
from absci import de_novo_model model = de_novo_model.load_latest() antigen = model.load_pdb("7olz.pdb", chain="A") antibodies = model.predict(antigen, N=300000) from absci_library import codon_optimizer library = codon_optimizer.reverse_translate(library) library.to_csv("covid-antibody-designs.csv") library.to_wet_lab(assay="ACE") from absci import lead_opt_model lead_optimizer = lead_opt_model.load_latest() library.naturalness = lead_optimizer.naturalness(library) lead_optimizer.optimize(library).to_wet_lab(as say="SPR") from absci import genetic_algorithm; parameters=["maximize|binding_affinity:pH=7.5", "minimize|binding_affinity:pH=6.0", "maximize|human_naturalness"]; library = genetic_algorithm.multiparametric_optimization(library, parameters, evolutions=100); library.to_wet_lab(assays=["ACE", "SPR", "Bioassays"]) C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . CORPORATE PRESENTATION SUMMER 2025
2C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . Disclaimers Forward-Looking Statements Certain statements in this presentation that are not historical facts are considered forward-looking within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, including statements containing the words “will,” “may,” “anticipates,” “plans,” “believes,” “forecast,” “estimates,” “expects,” “predicts,” “advancing,” “aim,” and “intends,” or similar expressions. We intend these forward-looking statements, including statements regarding our strategy, our expectations regarding the clinical, therapeutic and market potential of product candidates discovered and developed through our platform; the potential advantages of our technology and the assets in our internal pipeline; our ability to achieve catalysts in our preclinical and clinical development programs, such as the initiation of IND-enabling studies and Phase 1 clinical development and the receipt of clinical data; the anticipated timing of such events; the expected evolution of our portfolio over time; guidance regarding cash, cash equivalents and our projected cash runway, our future operations, internal research and technological development activities, estimated speed and cost advantages of leveraging our AI drug creation platform; our expectations regarding the status and progress of our existing partnerships and our plans for potential new partnerships; our expected operational efficiencies, research and technology development collaboration efforts, growth plans, prospects, plans and objectives of management, to be covered by the safe harbor provisions for forward-looking statements contained in Section 27A of the Securities Act and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act, and we make this statement for purposes of complying with those safe harbor provisions. These forward-looking statements reflect our current views about our plans, intentions, expectations, strategies, and prospects, which are based on the information currently available to us and on assumptions we have made. We can give no assurance that the plans, intentions, expectations, or strategies will be attained or achieved, and, furthermore, actual results may differ materially from those described in the forward-looking statements and will be affected by a variety of risks and factors that are beyond our control, including, without limitation, risks and uncertainties relating to the development of our technology as well as the assets in our internal pipeline, our ability to secure milestone payments and royalties, and our ability to effectively conduct research, drug discovery and development activities with respect to our internal programs and to collaborate with our partners or potential partners with respect to their research, drug discovery and development activities; along with those risks set forth in our most recent periodic report filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, as well as discussions of potential risks, uncertainties, and other important factors in our subsequent filings with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. Except as required by law, we assume no obligation to update publicly any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events, or otherwise. Market and Statistical Information This presentation also contains estimates and other statistical data made by independent parties and by us relating to market size and growth and other industry data. These data involve a number of assumptions and limitations, and you are cautioned not to give undue weight to such estimates. We have not independently verified the data generated by independent parties and cannot guarantee their accuracy or completeness. Trademark usage This presentation/document/webpage contains references to our trademarks and service marks and to those belonging to third parties. Absci®, ®, SoluPro®, Bionic SoluPro® and SoluPure® are Absci registered trademarks with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. We also use various other trademarks, service marks and trade names in our business, including the Absci AI logo mark ( ), the Unlimit with us mark ( ), Denovium, Integrated Drug Creation, HiPrBind, and IgDesign. All other trademarks, service marks or trade names referred to in this presentation/document/webpage are the property of their respective owners. Solely for convenience, the trademarks and trade names in this presentation/document/webpage may be referred to with or without the trademark symbols, but references which omit the symbols should not be construed as any indicator that their respective owners will not assert, to the fullest extent under applicable law, their rights thereto.

3C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . Data-first generative AI for Drug Creation™ P I P E L I N E W I T H N E A R - T E R M C A T A L Y S T N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . A P R O V E N A I × B I O P L A T F O R M LEADING AI MODELS De novo AI models now unlock first-in-class biology by cracking tough epitopes—from HIV’s caldera to ion channels PURPOSE BUILT TEAM 10+ approved drugs by our scientists + AI talent from OpenAI, Google, Tesla, NVIDIA. INTEGRATED DATA FLYWHEEL 77 k ft² automated lab generating hundreds of millions of sequence-function datapoints since 2020 A B S - 1 0 1 (anti-TL1A) Phase 1 clinical trial initiated in May 2025. Interim readout expected 2H2025 A B S - 2 0 1 (anti-prolactin receptor) IND-enabling studies on track for anti-PRLR antibody targeting androgenetic alopecia—Anticipated Phase 1/2a start early 2026, with interim efficacy expected 2H2026. E A R L Y P I P E L I N E Advancing early-stage oncology and I&I programs including ABS-301, ABS-501, and TL1A bi-specific PIPELINE MOMENTUM Anticipate two clinical-stage assets within 12 months
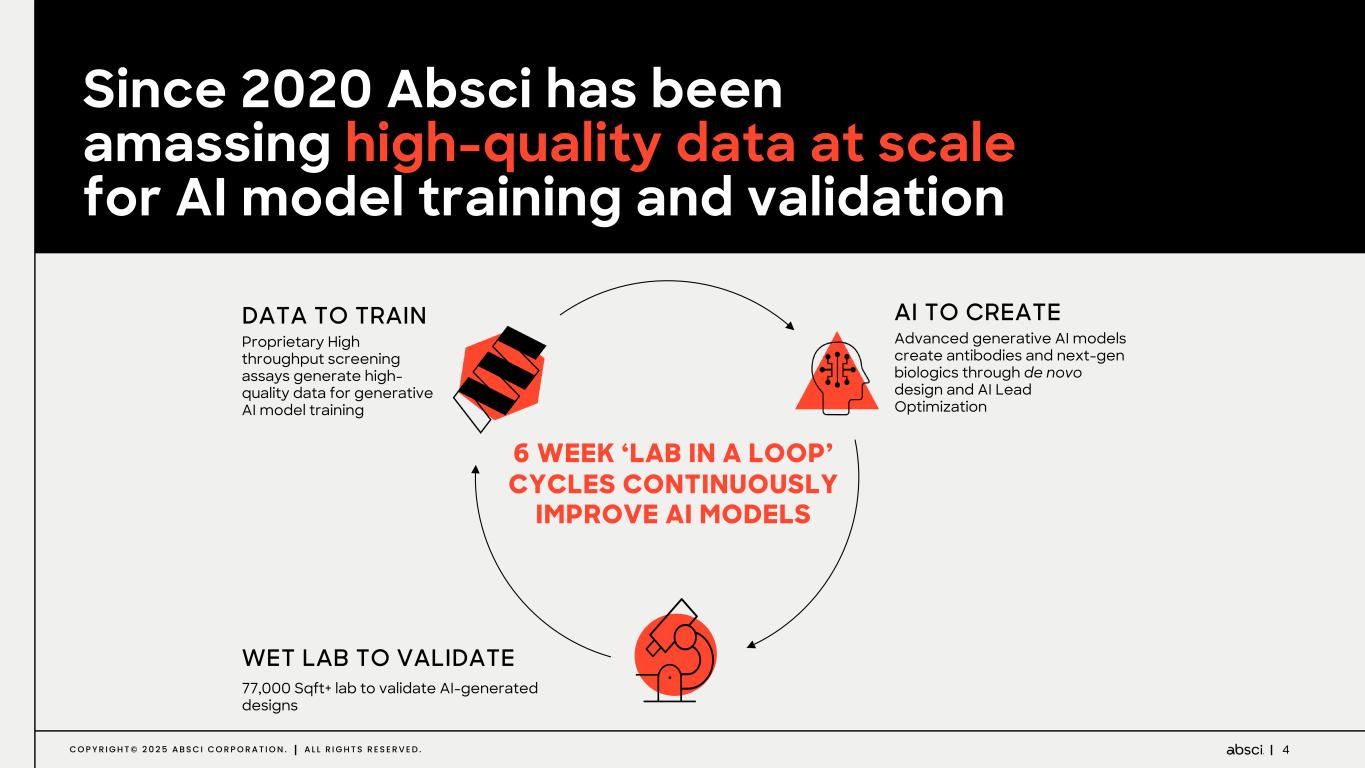
4C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . Since 2020 Absci has been amassing high-quality data at scale for AI model training and validation DATA TO TRAIN Proprietary High throughput screening assays generate high- quality data for generative AI model training WET LAB TO VALIDATE 77,000 Sqft+ lab to validate AI-generated designs AI TO CREATE Advanced generative AI models create antibodies and next-gen biologics through de novo design and AI Lead Optimization 6 WEEK ‘LAB IN A LOOP’ CYCLES CONTINUOUSLY IMPROVE AI MODELS
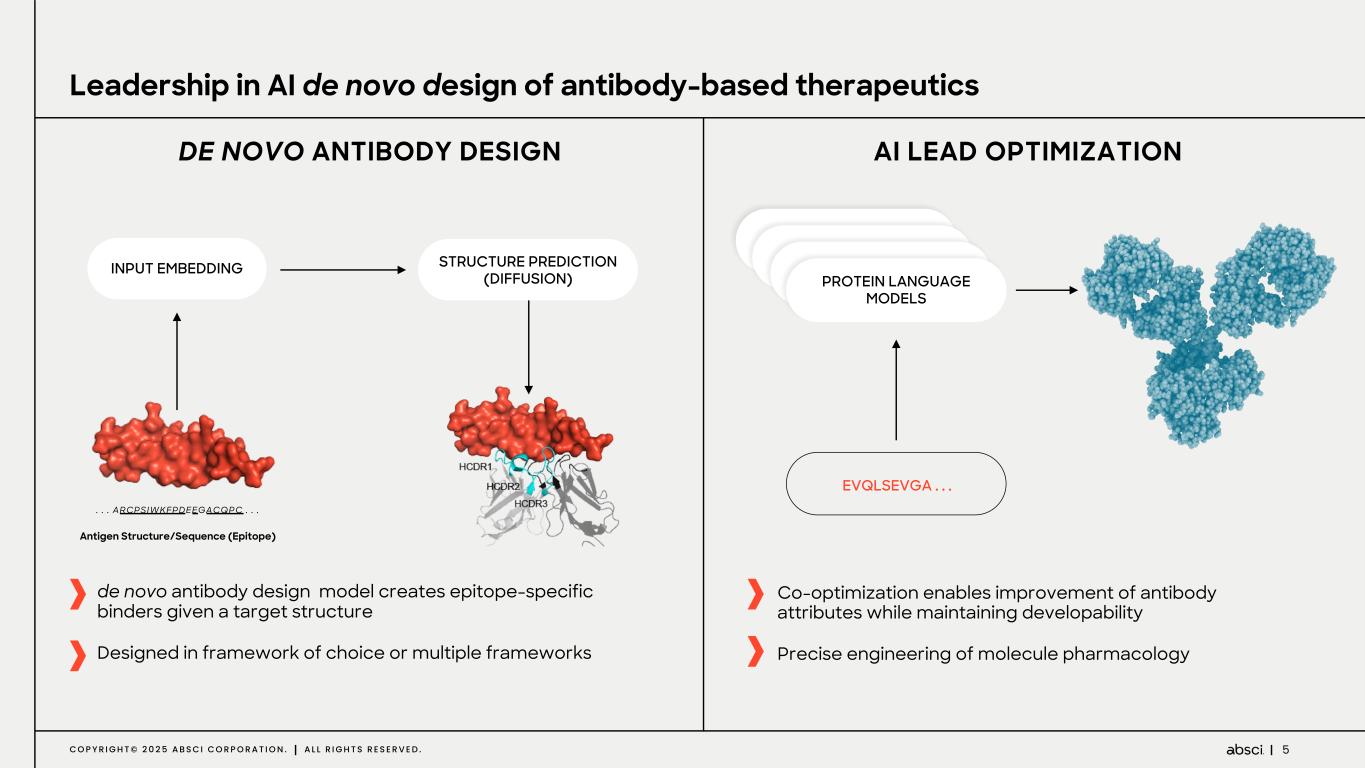
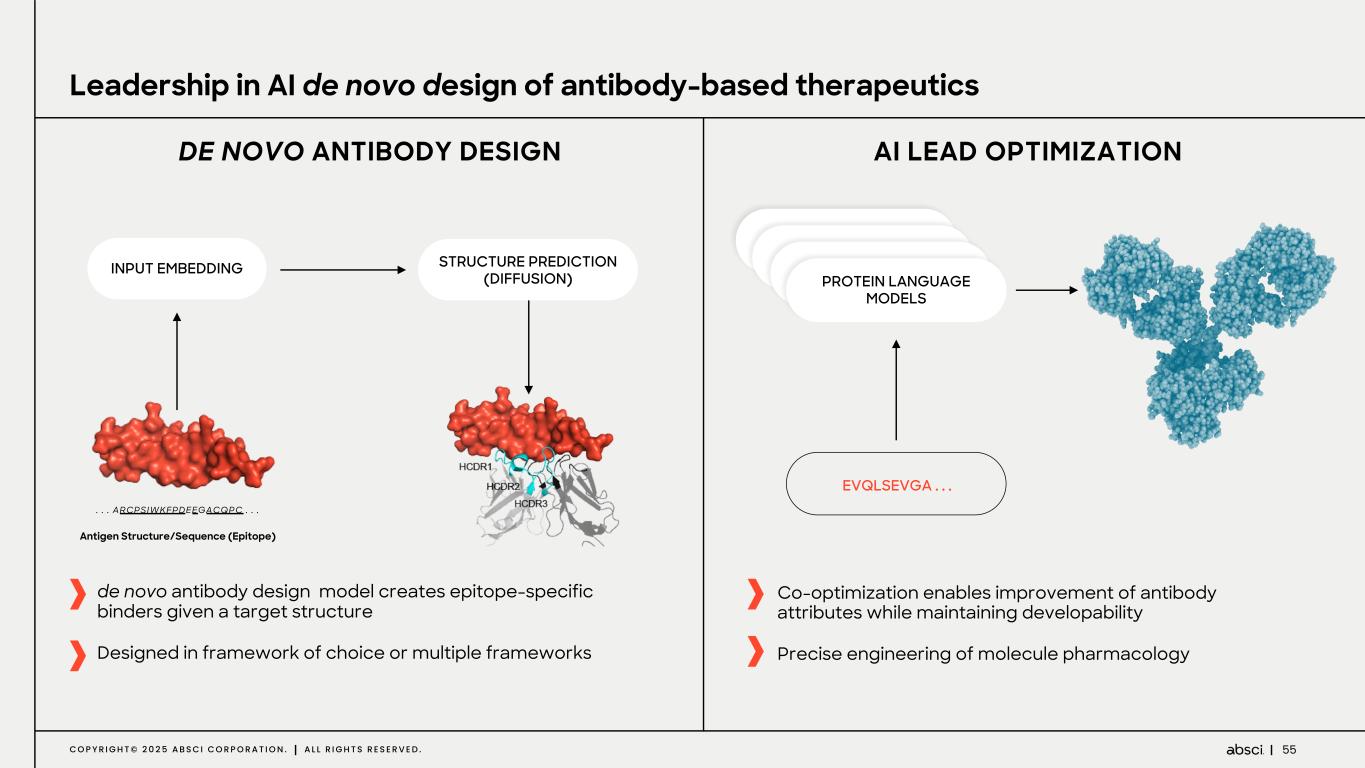
5C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . Leadership in AI de novo design of antibody-based therapeutics EVQLSEVGA . . . de novo antibody design model creates epitope-specific binders given a target structure Designed in framework of choice or multiple frameworks INPUT EMBEDDING STRUCTURE PREDICTION (DIFFUSION) . . . ARCPSIWKFPDEEGACQPC . . . Antigen Structure/Sequence (Epitope) PROTEIN LANGUAGE MODELS Co-optimization enables improvement of antibody attributes while maintaining developability Precise engineering of molecule pharmacology AI LEAD OPTIMIZATIONDE NOVO ANTIBODY DESIGN
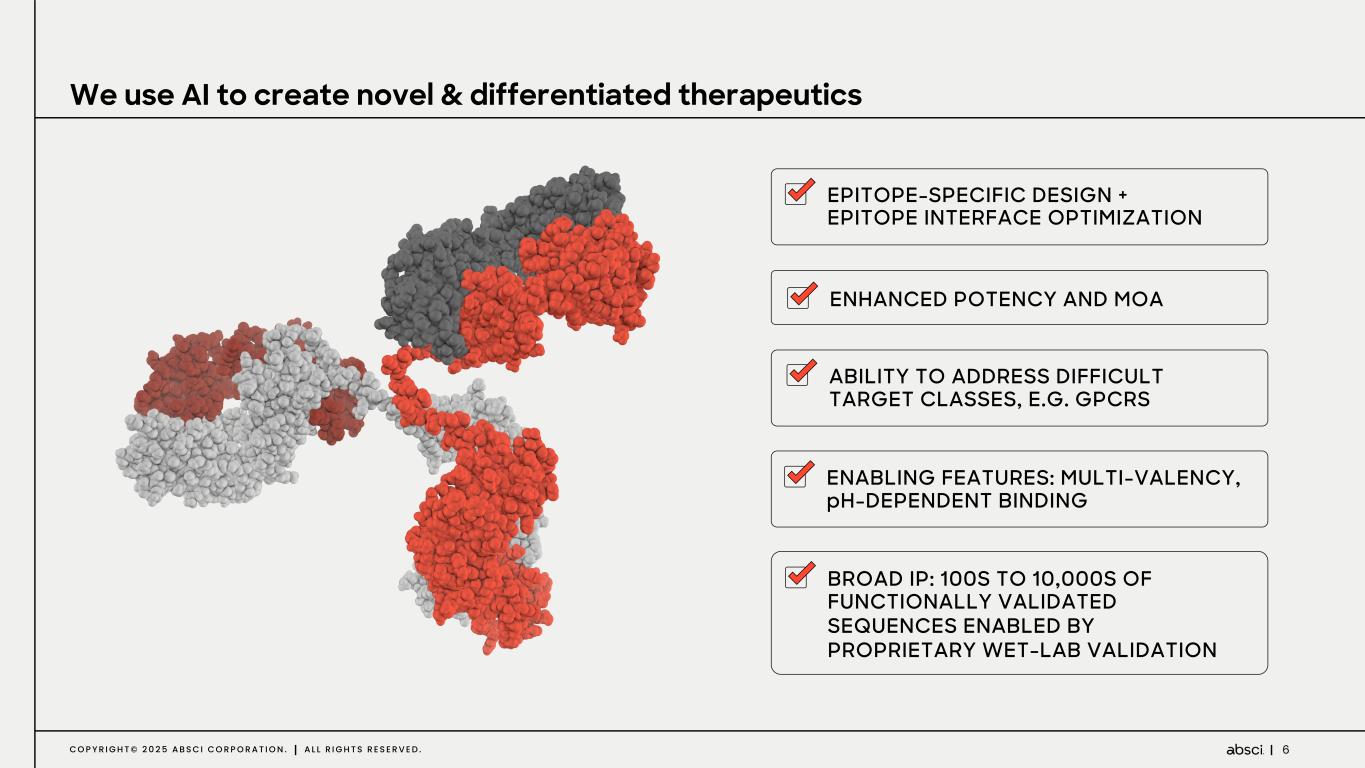
6C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . ENABLING FEATURES: MULTI-VALENCY, pH-DEPENDENT BINDING ABILITY TO ADDRESS DIFFICULT TARGET CLASSES, E.G. GPCRS EPITOPE-SPECIFIC DESIGN + EPITOPE INTERFACE OPTIMIZATION BROAD IP: 100S TO 10,000S OF FUNCTIONALLY VALIDATED SEQUENCES ENABLED BY PROPRIETARY WET-LAB VALIDATION ENHANCED POTENCY AND MOA We use AI to create novel & differentiated therapeutics
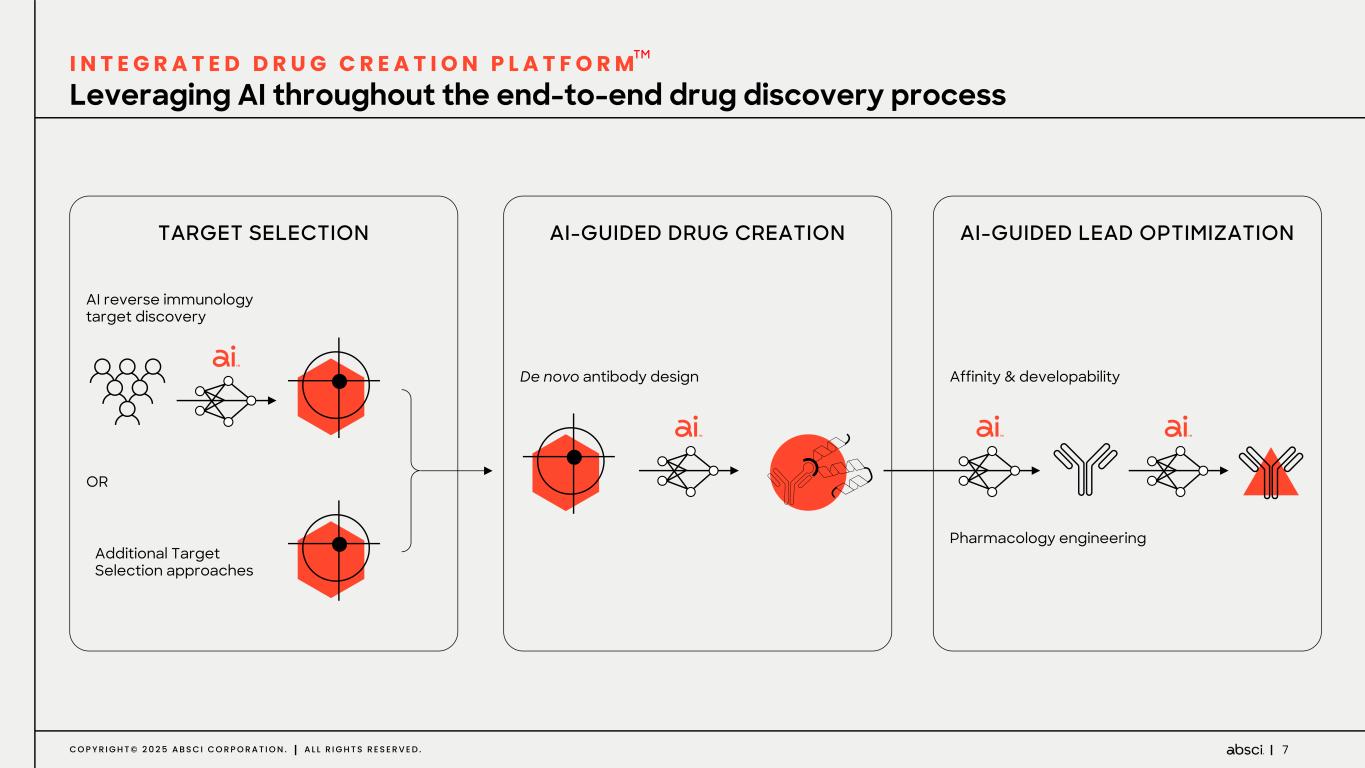
7C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . Leveraging AI throughout the end-to-end drug discovery process I N T E G R A T E D D R U G C R E A T I O N P L A T F O R M TARGET SELECTION AI reverse immunology target discovery OR Additional Target Selection approaches AI-GUIDED DRUG CREATION De novo antibody design AI-GUIDED LEAD OPTIMIZATION Affinity & developability Pharmacology engineering TM
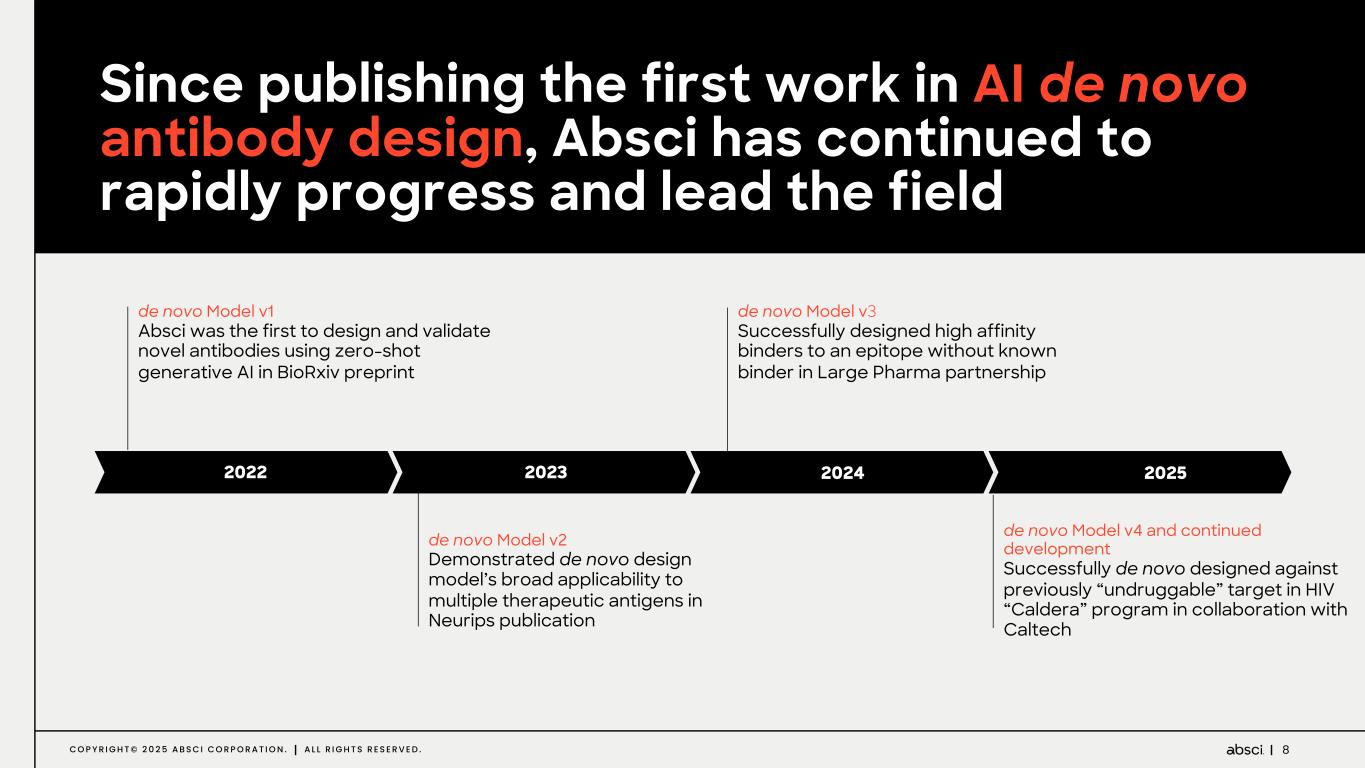
8C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . de novo Model v1 Absci was the first to design and validate novel antibodies using zero-shot generative AI in BioRxiv preprint de novo Model v2 Demonstrated de novo design model’s broad applicability to multiple therapeutic antigens in Neurips publication de novo Model v3 Successfully designed high affinity binders to an epitope without known binder in Large Pharma partnership de novo Model v4 and continued development Successfully de novo designed against previously “undruggable” target in HIV “Caldera” program in collaboration with Caltech 2022 2023 2024 2025 Since publishing the first work in AI de novo antibody design, Absci has continued to rapidly progress and lead the field
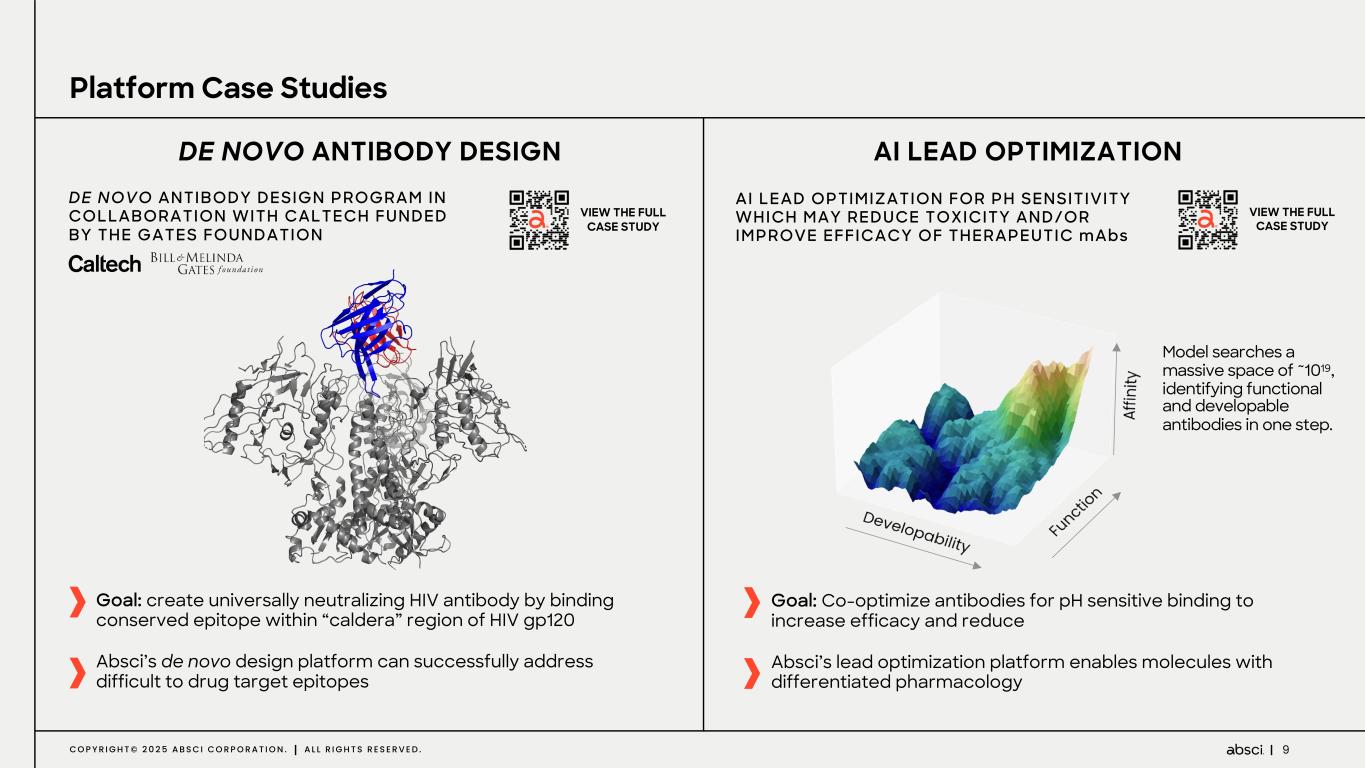
9C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . Platform Case Studies AI LEAD OPTIMIZATIONDE NOVO ANTIBODY DESIGN Goal: create universally neutralizing HIV antibody by binding conserved epitope within “caldera” region of HIV gp120 Absci’s de novo design platform can successfully address difficult to drug target epitopes Goal: Co-optimize antibodies for pH sensitive binding to increase efficacy and reduce Absci’s lead optimization platform enables molecules with differentiated pharmacology AI LEAD OPTIMIZATION FOR PH SENSITIVITY WHICH MAY REDUCE TOXICITY AND/OR IMPROVE EFFICACY OF THERAPEUTIC mAbs VIEW THE FULL CASE STUDY DE NOVO ANTIBODY DESIGN PROGRAM IN COLLABORATION WITH CALTECH FUNDED BY THE GATES FOUNDATION VIEW THE FULL CASE STUDY Model searches a massive space of ~1019, identifying functional and developable antibodies in one step.

10C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . ”Multilingual” team with expertise in AI and drug creation Sean McClain Founder, CEO & Director Andreas Busch, PHD Chief Innovation Officer Zach Jonasson, PHD Chief Financial Officer & Chief Business Officer Amir Shanehsazzadeh SVP, Chief AI Officer Karin Wierinck Chief People Officer Christian Stegmann, PHD SVP, Drug Creation Christine Lemke, DVM SVP, Portfolio & Growth Strategy Shelby Walker, JD Chief Legal Officer Karen Mcginnis, CPA Former Chief Accounting Officer, Illumina Joseph Sirosh, PHD Former CTO, Compass VP, Amazon & Microsoft Dan Rabinovitsj VP Hardware Engineering, Meta Frans Van Houten Chairman of the Board Former CEO, Royal Phillips Sir Mene Pangalos, PHD Former EVP R&D AstraZeneca Sean McClain Founder, CEO & Board Director Ian McInnes, PHD Vice Principal and Head of College University of Glasgow Hubert Truebel, MD, PHD, MBA Chief Medical Officer AiCuris Luis Diaz, MD Head, Division of Solid Tumor Oncology Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center John Wherry, PHD Director, Institute for Immunology & Immune Health, University of Pennsylvania Victor Greiff, PHD Associate Professor University of Oslo Sir Mene Pangalos, PHD Co-Chair SAB Former EVP R&D AstraZeneca Andreas Busch, PHD Co-Chair SAB Chief Innovation Officer L E A D E R S H I P T E A M B O A R D O F D I R E C T O R S S C I E N T I F I C A D V I S O R Y B O A R D E X P E R T I S E & B A C K G R O U N D F R O M Penelope Chief Morale Officer O U R P E O P L E Trademarks, service marks or trade names referred to herein are the intellectual property of their respective owners. Use of this IP does not imply affiliation, endorsement or sponsorship of any kind Mary Szela CEO & President TriSalus Life Sciences

11C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . ~150 77,000+ Square Feet >$600M Unlimiters with deep experience in AI, drug discovery, immunology, and synthetic biology State-of-the-art drug creation and wet lab space in Vancouver WA, Absci AI Research (AAIR) lab in NYC, and the Innovation Centre in Zug Switzerland Capital raised to date Biologics drug discovery expertise from: Leading AI team with expertise from: Absci’s Talent and Infrastructure for Better Biologics Faster Trademarks, service marks or trade names referred to herein are the intellectual property of their respective owners. Use of this IP does not imply affiliation, endorsement or sponsorship of any kind W E L L - P O S I T I O N E D T O D E L I V E R
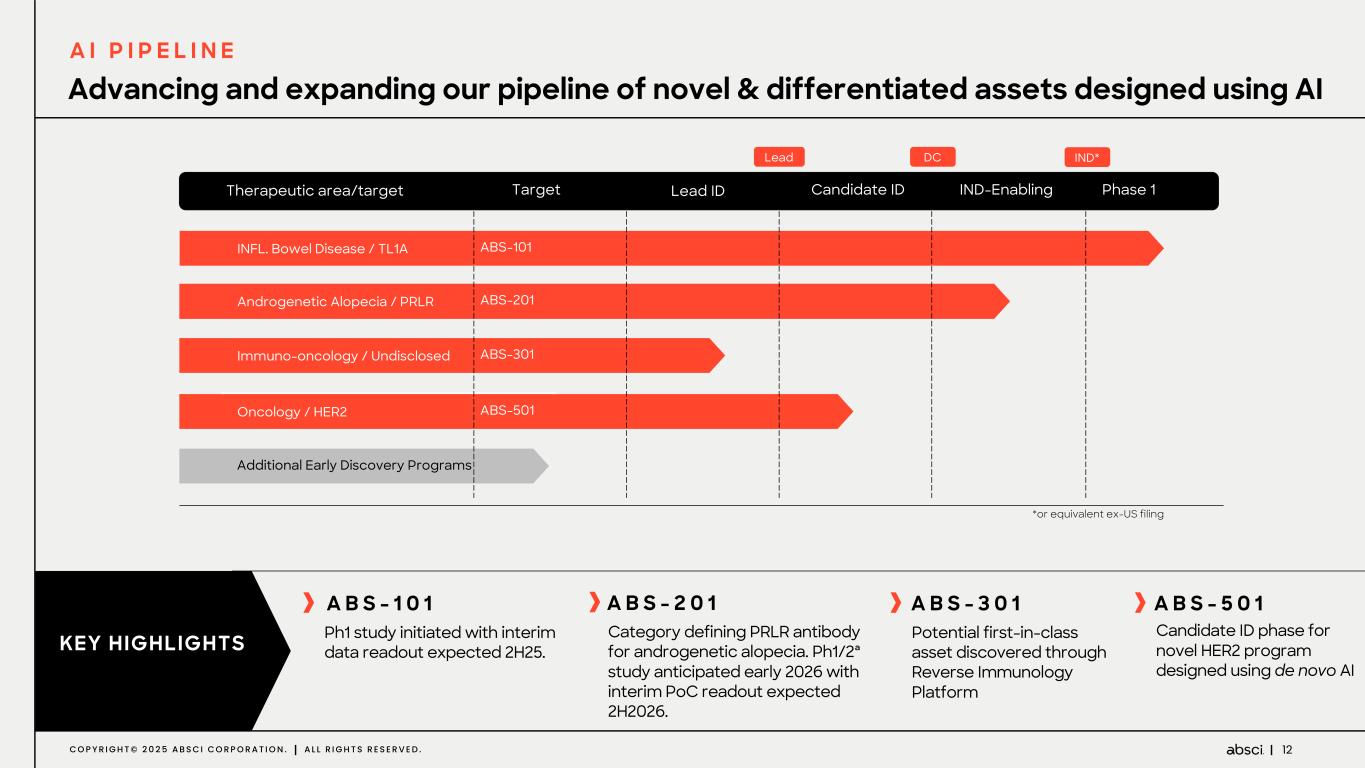
12C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . INFL. Bowel Disease / TL1A Androgenetic Alopecia / PRLR Immuno-oncology / Undisclosed Additional Early Discovery Programs Target Lead ID Candidate ID IND-Enabling ABS-101 ABS-201 ABS-301 Phase 1 Oncology / HER2 ABS-501 IND* Therapeutic area/target DC Advancing and expanding our pipeline of novel & differentiated assets designed using AI Lead *or equivalent ex-US filing A B S - 1 0 1 Ph1 study initiated with interim data readout expected 2H25. KEY HIGHLIGHTS A B S - 2 0 1 Category defining PRLR antibody for androgenetic alopecia. Ph1/2ª study anticipated early 2026 with interim PoC readout expected 2H2026. A B S - 3 0 1 Potential first-in-class asset discovered through Reverse Immunology Platform A B S - 5 0 1 Candidate ID phase for novel HER2 program designed using de novo AI A I P I P E L I N E
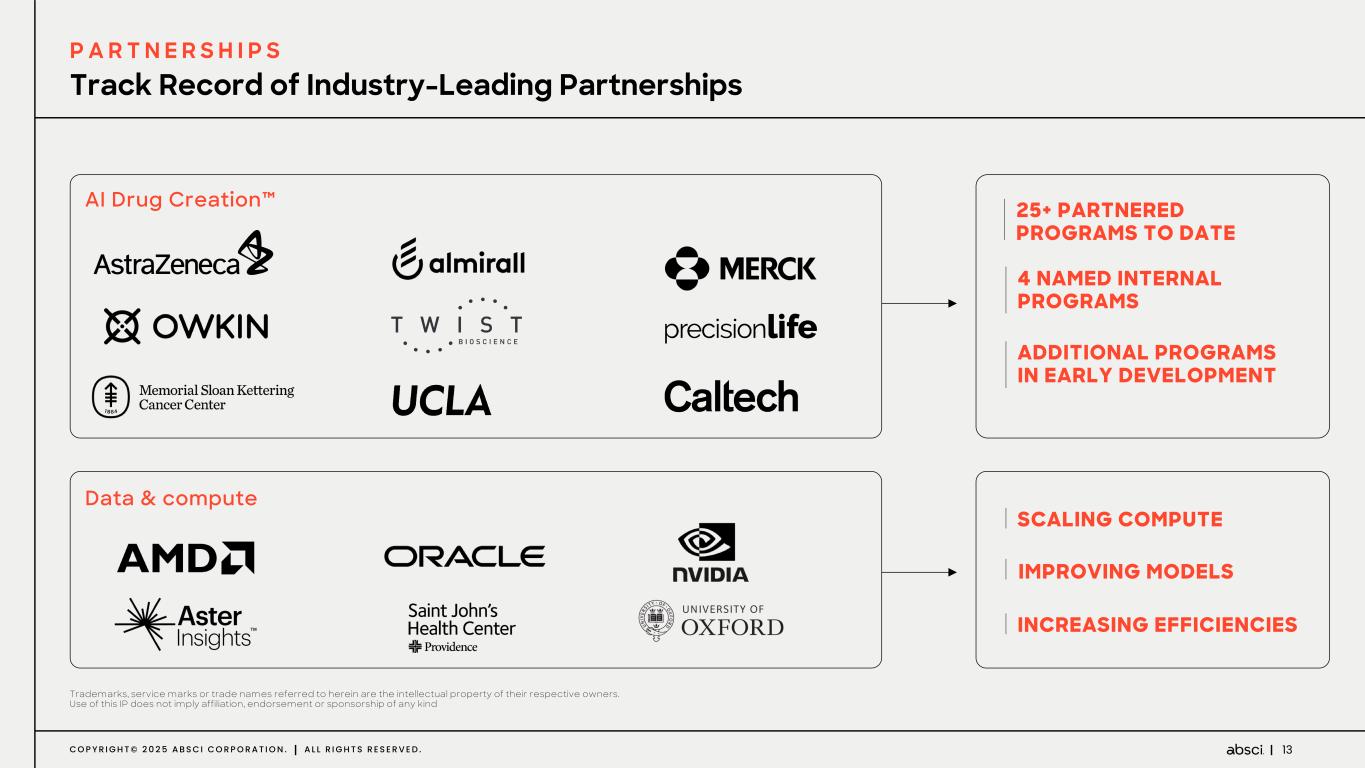
13C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . AI Drug Creation™ Data & compute 25+ PARTNERED PROGRAMS TO DATE SCALING COMPUTE 4 NAMED INTERNAL PROGRAMS ADDITIONAL PROGRAMS IN EARLY DEVELOPMENT IMPROVING MODELS INCREASING EFFICIENCIES Trademarks, service marks or trade names referred to herein are the intellectual property of their respective owners. Use of this IP does not imply affiliation, endorsement or sponsorship of any kind Track Record of Industry-Leading Partnerships P A R T N E R S H I P S
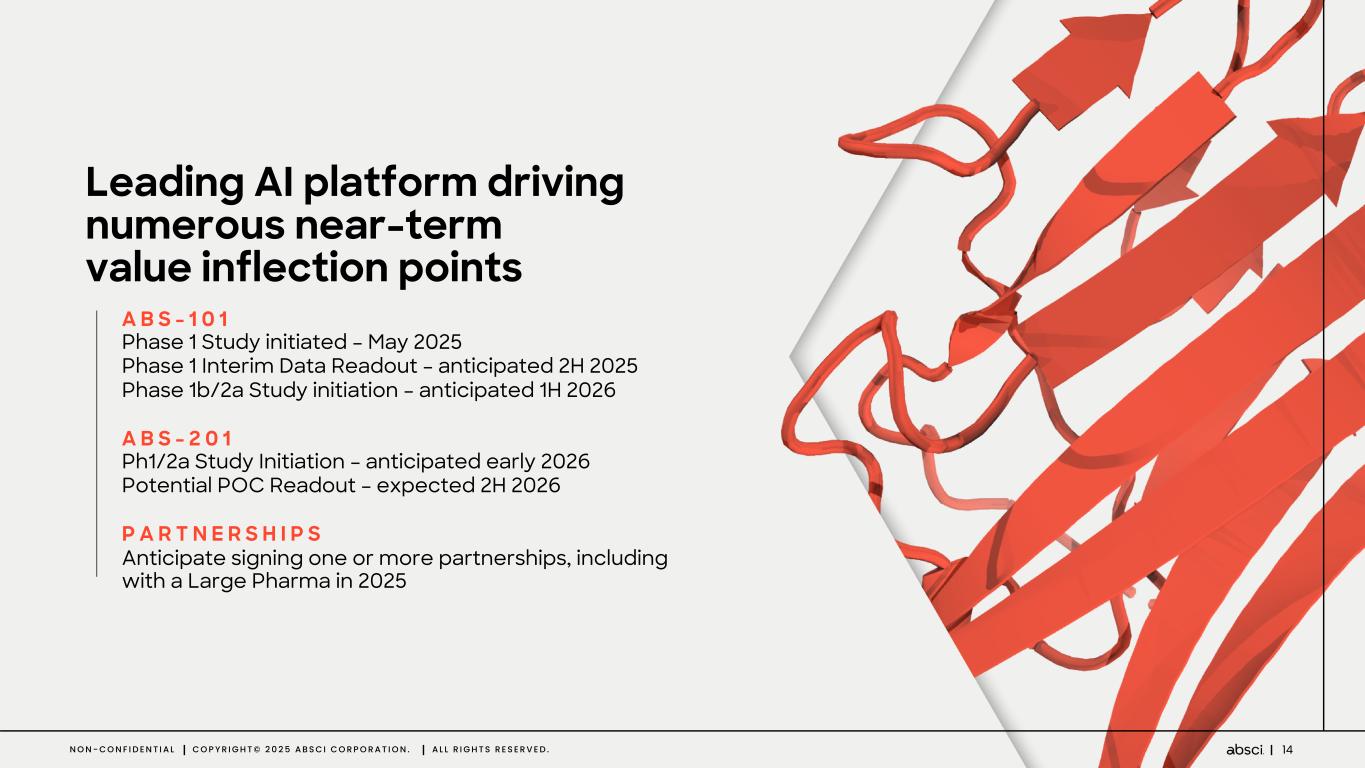
14N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . Leading AI platform driving numerous near-term value inflection points A B S - 1 0 1 Phase 1 Study initiated – May 2025 Phase 1 Interim Data Readout – anticipated 2H 2025 Phase 1b/2a Study initiation – anticipated 1H 2026 A B S - 2 0 1 Ph1/2a Study Initiation – anticipated early 2026 Potential POC Readout – expected 2H 2026 P A R T N E R S H I P S Anticipate signing one or more partnerships, including with a Large Pharma in 2025

15N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . A B S - 1 0 1 Phase 1 Program initiated in May 2025 • New preclinical data supporting superior immunogenicity profile • Phase 1 Interim data readout expected 2H 2025 A B S - 2 0 1 IND-enabling activities on-track for PRLR (prolactin receptor) program with anticipated initiation of Ph1/2a studies in early 2026 A B S - 3 0 1 Progress of first-in-class asset discovered through Absci’s Reverse Immunology Platform A B S - 5 0 1 Nomination of a potential best-in-class HER2 asset C o n t i n u e d a d v a n c e m e n t o f l e a d a s s e t s D i s c o v e r y o f n e x t a s s e t s Absci’s progress in Drug Creation I N T E R N A L P I P E L I N E
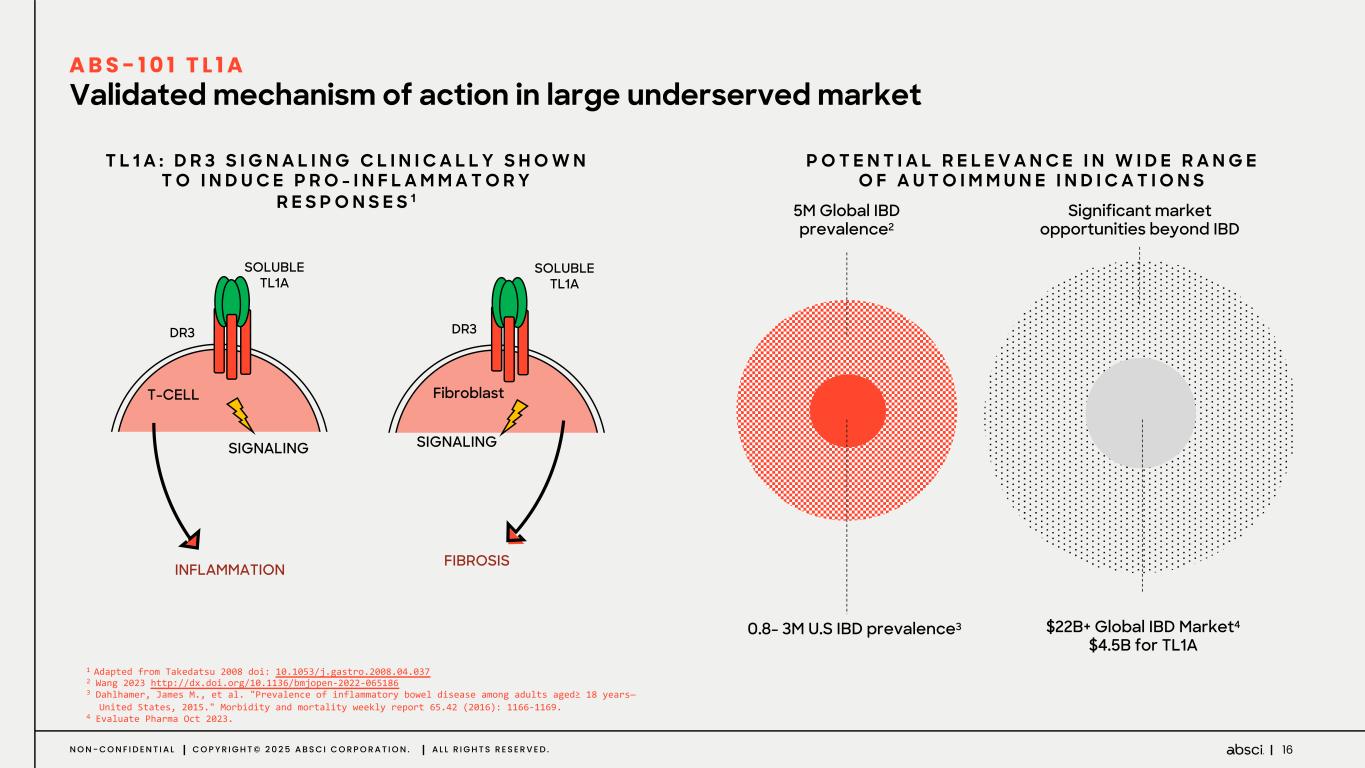
16N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . Validated mechanism of action in large underserved market A B S - 1 0 1 T L 1 A P O T E N T I A L R E L E V A N C E I N W I D E R A N G E O F A U T O I M M U N E I N D I C A T I O N S T L 1 A : D R 3 S I G N A L I N G C L I N I C A L L Y S H O W N T O I N D U C E P R O - I N F L A M M A T O R Y R E S P O N S E S 1 Significant market opportunities beyond IBD $22B+ Global IBD Market4 $4.5B for TL1A 0.8- 3M U.S IBD prevalence3 5M Global IBD prevalence2 1 Adapted from Takedatsu 2008 doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.04.037 2 Wang 2023 http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2022-065186 3 Dahlhamer, James M., et al. "Prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease among adults aged≥ 18 years— United States, 2015." Morbidity and mortality weekly report 65.42 (2016): 1166-1169. 4 Evaluate Pharma Oct 2023. T-CELL Fibroblast SIGNALING SIGNALING FIBROSIS SOLUBLE TL1A DR3 DR3 SOLUBLE TL1A INFLAMMATION
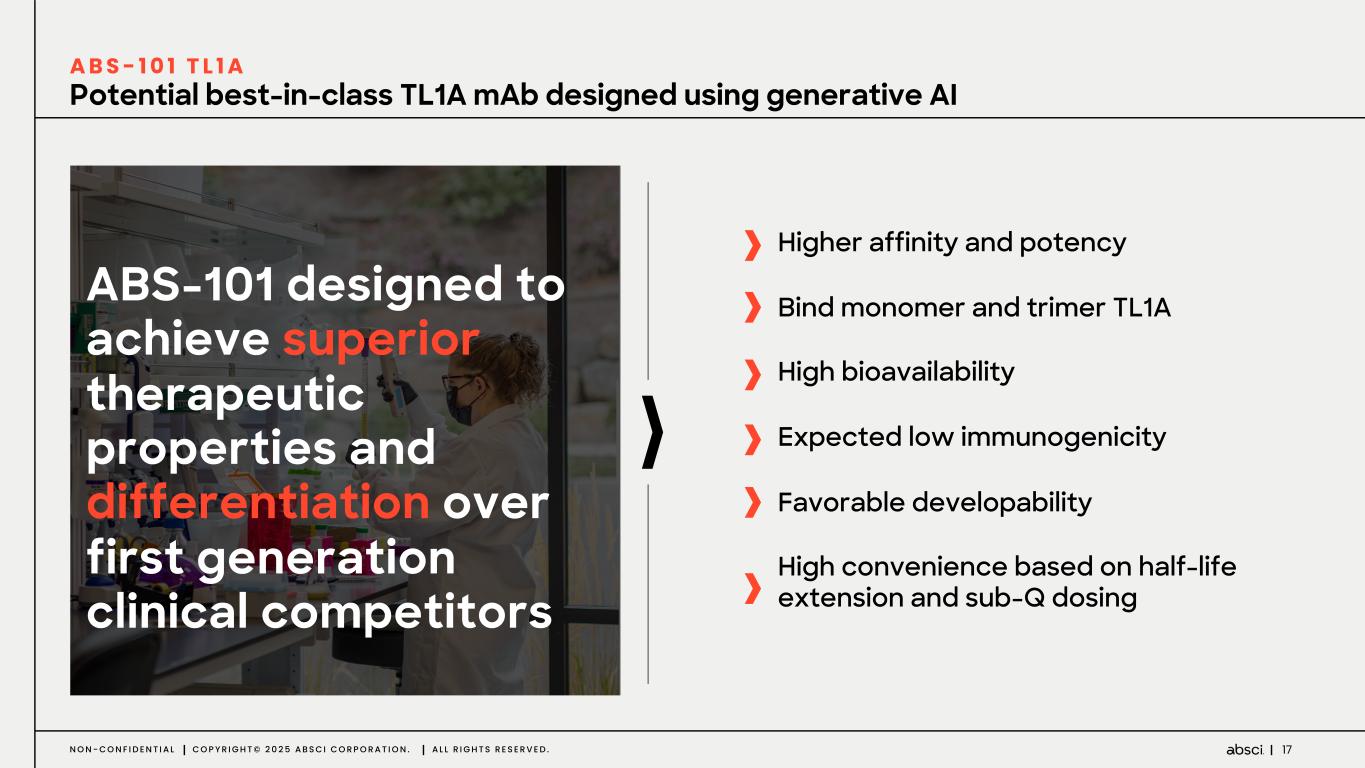
17N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . Potential best-in-class TL1A mAb designed using generative AI ABS-101 designed to achieve superior therapeutic properties and differentiation over first generation clinical competitors A B S - 1 0 1 T L 1 A Higher affinity and potency Bind monomer and trimer TL1A High bioavailability Expected low immunogenicity Favorable developability High convenience based on half-life extension and sub-Q dosing
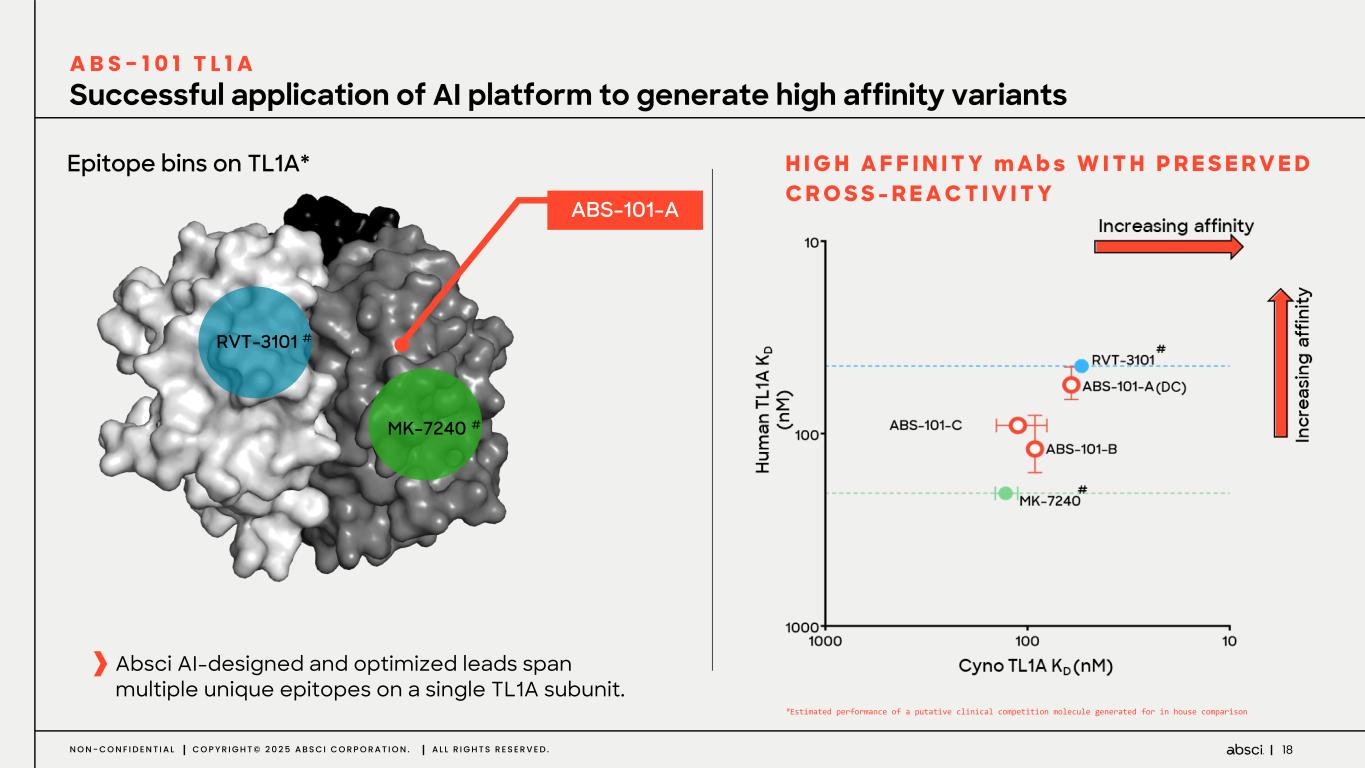
18N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . Successful application of AI platform to generate high affinity variants A B S - 1 0 1 T L 1 A H I G H A F F I N I T Y m A b s W I T H P R E S E R V E D C R O S S - R E A C T I V I T Y MK-7240 # RVT-3101 # Epitope bins on TL1A* ABS-101-A Absci AI-designed and optimized leads span multiple unique epitopes on a single TL1A subunit. #Estimated performance of a putative clinical competition molecule generated for in house comparison
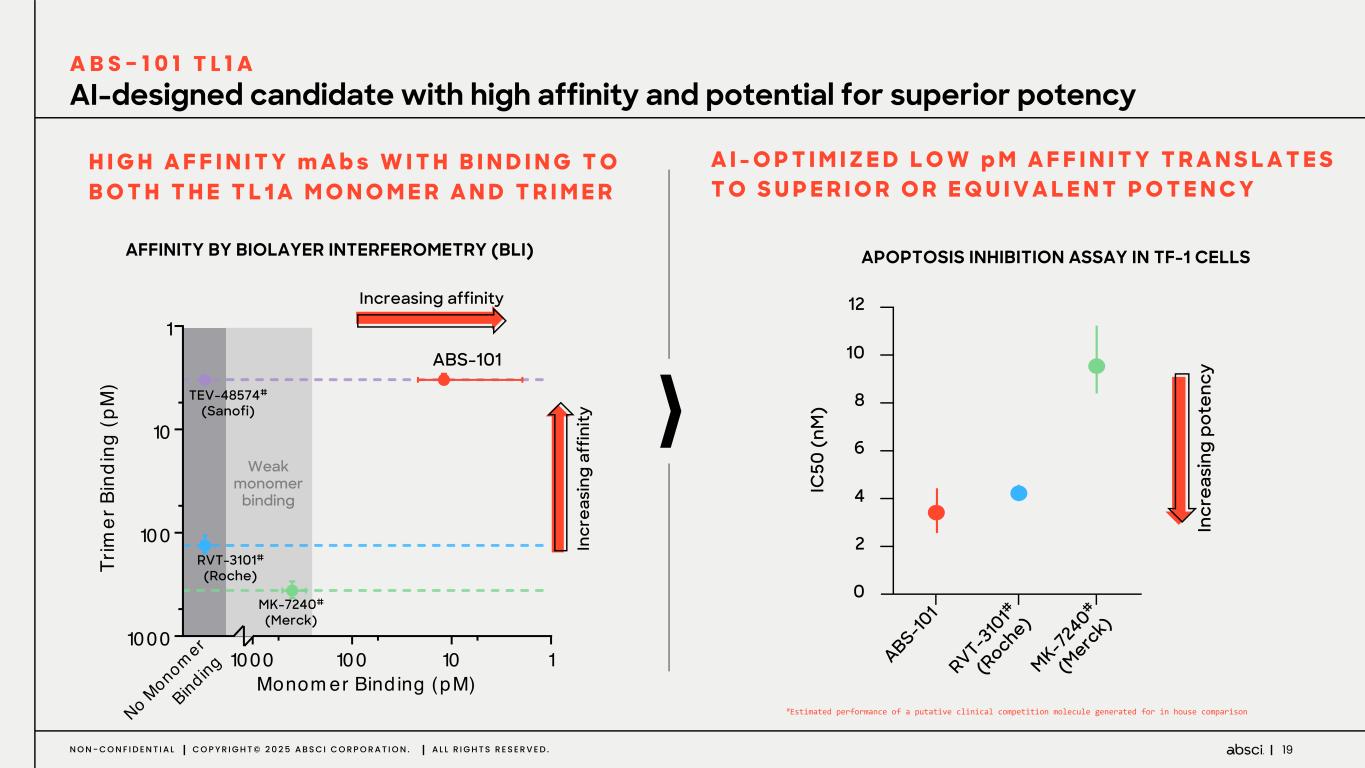
19N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . 1101001000 1 10 100 1000 Monom er Bind ing (pM) Tr im er B in di ng (p M ) No M onomer Bind ing H I G H A F F I N I T Y m A b s W I T H B I N D I N G T O B O T H T H E T L 1 A M O N O M E R A N D T R I M E R A I - O P T I M I Z E D L O W p M A F F I N I T Y T R A N S L A T E S T O S U P E R I O R O R E Q U I V A L E N T P O T E N C Y In cr ea si ng p ot en cy IC 50 ( nM ) 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 ABS-10 1 RVT-3 10 1# (R oche) MK-7 240 # (M erc k) APOPTOSIS INHIBITION ASSAY IN TF-1 CELLSAFFINITY BY BIOLAYER INTERFEROMETRY (BLI) AI-designed candidate with high affinity and potential for superior potency A B S - 1 0 1 T L 1 A Increasing affinity In cr ea si ng a ff in ity Weak monomer binding ABS-101 RVT-3101# (Roche) MK-7240# (Merck) TEV-48574# (Sanofi) #Estimated performance of a putative clinical competition molecule generated for in house comparison
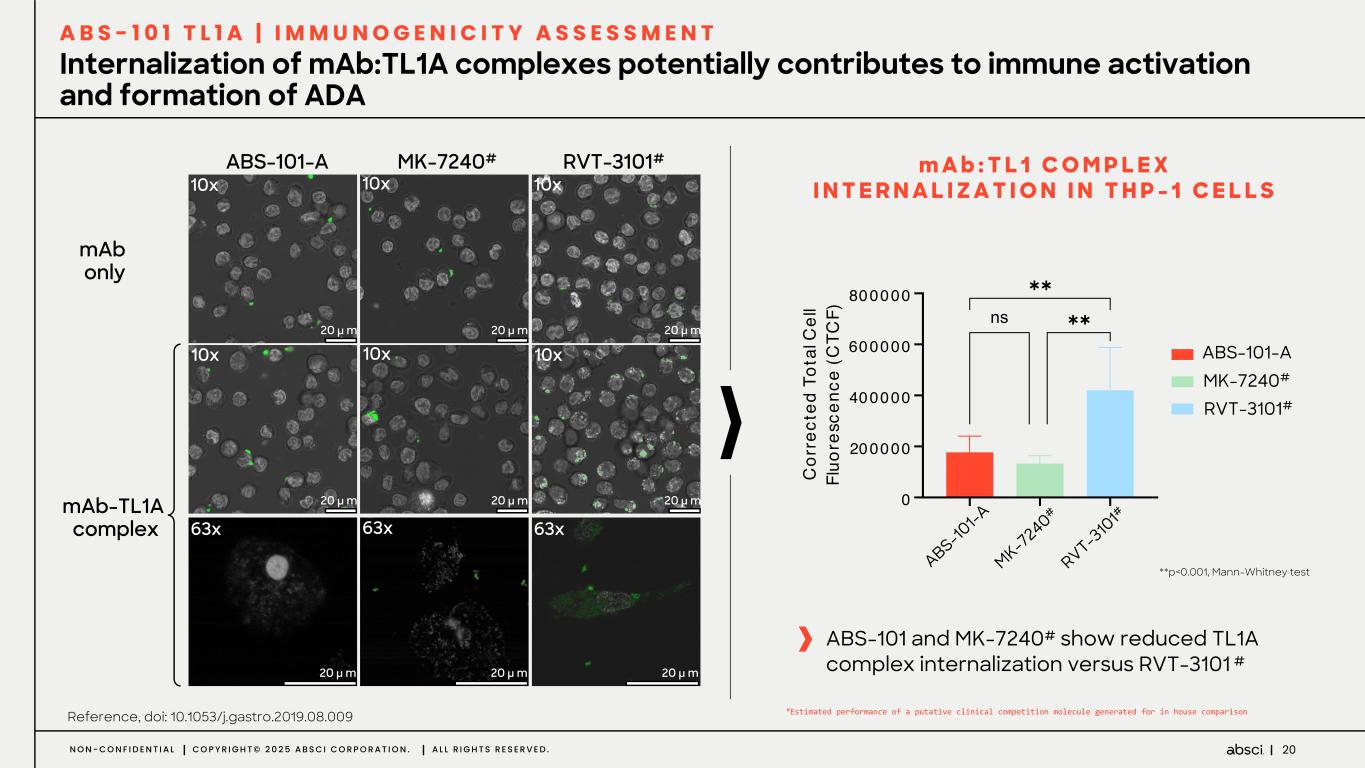
20N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . Internalization of mAb:TL1A complexes potentially contributes to immune activation and formation of ADA A B S - 1 0 1 T L 1 A | I M M U N O G E N I C I T Y A S S E S S M E N T mAb only ABS-101-A RVT-3101#MK-7240# 10x 10x 10x 10x 10x 10x 63x 63x 63x 20 µ m 20 µ m 20 µ m 20 µ m 20 µ m 20 µ m 20 µ m 20 µ m 20 µ m mAb-TL1A complex m A b : T L 1 C O M P L E X I N T E R N A L I Z A T I O N I N T H P - 1 C E L L S **p<0.001, Mann-Whitney test Reference, doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.08.009 ABS-101 and MK-7240# show reduced TL1A complex internalization versus RVT-3101 # AB S- 10 1 MK - 7 24 0 RV T- 310 1 0 200000 400000 600000 800000 C or re ct ed T ot al C el l Fl uo re sc en ce (C TC F) !"#AB&B '(A)*+& ,-KA/B&B M1 !! !! ABS-101-A MK-7240# RVT-3101# S-10 1-A MK-7 240# RVT-3 10 1# #Estimated performance of a putative clinical competition molecule generated for in house comparison
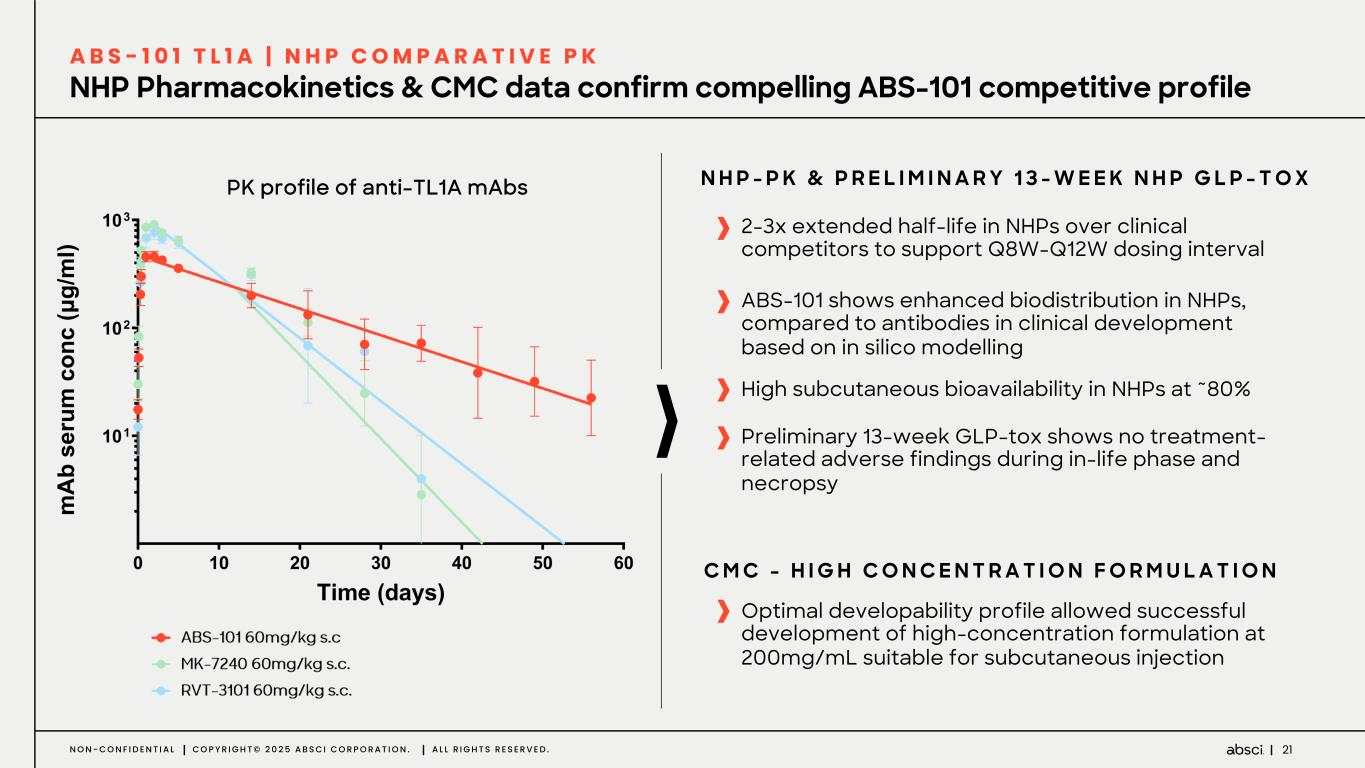
21N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . NHP Pharmacokinetics & CMC data confirm compelling ABS-101 competitive profile A B S - 1 0 1 T L 1 A | N H P C O M P A R A T I V E P K 2-3x extended half-life in NHPs over clinical competitors to support Q8W-Q12W dosing interval ABS-101 shows enhanced biodistribution in NHPs, compared to antibodies in clinical development based on in silico modelling Optimal developability profile allowed successful development of high-concentration formulation at 200mg/mL suitable for subcutaneous injection C M C - H I G H C O N C E N T R A T I O N F O R M U L A T I O N Preliminary 13-week GLP-tox shows no treatment- related adverse findings during in-life phase and necropsy High subcutaneous bioavailability in NHPs at ~80% N H P - P K & P R E L I M I N A R Y 1 3 - W E E K N H P G L P - T O XPK profile of anti-TL1A mAbs
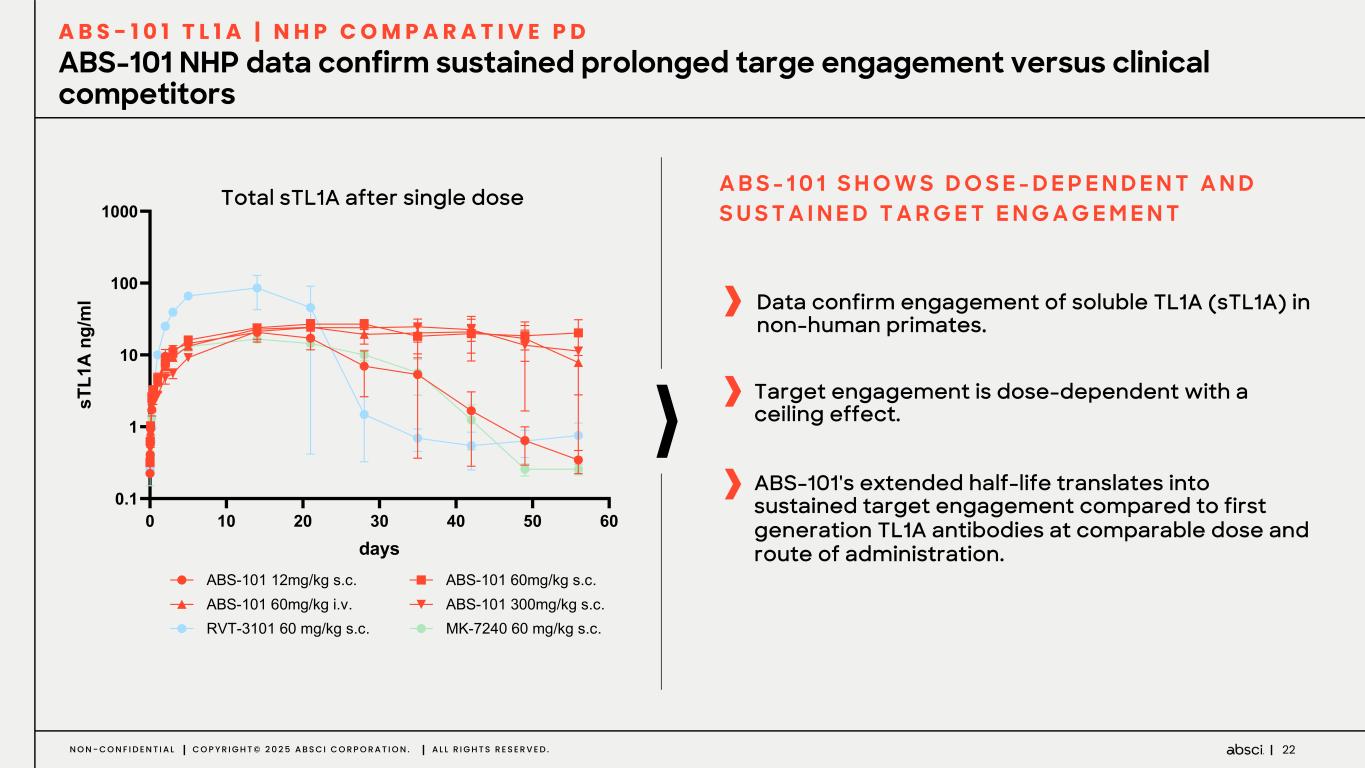
22N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . ABS-101 NHP data confirm sustained prolonged targe engagement versus clinical competitors A B S - 1 0 1 T L 1 A | N H P C O M P A R A T I V E P D ! "! #! A! %! &! '! !(" " "! "!! "!!! )*+, ,- ." L 01 23 4 5 !"#AB&B'B()*+,*'-K/K !"#AB&B'M&)*+,*'-K/K !"#AB&B'M&)*+,*'1K2K !"#AB&B'3&&)*+,*'-K/K 4RSA3B&B'M&')*+,*'-K/K T8AV(:&'M&')*+,*'-K/K Data confirm engagement of soluble TL1A (sTL1A) in non-human primates. A B S - 1 0 1 S H O W S D O S E - D E P E N D E N T A N D S U S T A I N E D T A R G E T E N G A G E M E N T ABS-101's extended half-life translates into sustained target engagement compared to first generation TL1A antibodies at comparable dose and route of administration. Target engagement is dose-dependent with a ceiling effect. Total sTL1A after single dose
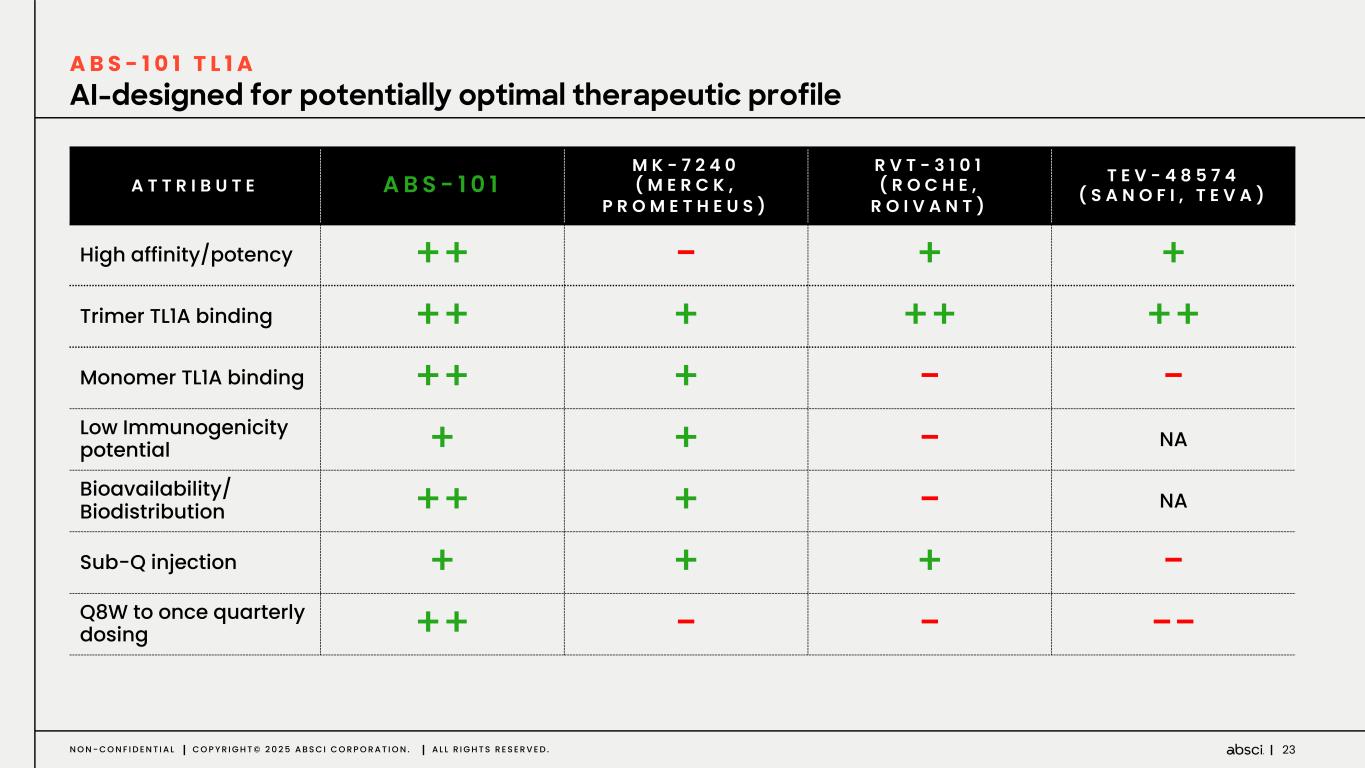
23N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . AI-designed for potentially optimal therapeutic profile A B S - 1 0 1 T L 1 A A T T R I B U T E ABS - 1 0 1 M K - 7 2 4 0 ( M E R C K , P R O M E T H E U S ) R V T - 3 1 0 1 ( R O C H E , R O I V A N T ) T E V - 4 8 5 7 4 ( S A N O F I , T E V A ) High affinity/potency ++ - + + Trimer TL1A binding ++ + ++ ++ Monomer TL1A binding ++ + - - Low Immunogenicity potential + + - NA Bioavailability/ Biodistribution ++ + - NA Sub-Q injection + + + - Q8W to once quarterly dosing ++ - - --
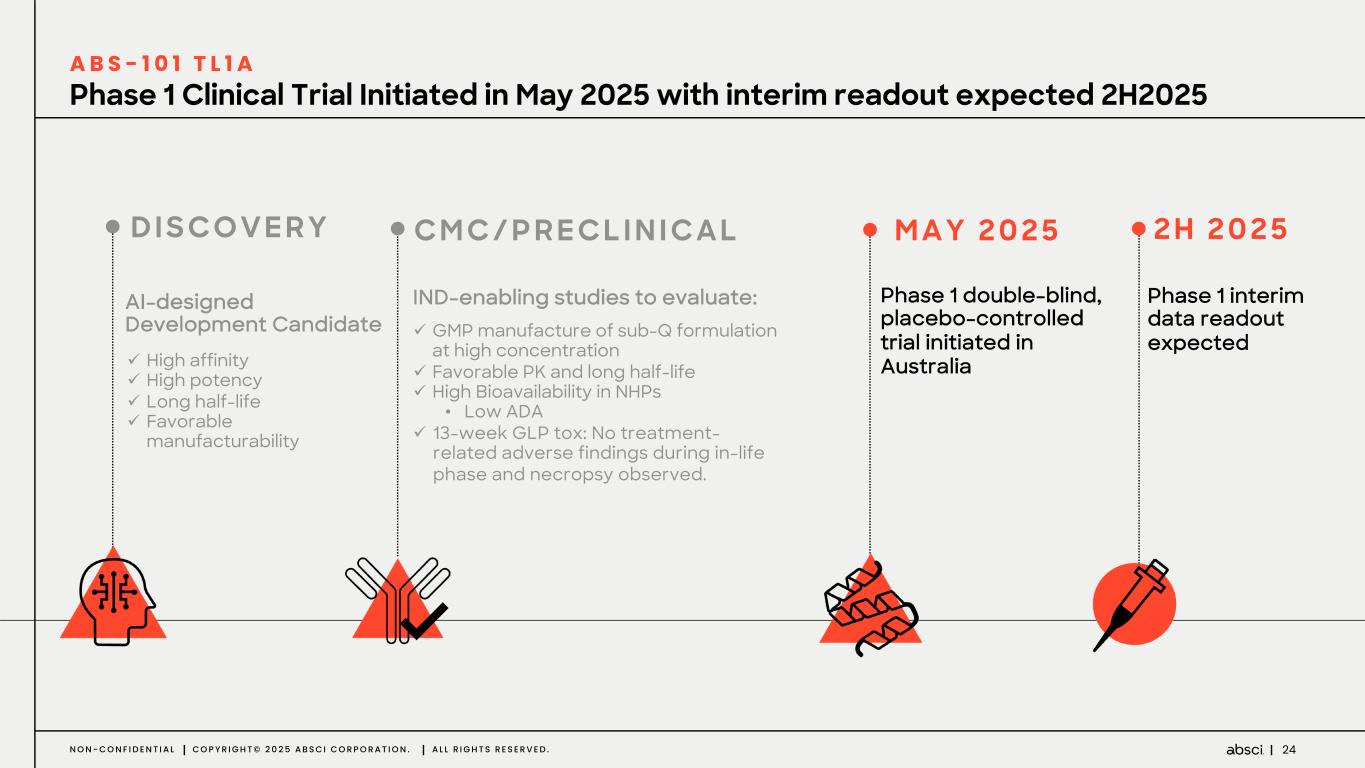
24N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . Phase 1 Clinical Trial Initiated in May 2025 with interim readout expected 2H2025 A B S - 1 0 1 T L 1 A AI-designed Development Candidate ü High affinity ü High potency ü Long half-life ü Favorable manufacturability D I S CO V E R Y C M C / P R E C L I N I C A L M A Y 2 0 2 5 IND-enabling studies to evaluate: ü GMP manufacture of sub-Q formulation at high concentration ü Favorable PK and long half-life ü High Bioavailability in NHPs • Low ADA ü 13-week GLP tox: No treatment- related adverse findings during in-life phase and necropsy observed. Phase 1 double-blind, placebo-controlled trial initiated in Australia Phase 1 interim data readout expected 2 H 2 0 2 5

25N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . A B S - 1 0 1 Continued progress of TL1A asset with FiH in 1H 2025 • New preclinical data supporting superior immunogenicity profile • Phase 1 Interim data readout in 2H 2025 A B S - 2 0 1 IND-enabling activities on-track for PRLR (prolactin receptor) program with anticipated initiation of Ph1/2a studies in early 2026 A B S - 3 0 1 Progress of first-in-class asset discovered through Absci’s Reverse Immunology Platform A B S - 5 0 1 Nomination of a potential best-in-class HER2 asset C o n t i n u e d a d v a n c e m e n t o f l e a d a s s e t s D i s c o v e r y o f n e x t a s s e t s Absci’s progress in Drug Creation I N T E R N A L P I P E L I N E

26N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . ABS-201 has the potential to unlock a wholly new category of therapy in hair “re-growth” Significant unmet clinical need for androgenetic alopecia Large market: approximately 80 million patients in U.S.; highly motivated patient population CLINICAL AND COMMERCIAL UNMET NEED Straightforward clinical development path with potential for early Proof of Concept Low competition, potentially first to U.S. market DEVELOPMENT PATH Strong target validation (efficacy & safety) for treatment of androgenetic alopecia Mode of action conserved across many species Supportive pharmacological profile of ABS-201 SCIENTIFIC RATIONALE
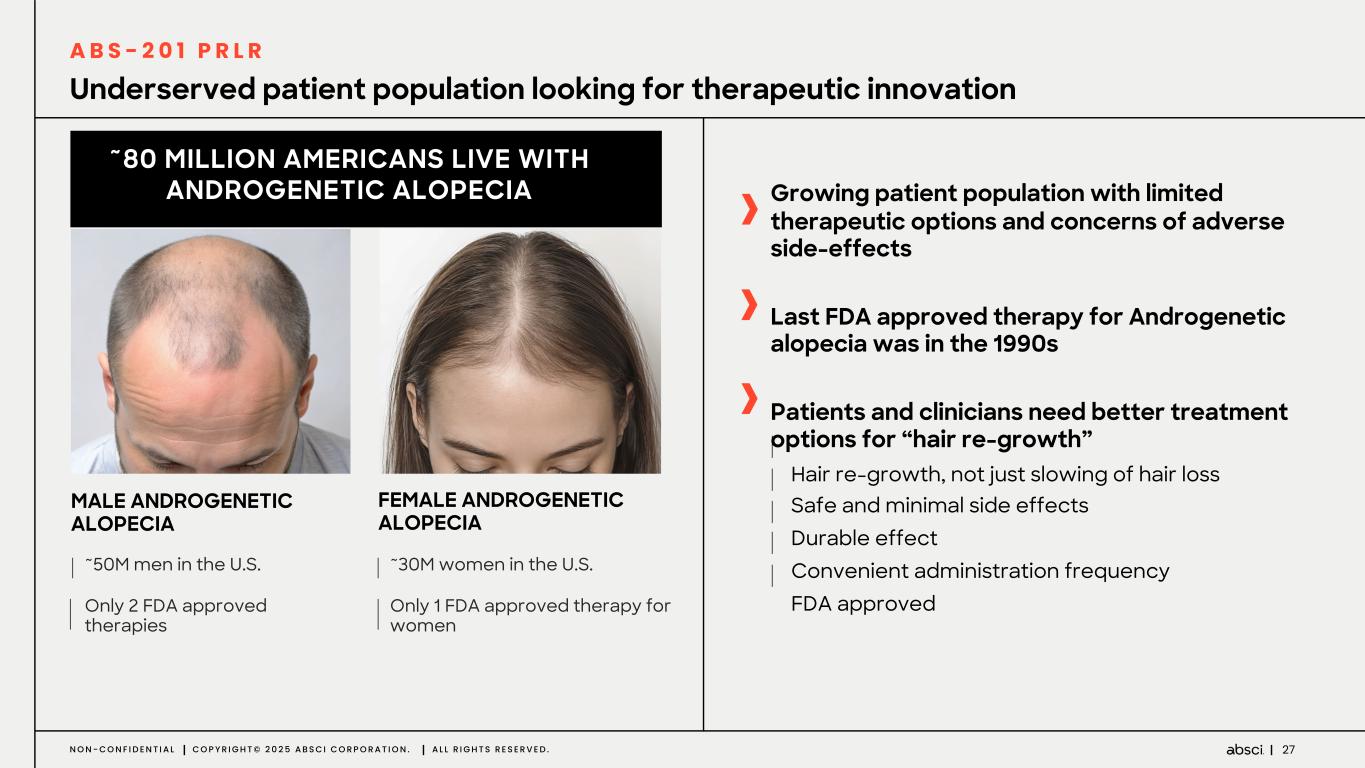
27N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . Underserved patient population looking for therapeutic innovation FEMALE ANDROGENETIC ALOPECIA ~30M women in the U.S. Only 1 FDA approved therapy for women ~50M men in the U.S. Only 2 FDA approved therapies ~80 MILLION AMERICANS LIVE WITH ANDROGENETIC ALOPECIA MALE ANDROGENETIC ALOPECIA Growing patient population with limited therapeutic options and concerns of adverse side-effects Last FDA approved therapy for Androgenetic alopecia was in the 1990s Patients and clinicians need better treatment options for “hair re-growth” Hair re-growth, not just slowing of hair loss Safe and minimal side effects Durable effect Convenient administration frequency FDA approved A B S - 2 0 1 P R L R

28N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . Patients and clinicians need better treatment options for “hair re-growth” • Hair re-growth, not just slowing of hair loss • Safe • Minimal side effects • Durable effect • Convenient administration frequency • FDA approved L A C K O F I N N O V A T I O N I N T H E A N D R O G E N I C A L O P E C I A T H E R A P E U T I C L A N D S C A P E O V E R T H E P A S T 2 5 + Y E A R S L A S T F D A A P P R O V E D T H E R A P Y I N 1 9 9 7

29N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . Potential best-in-class PRLR antibody for treating androgenic alopecia A B S - 2 0 1 P R L R AI-designed PRLR program for durable hair regrowth therapy addressing patient population of >80M in the US alone High affinity and potency Excellent developability profile à high- concentration formulation and great stability Anticipated low immunogenicity Extended half-life and expected longer dosing intervals Clinical development strategy expected to enable PoC in H2-2026 Potential to be first to market in the U.S.
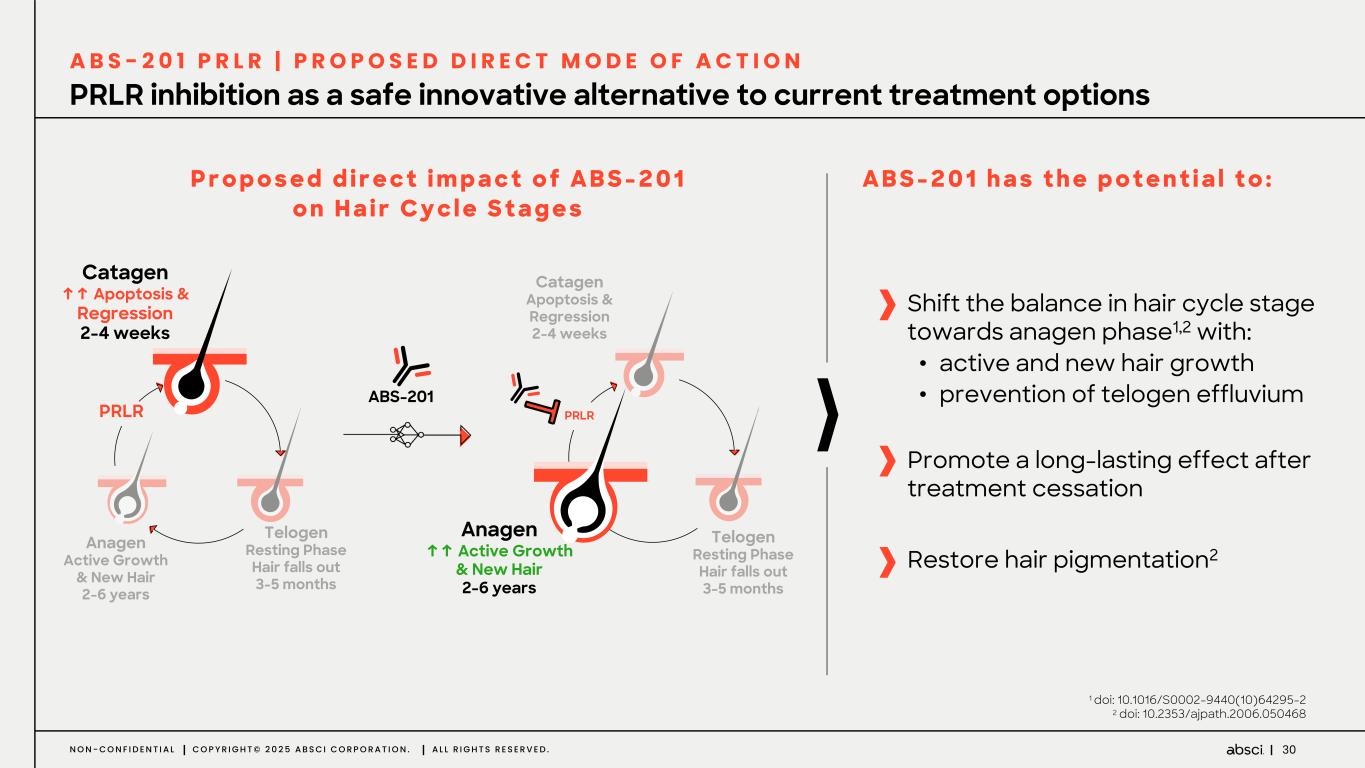
30N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . PRLR inhibition as a safe innovative alternative to current treatment options A B S - 2 0 1 P R L R | P R O P O S E D D I R E C T M O D E O F A C T I O N P r o p o s e d d i r e c t i m p a c t o f A B S - 2 0 1 o n H a i r C y c l e S t a g e s A B S - 2 0 1 h a s t h e p o t e n t i a l t o : Catagen ↑↑ Apoptosis & Regression 2-4 weeks Telogen Resting Phase Hair falls out 3-5 months PRLR Anagen Active Growth & New Hair 2-6 years ABS-201 Anagen ↑↑ Active Growth & New Hair 2-6 years Telogen Resting Phase Hair falls out 3-5 months PRLR Catagen Apoptosis & Regression 2-4 weeks Shift the balance in hair cycle stage towards anagen phase1,2 with: • active and new hair growth • prevention of telogen effluvium Restore hair pigmentation2 Promote a long-lasting effect after treatment cessation 1 doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64295-2 2 doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.050468
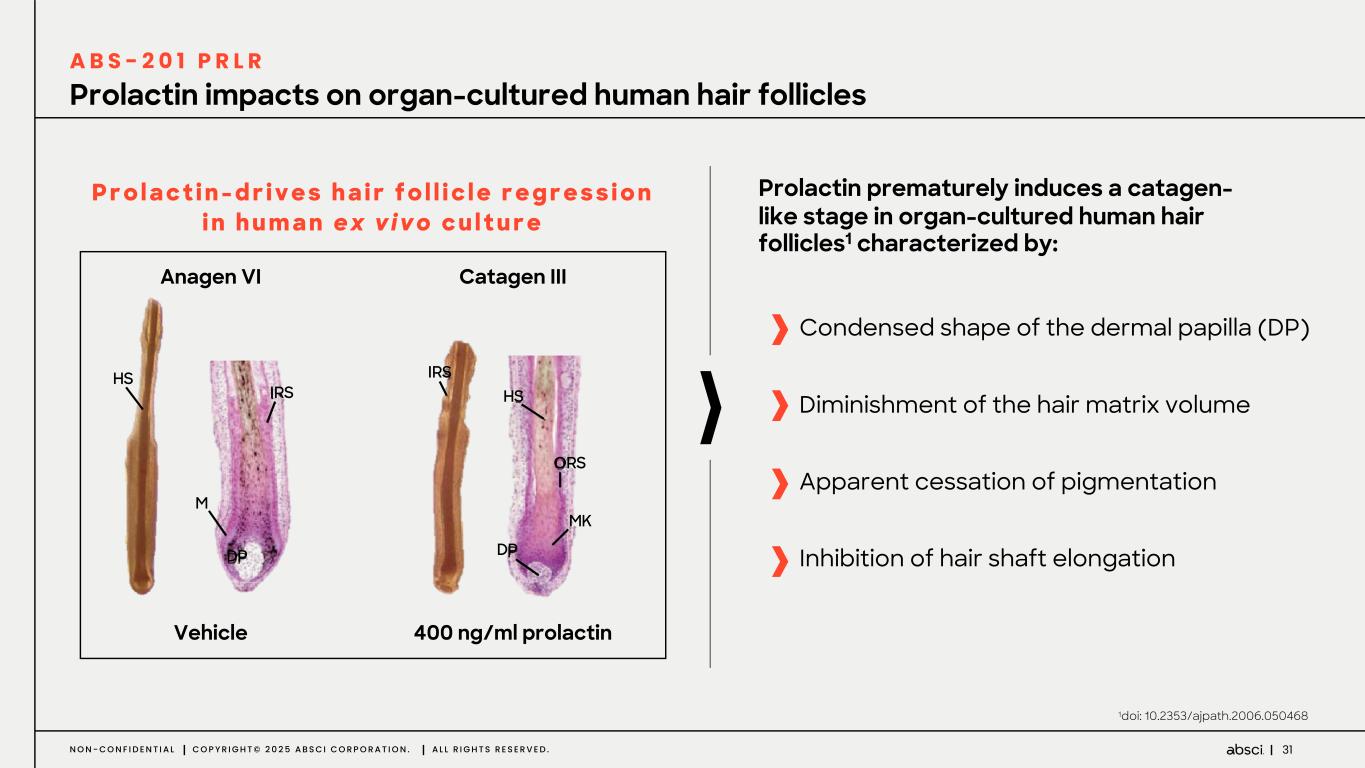
31N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . Prolactin impacts on organ-cultured human hair follicles 1doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.050468 P r o l a c t i n - d r i v e s h a i r f o l l i c l e r e g r e s s i o n i n h u m a n e x v i v o c u l t u r e Prolactin prematurely induces a catagen- like stage in organ-cultured human hair follicles1 characterized by: Apparent cessation of pigmentation Condensed shape of the dermal papilla (DP) Diminishment of the hair matrix volume Vehicle 400 ng/ml prolactin Catagen IIIAnagen VI HS M DP IRS IRS HS ORS DP MK Inhibition of hair shaft elongation A B S - 2 0 1 P R L R
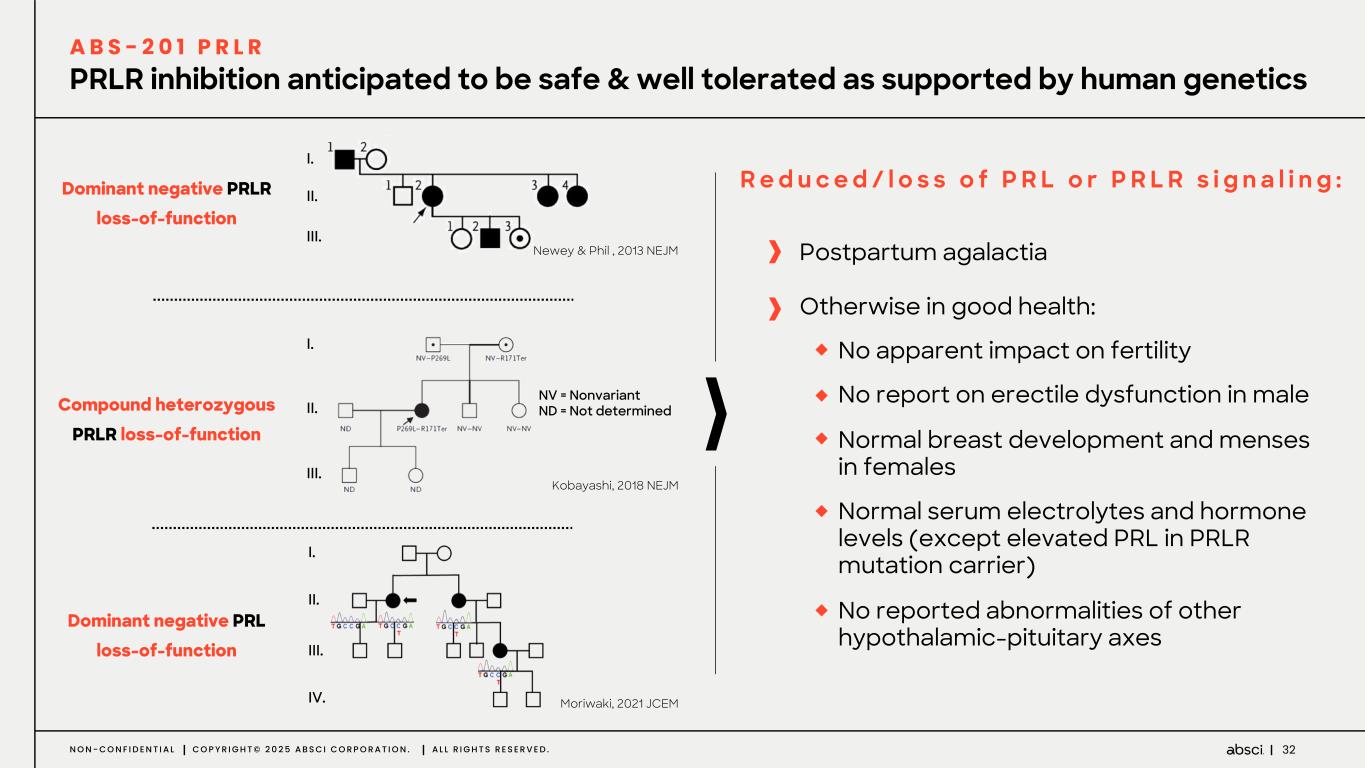
32N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . PRLR inhibition anticipated to be safe & well tolerated as supported by human genetics A B S - 2 0 1 P R L R I. II. III. NV = Nonvariant ND = Not determined I. II. III. I. II. III. IV. Kobayashi, 2018 NEJM Moriwaki, 2021 JCEM Newey & Phil , 2013 NEJM Compound heterozygous PRLR loss-of-function Dominant negative PRL loss-of-function Dominant negative PRLR loss-of-function R e d u c e d / l o s s o f P R L o r P R L R s i g n a l i n g : Postpartum agalactia Otherwise in good health: No apparent impact on fertility No report on erectile dysfunction in male Normal breast development and menses in females Normal serum electrolytes and hormone levels (except elevated PRL in PRLR mutation carrier) No reported abnormalities of other hypothalamic-pituitary axes

33N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . TREATMENT WITH AN ANTI-PRLR MAB PROMOTES AND SUSTAINS LONG-TERM HAIR GROWTH IN NHP Hair density & thickness improved with short treatment duration in primate model of androgenic alopecia Hair growth remains several years post cessation Hair re-growth observed for both male and female animals TOP HEAD VIEW OF STUMPTAILED MACAQUE’S SHOWING PHENOTYPIC CHANGE OVER TIME 40mg/kg s.c. Q2W for 28 weeks Disclosure from competitor M al e Fe m al e Baseline 12 weeks 28 weeks 6 months 2 years 4 years Post-treatmentTreatment Translational Model validates PRLR Target A B S - 2 0 1 P R L R
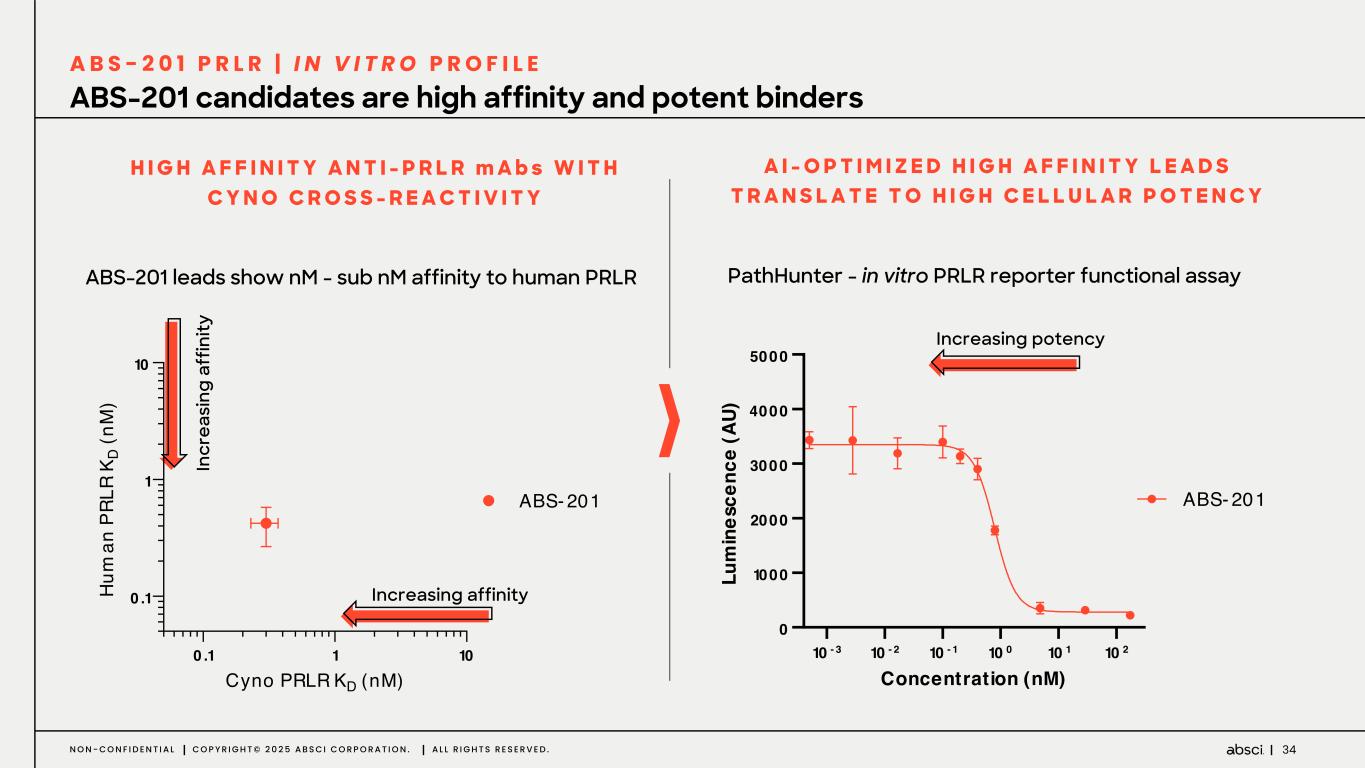
34N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . ABS-201 candidates are high affinity and potent binders A B S - 2 0 1 P R L R | I N V I T R O P R O F I L E PathHunter - in vitro PRLR reporter functional assay 10 - 3 10 - 2 10 - 1 10 0 10 1 10 2 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 Concentration (nM) Lu m in es ce nc e (A U) ABS- 201 ABS-201 leads show nM - sub nM affinity to human PRLR A I - O P T I M I Z E D H I G H A F F I N I T Y L E A D S T R A N S L A T E T O H I G H C E L L U L A R P O T E N C Y In cr ea si ng a ff in ity Increasing potency 0 .1 1 10 0 .1 1 10 Cyno PRLR KD (nM) H um an P RL R K D (n M ) ABS- 201 Increasing affinity H I G H A F F I N I T Y A N T I - P R L R m A b s W I T H C Y N O C R O S S - R E A C T I V I T Y
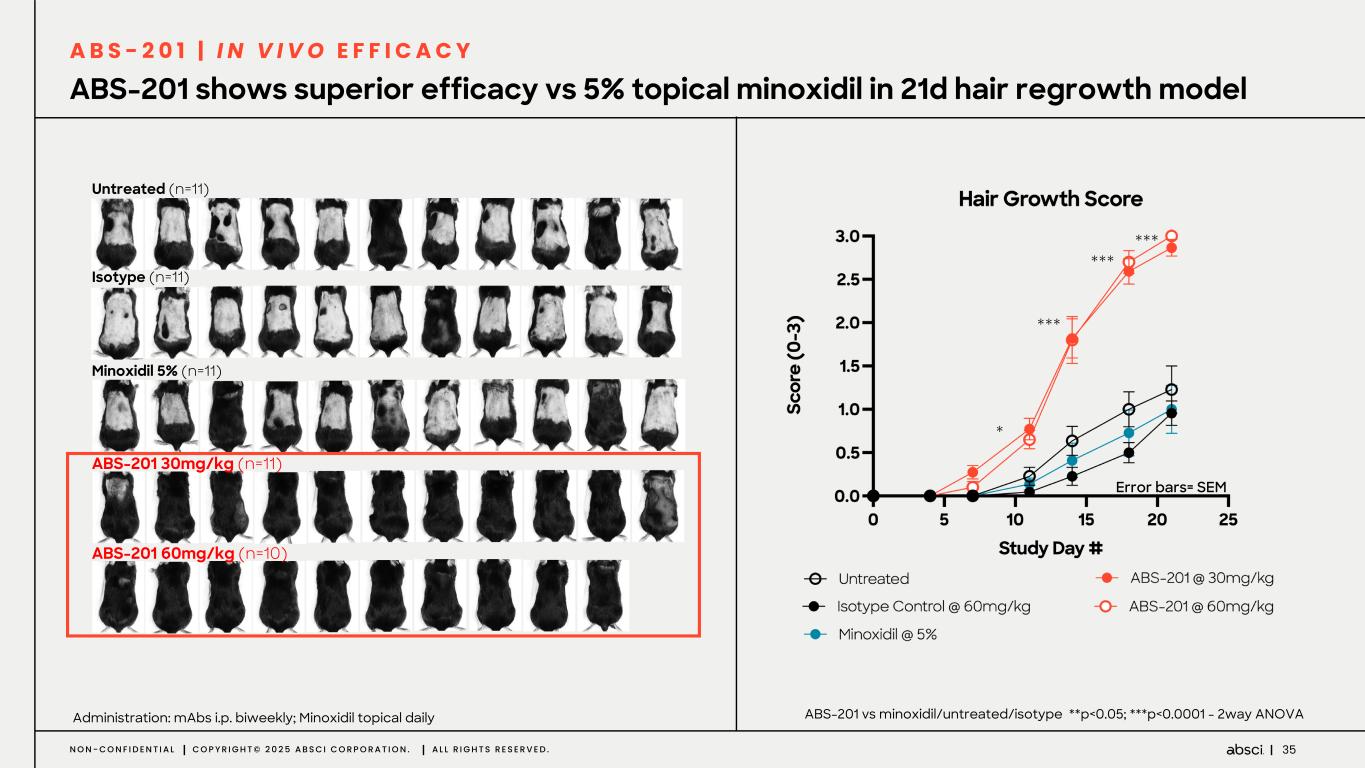
35N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . ABS-201 shows superior efficacy vs 5% topical minoxidil in 21d hair regrowth model Administration: mAbs i.p. biweekly; Minoxidil topical daily Untreated (n=11) Isotype (n=11) Minoxidil 5% (n=11) ABS-201 30mg/kg (n=11) ABS-201 60mg/kg (n=10) ABS-201 vs minoxidil/untreated/isotype **p<0.05; ***p<0.0001 - 2way ANOVA Error bars= SEM *** *** *** * A B S - 2 0 1 | I N V I V O E F F I C A C Y
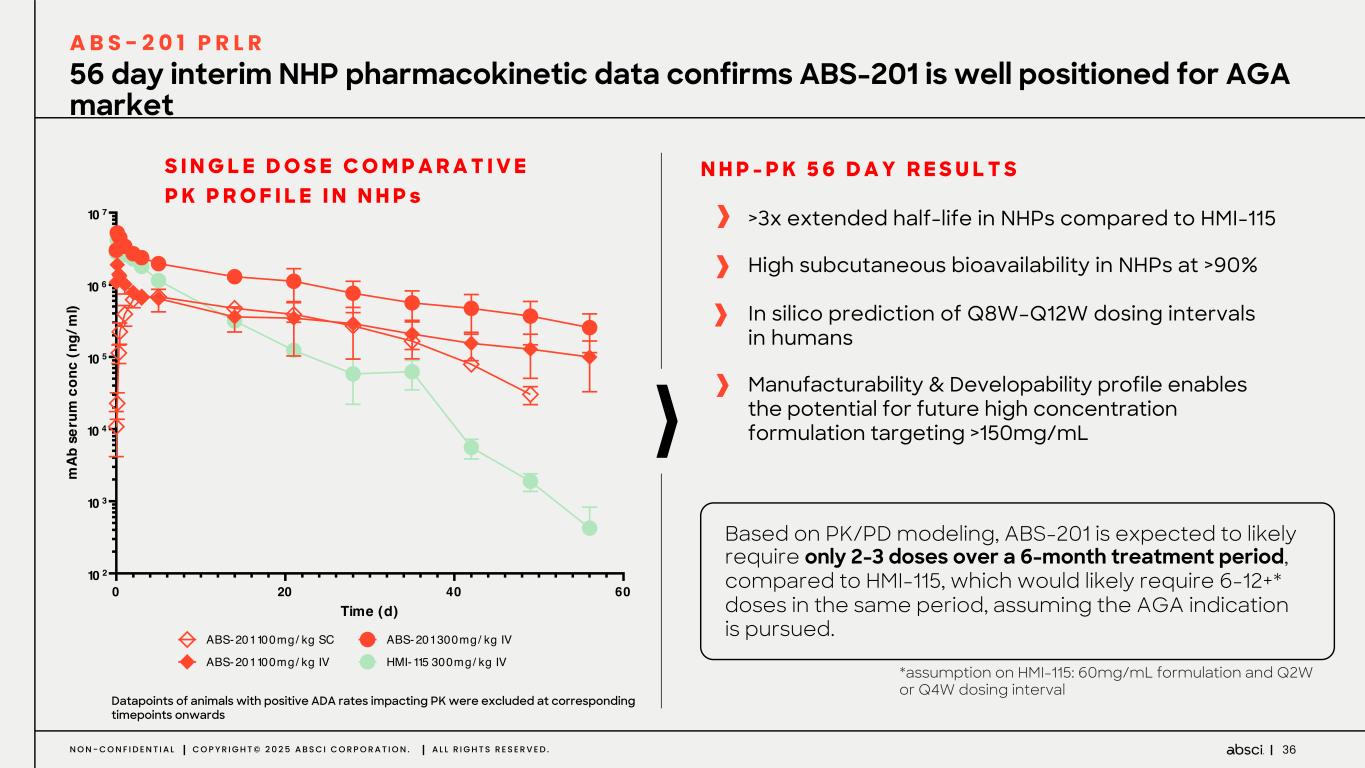
36N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . 56 day interim NHP pharmacokinetic data confirms ABS-201 is well positioned for AGA market A B S - 2 0 1 P R L R >3x extended half-life in NHPs compared to HMI-115 High subcutaneous bioavailability in NHPs at >90% In silico prediction of Q8W–Q12W dosing intervals in humans Manufacturability & Developability profile enables the potential for future high concentration formulation targeting >150mg/mL N H P - P K 5 6 D A Y R E S U L T S 0 20 40 60 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 Single Dose Comparative PK Profile in NHPs Time (d) m Ab s er um c on c (n g/ m l) ABS-201 100mg/ kg SC ABS- 201 100mg/ kg IV ABS- 201 300mg/ kg IV HMI-115 300mg/ kg IV Datapoints of animals with positive ADA rates impacting PK were excluded at corresponding timepoints onwards S I N G L E D O S E C O M P A R A T I V E P K P R O F I L E I N N H P s *assumption on HMI-115: 60mg/mL formulation and Q2W or Q4W dosing interval Based on PK/PD modeling, ABS-201 is expected to likely require only 2-3 doses over a 6-month treatment period, compared to HMI-115, which would likely require 6-12+* doses in the same period, assuming the AGA indication is pursued.
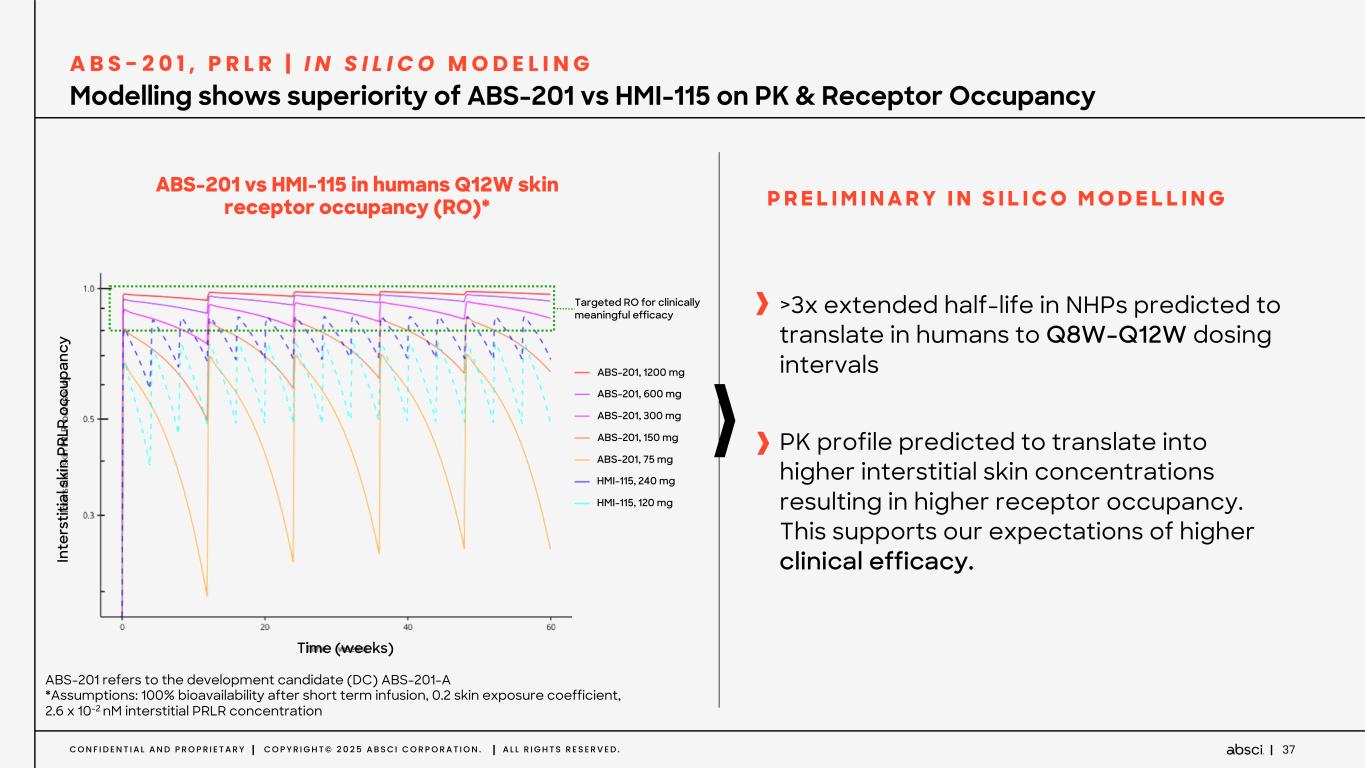
37C O N F I D E N T I A L A N D P R O P R I E T A R Y C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . Modelling shows superiority of ABS-201 vs HMI-115 on PK & Receptor Occupancy A B S - 2 0 1 , P R L R | I N S I L I C O M O D E L I N G >3x extended half-life in NHPs predicted to translate in humans to Q8W-Q12W dosing intervals PK profile predicted to translate into higher interstitial skin concentrations resulting in higher receptor occupancy. This supports our expectations of higher clinical efficacy. P R E L I M I N A R Y I N S I L I C O M O D E L L I N G Time (weeks) In te rs tit ia l s ki n PR LR o cc up an cy ABS-201, 1200 mg ABS-201, 600 mg ABS-201, 300 mg ABS-201, 150 mg ABS-201, 75 mg HMI-115, 240 mg HMI-115, 120 mg ABS-201 vs HMI-115 in humans Q12W skin receptor occupancy (RO)* Targeted RO for clinically meaningful efficacy ABS-201 refers to the development candidate (DC) ABS-201-A *Assumptions: 100% bioavailability after short term infusion, 0.2 skin exposure coefficient, 2.6 x 10-2 nM interstitial PRLR concentration
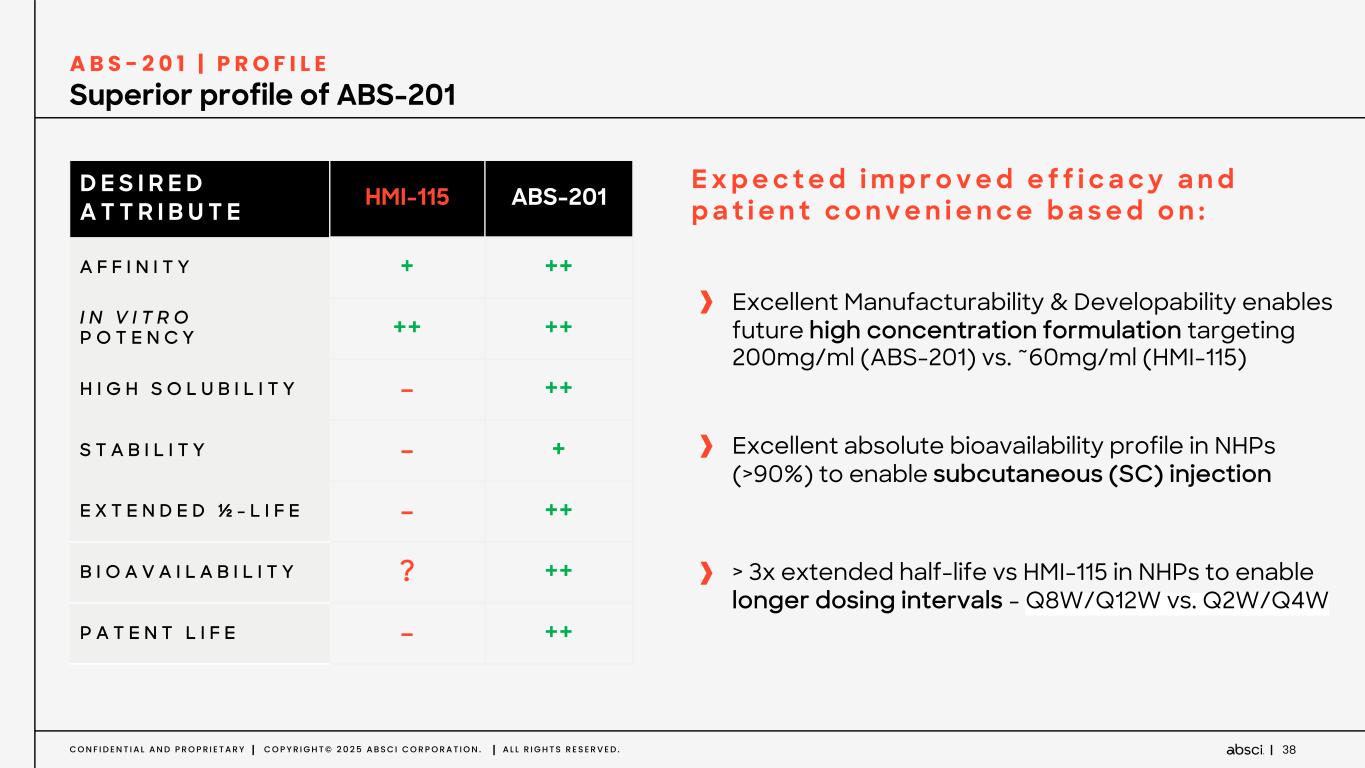
38C O N F I D E N T I A L A N D P R O P R I E T A R Y C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . D E S I R E D A T T R I B U T E HMI-115 ABS-201 A F F I N I T Y + ++ I N V I T R O P O T E N C Y ++ ++ H I G H S O L U B I L I T Y - ++ S T A B I L I T Y - + E X T E N D E D ½ - L I F E - ++ B I O A V A I L A B I L I T Y ? ++ P A T E N T L I F E - ++ Superior profile of ABS-201 A B S - 2 0 1 | P R O F I L E Excellent Manufacturability & Developability enables future high concentration formulation targeting 200mg/ml (ABS-201) vs. ~60mg/ml (HMI-115) E x p e c t e d i m p r o v e d e f f i c a c y a n d p a t i e n t c o n v e n i e n c e b a s e d o n : Excellent absolute bioavailability profile in NHPs (>90%) to enable subcutaneous (SC) injection > 3x extended half-life vs HMI-115 in NHPs to enable longer dosing intervals - Q8W/Q12W vs. Q2W/Q4W

39N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . Straightforward path for ABS-201 clinical development C L I N I C A L T R I A L S F O R H A I R T R E A T M E N T S A R E E X P E C T E D T O B E S T R A I G H T F O R W A R D • Ease of patient recruitment • High level of KOL Interest • Ability to conduct multi-center trials • Non-invasive trial conduct W E L L D E F I N E D E N D P O I N T S W I T H V A L I D A T E D M E A S U R E S Primary Endpoints: Quantitative measurements with follicular dermatoscope (trichoscopy) • Terminal Hair Growth • Total Hair Count • Total hair density (per cm2) Secondary Endpoints: • Patient Reported Outcomes as measured by validated scales accepted by the FDA (HairDex; Hair Specific Skindex-29 (FPHL); The Men’s Hair Growth Questionnaire (MHGQ)); Women’s Hair Growth Questionnaire (WHGQ) • Re-pigmentation B E N C H T O B E D S I D E

40N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . Leading Scientific Advisory Board of Hair Experts DR. ANTHONY ROSSI Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center DR. CHESAHNA KINDRED Kindred Hair & Skin Center DR. MATT L. LEAVITT Advanced Dermatology and Cosmetic Surgery DR. MEENA SINGH Skin and Hair Center DR. MARIA K. HORDINSKY Univ. of Minnesota DR. SUZANNE KILMER Laser & Skin Surgery Center of Northern California DR. KEN WASHENIK Bosley Medical Group DR. GLYNIS ABLON Ablon Skin Institute DR. NEIL S. SADICK Sadick Dermatology DR. DORIS DAY Day Dermatology & Aesthetics Over Half a Million alopecia patients treated each year by these KOL practice networks DR. DAVID GOLDBERG Schweiger Dermatology DR. RODNEY SINCLAIR Sinclair Dermatology

41N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . A B S - 1 0 1 Continued progress of TL1A asset with FiH in 1H 2025 • New preclinical data supporting superior immunogenicity profile • Phase 1 Interim data readout in 2H 2025 A B S - 2 0 1 IND-enabling activities on-track for PRLR (prolactin receptor) program with anticipated initiation of Ph1/2a studies in early 2026 A B S - 3 0 1 Progress of first-in-class asset discovered through Absci’s Reverse Immunology Platform A B S - 5 0 1 Nomination of a potential best-in-class HER2 asset C o n t i n u e d a d v a n c e m e n t o f l e a d a s s e t s D i s c o v e r y o f n e x t a s s e t s Absci’s progress in Drug Creation I N T E R N A L P I P E L I N E
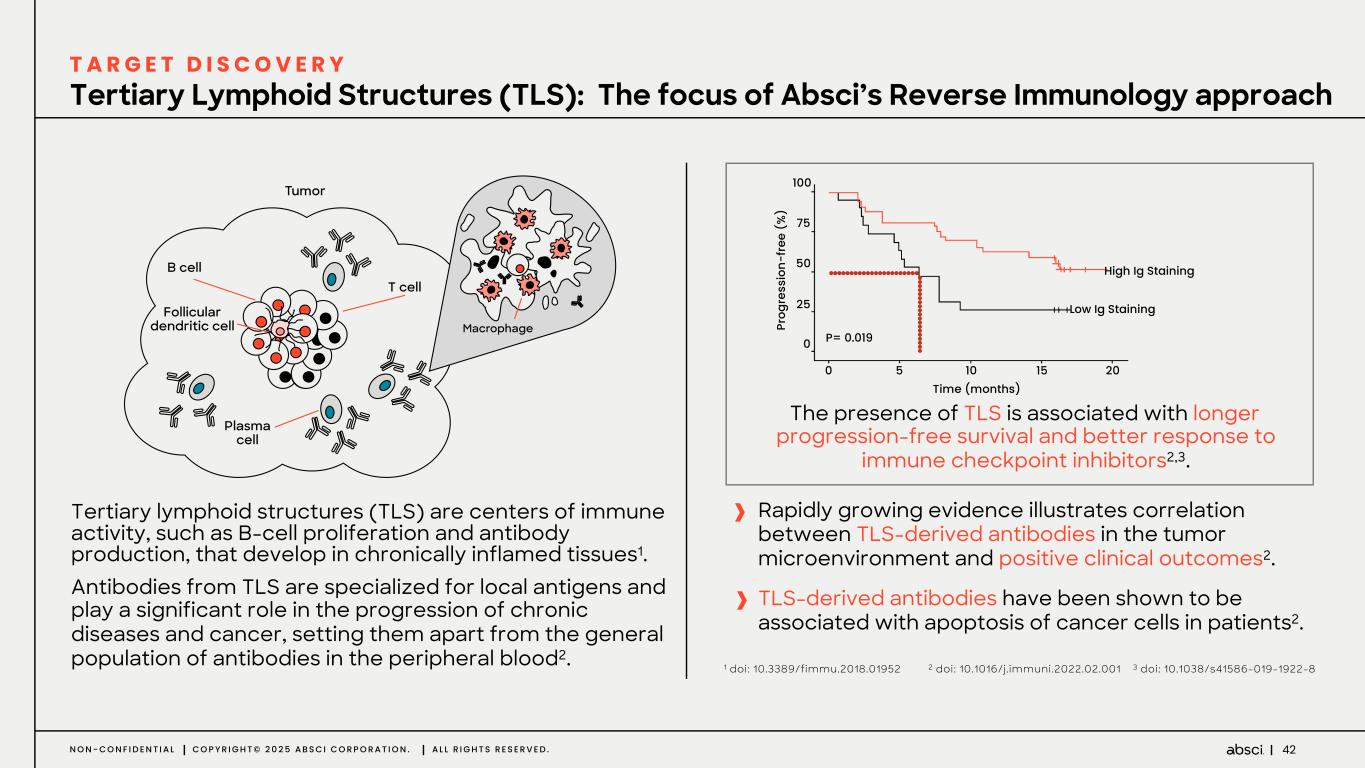
42N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . The presence of TLS is associated with longer progression-free survival and better response to immune checkpoint inhibitors2,3. Rapidly growing evidence illustrates correlation between TLS-derived antibodies in the tumor microenvironment and positive clinical outcomes2. TLS-derived antibodies have been shown to be associated with apoptosis of cancer cells in patients2. Tertiary lymphoid structures (TLS) are centers of immune activity, such as B-cell proliferation and antibody production, that develop in chronically inflamed tissues1. Antibodies from TLS are specialized for local antigens and play a significant role in the progression of chronic diseases and cancer, setting them apart from the general population of antibodies in the peripheral blood2. 100 75 50 25 10 15 20 0 0 5 High Ig Staining Low Ig Staining Pr og re ss io n- fr ee ( % ) Time (months) P= 0.019 Tertiary Lymphoid Structures (TLS): The focus of Absci’s Reverse Immunology approach T A R G E T D I S C O V E R Y 1 doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01952 2 doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.02.001 3 doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1922-8
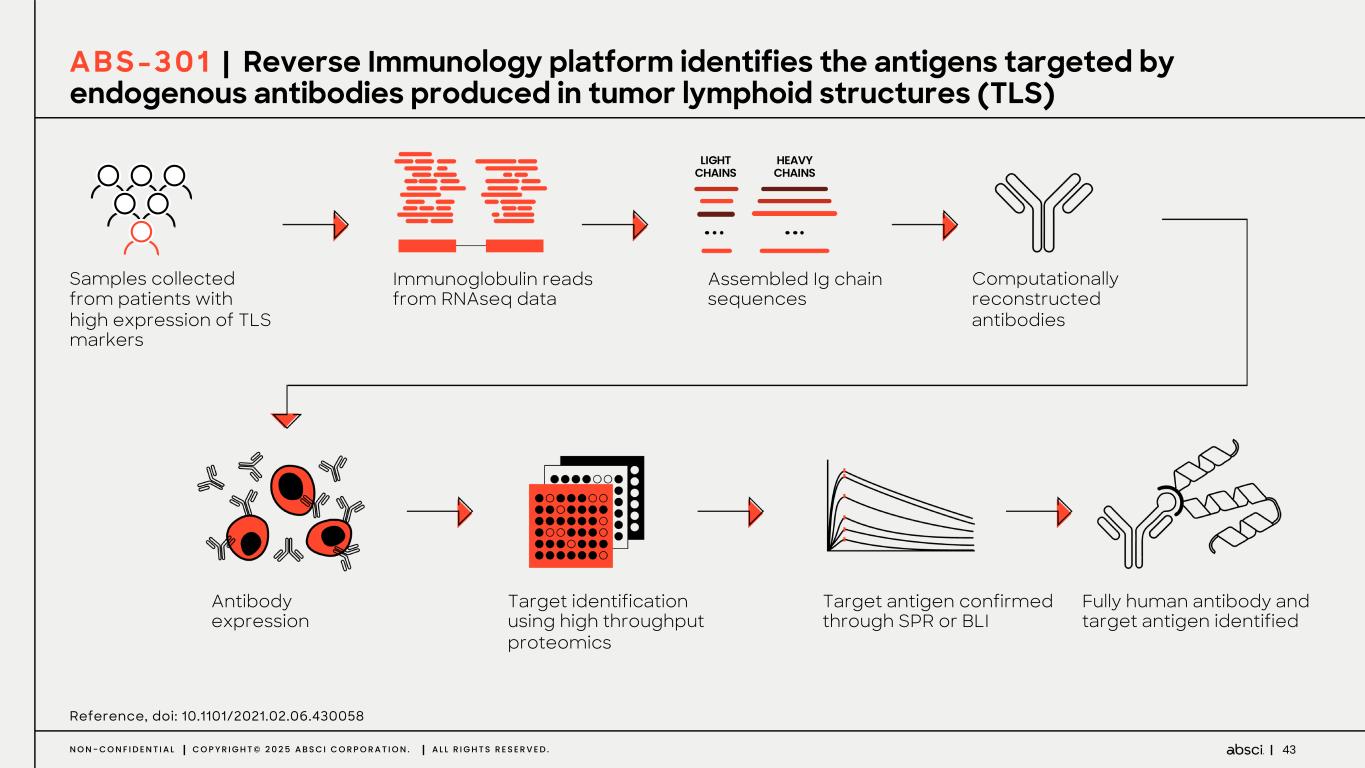
43N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . LIGHT CHAINS HEAVY CHAINS Samples collected from patients with high expression of TLS markers Antibody expression Immunoglobulin reads from RNAseq data Target identification using high throughput proteomics Assembled Ig chain sequences Target antigen confirmed through SPR or BLI Computationally reconstructed antibodies Fully human antibody and target antigen identified Reference, doi: 10.1101/2021.02.06.430058 A B S - 3 0 1 | Reverse Immunology platform identifies the antigens targeted by endogenous antibodies produced in tumor lymphoid structures (TLS)
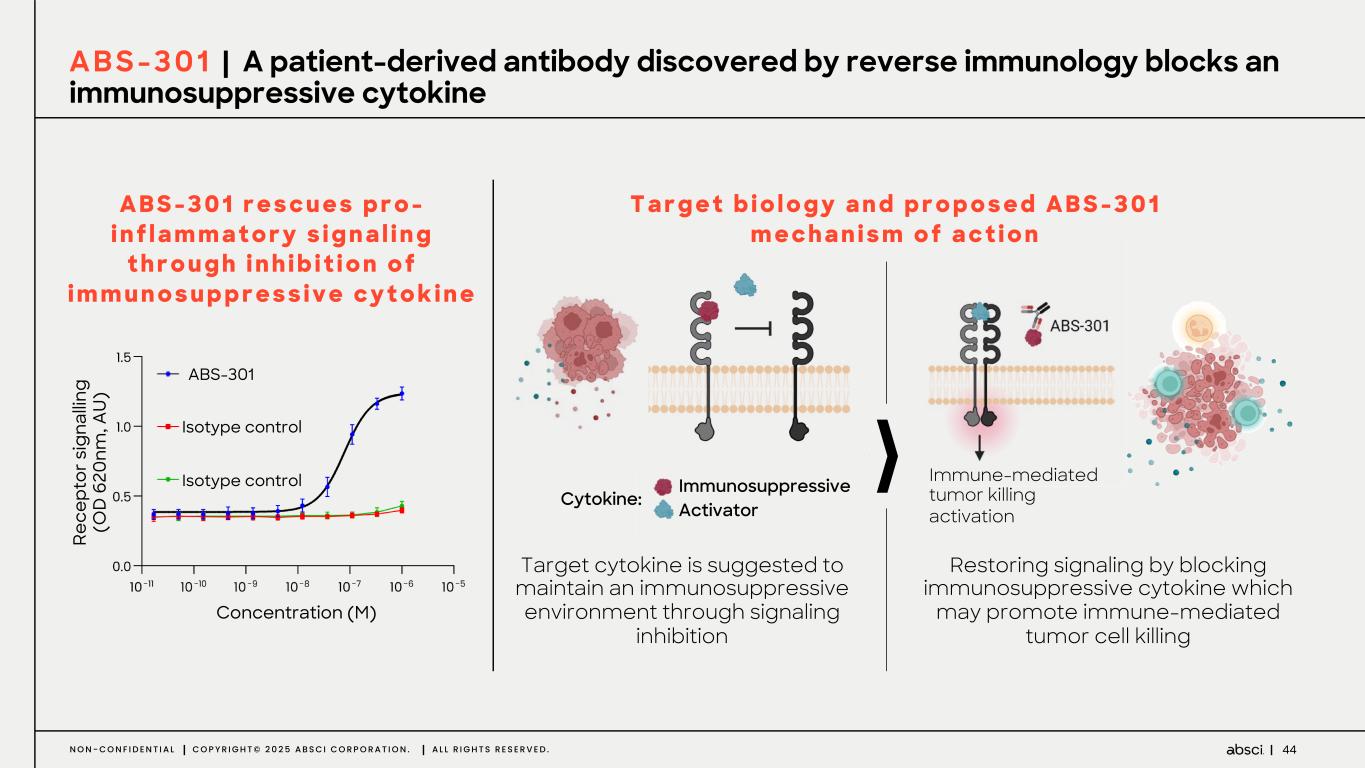
44N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . A B S - 3 0 1 r e s c u e s p r o - i n f l a m m a t o r y s i g n a l i n g t h r o u g h i n h i b i t i o n o f i m m u n o s u p p r e s s i v e c y t o k i n e A B S - 3 0 1 | A patient-derived antibody discovered by reverse immunology blocks an immunosuppressive cytokine Restoring signaling by blocking immunosuppressive cytokine which may promote immune-mediated tumor cell killing Target cytokine is suggested to maintain an immunosuppressive environment through signaling inhibition Re ce pt or s ig na llin g (O D 6 20 nm , A U ) ABS-301 Isotype control Isotype control Concentration (M) Immunosuppressive Activator Immune-mediated tumor killing activation Cytokine: T a r g e t b i o l o g y a n d p r o p o s e d A B S - 3 0 1 m e c h a n i s m o f a c t i o n
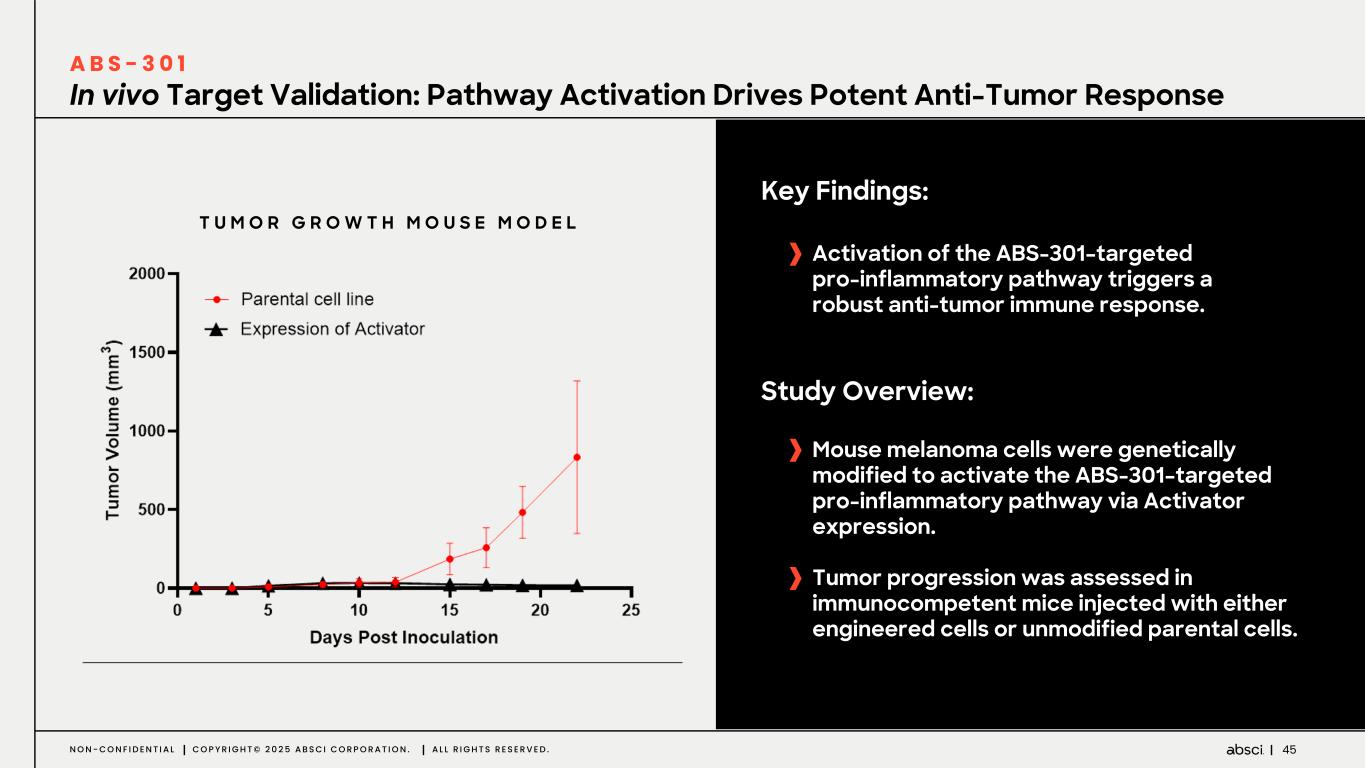
45N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . In vivo Target Validation: Pathway Activation Drives Potent Anti-Tumor Response A B S - 3 0 1 Key Findings: Activation of the ABS-301–targeted pro-inflammatory pathway triggers a robust anti-tumor immune response. Study Overview: Mouse melanoma cells were genetically modified to activate the ABS-301–targeted pro-inflammatory pathway via Activator expression. Tumor progression was assessed in immunocompetent mice injected with either engineered cells or unmodified parental cells. T U M O R G R O W T H M O U S E M O D E L
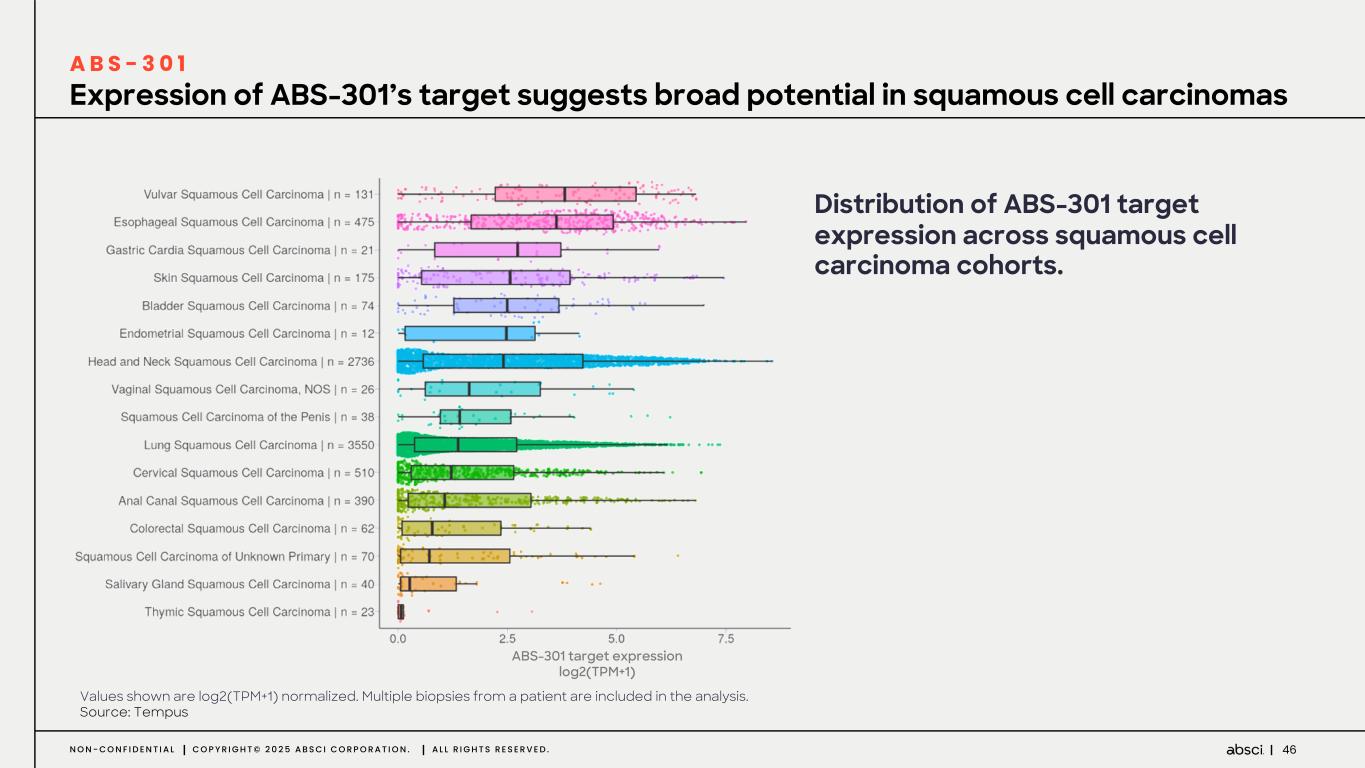
46N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . Expression of ABS-301’s target suggests broad potential in squamous cell carcinomas A B S - 3 0 1 Distribution of ABS-301 target expression across squamous cell carcinoma cohorts. ABS-301 target expression log2(TPM+1) Values shown are log2(TPM+1) normalized. Multiple biopsies from a patient are included in the analysis. Source: Tempus
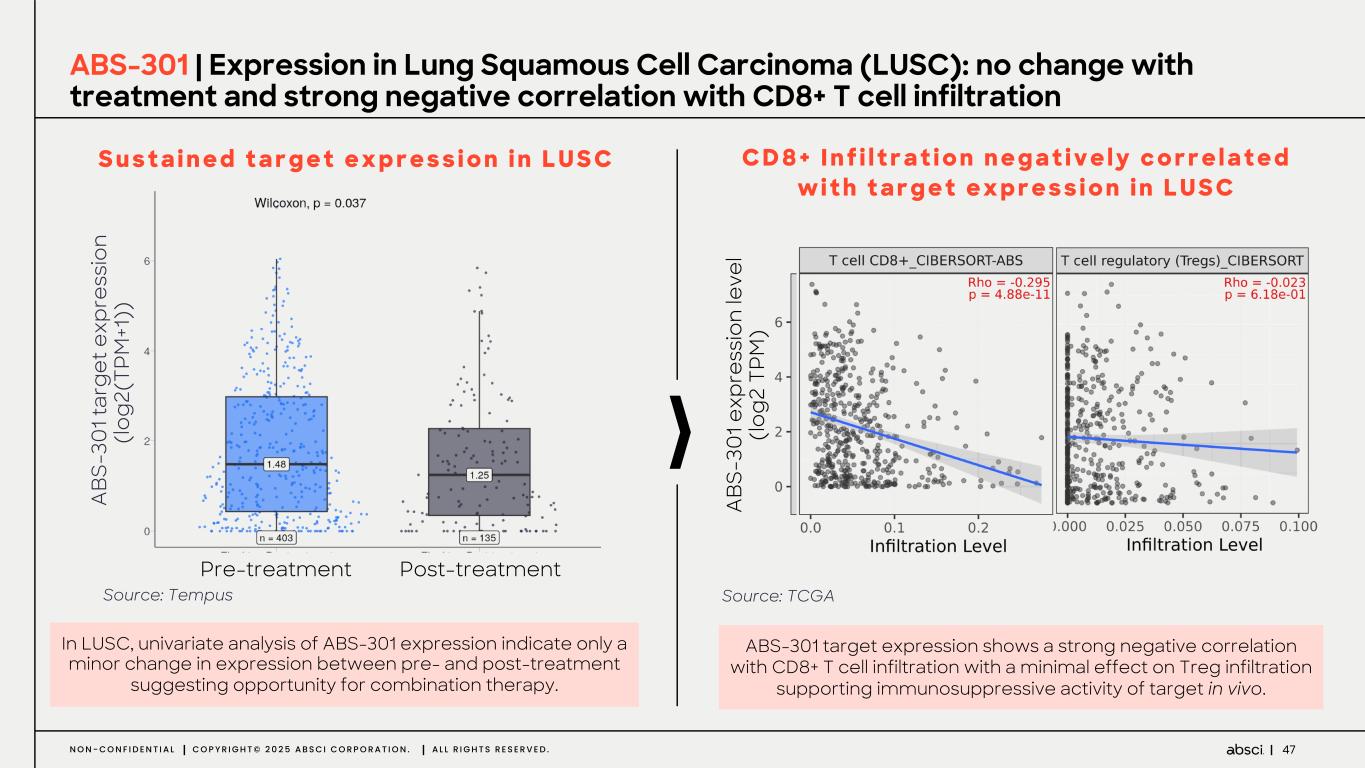
47N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . ABS-301 | Expression in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma (LUSC): no change with treatment and strong negative correlation with CD8+ T cell infiltration In LUSC, univariate analysis of ABS-301 expression indicate only a minor change in expression between pre- and post-treatment suggesting opportunity for combination therapy. S u s t a i n e d t a r g e t e x p r e s s i o n i n L U S C ABS-301 target expression shows a strong negative correlation with CD8+ T cell infiltration with a minimal effect on Treg infiltration supporting immunosuppressive activity of target in vivo. C D 8 + I n f i l t r a t i o n n e g a t i v e l y c o r r e l a t e d w i t h t a r g e t e x p r e s s i o n i n L U S C Source: Tempus Source: TCGA Pre-treatment Post-treatment A BS -3 01 ta rg et e xp re ss io n (lo g2 (T PM +1 )) A BS -3 01 e xp re ss io n le ve l (lo g2 T PM )
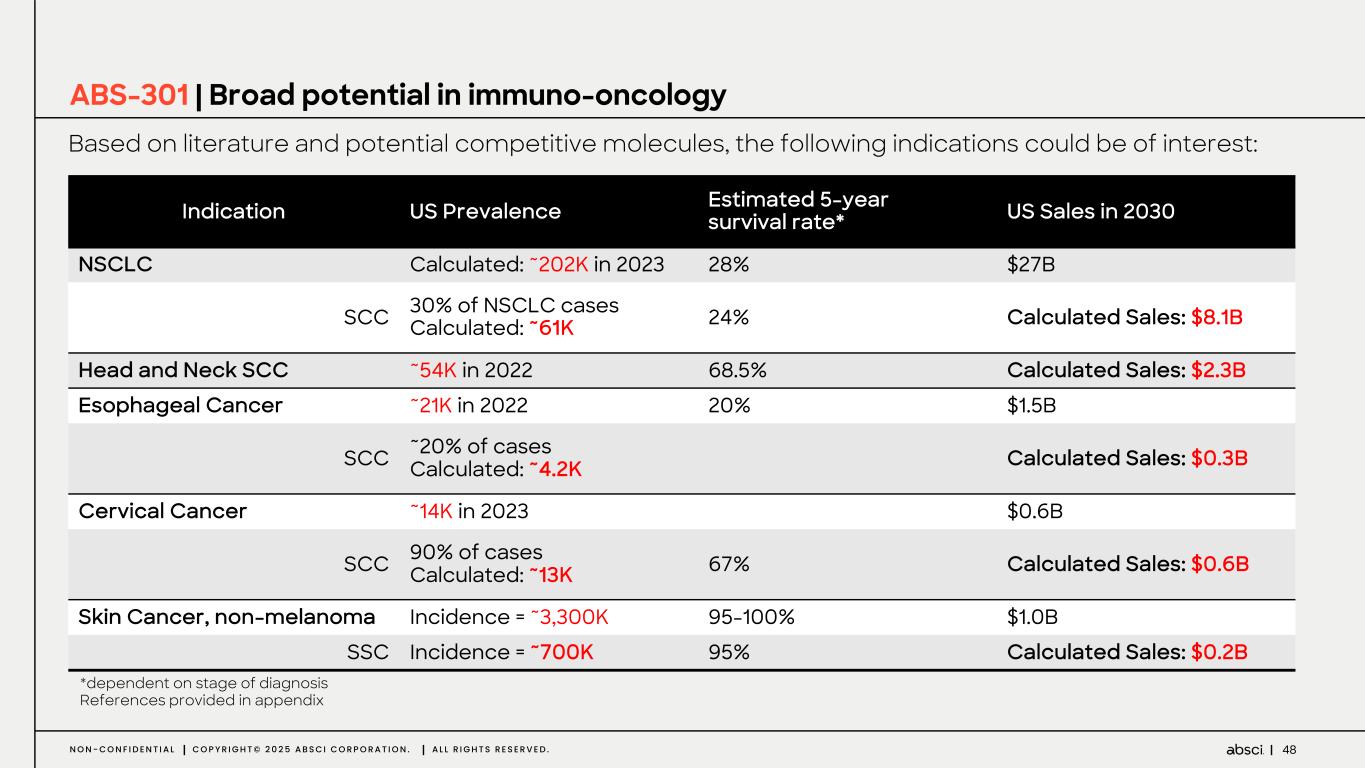
48N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . ABS-301 | Broad potential in immuno-oncology Based on literature and potential competitive molecules, the following indications could be of interest: *dependent on stage of diagnosis References provided in appendix Indication US Prevalence Estimated 5-year survival rate* US Sales in 2030 NSCLC Calculated: ~202K in 2023 28% $27B SCC 30% of NSCLC cases Calculated: ~61K 24% Calculated Sales: $8.1B Head and Neck SCC ~54K in 2022 68.5% Calculated Sales: $2.3B Esophageal Cancer ~21K in 2022 20% $1.5B SCC ~20% of cases Calculated: ~4.2K Calculated Sales: $0.3B Cervical Cancer ~14K in 2023 $0.6B SCC 90% of cases Calculated: ~13K 67% Calculated Sales: $0.6B Skin Cancer, non-melanoma Incidence = ~3,300K 95-100% $1.0B SSC Incidence = ~700K 95% Calculated Sales: $0.2B

49N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . A B S - 1 0 1 Continued progress of TL1A asset with FiH in 1H 2025 • New preclinical data supporting superior immunogenicity profile • Phase 1 Interim data readout in 2H 2025 A B S - 2 0 1 IND-enabling activities on-track for PRLR (prolactin receptor) program with anticipated initiation of Ph1/2a studies in early 2026 A B S - 3 0 1 Progress of first-in-class asset discovered through Absci’s Reverse Immunology Platform A B S - 5 0 1 Nomination of a potential best-in-class HER2 asset C o n t i n u e d a d v a n c e m e n t o f l e a d a s s e t s D i s c o v e r y o f n e x t a s s e t s Absci’s progress in Drug Creation I N T E R N A L P I P E L I N E
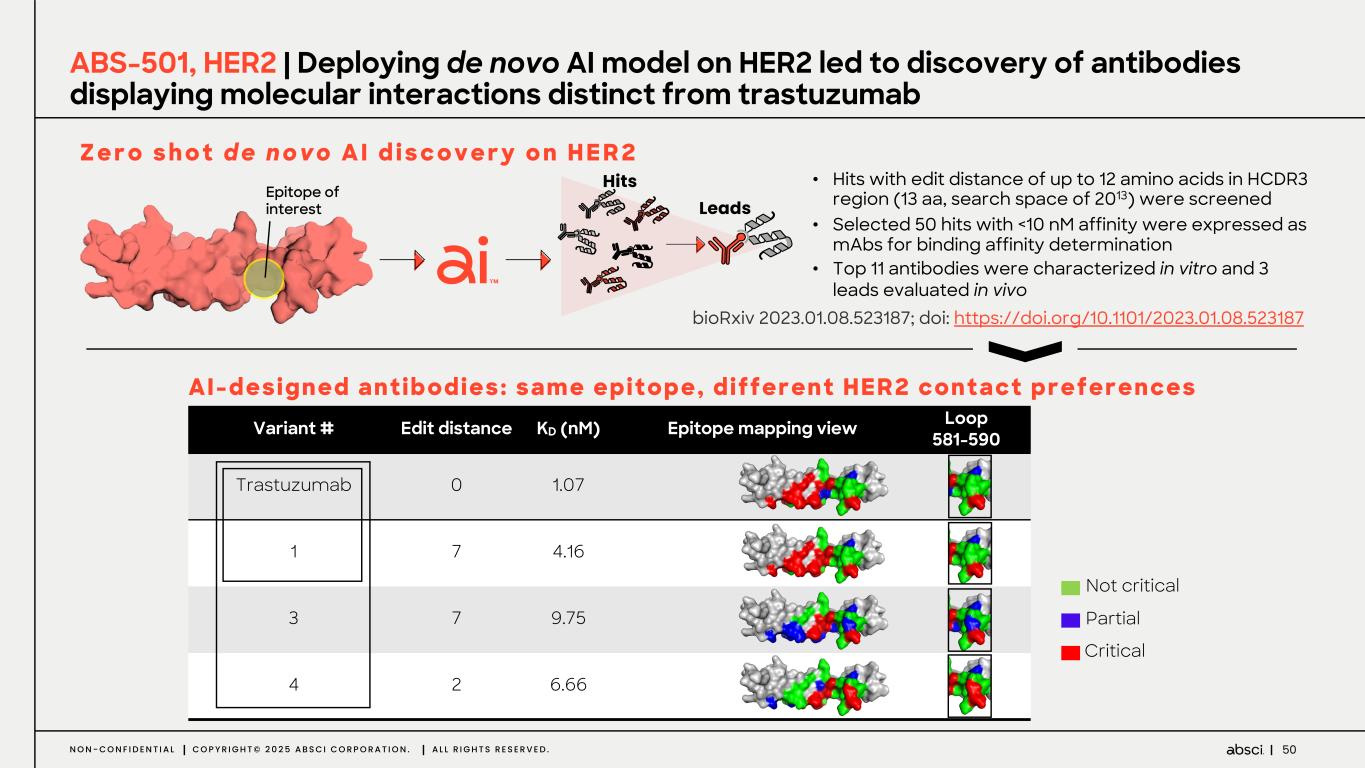
50N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . • Hits with edit distance of up to 12 amino acids in HCDR3 region (13 aa, search space of 2013) were screened • Selected 50 hits with <10 nM affinity were expressed as mAbs for binding affinity determination • Top 11 antibodies were characterized in vitro and 3 leads evaluated in vivo ABS-501, HER2 | Deploying de novo AI model on HER2 led to discovery of antibodies displaying molecular interactions distinct from trastuzumab Variant # Edit distance KD (nM) Epitope mapping view Loop 581-590 Trastuzumab 0 1.07 1 7 4.16 3 7 9.75 4 2 6.66 Partial Critical Not critical Z e r o s h o t d e n o v o A I d i s c o v e r y o n H E R 2 AI-designed antibodies: same epitope, different HER2 contact preferences Epitope of interest Hits Leads bioRxiv 2023.01.08.523187; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.01.08.523187
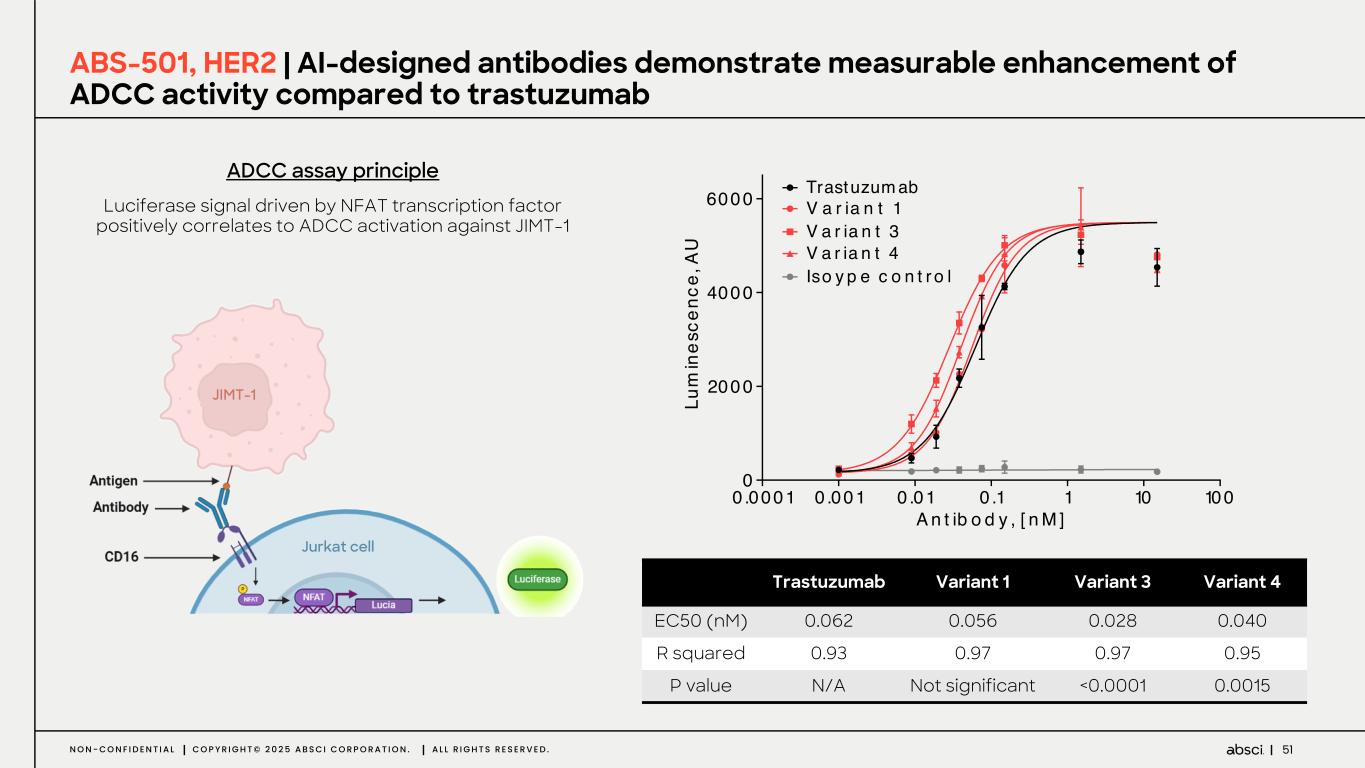
51N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . Luciferase signal driven by NFAT transcription factor positively correlates to ADCC activation against JIMT-1 ABS-501, HER2 | AI-designed antibodies demonstrate measurable enhancement of ADCC activity compared to trastuzumab ADCC assay principle Trastuzumab Variant 1 Variant 3 Variant 4 EC50 (nM) 0.062 0.056 0.028 0.040 R squared 0.93 0.97 0.97 0.95 P value N/A Not significant <0.0001 0.0015 0 .0001 0 .001 0 .01 0 .1 1 10 100 0 2000 4000 6000 A n t ib o d y , [ n M ] Lu m in es ce nc e, A U Trastuzum ab V a r ia n t 1 V a r ia n t 3 V a r ia n t 4 Iso y p e c o n t r o l JIMT-1 Jurkat cell
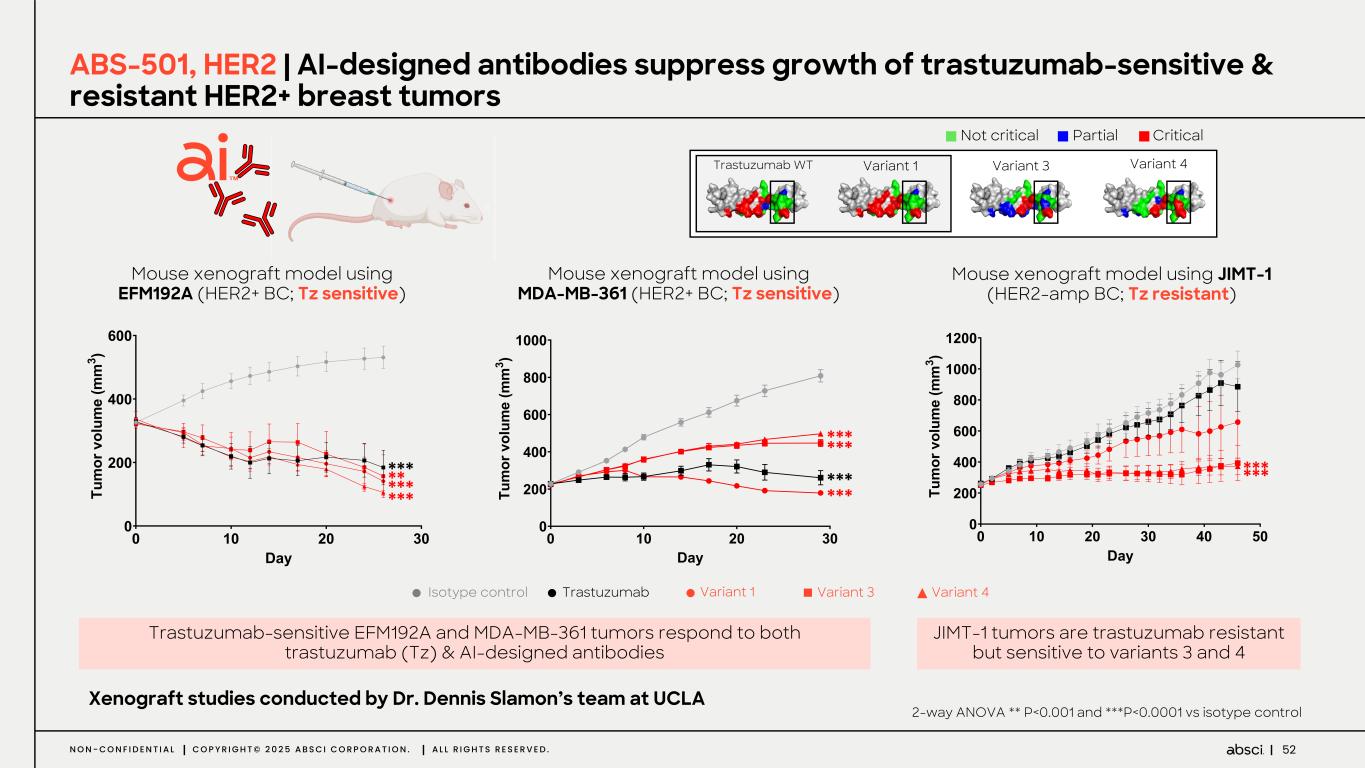
52N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . ABS-501, HER2 | AI-designed antibodies suppress growth of trastuzumab-sensitive & resistant HER2+ breast tumors Partial Critical Not critical Trastuzumab WT Variant 1 Variant 3 Variant 4 Mouse xenograft model using EFM192A (HER2+ BC; Tz sensitive) Mouse xenograft model using JIMT-1 (HER2-amp BC; Tz resistant) Trastuzumab-sensitive EFM192A and MDA-MB-361 tumors respond to both trastuzumab (Tz) & AI-designed antibodies Xenograft studies conducted by Dr. Dennis Slamon’s team at UCLA Isotype control Trastuzumab Variant 1 Variant 3 Variant 4 ! "! #! $! ! #!! %!! &!! D() *+ , -. /0 -1 +, 2/ 3, , $ 4 ! "! #! $! %! &! ! #!! %!! D!! (!! "!!! "#!! )*+ ,- . /0 12 /3 -. 41 5. . $ 6 *** ****** *** *** Mouse xenograft model using MDA-MB-361 (HER2+ BC; Tz sensitive) ! "! #! $! ! #!! %!! &!! D!! "!!! ()* +, - ./ 01 .2 ,- 30 4- - $ 5 *** *** ****** 2-way ANOVA ** P<0.001 and ***P<0.0001 vs isotype control JIMT-1 tumors are trastuzumab resistant but sensitive to variants 3 and 4 **
53N O N - C O N F I D E N T I A L C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . ABS-501, HER2 | AI-designed antibodies create opportunities to address unmet medical need Modality switch or combination opportunities under consideration to address unmet medical needs Later-line treatment regimens for HER2-positive cancer: • Monotherapy • Combination therapy with targeted small molecules M u l t i p l e p a t h s p o s s i b l e f o r t h e r a p e u t i c d e v e l o p m e n t : C u r r e n t l y e x p l o r i n g b r e a s t c a n c e r a s o p p o r t u n i t y : a l t e r n a t i v e t o o r p o s t E n h e r t u® Despite Enhertu’s good efficacy, leading oncologists are only moderately satisfied due to toxicity (e.g. interstitial lung disease); less toxic therapy and effective treatment post-Enhertu are key unmet needs. “Post-Enhertu is really where the action is right now in the field. I think the first company that comes up with something that has significant benefit in Enhertu progressive disease is going to win.” – KOL Enhancing efficacy and expanding indications (e.g. Enhertu resistance): • Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) • Multi-specific antibodies +
54C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . Leading AI models to create novel & differentiated therapeutics “Smart” biologics Enhanced Potency & MOA Engineer selectivity, minimizing off target toxicity Agonism vs. Antagonism Bind Specific extracellular domains Target Specific conformations Address difficult target classes e.g. GPCRs ADDRESS COMPLEX AND PREVIOUSLY “HARD TO DRUG” TARGETS INTRODUCE PRECISE CONTROL OVER ANTIBODY DESIGN
55C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . Leadership in AI de novo design of antibody-based therapeutics EVQLSEVGA . . . de novo antibody design model creates epitope-specific binders given a target structure Designed in framework of choice or multiple frameworks INPUT EMBEDDING STRUCTURE PREDICTION (DIFFUSION) . . . ARCPSIWKFPDEEGACQPC . . . Antigen Structure/Sequence (Epitope) PROTEIN LANGUAGE MODELS Co-optimization enables improvement of antibody attributes while maintaining developability Precise engineering of molecule pharmacology AI LEAD OPTIMIZATIONDE NOVO ANTIBODY DESIGN
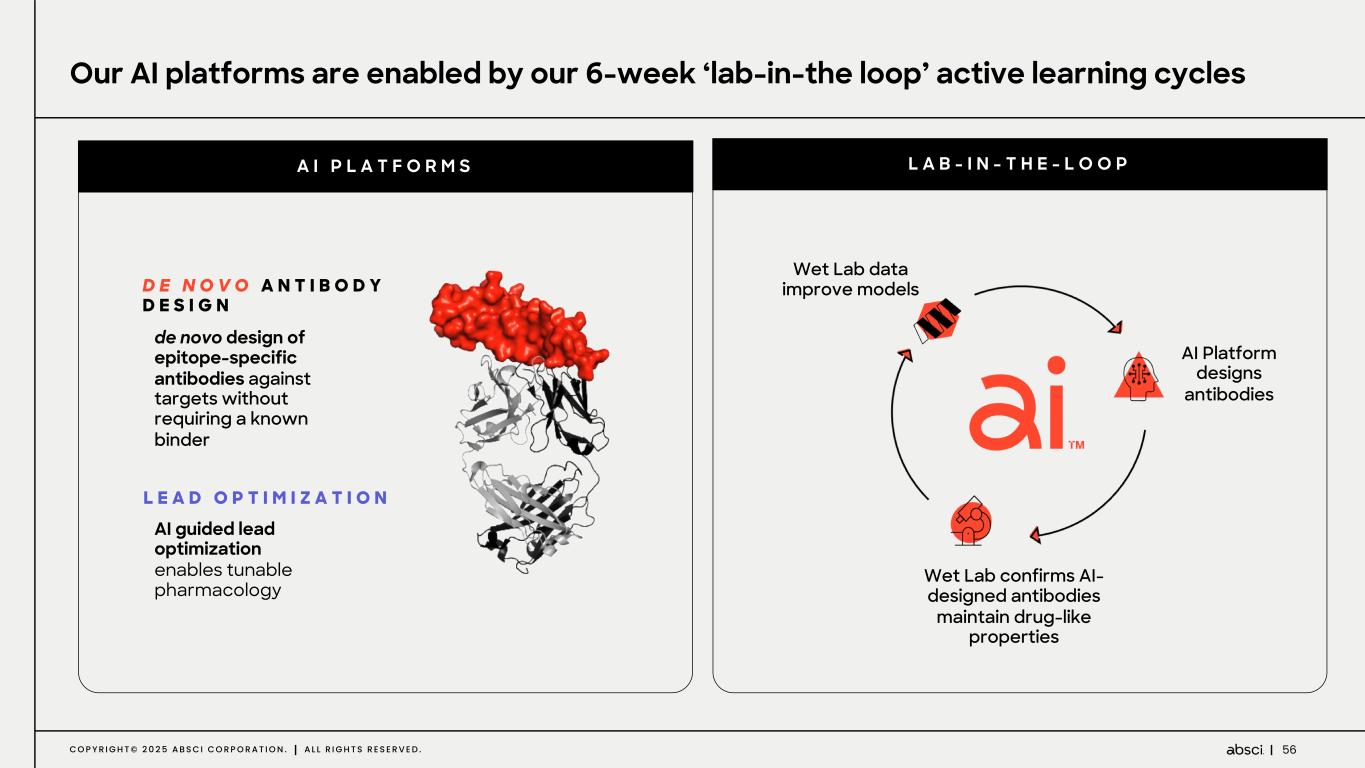
56C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . AI Platform designs antibodies Wet Lab confirms AI- designed antibodies maintain drug-like properties Wet Lab data improve models D E N O V O A N T I B O D Y D E S I G N Our AI platforms are enabled by our 6-week ‘lab-in-the loop’ active learning cycles A I P L A T F O R M S L A B - I N - T H E - L O O P L E A D O P T I M I Z A T I O N AI guided lead optimization enables tunable pharmacology de novo design of epitope-specific antibodies against targets without requiring a known binder
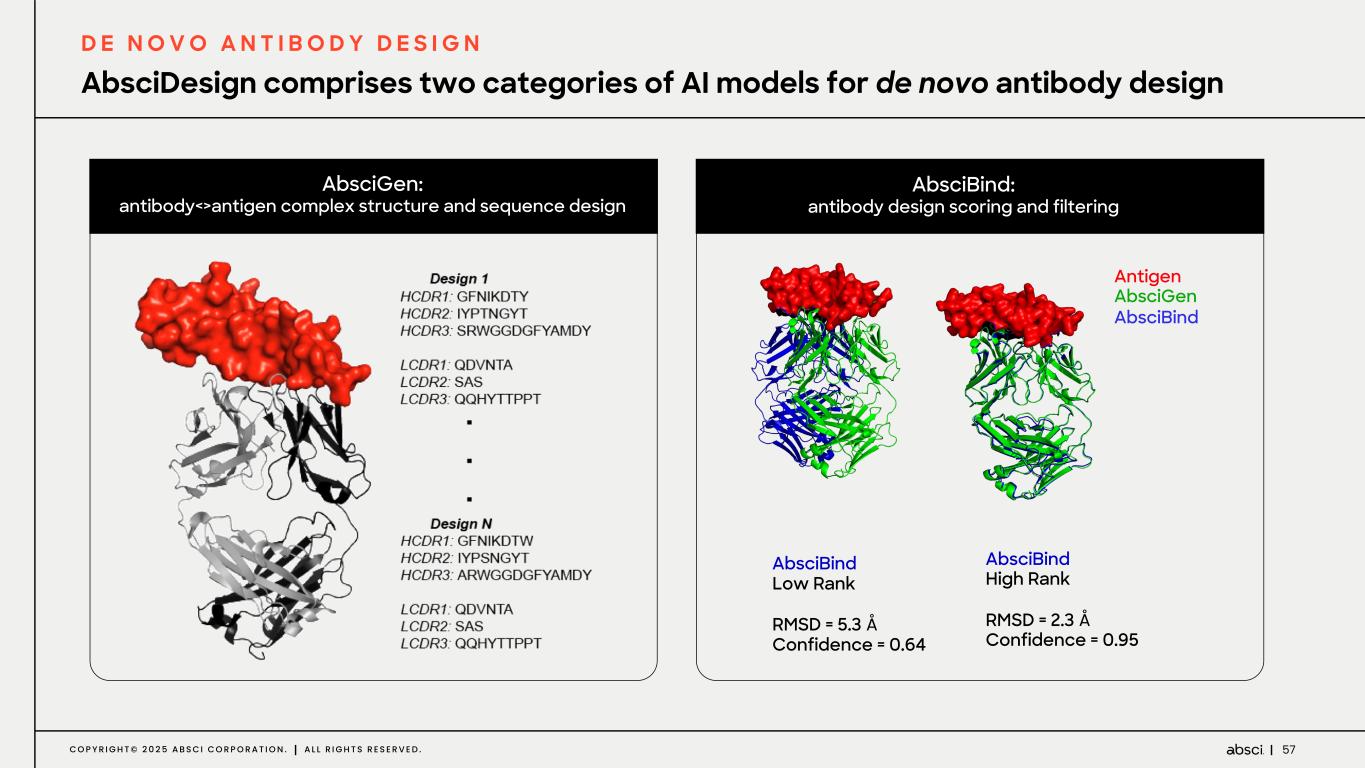
57C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . AbsciGen: antibody<>antigen complex structure and sequence design AbsciBind: antibody design scoring and filtering Antigen AbsciGen AbsciBind AbsciBind High Rank RMSD = 2.3 Å Confidence = 0.95 AbsciBind Low Rank RMSD = 5.3 Å Confidence = 0.64 AbsciDesign comprises two categories of AI models for de novo antibody design D E N O V O A N T I B O D Y D E S I G N
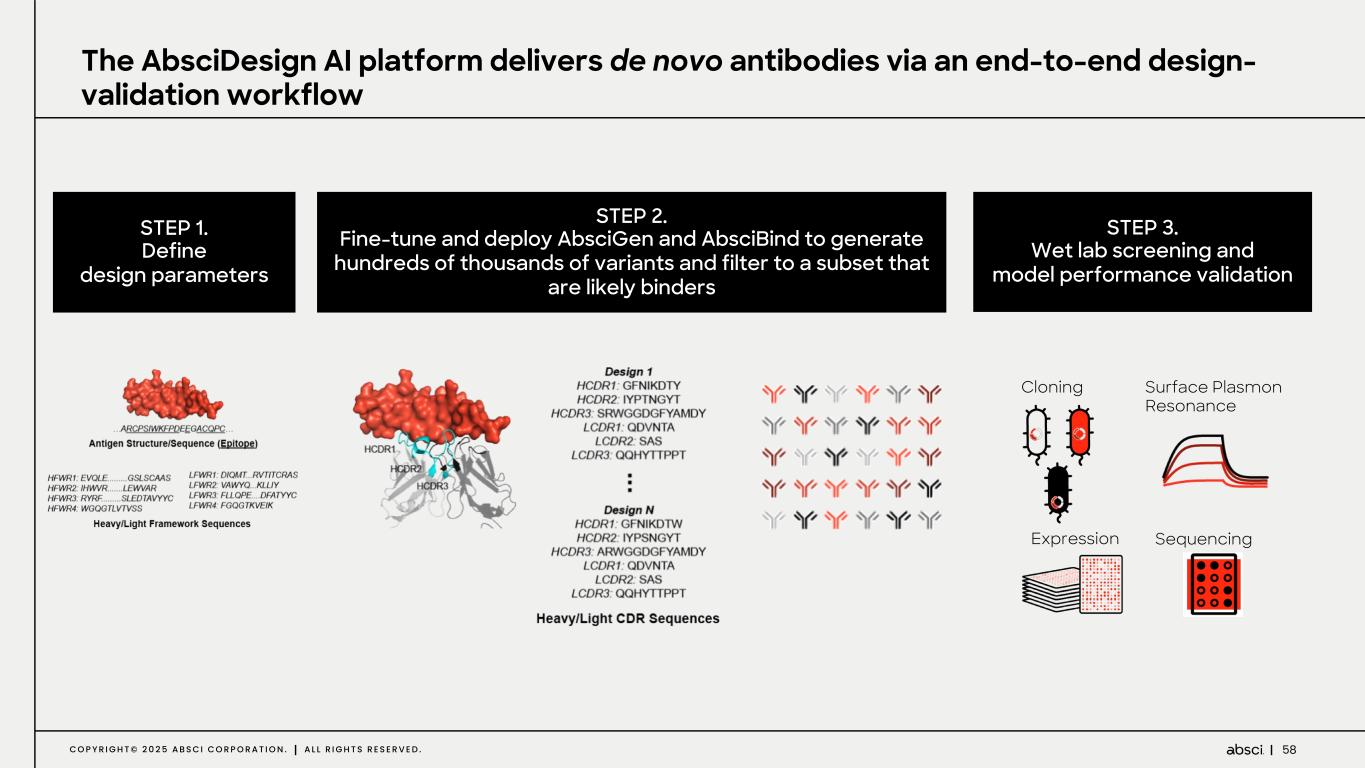
58C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . STEP 1. Define design parameters STEP 2. Fine-tune and deploy AbsciGen and AbsciBind to generate hundreds of thousands of variants and filter to a subset that are likely binders STEP 3. Wet lab screening and model performance validation The AbsciDesign AI platform delivers de novo antibodies via an end-to-end design- validation workflow Cloning Expression Surface Plasmon Resonance Sequencing

59C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . C A S E S T U D Y de novo design of an antibody that binds the Caldera region of HIV-1 trimer
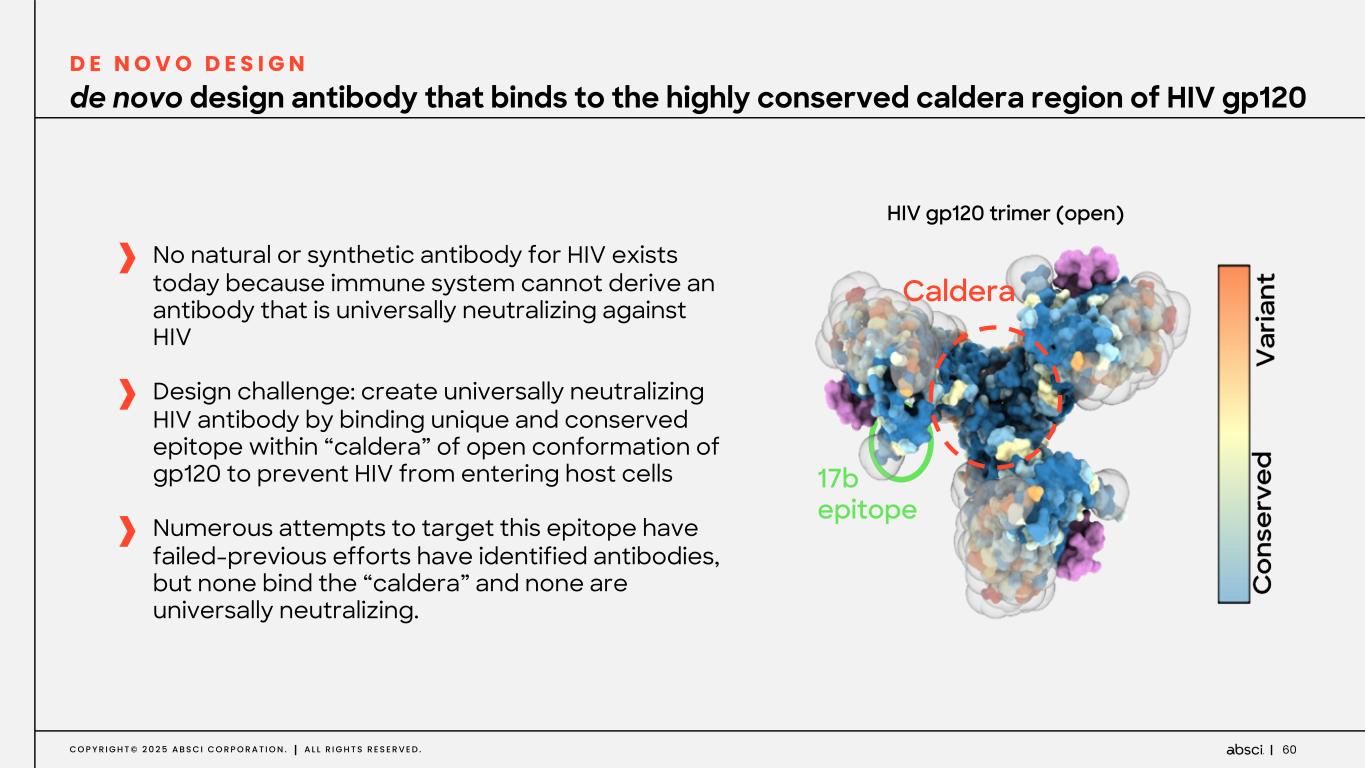
60C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . No natural or synthetic antibody for HIV exists today because immune system cannot derive an antibody that is universally neutralizing against HIV Design challenge: create universally neutralizing HIV antibody by binding unique and conserved epitope within “caldera” of open conformation of gp120 to prevent HIV from entering host cells Numerous attempts to target this epitope have failed-previous efforts have identified antibodies, but none bind the “caldera” and none are universally neutralizing. de novo design antibody that binds to the highly conserved caldera region of HIV gp120 D E N O V O D E S I G N 17b epitope Caldera HIV gp120 trimer (open)
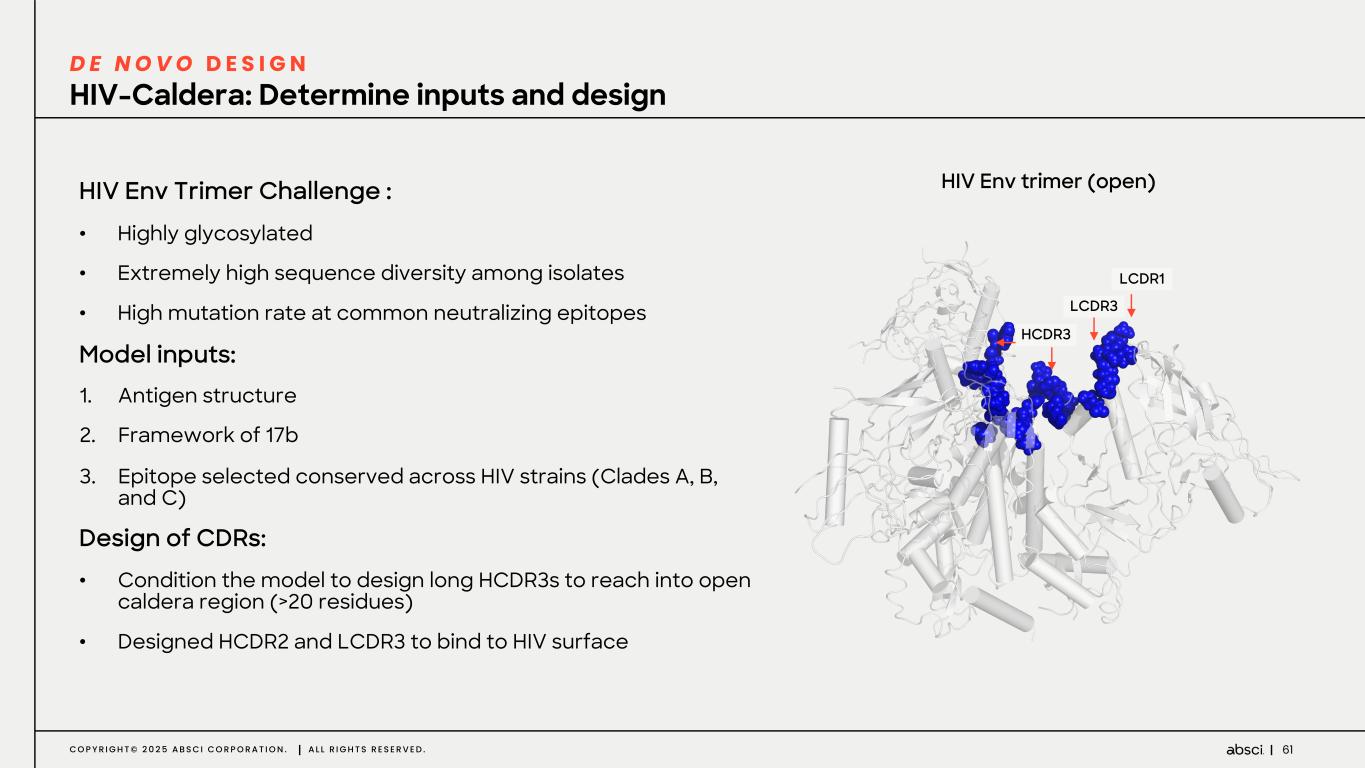
61C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . HIV-Caldera: Determine inputs and design D E N O V O D E S I G N HIV Env Trimer Challenge : • Highly glycosylated • Extremely high sequence diversity among isolates • High mutation rate at common neutralizing epitopes Model inputs: 1. Antigen structure 2. Framework of 17b 3. Epitope selected conserved across HIV strains (Clades A, B, and C) Design of CDRs: • Condition the model to design long HCDR3s to reach into open caldera region (>20 residues) • Designed HCDR2 and LCDR3 to bind to HIV surface HIV Env trimer (open) HCDR3 LCDR1 LCDR3
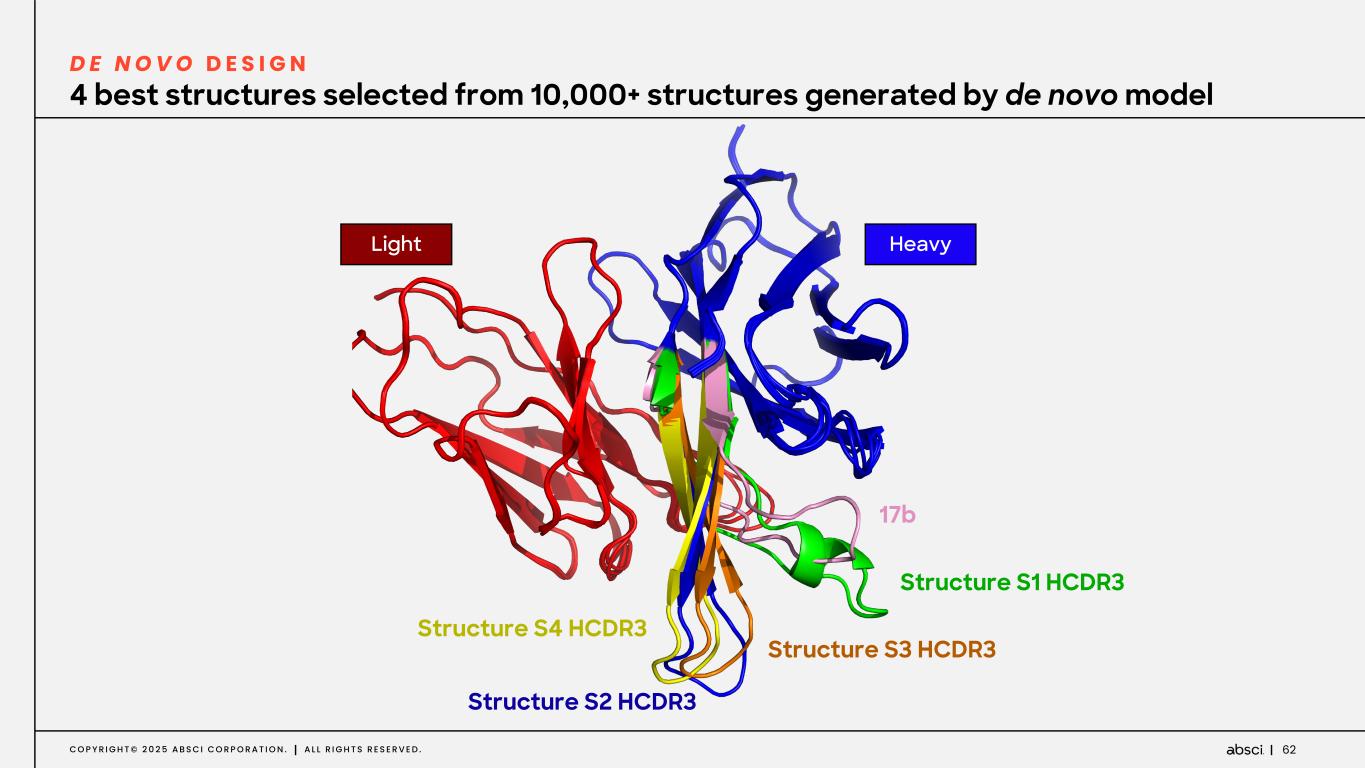
62C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . 4 best structures selected from 10,000+ structures generated by de novo model D E N O V O D E S I G N 17b Structure S1 HCDR3 Structure S3 HCDR3 Structure S2 HCDR3 Structure S4 HCDR3 HeavyLight
63C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . Applied molecular dynamics simulation to de novo designed antibodies D E N O V O D E S I G N
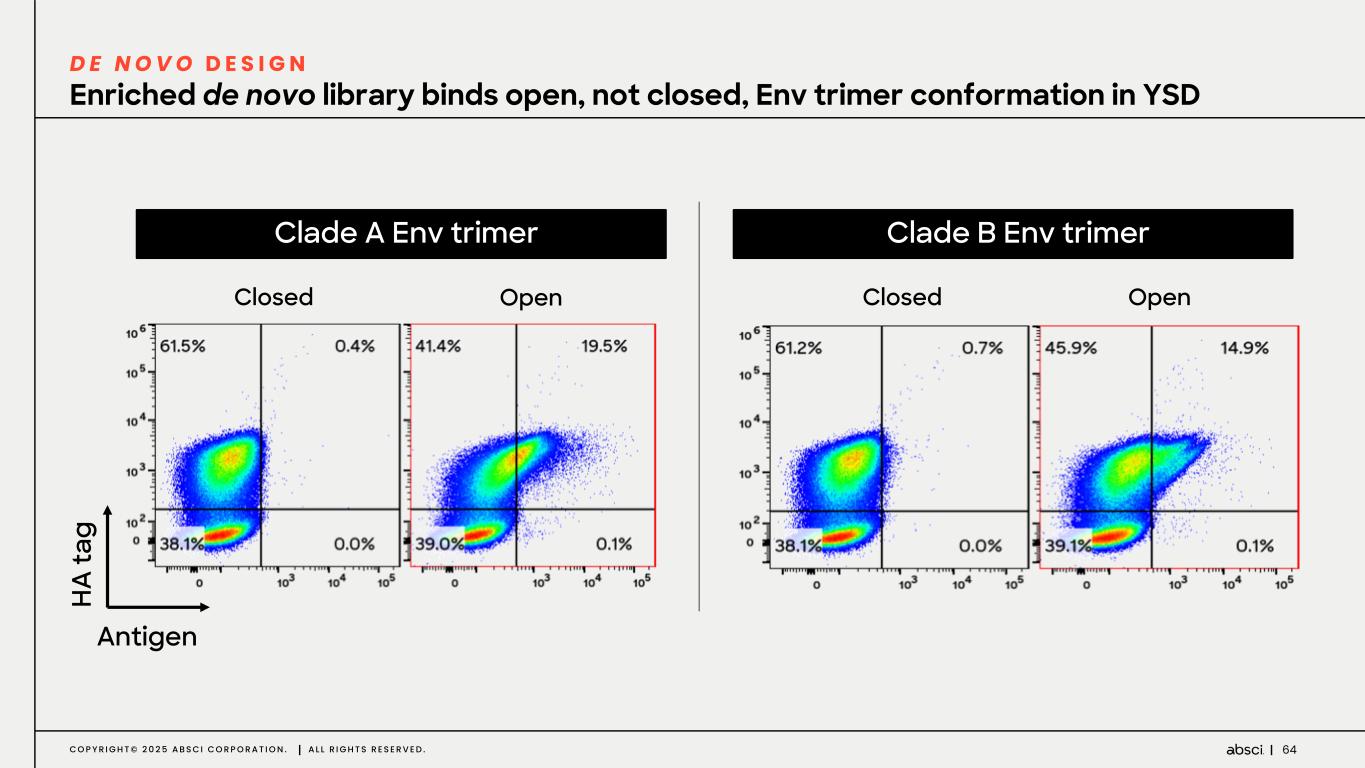
64C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . H A ta g Antigen Clade A Env trimer Closed Open Enriched de novo library binds open, not closed, Env trimer conformation in YSD D E N O V O D E S I G N Closed Open Clade B Env trimer
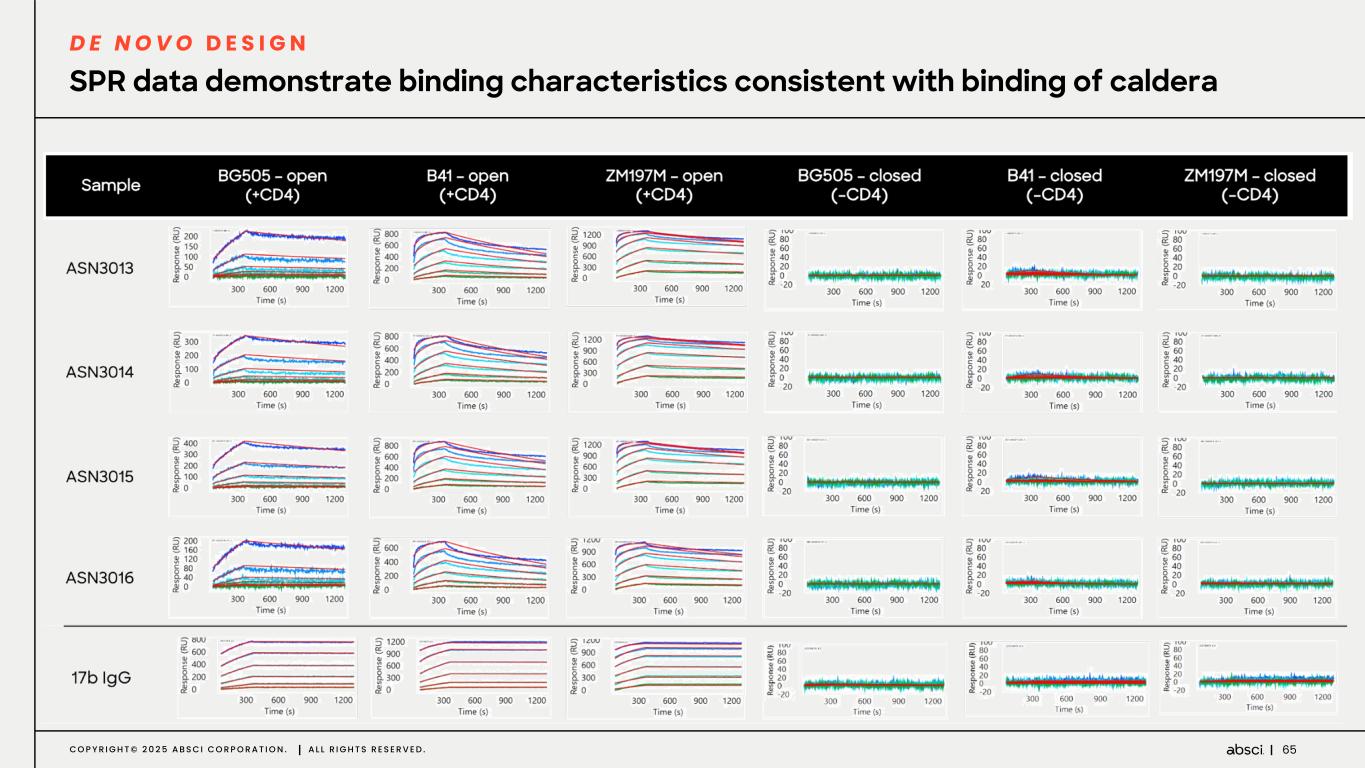
65C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . SPR data demonstrate binding characteristics consistent with binding of caldera D E N O V O D E S I G N
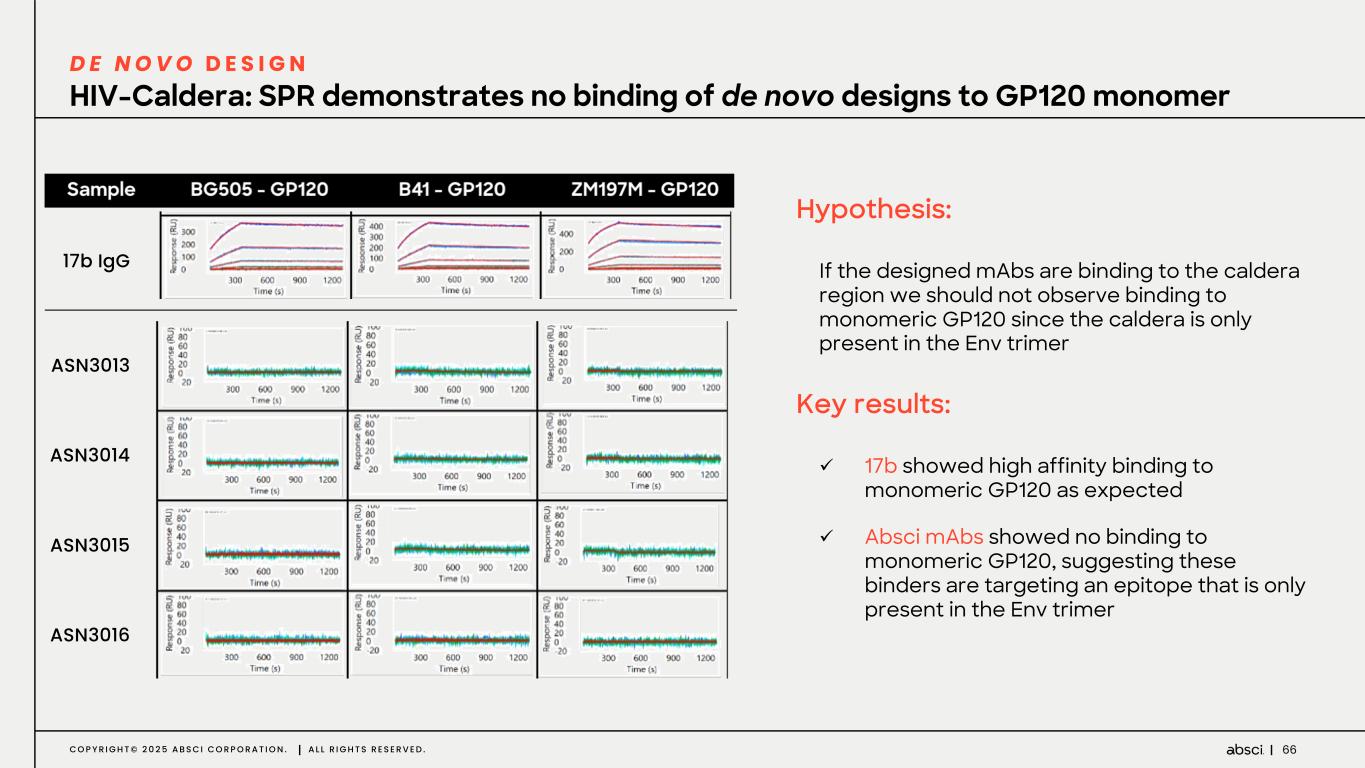
66C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . HIV-Caldera: SPR demonstrates no binding of de novo designs to GP120 monomer D E N O V O D E S I G N Hypothesis: If the designed mAbs are binding to the caldera region we should not observe binding to monomeric GP120 since the caldera is only present in the Env trimer Key results: ü 17b showed high affinity binding to monomeric GP120 as expected ü Absci mAbs showed no binding to monomeric GP120, suggesting these binders are targeting an epitope that is only present in the Env trimer ASN3013 ASN3014 ASN3015 ASN3016 17b IgG
67C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . HIV-Caldera: demonstrating AI de novo design for challenging target H I V D E N O V O D E S I G N SUMMARY de novo design model created a novel and diverse antibody which binds multiple clades of HIV indicating successful targeting of the caldera epitope Screening cascade enabled selection of differentially binding variants NEXT STEPS Binders from this study will be selected for affinity maturation Structure of de novo binder and epitope specificity will be experimentally solved to confirm fidelity with designed structure and targeted epitope

68C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . CASE STUDY A I O p t i m i z a t i o n f o r p H s e n s i t i v i t y
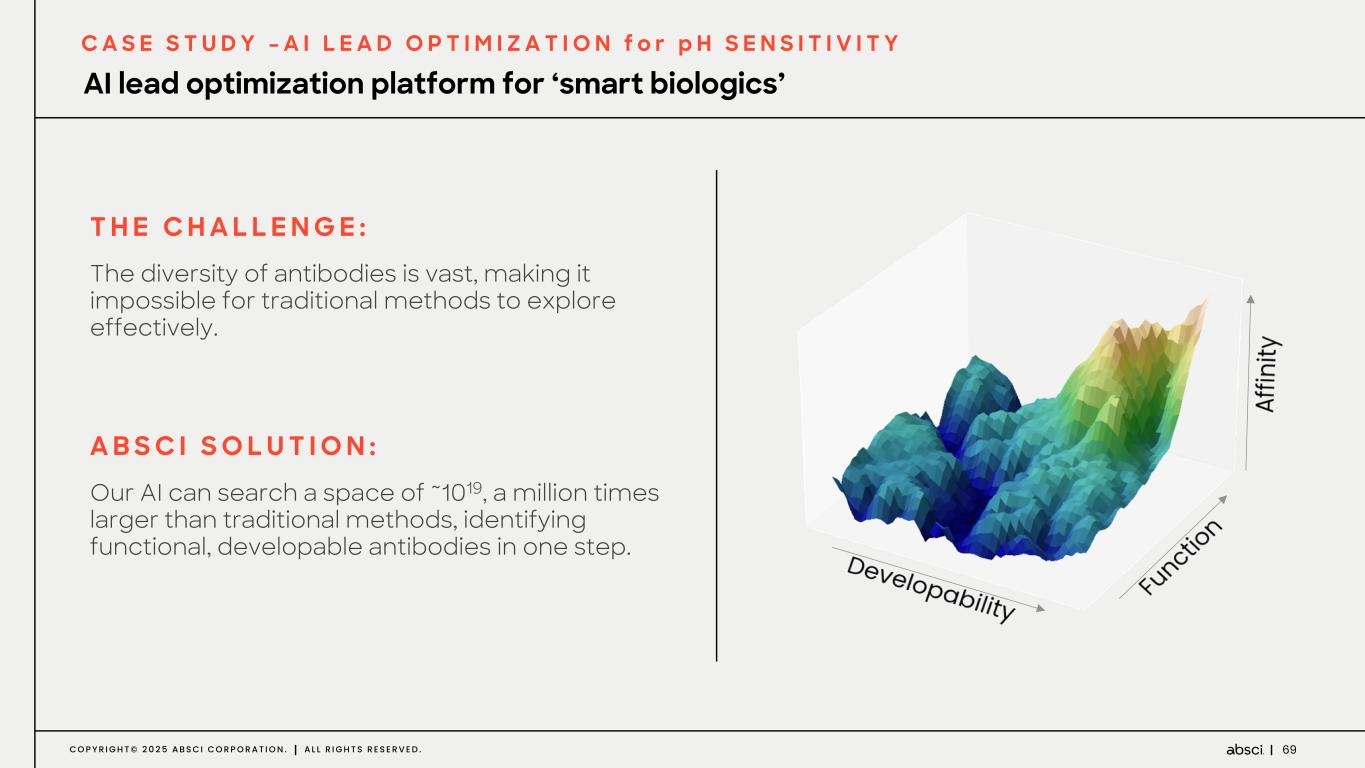
69C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . C A S E S T U D Y – A I L E A D O P T I M I Z A T I O N f o r p H S E N S I T I V I T Y AI lead optimization platform for ‘smart biologics’ T H E C H A L L E N G E : The diversity of antibodies is vast, making it impossible for traditional methods to explore effectively. A B S C I S O L U T I O N : Our AI can search a space of ~1019, a million times larger than traditional methods, identifying functional, developable antibodies in one step.
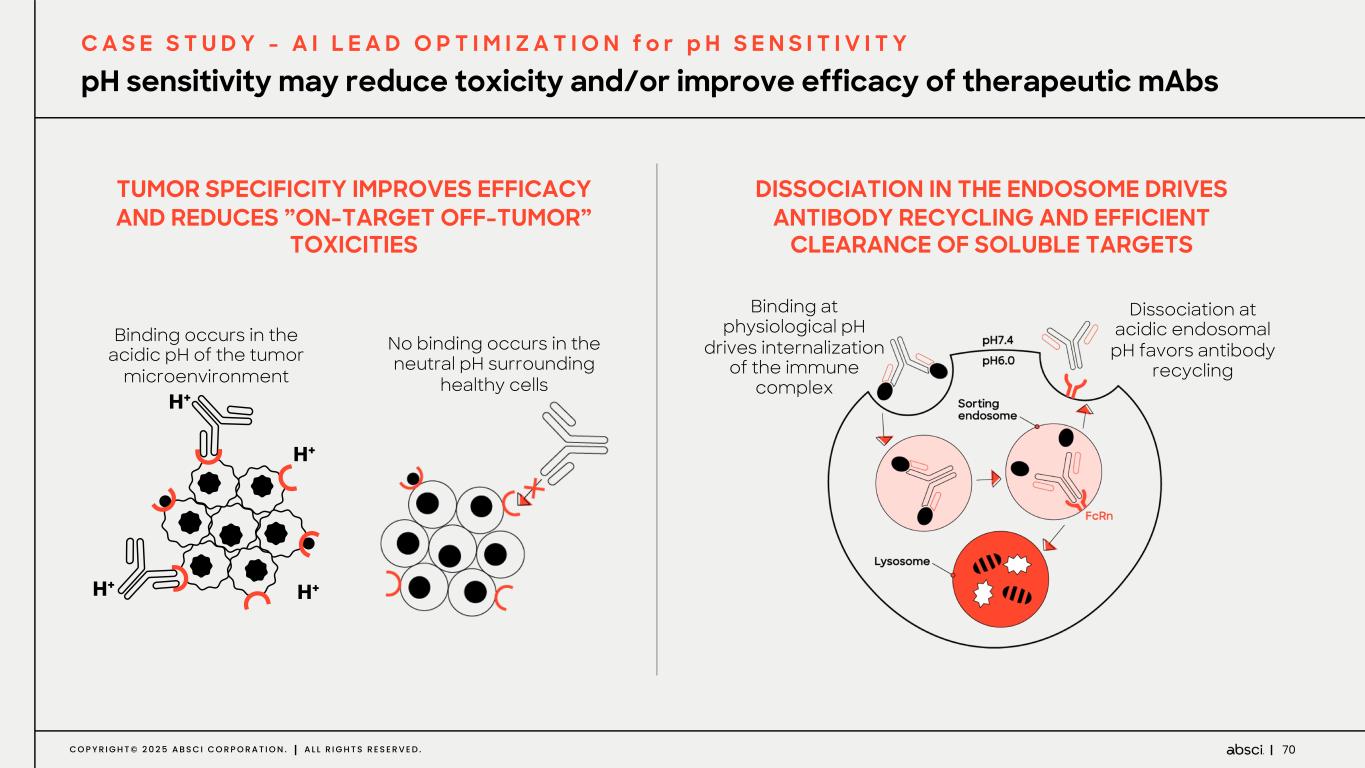
70C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . TUMOR SPECIFICITY IMPROVES EFFICACY AND REDUCES ”ON-TARGET OFF-TUMOR” TOXICITIES pH sensitivity may reduce toxicity and/or improve efficacy of therapeutic mAbs C A S E S T U D Y - A I L E A D O P T I M I Z A T I O N f o r p H S E N S I T I V I T Y Binding occurs in the acidic pH of the tumor microenvironment No binding occurs in the neutral pH surrounding healthy cells DISSOCIATION IN THE ENDOSOME DRIVES ANTIBODY RECYCLING AND EFFICIENT CLEARANCE OF SOLUBLE TARGETS Dissociation at acidic endosomal pH favors antibody recycling Binding at physiological pH drives internalization of the immune complex
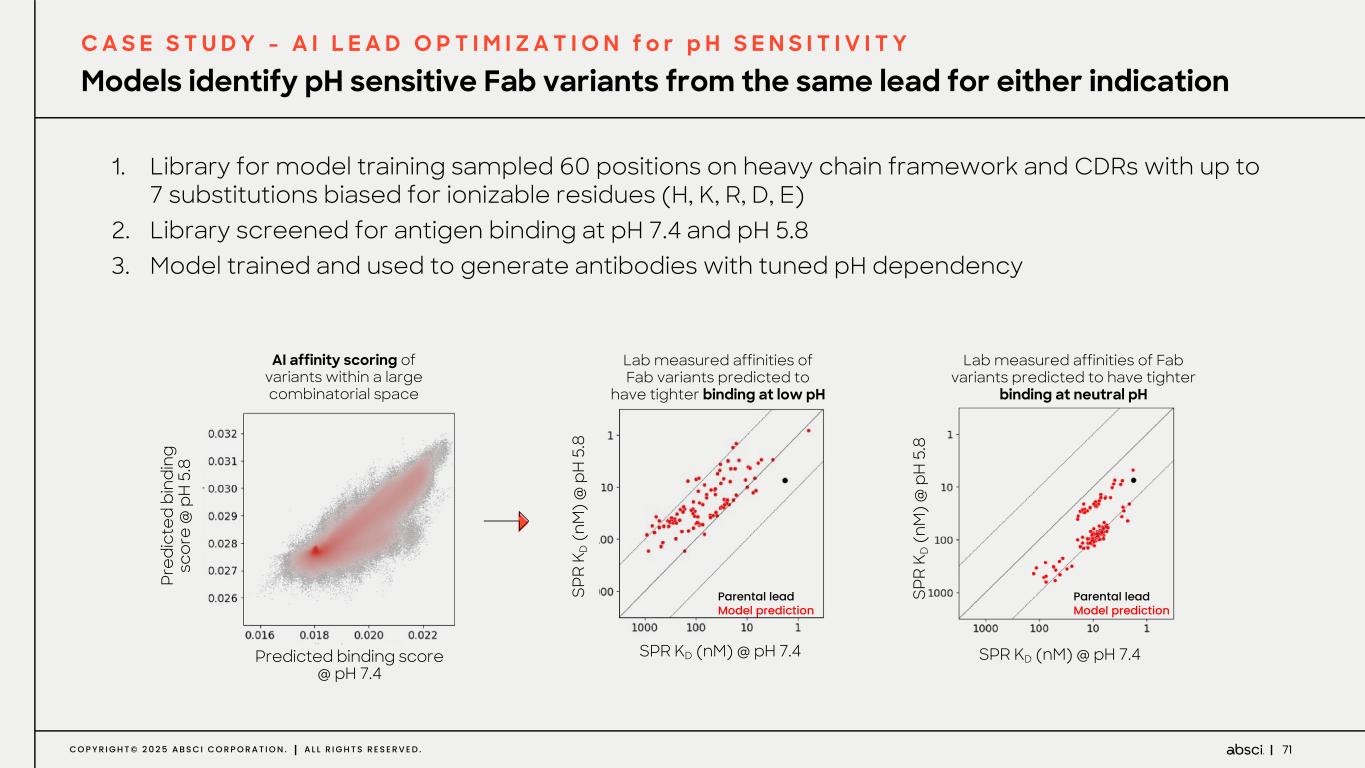
71C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . Models identify pH sensitive Fab variants from the same lead for either indication C A S E S T U D Y - A I L E A D O P T I M I Z A T I O N f o r p H S E N S I T I V I T Y 1. Library for model training sampled 60 positions on heavy chain framework and CDRs with up to 7 substitutions biased for ionizable residues (H, K, R, D, E) 2. Library screened for antigen binding at pH 7.4 and pH 5.8 3. Model trained and used to generate antibodies with tuned pH dependency Pr ed ic te d bi nd in g sc or e @ p H 5 .8 Predicted binding score @ pH 7.4 AI affinity scoring of variants within a large combinatorial space SPR KD (nM) @ pH 7.4 SP R K D (n M ) @ p H 5 .8 Lab measured affinities of Fab variants predicted to have tighter binding at neutral pH Parental lead Model predictionSP R K D ( nM ) @ p H 5. 8 Lab measured affinities of Fab variants predicted to have tighter binding at low pH Parental lead Model prediction SPR KD (nM) @ pH 7.4 SP R K D (n M ) @ p H 5 .8
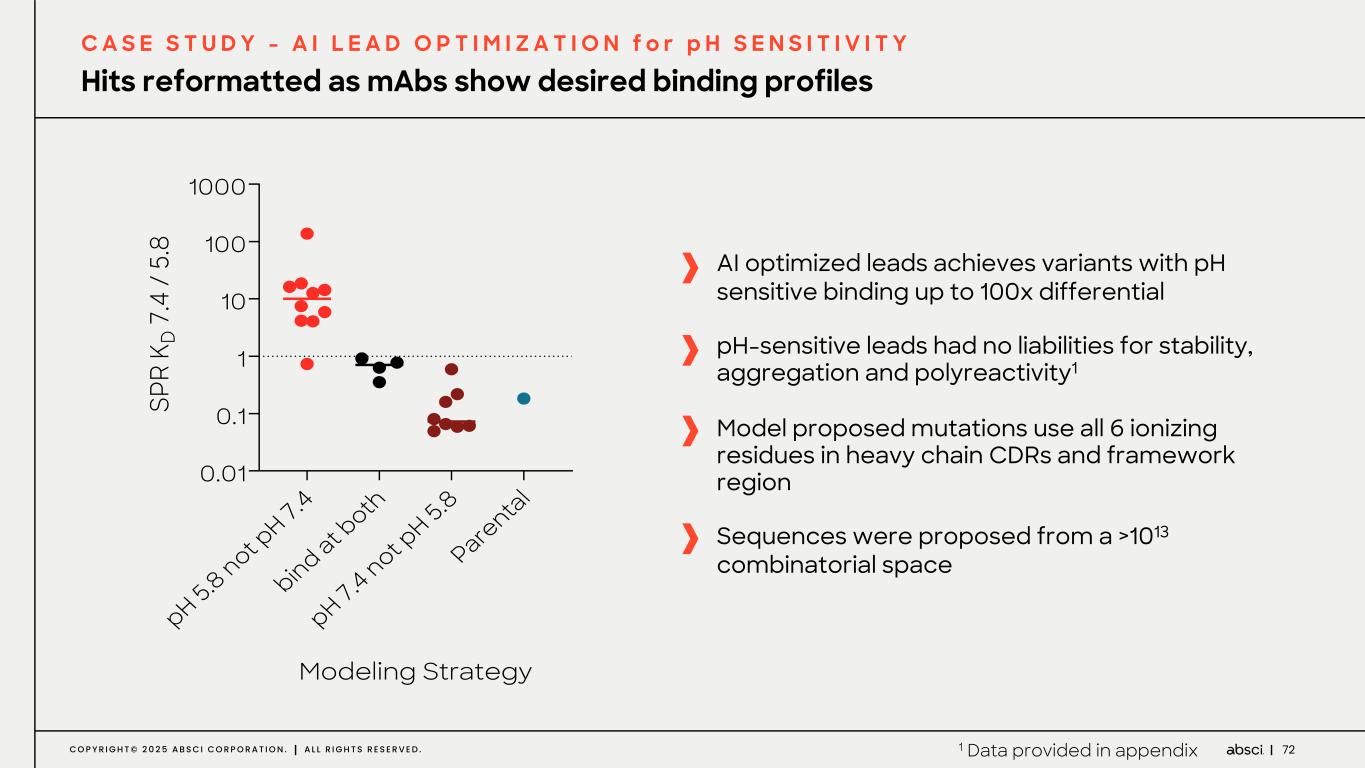
72C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . Hits reformatted as mAbs show desired binding profiles C A S E S T U D Y - A I L E A D O P T I M I Z A T I O N f o r p H S E N S I T I V I T Y AI optimized leads achieves variants with pH sensitive binding up to 100x differential pH-sensitive leads had no liabilities for stability, aggregation and polyreactivity1 Model proposed mutations use all 6 ionizing residues in heavy chain CDRs and framework region Sequences were proposed from a >1013 combinatorial space pH 5.8 not p H 7.4 bind at b oth pH 7.4 not p H 5.8 Pare ntal 0.01 0.1 1 10 100 1000 Modeling Strategy SP R K D 7 .4 / 5. 8 1 Data provided in appendix

73C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D . D E N O V O D E S I G N de novo design model created molecule binds multiple clades of HIV suggesting successful targeting of the caldera epitope Represents second disclosed target success for our de novo platform in the 2nd half of this year Absci’s de novo design platform can successfully address difficult to drug target epitopes A I O P T I M I Z A T I O N Models identify unseen variants with 10x-20x pH sensitivity in both directions, and up to 100x differential compared to parental molecule after only one round Designed leads had no liabilities indicating the ability to successfully search a fitness landscape Absci’s lead optimization platform enables molecules with differentiated pharmacology Summarized platform case studies

Better biologics for patients, faster 74C O P Y R I G H T © 2 0 2 5 A B S C I C O R P O R A T I O N . A L L R I G H T S R E S E R V E D .