
J.P. Morgan Healthcare Conference 2026 Agios Pharmaceuticals Brian Goff, Chief Executive Officer 14 January 2026 .2
Forward-Looking Statements 2 This presentation and various remarks we make during this presentation contain forward-looking statements within the meaning of The Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Such forward-looking statements include those regarding the potential benefits of AQVESMETM (mitapivat) and PYRUKYND® (mitapivat); Agios’ plans for future meetings with, or submissions to, regulators, including the FDA; Agios’ plans for the development of mitapivat, tebapivat, AG-236 and AG-181; Agios' estimates regarding market sizes for various indications; and the potential benefits of Agios’ strategic plans and focus. The words “anticipate”, "estimate", “expect”, “goal”, “hope”, “milestone”, “opportunity”, “plan”, “potential”, “possible”, “strategy”, “will”, “vision”, and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements, although not all forward-looking statements contain these identifying words. Such statements are subject to numerous important factors, risks and uncertainties that may cause actual events or results to differ materially from Agios’ current expectations and beliefs. For example, there can be no guarantee that any product candidate Agios is developing will successfully commence or complete necessary preclinical and clinical development phases, or that development of any of Agios’ product candidates will successfully continue. There can be no guarantee that any positive developments in Agios’ business will result in stock price appreciation. Management's expectations and, therefore, any forward-looking statements in this presentation and various remarks we make during this presentation could also be affected by risks and uncertainties relating to a number of other important factors, including, without limitation: risks and uncertainties related to the impact of pandemics or other public health emergencies to Agios’ business, operations, strategy, goals and anticipated milestones, including its ongoing and planned research activities, ability to conduct ongoing and planned clinical trials, clinical supply of current or future drug candidates, commercial supply of current or future approved products, and launching, marketing and selling current or future approved products; Agios’ results of clinical trials and preclinical studies, including subsequent analysis of existing data and new data received from ongoing and future studies; the content and timing of decisions made by the U.S. FDA, the EMA or other regulatory authorities, investigational review boards at clinical trial sites and publication review bodies; Agios’ ability to obtain and maintain requisite regulatory approvals and to enroll patients in its planned clinical trials; unplanned cash requirements and expenditures; competitive factors; Agios' ability to obtain, maintain and enforce patent and other intellectual property protection for any product candidates it is developing; Agios’ ability to establish and maintain key collaborations; uncertainty regarding any royalty payments related to the sale of its oncology business or any milestone or royalty payments related to its in-licensing of AG-236, and the uncertainty of the timing of any such payments; uncertainty of the results and effectiveness of the use of Agios’ cash and cash equivalents; and general economic and market conditions. These and other risks are described in greater detail under the caption "Risk Factors" included in Agios’ public filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission. Any forward-looking statements contained in this presentation and various remarks we make during this presentation speak only as of the date hereof, and Agios expressly disclaims any obligation to update any forward- looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required by law.
3 Agios – positioned for a growth inflection, advancing pipeline with path to profitability PK activator franchise as standard of care in multiple hemolytic anemias Potential to unlock additional value with robust early and mid-stage pipeline Clear path to profitability with existing commercial portfolio Strong foundation in hematology with ambition to become sustainable rare disease company
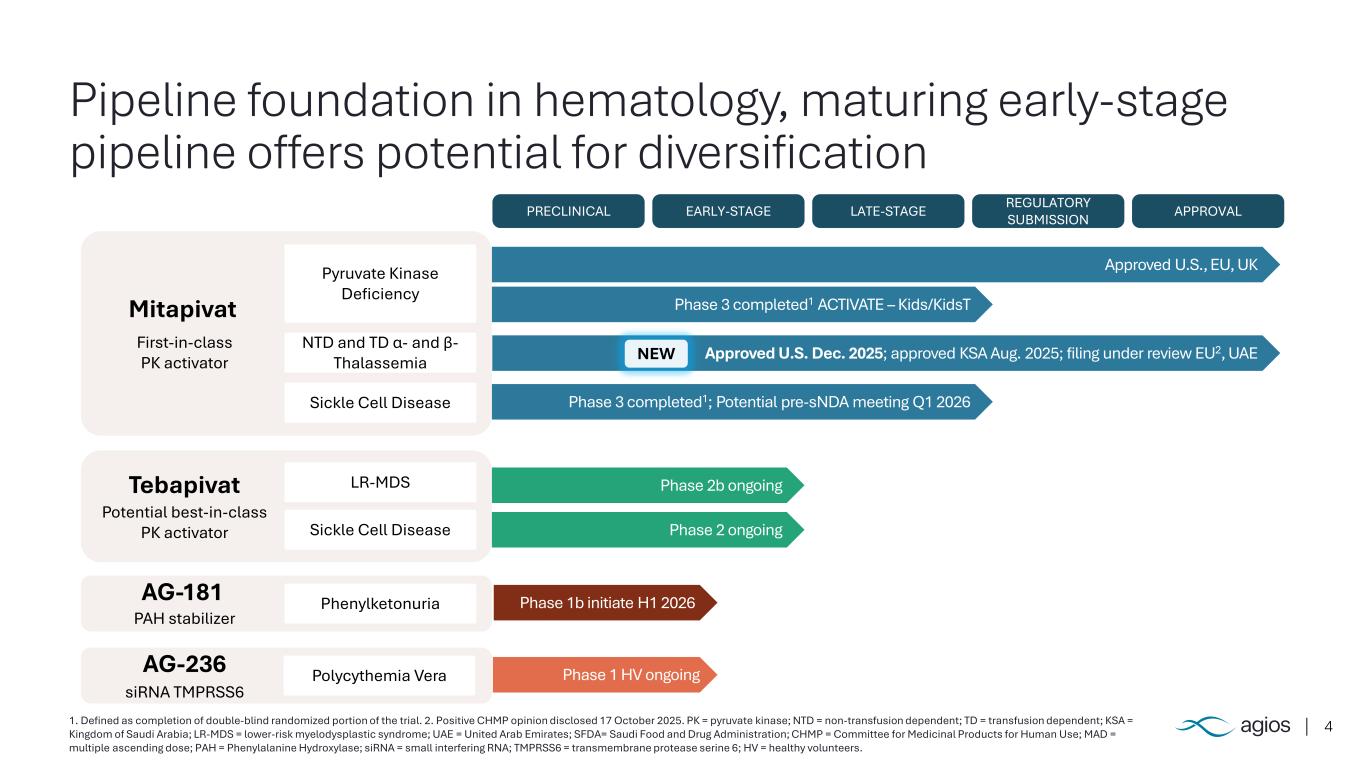
4 Pipeline foundation in hematology, maturing early-stage pipeline offers potential for diversification 1. Defined as completion of double-blind randomized portion of the trial. 2. Positive CHMP opinion disclosed 17 October 2025. PK = pyruvate kinase; NTD = non-transfusion dependent; TD = transfusion dependent; KSA = Kingdom of Saudi Arabia; LR-MDS = lower-risk myelodysplastic syndrome; UAE = United Arab Emirates; SFDA= Saudi Food and Drug Administration; CHMP = Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use; MAD = multiple ascending dose; PAH = Phenylalanine Hydroxylase; siRNA = small interfering RNA; TMPRSS6 = transmembrane protease serine 6; HV = healthy volunteers. PRECLINICAL EARLY-STAGE LATE-STAGE REGULATORY SUBMISSION APPROVAL Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency NTD and TD α- and β- Thalassemia Sickle Cell Disease Mitapivat First-in-class PK activator LR-MDS Sickle Cell Disease Tebapivat Potential best-in-class PK activator PhenylketonuriaAG-181 PAH stabilizer Polycythemia VeraAG-236 siRNA TMPRSS6 Approved U.S., EU, UK Phase 3 completed1 ACTIVATE – Kids/KidsT Approved U.S. Dec. 2025; approved KSA Aug. 2025; filing under review EU2, UAE Phase 3 completed1; Potential pre-sNDA meeting Q1 2026 Phase 2b ongoing Phase 2 ongoing Phase 1b initiate H1 2026 Phase 1 HV ongoing NEW
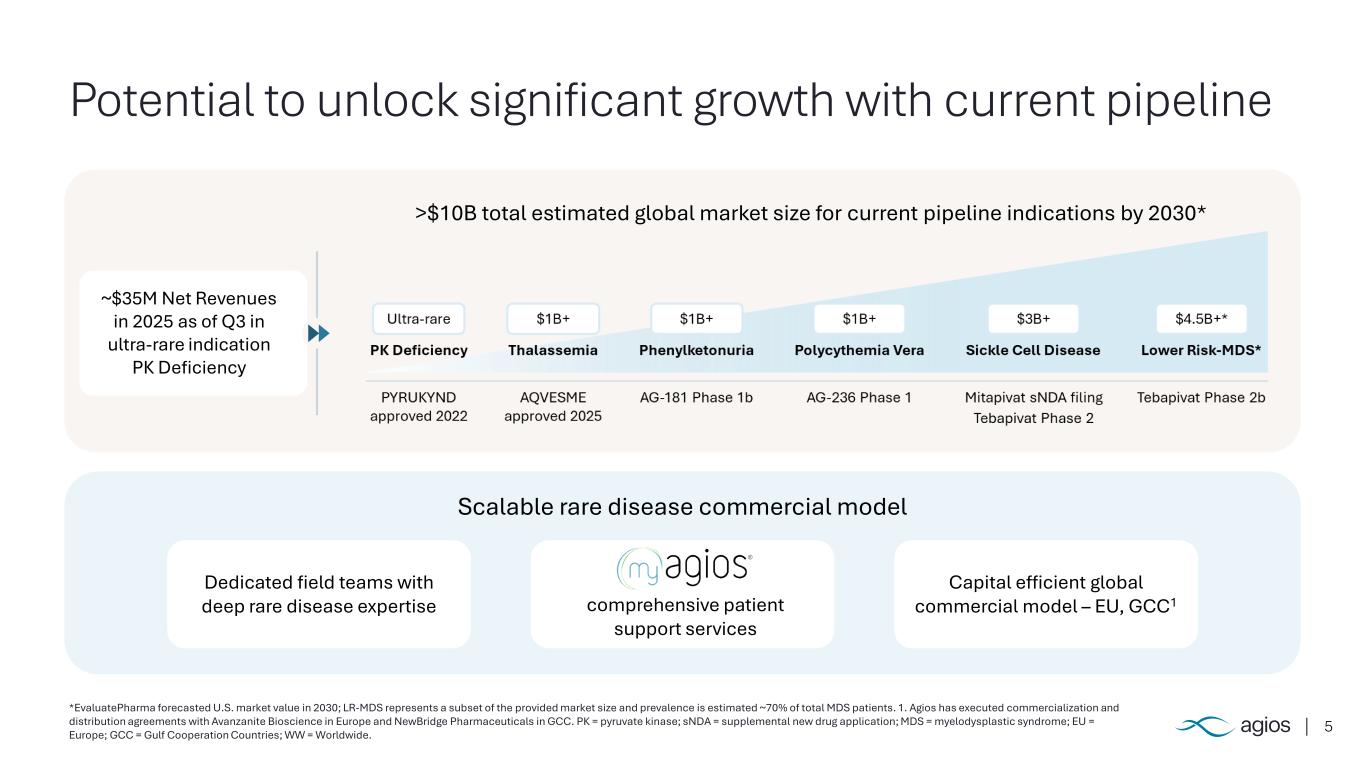
5 Potential to unlock significant growth with current pipeline *EvaluatePharma forecasted U.S. market value in 2030; LR-MDS represents a subset of the provided market size and prevalence is estimated ~70% of total MDS patients. 1. Agios has executed commercialization and distribution agreements with Avanzanite Bioscience in Europe and NewBridge Pharmaceuticals in GCC. PK = pyruvate kinase; sNDA = supplemental new drug application; MDS = myelodysplastic syndrome; EU = Europe; GCC = Gulf Cooperation Countries; WW = Worldwide. Scalable rare disease commercial model comprehensive patient support services Dedicated field teams with deep rare disease expertise Capital efficient global commercial model – EU, GCC1 >$10B total estimated global market size for current pipeline indications by 2030* ~$35M Net Revenues in 2025 as of Q3 in ultra-rare indication PK Deficiency
6 2026 strategic priorities – driving long-term value creation Execute high-impact launch for AQVESME (mitapivat) in thalassemia Potential to expand PK activation franchise into sickle cell disease and LR-MDS Unlock future value in hematology and other rare disease by advancing early-stage pipeline Ensure long-term sustainability through disciplined capital allocation and operational efficiency PK = pyruvate kinase; LR-MDS = lower risk myelodysplastic syndrome.

7 Execute high impact launch for AQVESME in thalassemia

8 AQVESME (mitapivat) – now approved in U.S. with broad thalassemia label A pyruvate kinase activator indicated for the treatment of anemia in adults with alpha- or beta-thalassemia Only FDA approved medicine for anemia in both non-transfusion dependent and transfusion-dependent alpha- or beta-thalassemia
91. Phase 3 ENERGIZE clinical trial achieved significance on primary and key secondary endpoints; 2. Phase 3 ENERGIZE-T clinical trial achieved significance on primary and key secondary endpoints ; durable reduction in transfusion burden observed up to 36 weeks in ENERGIZE-T. – delivering a series of “firsts” in thalassemia First medicine to address α- or β-thalassemia, regardless of transfusion burden First medicine to show quality of life improvements in NTDT patients1 First medicine to show durable reduction in transfusion burden in TDT patients2 First oral medicine

101. Phase 3 ENERGIZE clinical trial achieved significance on primary and key secondary endpoints. 2. Phase 3 ENERGIZE-T clinical trial achieved significance on primary and key secondary endpoints. QoL = quality of life; PKD = pyruvate kinase deficiency. – ready to execute a high-impact commercial launch in the U.S. Potential to deliver $1B global peak-year-sales across PKD and thalassemia indications 4,000 addressable patients at launch $425k annual U.S. WAC for thalassemia leading patient support services

11 Potential to expand PK activation franchise into Sickle Cell Disease and LR-MDS
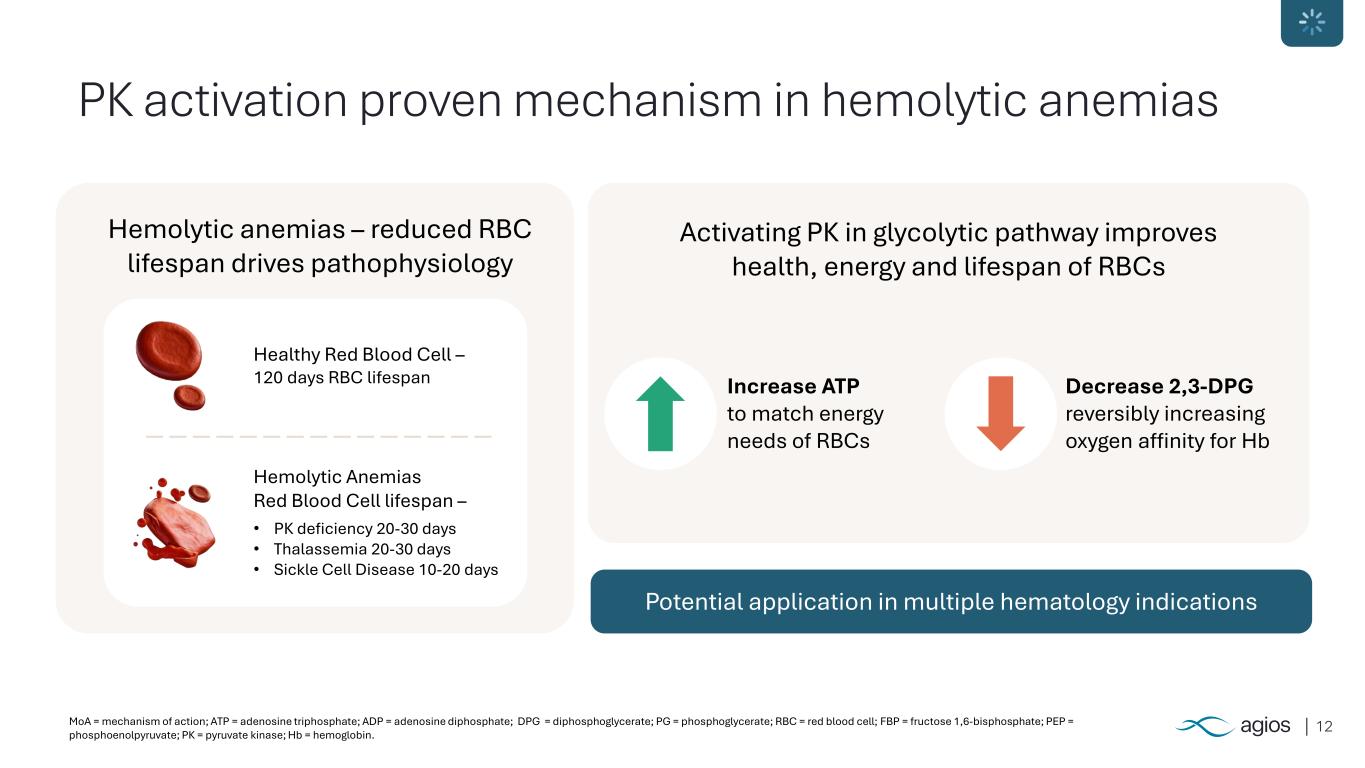
12MoA = mechanism of action; ATP = adenosine triphosphate; ADP = adenosine diphosphate; DPG = diphosphoglycerate; PG = phosphoglycerate; RBC = red blood cell; FBP = fructose 1,6-bisphosphate; PEP = phosphoenolpyruvate; PK = pyruvate kinase; Hb = hemoglobin. PK activation proven mechanism in hemolytic anemias Hemolytic anemias – reduced RBC lifespan drives pathophysiology Activating PK in glycolytic pathway improves health, energy and lifespan of RBCs Potential application in multiple hematology indications Increase ATP to match energy needs of RBCs Decrease 2,3-DPG reversibly increasing oxygen affinity for Hb Healthy Red Blood Cell – 120 days RBC lifespan • PK deficiency 20-30 days • Thalassemia 20-30 days • Sickle Cell Disease 10-20 days Hemolytic Anemias Red Blood Cell lifespan –
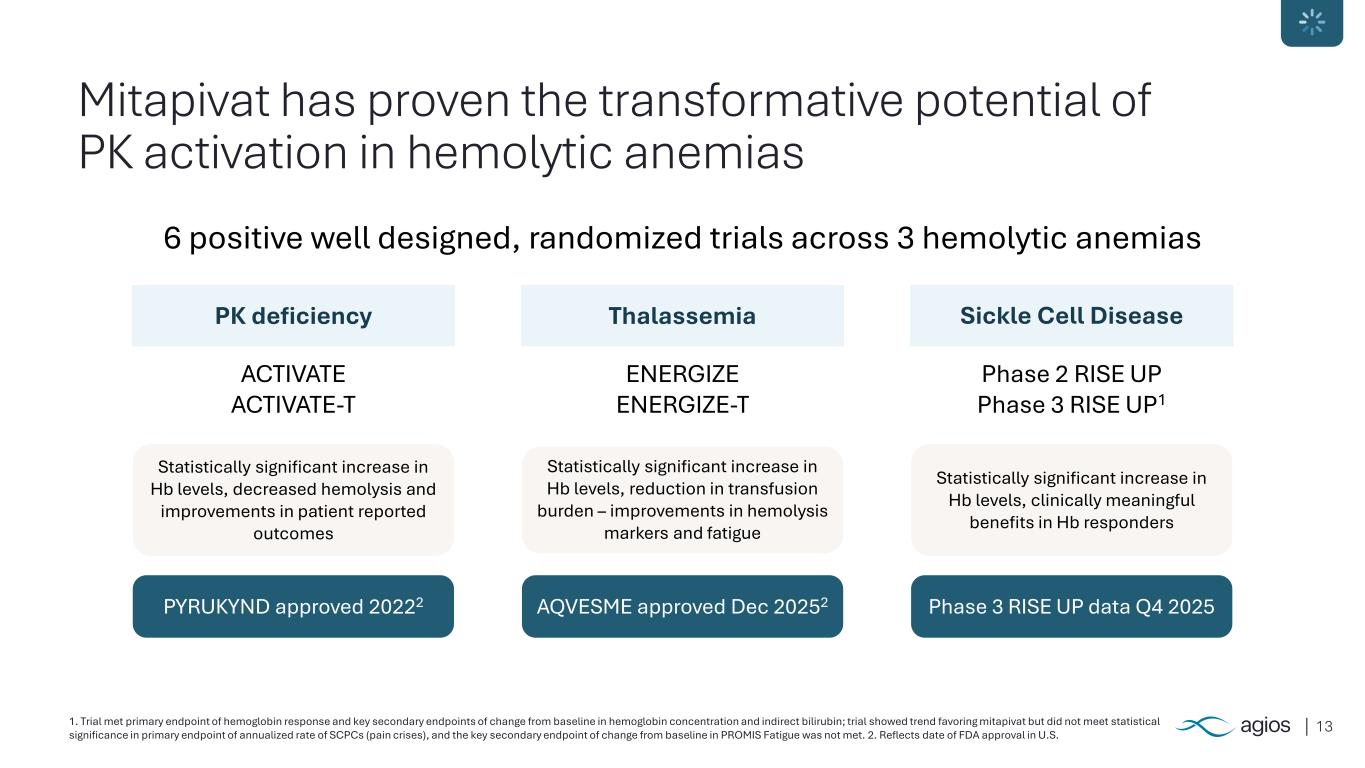
131. Trial met primary endpoint of hemoglobin response and key secondary endpoints of change from baseline in hemoglobin concentration and indirect bilirubin; trial showed trend favoring mitapivat but did not meet statistical significance in primary endpoint of annualized rate of SCPCs (pain crises), and the key secondary endpoint of change from baseline in PROMIS Fatigue was not met. 2. Reflects date of FDA approval in U.S. Mitapivat has proven the transformative potential of PK activation in hemolytic anemias 6 positive well designed, randomized trials across 3 hemolytic anemias ACTIVATE ACTIVATE-T PK deficiency Statistically significant increase in Hb levels, decreased hemolysis and improvements in patient reported outcomes PYRUKYND approved 20222 ENERGIZE ENERGIZE-T Thalassemia Statistically significant increase in Hb levels, reduction in transfusion burden – improvements in hemolysis markers and fatigue AQVESME approved Dec 20252 Phase 2 RISE UP Phase 3 RISE UP1 Sickle Cell Disease Statistically significant increase in Hb levels, clinically meaningful benefits in Hb responders Phase 3 RISE UP data Q4 2025
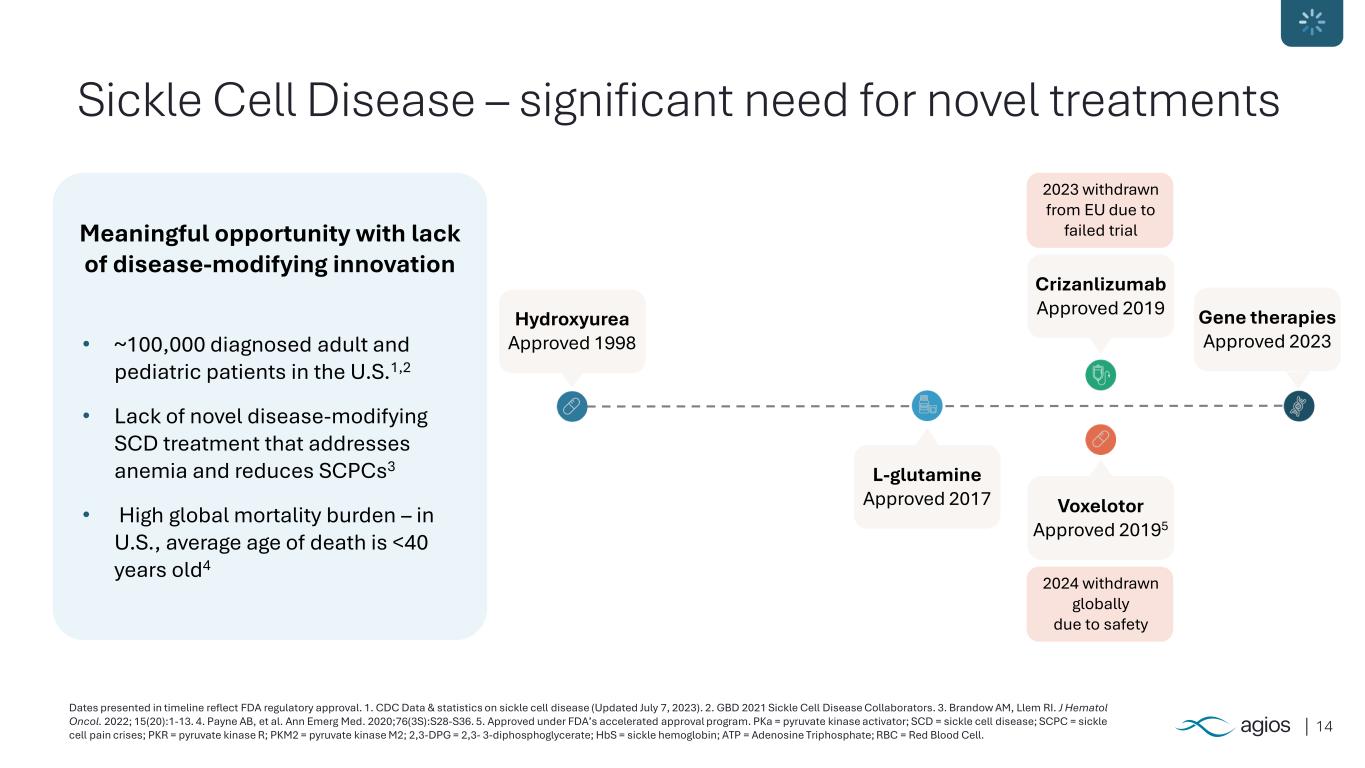
14 Sickle Cell Disease – significant need for novel treatments Dates presented in timeline reflect FDA regulatory approval. 1. CDC Data & statistics on sickle cell disease (Updated July 7, 2023). 2. GBD 2021 Sickle Cell Disease Collaborators. 3. Brandow AM, Llem RI. J Hematol Oncol. 2022; 15(20):1-13. 4. Payne AB, et al. Ann Emerg Med. 2020;76(3S):S28-S36. 5. Approved under FDA’s accelerated approval program. PKa = pyruvate kinase activator; SCD = sickle cell disease; SCPC = sickle cell pain crises; PKR = pyruvate kinase R; PKM2 = pyruvate kinase M2; 2,3-DPG = 2,3- 3-diphosphoglycerate; HbS = sickle hemoglobin; ATP = Adenosine Triphosphate; RBC = Red Blood Cell. Meaningful opportunity with lack of disease-modifying innovation • ~100,000 diagnosed adult and pediatric patients in the U.S.1,2 • Lack of novel disease-modifying SCD treatment that addresses anemia and reduces SCPCs3 • High global mortality burden – in U.S., average age of death is <40 years old4 Hydroxyurea Approved 1998 L-glutamine Approved 2017 Voxelotor Approved 20195 Crizanlizumab Approved 2019 Gene therapies Approved 2023 2024 withdrawn globally due to safety 2023 withdrawn from EU due to failed trial
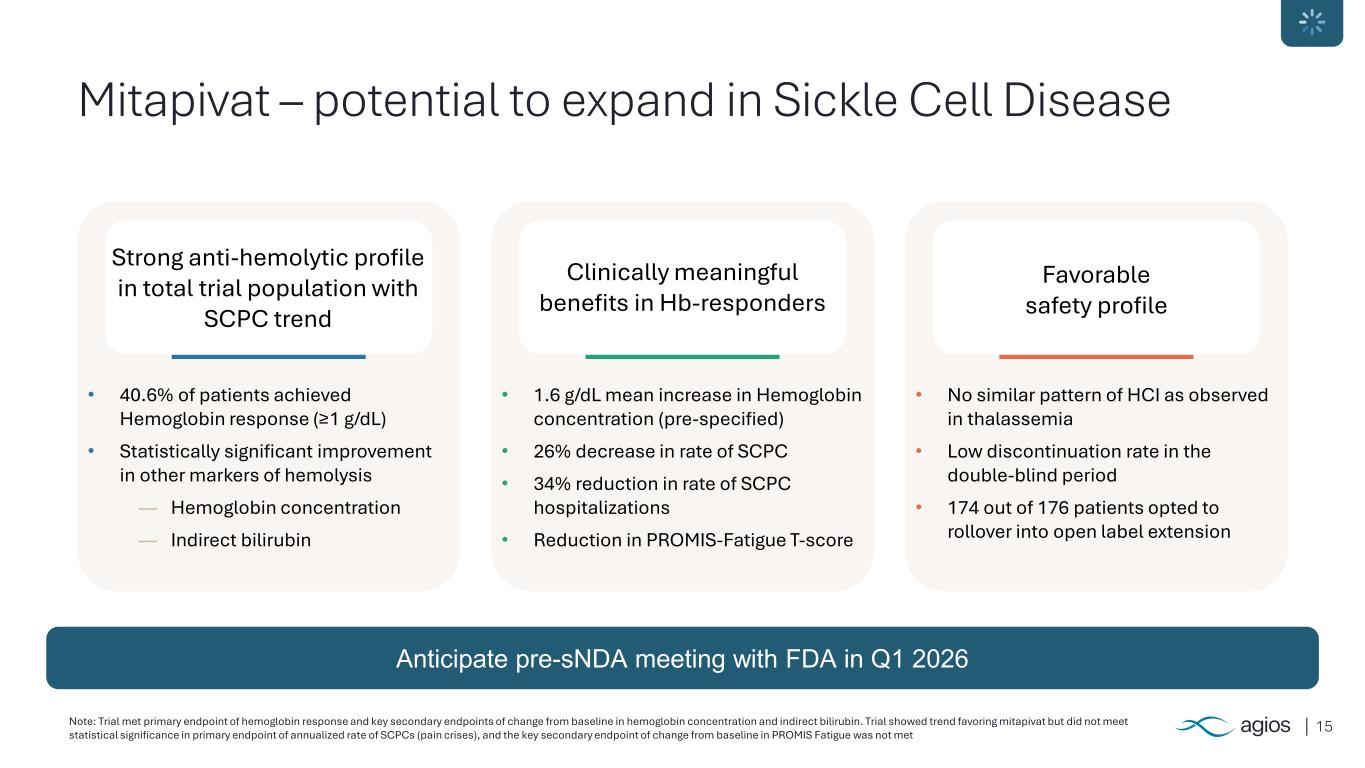
15 Mitapivat – potential to expand in Sickle Cell Disease Strong anti-hemolytic profile in total trial population with SCPC trend Clinically meaningful benefits in Hb-responders Favorable safety profile • 40.6% of patients achieved Hemoglobin response (≥1 g/dL) • Statistically significant improvement in other markers of hemolysis ― Hemoglobin concentration ― Indirect bilirubin • 1.6 g/dL mean increase in Hemoglobin concentration (pre-specified) • 26% decrease in rate of SCPC • 34% reduction in rate of SCPC hospitalizations • Reduction in PROMIS-Fatigue T-score • No similar pattern of HCI as observed in thalassemia • Low discontinuation rate in the double-blind period • 174 out of 176 patients opted to rollover into open label extension Anticipate pre-sNDA meeting with FDA in Q1 2026 Note: Trial met primary endpoint of hemoglobin response and key secondary endpoints of change from baseline in hemoglobin concentration and indirect bilirubin. Trial showed trend favoring mitapivat but did not meet statistical significance in primary endpoint of annualized rate of SCPCs (pain crises), and the key secondary endpoint of change from baseline in PROMIS Fatigue was not met
16 Xu JZ, Novelli EM, Ribeil J-A, et al. Results from a Phase 1 Study to Assess the Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of Tebapivat (AG-946) in Patients with Sickle Cell Disease. Blood. 2024;144(Suppl 1):2496. doi:10.1182/blood-2024-203509. 1. Based on in vitro profiling - no CYP inhibition or PXR activation. PKR = pyruvate kinase R; PKM2 = pyruvate kinase M2; RBC = red blood cell; DDI = drug-drug interaction; PKa = pyruvate kinase activator; Hb = hemoglobin. Tebapivat – more potent PK activator Potential best-in-class PKa – opportunity to deepen Hb response and expand patient reach Binds longer and stronger to PKR and PKM2 enzymes that regulate RBC energy Reduced potential for Drug-drug interaction1 Improved metabolic stability – longer half-life and once-daily dosing
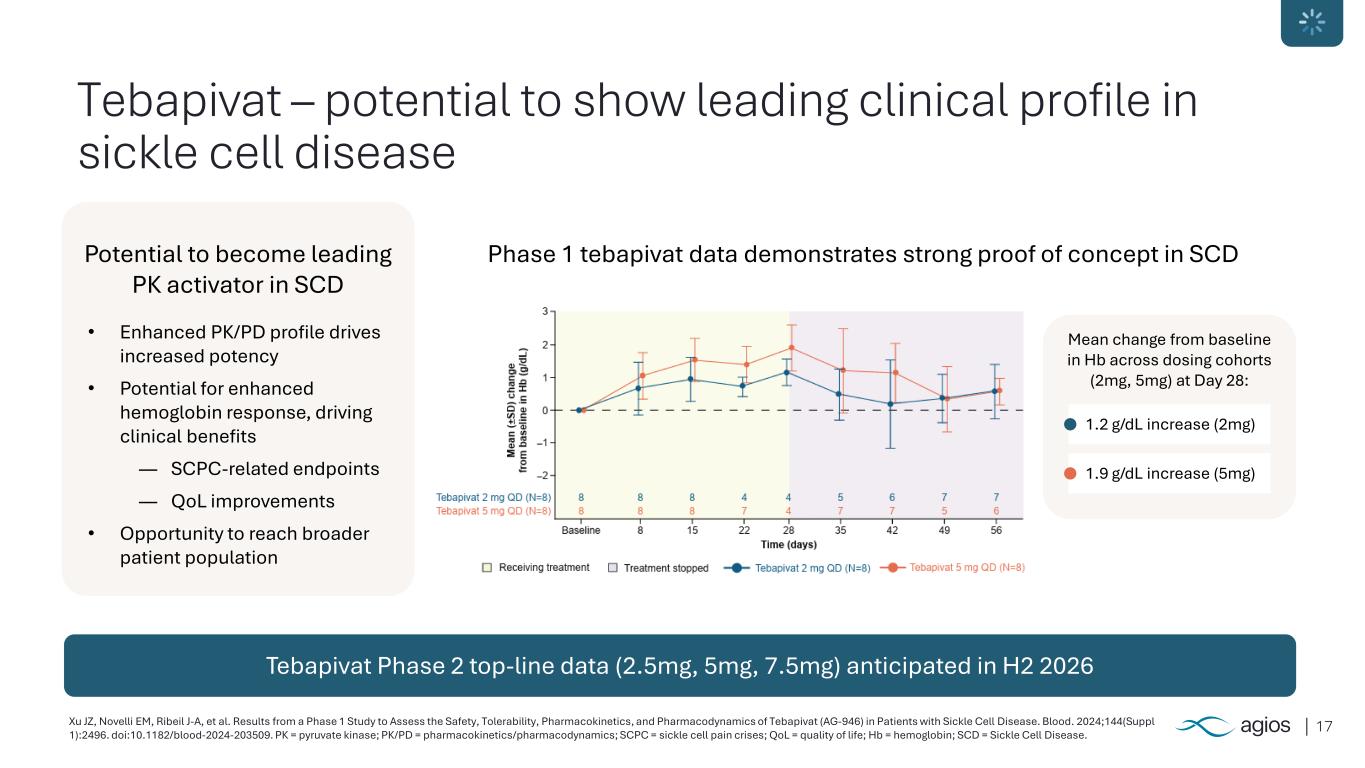
17Xu JZ, Novelli EM, Ribeil J-A, et al. Results from a Phase 1 Study to Assess the Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of Tebapivat (AG-946) in Patients with Sickle Cell Disease. Blood. 2024;144(Suppl 1):2496. doi:10.1182/blood-2024-203509. PK = pyruvate kinase; PK/PD = pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics; SCPC = sickle cell pain crises; QoL = quality of life; Hb = hemoglobin; SCD = Sickle Cell Disease. Tebapivat – potential to show leading clinical profile in sickle cell disease Tebapivat Phase 2 top-line data (2.5mg, 5mg, 7.5mg) anticipated in H2 2026 Potential to become leading PK activator in SCD • Enhanced PK/PD profile drives increased potency • Potential for enhanced hemoglobin response, driving clinical benefits ― SCPC-related endpoints ― QoL improvements • Opportunity to reach broader patient population Phase 1 tebapivat data demonstrates strong proof of concept in SCD Mean change from baseline in Hb across dosing cohorts (2mg, 5mg) at Day 28: 1.2 g/dL increase (2mg) 1.9 g/dL increase (5mg)
18LR-MDS = lower risk myelodysplastic syndrome; PoC = proof of concept; Hb = hemoglobin; RS = ring sideroblasts. Tebapivat – novel mechanism and oral dosing with potential for durable response Tebapivat – high-risk, high-reward opportunity in LR-MDS Phase 2a showed clinical PoC for tebapivat in LR-MDS • 40% of low transfusion burden cohort achieved transfusion independence • One patient achieved Hb response in 16-week period • Safety consistent with Phase 1 healthy volunteer study • Exposure lower than anticipated at 5mg; need to investigate higher doses Ongoing open-label Phase 2b designed to test higher doses in heterogeneous patient population reflective of real world Phase 2b (10mg, 15mg and 20mg) top-line data anticipated H1 2026 Low or high transfusion burden Regardless of RS status (+ or -) ≤2 prior treatments 2L+

19 Drive future growth with diversified rare disease pipeline
20HU = hydroxyurea; GalNAc = N-acetylgalactosamine; siRNA = small interfering RNA; Q6M = every 6 months; HV = healthy volunteer. Expanding in hematology – AG-236 for Polycythemia Vera 100K diagnosed in U.S. 35% phlebotomy dependent Currently approved treatments consist of phlebotomy, HU, cytoreductive therapies Treatment goal – better hematocrit control and well tolerated Phase 1 HV data in H1 2026 AG-236 – GalNAc siRNA-based TMPRSS6 inhibitor targeting iron homeostasis regulation Q6M dosing – maintenance of effect GalNAc siRNA has well characterized immunogenicity profile No titration, single dose strength drives to maximum effect Potential to show differentiated profile with applications in other iron dysregulation indications
21PKU = Phenylketonuria; PAH = Phenylalanine Hydroxylase; Phe = Phenylalanine; PoM = Proof of Mechanism; Tyr = Tyrosine. Anticipate first patient dosed in Phase 1b proof of mechanism trial in H1 2026 with results in H2 2026 Significant opportunity to transform treatment of PKU • PKU caused by dysfunctional PAH enzyme • ~15-20k PKU patients in the U.S. • Only ~1/6 patients are on active treatment • Majority of patients rely on diet modification alone AG-181 novel mechanism of action AG-181 unique attributes Oral medicine targeting classical Phenylketonuria Potential fast onset and durable response – no titration Potential for improved safety and tolerabilityAG-181 is a chaperone of PAH – selectively binds and stabilizes enzyme to enhance and restore function Diversification beyond hematology – AG-181 for PKU Phe Tyr AG-181 Novel mechanism enables potential combinability PAH

22 Financial discipline to achieve growth and long-term sustainability
231. Does not include potential business development activities or one-time costs. 2. Non-GAAP. As of September 30, 2025, Agios reported approximately $1.3 billion in cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities. Financial discipline to deliver long-term sustainability Clear path to profitability based on thalassemia and PK deficiency alone2 Anticipate Operating Expenses in 2026 to be flat compared to 2025 with potential for greater efficiencies beyond 20261 Gated investment for Sickle Cell Disease Operating model refinement Maximize launch of AQVESME in thalassemia

24 Agios – Transforming for tomorrow
25 2025 in review – continued track record for execution EARLY MID-YEAR LATE Pediatric PK Deficiency PYRUKYND Phase 3 readout ACTIVATE-Kids Sickle Cell Disease tebapivat Initiate enrollment in Phase 2 trial Polycythemia Vera AG-236 File IND application Thalassemia AQVESMETM (mitapivat) FDA approval Sickle Cell Disease mitapivat Phase 3 readout RISE UP trial Lower-Risk MDS tebapivat Complete enrollment in Phase 2b trial PK = pyruvate kinase; IND = investigational new drug; FDA = Food and Drug Administration; PDUFA = Prescription Drug User Fee Act.
26PK = pyruvate kinase; LR-MDS = lower risk myelodysplastic syndrome. 2026 strategic priorities – driving long-term value creation Execute high impact launch for AQVESME (mitapivat) in thalassemia Potential to expand PK activation franchise into sickle cell disease and LR-MDS Unlock future value in hematology and other rare disease by advancing early-stage pipeline Ensure long-term sustainability through disciplined capital allocation and operational efficiency
27sNDA = supplemental new drug application; MDS = myelodysplastic syndrome; TMPRSS6 = transmembrane protease, serine 6; HV = healthy volunteer; PAH = phenylalanine hydroxylase; PoM = proof of mechanism. 2026 catalysts reinforce hemolytic anemia leadership and rare disease pipeline potential Sickle Cell Disease Mitapivat Pre-sNDA meeting Q1 Lower-Risk MDS tebapivat Phase 2b topline data Polycythemia Vera AG-236 (TMPRSS6) Phase 1 HV topline data Sickle Cell Disease tebapivat Phase 2 topline data Phenylketonuria AG-181 (PAH stabilizer) Phase 1b PoM data H1 2026 H2 2026 AQVESME (mitapivat) U.S. launch underway in thalassemia

28 Appendix

29 Appendix – AQVESME is first-and-only PK activator indicated for use in adult thalassemia patients Indication statement AQVESME is indicated for the treatment of anemia in adults with alpha- or beta-thalassemia Dosage and administration Tablets: 100 mg orally twice daily Mechanism of action Pyruvate kinase activator that allosterically binds to the pyruvate kinase tetramer and increases pyruvate kinase activity For full prescribing information, visit www.aqvesme.com
30 1. Obtain liver tests (including ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, total bilirubin with fractionation) prior to the initiation of AQVESME, then every 4 weeks for the first 24 weeks, and as clinically indicated thereafter. Interrupt AQVESME if clinically significant increases in liver tests are observed or alanine aminotransferase is >5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN). Complete a comprehensive evaluation to rule out other causes of liver injury when drug-induced liver injury is suspected. Discontinue AQVESME if hepatocellular injury due to AQVESME is suspected. REMS = risk evaluation and mitigation strategy Appendix – AQVESME REMS for liver monitoring v BOXED WARNING – HEPATOCELLULAR INJURY – AQVESME can cause serious hepatocellular injury. Measure liver laboratory tests (ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase and total bilirubin with fractionation) at baseline and every 4 weeks for 24 weeks and then as clinically indicated. Avoid use of AQVESME in patients with cirrhosis. Discontinue AQVESME if hepatic injury is suspected. REMS Monitoring • Prescriber, patient and pharmacy education and certification • Liver testing every 4 weeks for the first 24 weeks of treatment • After 24 weeks, liver testing as clinically indicated Warnings and Precautions Label Language During the double-blind period, 2 of 301 patients (0.66%) with thalassemia treated with AQVESME experienced adverse reactions suggestive of hepatocellular injury. Three additional patients experienced adverse reactions suggestive of hepatocellular injury during the open- label extension periods after switching from placebo to AQVESME. Of these 5 patients, two had serious liver injury and were hospitalized including 1 patient who developed jaundice (peak bilirubin 32 mg/dL). Another patient developed jaundice (peak bilirubin 4 mg/dL) without being hospitalized. These reactions were characterized by a time to onset within the first 6 months of treatment with peak elevations of alanine aminotransferase of >5×ULN with or without jaundice. All patients discontinued treatment with AQVESME, and these reactions improved upon treatment discontinuation. For full prescribing information, visit www.aqvesme.com
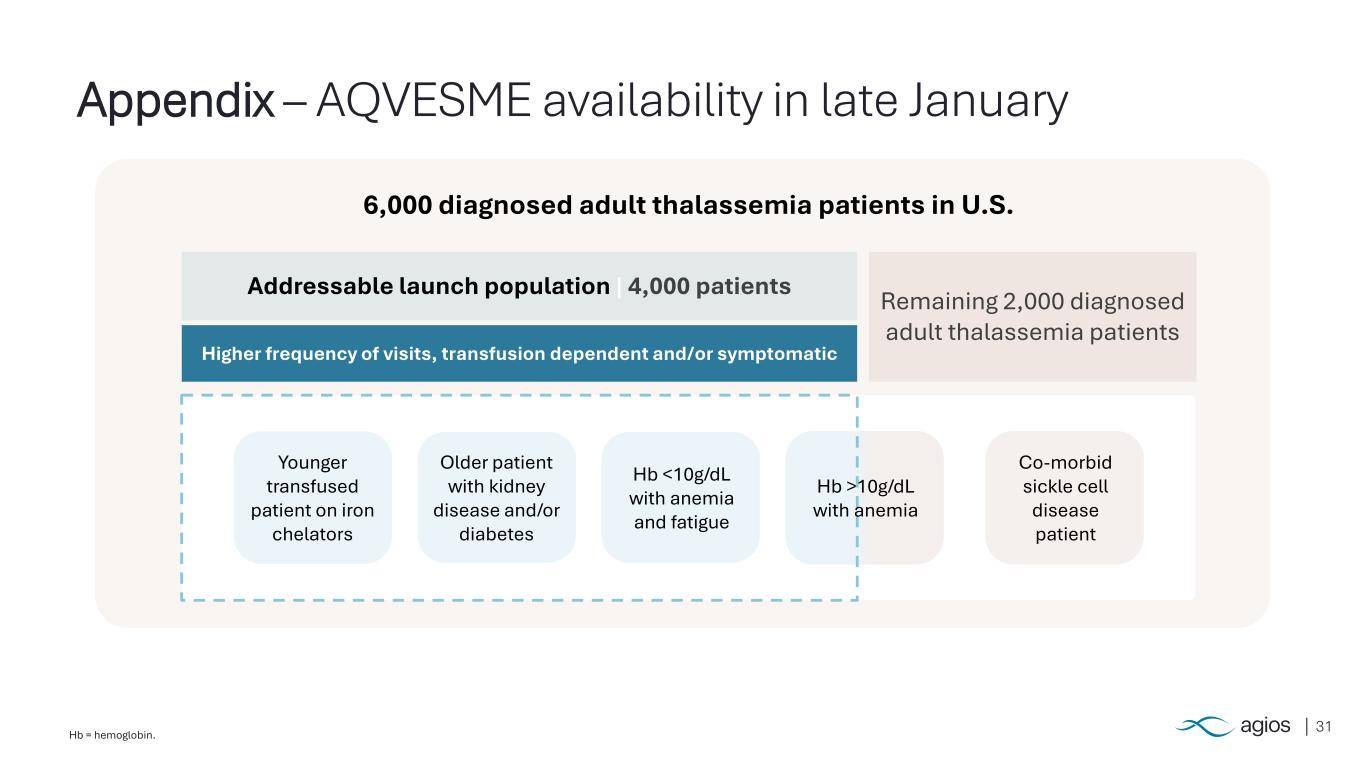
31Hb = hemoglobin. Appendix – AQVESME availability in late January 6,000 diagnosed adult thalassemia patients in U.S. Addressable launch population | 4,000 patients Higher frequency of visits, transfusion dependent and/or symptomatic Remaining 2,000 diagnosed adult thalassemia patients Hb <10g/dL with anemia and fatigue Older patient with kidney disease and/or diabetes Younger transfused patient on iron chelators Co-morbid sickle cell disease patient Hb >10g/dL with anemia
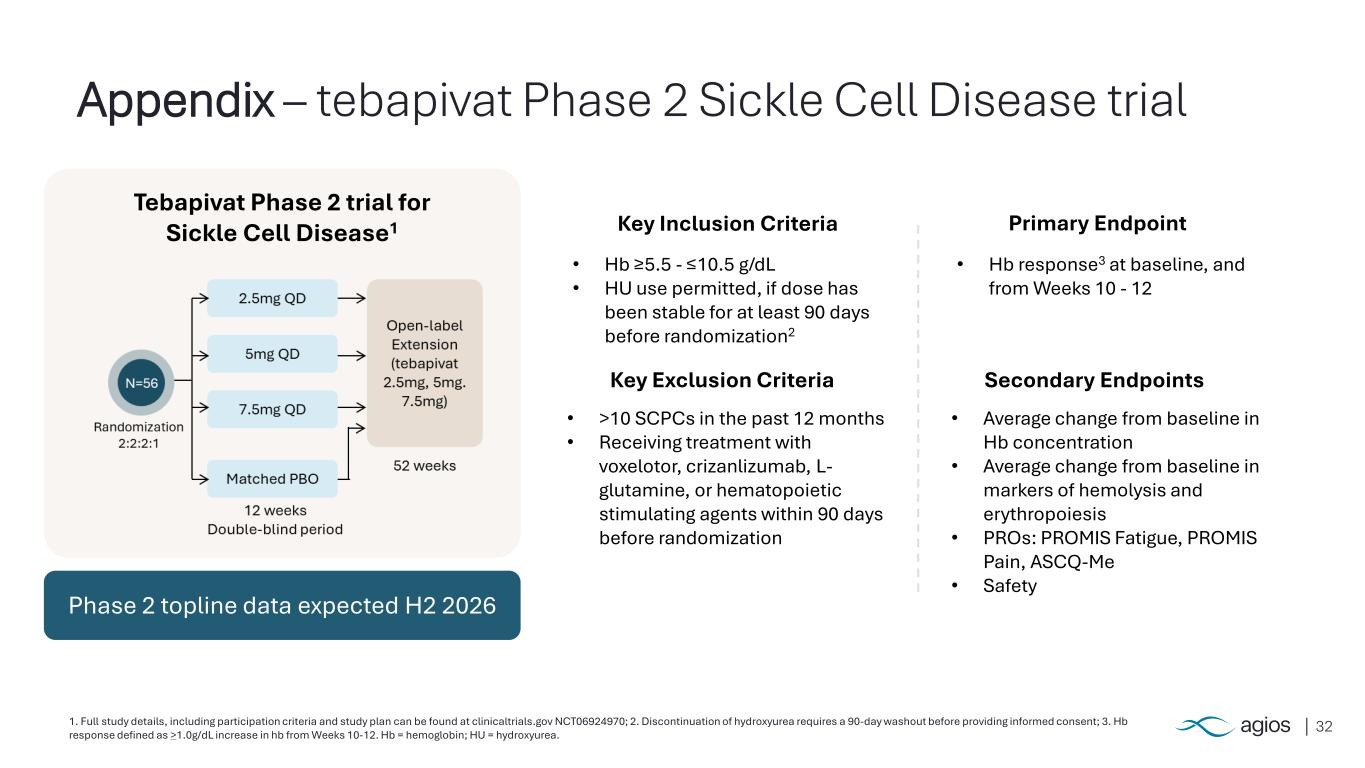
321. Full study details, including participation criteria and study plan can be found at clinicaltrials.gov NCT06924970; 2. Discontinuation of hydroxyurea requires a 90-day washout before providing informed consent; 3. Hb response defined as >1.0g/dL increase in hb from Weeks 10-12. Hb = hemoglobin; HU = hydroxyurea. Appendix – tebapivat Phase 2 Sickle Cell Disease trial Primary Endpoint Secondary Endpoints Key Inclusion Criteria • Hb ≥5.5 - ≤10.5 g/dL • HU use permitted, if dose has been stable for at least 90 days before randomization2 Key Exclusion Criteria • >10 SCPCs in the past 12 months • Receiving treatment with voxelotor, crizanlizumab, L- glutamine, or hematopoietic stimulating agents within 90 days before randomization • Hb response3 at baseline, and from Weeks 10 - 12 • Average change from baseline in Hb concentration • Average change from baseline in markers of hemolysis and erythropoiesis • PROs: PROMIS Fatigue, PROMIS Pain, ASCQ-Me • Safety Tebapivat Phase 2 trial for Sickle Cell Disease1 Phase 2 topline data expected H2 2026
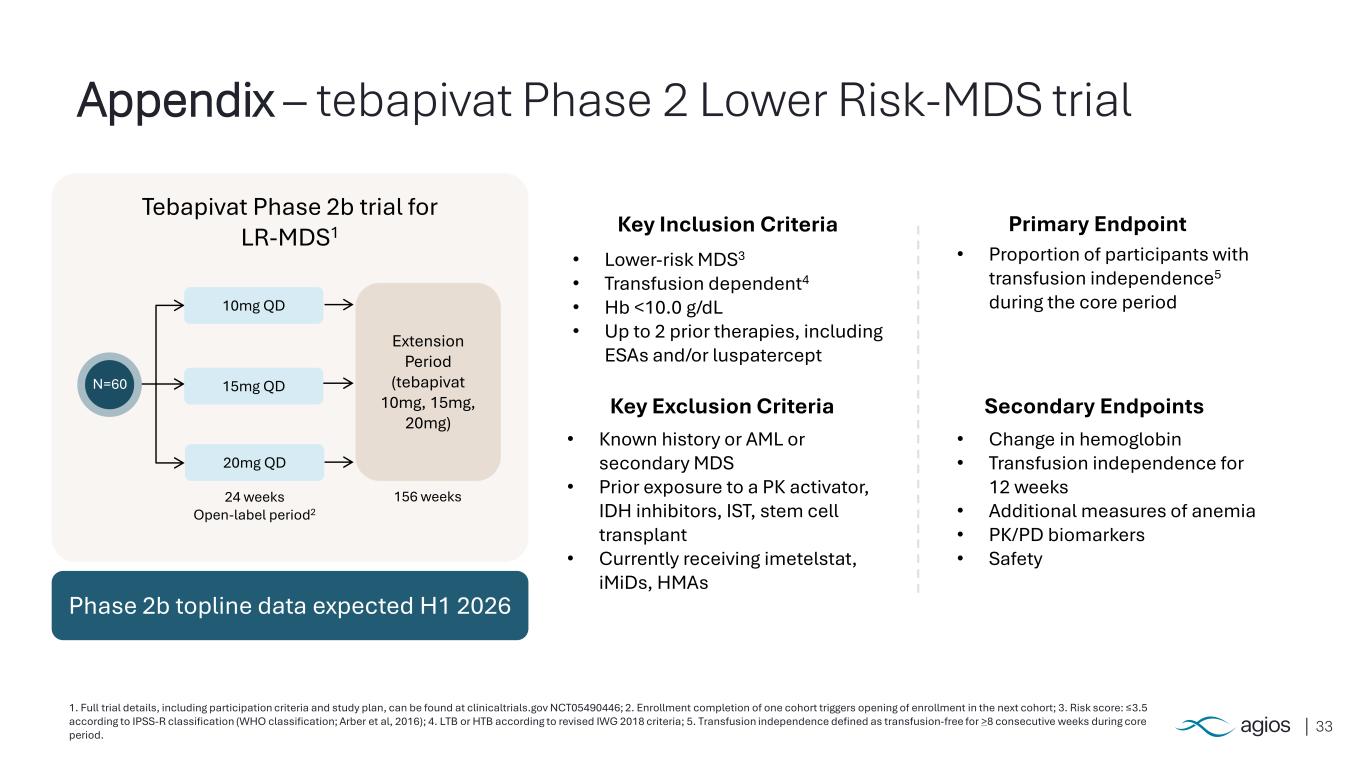
33 1. Full trial details, including participation criteria and study plan, can be found at clinicaltrials.gov NCT05490446; 2. Enrollment completion of one cohort triggers opening of enrollment in the next cohort; 3. Risk score: ≤3.5 according to IPSS-R classification (WHO classification; Arber et al, 2016); 4. LTB or HTB according to revised IWG 2018 criteria; 5. Transfusion independence defined as transfusion-free for >8 consecutive weeks during core period. Appendix – tebapivat Phase 2 Lower Risk-MDS trial Primary Endpoint Secondary Endpoints Key Inclusion Criteria • Lower-risk MDS3 • Transfusion dependent4 • Hb <10.0 g/dL • Up to 2 prior therapies, including ESAs and/or luspatercept Key Exclusion Criteria • Known history or AML or secondary MDS • Prior exposure to a PK activator, IDH inhibitors, IST, stem cell transplant • Currently receiving imetelstat, iMiDs, HMAs • Proportion of participants with transfusion independence5 during the core period • Change in hemoglobin • Transfusion independence for 12 weeks • Additional measures of anemia • PK/PD biomarkers • Safety Tebapivat Phase 2b trial for LR-MDS1 N=60 10mg QD 15mg QD 20mg QD 24 weeks Open-label period2 Extension Period (tebapivat 10mg, 15mg, 20mg) 156 weeks Phase 2b topline data expected H1 2026