

.2 Corporate Presentation October 2025

Forward-looking Statement This presentation contains forward-looking statements as defined in the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, as amended, including without limitation, statements regarding, among other things, the potential number of patients who could be treated by tebipenem HBr and market demand for tebipenem HBr generally; the potential regulatory path forward for tebipenem HBr, the potential approval of tebipenem HBr by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the timing thereof; the potential commercialization of tebipenem HBr and its future value, the potential receipt of milestone payments and royalties on future sales of tebipenem HBr under the GlaxoSmithKline Intellectual Property (No. 3) Limited (GSK) license agreement; the effectiveness of tebipenem HBr and its potential impact on healthcare resource utilizations; the status of the data analysis for SPR720; the timing, progress and results of the Company’s clinical trials and its research and development programs, including management’s assessment of such results; the timing of the availability of data from the Company’s clinical trials; the timing of the Company’s filings with regulatory agencies; product candidate benefits; competitive position; cash runway, business strategies; potential growth opportunities; potential market size; projected costs and the availability of additional non-dilutive funding from governmental agencies beyond any initially funded awards. In some cases, forward-looking statements can be identified by terms such as “may,” “will,” “should,” “expect,” “plan,” “aim,” “anticipate,” “could,” “intent,” “target,” “project,” “contemplate,” “believe,” “estimate,” “predict,” “potential” or “continue” or the negative of these terms or other similar expressions. All statements other than statements of historical facts contained in this presentation are forward-looking statements. The Company may not actually achieve the plans, intentions or expectations disclosed in these forward-looking statements. Actual results or events could differ materially from the plans, intentions and expectations disclosed in these forward-looking statements as a result of various factors, including whether the FDA will ultimately approve tebipenem HBr and, if so, the timing of any such approval; whether the FDA will require any additional clinical data or place labeling restrictions on the use of tebipenem HBr that would add costs for the Company, delay approval and/or reduce the commercial prospects of tebipenem HBr; the Company’s need for additional funding; the lengthy, expensive, and uncertain process of clinical drug development; the Company’s reliance on third parties to manufacture, develop, and commercialize its product candidates, if approved; the ability to develop and commercialize the Company’s product candidates, if approved; the Company’s ability to retain key personnel; whether results obtained in preclinical studies and clinical trials will be indicative of results obtained in future clinical trials and whether preliminary data from the Company’s clinical trials will be predictive of final results from such trials; the Company’s dependence on raising capital and whether the Company’s product candidates will advance through the preclinical development and clinical trial process on a timely basis, or at all, taking into account such factors as the effects of possible regulatory delays, slower than anticipated patient enrollment, manufacturing challenges, clinical trial design, clinical data requirements and clinical outcomes; whether the results of such clinical trials will warrant submission for approval from the FDA or equivalent foreign regulatory agencies; decisions made by the FDA and equivalent foreign regulatory agencies with respect to the development and commercialization of the Company’s product candidates; the commercial potential of the Company’s product candidates; the Company’s ability to obtain adequate third-party reimbursement for its product candidates; whether the Company will satisfy all of the pre-conditions to receipt of the milestone payments under its various license and collaboration agreements; the Company’s ability to implement its strategic plans; the Company’s ability to obtain, maintain and enforce intellectual property and other proprietary rights for its product candidates; the risks and uncertainties related to market conditions; whether the Company’s cash resources will be sufficient to fund its continuing operations for the periods and/or trials anticipated; and other factors discussed in the “Risk Factors” section of the Company’s periodic reports filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), and risks described in other filings the Company may make with the SEC in the future. The forward- looking statements included in this presentation represent the Company’s views as of the date of this presentation. The Company anticipates that subsequent events and developments will cause its views to change. However, while the Company may elect to update these forward-looking statements at some point in the future, it specifically disclaims any obligation to do so. These forward-looking statements should not be relied upon as representing the Company’s views as of any date subsequent to the date of this presentation. 2
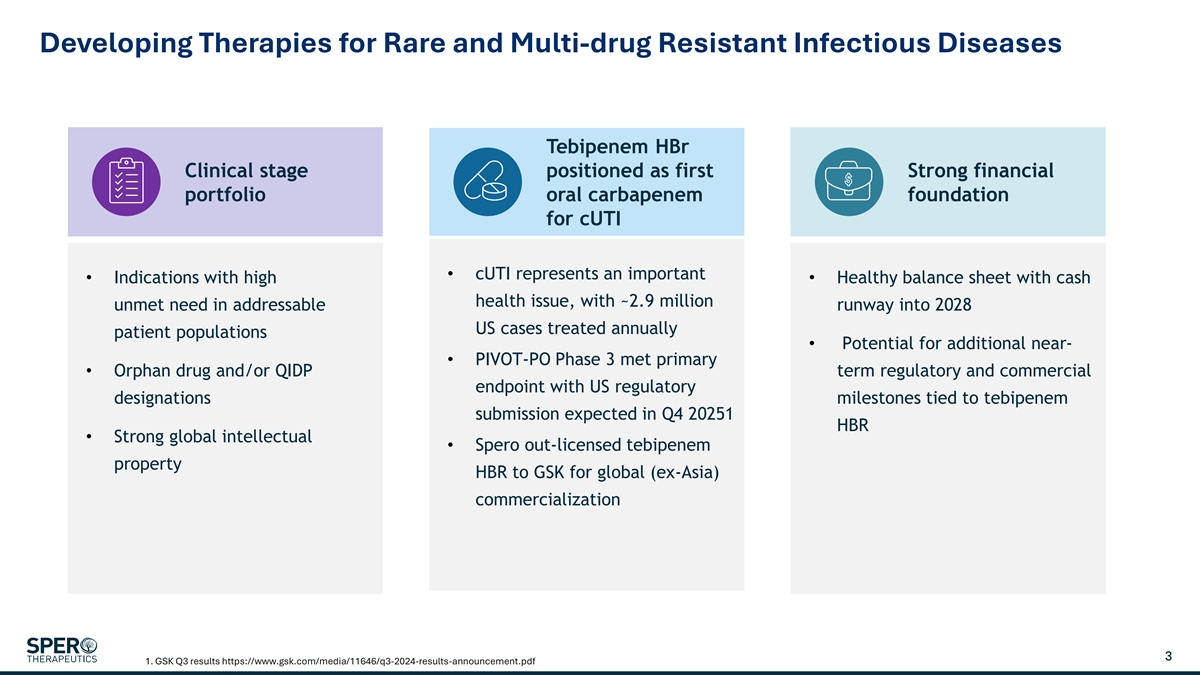
Developing Therapies for Rare and Multi-drug Resistant Infectious Diseases Tebipenem HBr Clinical stage positioned as first Strong financial portfolio oral carbapenem foundation for cUTI • cUTI represents an important • Indications with high • Healthy balance sheet with cash health issue, with ~2.9 million unmet need in addressable runway into 2028 US cases treated annually patient populations • Potential for additional near- • PIVOT-PO Phase 3 met primary • Orphan drug and/or QIDP term regulatory and commercial endpoint with US regulatory designations milestones tied to tebipenem submission expected in Q4 20251 HBR • Strong global intellectual • Spero out-licensed tebipenem property HBR to GSK for global (ex-Asia) commercialization 3 1. GSK Q3 results https://www.gsk.com/media/11646/q3-2024-results-announcement.pdf
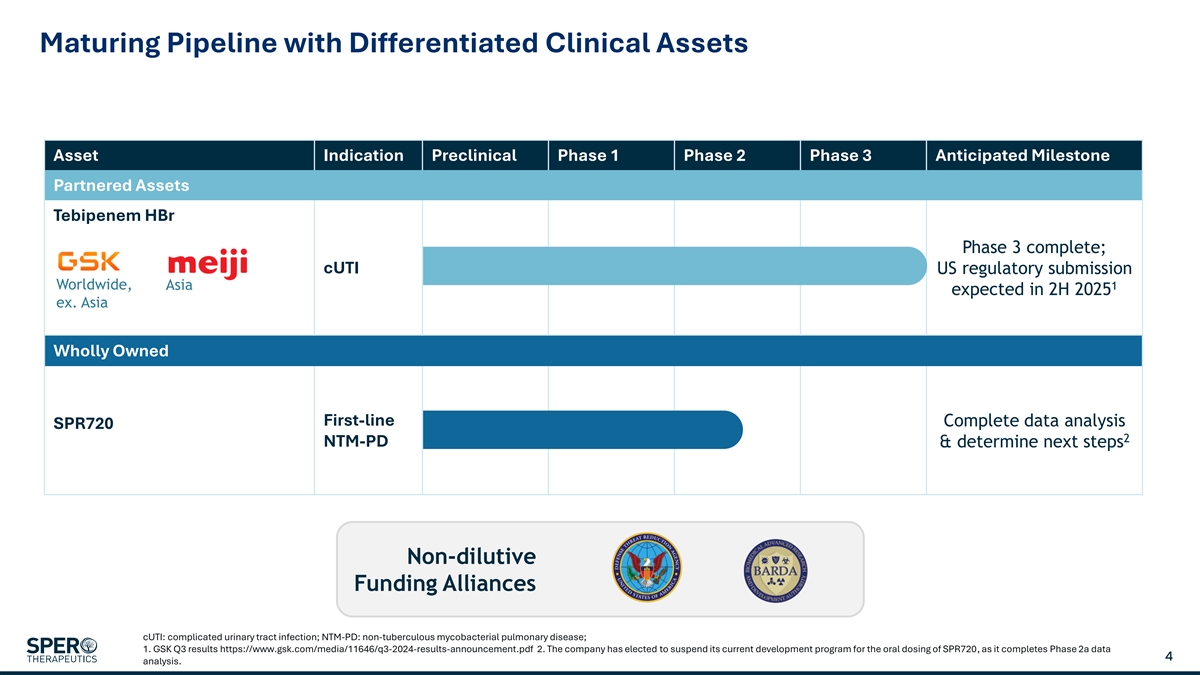
Maturing Pipeline with Differentiated Clinical Assets Asset Indication Preclinical Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Anticipated Milestone Partnered Assets Tebipenem HBr Phase 3 complete; cUTI US regulatory submission Worldwide, Asia 1 expected in 2H 2025 ex. Asia Wholly Owned First-line Complete data analysis SPR720 2 NTM-PD & determine next steps Non-dilutive Funding Alliances cUTI: complicated urinary tract infection; NTM-PD: non-tuberculous mycobacterial pulmonary disease; 1. GSK Q3 results https://www.gsk.com/media/11646/q3-2024-results-announcement.pdf 2. The company has elected to suspend its current development program for the oral dosing of SPR720, as it completes Phase 2a data 4 analysis.

Tebipenem HBr Oral Carbapenem for cUTI 5
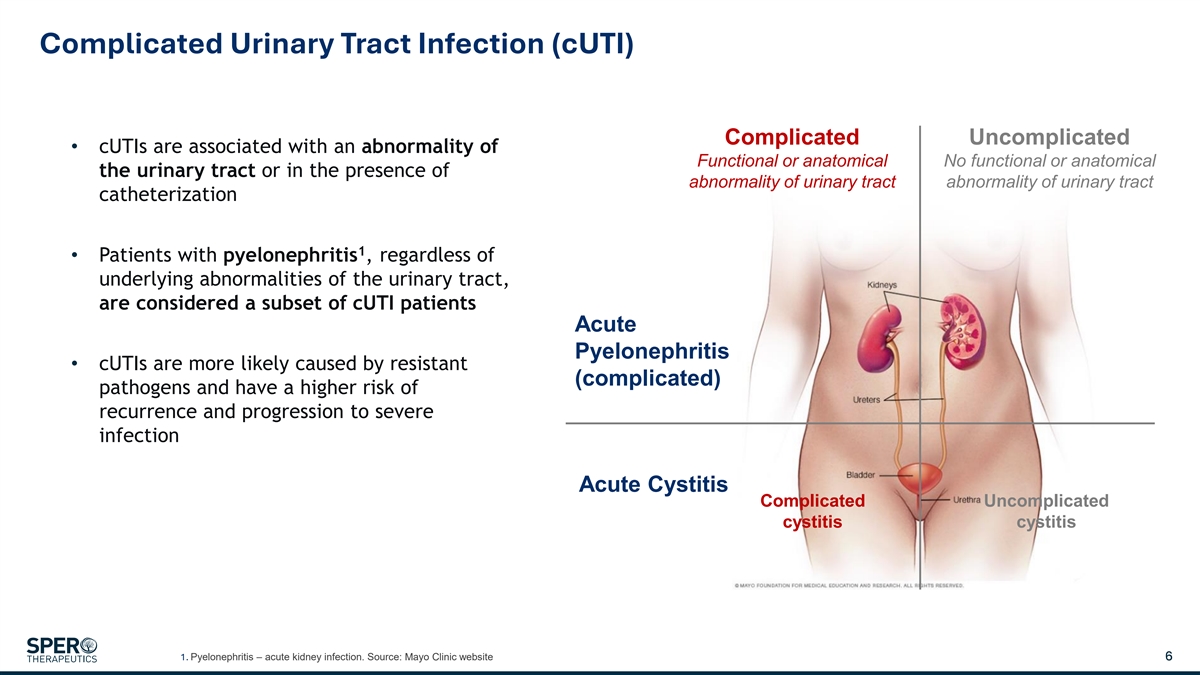
Complicated Urinary Tract Infection (cUTI) Complicated Uncomplicated • cUTIs are associated with an abnormality of Functional or anatomical No functional or anatomical the urinary tract or in the presence of abnormality of urinary tract abnormality of urinary tract catheterization 1 • Patients with pyelonephritis , regardless of underlying abnormalities of the urinary tract, are considered a subset of cUTI patients Acute Pyelonephritis • cUTIs are more likely caused by resistant (complicated) pathogens and have a higher risk of recurrence and progression to severe infection Acute Cystitis Complicated Uncomplicated cystitis cystitis 1. Pyelonephritis – acute kidney infection. Source: Mayo Clinic website 6
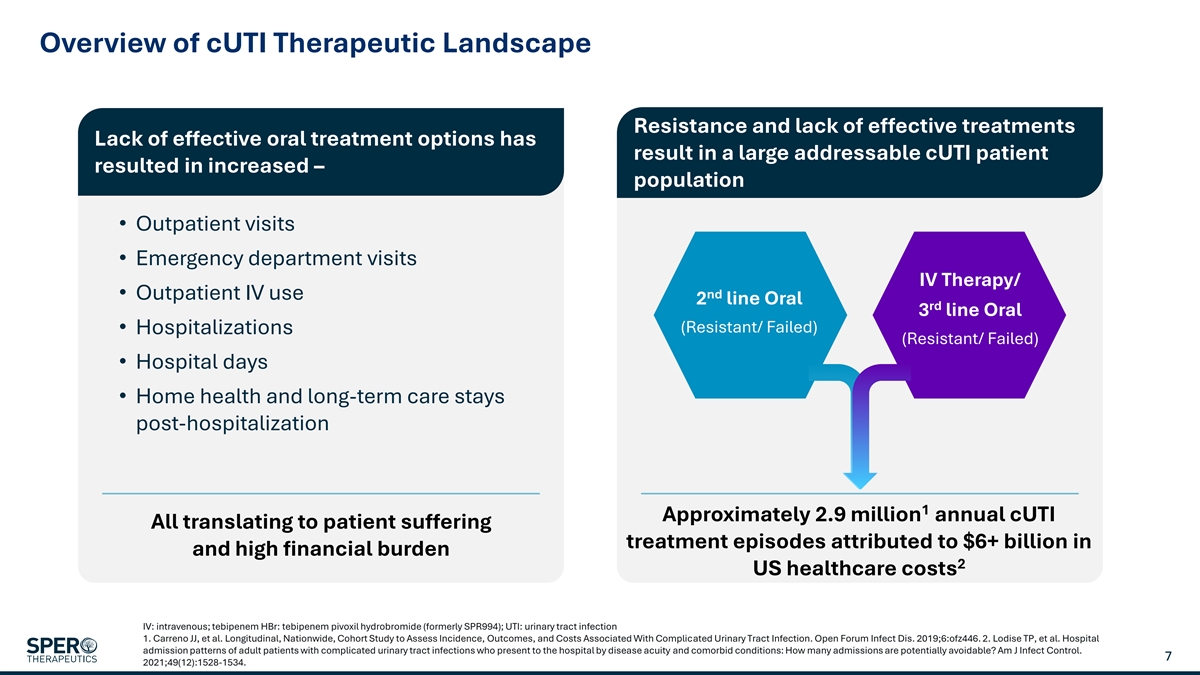
Overview of cUTI Therapeutic Landscape Resistance and lack of effective treatments Lack of effective oral treatment options has result in a large addressable cUTI patient resulted in increased – population • Outpatient visits • Emergency department visits IV Therapy/ nd • Outpatient IV use 2 line Oral rd 3 line Oral (Resistant/ Failed) • Hospitalizations (Resistant/ Failed) • Hospital days • Home health and long-term care stays post-hospitalization 1 Approximately 2.9 million annual cUTI All translating to patient suffering treatment episodes attributed to $6+ billion in and high financial burden 2 US healthcare costs IV: intravenous; tebipenem HBr: tebipenem pivoxil hydrobromide (formerly SPR994); UTI: urinary tract infection 1. Carreno JJ, et al. Longitudinal, Nationwide, Cohort Study to Assess Incidence, Outcomes, and Costs Associated With Complicated Urinary Tract Infection. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2019;6:ofz446. 2. Lodise TP, et al. Hospital admission patterns of adult patients with complicated urinary tract infections who present to the hospital by disease acuity and comorbid conditions: How many admissions are potentially avoidable? Am J Infect Control. 7 2021;49(12):1528-1534.
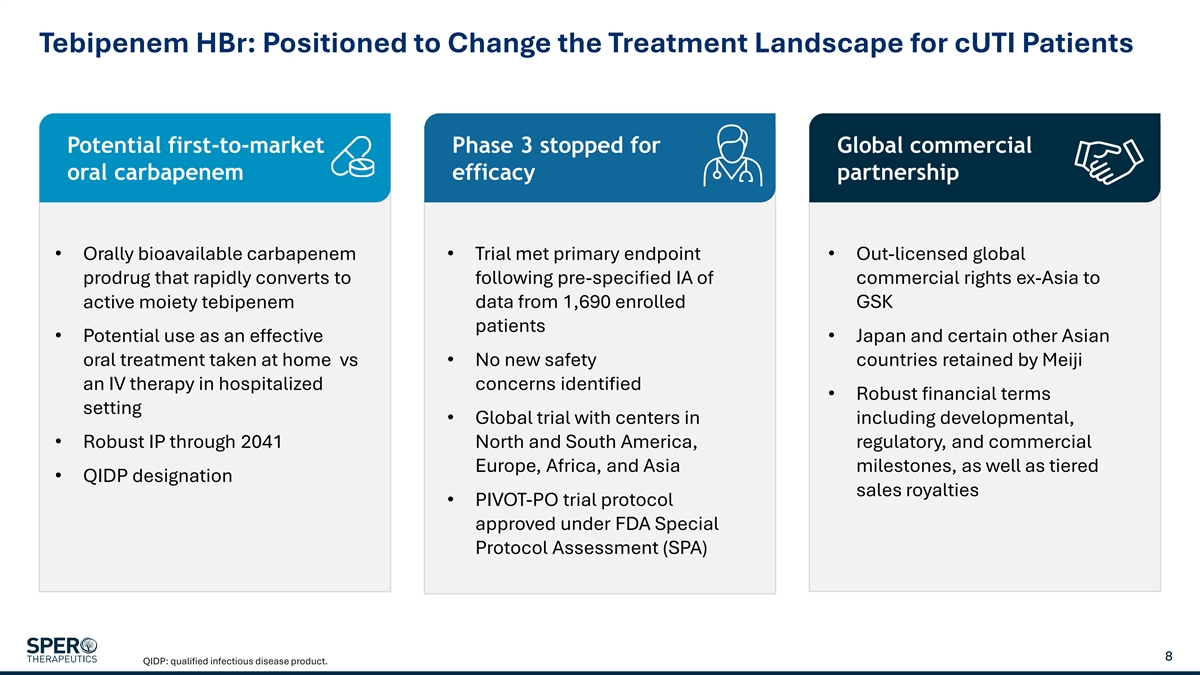
Tebipenem HBr: Positioned to Change the Treatment Landscape for cUTI Patients Potential first-to-market Phase 3 stopped for Global commercial oral carbapenem efficacy partnership • Orally bioavailable carbapenem • Trial met primary endpoint • Out-licensed global prodrug that rapidly converts to following pre-specified IA of commercial rights ex-Asia to active moiety tebipenem data from 1,690 enrolled GSK patients • Potential use as an effective • Japan and certain other Asian oral treatment taken at home vs • No new safety countries retained by Meiji an IV therapy in hospitalized concerns identified • Robust financial terms setting • Global trial with centers in including developmental, • Robust IP through 2041 North and South America, regulatory, and commercial Europe, Africa, and Asia milestones, as well as tiered • QIDP designation sales royalties • PIVOT-PO trial protocol approved under FDA Special Protocol Assessment (SPA) 8 QIDP: qualified infectious disease product.
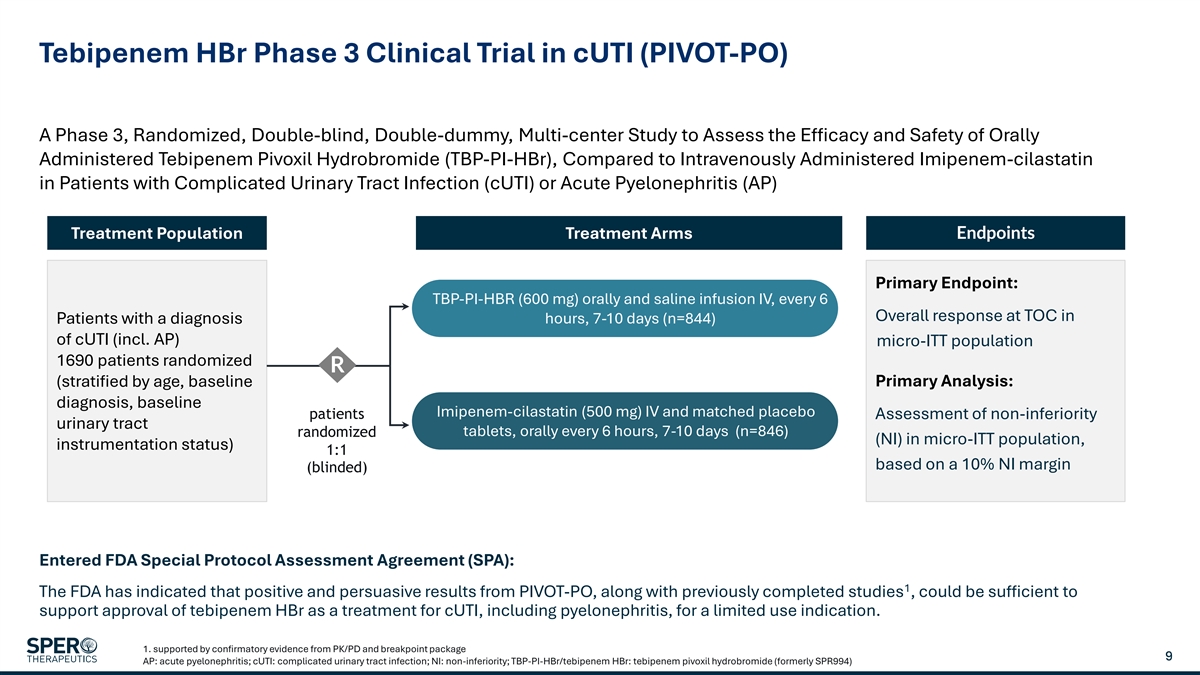
Tebipenem HBr Phase 3 Clinical Trial in cUTI (PIVOT-PO) A Phase 3, Randomized, Double-blind, Double-dummy, Multi-center Study to Assess the Efficacy and Safety of Orally Administered Tebipenem Pivoxil Hydrobromide (TBP-PI-HBr), Compared to Intravenously Administered Imipenem-cilastatin in Patients with Complicated Urinary Tract Infection (cUTI) or Acute Pyelonephritis (AP) Treatment Population Treatment Arms Endpoints Primary Endpoint: TBP-PI-HBR (600 mg) orally and saline infusion IV, every 6 Overall response at TOC in Patients with a diagnosis hours, 7-10 days (n=844) of cUTI (incl. AP) micro-ITT population 1690 patients randomized R Primary Analysis: (stratified by age, baseline diagnosis, baseline Imipenem-cilastatin (500 mg) IV and matched placebo patients Assessment of non-inferiority urinary tract tablets, orally every 6 hours, 7-10 days (n=846) randomized (NI) in micro-ITT population, instrumentation status) 1:1 based on a 10% NI margin (blinded) Entered FDA Special Protocol Assessment Agreement (SPA): 1 The FDA has indicated that positive and persuasive results from PIVOT-PO, along with previously completed studies , could be sufficient to support approval of tebipenem HBr as a treatment for cUTI, including pyelonephritis, for a limited use indication. 1. supported by confirmatory evidence from PK/PD and breakpoint package 9 AP: acute pyelonephritis; cUTI: complicated urinary tract infection; NI: non-inferiority; TBP-PI-HBr/tebipenem HBr: tebipenem pivoxil hydrobromide (formerly SPR994)
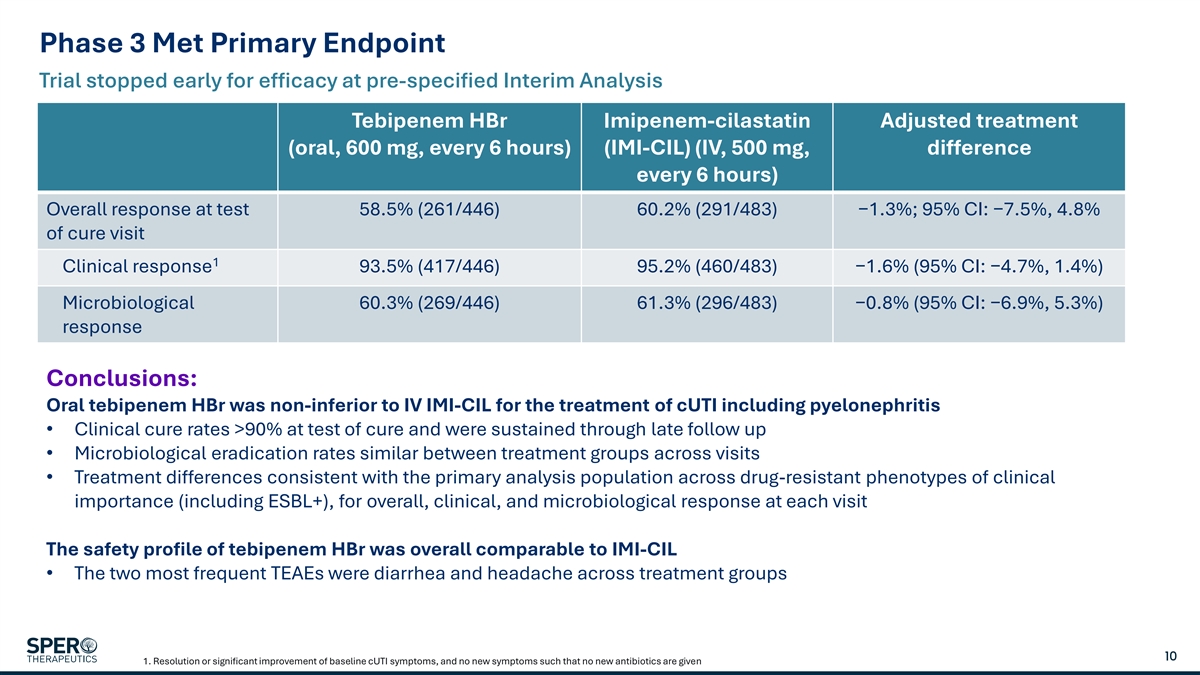
Phase 3 Met Primary Endpoint Trial stopped early for efficacy at pre-specified Interim Analysis Tebipenem HBr Imipenem-cilastatin Adjusted treatment (oral, 600 mg, every 6 hours) (IMI-CIL) (IV, 500 mg, difference every 6 hours) Overall response at test 58.5% (261/446) 60.2% (291/483) −1.3%; 95% CI: −7.5%, 4.8% of cure visit 1 Clinical response 93.5% (417/446) 95.2% (460/483) −1.6% (95% CI: −4.7%, 1.4%) Microbiological 60.3% (269/446) 61.3% (296/483) −0.8% (95% CI: −6.9%, 5.3%) response Conclusions: Oral tebipenem HBr was non-inferior to IV IMI-CIL for the treatment of cUTI including pyelonephritis • Clinical cure rates >90% at test of cure and were sustained through late follow up • Microbiological eradication rates similar between treatment groups across visits • Treatment differences consistent with the primary analysis population across drug-resistant phenotypes of clinical importance (including ESBL+), for overall, clinical, and microbiological response at each visit The safety profile of tebipenem HBr was overall comparable to IMI-CIL • The two most frequent TEAEs were diarrhea and headache across treatment groups 10 1. Resolution or significant improvement of baseline cUTI symptoms, and no new symptoms such that no new antibiotics are given
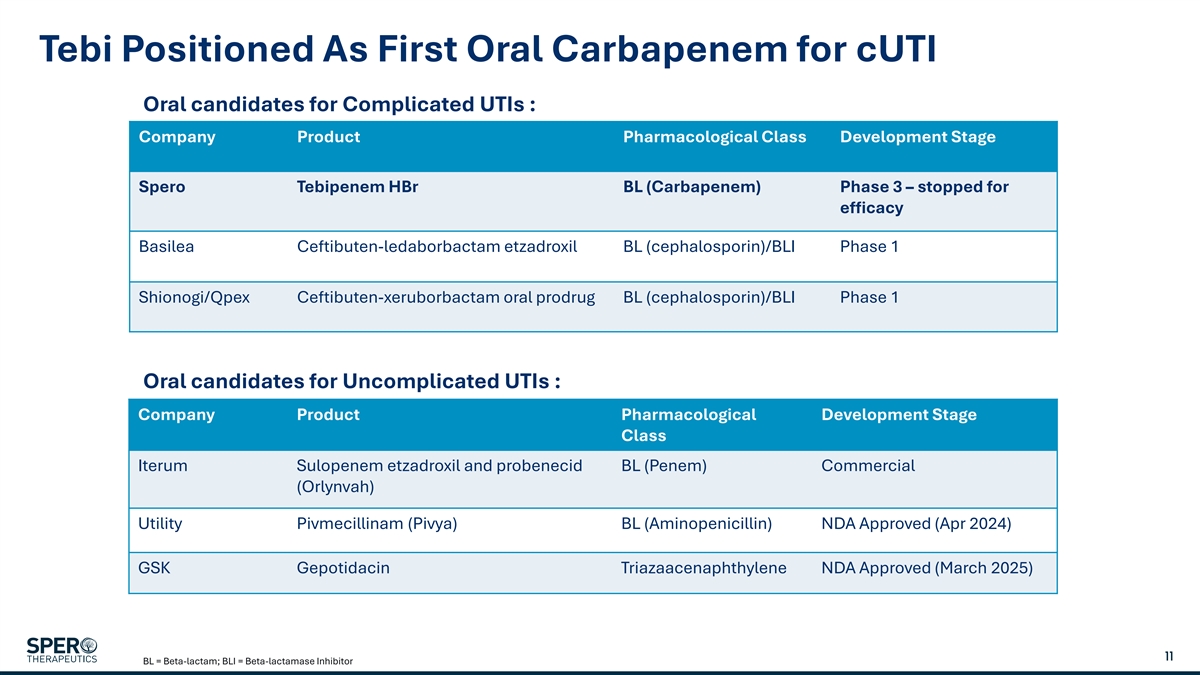
Tebi Positioned As First Oral Carbapenem for cUTI Oral candidates for Complicated UTIs : Company Product Pharmacological Class Development Stage Spero Tebipenem HBr BL (Carbapenem) Phase 3 – stopped for efficacy Basilea Ceftibuten-ledaborbactam etzadroxil BL (cephalosporin)/BLI Phase 1 Shionogi/Qpex Ceftibuten-xeruborbactam oral prodrug BL (cephalosporin)/BLI Phase 1 Oral candidates for Uncomplicated UTIs : Company Product Pharmacological Development Stage Class Iterum Sulopenem etzadroxil and probenecid BL (Penem) Commercial (Orlynvah) Utility Pivmecillinam (Pivya) BL (Aminopenicillin) NDA Approved (Apr 2024) GSK Gepotidacin Triazaacenaphthylene NDA Approved (March 2025) 11 BL = Beta-lactam; BLI = Beta-lactamase Inhibitor
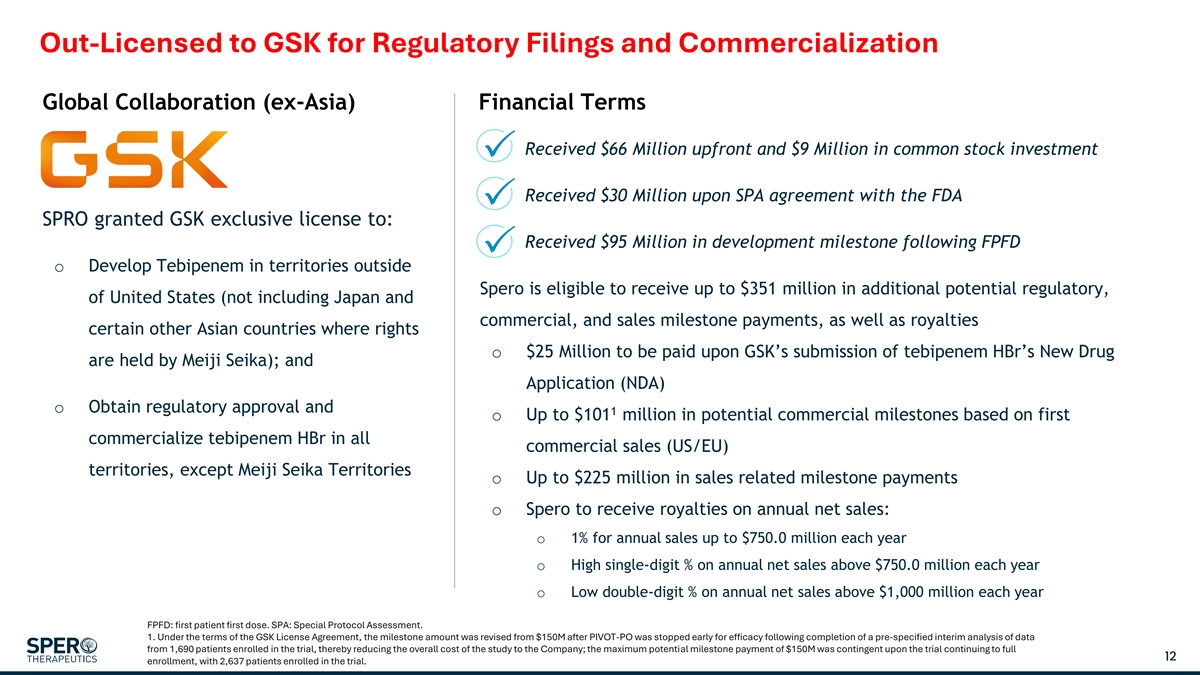
Out-Licensed to GSK for Regulatory Filings and Commercialization Global Collaboration (ex-Asia) Financial Terms Received $66 Million upfront and $9 Million in common stock investment Received $30 Million upon SPA agreement with the FDA SPRO granted GSK exclusive license to: Received $95 Million in development milestone following FPFD o Develop Tebipenem in territories outside Spero is eligible to receive up to $351 million in additional potential regulatory, of United States (not including Japan and commercial, and sales milestone payments, as well as royalties certain other Asian countries where rights o $25 Million to be paid upon GSK’s submission of tebipenem HBr’s New Drug are held by Meiji Seika); and Application (NDA) o Obtain regulatory approval and 1 o Up to $101 million in potential commercial milestones based on first commercialize tebipenem HBr in all commercial sales (US/EU) territories, except Meiji Seika Territories o Up to $225 million in sales related milestone payments o Spero to receive royalties on annual net sales: o 1% for annual sales up to $750.0 million each year o High single-digit % on annual net sales above $750.0 million each year o Low double-digit % on annual net sales above $1,000 million each year FPFD: first patient first dose. SPA: Special Protocol Assessment. 1. Under the terms of the GSK License Agreement, the milestone amount was revised from $150M after PIVOT-PO was stopped early for efficacy following completion of a pre-specified interim analysis of data from 1,690 patients enrolled in the trial, thereby reducing the overall cost of the study to the Company; the maximum potential milestone payment of $150M was contingent upon the trial continuing to full 12 enrollment, with 2,637 patients enrolled in the trial.

SPR720 Antibiotic for Non- Tuberculosis Mycobacterium Pulmonary Disease (NTM-PD) The company has suspended its current development for SPR720 13
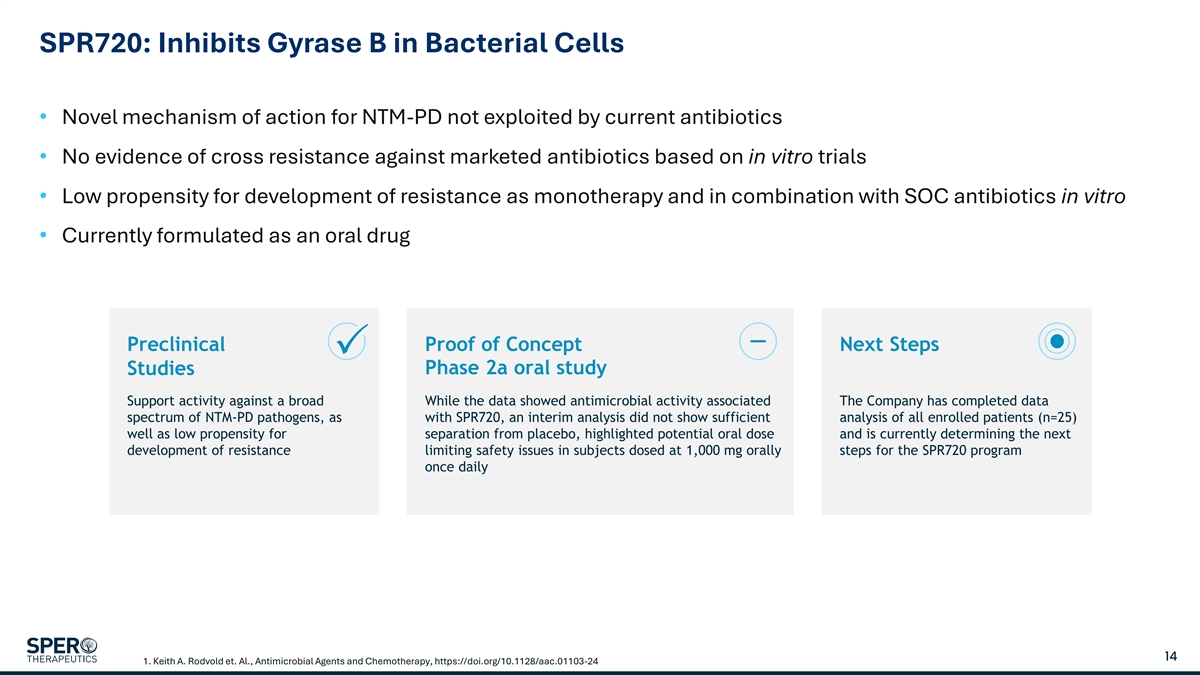
SPR720: Inhibits Gyrase B in Bacterial Cells • Novel mechanism of action for NTM-PD not exploited by current antibiotics • No evidence of cross resistance against marketed antibiotics based on in vitro trials • Low propensity for development of resistance as monotherapy and in combination with SOC antibiotics in vitro • Currently formulated as an oral drug Preclinical Proof of Concept Next Steps Studies Phase 2a oral study Support activity against a broad While the data showed antimicrobial activity associated The Company has completed data spectrum of NTM-PD pathogens, as with SPR720, an interim analysis did not show sufficient analysis of all enrolled patients (n=25) well as low propensity for separation from placebo, highlighted potential oral dose and is currently determining the next development of resistance limiting safety issues in subjects dosed at 1,000 mg orally steps for the SPR720 program once daily 14 1. Keith A. Rodvold et. Al., Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.01103-24

Thank You

1 Clinical Experience Supports Safety, Efficacy of Tebipenem • 741 Adult subjects evaluated, across 17 efficacy and pharmacology trials Tebipenem Pivoxil evaluated in 23 • 440 pediatric subjects evaluated, across 6 efficacy and pharmacology trials trials enrolling over 1,300 • Generally well tolerated, comparable to common, approved oral beta lactam antibiotics and IV subjects (Meiji-Seika experience) carbapenems • Met its primary endpoint in 3 double blind controlled efficacy trials in pediatric pneumonia, otitis media, and sinusitis • Approved for pediatric pneumonia, otitis media, sinusitis, over 4 million patients dosed to date • Extensive post-marketing safety and efficacy surveillance completed, covering 3,331 patients Tebipenem Pivoxil approved in Japan since 2009 • No issues of safety were observed, and adequate efficacy was demonstrated • 964 subjects have received at least one dose of TBP-PI-HBr Tebipenem HBr evaluated in 10 • 279 healthy volunteers or patients with renal impairment across Phase 1 studies trials enrolling over 950 subjects till date (Spero experience) • 685 patients with cUTI including pyelonephritis in a previous Phase 3 study (SPR994-301; ADAPT- PO) 16 1. Akash Jain, Luke Utley, Thomas R. Parr, Thomas Zabawa & Michael J. Pucci (2018): Tebipenem, the first oral carbapenem antibiotic, Expert Review of Anti-infective Therapy, DOI: 10.1080/14787210.2018.1496821
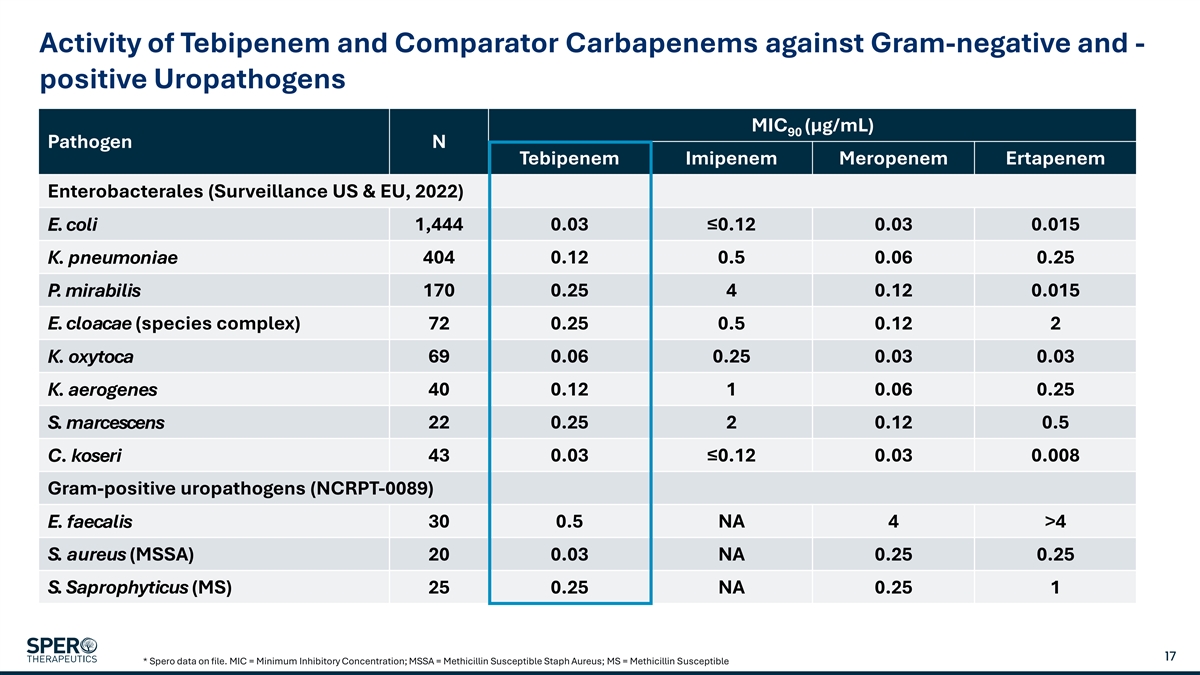
Activity of Tebipenem and Comparator Carbapenems against Gram-negative and - positive Uropathogens MIC (µg/mL) 90 Pathogen N Tebipenem Imipenem Meropenem Ertapenem Enterobacterales (Surveillance US & EU, 2022) E. coli 1,444 0.03≤0.12 0.03 0.015 K. pneumoniae 404 0.12 0.5 0.06 0.25 170 0.25 4 0.12 0.015 P. mirabilis E. cloacae (species complex) 72 0.25 0.5 0.12 2 K. oxytoca 69 0.06 0.25 0.03 0.03 K. aerogenes 40 0.12 1 0.06 0.25 S. marcescens 22 0.25 2 0.12 0.5 43 0.03≤0.12 0.03 0.008 C. koseri Gram-positive uropathogens (NCRPT-0089) E. faecalis 30 0.5 NA 4 >4 S. aureus (MSSA) 20 0.03 NA 0.25 0.25 S. Saprophyticus (MS) 25 0.25 NA 0.25 1 17 * Spero data on file. MIC = Minimum Inhibitory Concentration; MSSA = Methicillin Susceptible Staph Aureus; MS = Methicillin Susceptible
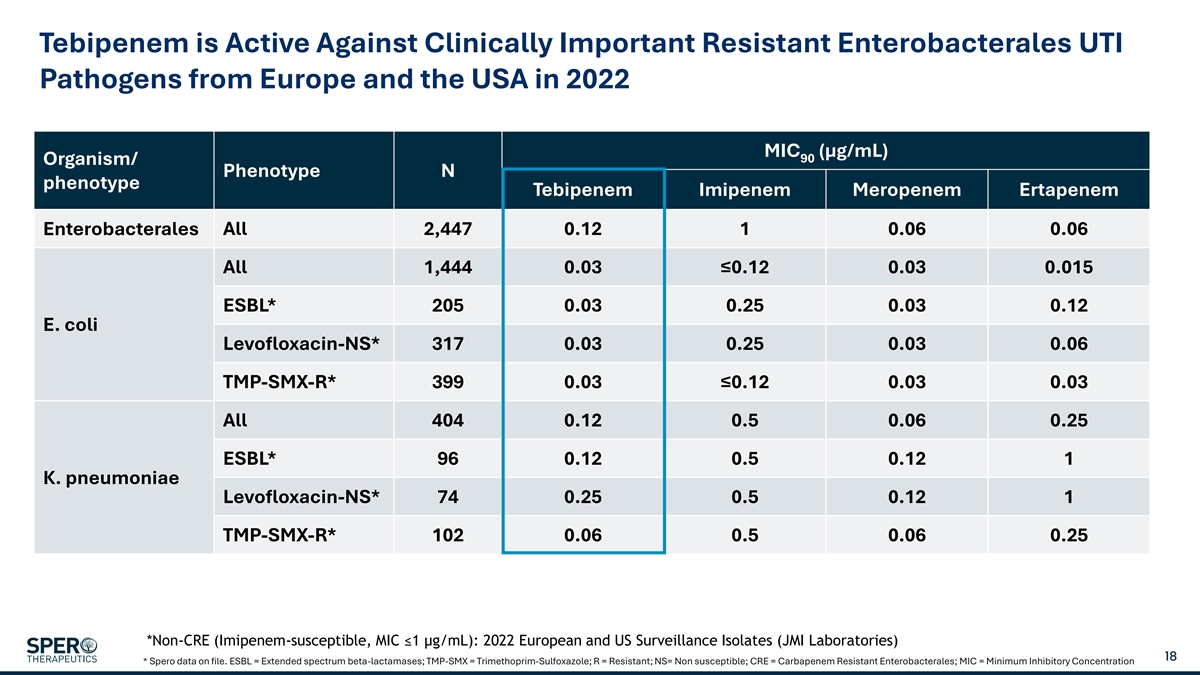
Tebipenem is Active Against Clinically Important Resistant Enterobacterales UTI Pathogens from Europe and the USA in 2022 MIC (µg/mL) 90 Organism/ Phenotype N phenotype Tebipenem Imipenem Meropenem Ertapenem Enterobacterales All 2,447 0.12 1 0.06 0.06 All 1,444 0.03≤0.12 0.03 0.015 ESBL* 205 0.03 0.25 0.03 0.12 E. coli Levofloxacin-NS* 317 0.03 0.25 0.03 0.06 TMP-SMX-R* 399 0.03≤0.12 0.03 0.03 All 404 0.12 0.5 0.06 0.25 ESBL* 96 0.12 0.5 0.12 1 K. pneumoniae Levofloxacin-NS* 74 0.25 0.5 0.12 1 TMP-SMX-R* 102 0.06 0.5 0.06 0.25 *Non-CRE (Imipenem-susceptible, MIC ≤1 µg/mL): 2022 European and US Surveillance Isolates (JMI Laboratories) 18 * Spero data on file. ESBL = Extended spectrum beta-lactamases; TMP-SMX = Trimethoprim-Sulfoxazole; R = Resistant; NS= Non susceptible; CRE = Carbapenem Resistant Enterobacterales; MIC = Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
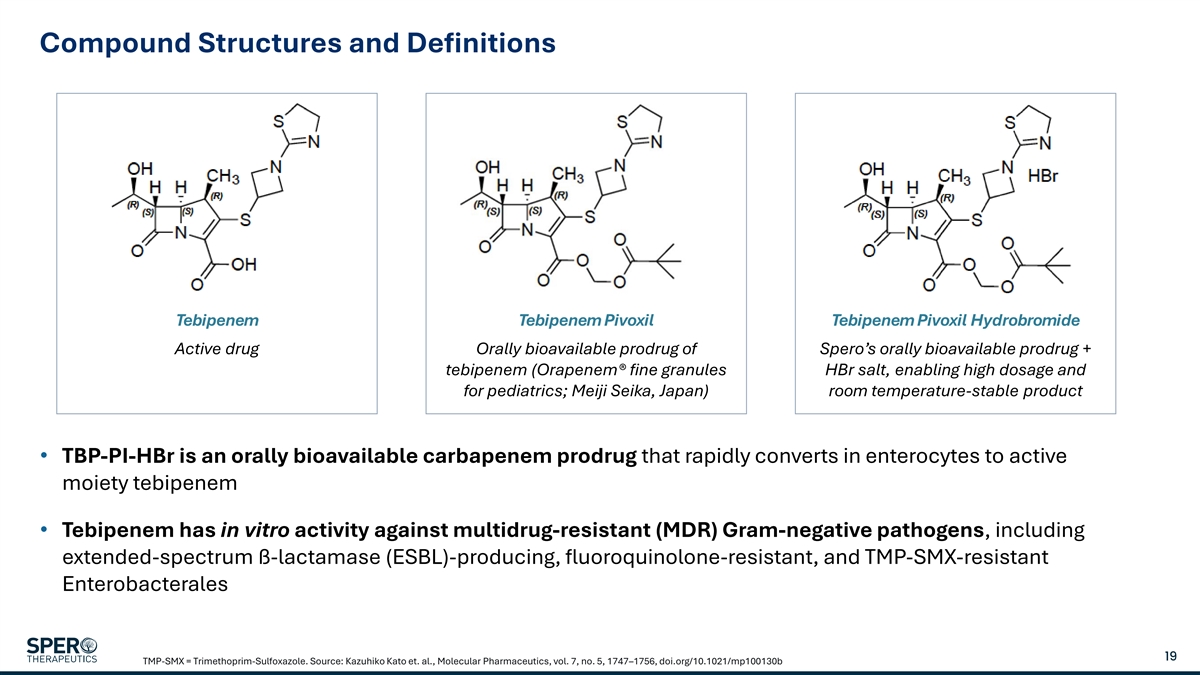
Compound Structures and Definitions Tebipenem Tebipenem Pivoxil Tebipenem Pivoxil Hydrobromide Active drug Orally bioavailable prodrug of Spero’s orally bioavailable prodrug + tebipenem (Orapenem® fine granules HBr salt, enabling high dosage and for pediatrics; Meiji Seika, Japan) room temperature-stable product • TBP-PI-HBr is an orally bioavailable carbapenem prodrug that rapidly converts in enterocytes to active moiety tebipenem • Tebipenem has in vitro activity against multidrug-resistant (MDR) Gram-negative pathogens, including extended-spectrum ß-lactamase (ESBL)-producing, fluoroquinolone-resistant, and TMP-SMX-resistant Enterobacterales 19 TMP-SMX = Trimethoprim-Sulfoxazole. Source: Kazuhiko Kato et. al., Molecular Pharmaceutics, vol. 7, no. 5, 1747–1756, doi.org/10.1021/mp100130b
Tebipenem Pharmacokinetic Profile • Prodrug rapidly converts to tebipenem in enterocytes of GI tract • Plasma Half-life ~1 hour • Dose-proportional PK relationship when administered fed or fasted state • Low potential for drug-drug interactions • No CYP450-dependent metabolism • No induction of CYP450 enzymes • Elimination through fecal and renal excretion • No dose adjustment for hepatic impairment • Dose adjustment for moderate and severe renal impairment • Oral bioavailability of tebipenem ~60% 20 Spero data on file