

Improving Lives Through Transformative Precision Medicines JPM 2026 | 44th Annual Healthcare Conference January 2026

Certain statements in this presentation and the accompanying oral commentary are forward-looking statements. These statements relate to future events or the future financial performance of IDEAYA Biosciences, Inc. (the “Company”) and involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that may cause the actual results, levels of activity, performance or achievements of the Company or its industry to be materially different from those expressed or implied by any forward-looking statements. In some cases, forward-looking statements can be identified by terminology such as “may,” “will,” “could,” “would,” “should,” “expect,” “plan,” “anticipate,” “intend,” “believe,” “estimate,” “predict,” “potential” or other comparable terminology. All statements other than statements of historical fact could be deemed forward-looking, assumptions, estimates or projections that are subject to change, including expectations regarding the clinical activity profile, potential clinical benefit and potential advantages of the Company’s clinical programs; the translation of preliminary clinical trial results into future clinical trial results; the enrollment of clinical trials; the potentially addressable patient population for the Company’s programs; any expectations regarding the Company’s target discovery platform or new target validation efforts as creating opportunities for research and development initiatives; any projections of financial information, market opportunities, cash runway or profitability, including the estimated funding of operations into 2030; any statements about historical results that may suggest trends for the Company's business; any statements of the plans, strategies, and objectives of management for development programs or future operations; any statements about the timing of preclinical research, clinical development, regulatory filings, regulatory approvals, manufacturing or release of data; any statements of expectation or belief regarding future events, potential markets dynamics , technology developments, or receipt of cash milestones, option exercise fees or royalties; and any statements of assumptions underlying any of the items mentioned. The Company has based these forward-looking statements on its current expectations, assumptions, estimates and projections. While the Company believes these expectations, assumptions, estimates and projections are reasonable, such forward-looking statements are only predictions and involve known and unknown risks and uncertainties, many of which are beyond the Company's control. Such risks and uncertainties include, among others, the uncertainties inherent in the drug development process, including the Company’s programs’ early stage of development, the process of designing and conducting preclinical and clinical trials, serious adverse events, undesirable side effects or unexpected characteristics of drug development, the regulatory approval processes, the timing of regulatory filings, the challenges associated with the manufacturing and/or commercialization; timing of product launches, potential pricing and reimbursement; potential revenue, expected breakthrough, best or -in-class or blockbuster status, regulatory landscape, economic conditions, competitive landscape, the Company’s ability to successfully establish, protect and defend its intellectual property, and other matters that could affect the sufficiency of existing cash to fund operations. These and other important factors may cause actual results, performance or achievements to differ materially from those expressed or implied by these forward-looking statements. The forward-looking statements in this presentation are made only as of the date hereof. For a further description of the risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ from those expressed in these forward-looking statements, as well as risks relating to the business of the Company in general, see the Company's periodic filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the "SEC"), including its Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2024 and any current or periodic reports filed with the SEC. Except as required by law, the Company assumes no obligation and does not intend to update these forward-looking statements or to conform these statements to actual results or to changes in the Company's expectations. Other This presentation concerns anticipated products that are under clinical investigation and which have not yet been approved for marketing by the FDA or any other country regulatory authority. These anticipated products are currently limited by Federal law to investigational use, and no representation is made as to their safety or effectiveness for the purposes for which they are being investigated. Certain information contained in this presentation relates to or is based on studies, publications, surveys and other data obtained from third-party sources and the Company’s own internal estimates and research. The Company has not independently verified, and makes no representation as to the adequacy, fairness, accuracy or completeness of any information obtained from third-party sources. In addition, all of the market data included in this presentation involves a number of assumptions and limitations, and there can be no guarantee as to the accuracy or reliability of such assumptions. Finally, the Company's own internal estimates and research have not been verified by any independent source. IDEAYA and the IDEAYA logo are trademarks of IDEAYA Biosciences, Inc. All other trademarks used herein are the property of their respective owners. Safe Harbor Statement
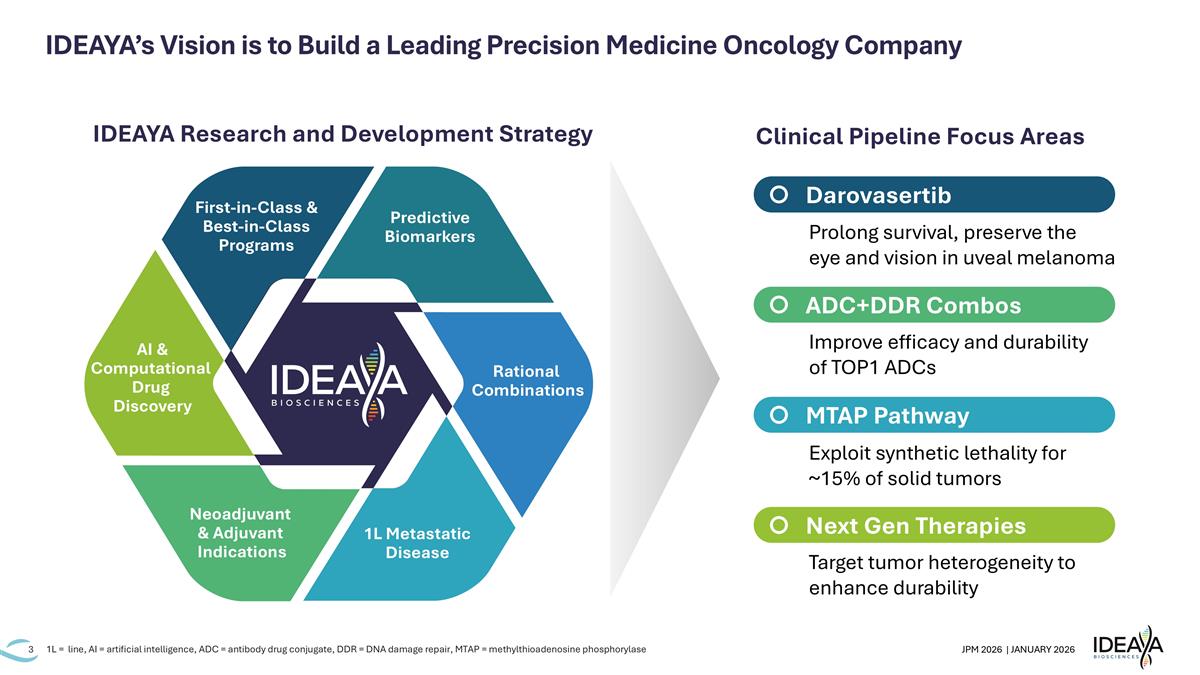
IDEAYA’s Vision is to Build a Leading Precision Medicine Oncology Company 1L = line, AI = artificial intelligence, ADC = antibody drug conjugate, DDR = DNA damage repair, MTAP = methylthioadenosine phosphorylase IDEAYA Research and Development Strategy Prolong survival, preserve the eye and vision in uveal melanoma Improve efficacy and durability of TOP1 ADCs Exploit synthetic lethality for ~15% of solid tumors Target tumor heterogeneity to enhance durability Clinical Pipeline Focus Areas Darovasertib ADC+DDR Combos MTAP Pathway Next Gen Therapies Predictive Biomarkers Rational Combinations Neoadjuvant & Adjuvant Indications 1L Metastatic Disease AI & Computational Drug Discovery First-in-Class & Best-in-Class Programs
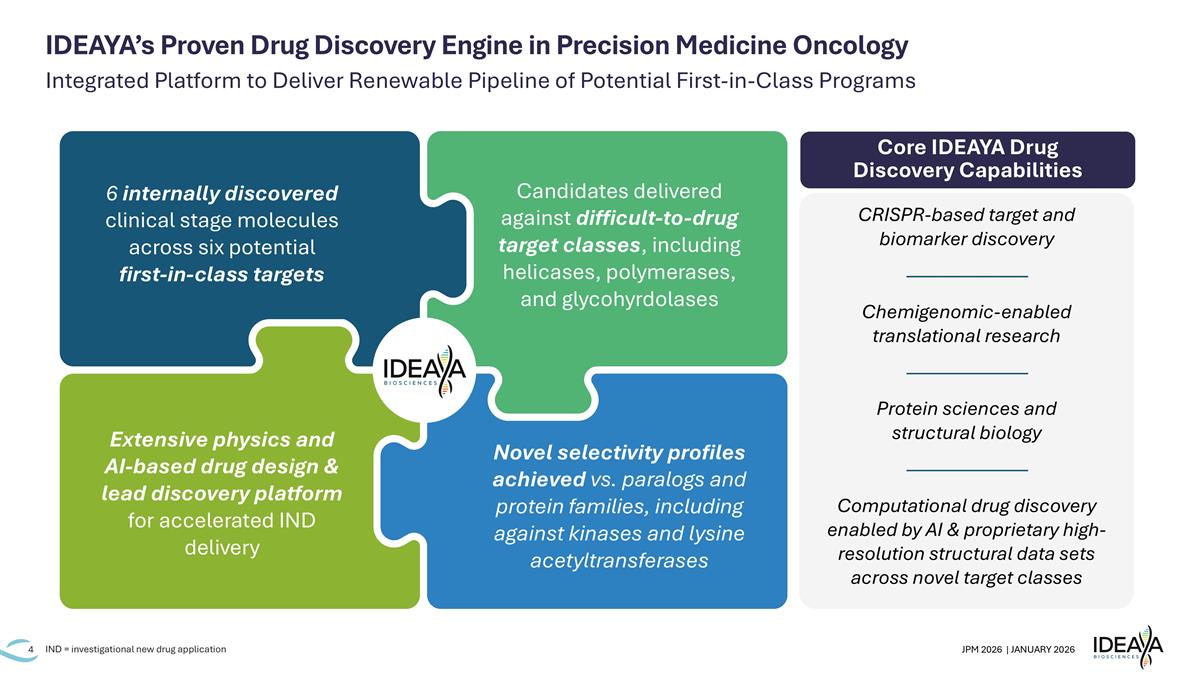
Integrated Platform to Deliver Renewable Pipeline of Potential First-in-Class Programs IND = investigational new drug application IDEAYA’s Proven Drug Discovery Engine in Precision Medicine Oncology Core IDEAYA Drug Discovery Capabilities 6 internally discovered clinical stage molecules across six potential first-in-class targets Extensive physics and AI-based drug design & lead discovery platform for accelerated IND delivery Candidates delivered against difficult-to-drug target classes, including helicases, polymerases, and glycohyrdolases Novel selectivity profiles achieved vs. paralogs and protein families, including against kinases and lysine acetyltransferases CRISPR-based target and biomarker discovery ——————— Chemigenomic-enabled translational research ——————— Protein sciences and structural biology ——————— Computational drug discovery enabled by AI & proprietary high-resolution structural data sets across novel target classes
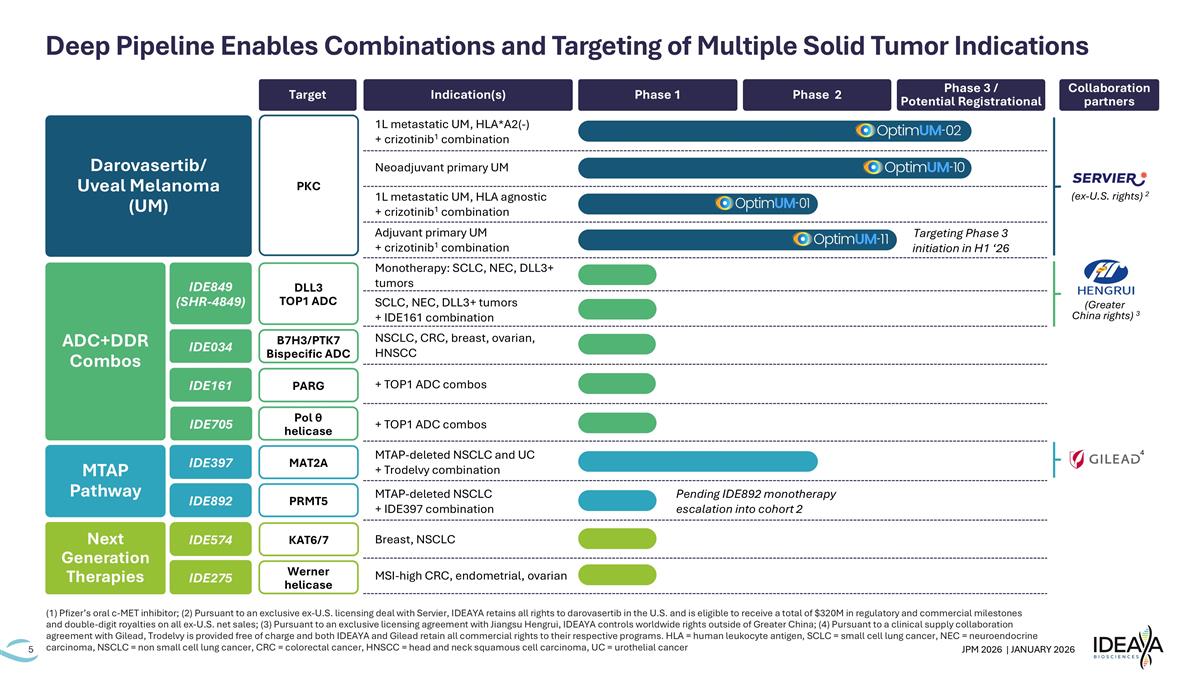
Deep Pipeline Enables Combinations and Targeting of Multiple Solid Tumor Indications Indication(s) Target Phase 1 Collaboration partners Phase 2 Phase 3 / Potential Registrational IDE275 Next Generation Therapies IDE574 Werner helicase KAT6/7 MSI-high CRC, endometrial, ovarian Breast, NSCLC 4 MTAP-deleted NSCLC and UC + Trodelvy combination MTAP Pathway IDE397 IDE892 MAT2A PRMT5 MTAP-deleted NSCLC + IDE397 combination Pending IDE892 monotherapy escalation into cohort 2 (Greater China rights) 3 IDE705 Pol θ helicase + TOP1 ADC combos Monotherapy: SCLC, NEC, DLL3+ tumors SCLC, NEC, DLL3+ tumors + IDE161 combination NSCLC, CRC, breast, ovarian, HNSCC ADC+DDR Combos IDE849 (SHR-4849) IDE034 IDE161 + TOP1 ADC combos DLL3 TOP1 ADC B7H3/PTK7 Bispecific ADC PARG Darovasertib/ Uveal Melanoma (UM) 1L metastatic UM, HLA*A2(-) + crizotinib1 combination Neoadjuvant primary UM 1L metastatic UM, HLA agnostic + crizotinib1 combination PKC Adjuvant primary UM + crizotinib1 combination (ex-U.S. rights) 2 (1) Pfizer’s oral c-MET inhibitor; (2) Pursuant to an exclusive ex-U.S. licensing deal with Servier, IDEAYA retains all rights to darovasertib in the U.S. and is eligible to receive a total of $320M in regulatory and commercial milestones and double-digit royalties on all ex-U.S. net sales; (3) Pursuant to an exclusive licensing agreement with Jiangsu Hengrui, IDEAYA controls worldwide rights outside of Greater China; (4) Pursuant to a clinical supply collaboration agreement with Gilead, Trodelvy is provided free of charge and both IDEAYA and Gilead retain all commercial rights to their respective programs. HLA = human leukocyte antigen, SCLC = small cell lung cancer, NEC = neuroendocrine carcinoma, NSCLC = non small cell lung cancer, CRC = colorectal cancer, HNSCC = head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, UC = urothelial cancer Targeting Phase 3 initiation in H1 ‘26
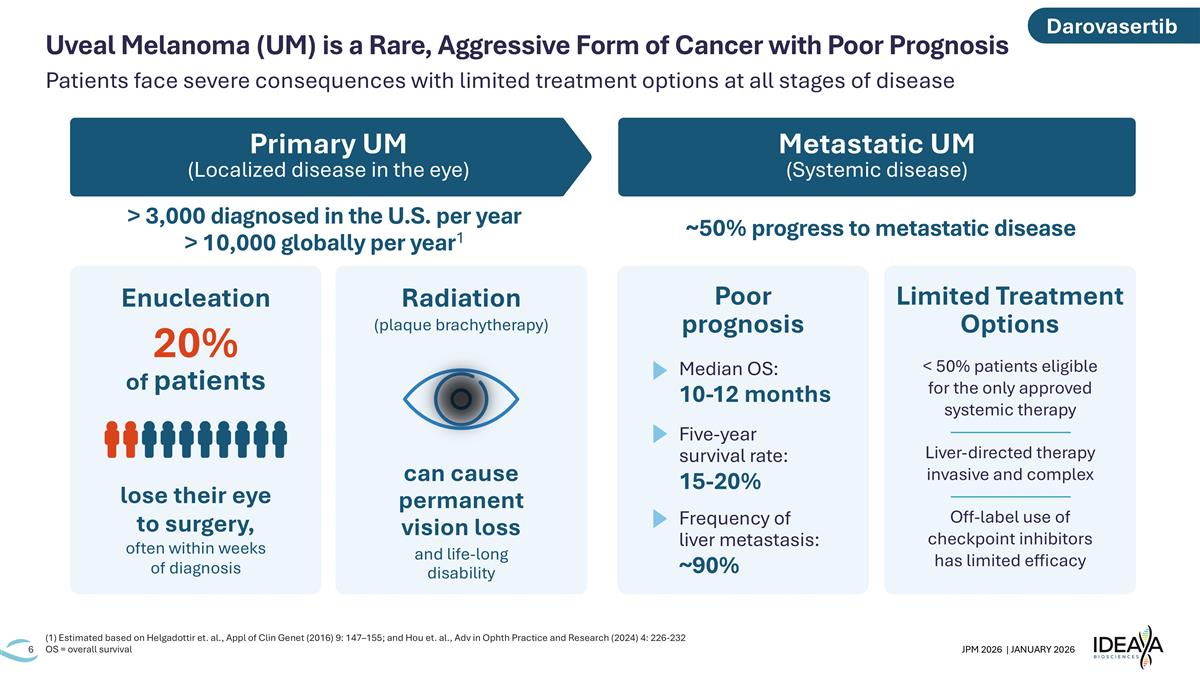
Primary UM (Localized disease in the eye) Metastatic UM (Systemic disease) > 3,000 diagnosed in the U.S. per year > 10,000 globally per year1 ~50% progress to metastatic disease Patients face severe consequences with limited treatment options at all stages of disease (1) Estimated based on Helgadottir et. al., Appl of Clin Genet (2016) 9: 147–155; and Hou et. al., Adv in Ophth Practice and Research (2024) 4: 226-232 OS = overall survival Uveal Melanoma (UM) is a Rare, Aggressive Form of Cancer with Poor Prognosis lose their eye to surgery, often within weeks of diagnosis 20% of patients Radiation (plaque brachytherapy) can cause permanent vision loss and life-long disability Median OS: 10-12 months Five-year survival rate: 15-20% Poor prognosis Limited Treatment Options < 50% patients eligible for the only approved systemic therapy ———————— Liver-directed therapy invasive and complex ———————— Off-label use of checkpoint inhibitors has limited efficacy Frequency of liver metastasis: ~90% Enucleation Darovasertib
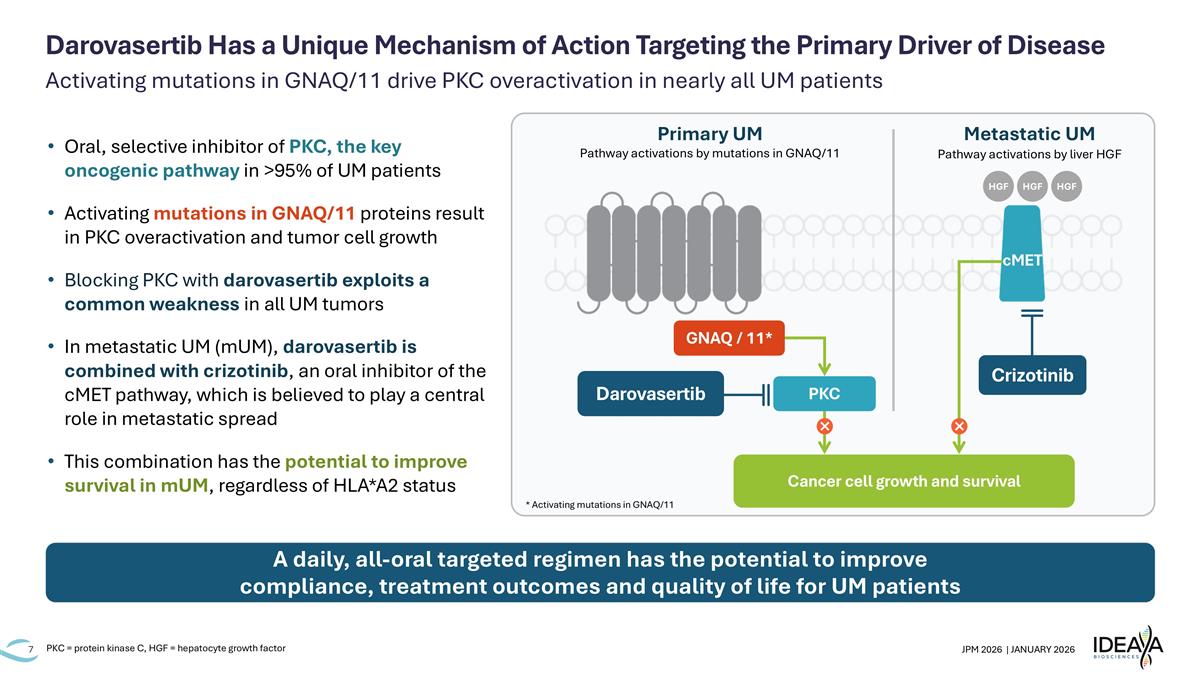
Activating mutations in GNAQ/11 drive PKC overactivation in nearly all UM patients Darovasertib Has a Unique Mechanism of Action Targeting the Primary Driver of Disease Oral, selective inhibitor of PKC, the key oncogenic pathway in >95% of UM patients Activating mutations in GNAQ/11 proteins result in PKC overactivation and tumor cell growth Blocking PKC with darovasertib exploits a common weakness in all UM tumors In metastatic UM (mUM), darovasertib is combined with crizotinib, an oral inhibitor of the cMET pathway, which is believed to play a central role in metastatic spread This combination has the potential to improve survival in mUM, regardless of HLA*A2 status A daily, all-oral targeted regimen has the potential to improve compliance, treatment outcomes and quality of life for UM patients PKC = protein kinase C, HGF = hepatocyte growth factor Primary UM Metastatic UM Cancer cell growth and survival GNAQ / 11* PKC Darovasertib cMET Pathway activations by mutations in GNAQ/11 Pathway activations by liver HGF Crizotinib HGF HGF HGF * Activating mutations in GNAQ/11
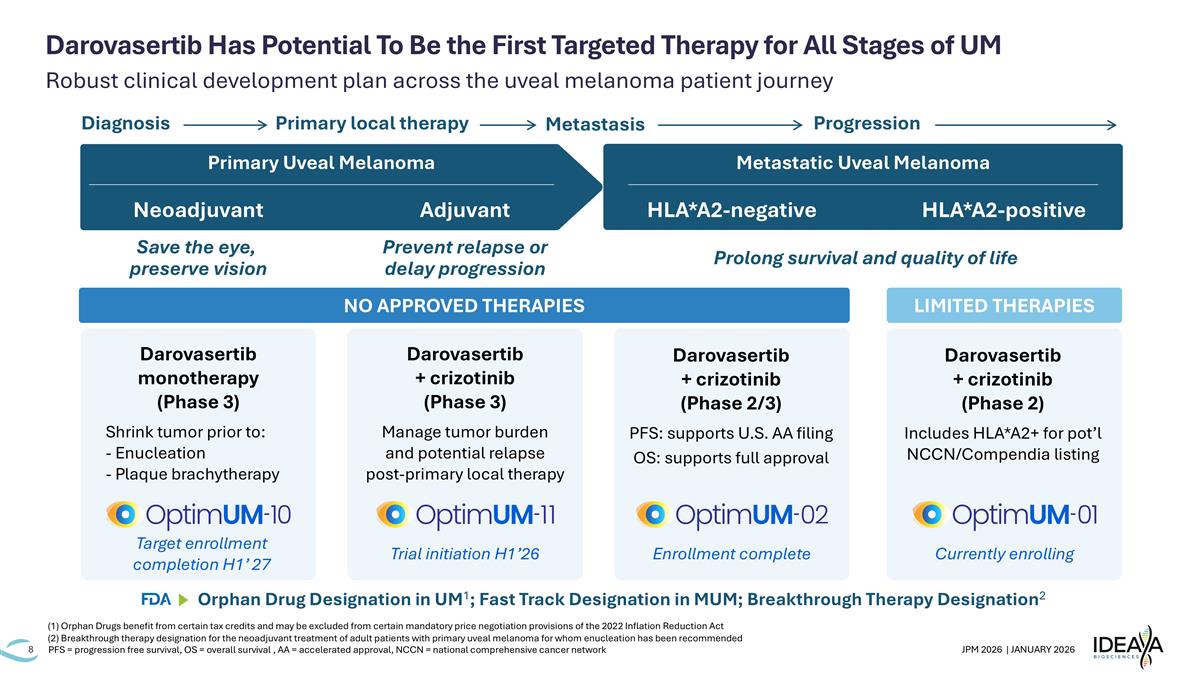
Robust clinical development plan across the uveal melanoma patient journey Darovasertib Has Potential To Be the First Targeted Therapy for All Stages of UM PFS = progression free survival, OS = overall survival , AA = accelerated approval, NCCN = national comprehensive cancer network Neoadjuvant Adjuvant Metastatic Uveal Melanoma LIMITED THERAPIES Save the eye, preserve vision Prevent relapse or delay progression Diagnosis Primary local therapy Metastasis Progression NO APPROVED THERAPIES Primary Uveal Melanoma Darovasertib monotherapy (Phase 3) Shrink tumor prior to: - Enucleation - Plaque brachytherapy Target enrollment completion H1’ 27 Darovasertib + crizotinib (Phase 3) Manage tumor burden and potential relapse post-primary local therapy Trial initiation H1’26 Darovasertib + crizotinib (Phase 2/3) PFS: supports U.S. AA filing OS: supports full approval Enrollment complete Darovasertib + crizotinib (Phase 2) Includes HLA*A2+ for pot’l NCCN/Compendia listing Currently enrolling HLA*A2-negative HLA*A2-positive Prolong survival and quality of life Orphan Drug Designation in UM1; Fast Track Designation in MUM; Breakthrough Therapy Designation2 (1) Orphan Drugs benefit from certain tax credits and may be excluded from certain mandatory price negotiation provisions of the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act (2) Breakthrough therapy designation for the neoadjuvant treatment of adult patients with primary uveal melanoma for whom enucleation has been recommended
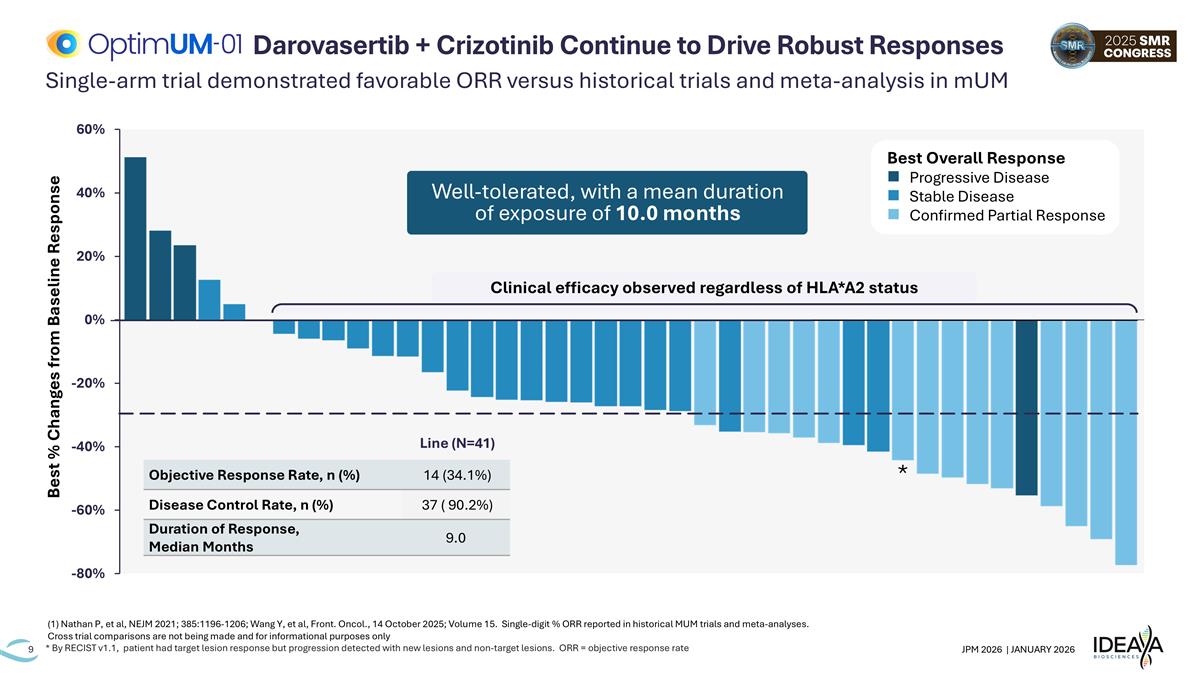
* Clinical efficacy observed regardless of HLA*A2 status Best % Changes from Baseline Response Single-arm trial demonstrated favorable ORR versus historical trials and meta-analysis in mUM * By RECIST v1.1, patient had target lesion response but progression detected with new lesions and non-target lesions. ORR = objective response rate Darovasertib + Crizotinib Continue to Drive Robust Responses Line (N=41) Objective Response Rate, n (%) 14 (34.1%) Disease Control Rate, n (%) 37 ( 90.2%) Duration of Response, Median Months 9.0 Best Overall Response n Progressive Disease n Stable Disease n Confirmed Partial Response Well-tolerated, with a mean duration of exposure of 10.0 months (1) Nathan P, et al, NEJM 2021; 385:1196-1206; Wang Y, et al, Front. Oncol., 14 October 2025; Volume 15. Single-digit % ORR reported in historical MUM trials and meta-analyses. Cross trial comparisons are not being made and for informational purposes only
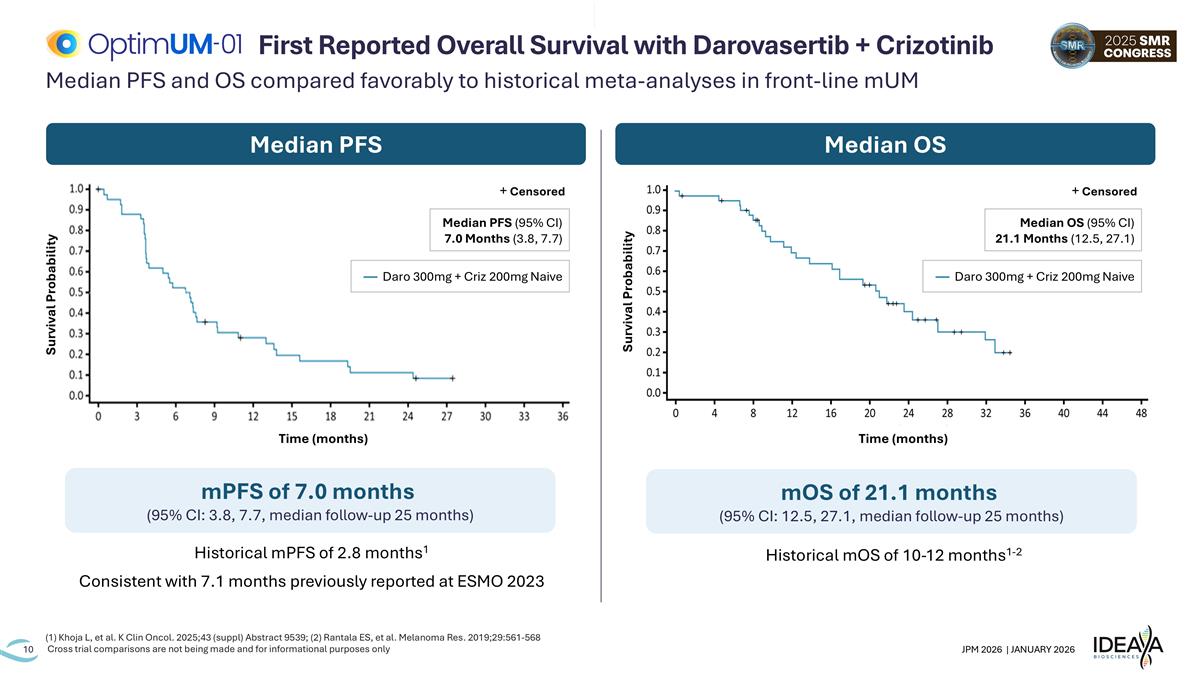
Median PFS and OS compared favorably to historical meta-analyses in front-line mUM (1) Khoja L, et al. K Clin Oncol. 2025;43 (suppl) Abstract 9539; (2) Rantala ES, et al. Melanoma Res. 2019;29:561-568 Cross trial comparisons are not being made and for informational purposes only First Reported Overall Survival with Darovasertib + Crizotinib Median PFS Median OS mOS of 21.1 months (95% CI: 12.5, 27.1, median follow-up 25 months) mPFS of 7.0 months (95% CI: 3.8, 7.7, median follow-up 25 months) Historical mPFS of 2.8 months1 Consistent with 7.1 months previously reported at ESMO 2023 Historical mOS of 10-12 months1-2 Survival Probability Time (months) + Censored Median OS (95% CI) 21.1 Months (12.5, 27.1) — Daro 300mg + Criz 200mg Naive Survival Probability Time (months) + Censored Median PFS (95% CI) 7.0 Months (3.8, 7.7) — Daro 300mg + Criz 200mg Naive
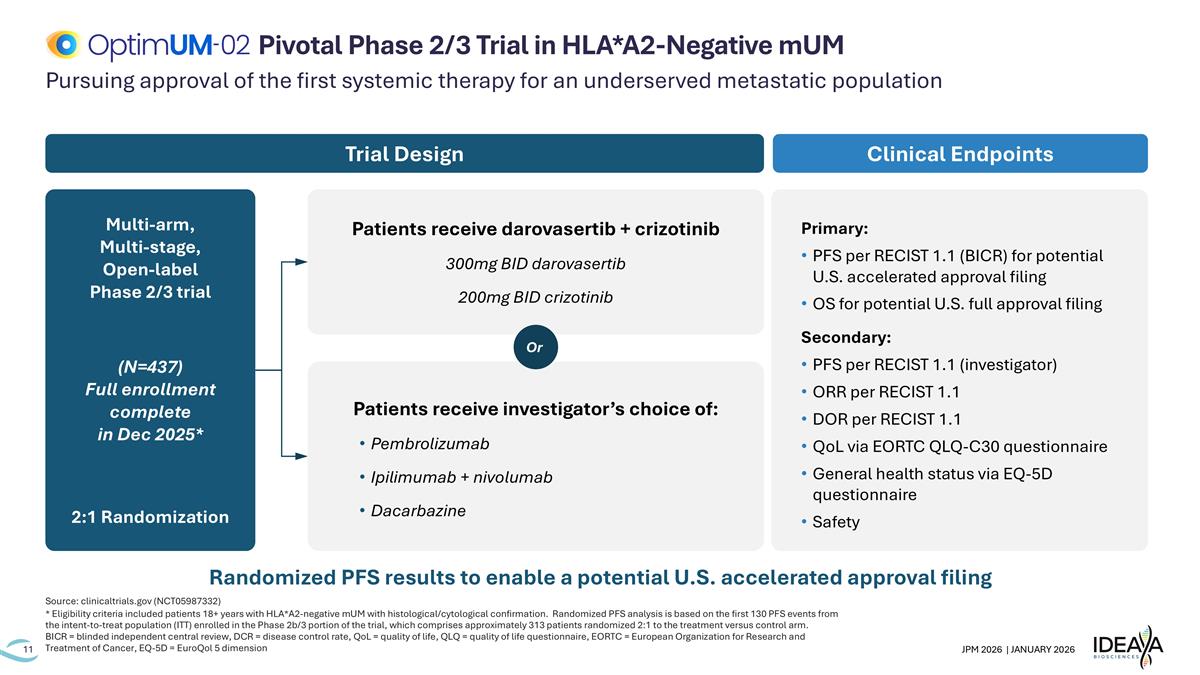
Pursuing approval of the first systemic therapy for an underserved metastatic population Source: clinicaltrials.gov (NCT05987332) * Eligibility criteria included patients 18+ years with HLA*A2-negative mUM with histological/cytological confirmation. Randomized PFS analysis is based on the first 130 PFS events from the intent-to-treat population (ITT) enrolled in the Phase 2b/3 portion of the trial, which comprises approximately 313 patients randomized 2:1 to the treatment versus control arm. BICR = blinded independent central review, DCR = disease control rate, QoL = quality of life, QLQ = quality of life questionnaire, EORTC = European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, EQ-5D = EuroQol 5 dimension Pivotal Phase 2/3 Trial in HLA*A2-Negative mUM Primary: PFS per RECIST 1.1 (BICR) for potential U.S. accelerated approval filing OS for potential U.S. full approval filing Secondary: PFS per RECIST 1.1 (investigator) ORR per RECIST 1.1 DOR per RECIST 1.1 QoL via EORTC QLQ-C30 questionnaire General health status via EQ-5D questionnaire Safety Clinical Endpoints Multi-arm, Multi-stage, Open-label Phase 2/3 trial (N=437) Full enrollment complete in Dec 2025* 2:1 Randomization Trial Design Patients receive darovasertib + crizotinib 300mg BID darovasertib 200mg BID crizotinib Patients receive investigator’s choice of: Pembrolizumab Ipilimumab + nivolumab Dacarbazine Or Randomized PFS results to enable a potential U.S. accelerated approval filing
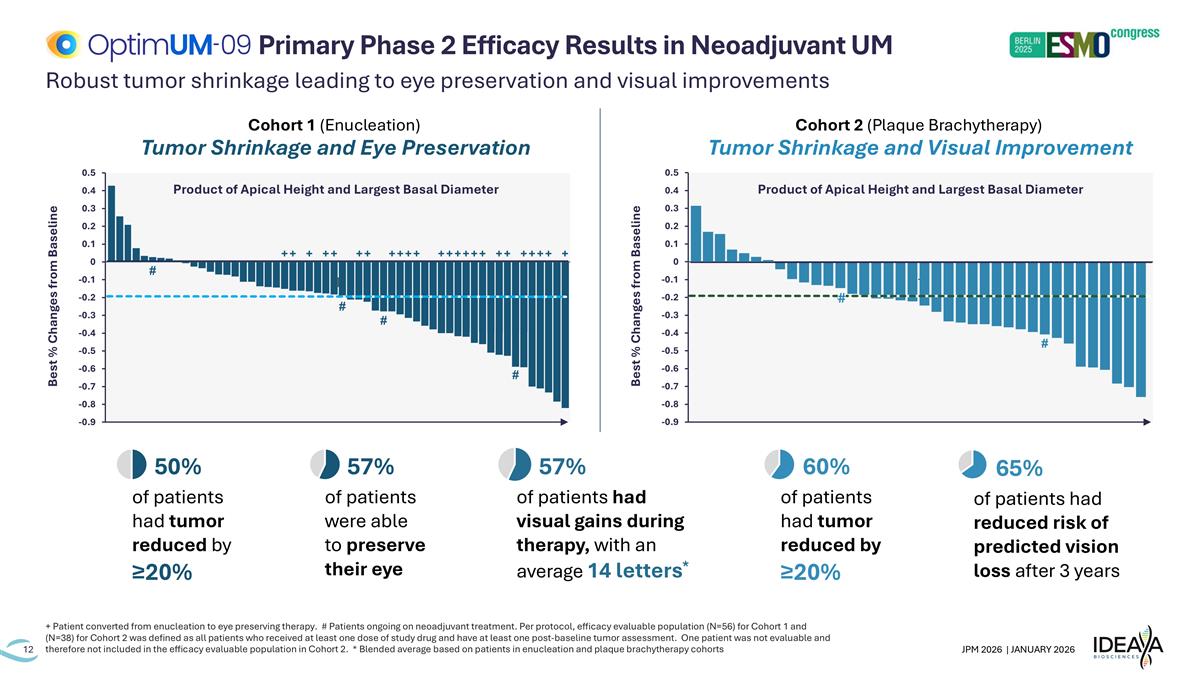
Robust tumor shrinkage leading to eye preservation and visual improvements + Patient converted from enucleation to eye preserving therapy. # Patients ongoing on neoadjuvant treatment. Per protocol, efficacy evaluable population (N=56) for Cohort 1 and (N=38) for Cohort 2 was defined as all patients who received at least one dose of study drug and have at least one post-baseline tumor assessment. One patient was not evaluable and therefore not included in the efficacy evaluable population in Cohort 2. * Blended average based on patients in enucleation and plaque brachytherapy cohorts Primary Phase 2 Efficacy Results in Neoadjuvant UM Cohort 1 (Enucleation) Tumor Shrinkage and Eye Preservation Cohort 2 (Plaque Brachytherapy) Tumor Shrinkage and Visual Improvement Best % Changes from Baseline Product of Apical Height and Largest Basal Diameter Best % Changes from Baseline Product of Apical Height and Largest Basal Diameter # 57% of patients were able to preserve their eye 50% of patients had tumor reduced by ≥20% 60% of patients had tumor reduced by ≥20% 57% of patients had visual gains during therapy, with an average 14 letters* 65% of patients had reduced risk of predicted vision loss after 3 years
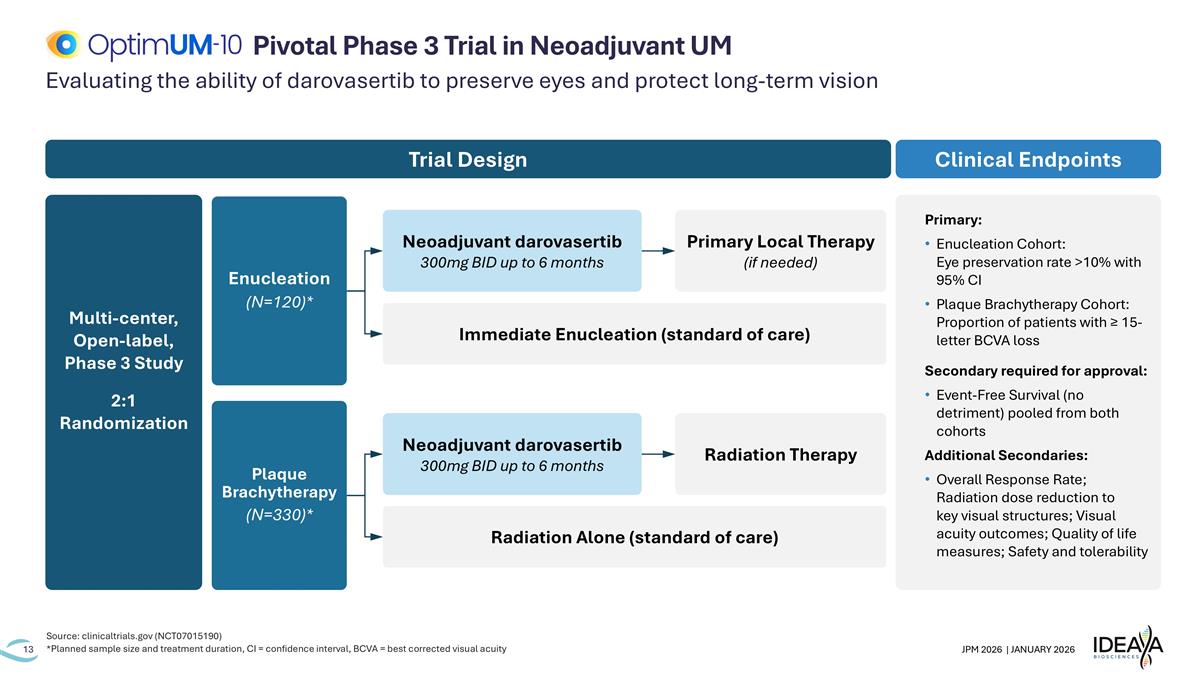
Evaluating the ability of darovasertib to preserve eyes and protect long-term vision Source: clinicaltrials.gov (NCT07015190) *Planned sample size and treatment duration, CI = confidence interval, BCVA = best corrected visual acuity Pivotal Phase 3 Trial in Neoadjuvant UM Primary: Enucleation Cohort: Eye preservation rate >10% with 95% CI Plaque Brachytherapy Cohort: Proportion of patients with ≥ 15-letter BCVA loss Secondary required for approval: Event-Free Survival (no detriment) pooled from both cohorts Additional Secondaries: Overall Response Rate; Radiation dose reduction to key visual structures; Visual acuity outcomes; Quality of life measures; Safety and tolerability Clinical Endpoints Multi-center, Open-label, Phase 3 Study 2:1 Randomization Trial Design Immediate Enucleation (standard of care) Enucleation (N=120)* Plaque Brachytherapy (N=330)* Neoadjuvant darovasertib 300mg BID up to 6 months Primary Local Therapy (if needed) Radiation Alone (standard of care) Neoadjuvant darovasertib 300mg BID up to 6 months Radiation Therapy
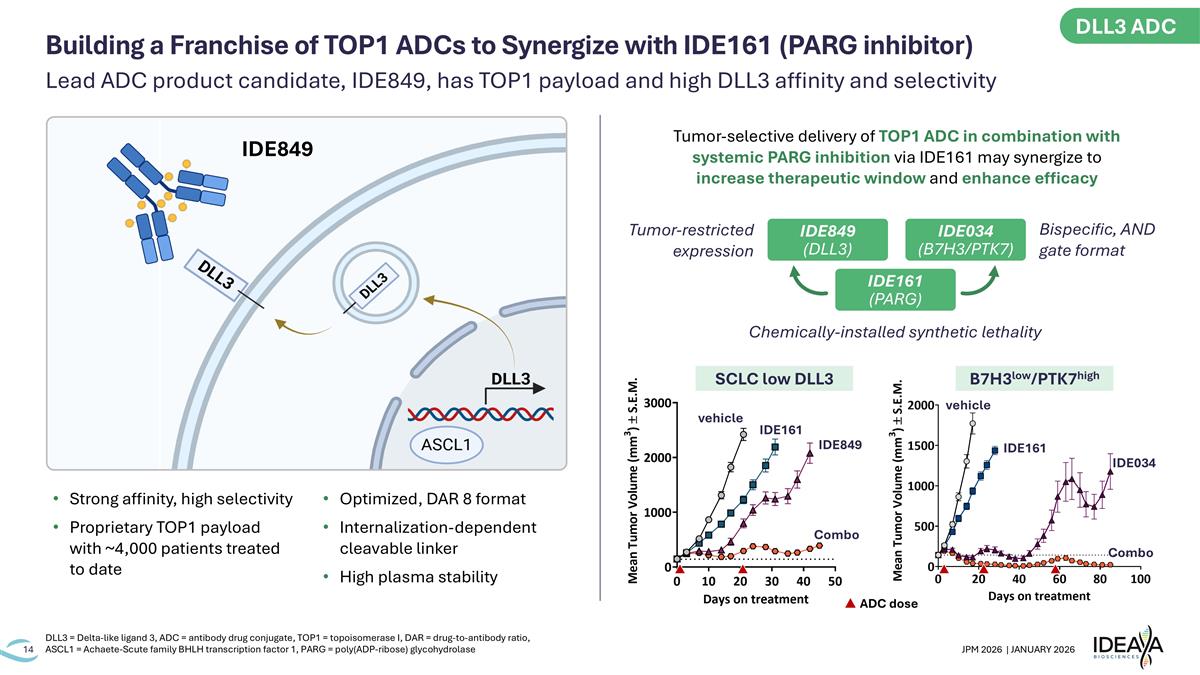
Lead ADC product candidate, IDE849, has TOP1 payload and high DLL3 affinity and selectivity DLL3 = Delta-like ligand 3, ADC = antibody drug conjugate, TOP1 = topoisomerase I, DAR = drug-to-antibody ratio, ASCL1 = Achaete-Scute family BHLH transcription factor 1, PARG = poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase Building a Franchise of TOP1 ADCs to Synergize with IDE161 (PARG inhibitor) Strong affinity, high selectivity Proprietary TOP1 payload with ~4,000 patients treated to date Optimized, DAR 8 format Internalization-dependent cleavable linker High plasma stability Tumor-selective delivery of TOP1 ADC in combination with systemic PARG inhibition via IDE161 may synergize to increase therapeutic window and enhance efficacy Chemically-installed synthetic lethality ADC dose SCLC low DLL3 Combo vehicle IDE161 IDE849 B7H3low/PTK7high Combo vehicle IDE161 IDE034 IDE034 (B7H3/PTK7) IDE849 (DLL3) IDE161 (PARG) IDE849 Tumor-restricted expression Bispecific, AND gate format DLL3 ADC
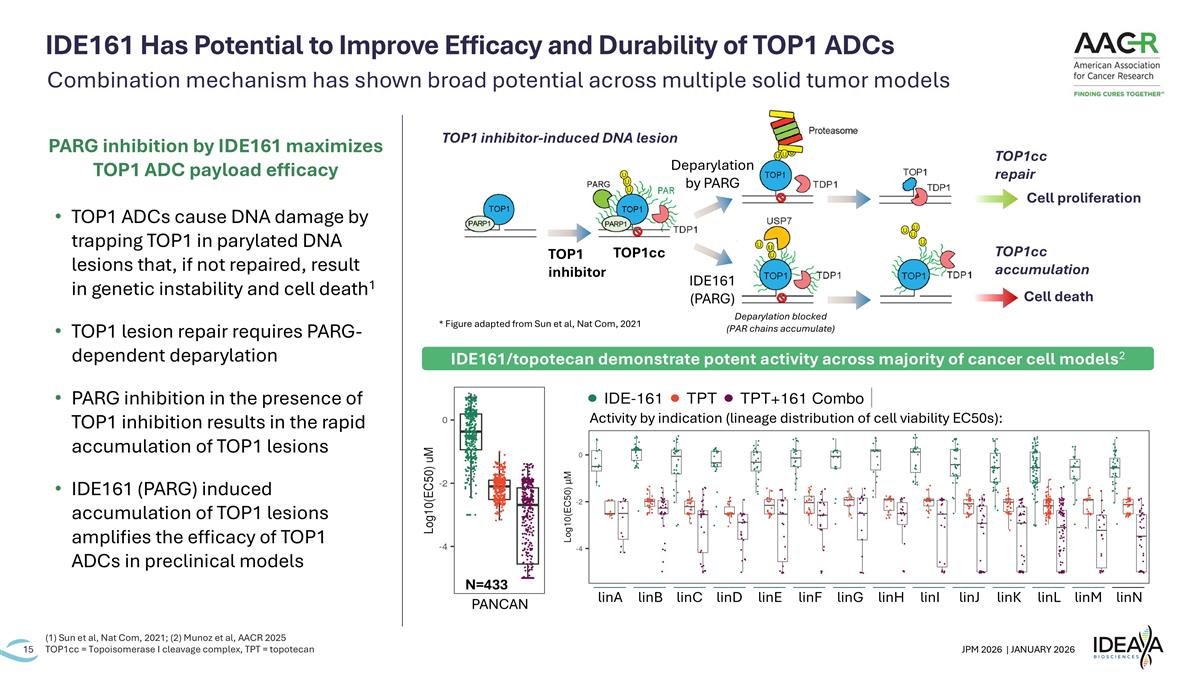
IDE161 Has Potential to Improve Efficacy and Durability of TOP1 ADCs (1) Sun et al, Nat Com, 2021; (2) Munoz et al, AACR 2025 TOP1cc = Topoisomerase I cleavage complex, TPT = topotecan TOP1cc Cell death Cell proliferation TOP1 inhibitor-induced DNA lesion TOP1 inhibitor Deparylation by PARG IDE161 (PARG) TOP1cc accumulation TOP1cc repair Deparylation blocked (PAR chains accumulate) linA linK linJ linI linH linG linF linE linD linC linB linN linM linL PANCAN N=433 Activity by indication (lineage distribution of cell viability EC50s): IDE161/topotecan demonstrate potent activity across majority of cancer cell models2 Combination mechanism has shown broad potential across multiple solid tumor models * Figure adapted from Sun et al, Nat Com, 2021 TOP1 ADCs cause DNA damage by trapping TOP1 in parylated DNA lesions that, if not repaired, result in genetic instability and cell death1 TOP1 lesion repair requires PARG-dependent deparylation PARG inhibition in the presence of TOP1 inhibition results in the rapid accumulation of TOP1 lesions IDE161 (PARG) induced accumulation of TOP1 lesions amplifies the efficacy of TOP1 ADCs in preclinical models PARG inhibition by IDE161 maximizes TOP1 ADC payload efficacy
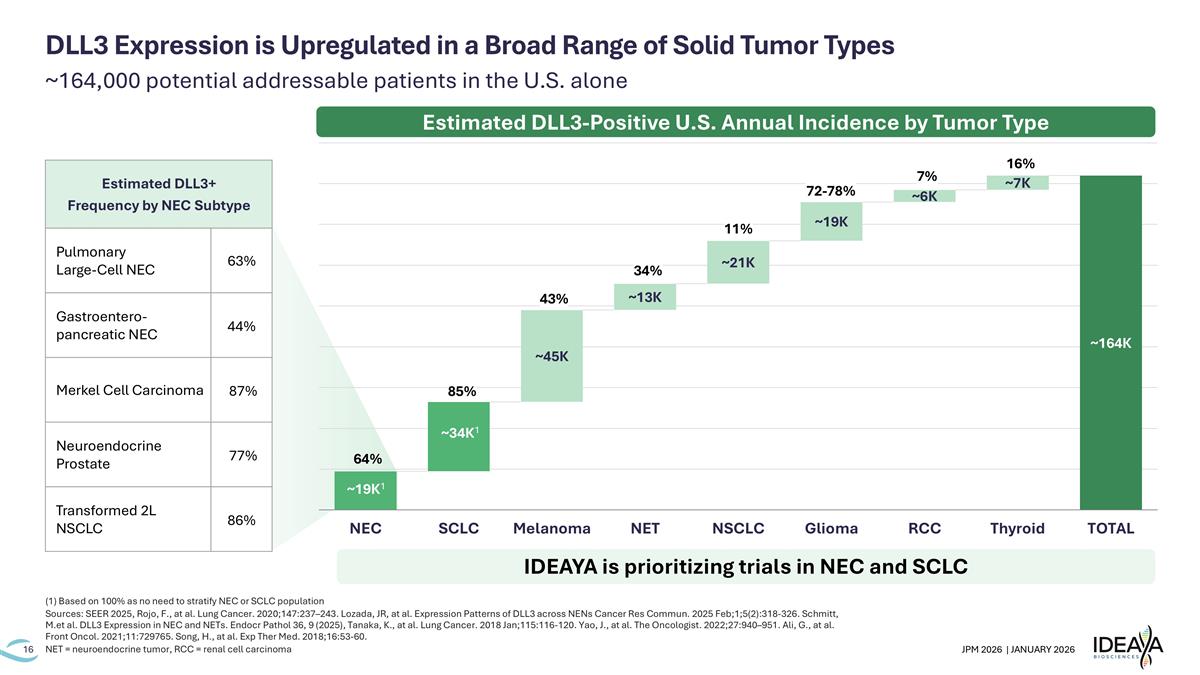
~164,000 potential addressable patients in the U.S. alone (1) Based on 100% as no need to stratify NEC or SCLC population Sources: SEER 2025, Rojo, F., at al. Lung Cancer. 2020;147:237–243. Lozada, JR, at al. Expression Patterns of DLL3 across NENs Cancer Res Commun. 2025 Feb;1;5(2):318-326. Schmitt, M.et al. DLL3 Expression in NEC and NETs. Endocr Pathol 36, 9 (2025), Tanaka, K., at al. Lung Cancer. 2018 Jan;115:116-120. Yao, J., at al. The Oncologist. 2022;27:940–951. Ali, G., at al. Front Oncol. 2021;11:729765. Song, H., at al. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16:53-60. NET = neuroendocrine tumor, RCC = renal cell carcinoma DLL3 Expression is Upregulated in a Broad Range of Solid Tumor Types 85% 64% 11% 43% 72-78% 7% 16% 34% ~34K1 Estimated DLL3-Positive U.S. Annual Incidence by Tumor Type IDEAYA is prioritizing trials in NEC and SCLC Estimated DLL3+ Frequency by NEC Subtype Pulmonary Large-Cell NEC 63% Gastroentero-pancreatic NEC 44% Merkel Cell Carcinoma 87% Neuroendocrine Prostate 77% Transformed 2L NSCLC 86% ~19K1
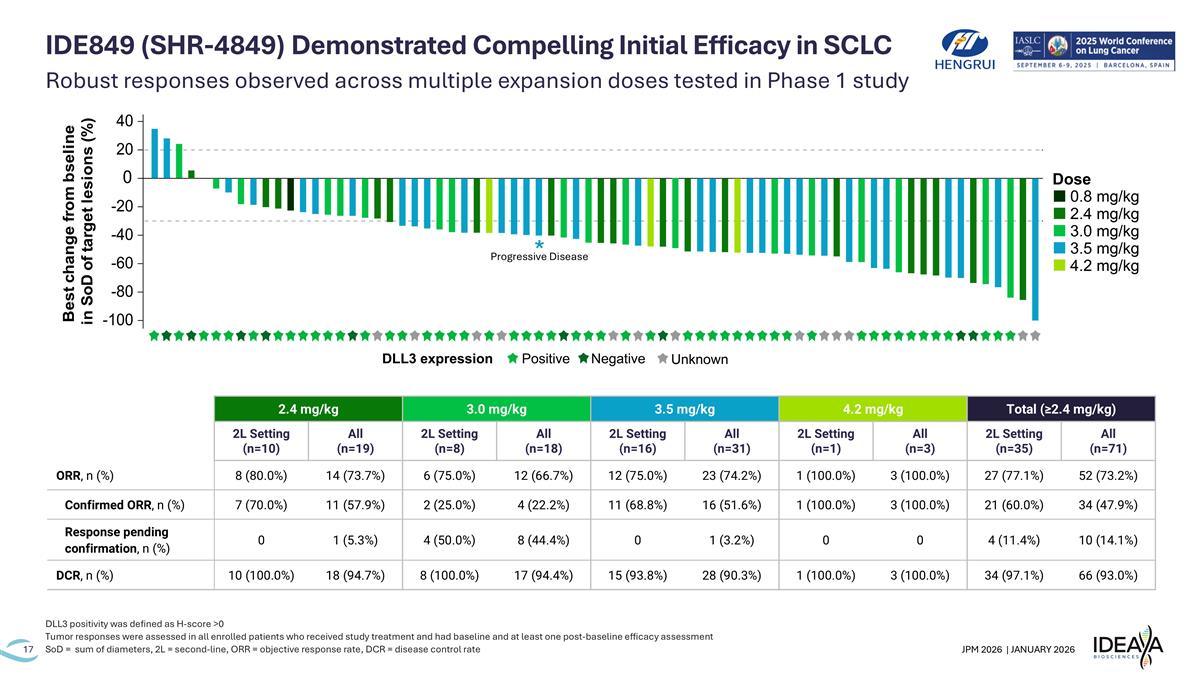
Robust responses observed across multiple expansion doses tested in Phase 1 study DLL3 positivity was defined as H-score >0 Tumor responses were assessed in all enrolled patients who received study treatment and had baseline and at least one post-baseline efficacy assessment SoD = sum of diameters, 2L = second-line, ORR = objective response rate, DCR = disease control rate IDE849 (SHR-4849) Demonstrated Compelling Initial Efficacy in SCLC 2.4 mg/kg 3.0 mg/kg 3.5 mg/kg 4.2 mg/kg Total (≥2.4 mg/kg) 2L Setting (n=10) All (n=19) 2L Setting (n=8) All (n=18) 2L Setting (n=16) All (n=31) 2L Setting (n=1) All (n=3) 2L Setting (n=35) All (n=71) ORR, n (%) 8 (80.0%) 14 (73.7%) 6 (75.0%) 12 (66.7%) 12 (75.0%) 23 (74.2%) 1 (100.0%) 3 (100.0%) 27 (77.1%) 52 (73.2%) Confirmed ORR, n (%) 7 (70.0%) 11 (57.9%) 2 (25.0%) 4 (22.2%) 11 (68.8%) 16 (51.6%) 1 (100.0%) 3 (100.0%) 21 (60.0%) 34 (47.9%) Response pending confirmation, n (%) 0 1 (5.3%) 4 (50.0%) 8 (44.4%) 0 1 (3.2%) 0 0 4 (11.4%) 10 (14.1%) DCR, n (%) 10 (100.0%) 18 (94.7%) 8 (100.0%) 17 (94.4%) 15 (93.8%) 28 (90.3%) 1 (100.0%) 3 (100.0%) 34 (97.1%) 66 (93.0%) Progressive Disease *
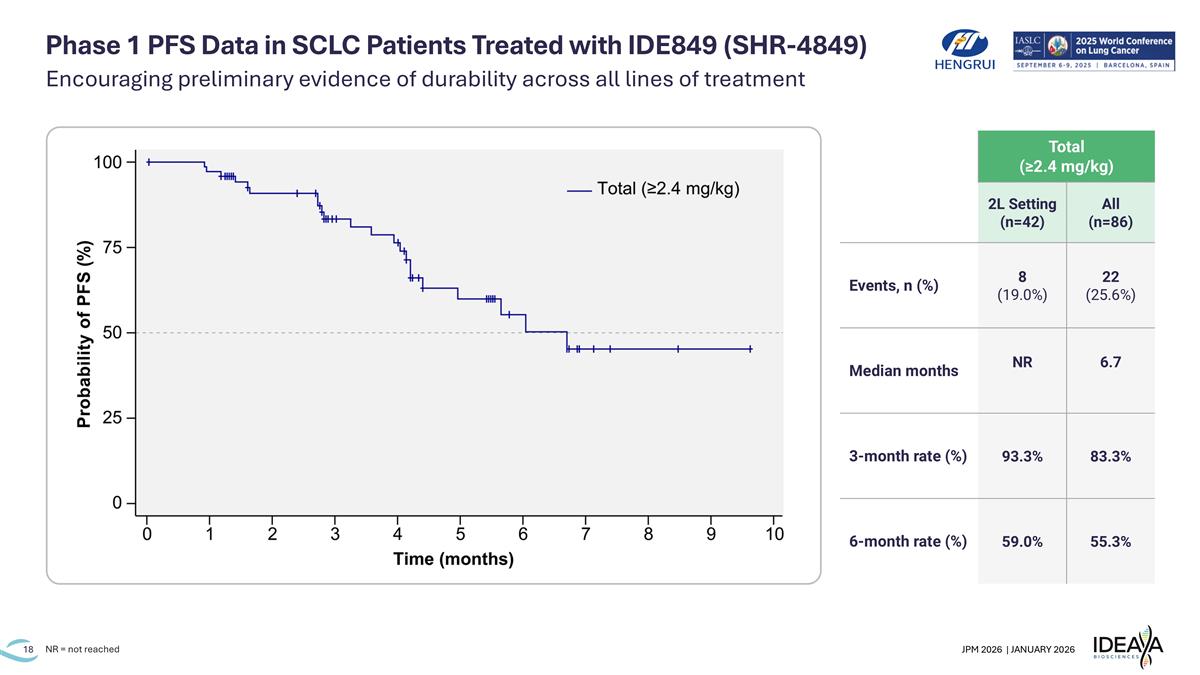
Phase 1 PFS Data in SCLC Patients Treated with IDE849 (SHR-4849) NR = not reached Total (≥2.4 mg/kg) 2L Setting (n=42) All (n=86) Events, n (%) 8 (19.0%) 22 (25.6%) Median months NR 6.7 3-month rate (%) 93.3% 83.3% 6-month rate (%) 59.0% 55.3% Encouraging preliminary evidence of durability across all lines of treatment
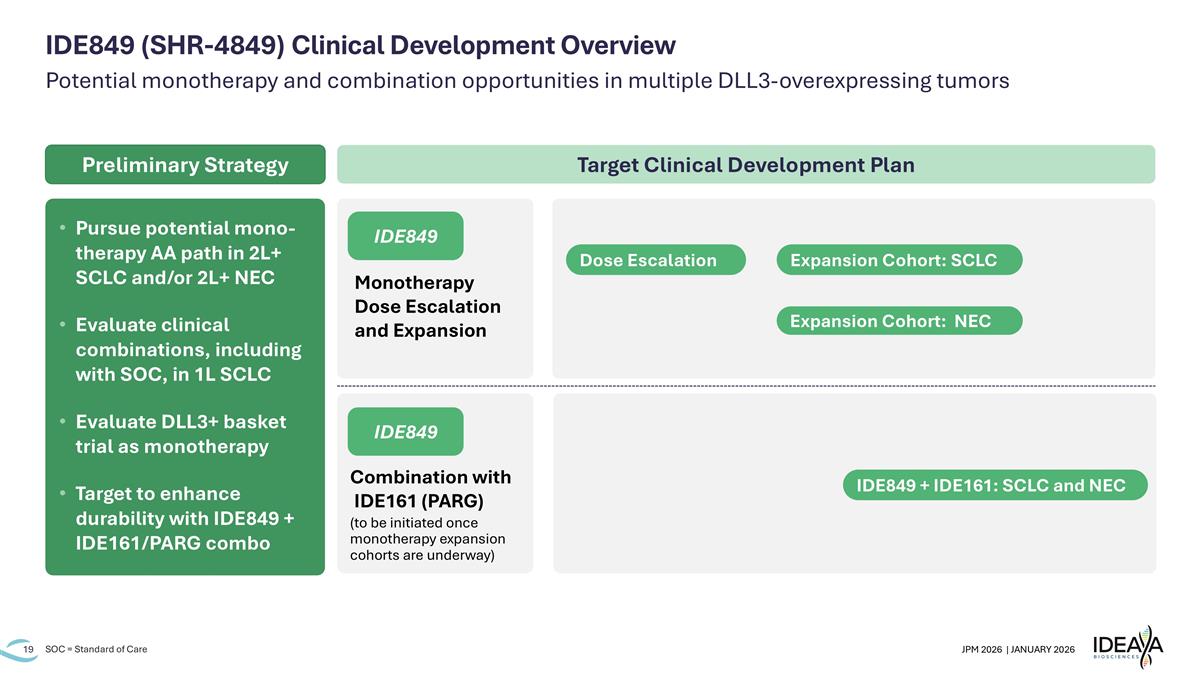
Potential monotherapy and combination opportunities in multiple DLL3-overexpressing tumors SOC = Standard of Care IDE849 (SHR-4849) Clinical Development Overview Combination with IDE161 (PARG) (to be initiated once monotherapy expansion cohorts are underway) Monotherapy Dose Escalation and Expansion IDE849 IDE849 Pursue potential mono-therapy AA path in 2L+ SCLC and/or 2L+ NEC Evaluate clinical combinations, including with SOC, in 1L SCLC Evaluate DLL3+ basket trial as monotherapy Target to enhance durability with IDE849 + IDE161/PARG combo Target Clinical Development Plan Preliminary Strategy Dose Escalation Expansion Cohort: SCLC Expansion Cohort: NEC IDE849 + IDE161: SCLC and NEC
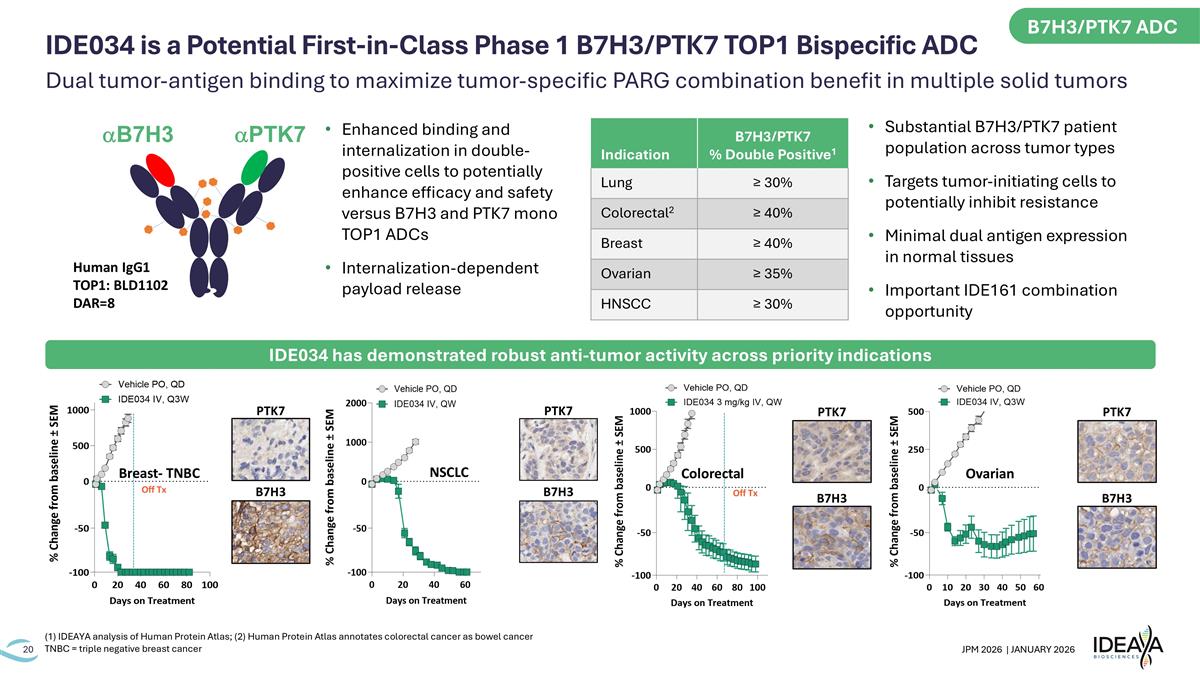
B7H3 PTK7 Off Tx Breast- TNBC B7H3 PTK7 Off Tx Colorectal B7H3 PTK7 Ovarian B7H3 PTK7 NSCLC Indication B7H3/PTK7 % Double Positive1 Lung ≥ 30% Colorectal2 ≥ 40% Breast ≥ 40% Ovarian ≥ 35% HNSCC ≥ 30% Substantial B7H3/PTK7 patient population across tumor types Targets tumor-initiating cells to potentially inhibit resistance Minimal dual antigen expression in normal tissues Important IDE161 combination opportunity Human IgG1 TOP1: BLD1102 DAR=8 aPTK7 aB7H3 Enhanced binding and internalization in double-positive cells to potentially enhance efficacy and safety versus B7H3 and PTK7 mono TOP1 ADCs Internalization-dependent payload release (1) IDEAYA analysis of Human Protein Atlas; (2) Human Protein Atlas annotates colorectal cancer as bowel cancer TNBC = triple negative breast cancer IDE034 has demonstrated robust anti-tumor activity across priority indications B7H3/PTK7 ADC Dual tumor-antigen binding to maximize tumor-specific PARG combination benefit in multiple solid tumors IDE034 is a Potential First-in-Class Phase 1 B7H3/PTK7 TOP1 Bispecific ADC
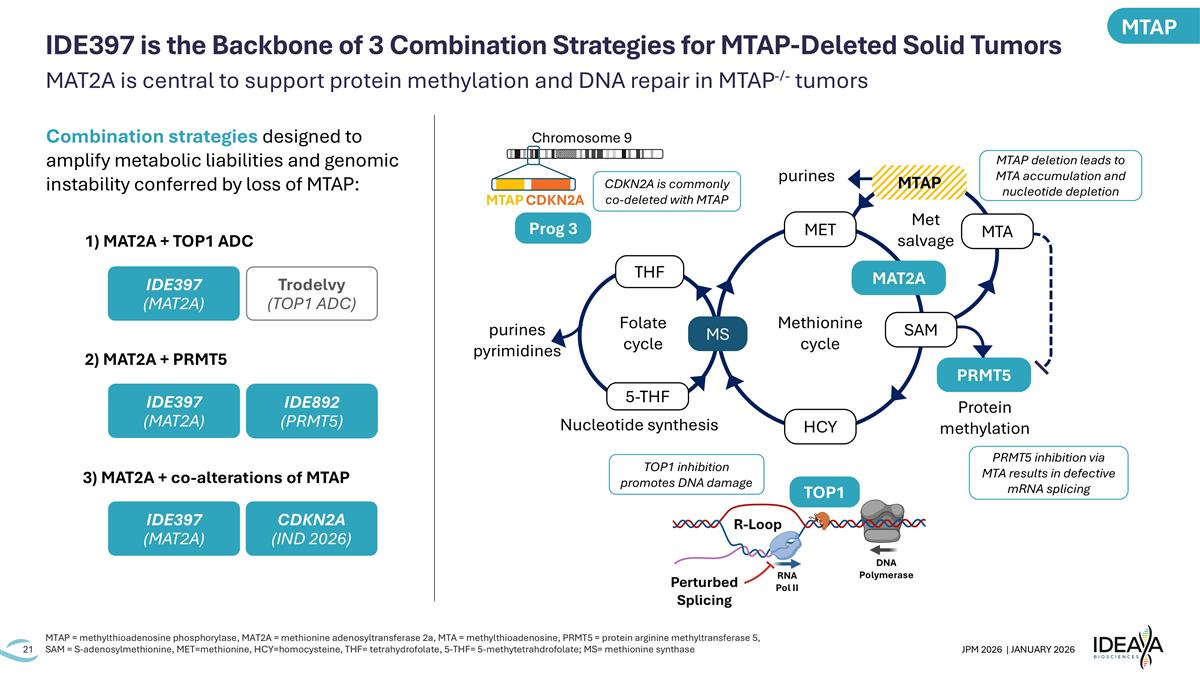
MAT2A is central to support protein methylation and DNA repair in MTAP-/- tumors MTAP = methylthioadenosine phosphorylase, MAT2A = methionine adenosyltransferase 2a, MTA = methylthioadenosine, PRMT5 = protein arginine methyltransferase 5, SAM = S-adenosylmethionine, MET=methionine, HCY=homocysteine, THF= tetrahydrofolate, 5-THF= 5-methytetrahdrofolate; MS= methionine synthase IDE397 is the Backbone of 3 Combination Strategies for MTAP-Deleted Solid Tumors Prog 3 Chromosome 9 MTAP CDKN2A R-Loop RNA Pol II DNA Polymerase Perturbed Splicing TOP1 Folate cycle Methionine cycle Met salvage Protein methylation Nucleotide synthesis MTAP MAT2A PRMT5 SAM MET MTA HCY MS THF 5-THF purines purines pyrimidines MTAP deletion leads to MTA accumulation and nucleotide depletion PRMT5 inhibition via MTA results in defective mRNA splicing TOP1 inhibition promotes DNA damage CDKN2A is commonly co-deleted with MTAP 1) MAT2A + TOP1 ADC IDE397 (MAT2A) IDE892 (PRMT5) Trodelvy (TOP1 ADC) IDE397 (MAT2A) IDE397 (MAT2A) 2) MAT2A + PRMT5 3) MAT2A + co-alterations of MTAP CDKN2A (IND 2026) Combination strategies designed to amplify metabolic liabilities and genomic instability conferred by loss of MTAP: MTAP
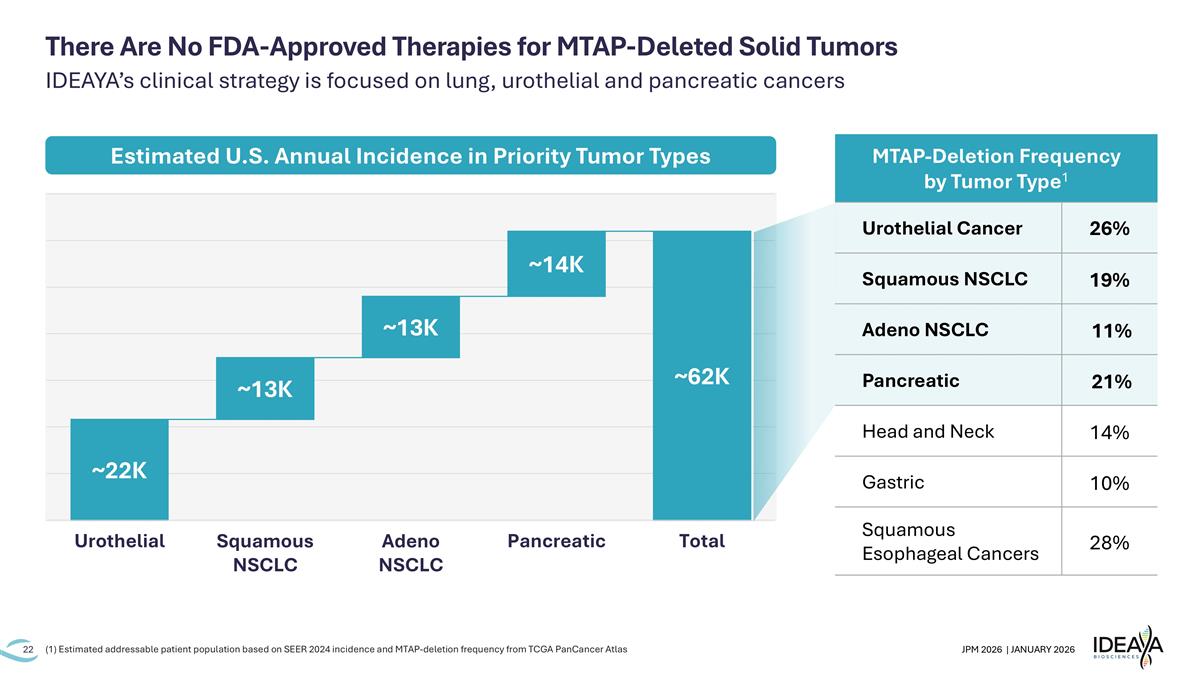
There Are No FDA-Approved Therapies for MTAP-Deleted Solid Tumors IDEAYA’s clinical strategy is focused on lung, urothelial and pancreatic cancers Estimated U.S. Annual Incidence in Priority Tumor Types (1) Estimated addressable patient population based on SEER 2024 incidence and MTAP-deletion frequency from TCGA PanCancer Atlas MTAP-Deletion Frequency by Tumor Type1 Urothelial Cancer 26% Squamous NSCLC 19% Adeno NSCLC 11% Pancreatic 21% Head and Neck 14% Gastric 10% Squamous Esophageal Cancers 28%
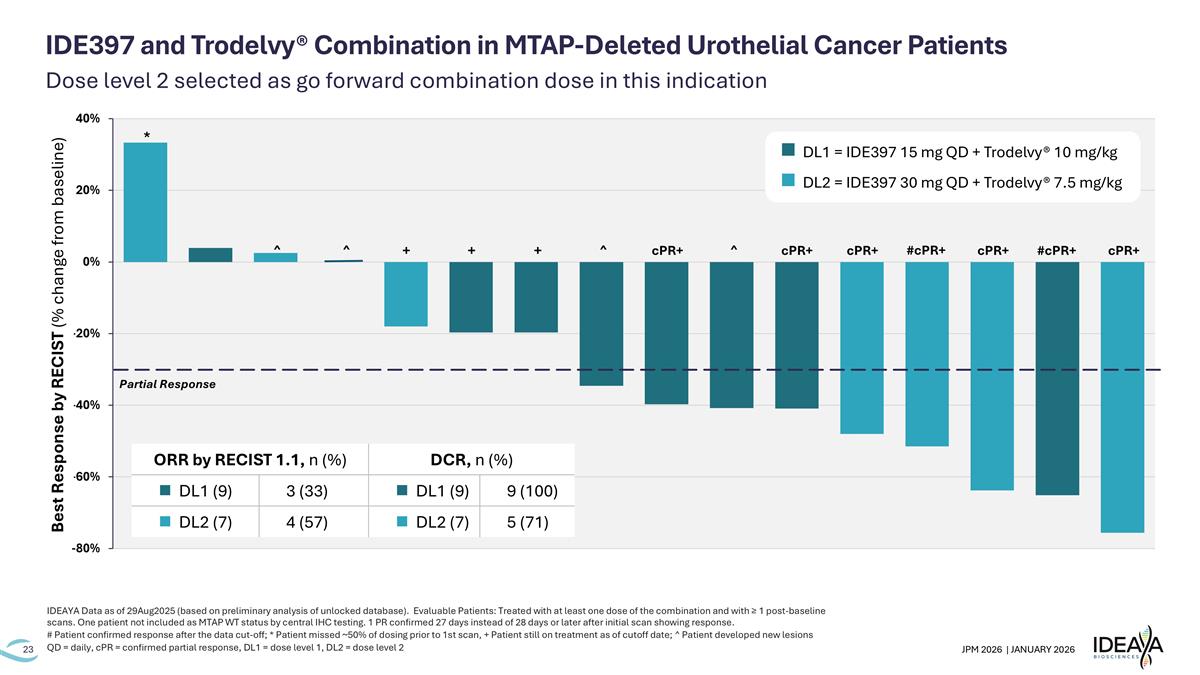
Dose level 2 selected as go forward combination dose in this indication IDEAYA Data as of 29Aug2025 (based on preliminary analysis of unlocked database). Evaluable Patients: Treated with at least one dose of the combination and with ≥ 1 post-baseline scans. One patient not included as MTAP WT status by central IHC testing. 1 PR confirmed 27 days instead of 28 days or later after initial scan showing response. # Patient confirmed response after the data cut-off; * Patient missed ~50% of dosing prior to 1st scan, + Patient still on treatment as of cutoff date; ^ Patient developed new lesions QD = daily, cPR = confirmed partial response, DL1 = dose level 1, DL2 = dose level 2 IDE397 and Trodelvy® Combination in MTAP-Deleted Urothelial Cancer Patients + + cPR+ ^ ^ ^ cPR+ cPR+ cPR+ cPR+ #cPR+ Partial Response * + ^ #cPR+ n DL1 = IDE397 15 mg QD + Trodelvy® 10 mg/kg n DL2 = IDE397 30 mg QD + Trodelvy® 7.5 mg/kg Best Response by RECIST (% change from baseline) ORR by RECIST 1.1, n (%) DCR, n (%) n DL1 (9) 3 (33) n DL1 (9) 9 (100) n DL2 (7) 4 (57) n DL2 (7) 5 (71)
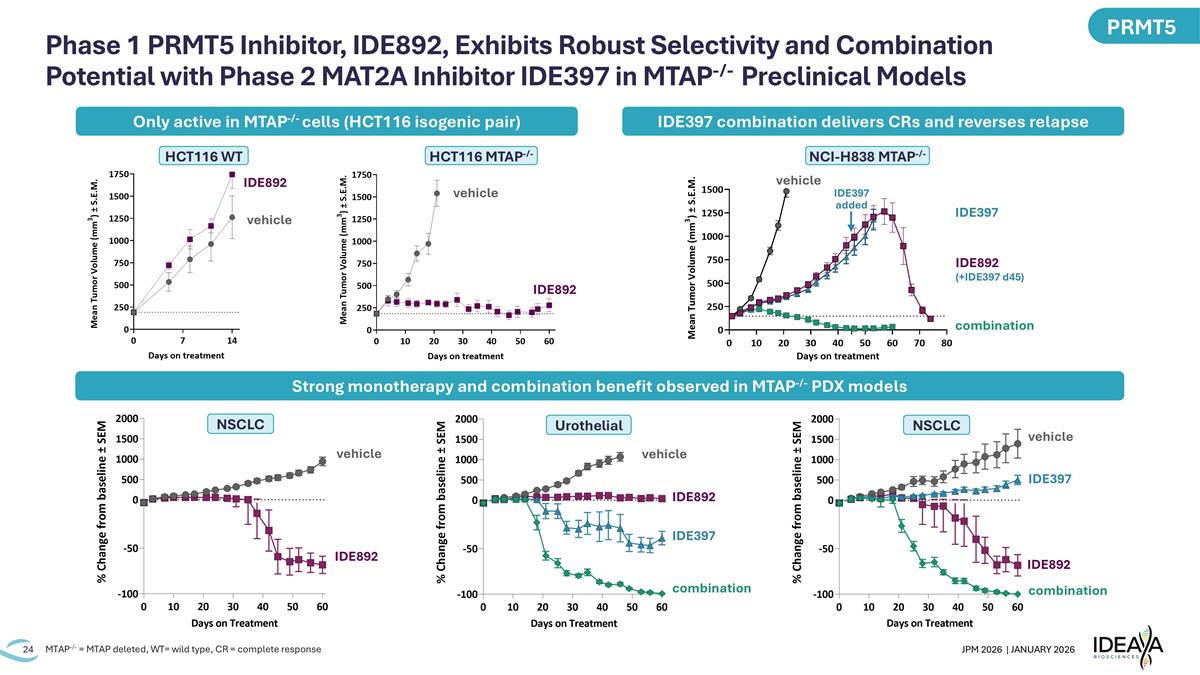
Phase 1 PRMT5 Inhibitor, IDE892, Exhibits Robust Selectivity and Combination Potential with Phase 2 MAT2A Inhibitor IDE397 in MTAP-/- Preclinical Models HCT116 WT vehicle IDE892 HCT116 MTAP-/- vehicle IDE892 vehicle IDE892 NSCLC vehicle IDE892 IDE397 combination NSCLC IDE892 IDE397 combination Urothelial vehicle MTAP-/- = MTAP deleted, WT= wild type, CR = complete response Only active in MTAP-/- cells (HCT116 isogenic pair) IDE397 combination delivers CRs and reverses relapse PRMT5 NCI-H838 MTAP-/- IDE397 combination vehicle IDE892 (+IDE397 d45) IDE397 added Strong monotherapy and combination benefit observed in MTAP-/- PDX models
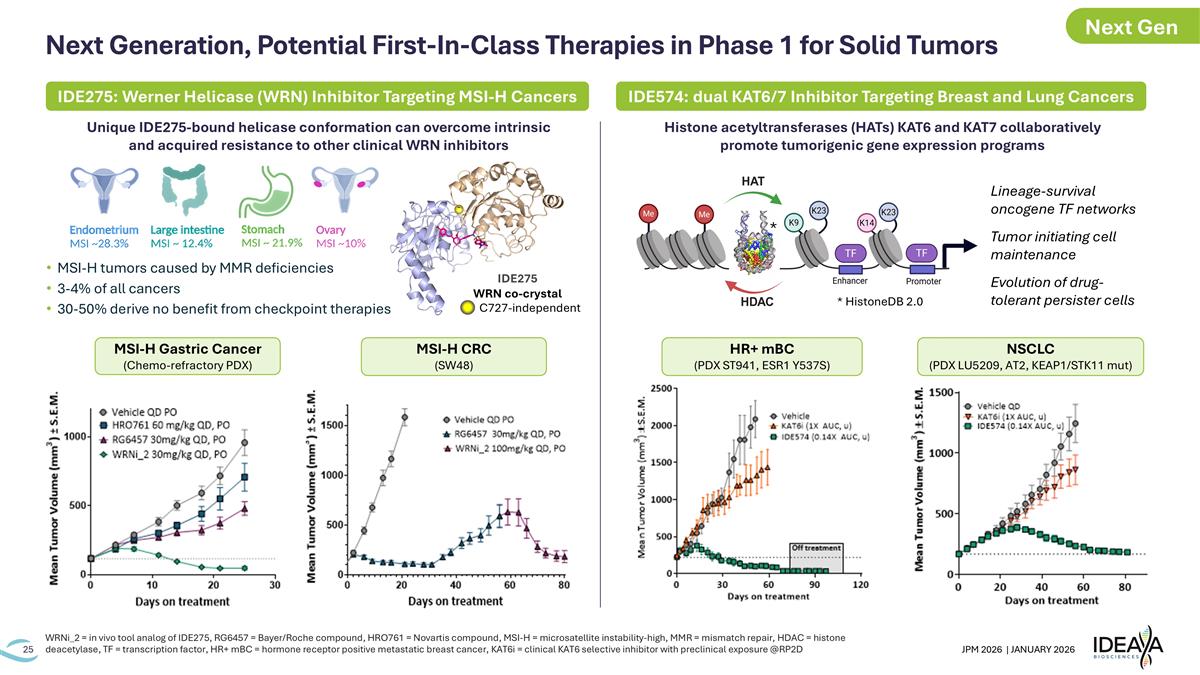
Next Generation, Potential First-In-Class Therapies in Phase 1 for Solid Tumors WRNi_2 = in vivo tool analog of IDE275, RG6457 = Bayer/Roche compound, HRO761 = Novartis compound, MSI-H = microsatellite instability-high, MMR = mismatch repair, HDAC = histone deacetylase, TF = transcription factor, HR+ mBC = hormone receptor positive metastatic breast cancer, KAT6i = clinical KAT6 selective inhibitor with preclinical exposure @RP2D Unique IDE275-bound helicase conformation can overcome intrinsic and acquired resistance to other clinical WRN inhibitors MSI-H tumors caused by MMR deficiencies 3-4% of all cancers 30-50% derive no benefit from checkpoint therapies Histone acetyltransferases (HATs) KAT6 and KAT7 collaboratively promote tumorigenic gene expression programs IDE275 WRN co-crystal C727-independent * HistoneDB 2.0 * IDE275: Werner Helicase (WRN) Inhibitor Targeting MSI-H Cancers IDE574: dual KAT6/7 Inhibitor Targeting Breast and Lung Cancers Lineage-survival oncogene TF networks Tumor initiating cell maintenance Evolution of drug-tolerant persister cells HR+ mBC (PDX ST941, ESR1 Y537S) NSCLC (PDX LU5209, AT2, KEAP1/STK11 mut) MSI-H CRC (SW48) MSI-H Gastric Cancer (Chemo-refractory PDX) Next Gen
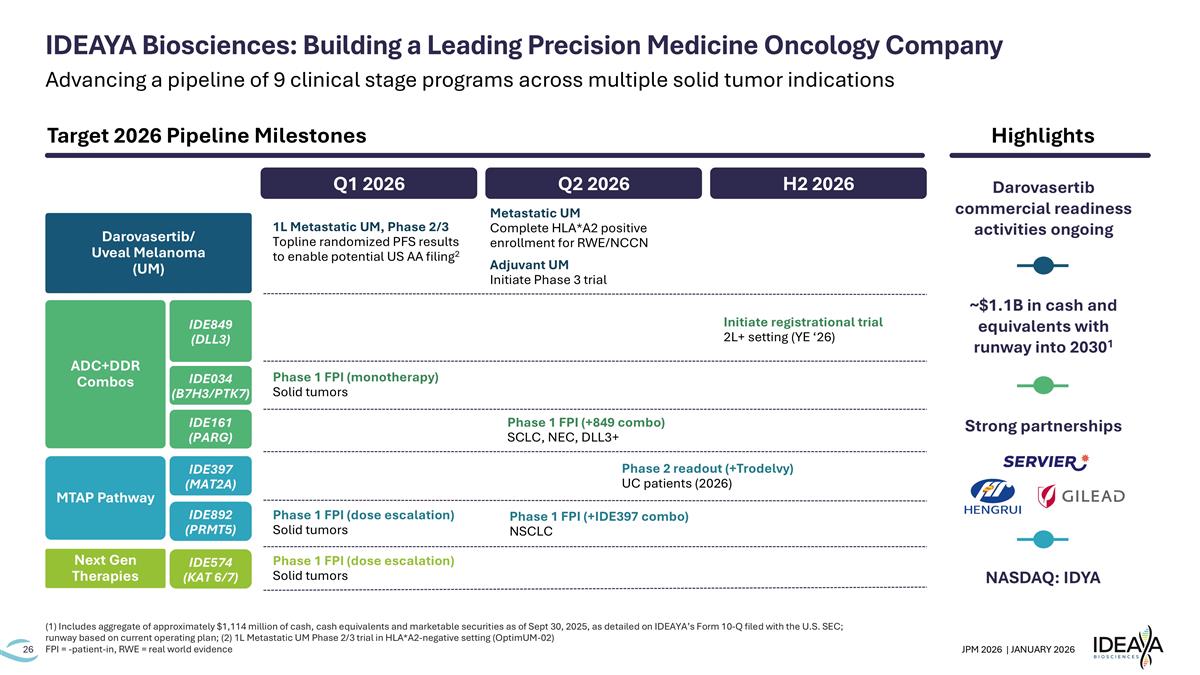
(1) Includes aggregate of approximately $1,114 million of cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities as of Sept 30, 2025, as detailed on IDEAYA’s Form 10-Q filed with the U.S. SEC; runway based on current operating plan; (2) 1L Metastatic UM Phase 2/3 trial in HLA*A2-negative setting (OptimUM-02) FPI = -patient-in, RWE = real world evidence Q1 2026 Q2 2026 H2 2026 Phase 1 FPI (dose escalation) Solid tumors Phase 2 readout (+Trodelvy) UC patients (2026) Phase 1 FPI (+IDE397 combo) NSCLC IDEAYA Biosciences: Building a Leading Precision Medicine Oncology Company 1L Metastatic UM, Phase 2/3 Topline randomized PFS results to enable potential US AA filing2 Adjuvant UM Initiate Phase 3 trial Phase 1 FPI (+849 combo) SCLC, NEC, DLL3+ Phase 1 FPI (monotherapy) Solid tumors Initiate registrational trial 2L+ setting (YE ‘26) Next Gen Therapies IDE574 (KAT 6/7) MTAP Pathway IDE397 (MAT2A) IDE892 (PRMT5) ADC+DDR Combos IDE849 (DLL3) IDE034 (B7H3/PTK7) IDE161 (PARG) Darovasertib/ Uveal Melanoma (UM) Phase 1 FPI (dose escalation) Solid tumors Highlights NASDAQ: IDYA Strong partnerships ~$1.1B in cash and equivalents with runway into 20301 Target 2026 Pipeline Milestones Metastatic UM Complete HLA*A2 positive enrollment for RWE/NCCN Darovasertib commercial readiness activities ongoing Advancing a pipeline of 9 clinical stage programs across multiple solid tumor indications

Improving Lives Through Transformative Precision Medicines JPM 2026 | 44th Annual Healthcare Conference January 2026