. (See further discussion in the "Receivables Securitization Facility" section of Note 10.)
15. Variable Interest Entities
We have entered into various lease transactions in which the structure of the leases contain variable interest entities (VIEs). These VIEs were created solely for the purpose of doing lease transactions (principally involving railroad equipment and facilities) and have no other activities, assets, or liabilities outside of the lease transactions. Within these lease arrangements, we have the right to purchase some or all of the assets at fixed prices. Depending on market conditions, fixed-price purchase options available in the leases could potentially provide benefits to us; however, these benefits are not expected to be significant.
We maintain and operate the assets based on contractual obligations within the lease arrangements, which set specific guidelines consistent within the railroad industry. As such, we have no control over activities that could materially impact the fair value of the leased assets. We do not hold the power to direct the activities of the VIEs and, therefore, do not control the ongoing activities that have a significant impact on the economic performance of the VIEs. Additionally, we do not have the obligation to absorb losses of the VIEs or the right to receive benefits of the VIEs that could potentially be significant to the VIEs.
We are not considered to be the primary beneficiary and do not consolidate these VIEs because our actions and decisions do not have the most significant effect on the VIE’s performance and our fixed-price purchase options are not considered to be potentially significant to the VIEs. The future minimum lease payments associated with the VIE leases totaled $331 million as of December 31, 2025, and are recorded as operating lease liabilities at present value in our Consolidated Statements of Financial Position.
16. Leases
We lease certain locomotives, freight cars, and other property for use in our rail operations.
The following are details related to our lease portfolio as of December 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions | Classification | 2025 | 2024 |
| Assets | | | |
| Operating leases | Operating lease assets | $ | 1,036 | | $ | 1,297 | |
| Finance leases | Properties, net [a] | 185 | | 172 | |
| Total leased assets | | $ | 1,221 | | $ | 1,469 | |
| Liabilities | | | |
| Current | | | |
| Operating | Accounts payable and other current liabilities | $ | 270 | | $ | 346 | |
| Finance | Debt due within one year | 39 | | 37 | |
| Noncurrent | | | |
| Operating | Operating lease liabilities | 738 | | 925 | |
| Finance | Debt due after one year | 66 | | 72 | |
| Total lease liabilities | | $ | 1,113 | | $ | 1,380 | |
[a]Finance lease assets are recorded net of accumulated amortization of $456 million and $472 million as of December 31, 2025 and 2024, respectively.
The following table presents the classification of lease cost components for the year-ended December 31:
| | | | | | | | |
| Millions | 2025 | 2024 |
| Operating lease cost [a] | $ | 305 | | $ | 340 | |
| Short-term lease cost | 23 | | 24 | |
| Variable lease cost | 39 | | 37 | |
| Finance lease cost | | |
| Amortization of leased assets [b] | 28 | | 31 | |
| Interest on lease liabilities [c] | 5 | | 5 | |
| Net lease cost | $ | 400 | | $ | 437 | |
[a]Operating lease cost is primarily reported in equipment and other rents in our Consolidated Statements of Income.
[b]Amortization of leased assets is reported in depreciation in our Consolidated Statements of Income.
[c]Interest on lease liabilities is reported in interest expense in our Consolidated Statements of Income.
The following table presents aggregate lease maturities as of December 31, 2025:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions | Operating leases | Finance leases | Total |
| 2026 | $ | 276 | | $ | 42 | | $ | 318 | |
| 2027 | 238 | | 37 | | 275 | |
| 2028 | 191 | | 14 | | 205 | |
| 2029 | 123 | | 21 | | 144 | |
| 2030 | 121 | | - | | 121 | |
| After 2030 | 176 | | - | | 176 | |
| Total lease payments | $ | 1,125 | | $ | 114 | | $ | 1,239 | |
| Less: Interest | 117 | | 9 | | 126 | |
| Present value of lease liabilities | $ | 1,008 | | $ | 105 | | $ | 1,113 | |
The following table presents the weighted average remaining lease term and discount rate as of December 31:
| | | | | |
| 2025 |
| Weighted-average remaining lease term (years) | |
| Operating leases | 5.4 |
| Finance leases | 2.6 |
| Weighted-average discount rate (%) | |
| Operating leases | 4.0 | |
| Finance leases | 4.5 | |
The following table presents other information related to our operating and finance leases for the years ended December 31:
| | | | | | | | |
| Millions | 2025 | 2024 |
| Cash paid for amounts included in the measurement of lease liabilities | | |
| Operating cash flows from operating leases | $ | 310 | | $ | 319 | |
| Investing cash flows from operating leases | 32 | | 32 | |
| Operating cash flows from finance leases | 4 | | 6 | |
| Financing cash flows from finance leases | 36 | | 47 | |
| | |
| Leased assets obtained in exchange for operating lease liabilities | $ | 198 | | $ | 119 | |
17. Commitments and Contingencies
See Note 20 for a discussion on the pending acquisition of Norfolk Southern.
Asserted and unasserted claims – Various claims and lawsuits are pending against us and certain of our subsidiaries. We cannot fully determine the effect of all asserted and unasserted claims on our consolidated results of operations, financial condition, or liquidity. We have recorded a liability where asserted and unasserted claims are considered probable and where such claims can be reasonably estimated. We currently do not expect that any known lawsuits, claims, environmental costs, commitments, contingent liabilities, or guarantees will have a material adverse effect on our consolidated results of operations, financial condition, or liquidity after taking into account liabilities and insurance recoveries previously recorded for these matters.
In December 2019, we received a putative class action complaint under the Illinois Biometric Information Privacy Act, alleging violation due to the use of a finger scan system developed and managed by third parties. While we believe that we have strong defenses to the claims made in the complaint and will vigorously defend ourselves, there is no assurance regarding the ultimate outcome. The outcome of this litigation is inherently uncertain, and we cannot reasonably estimate any loss or range of loss that may arise from this matter.
Personal injury – The Federal Employers’ Liability Act (FELA) governs compensation for work-related accidents. Under FELA, damages are assessed based on a finding of fault through litigation or out-of-court settlements. We offer a comprehensive variety of services and rehabilitation programs for employees who are injured at work.
Because of the uncertainty surrounding the ultimate outcome of personal injury claims, it is reasonably possible that future costs to settle these claims may range from approximately $413 million to $530 million. We record an accrual at the low end of the range as no amount of loss within the range is more probable than any other. Estimates can vary over time due to evolving trends in litigation.
Our personal injury liability activity was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Beginning balance | $ | 379 | | $ | 383 | | $ | 361 | |
| Current year accruals | 123 | | 121 | | 112 | |
| Changes in estimates for prior years | 17 | | (14) | | 89 | |
| Payments | (106) | | (111) | | (179) | |
| Ending balance at December 31 | $ | 413 | | $ | 379 | | $ | 383 | |
| Current portion, ending balance at December 31 | $ | 93 | | $ | 106 | | $ | 113 | |
Environmental costs – We are subject to federal, state, and local environmental laws and regulations. We have identified 343 sites where we are or may be liable for remediation costs associated with alleged contamination or for violations of environmental requirements. This includes 29 sites that are the subject of actions taken by the U.S. government, including 17 that are currently on the Superfund National Priorities List. Certain federal legislation imposes joint and several liability for the remediation of identified sites; consequently, our ultimate environmental liability may include costs relating to activities of other parties, in addition to costs relating to our own activities at each site.
Our environmental liability activity was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Millions | 2025 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Beginning balance | $ | 268 | | $ | 245 | | $ | 253 | |
| Accruals | 70 | | 129 | | 99 | |
| Payments | (79) | | (106) | | (107) | |
| Ending balance at December 31 | $ | 259 | | $ | 268 | | $ | 245 | |
| Current portion, ending balance at December 31 | $ | 62 | | $ | 83 | | $ | 91 | |
The environmental liability includes future costs for remediation and restoration of sites, as well as ongoing monitoring costs, but excludes any anticipated recoveries from third parties. Cost estimates are based on information available for each site, financial viability of other potentially responsible parties, and existing technology, laws, and regulations. The ultimate liability for remediation is difficult to determine because of the number of potentially responsible parties, site-specific cost sharing arrangements with other potentially responsible parties, the degree of contamination by various wastes, the scarcity and quality of volumetric data related to many of the sites, and the speculative nature of remediation costs. Estimates of liability may vary over time due to changes in federal, state, and local laws governing environmental remediation. Current obligations are not expected to have a material adverse effect on our consolidated results of operations, financial condition, or liquidity.
Indemnities – Our maximum potential exposure under indemnification arrangements, including certain tax indemnifications, can range from a specified dollar amount to an unlimited amount, depending on the nature of the transactions and the agreements. Due to uncertainty as to whether claims will be made or how they will be resolved, we cannot reasonably determine the probability of an adverse claim or reasonably estimate any adverse liability or the total maximum exposure under these indemnification arrangements. We do not have any reason to believe that we will be required to make any material payments under these indemnity provisions.
18. Share Repurchase Programs
Effective April 1, 2025, our Board of Directors authorized the repurchase of up to 100 million shares of our common stock by March 31, 2028. As of December 31, 2025, we repurchased a total of 6.1 million shares of our common stock under the 2025 authorization. As part of the pending acquisition of Norfolk Southern described in Note 20, we paused our share repurchase program.
Our previous authorization, which was effective April 1, 2022, through March 31, 2025, was approved by our Board of Directors for up to 100 million shares of common stock. We repurchased a total of 31.7 million shares of our common stock under the 2022 authorization.
The table below represents shares repurchased under repurchase programs during 2025 and 2024:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Number of shares purchased | Average price paid [a] |
| 2025 | 2024 | 2025 | 2024 |
| First quarter [b] | 5,745,601 | - | $ | 250.74 | | $ | - | |
| Second quarter [c] | 6,111,558 | 492,320 | 205.06 | | 225.96 | |
| Third quarter | - | 3,006,061 | - | | 245.44 | |
| Fourth quarter | - | 2,804,785 | - | | 237.43 | |
| Total | 11,857,159 | 6,303,166 | $ | 227.20 | | $ | 240.35 | |
| Remaining number of shares that may be repurchased under current authority | 93,888,442 |
[a]In the period of the final settlement, the average price under the accelerated share repurchase programs (ASRs) is calculated based on the total program value less the value assigned to the initial delivery of shares. The average price of the completed 2025 ASRs was $229.32.
[b]Includes 4,815,022 shares repurchased in 2025 under the ASRs at the average price of $251.73
[c]Includes an incremental 1,795,904 shares received upon the final settlement in 2025 under the ASRs at the average price of $169.22
Accelerated share repurchase programs – The Company has established ASRs with financial institutions to repurchase shares of our common stock. These ASRs have been structured so that at the time of commencement, we pay a specified amount to the financial institutions and receive an initial delivery of shares. Additional shares may be received at the time of settlement. The final number of shares to be received is based on the volume weighted average price of the Company's common stock during the ASR term, less a discount and subject to potential adjustments pursuant to the terms of such ASR.
On February 18, 2025, the Company received 4,815,022 shares of its common stock repurchased under ASRs for an aggregate of $1.5 billion. Upon settlement of these ASRs in the second quarter of 2025, we received 1,795,904 additional shares.
ASRs are accounted for as equity transactions, and at the time of receipt, shares are included in treasury stock at fair market value as of the corresponding initiation or settlement date. The Company reflects shares received as a repurchase of common stock in the weighted average common shares outstanding calculation for basic and diluted earnings per share.
19. Related Parties
UPRR and other North American railroad companies jointly own TTX Company (TTX). UPRR has a 37.03% economic interest in TTX while the other North American railroads own the remaining interest. In accordance with ASC 323 Investments - Equity Method and Joint Venture, UPRR applies the equity method of accounting to our investment in TTX.
TTX is a rail car pooling company that owns rail cars and intermodal wells to serve North America’s railroads. TTX assists railroads in meeting the needs of their customers by providing rail cars in an efficient, pooled environment. All railroads may utilize TTX rail cars through car hire by renting rail cars at stated rates.
UPRR had $2.0 billion and $1.9 billion recognized as investments related to TTX in our Consolidated Statements of Financial Position as of December 31, 2025 and 2024, respectively. TTX car hire expense of $447 million in 2025, $432 million in 2024, and $399 million in 2023 are included in equipment and other rents in our Consolidated Statements of Income. In addition, UPRR had accounts payable to TTX of $72 million and $70 million at December 31, 2025 and 2024, respectively.
20. Pending Acquisition
Norfolk Southern Corporation (Norfolk Southern), a Virginia corporation, is one of the nation’s premier transportation companies, moving goods and materials that help drive the U.S. economy. Norfolk Southern connects customers to markets and communities to economic opportunity with safe, reliable, and cost-effective shipping solutions. Its Norfolk Southern Railway Company subsidiary operates in 22 states and the District of Columbia. Norfolk Southern is a major transporter of industrial products, including agriculture, forest, and consumer products, chemicals, and metals and construction materials. In addition, in the East, it serves every major container port and operates the most extensive intermodal network. Norfolk Southern is also a principal carrier of coal, automobiles, and automotive parts. Norfolk Southern’s stock is publicly traded on the NYSE under the ticker symbol NSC.
On July 28, 2025, Union Pacific, Norfolk Southern, Ruby Merger Sub 1 Corporation, and Ruby Merger Sub 2 LLC, entered into an agreement and plan of merger (the merger agreement). The merger agreement provides, among other things, for the acquisition of Norfolk Southern by Union Pacific, subject to the satisfaction or waiver of the conditions specified therein, through two mergers: (i) first, Ruby Merger Sub 1 Corporation will merge with and into Norfolk Southern with Norfolk Southern surviving as a direct, wholly owned subsidiary of Union Pacific (the first merger); and (ii) second, immediately after the first merger, Norfolk Southern will merge with and into Ruby Merger Sub 2 LLC with Ruby Merger Sub 2 LLC surviving as a direct, wholly owned subsidiary of Union Pacific (second merger). The first merger and the second merger are collectively referred to as the mergers.
At the effective time of the first merger (first effective time), each share of Norfolk Southern common stock issued and outstanding immediately prior to the first effective time, except for shares held by Union Pacific or Norfolk Southern, or their direct or indirect subsidiaries (other than, with respect to shares held by Union Pacific, Norfolk Southern, Ruby Merger Sub 1 Corporation, or Ruby Merger Sub 2 LLC, shares held on behalf of third parties), will be converted automatically into the right to receive one validly issued, fully paid, and nonassessable share of Union Pacific common stock and $88.82 in cash, without interest. Assuming completion of the mergers, we expect approximately 224.8 million shares of common stock to be issued and approximately $20 billion of cash consideration to be paid. The cash consideration is expected to be funded through a combination of new debt and cash accumulated through cash provided by operating activities. The actual value of the transaction may fluctuate based upon changes in the price of Union Pacific common stock and the number of Norfolk Southern common stock outstanding at the first effective time.
The combination of Norfolk Southern and Union Pacific would create America’s first transcontinental railroad that spans over 50,000 miles across 43 states with access to 10 international interchanges and approximately 100 ports.
Union Pacific filed a registration statement on Form S-4 (File No. 333-290282), which the SEC declared effective on September 30, 2025. Union Pacific and Norfolk Southern each also filed definitive proxy statements on October 1, 2025. Both Union Pacific's and Norfolk Southern's special meetings of shareholders was held on November 14, 2025. Union Pacific shareholders approved the share issuance proposal, and Norfolk Southern shareholders approved the merger agreement proposal (each as described in the companies' definitive proxy statements).
Completion of the mergers is conditioned on the receipt of Surface Transportation Board (STB) approval and a number of other conditions before the mergers can be consummated, as described in the merger agreement. On December 19, 2025, Union Pacific and Norfolk Southern (applicants) submitted a joint application to the STB seeking approval of the mergers. On December 19, 2025, the STB issued a decision inviting public comment on the application's completeness. Comments were due December 29, 2025. The applicants replied to comments on January 2, 2026. On January 16, 2026, the STB issued a decision that the joint application was not accepted as complete. The decision does not result in the dismissal of the merger proceeding nor should it be read as an indication of how the STB might ultimately assess any future revised application. The applicants are permitted to file a revised application, which would commence a new review by the STB for completeness. The STB decision directs the applicants to file a letter by February 17, 2026, indicating if and when the applicants anticipate filing a revised application.
Norfolk Southern's management and Board of Directors will continue to manage Norfolk Southern until the first effective time, pursuing its independent business plans and growth strategies. Subject to completion of the mergers, the acquisition is expected to be accounted for as a business combination using the acquisition method of accounting and currently expected to be completed in 2027.
Union Pacific incurred the following acquisition-related expense associated with the merger agreement for the year ended December 31:
| | | | | | | |
| Millions | 2025 | | |
| Acquisition-related expense | | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Purchased services and materials | $ | 68 | | | |
| Other | 4 | | | |
| Total acquisition-related expense [a] | $ | 72 | | | |
[a]Certain acquisition-related costs are non-deductible for income tax purposes.
At December 31, 2025, deferred share issuance costs of $13 million was recorded and will be recognized in paid-in-surplus upon completion of the mergers.
Both Union Pacific and Norfolk Southern may be required to pay the other a termination fee of $2.5 billion if the merger agreement is terminated under certain circumstances described in the merger agreement.
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
As of the end of the period covered by this report, the Corporation carried out an evaluation, under the supervision and with the participation of the Corporation’s management, including the Corporation’s Chief Executive Officer (CEO) and Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (CFO), of the effectiveness of the design and operation of the Corporation’s disclosure controls and procedures pursuant to Exchange Act Rules 13a-15 and 15d-15. In designing and evaluating the disclosure controls and procedures, management recognized that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving the desired control objectives. Based upon that evaluation, the CEO and the CFO concluded that, as of the end of the period covered by this report, the Corporation’s disclosure controls and procedures were effective to provide reasonable assurance that information required to be disclosed in our Exchange Act reports is recorded, processed, summarized, and reported within the time periods specified by the SEC, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to management, including the CEO and CFO, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Additionally, the CEO and CFO determined that there were no changes to the Corporation’s internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)) during the last fiscal quarter that materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the Corporation’s internal control over financial reporting.
MANAGEMENT’S ANNUAL REPORT ON INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
The management of Union Pacific Corporation and Subsidiary Companies (the Corporation) is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)). The Corporation’s internal control system was designed to provide reasonable assurance to the Corporation’s management and Board of Directors regarding the preparation and fair presentation of published financial statements.
All internal control systems, no matter how well designed, have inherent limitations. Therefore, even those systems determined to be effective can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation and presentation.
The Corporation’s management assessed the effectiveness of the Corporation’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2025. In making this assessment, it used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013). Based on our assessment, management believes that, as of December 31, 2025, the Corporation’s internal control over financial reporting is effective based on those criteria.
The Corporation’s independent registered public accounting firm has issued an attestation report on the effectiveness of the Corporation’s internal control over financial reporting. This report appears on the next page.
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Shareholders and the Board of Directors of Union Pacific Corporation
Opinion on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited the internal control over financial reporting of Union Pacific Corporation and Subsidiary Companies (the "Corporation") as of December 31, 2025, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). In our opinion, the Corporation maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2025, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by COSO.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2025, of the Corporation and our report dated February 6, 2026, expressed an unqualified opinion on those financial statements.
Basis for Opinion
The Corporation's management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management's Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Corporation's internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Corporation in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control over Financial Reporting
A company's internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company's assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Omaha, Nebraska
February 6, 2026
Item 9B. Other Information
On December 19, 2025, Eric G. Gehringer, Executive Vice President - Operations, adopted a trading plan intended to satisfy Rule 10b5-1(c) to sell up to 1,999 shares of Union Pacific Corporation common stock between March 20, 2026, and December 31, 2026, subject to certain conditions.
Item 9C. Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspections
Not applicable.
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers, and Corporate Governance
(a)Directors of Registrant.
Information as to the names, ages, positions, and offices with UPC, terms of office, periods of service, business experience during the past five years, and certain other directorships held by each director or person nominated to become a director of UPC is set forth in the Election of Directors segment of the Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
Information concerning our Audit Committee and the independence of its members, along with information about the audit committee financial expert(s) serving on the Audit Committee, is set forth in the Audit Committee segment of the Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
(b)Executive Officers of Registrant.
Information concerning the executive officers of UPC and its subsidiaries is presented in Part I of this report under Information About Our Executive Officers and Principal Executive Officers of Our Subsidiaries.
(c)Delinquent Section 16(a) Reports.
Information concerning compliance with Section 16(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 is set forth in the Delinquent Section 16(a) Reports segment of the Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
(d)Code of Ethics for Chief Executive Officer and Senior Financial Officers of Registrant.
The Board of Directors of UPC has adopted the UPC Code of Ethics for the Chief Executive Officer and Senior Financial Officers (the Code). A copy of the Code may be found on the Internet at our website https://investor.unionpacific.com/governance/governance-overview. We intend to disclose any amendments to the Code or any waiver from a provision of the Code on our website.
(e)Insider Trading Arrangements and Policies.
Information concerning UPC's Confidentiality and Insider Trading Policy is set forth in the Insider Trading Arrangements and Policies segment of the Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference. UPC's Confidentiality and Insider Trading Policy is included as an exhibit to this report.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
Information concerning compensation received by our directors and our named executive officers is presented in the Compensation Discussion and Analysis, Summary Compensation Table, Grants of Plan-Based Awards in Fiscal Year 2025, Outstanding Equity Awards at 2025 Fiscal Year-End, Option Exercises and Stock Vested in Fiscal Year 2025, Pension Benefits at 2025 Fiscal Year-End, Nonqualified Deferred Compensation at 2025 Fiscal Year-End, Potential Payments Upon Termination or Change in Control and Director Compensation in Fiscal Year 2025 segments of the Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference. Additional information regarding compensation of directors, including Board committee members, is set forth in the By-Laws of UPC and the Stock Unit Grant and Deferred Compensation Plan for the Board of Directors, both of which are included as exhibits to this report. Information regarding the Compensation and Talent Committee is set forth in the Compensation Committee segment of the Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
Information as to the number of shares of our equity securities beneficially owned by each of our directors and nominees for director, our named executive officers, our directors and executive officers as a group, and certain beneficial owners is set forth in the Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management segment of the Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
The following table summarizes the equity compensation plans under which UPC common stock may be issued as of December 31, 2025:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | |
| Plan Category | Number of securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights | Weighted-average exercise price of outstanding options,
warrants and rights | Number of securities remaining available for future issuance under equity compensation plans (excluding securities reflected in column (a)) |
| Equity compensation plans approved by security holders | 2,487,690 | [1] | $ | 210.32 | | [1] | 29,874,539 | [2] |
| Total | 2,487,690 | | $ | 210.32 | | | 29,874,539 | |
[1]Includes 393,056 retention units that do not have an exercise price. Does not include 810,037 retention shares that have been issued and are outstanding.
[2]Does not include the retention units or retention shares described above in footnote [1].
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
Information on related transactions is set forth in the Related Party Policy and Procedures segment of the Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference. We do not have any relationship with any outside third-party that would enable such a party to negotiate terms of a material transaction that may not be available to, or available from, other parties on an arm’s-length basis.
Information regarding the independence of our directors is set forth in the Director Independence segment of the Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 14. Principal Accountant Fees and Services
Information concerning the fees billed by our independent registered public accounting firm and the nature of services comprising the fees for each of the two most recent fiscal years in each of the following categories: (a) audit fees, (b) audit-related fees, (c) tax fees, and (d) all other fees, is set forth in the Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm’s Fees and Services segment of the Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
Information concerning our Audit Committee’s policies and procedures pertaining to pre-approval of audit and non-audit services rendered by our independent registered public accounting firm is set forth in the Pre-approval of Audit and Non-Audit Services Policy segment of the Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibit and Financial Statement Schedules
(a)Financial Statements, Financial Statement Schedules, and Exhibits:
(1)Financial Statements
The financial statements filed as part of this filing are listed on the index to the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8, on page 43. (2)Financial Statement Schedules
Schedules have been omitted because they are not applicable or not required or the information required to be set forth therein is included in the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Item 8, or notes thereto.
(3)Exhibits
Exhibits are listed in the exhibit index beginning on page 80. The exhibits include management contracts, compensatory plans, and arrangements required to be filed as exhibits to the Form 10-K by Item 601 (10) (iii) of Regulation S-K. UNION PACIFIC CORPORATION
Exhibit Index
| | | | | |
| Exhibit No. | Description |
| |
| Filed with this Statement |
| |
| 10(a)† | |
| |
| 10(b)† | |
| |
| 19 | |
| |
| 21 | |
| |
| 23 | |
| |
| 24 | |
| |
| 31(a) | |
| |
| 31(b) | |
| |
| 32 | |
| |
| 101 | The following financial and related information from Union Pacific Corporation’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2025 (filed with the SEC on February 6, 2026), formatted in Inline Extensible Business Reporting Language (iXBRL) includes (a) Consolidated Statements of Income for the years ended December 31, 2025, 2024, and 2023, (b) Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income for the years ended December 31, 2025, 2024, and 2023, (c) Consolidated Statements of Financial Position at December 31, 2025 and 2024, (d) Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2025, 2024, and 2023, (e) Consolidated Statements of Changes in Common Shareholders’ Equity for the years ended December 31, 2025, 2024, and 2023, and (f) the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements. |
| |
| 104 | Cover Page Interactive Data File, formatted in Inline XBRL (contained in Exhibit 101). |
| |
| Incorporated by Reference |
| 2 | |
| |
| 3(a) | |
| |
| 3(b) | |
| |
| | | | | |
| 4(a) | |
| |
| 4(b) | |
| |
| 4(c) | |
| |
| 4(d) | |
| |
| 4(e) | |
| |
| Certain instruments evidencing long-term indebtedness of UPC are not filed as exhibits because the total amount of securities authorized under any single such instrument does not exceed 10% of the Corporation’s total consolidated assets. UPC agrees to furnish the Commission with a copy of any such instrument upon request by the Commission. |
| |
10(c)† | |
| |
10(d)† | |
| |
10(e)† | |
| |
10(f)† | |
| |
10(g)† | |
| |
10(h)† | |
| |
10(i)† | |
| |
10(j)† | |
| |
| | | | | |
10(k)† | |
| |
10(l)† | Union Pacific Corporation 2000 Directors Plan, effective as of April 21, 2000, as amended November 16, 2006, January 30, 2007, and January 1, 2009, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10(j) to the Corporation’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008. |
| |
10(m)† | |
| |
10(n)† | |
| |
10(o)† | |
| |
10(p)† | |
| |
10(q)† | |
| |
10(r) | |
| |
10(s) | Agreement, dated September 25, 1995, among UPC, UPRR, Missouri Pacific Railroad Company (MPRR), SP, Southern Pacific Transportation Company (SPT), The Denver & Rio Grande Western Railroad Company (D&RGW), St. Louis Southwestern Railway Company (SLSRC), and SPCSL Corp. (SPCSL), on the one hand, and Burlington Northern Railroad Company (BN) and The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway Company (Santa Fe), on the other hand, is incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.11 to UPC’s Registration Statement on Form S-4 (No. 33-64707). |
| |
10(t) | Supplemental Agreement, dated November 18, 1995, between UPC, UPRR, MPRR, SP, SPT, D&RGW, SLSRC and SPCSL, on the one hand, and BN and Santa Fe, on the other hand, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.12 to UPC’s Registration Statement on Form S-4 (No. 33-64707). |
| |
10(u)† | |
| |
10(v)† | |
| |
10(w)† | |
| |
10(x)† | |
| |
| | | | | |
10(y)† | |
| |
| 97 | |
| |
| † Indicates a management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. |
Item 16. Form 10-K Summary
None.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, on this 6th day of February, 2026.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| UNION PACIFIC CORPORATION | |
| | | |
| By | /s/ V. James Vena | |
| | V. James Vena | |
| | Chief Executive Officer | |
| | Union Pacific Corporation | |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below, on this 6th day of February, 2026, by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities indicated.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| PRINCIPAL EXECUTIVE OFFICER | |
| AND DIRECTOR: | |
| | | |
| By | /s/ V. James Vena | |
| | V. James Vena | |
| | Chief Executive Officer | |
| | Union Pacific Corporation | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| PRINCIPAL FINANCIAL OFFICER: |
| | | |
| By | /s/ Jennifer L. Hamann | |
| | Jennifer L. Hamann | |
| | Executive Vice President and | |
| | Chief Financial Officer | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING OFFICER: |
| | | |
| By | /s/ Carrie J. Powers | |
| | Carrie J. Powers | |
| | Vice President, Controller, and | |
| | Chief Accounting Officer | |
DIRECTORS:
| | | | | |
| David B. Dillon* | Doyle R. Simons* |
| Sheri H. Edison* | John K. Tien, Jr.* |
| Teresa M. Finley* | John P. Wiehoff* |
| Deborah C. Hopkins* | W Anthony Will* |
| Jane H. Lute* | Christopher J. Williams* |
| Michael R. McCarthy* | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| * By | /s/ Christina B. Conlin | |
| Christina B. Conlin, Attorney-in-fact | |