

VT - 1953 in Treating Symptoms of Malignant Fungating Wounds (MFW) PHASE 2 IST STUDY RESULTS & NEXT STEPS © Vyome Holdings, Inc. February 2026

VYOME HOLDINGS, INC. (“Vyome”) 2 Any statements contained in this presentation that do not describe historical facts may constitute forward - looking statements as that term is defined in the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 . These statements may be identified by words such as “believe,” “expect,” “may,” “plan,” “potential,” “will,” and similar expressions, and are based on Vyome’s current beliefs and expectations . These forward - looking statements include expectations regarding Vyome’s development of its drug candidates, including the timing of its clinical trials and regulatory ese statements involve risks and uncertainties that could c submissions. Th ause actual results to differ materially from those reflected in such statements. Risks and uncertainties that may cause actual results to differ materially include uncertainties inherent in the conduct of clinical eliance on third parties over which it may not always have trials, Vyome's r full control, public health crises, epidemics and pandemics such as the COVID - 19 pandemic, including its impact on the timing of Vyome’s regulatory and research and development activities, Any forward - looking statements speak only as of the date of this presentation and are based on information available to Vyome as of the date of this presentation . Given these risks and uncertainties, you are cautioned not to place undue reliance on such forward - looking statements . Except as required by law, Vyome assumes no obligation to, and does not intend to, update any forward - looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise . This presentation also contains estimates and other statistical data made by independent parties and by us relating to market size and other data about our industry . These data involve a number of assumptions and limitations, and you are cautioned not to give undue weight to such estimates . In addition, projections, assumptions and estimates of our future performance and the future performance of the markets in which we operate are necessarily subject to a high degree of uncertainty and risk . References to any publications, reports, surveys or articles prepared by third parties should not be construed as depicting the complete findings of the entire publication, report, survey or article . The information in any such publication, report, surveys or article is not incorporated by reference in this presentation .
Key Takeaways From Phase 2 Study Clear efficacy and safety signals to support further clinical development . VT - 1953 achieved a significant improvement (P=0.002) in the primary endpoint of malodor on Day 14 vs baseline as scored by investigators. The improvement seen with VT - 1953 was statistically significant (P=0.0015) compared with vehicle - treated patients. VT - 1953 resulted in a significant improvement (P=0.0256) in the secondary endpoint of patient - reported impact of malodor on the quality of life compared to vehicle - treatment by Day 14. Patients treated with VT - 1953 also reported a clinically significant improvement in lesion pain symptoms (exploratory endpoint) by Day 14 (P=0.002 compared with baseline; P=0.0026 vs vehicle - treated patients). 1 a n d u A n d a l e i nv e i f f N A a c y c D s t i G g y r i a t o n a n r e t r - d i n i a M t i t D n g i a 2 t / T t h e e d L R Ph 2 y m s n t e i s t r a p c o t u d y m s i t o t o n t o i e f n h M s t i b F i W V T t o - 1 9 , r 5 3 r o f , s a a t f e o p y t ical 2 3 4 5 VT - 1953 was well - tolerated by patients. 3
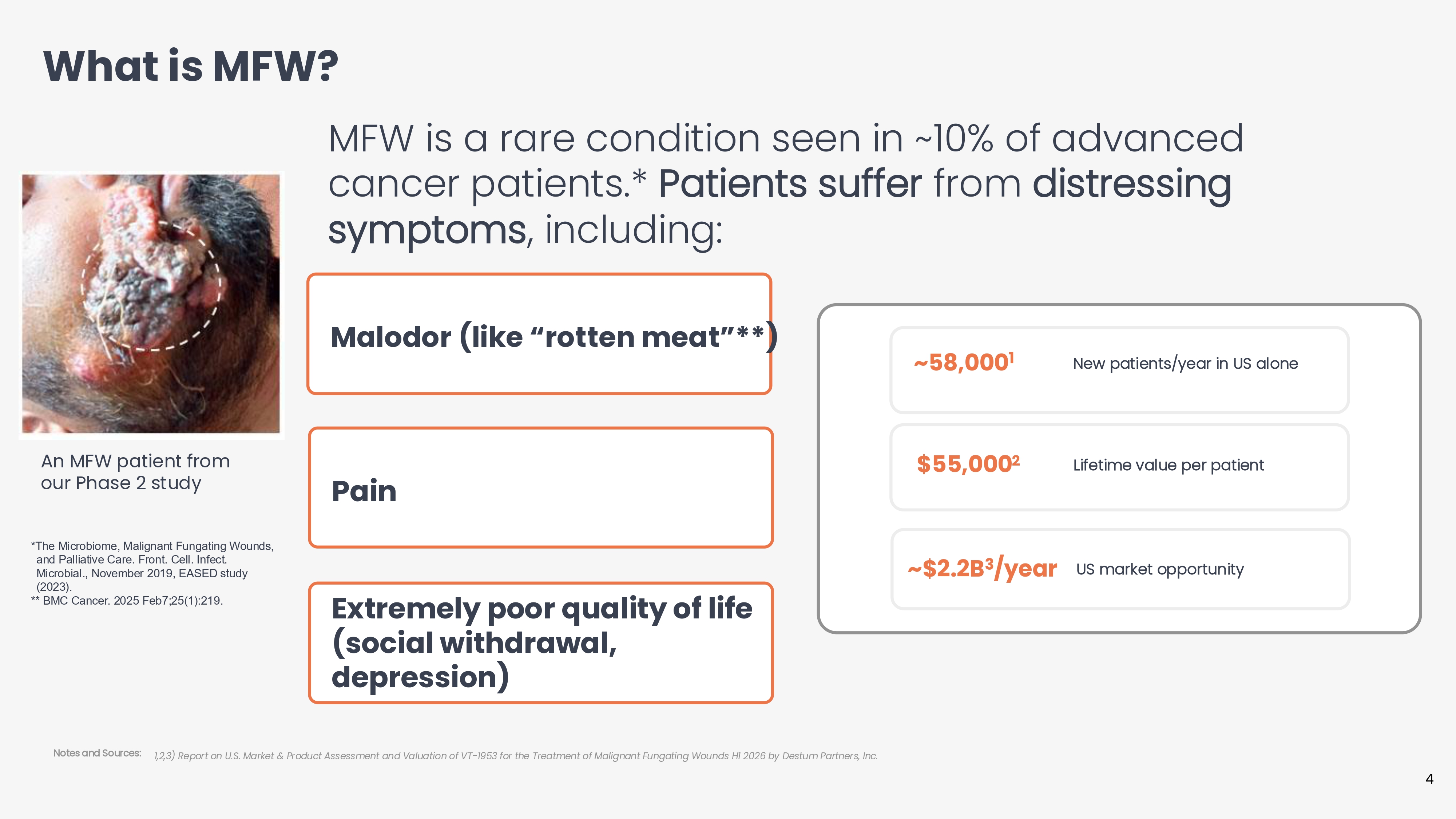
MFW is a rare condition seen in ~10% of advanced cancer patients.* Patients suffer from distressing symptoms, including: Malodor (like “rotten meat”**) What is MFW? *The Microbiome, Malignant Fungating Wounds, and Palliative Care. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbial., November 2019, EASED study (2023). ** BMC Cancer. 2025 Feb7;25(1):219. 1,2,3) Report on U.S. Market & Product Assessment and Valuation of VT - 1953 for the Treatment of Malignant Fungating Wounds H1 2026 by Destum Partners, Inc. Notes and Sources: An MFW patient from our Phase 2 study Pain Extremely poor quality of life (social withdrawal, depression) New patients/year in US alone ~58,000 1 Lifetime value per patient $55,000 2 ~$2.2B 3 /year 4 US market opportunity
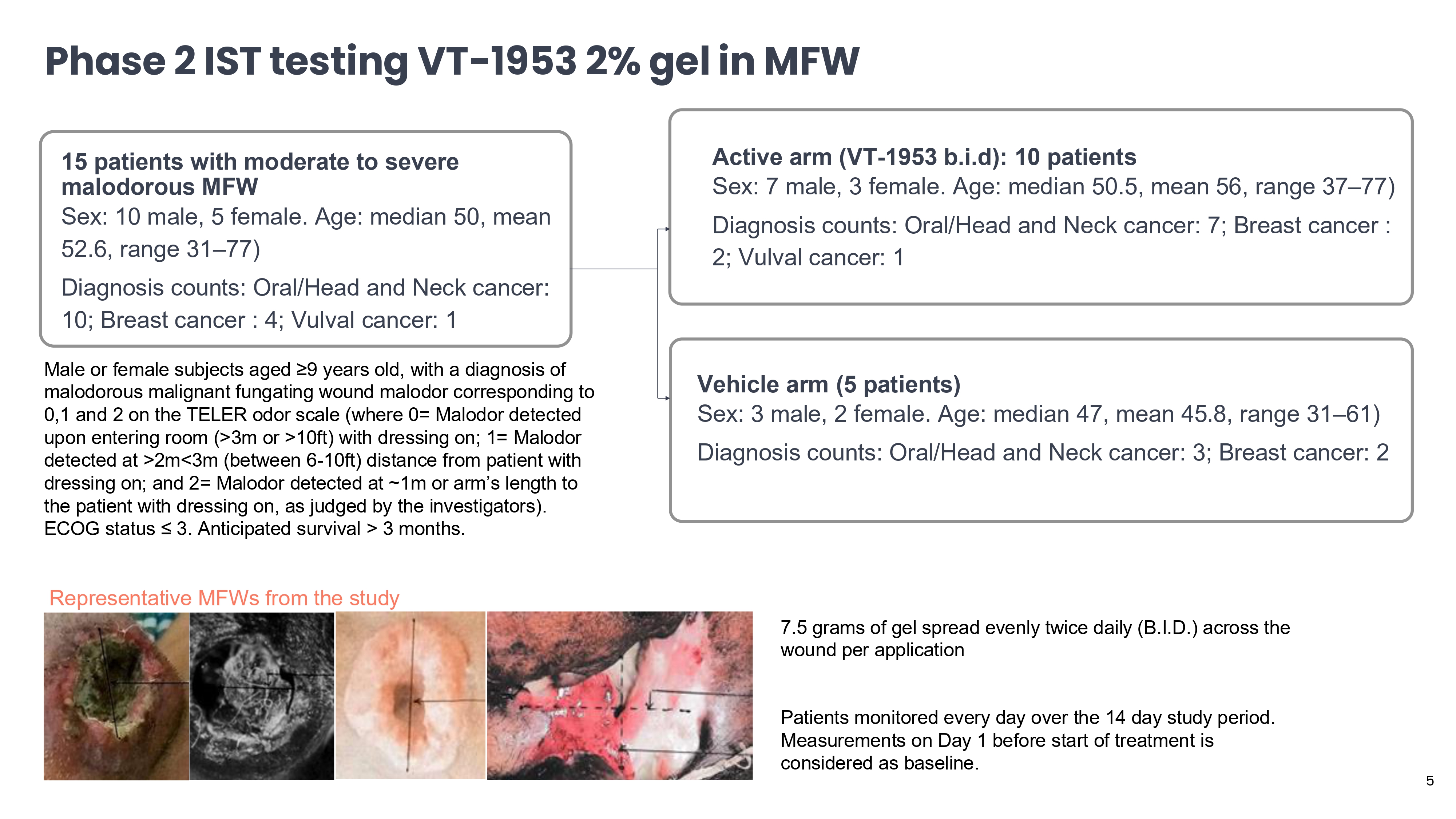
Active arm (VT - 1953 b.i.d): 10 patients Sex: 7 male, 3 female. Age: median 50.5, mean 56, range 37 – 77) Diagnosis counts: Oral/Head and Neck cancer: 7; Breast cancer : 2; Vulval cancer: 1 Vehicle arm (5 patients) Sex: 3 male, 2 female. Age: median 47, mean 45.8, range 31 – 61) Diagnosis counts: Oral/Head and Neck cancer: 3; Breast cancer: 2 15 patients with moderate to severe malodorous MFW Sex: 10 male, 5 female. Age: median 50, mean 52.6, range 31 – 77) Diagnosis counts: Oral/Head and Neck cancer: 10; Breast cancer : 4; Vulval cancer: 1 Male or female subjects aged ≥9 years old, with a diagnosis of malodorous malignant fungating wound malodor corresponding to 0,1 and 2 on the TELER odor scale (where 0= Malodor detected upon entering room (>3m or >10ft) with dressing on; 1= Malodor detected at >2m<3m (between 6 - 10ft) distance from patient with dressing on; and 2= Malodor detected at ~1m or arm’s length to the patient with dressing on, as judged by the investigators). ECOG status ≤ 3. Anticipated survival > 3 months. Representative MFWs from the study 7.5 grams of gel spread evenly twice daily (B.I.D.) across the wound per application Patients monitored every day over the 14 day study period. Measurements on Day 1 before start of treatment is considered as baseline. 5 Phase 2 IST testing VT - 1953 2% gel in MFW
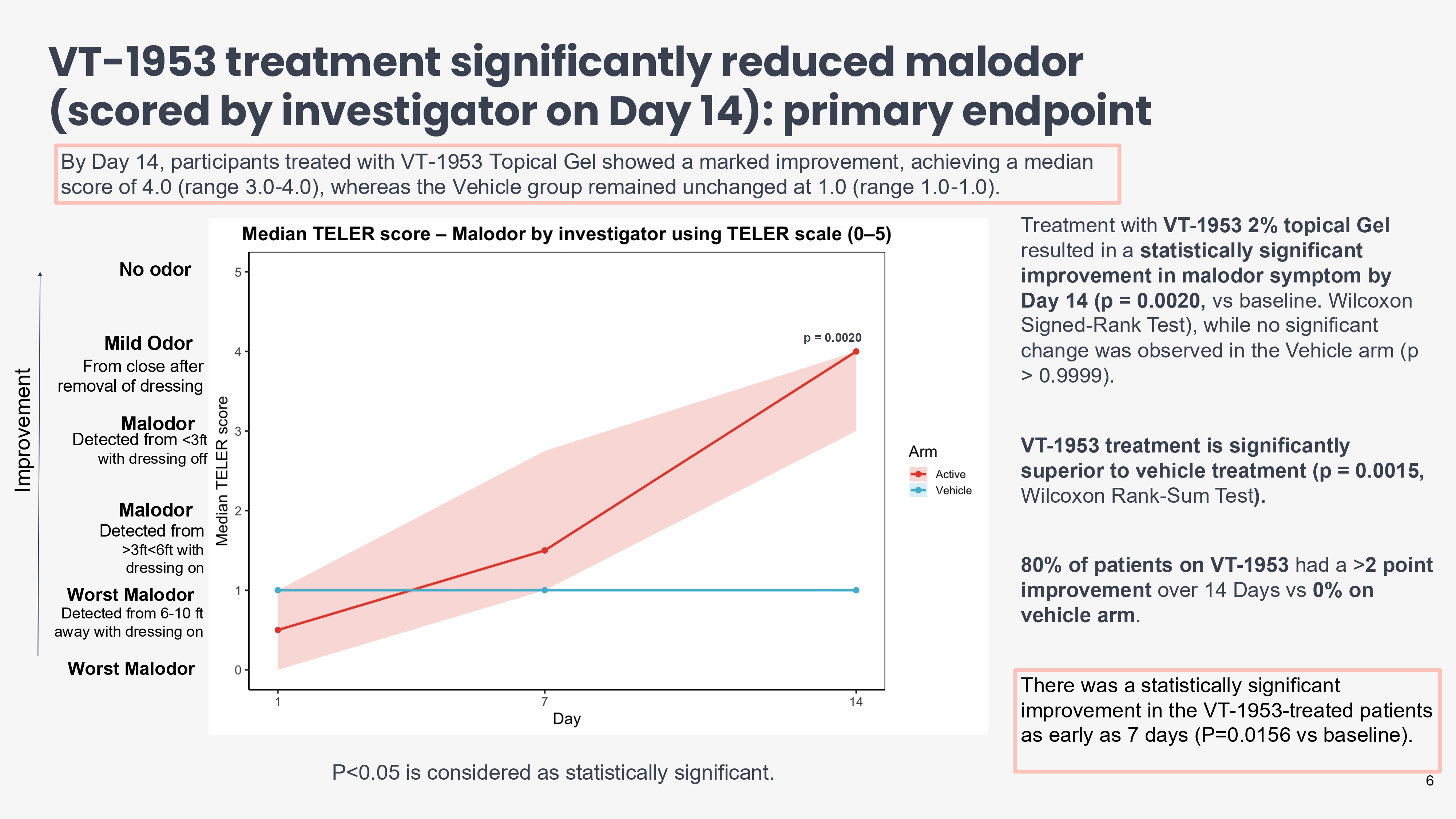
VT - 1953 treatment significantly reduced malodor (scored by investigator on Day 14): primary endpoint debt Treatment with VT - 1953 2% topical Gel resulted in a statistically significant improvement in malodor symptom by Day 14 (p = 0.0020, vs baseline. Wilcoxon Signed - Rank Test), while no significant change was observed in the Vehicle arm (p > 0.9999). VT - 1953 treatment is significantly superior to vehicle treatment (p = 0.0015, Wilcoxon Rank - Sum Test ). 80% of patients on VT - 1953 had a > 2 point improvement over 14 Days vs 0% on vehicle arm . There was a statistically significant improvement in the VT - 1953 - treated patients as early as 7 days (P=0.0156 vs baseline). By Day 14, participants treated with VT - 1953 Topical Gel showed a marked improvement, achieving a median score of 4.0 (range 3.0 - 4.0), whereas the Vehicle group remained unchanged at 1.0 (range 1.0 - 1.0). Improvement P<0.05 is considered as statistically significant. No odor Worst Malodor Mild Odor From close after removal of dressing Malodor Detected from <3ft with dressing off Malodor Detected from >3ft<6ft with dressing on Worst Malodor Detected from 6 - 10 ft away with dressing on 6 p = 0.0020
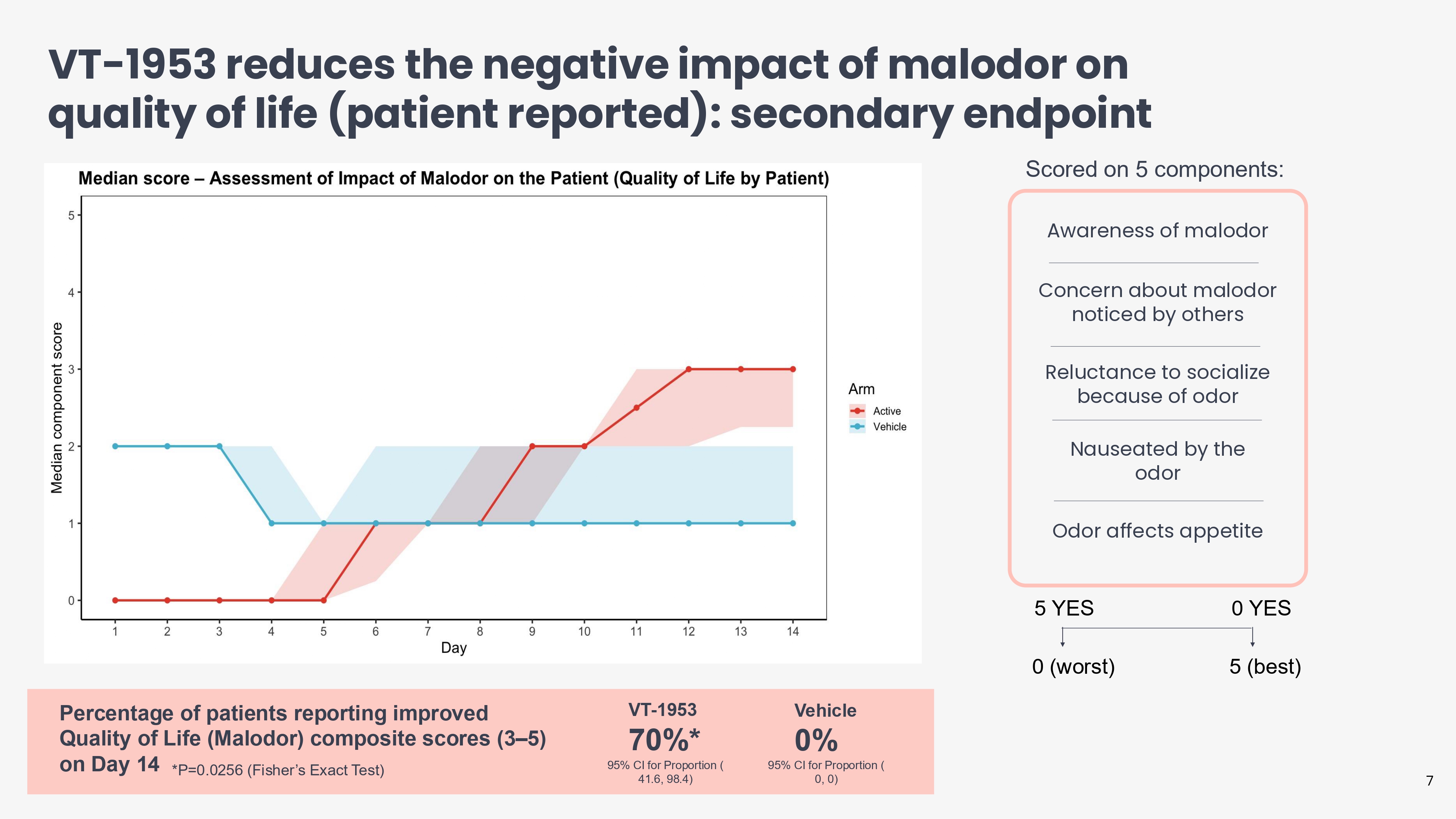
VT - 1953 reduces the negative impact of malodor on quality of life (patient reported): secondary endpoint Scored on 5 components: Awareness of malodor Concern about malodor noticed by others Reluctance to socialize because of odor Nauseated by the odor Odor affects appetite 5 YES 0 YES 0 (worst) 5 (best) VT - 1953 70%* 95% CI for Proportion ( 41.6, 98.4) *P=0.0256 (Fisher’s Exact Test) Percentage of patients reporting improved Quality of Life (Malodor) composite scores (3 – 5) on Day 14 Vehicle 0% 95% CI for Proportion ( 0, 0) 7
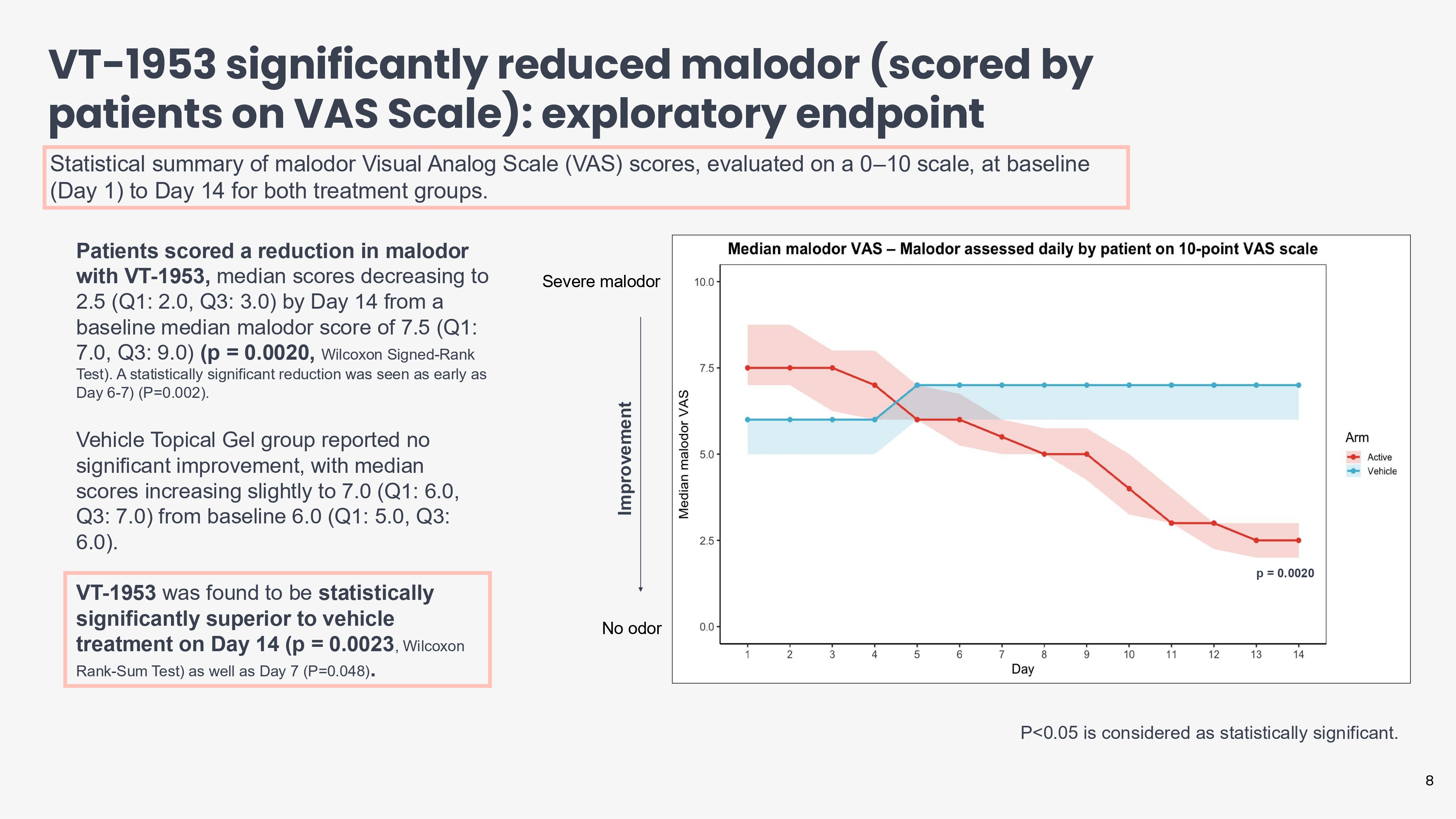
VT - 1953 significantly reduced malodor (scored by patients on VAS Scale): exploratory endpoint Patients scored a reduction in malodor with VT - 1953, median scores decreasing to 2.5 (Q1: 2.0, Q3: 3.0) by Day 14 from a baseline median malodor score of 7.5 (Q1: 7.0, Q3: 9.0) (p = 0.0020, Wilcoxon Signed - Rank Test). A statistically significant reduction was seen as early as Day 6 - 7) (P=0.002). Vehicle Topical Gel group reported no significant improvement, with median scores increasing slightly to 7.0 (Q1: 6.0, Q3: 7.0) from baseline 6.0 (Q1: 5.0, Q3: 6.0). VT - 1953 was found to be statistically significantly superior to vehicle treatment on Day 14 (p = 0.0023 , Wilcoxon Rank - Sum Test) as well as Day 7 (P=0.048) . Statistical summary of malodor Visual Analog Scale (VAS) scores, evaluated on a 0 – 10 scale, at baseline (Day 1) to Day 14 for both treatment groups. No odor Severe malodor P<0.05 is considered as statistically significant. 8 Improvement p = 0.0020
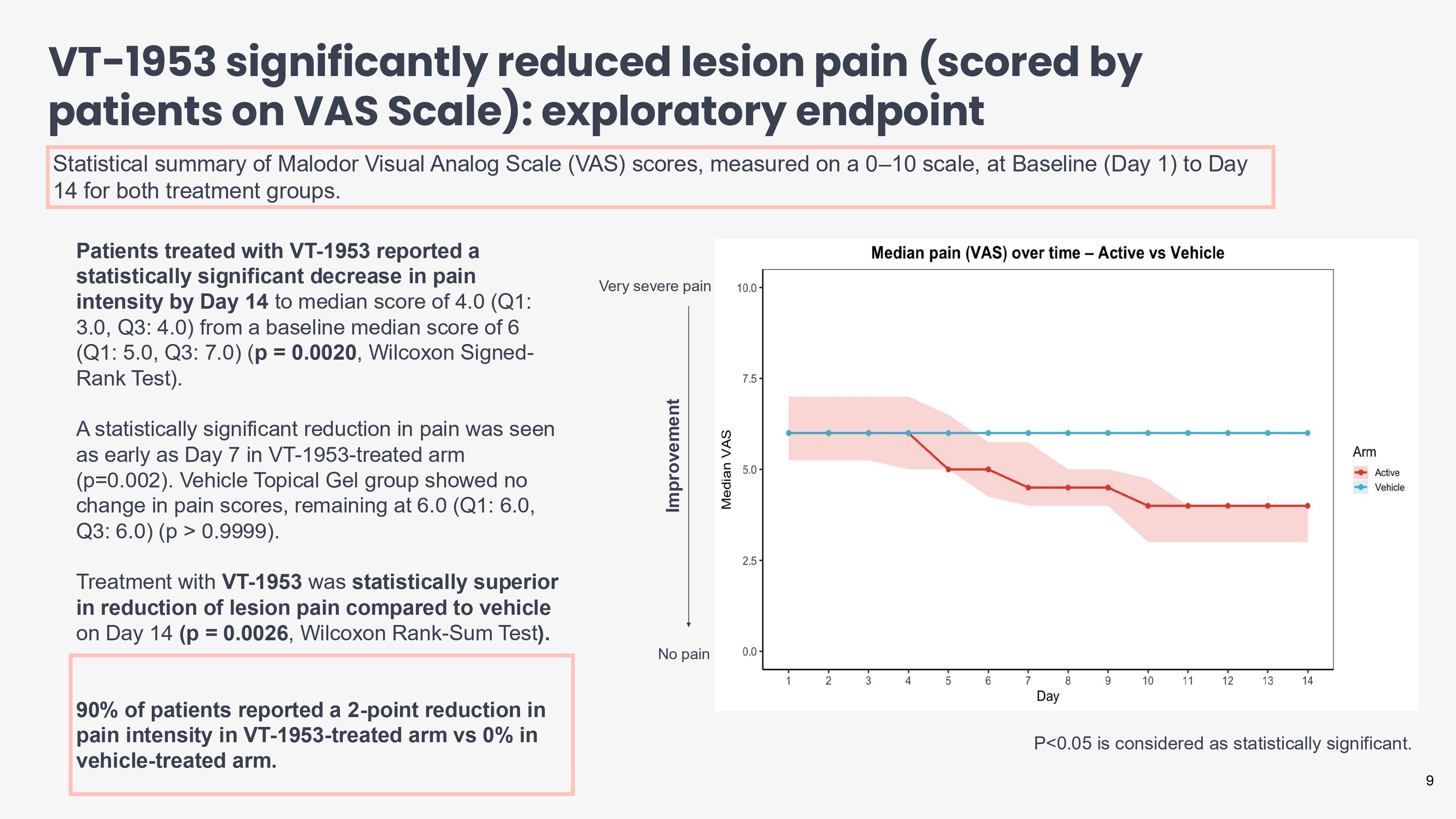
VT - 1953 significantly reduced lesion pain (scored by patients on VAS Scale): exploratory endpoint Patients treated with VT - 1953 reported a statistically significant decrease in pain intensity by Day 14 to median score of 4.0 (Q1: 3.0, Q3: 4.0) from a baseline median score of 6 (Q1: 5.0, Q3: 7.0) ( p = 0.0020 , Wilcoxon Signed - Rank Test). A statistically significant reduction in pain was seen as early as Day 7 in VT - 1953 - treated arm (p=0.002). Vehicle Topical Gel group showed no change in pain scores, remaining at 6.0 (Q1: 6.0, Q3: 6.0) (p > 0.9999). Treatment with VT - 1953 was statistically superior in reduction of lesion pain compared to vehicle on Day 14 (p = 0.0026 , Wilcoxon Rank - Sum Test ). 90% of patients reported a 2 - point reduction in pain intensity in VT - 1953 - treated arm vs 0% in vehicle - treated arm. Statistical summary of Malodor Visual Analog Scale (VAS) scores, measured on a 0 – 10 scale, at Baseline (Day 1) to Day 14 for both treatment groups. No pain Very severe pain Improvement 9 P<0.05 is considered as statistically significant.
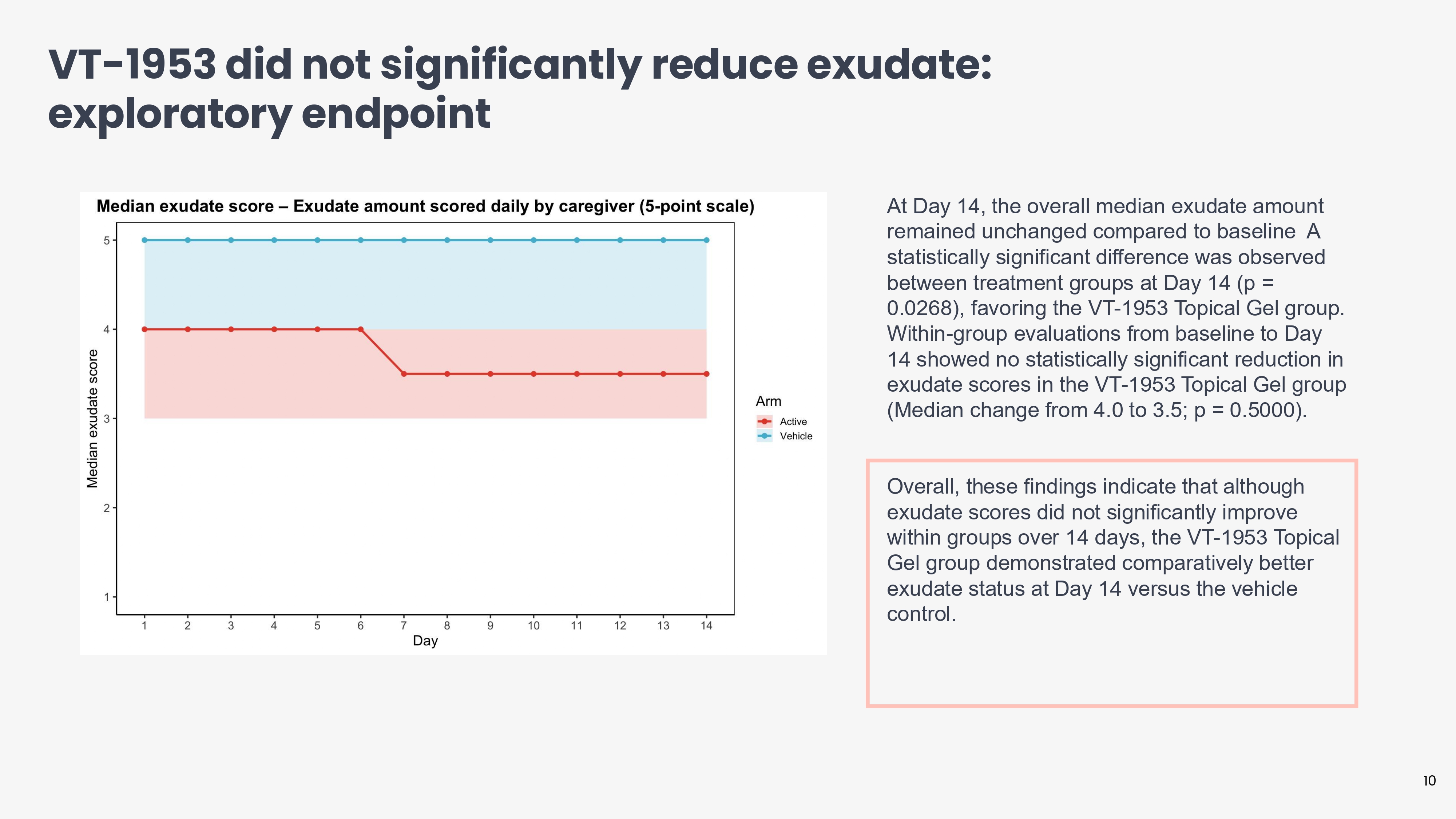
VT - 1953 did not significantly reduce exudate: exploratory endpoint At Day 14, the overall median exudate amount remained unchanged compared to baseline A statistically significant difference was observed between treatment groups at Day 14 (p = 0.0268), favoring the VT - 1953 Topical Gel group. Within - group evaluations from baseline to Day 14 showed no statistically significant reduction in exudate scores in the VT - 1953 Topical Gel group (Median change from 4.0 to 3.5; p = 0.5000). 10 Overall, these findings indicate that although exudate scores did not significantly improve within groups over 14 days, the VT - 1953 Topical Gel group demonstrated comparatively better exudate status at Day 14 versus the vehicle control.
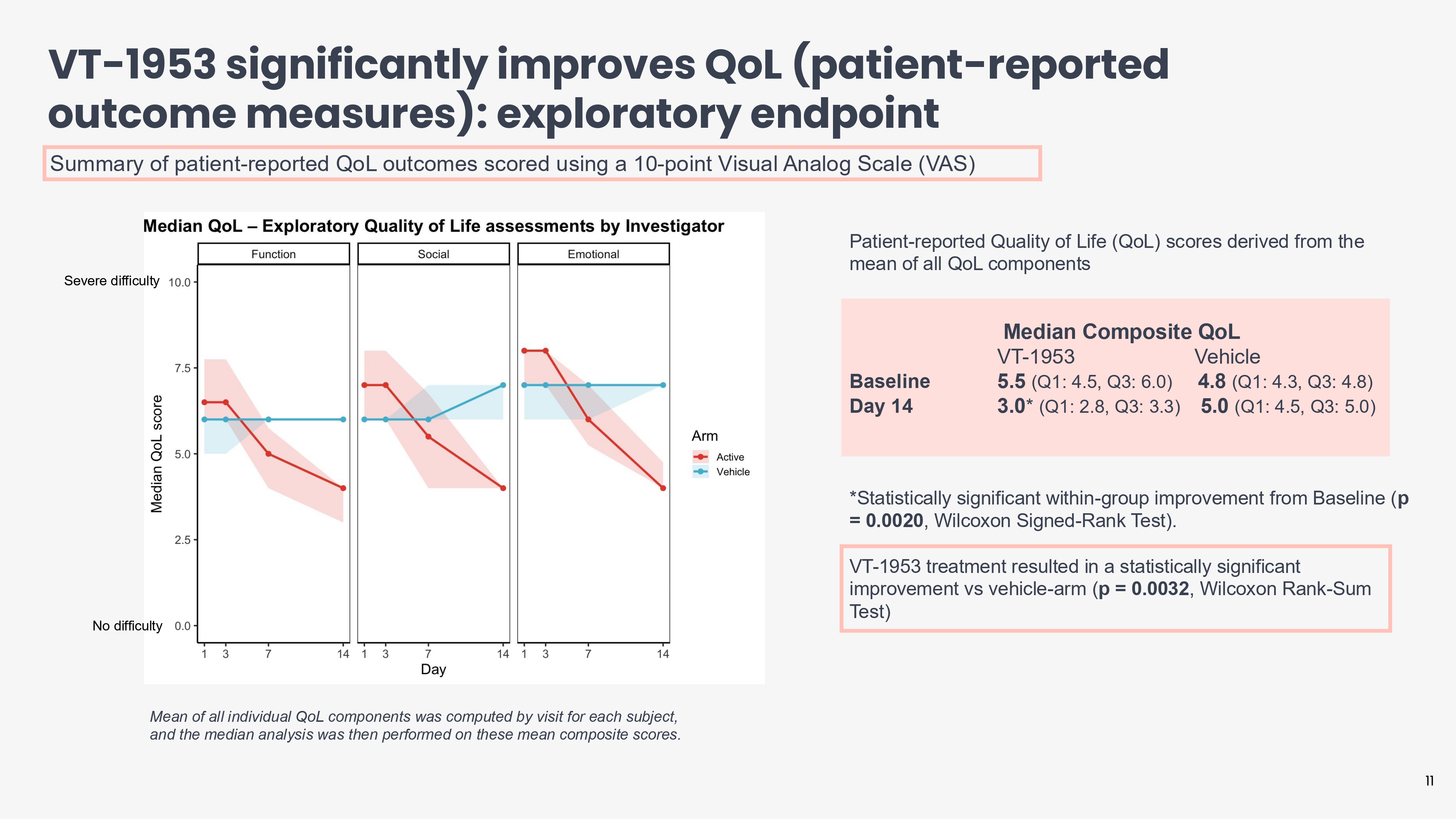
VT - 1953 significantly improves QoL (patient - reported outcome measures): exploratory endpoint Severe difficulty 11 No difficulty Mean of all individual QoL components was computed by visit for each subject, and the median analysis was then performed on these mean composite scores. Patient - reported Quality of Life (QoL) scores derived from the mean of all QoL components Median Composite QoL Vehicle VT - 1953 4.8 (Q1: 4.3, Q3: 4.8) 5.5 (Q1: 4.5, Q3: 6.0) Baseline 5.0 (Q1: 4.5, Q3: 5.0) 3.0 * (Q1: 2.8, Q3: 3.3) Day 14 *Statistically significant within - group improvement from Baseline ( p = 0.0020 , Wilcoxon Signed - Rank Test). VT - 1953 treatment resulted in a statistically significant improvement vs vehicle - arm ( p = 0.0032 , Wilcoxon Rank - Sum Test) Summary of patient - reported QoL outcomes scored using a 10 - point Visual Analog Scale (VAS)

VT - 1953 did not exhibit any safety signals during the study period at doses used • No TEAEs reported • No changes in vital signs • No reports of local skin reactions • *Consistent with observations from prior clinical trials with VT - 1953 12 * VT - 1953 (2% topical gel) has been studied for safety and efficacy in 5 clinical studies, including chronic use for 90 days
Treatment with VT - 1953 for 14 days successfully met its primary endpoint of significantly reducing malodor associated with MFW as scored by investigators. There is consistency between investigator scores (on TELER score) and malodor scored by patients using VAS (exploratory endpoint) Summary Patients treated with VT - 1953 for 14 days did not report any adverse effects or safety signals Treatment with VT - 1953 for 14 days achieved its secondary endpoint of significantly reducing impact of malodor associated with MFW as scored by patients, and exploratory endpoints of reducing lesion pain (scored by patients), and improved QoL (patient reported outcome measure). There was no significant change in exudates. These results provide a clear clinical rationale to advance VT - 1953 to pivotal studies for the treatment of symptoms associated with MFW. Clear statistical significance in Ph2 and low variance suggests the need for fewer patients in a pivotal study. 13
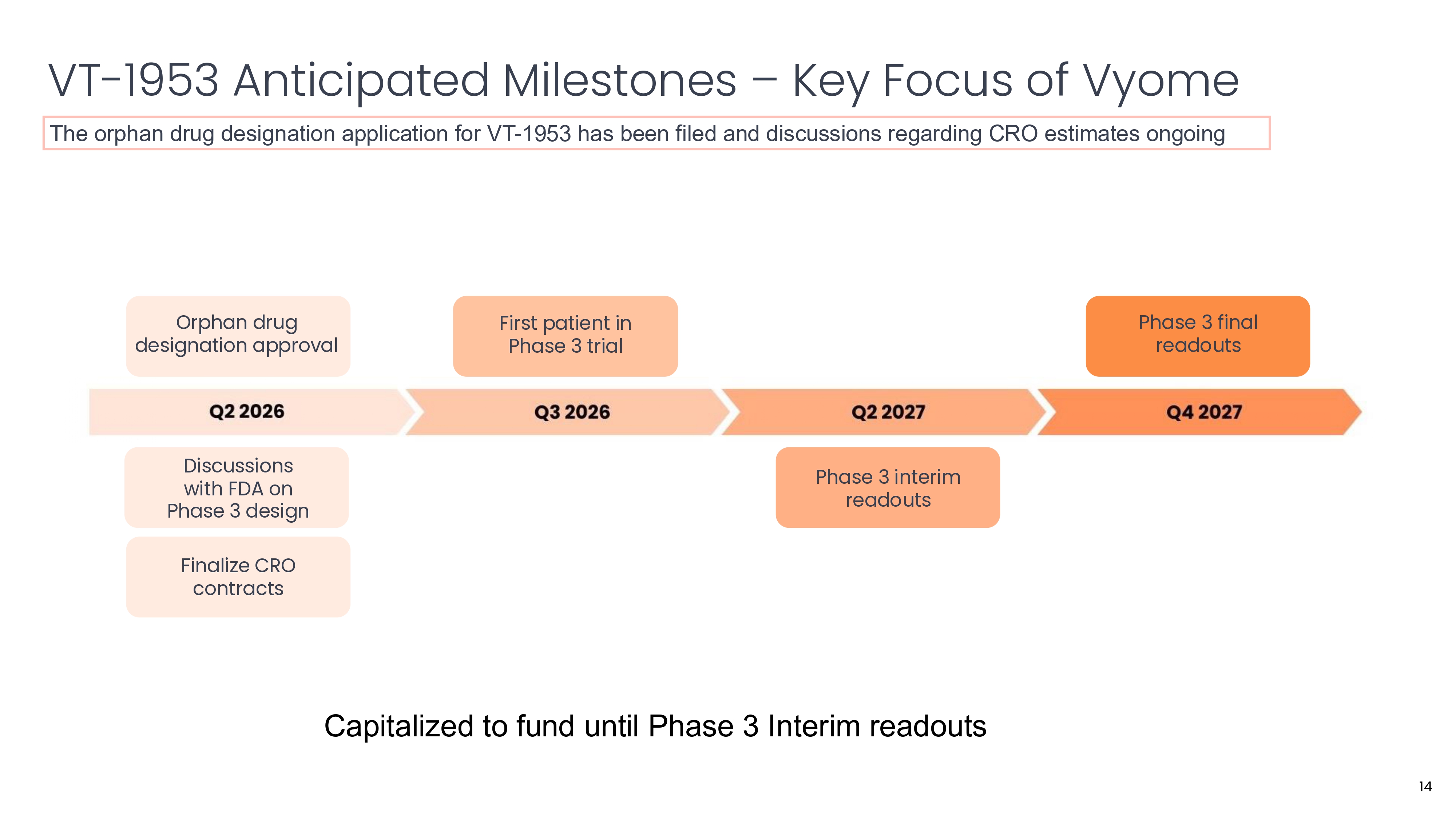
VT - 1953 Anticipated Milestones – Key Focus of Vyome The orphan drug designation application for VT - 1953 has been filed and discussions regarding CRO estimates ongoing Orphan drug designation approval Discussions with FDA on Phase 3 design Finalize CRO contracts First patient in Phase 3 trial Phase 3 interim readouts Phase 3 final readouts 14 Capitalized to fund until Phase 3 Interim readouts

Vyome Holdings, Inc. (“Vyome”) Venkat Nelabhotla, CEO & Co - Founder nvenkat@vyometx.com +1 (973) 832 - 8147 Suite 400, One Mifflin Place, Harvard Square Cambridge, MA 02138