
1 Nasdaq: VTVT Improving the Lives of Millions of People Living with Type 1 Diabetes May 2025

2 THE STATEMENTS MADE IN THIS PRESENTATION AND THE ACCOMPANYING ORAL COMMENTARY MAY INCLUDE FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS REGARDING (I) THE DIABETES MARKET AND OTHER MARKETS, (II) THE DEVELOPMENT, CLINICAL TRIAL PROCESS, REGULATORY APPROVAL PROCESS AND ATTRIBUTES OF INVESTIGATIONAL AND MARKETED PRODUCTS TO TREAT THESE DISEASES AND OTHER CONDITIONS, (III) THE ECONOMIC POTENTIAL OF THOSE PRODUCTS AND (IV) THE FUTURE OPERATIONS, FUND-RAISING ACTIVITIES, EXPENDITURES, OPPORTUNITIES, AND FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE OF VTV THERAPEUTICS INC. FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS INCLUDE ALL STATEMENTS THAT ARE NOT HISTORICAL FACTS AND CAN BE IDENTIFIED BY TERMS SUCH AS “ANTICIPATES,” “BELIEVES,” “COULD,” “ESTIMATES,” “EXPECTS,” “INTENDS,” “MAY,” “PLANS,” “POTENTIAL,” PREDICTS,” “PROJECTS,” “SEEKS,” “SHOULD,” “TARGET,” “WILL,” “WOULD” OR SIMILAR EXPRESSIONS AND THE NEGATIVES OF THOSE TERMS. THESE FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS ARE ONLY ESTIMATES BASED UPON THE INFORMATION AVAILABLE TO VTV THERAPEUTICS INC. (OR THE PARTY PREPARING SUCH FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS) AS OF THE DATE OF THIS PRESENTATION. THE FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS INCLUDED HEREIN INVOLVE KNOWN AND UNKNOWN RISKS AND UNCERTAINTIES AND OTHER IMPORTANT FACTORS SUCH THAT ACTUAL FUTURE OPERATIONS, OPPORTUNITIES, PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT PROCESSES AND OUTCOMES, CLINICAL TRIAL PROCESSES AND OUTCOMES, REGULATORY APPROVAL PROCESSES AND OUTCOMES, ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE OF PRODUCTS, FUND-RAISING ACTIVITIES AND FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE MAY DIFFER MATERIALLY FROM THOSE SET FORTH IN OR IMPLIED IN THESE FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS. THESE RISKS, UNCERTAINTIES, AND OTHER FACTORS, WHICH MAY NOT BE WITHIN OUR CONTROL, ARE DISCUSSED IN MORE DETAIL IN OUR QUARTERLY, ANNUAL AND CURRENT REPORTS FILED WITH THE SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, UNDER THE CAPTIONS, “RISK FACTORS,” “CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS” AND “MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS.” THEREFORE, YOU SHOULD READ THIS PRESENTATION IN CONJUNCTION WITH SUCH MEANINGFUL CAUTIONARY STATEMENTS. UNDUE RELIANCE SHOULD NOT BE PLACED ON FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS, WHICH SPEAK ONLY AS OF THE DATE HEREOF. EXCEPT AS REQUIRED BY LAW, WE EXPRESSLY DISCLAIM ANY RESPONSIBILITY TO PUBLICLY UPDATE OR REVISE OUR FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS, WHETHER AS A RESULT OF NEW INFORMATION, FUTURE EVENTS OR OTHERWISE. ALL FORWARD- LOOKING STATEMENTS CONTAINED HEREIN ARE QUALIFIED IN THEIR ENTIRETY BY THE FOREGOING CAUTIONARYSTATEMENTS. THIS PRESENTATION IS BEING PROVIDED TO YOU FOR INFORMATION PURPOSES ONLY. THIS PRESENTATION DOES NOT CONSTITUTE AN OFFER OR SALE OF (OR THE SOLICITATION OF AN OFFER TO BUY) ANY SECURITIES OF VTV THERAPEUTICS INC. OR ANY OF ITS SUBSIDIARIES. BY ACCEPTING THIS PRESENTATION, YOU ACKNOWLEDGE AND AGREE THAT (I) YOU WILL NOT RELY ON THIS PRESENTATION FOR MAKING ANY INVESTMENT DECISION WITH RESPECT TO ANY SECURITIES OF VTV THERAPEUTICS INC. OR ANY OF ITS SUBSIDIARIES, AND (II) ANY INVESTMENT DECISION MADE BY YOU WITH RESPECT TO ANY SUCH SECURITIES WILL BE BASED SOLELY ON AN OFFERING DOCUMENT RELATING TO SUCH SECURITIES (IF ANY), INCLUDING THE INFORMATION INCORPORATED BY REFERENCETHEREIN.

3 Experienced Leadership with Decades of Life Sciences Expertise Rich Nelson Chief Business Officer Carmen Valcarce, PhD Chief Scientific Officer Thomas Strack, MD Chief Medical Officer Dan Kirby SVP Strategic Ops Paul Sekhri Chair, President & CEO Martin Lafontaine Chief Commercial Officer
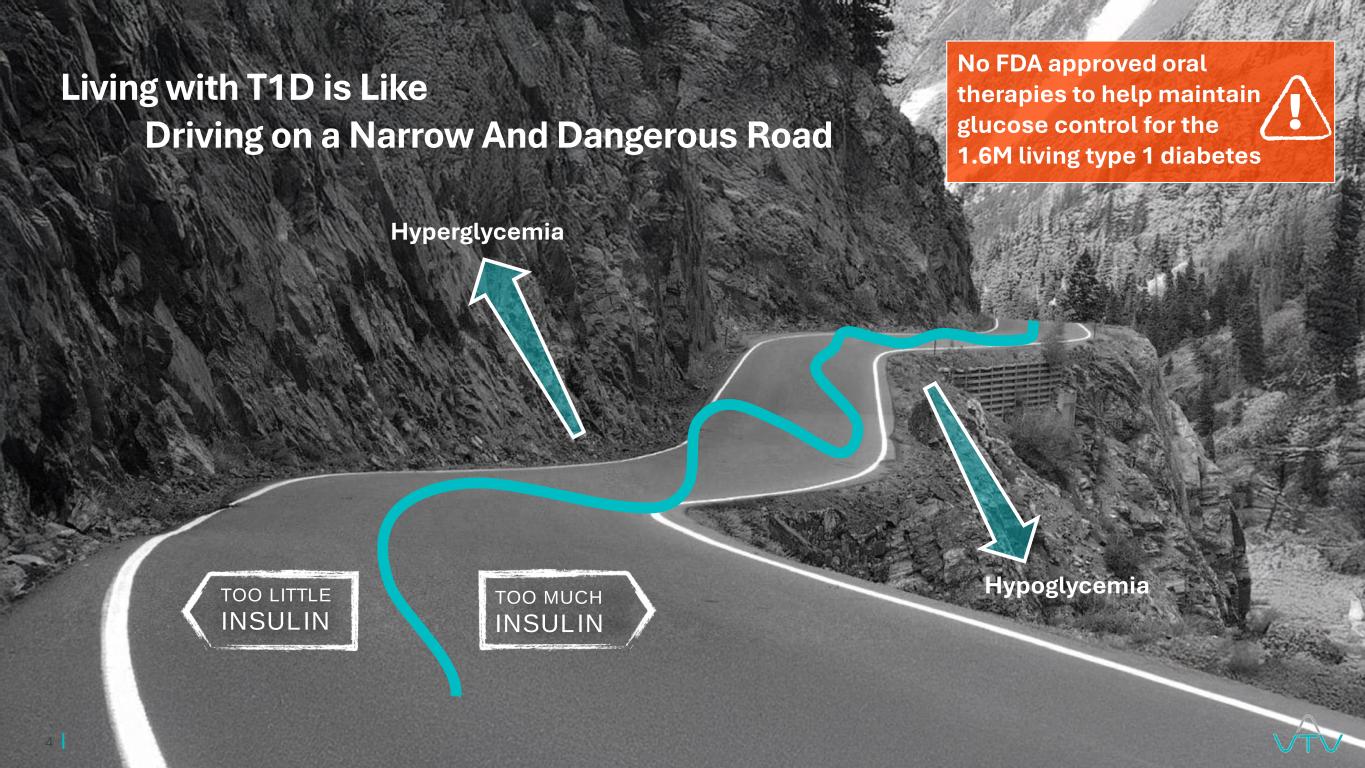
4 TOO MUCH INSULIN TOO LITTLE INSULIN Living with T1D is Like Driving on a Narrow And Dangerous Road No FDA approved oral therapies to help maintain glucose control for the 1.6M living type 1 diabetes Hyperglycemia Hypoglycemia !
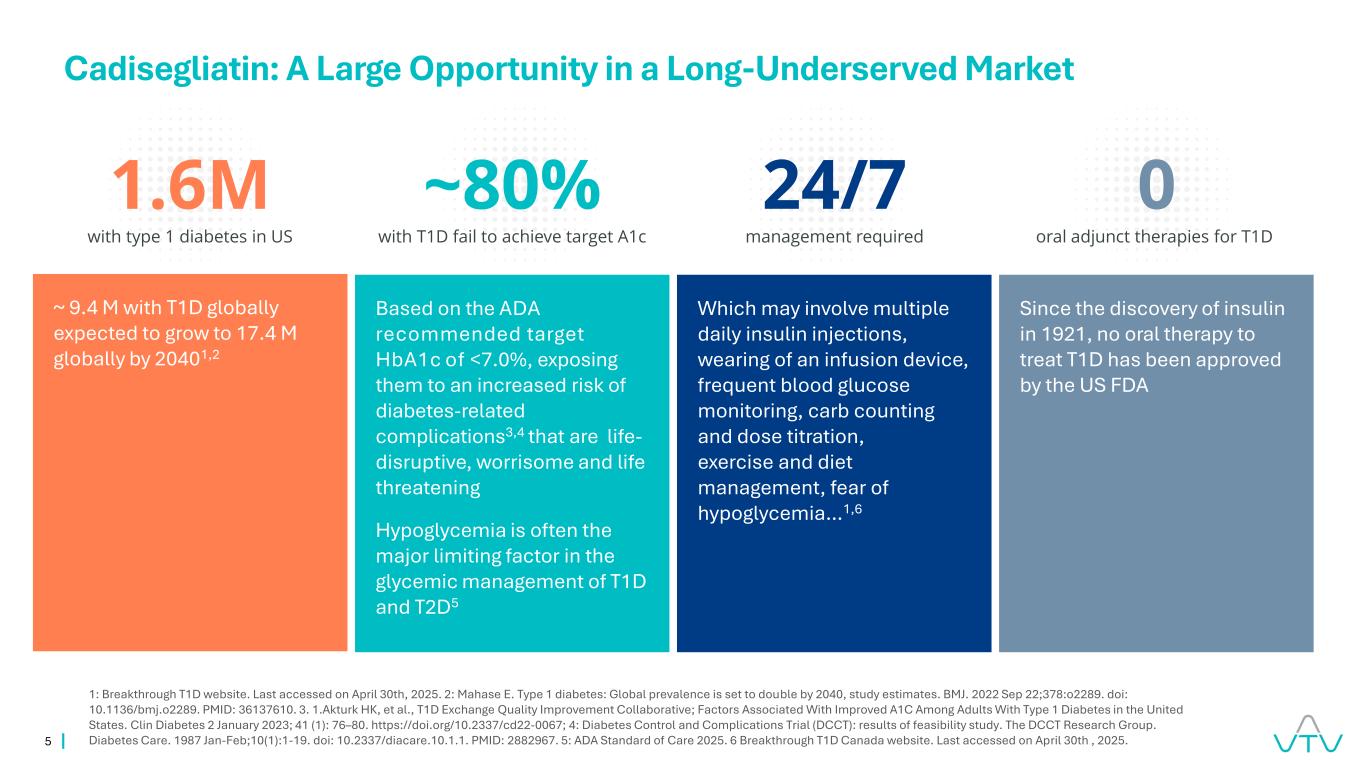
5 Which may involve multiple daily insulin injections, wearing of an infusion device, frequent blood glucose monitoring, carb counting and dose titration, exercise and diet management, fear of hypoglycemia…1,6 ~ 9.4 M with T1D globally expected to grow to 17.4 M globally by 20401,2 Based on the ADA recommended target HbA1c of <7.0%, exposing them to an increased risk of diabetes-related complications3,4 that are life- disruptive, worrisome and life threatening Hypoglycemia is often the major limiting factor in the glycemic management of T1D and T2D5 Since the discovery of insulin in 1921, no oral therapy to treat T1D has been approved by the US FDA 1.6M with type 1 diabetes in US ~80% with T1D fail to achieve target A1c 0 oral adjunct therapies for T1D 24/7 management required Cadisegliatin: A Large Opportunity in a Long-Underserved Market 1: Breakthrough T1D website. Last accessed on April 30th, 2025. 2: Mahase E. Type 1 diabetes: Global prevalence is set to double by 2040, study estimates. BMJ. 2022 Sep 22;378:o2289. doi: 10.1136/bmj.o2289. PMID: 36137610. 3. 1.Akturk HK, et al., T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Collaborative; Factors Associated With Improved A1C Among Adults With Type 1 Diabetes in the United States. Clin Diabetes 2 January 2023; 41 (1): 76–80. https://doi.org/10.2337/cd22-0067; 4: Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT): results of feasibility study. The DCCT Research Group. Diabetes Care. 1987 Jan-Feb;10(1):1-19. doi: 10.2337/diacare.10.1.1. PMID: 2882967. 5: ADA Standard of Care 2025. 6 Breakthrough T1D Canada website. Last accessed on April 30th , 2025.
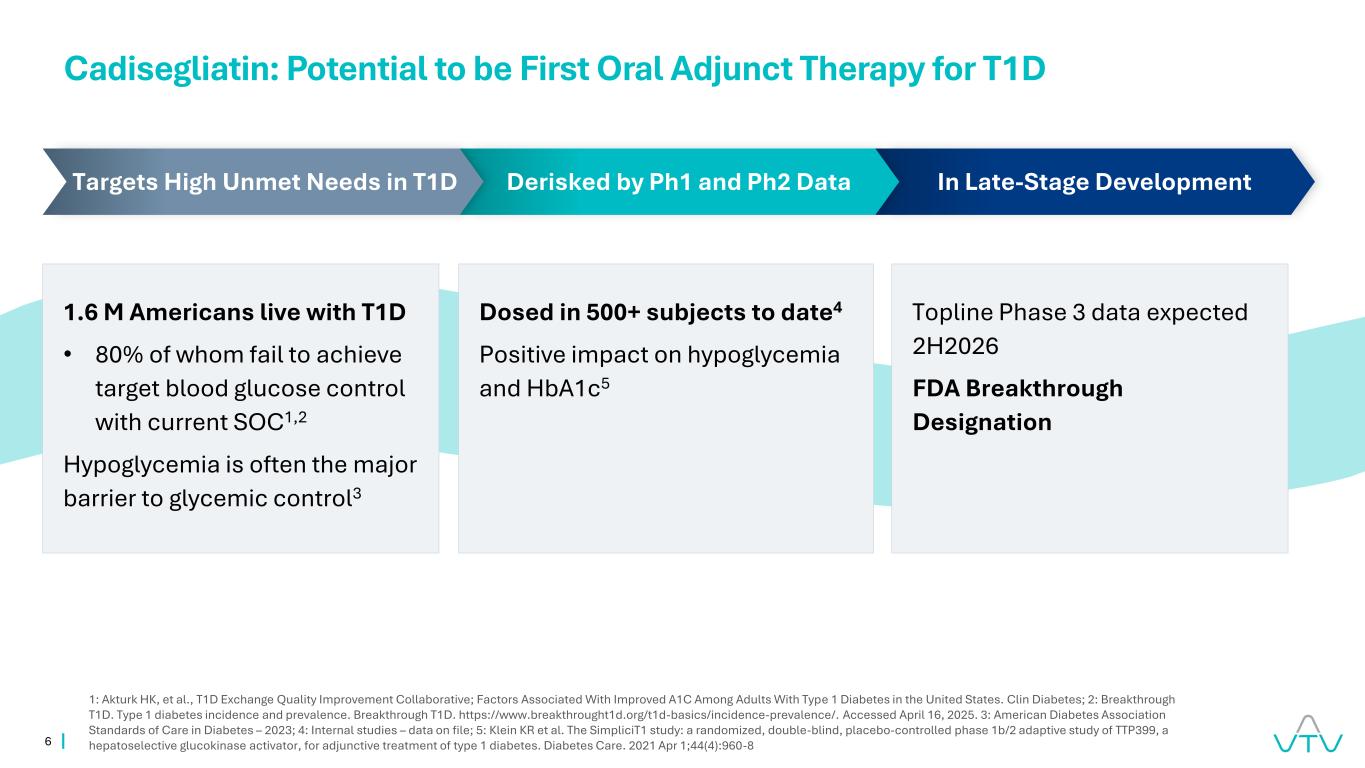
6 Cadisegliatin: Potential to be First Oral Adjunct Therapy for T1D 1: Akturk HK, et al., T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Collaborative; Factors Associated With Improved A1C Among Adults With Type 1 Diabetes in the United States. Clin Diabetes; 2: Breakthrough T1D. Type 1 diabetes incidence and prevalence. Breakthrough T1D. https://www.breakthrought1d.org/t1d-basics/incidence-prevalence/. Accessed April 16, 2025. 3: American Diabetes Association Standards of Care in Diabetes – 2023; 4: Internal studies – data on file; 5: Klein KR et al. The SimpliciT1 study: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 1b/2 adaptive study of TTP399, a hepatoselective glucokinase activator, for adjunctive treatment of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2021 Apr 1;44(4):960-8 1.6 M Americans live with T1D • 80% of whom fail to achieve target blood glucose control with current SOC1,2 Hypoglycemia is often the major barrier to glycemic control3 Dosed in 500+ subjects to date4 Positive impact on hypoglycemia and HbA1c5 Topline Phase 3 data expected 2H2026 FDA Breakthrough Designation In Late-Stage DevelopmentDerisked by Ph1 and Ph2 DataTargets High Unmet Needs in T1D
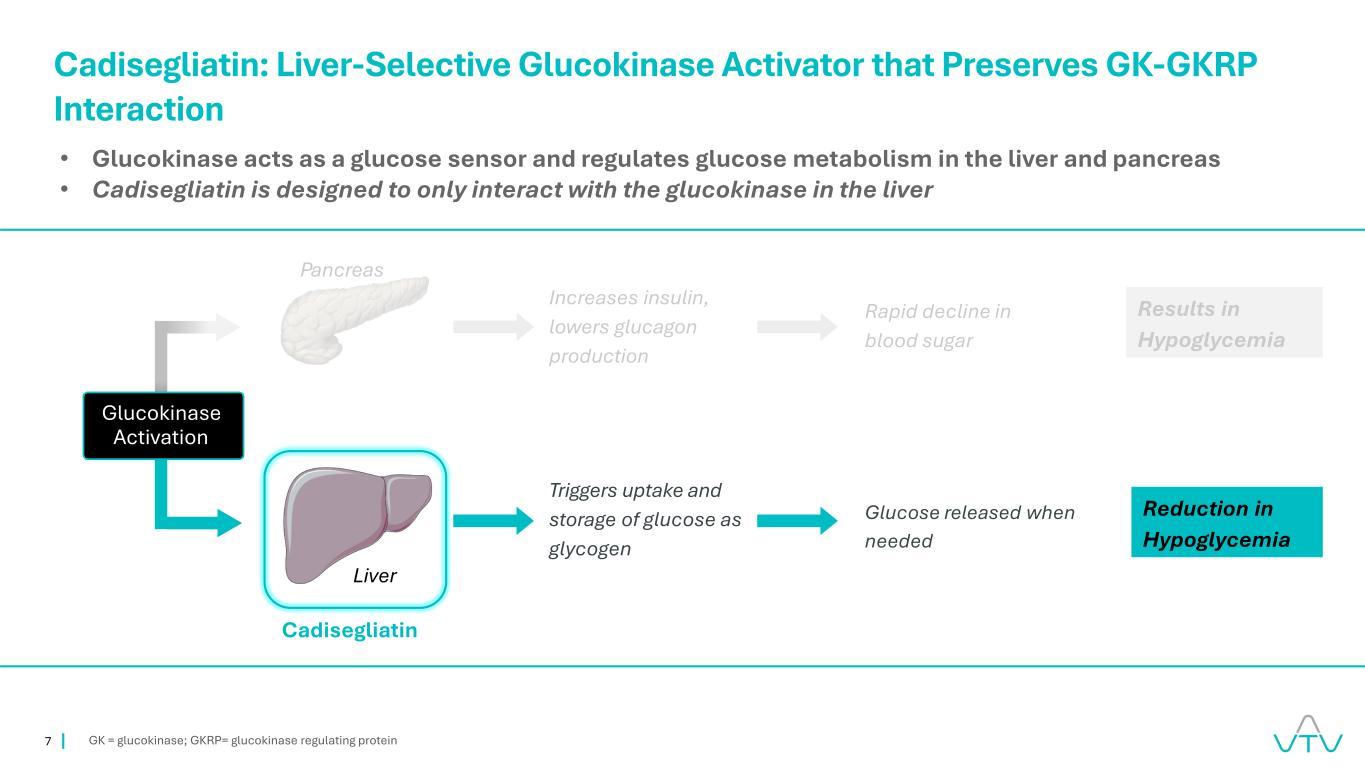
7 GK = glucokinase; GKRP= glucokinase regulating protein Cadisegliatin: Liver-Selective Glucokinase Activator that Preserves GK-GKRP Interaction • Glucokinase acts as a glucose sensor and regulates glucose metabolism in the liver and pancreas • Cadisegliatin is designed to only interact with the glucokinase in the liver Pancreas Increases insulin, lowers glucagon production Triggers uptake and storage of glucose as glycogen Rapid decline in blood sugar Results in Hypoglycemia Glucose released when needed Reduction in Hypoglycemia Cadisegliatin Liver Glucokinase Activation
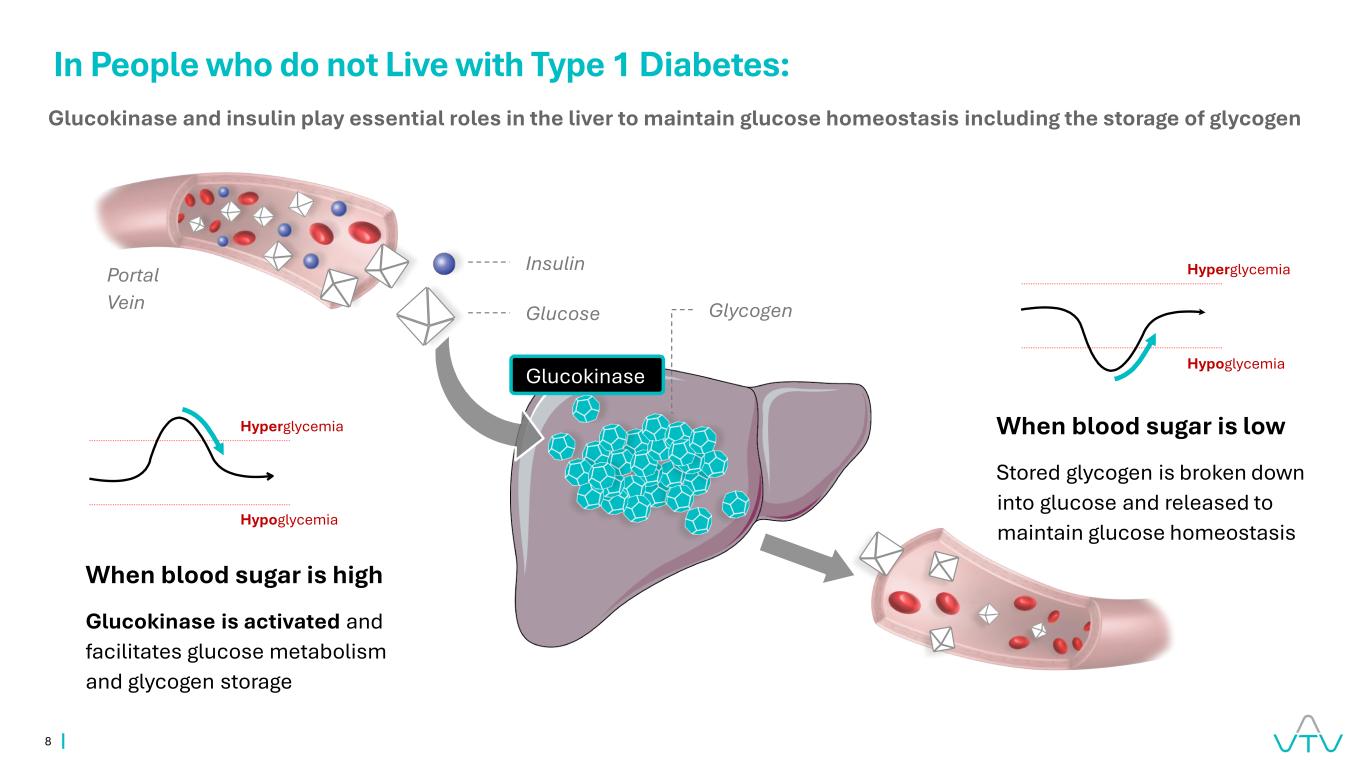
8 When blood sugar is low Stored glycogen is broken down into glucose and released to maintain glucose homeostasis Glucokinase Insulin Glucose Glycogen Portal Vein In People who do not Live with Type 1 Diabetes: Glucokinase and insulin play essential roles in the liver to maintain glucose homeostasis including the storage of glycogen Hyperglycemia Hypoglycemia Hyperglycemia Hypoglycemia When blood sugar is high Glucokinase is activated and facilitates glucose metabolism and glycogen storage
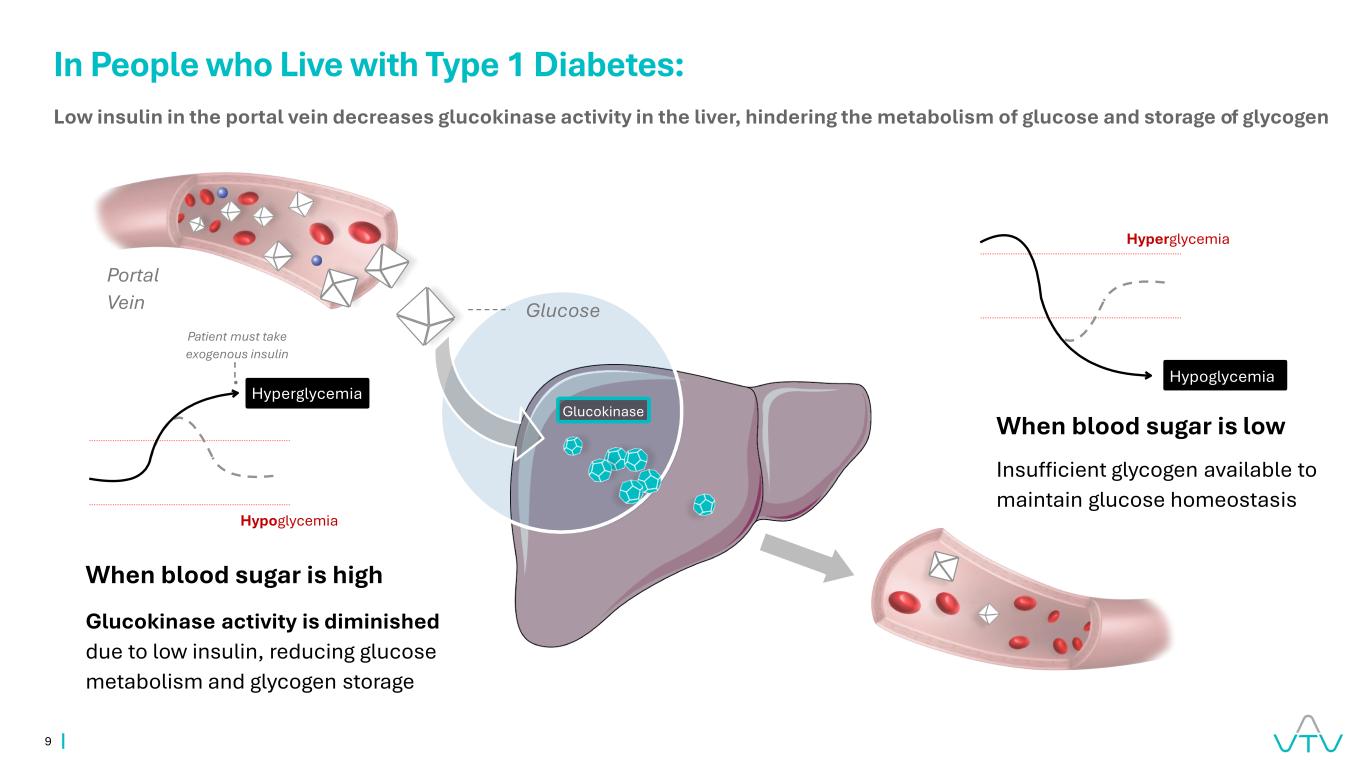
9 When blood sugar is high Glucokinase activity is diminished due to low insulin, reducing glucose metabolism and glycogen storage Hypoglycemia Patient must take exogenous insulin Glucose Portal Vein Low insulin in the portal vein decreases glucokinase activity in the liver, hindering the metabolism of glucose and storage of glycogen Hyperglycemia Hypoglycemia Hyperglycemia Glucokinase In People who Live with Type 1 Diabetes: When blood sugar is low Insufficient glycogen available to maintain glucose homeostasis
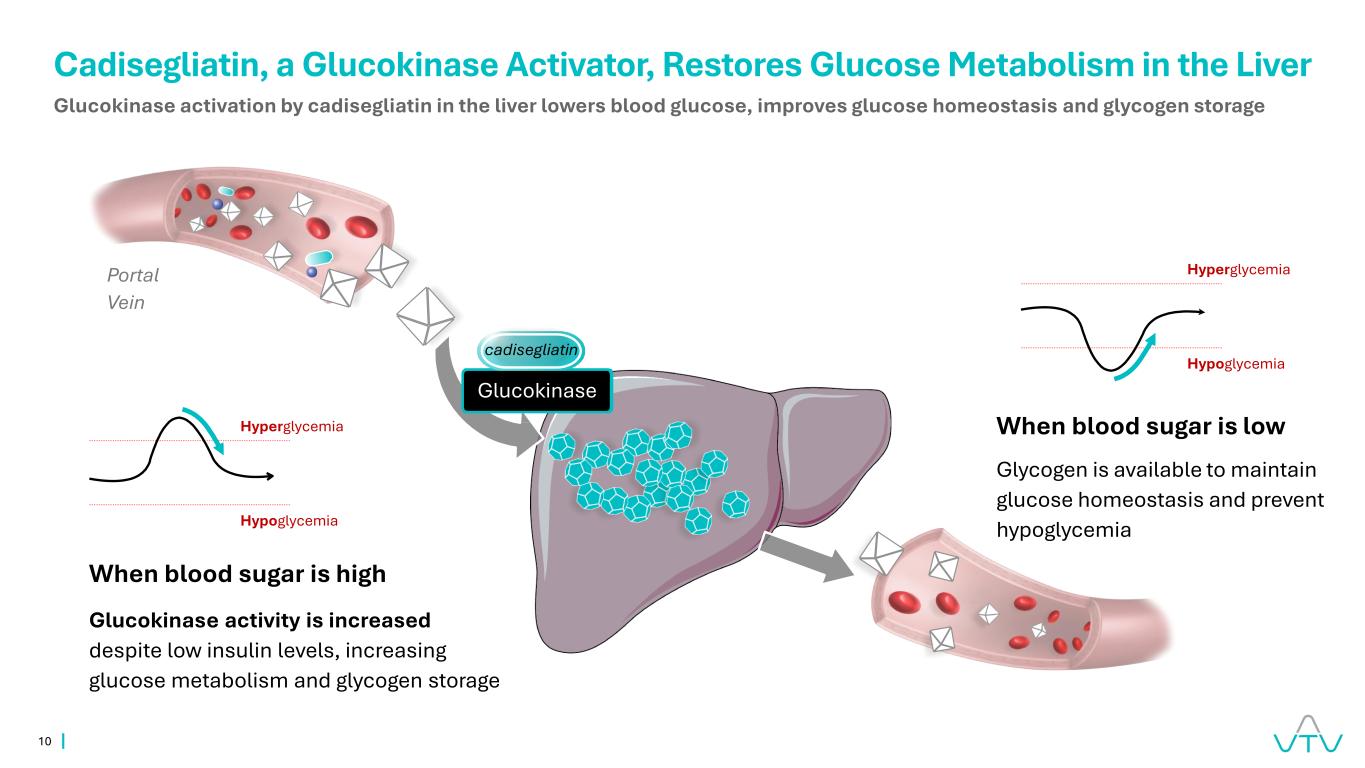
10 Portal Vein cadisegliatin Glucokinase activation by cadisegliatin in the liver lowers blood glucose, improves glucose homeostasis and glycogen storage Glucokinase Cadisegliatin, a Glucokinase Activator, Restores Glucose Metabolism in the Liver Hyperglycemia Hypoglycemia Hyperglycemia Hypoglycemia When blood sugar is high Glucokinase activity is increased despite low insulin levels, increasing glucose metabolism and glycogen storage When blood sugar is low Glycogen is available to maintain glucose homeostasis and prevent hypoglycemia
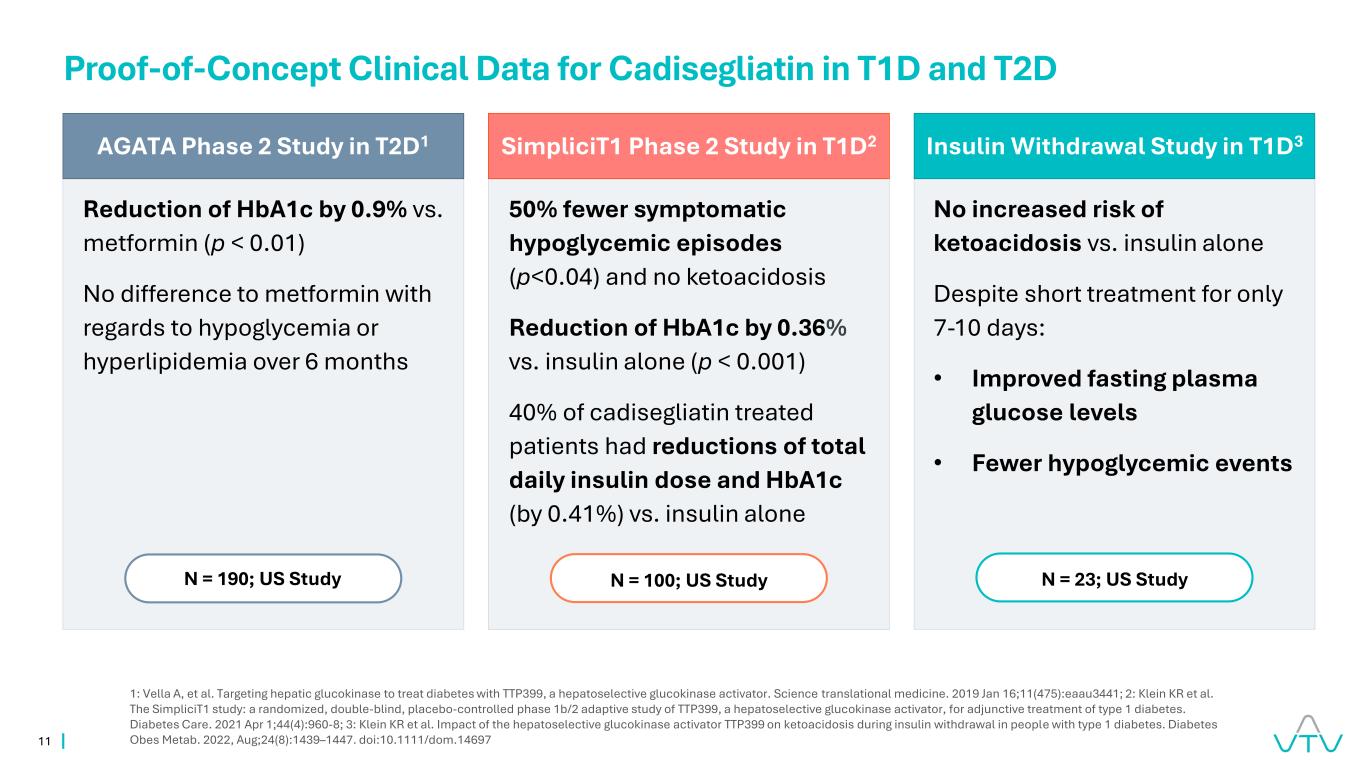
11 AGATA Phase 2 Study in T2D1 Reduction of HbA1c by 0.9% vs. metformin (p < 0.01) No difference to metformin with regards to hypoglycemia or hyperlipidemia over 6 months N = 190; US Study Proof-of-Concept Clinical Data for Cadisegliatin in T1D and T2D 1: Vella A, et al. Targeting hepatic glucokinase to treat diabetes with TTP399, a hepatoselective glucokinase activator. Science translational medicine. 2019 Jan 16;11(475):eaau3441; 2: Klein KR et al. The SimpliciT1 study: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 1b/2 adaptive study of TTP399, a hepatoselective glucokinase activator, for adjunctive treatment of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2021 Apr 1;44(4):960-8; 3: Klein KR et al. Impact of the hepatoselective glucokinase activator TTP399 on ketoacidosis during insulin withdrawal in people with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2022, Aug;24(8):1439–1447. doi:10.1111/dom.14697 Insulin Withdrawal Study in T1D3 No increased risk of ketoacidosis vs. insulin alone Despite short treatment for only 7-10 days: • Improved fasting plasma glucose levels • Fewer hypoglycemic events N = 23; US Study SimpliciT1 Phase 2 Study in T1D2 50% fewer symptomatic hypoglycemic episodes (p<0.04) and no ketoacidosis Reduction of HbA1c by 0.36% vs. insulin alone (p < 0.001) 40% of cadisegliatin treated patients had reductions of total daily insulin dose and HbA1c (by 0.41%) vs. insulin alone N = 100; US Study
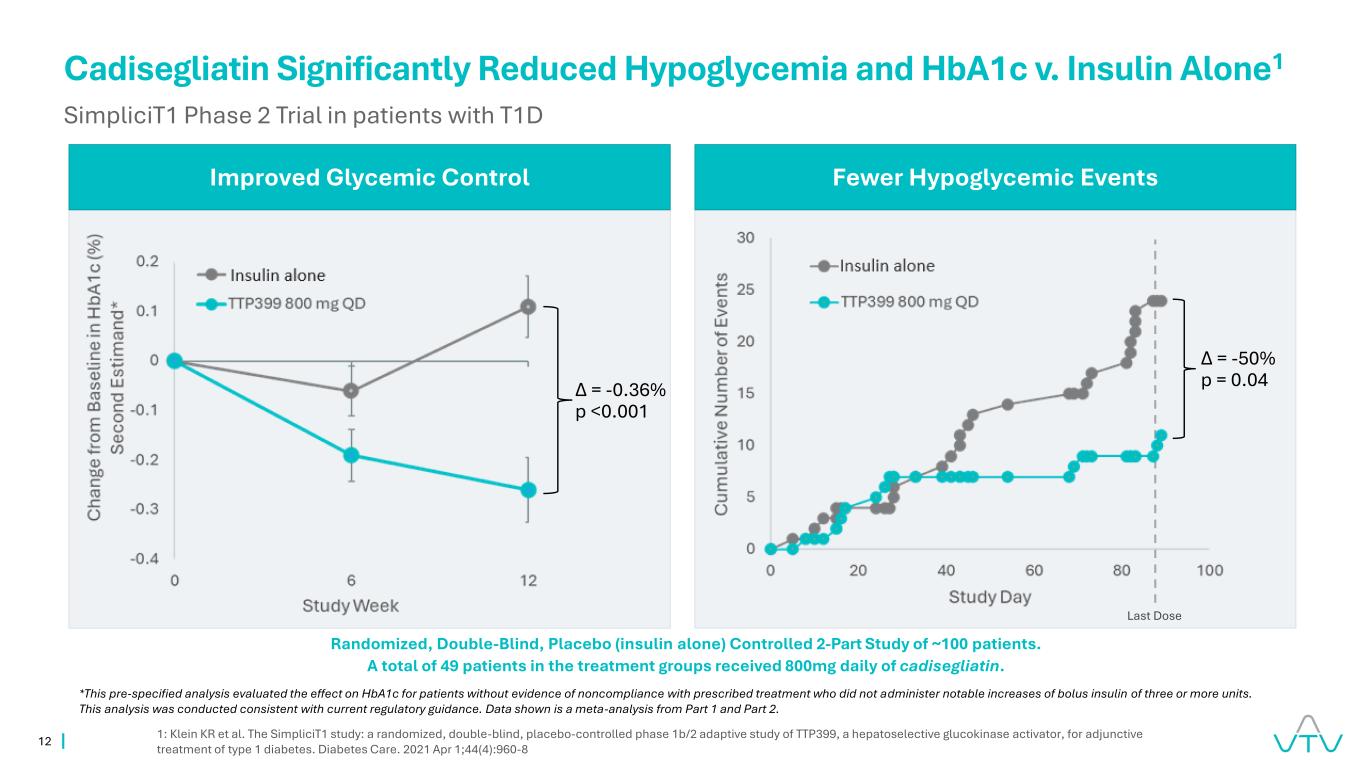
12 Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo (insulin alone) Controlled 2-Part Study of ~100 patients. A total of 49 patients in the treatment groups received 800mg daily of cadisegliatin. Cadisegliatin Significantly Reduced Hypoglycemia and HbA1c v. Insulin Alone1 SimpliciT1 Phase 2 Trial in patients with T1D 1: Klein KR et al. The SimpliciT1 study: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 1b/2 adaptive study of TTP399, a hepatoselective glucokinase activator, for adjunctive treatment of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2021 Apr 1;44(4):960-8 Improved Glycemic Control Fewer Hypoglycemic Events Δ = -0.36% p <0.001 *This pre-specified analysis evaluated the effect on HbA1c for patients without evidence of noncompliance with prescribed treatment who did not administer notable increases of bolus insulin of three or more units. This analysis was conducted consistent with current regulatory guidance. Data shown is a meta-analysis from Part 1 and Part 2. Δ = -50% p = 0.04 Last Dose
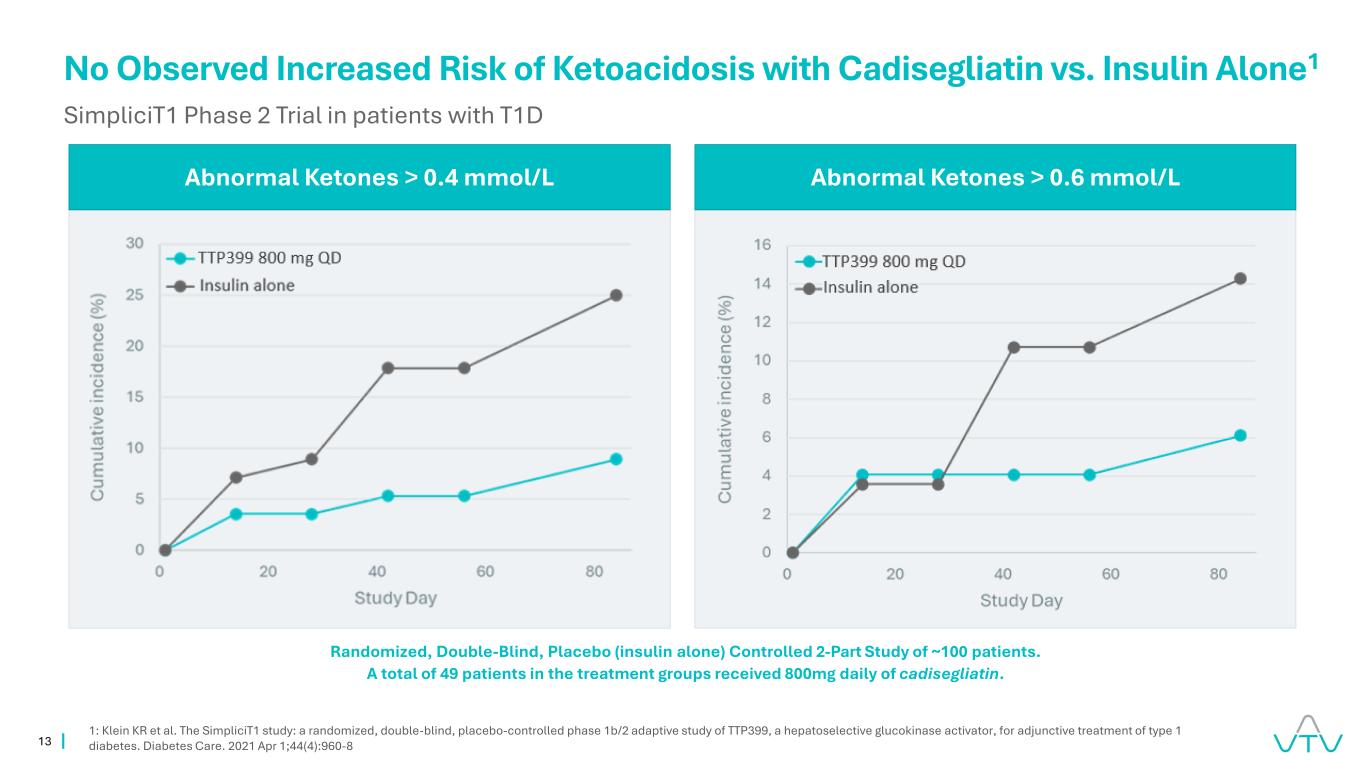
13 No Observed Increased Risk of Ketoacidosis with Cadisegliatin vs. Insulin Alone1 SimpliciT1 Phase 2 Trial in patients with T1D Abnormal Ketones > 0.4 mmol/L Abnormal Ketones > 0.6 mmol/L 1: Klein KR et al. The SimpliciT1 study: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 1b/2 adaptive study of TTP399, a hepatoselective glucokinase activator, for adjunctive treatment of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2021 Apr 1;44(4):960-8 Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo (insulin alone) Controlled 2-Part Study of ~100 patients. A total of 49 patients in the treatment groups received 800mg daily of cadisegliatin.
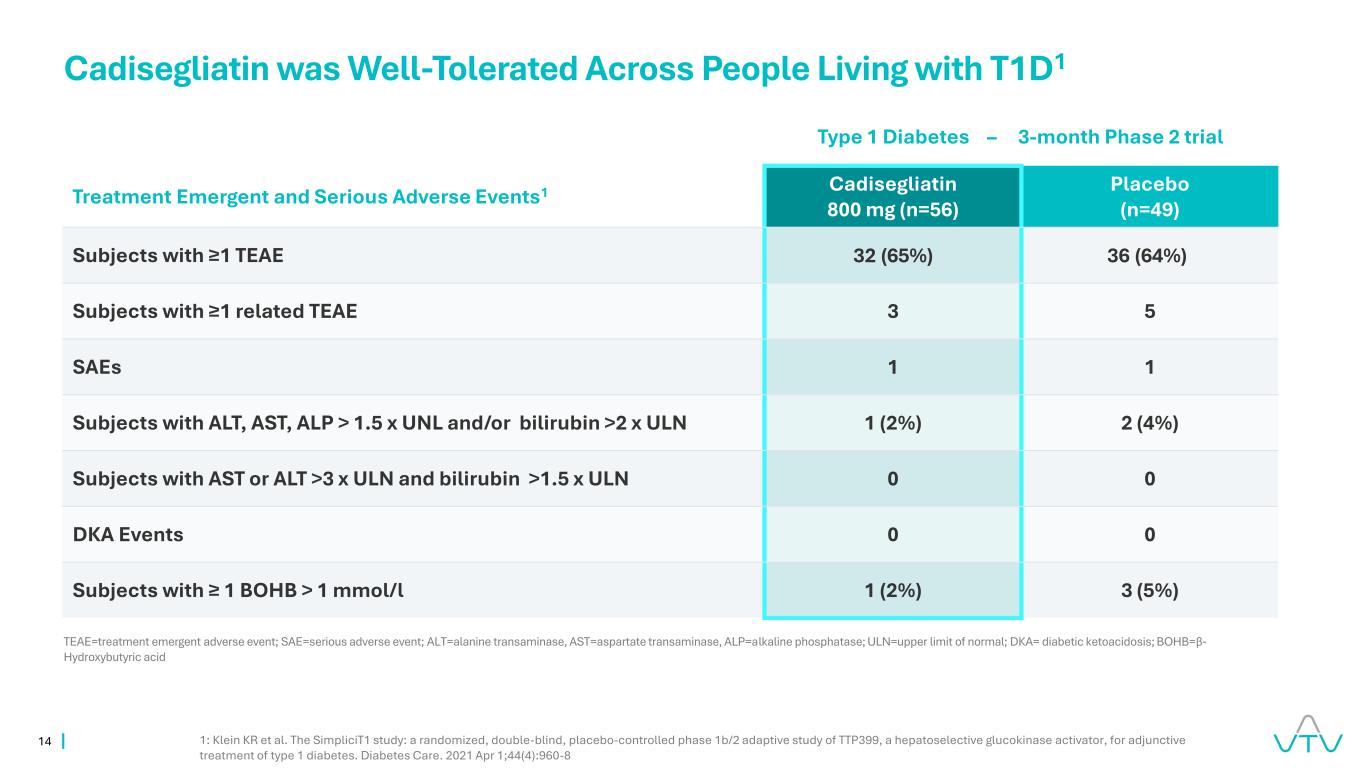
14 Cadisegliatin was Well-Tolerated Across People Living with T1D1 1: Klein KR et al. The SimpliciT1 study: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 1b/2 adaptive study of TTP399, a hepatoselective glucokinase activator, for adjunctive treatment of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2021 Apr 1;44(4):960-8 Treatment Emergent and Serious Adverse Events1 Cadisegliatin 800 mg (n=56) Placebo (n=49) Subjects with ≥1 TEAE 32 (65%) 36 (64%) Subjects with ≥1 related TEAE 3 5 SAEs 1 1 Subjects with ALT, AST, ALP > 1.5 x UNL and/or bilirubin >2 x ULN 1 (2%) 2 (4%) Subjects with AST or ALT >3 x ULN and bilirubin >1.5 x ULN 0 0 DKA Events 0 0 Subjects with ≥ 1 BOHB > 1 mmol/l 1 (2%) 3 (5%) TEAE=treatment emergent adverse event; SAE=serious adverse event; ALT=alanine transaminase, AST=aspartate transaminase, ALP=alkaline phosphatase; ULN=upper limit of normal; DKA= diabetic ketoacidosis; BOHB=β- Hydroxybutyric acid Type 1 Diabetes – 3-month Phase 2 trial
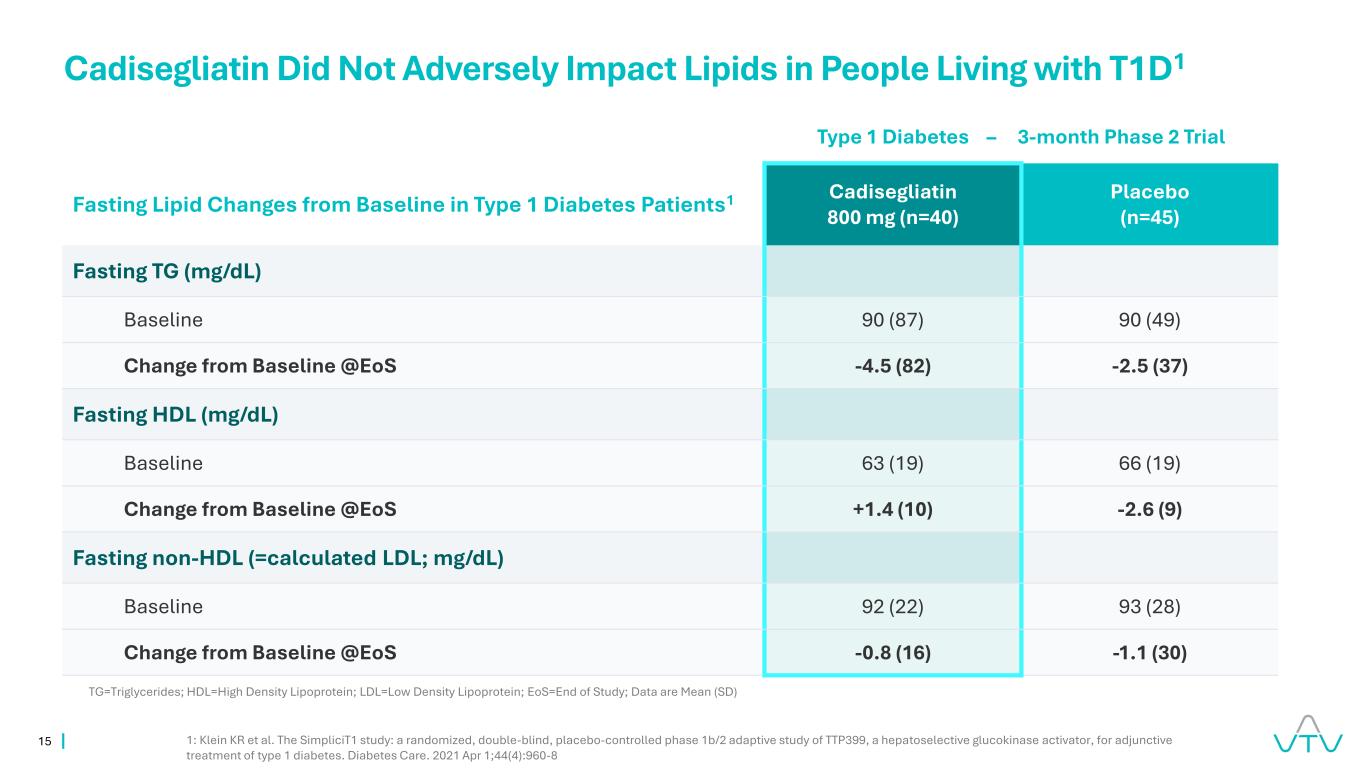
15 Cadisegliatin Did Not Adversely Impact Lipids in People Living with T1D1 Fasting Lipid Changes from Baseline in Type 1 Diabetes Patients1 Cadisegliatin 800 mg (n=40) Placebo (n=45) Fasting TG (mg/dL) Baseline 90 (87) 90 (49) Change from Baseline @EoS -4.5 (82) -2.5 (37) Fasting HDL (mg/dL) Baseline 63 (19) 66 (19) Change from Baseline @EoS +1.4 (10) -2.6 (9) Fasting non-HDL (=calculated LDL; mg/dL) Baseline 92 (22) 93 (28) Change from Baseline @EoS -0.8 (16) -1.1 (30) Type 1 Diabetes – 3-month Phase 2 Trial 1: Klein KR et al. The SimpliciT1 study: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 1b/2 adaptive study of TTP399, a hepatoselective glucokinase activator, for adjunctive treatment of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2021 Apr 1;44(4):960-8 TG=Triglycerides; HDL=High Density Lipoprotein; LDL=Low Density Lipoprotein; EoS=End of Study; Data are Mean (SD)
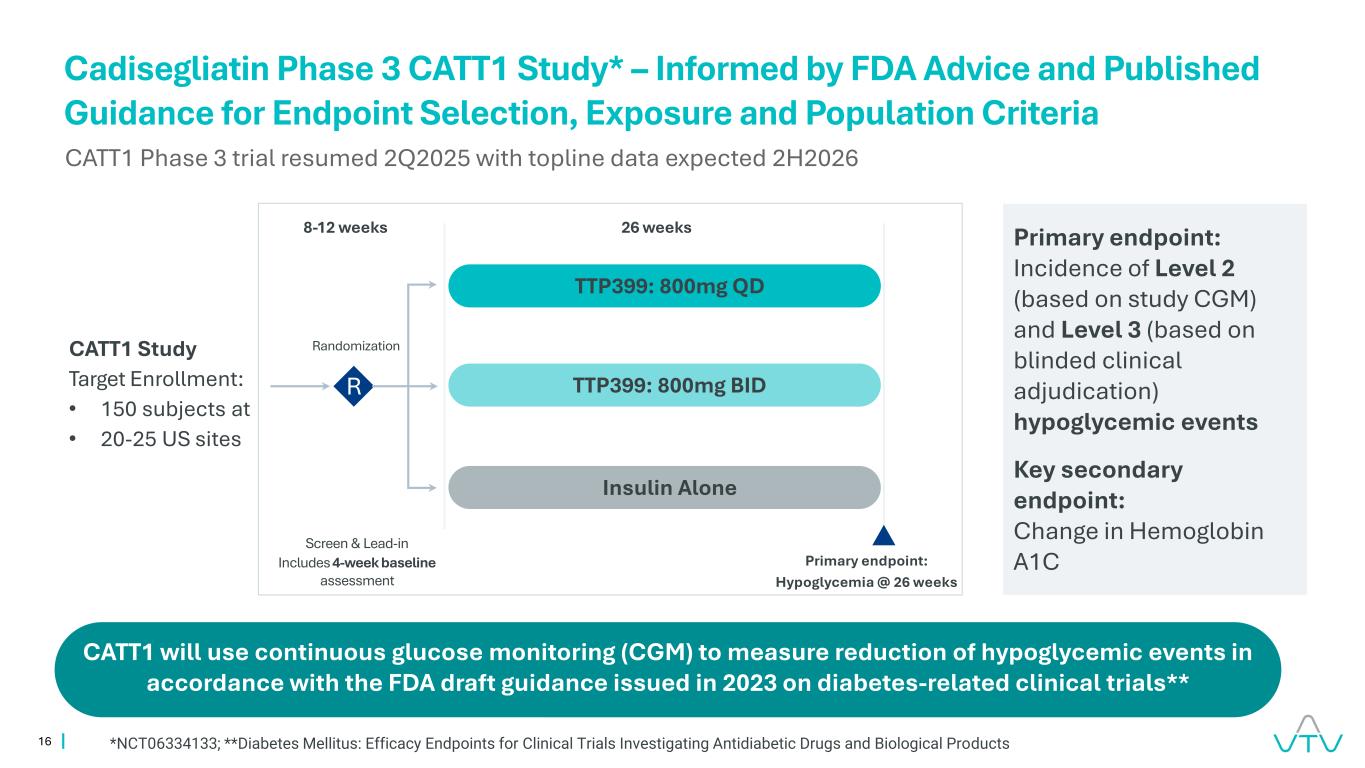
16 Cadisegliatin Phase 3 CATT1 Study* – Informed by FDA Advice and Published Guidance for Endpoint Selection, Exposure and Population Criteria CATT1 Study Target Enrollment: • 150 subjects at • 20-25 US sites Primary endpoint: Incidence of Level 2 (based on study CGM) and Level 3 (based on blinded clinical adjudication) hypoglycemic events Key secondary endpoint: Change in Hemoglobin A1C Screen & Lead-in Includes 4-week baseline assessment Randomization R Primary endpoint: Hypoglycemia @ 26 weeks TTP399: 800mg QD TTP399: 800mg BID Insulin Alone 26 weeks8-12 weeks CATT1 Phase 3 trial resumed 2Q2025 with topline data expected 2H2026 CATT1 will use continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) to measure reduction of hypoglycemic events in accordance with the FDA draft guidance issued in 2023 on diabetes-related clinical trials** *NCT06334133; **Diabetes Mellitus: Efficacy Endpoints for Clinical Trials Investigating Antidiabetic Drugs and Biological Products
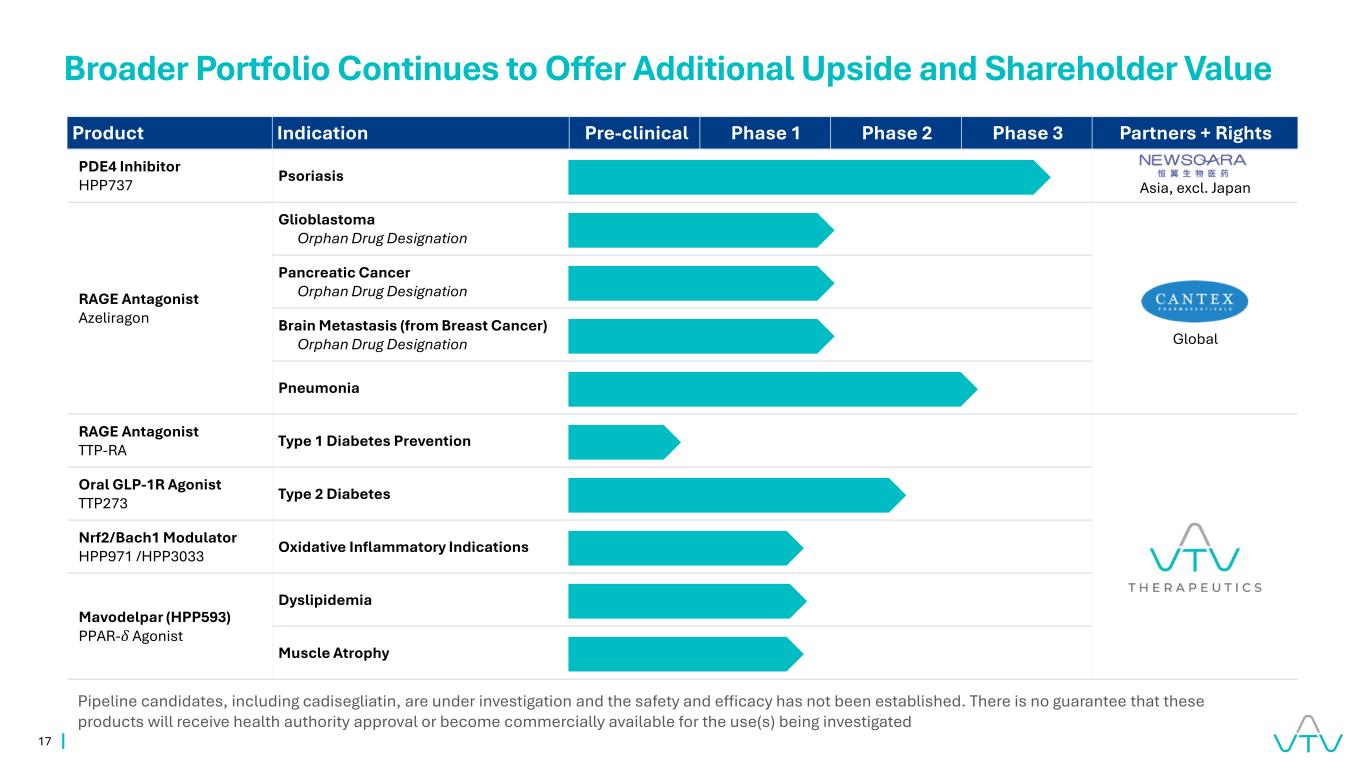
17 Product Indication Pre-clinical Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Partners + Rights PDE4 Inhibitor HPP737 Psoriasis Asia, excl. Japan RAGE Antagonist Azeliragon Glioblastoma Orphan Drug Designation Pancreatic Cancer Orphan Drug Designation Brain Metastasis (from Breast Cancer) Orphan Drug Designation Pneumonia RAGE Antagonist TTP-RA Type 1 Diabetes Prevention Oral GLP-1R Agonist TTP273 Type 2 Diabetes Nrf2/Bach1 Modulator HPP971 /HPP3033 Oxidative Inflammatory Indications Mavodelpar (HPP593) PPAR-𝛿 Agonist Dyslipidemia Muscle Atrophy Broader Portfolio Continues to Offer Additional Upside and Shareholder Value Pipeline candidates, including cadisegliatin, are under investigation and the safety and efficacy has not been established. There is no guarantee that these products will receive health authority approval or become commercially available for the use(s) being investigated Global
18 Cadisegliatin: Late-Stage Program with Potential to be the First Approved Oral Adjunct Therapy for T1D in the U.S. Derisked by Phase 1 and 2 data (n>500) which showed positive impact on hypoglycemia and HbA1C Granted Breakthrough Therapy designation by FDA Completed $51M PIPE in February 2024 with support of healthcare-focused investors, including Breakthrough T1D Fund (f/k/a JDRF T1D Fund) Topline Phase 3 data expected in 2H2026

19 Nasdaq: VTVT Thank You ! May 2025