
© Copyright 2026 Krystal Biotech, Inc. All rights reserved. KB407 for Cystic Fibrosis CORAL-1 Clinical Data Update January 2026 .2

Krystal | 2 Forward Looking Statements and Disclosures This presentation and our discussion contain forward-looking statements that involve substantial risks and uncertainties. Any statements about future expectations, plans, and prospects for Krystal Biotech, Inc. (the “Company”), including but not limited to statements about the Company’s investigational product candidate, KB407, and the CORAL-1 clinical trial evaluating KB407 for the treatment of cystic fibrosis (CF); the potential transformational implications from the positive interim clinical update from the highest dose cohort (Cohort 3) of CORAL-1, including a leadership opportunity in the treatment of CF, further validation of the Company’s lung platform, derisking of KB408 and KB707, support for pipeline expansion, and potential blockbuster opportunities; the Company’s planned CORAL-3 study designed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of repeat KB407 administration, including the timing of expected alignment on the CORAL-3 study design with the FDA and initiation of the study, and the potential for CORAL-3 to support registration of KB407; and other statements, constitute forward-looking statements within the meaning of The Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Actual results may differ materially from those indicated by such forward-looking statements as a result of various important factors, including: uncertainties associated with regulatory reviews and the content and timing of regulatory authorities’ decisions; uncertainties in the initiation and conduct of clinical trials and availability and timing of data from clinical trials; whether results of early clinical trials will be indicative of the results of later-stage studies; the availability or commercial potential of product candidates; and such other important factors as are set forth in the Company’s filings with the SEC. The forward-looking statements represent the Company’s views as of the date of this presentation and should not be relied upon as representing the Company’s views as of any subsequent date. The Company specifically disclaims any obligation to update forward-looking statements. The presentation and discussion may contain estimates and statistical data. Estimates involve assumptions and limitations, and investors are cautioned not to give undue weight to estimates. Neither the Company nor any other person makes any representation as to the accuracy or completeness of such estimates or data or undertakes any obligation to update such estimates or data. Today’s discussions and presentation are intended for the investor community only; they are not intended to promote the products or product candidates referenced herein or otherwise influence healthcare prescribing decisions. The Company is using the Aerogen Solo® Nebulizer System and Aerogen® Ultra in its clinical trials evaluating KB407, KB408, and inhaled KB707

Krystal | 3 Agenda Opening Remarks Krish Krishnan; Chairman and CEO Treatment Gap for Modulator-Ineligible Patients with Cystic Fibrosis Jorge Lascano, MD; Associate Director of Adult Cystic Fibrosis Program, University of Florida KB407 Program Overview Suma Krishnan, MS, MBA; President, Research & Development Closing Remarks Krish Krishnan; Chairman and CEO KB407 CORAL-1 Phase 1 Highest Dose Cohort Results David Sweet, MD, PhD; Director, Clinical Development KB407 Next Steps and Clinical Development Outlook Suma Krishnan, MS, MBA; President, Research & Development Q&A All Speakers and Trevor Parry, PhD; Vice President, Product Development
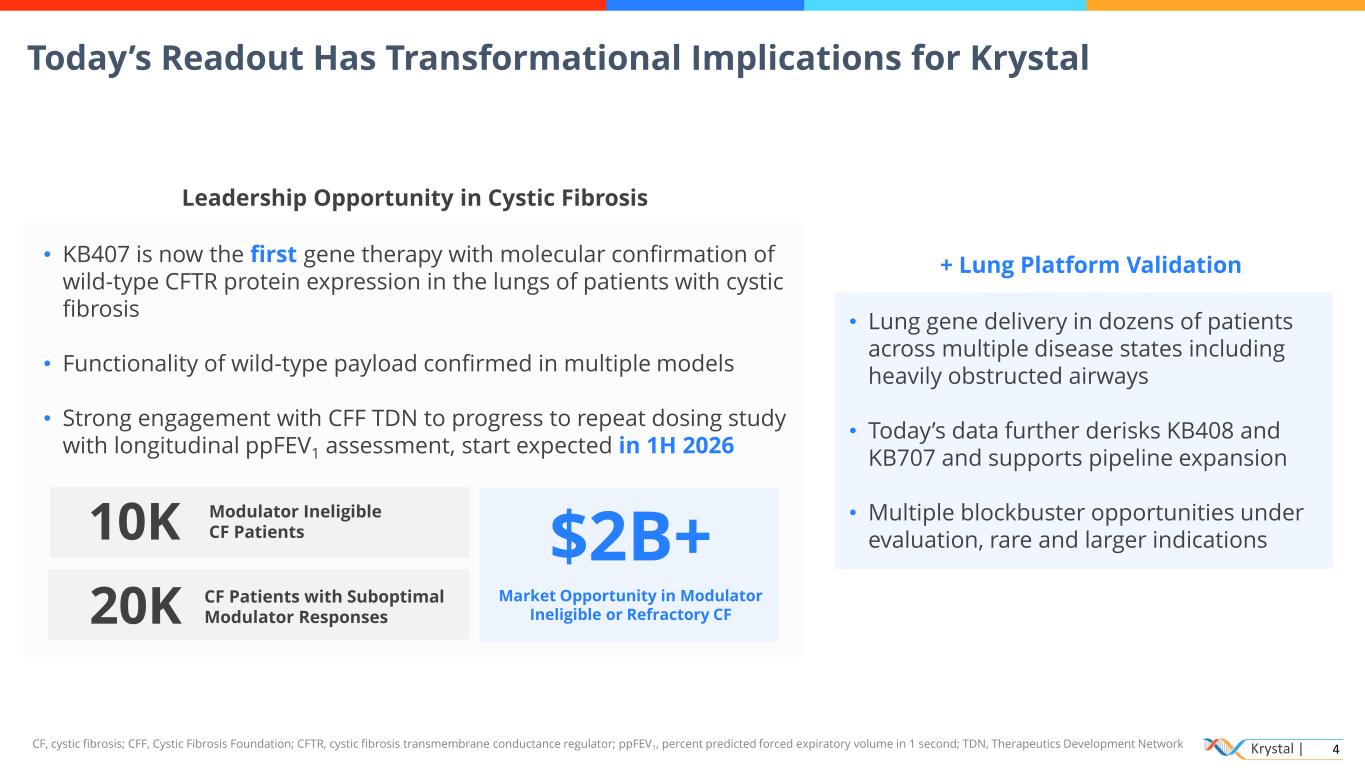
Krystal | 4 Today’s Readout Has Transformational Implications for Krystal + Lung Platform Validation • Lung gene delivery in dozens of patients across multiple disease states including heavily obstructed airways • Today’s data further derisks KB408 and KB707 and supports pipeline expansion • Multiple blockbuster opportunities under evaluation, rare and larger indications Leadership Opportunity in Cystic Fibrosis • KB407 is now the first gene therapy with molecular confirmation of wild-type CFTR protein expression in the lungs of patients with cystic fibrosis • Functionality of wild-type payload confirmed in multiple models • Strong engagement with CFF TDN to progress to repeat dosing study with longitudinal ppFEV1 assessment, start expected in 1H 2026 10K CF Patients with Suboptimal Modulator Responses $2B+ Market Opportunity in Modulator Ineligible or Refractory CF Modulator Ineligible CF Patients 20K CF, cystic fibrosis; CFF, Cystic Fibrosis Foundation; CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; ppFEV1, percent predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 second; TDN, Therapeutics Development Network

Cystic Fibrosis Beyond Modulators: Persistent Unmet Need Jorge Lascano, MD Professor of Medicine Associate Director of the Adult Cystic Fibrosis Program Director of the Cystic Fibrosis Therapeutics Development Center University of Florida CORAL-1 Investigator
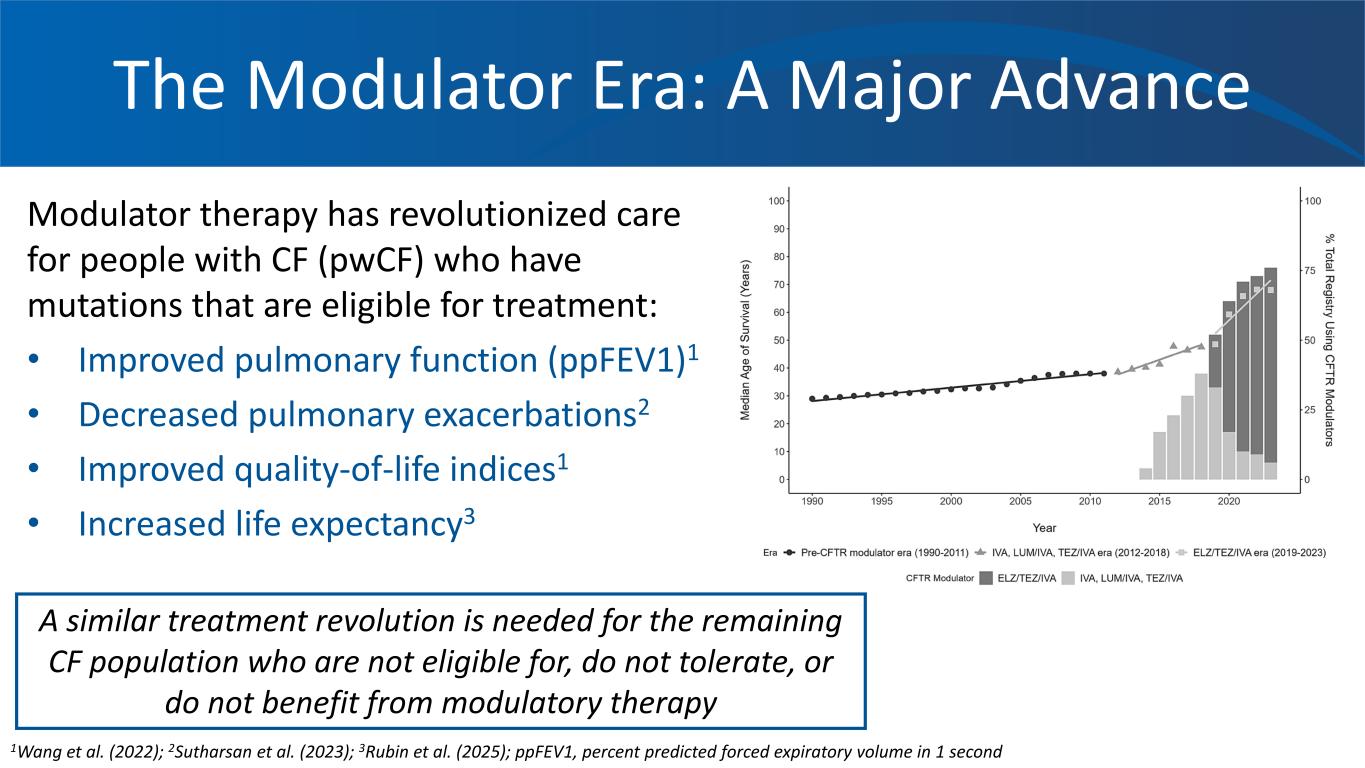
The Modulator Era: A Major Advance Modulator therapy has revolutionized care for people with CF (pwCF) who have mutations that are eligible for treatment: • Improved pulmonary function (ppFEV1)1 • Decreased pulmonary exacerbations2 • Improved quality-of-life indices1 • Increased life expectancy3 1Wang et al. (2022); 2Sutharsan et al. (2023); 3Rubin et al. (2025); ppFEV1, percent predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 second A similar treatment revolution is needed for the remaining CF population who are not eligible for, do not tolerate, or do not benefit from modulatory therapy
Who Is Left Behind? Unresponsive genotype: Mutations which result in no mRNA or functional protein produced (e.g., class 1 mutations) Poor response: ‘Modulator-refractory’ individuals exist due to extensive heterogeneity in CF populations (e.g. non-CFTR genetic variants, variable immune response, comorbid conditions) Poor tolerability: Side effects and drug-drug interactions can prove intolerable for some patients Access issues: Even those with mutations that are potentially responsive to modulator therapy are often unable to access therapy due to challenges with testing and diagnosis on nontraditional populations, understanding the functionality of uncommon mutations as well as drug availability. 10+% are modulator ineligible, with thousands more with suboptimal responses to modulator therapy Somerville et al. (2024)
Clinical Burden in the Non-Modulator Population • Ongoing pulmonary function decline • High exacerbation burden • Continued need for intensive daily therapy • Substantial negative influence on quality-of-life; patients can feel left behind compared to those who benefit from modulator therapy • More likely to require lung transplantation1 • Even when compared to those who are otherwise eligible but not on modulator therapy, patients that are not eligible have worse clinical outcomes2 – Underscoring critical need for novel therapeutics for this population in particular 1Clancy and Hamblett (2023); 2Buyuksahin et al. (2024)
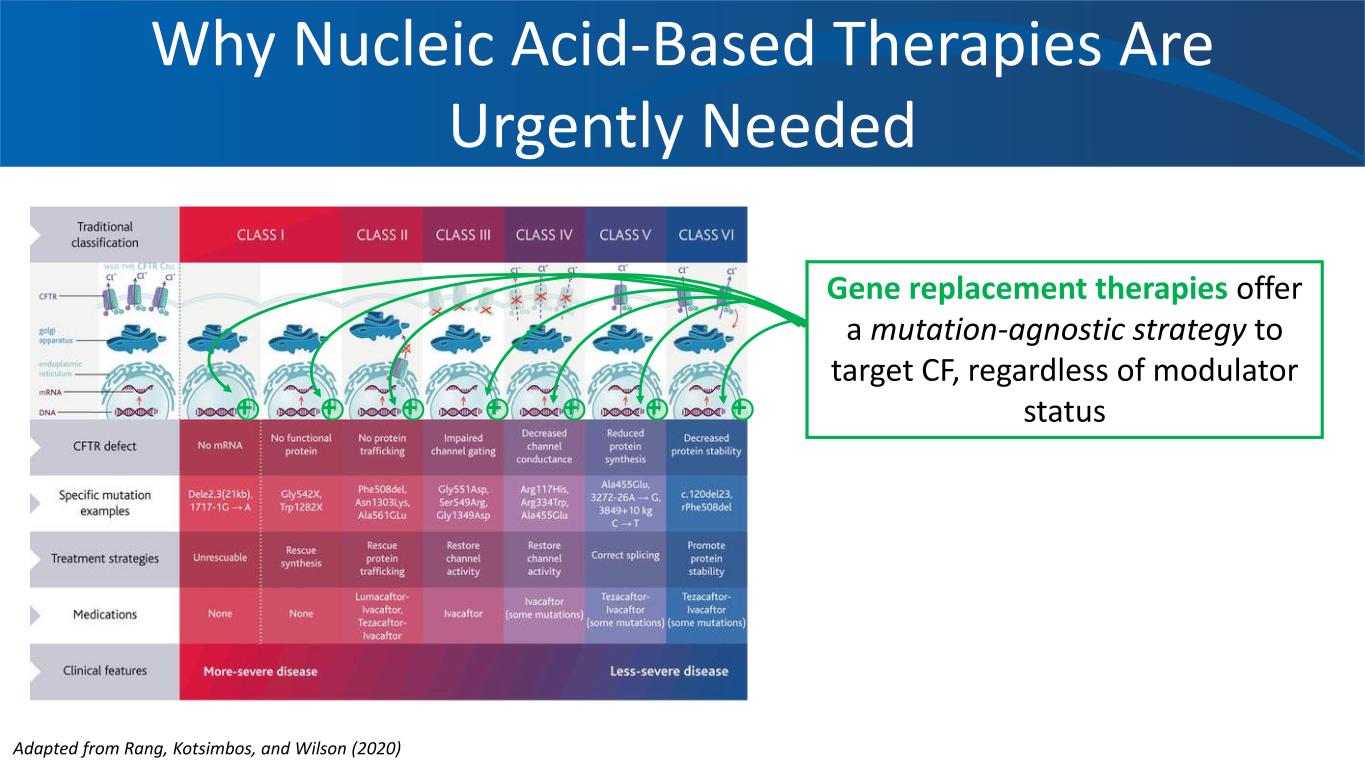
Why Nucleic Acid-Based Therapies Are Urgently Needed Gene replacement therapies offer a mutation-agnostic strategy to target CF, regardless of modulator status+ + + + + + + Adapted from Rang, Kotsimbos, and Wilson (2020)
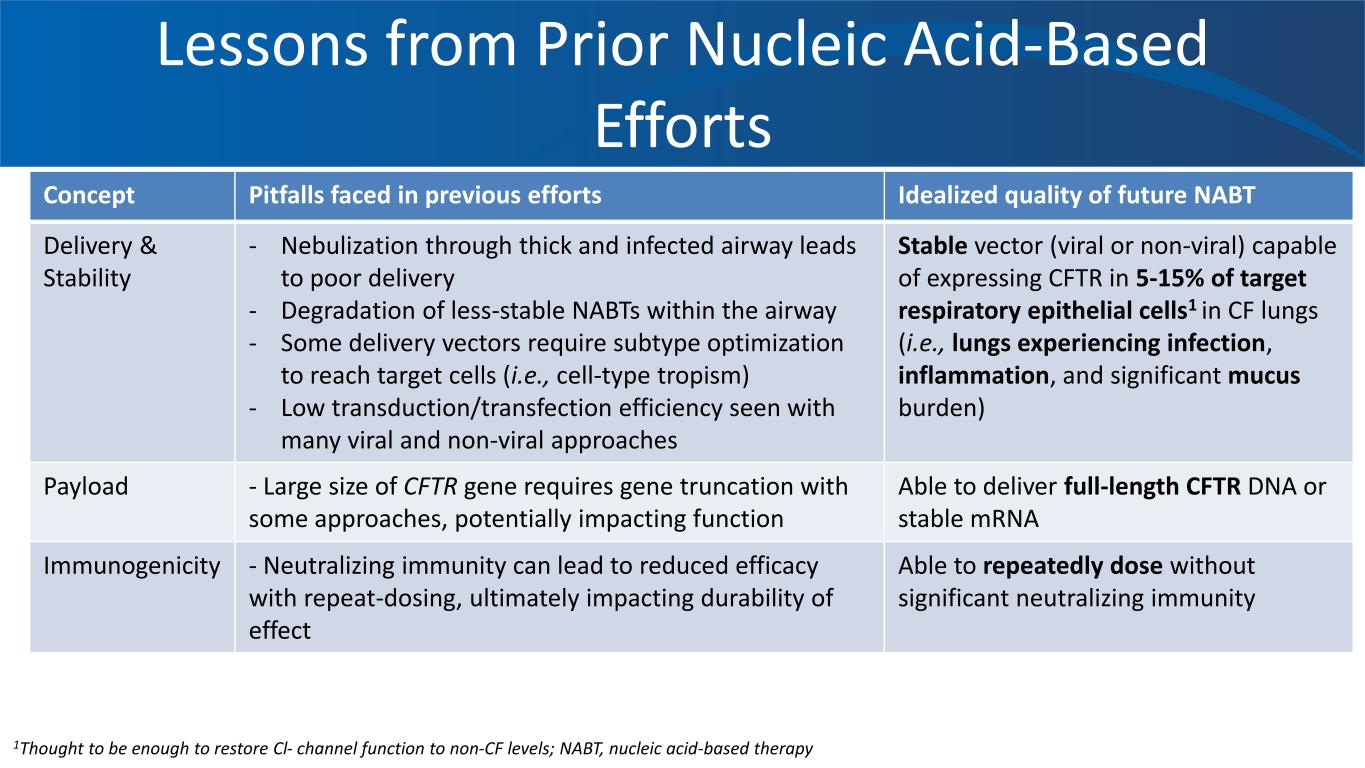
Lessons from Prior Nucleic Acid-Based Efforts Concept Pitfalls faced in previous efforts Idealized quality of future NABT Delivery & Stability - Nebulization through thick and infected airway leads to poor delivery - Degradation of less-stable NABTs within the airway - Some delivery vectors require subtype optimization to reach target cells (i.e., cell-type tropism) - Low transduction/transfection efficiency seen with many viral and non-viral approaches Stable vector (viral or non-viral) capable of expressing CFTR in 5-15% of target respiratory epithelial cells1 in CF lungs (i.e., lungs experiencing infection, inflammation, and significant mucus burden) Payload - Large size of CFTR gene requires gene truncation with some approaches, potentially impacting function Able to deliver full-length CFTR DNA or stable mRNA Immunogenicity - Neutralizing immunity can lead to reduced efficacy with repeat-dosing, ultimately impacting durability of effect Able to repeatedly dose without significant neutralizing immunity 1Thought to be enough to restore Cl- channel function to non-CF levels; NABT, nucleic acid-based therapy
Looking Forward
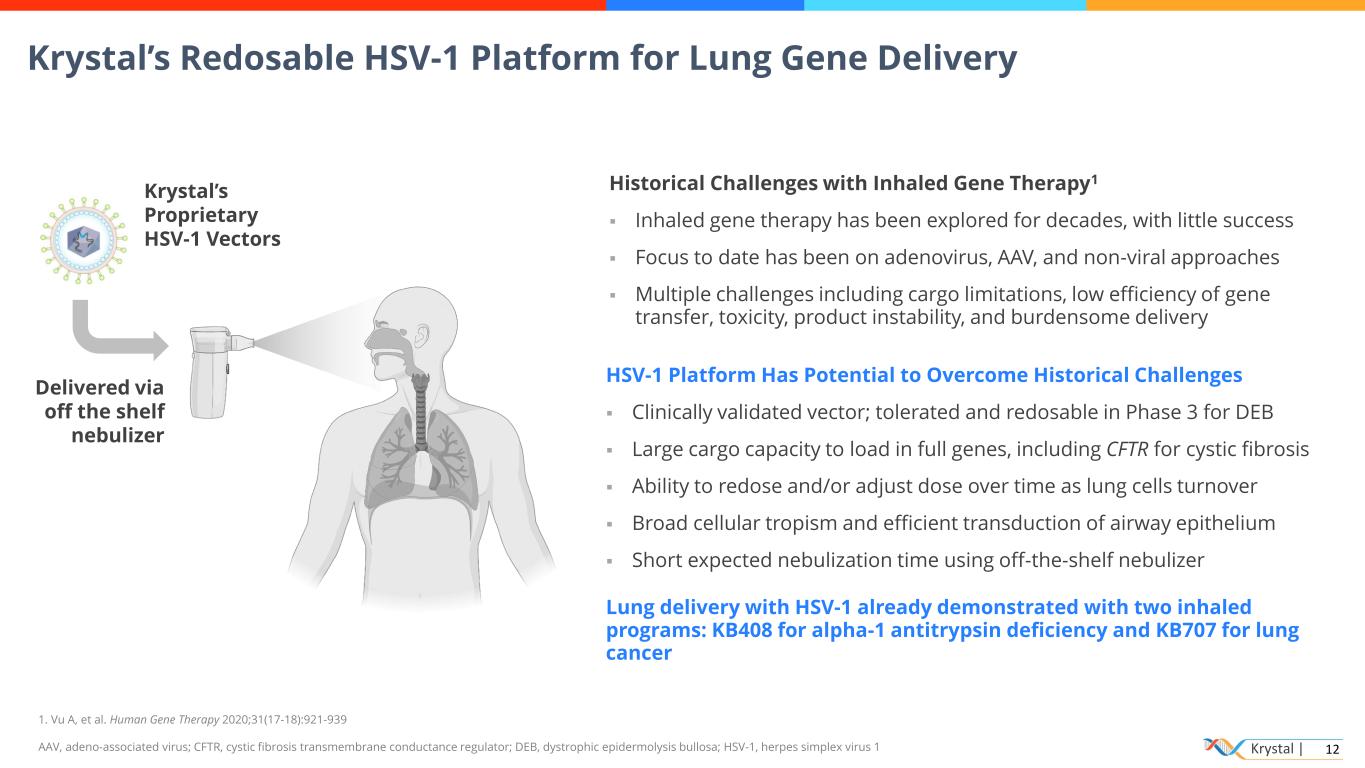
Krystal | 12 Historical Challenges with Inhaled Gene Therapy1 ▪ Inhaled gene therapy has been explored for decades, with little success ▪ Focus to date has been on adenovirus, AAV, and non-viral approaches ▪ Multiple challenges including cargo limitations, low efficiency of gene transfer, toxicity, product instability, and burdensome delivery HSV-1 Platform Has Potential to Overcome Historical Challenges ▪ Clinically validated vector; tolerated and redosable in Phase 3 for DEB ▪ Large cargo capacity to load in full genes, including CFTR for cystic fibrosis ▪ Ability to redose and/or adjust dose over time as lung cells turnover ▪ Broad cellular tropism and efficient transduction of airway epithelium ▪ Short expected nebulization time using off-the-shelf nebulizer Lung delivery with HSV-1 already demonstrated with two inhaled programs: KB408 for alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency and KB707 for lung cancer 1. Vu A, et al. Human Gene Therapy 2020;31(17-18):921-939 AAV, adeno-associated virus; CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; DEB, dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa; HSV-1, herpes simplex virus 1 Krystal’s Redosable HSV-1 Platform for Lung Gene Delivery Delivered via off the shelf nebulizer Krystal’s Proprietary HSV-1 Vectors
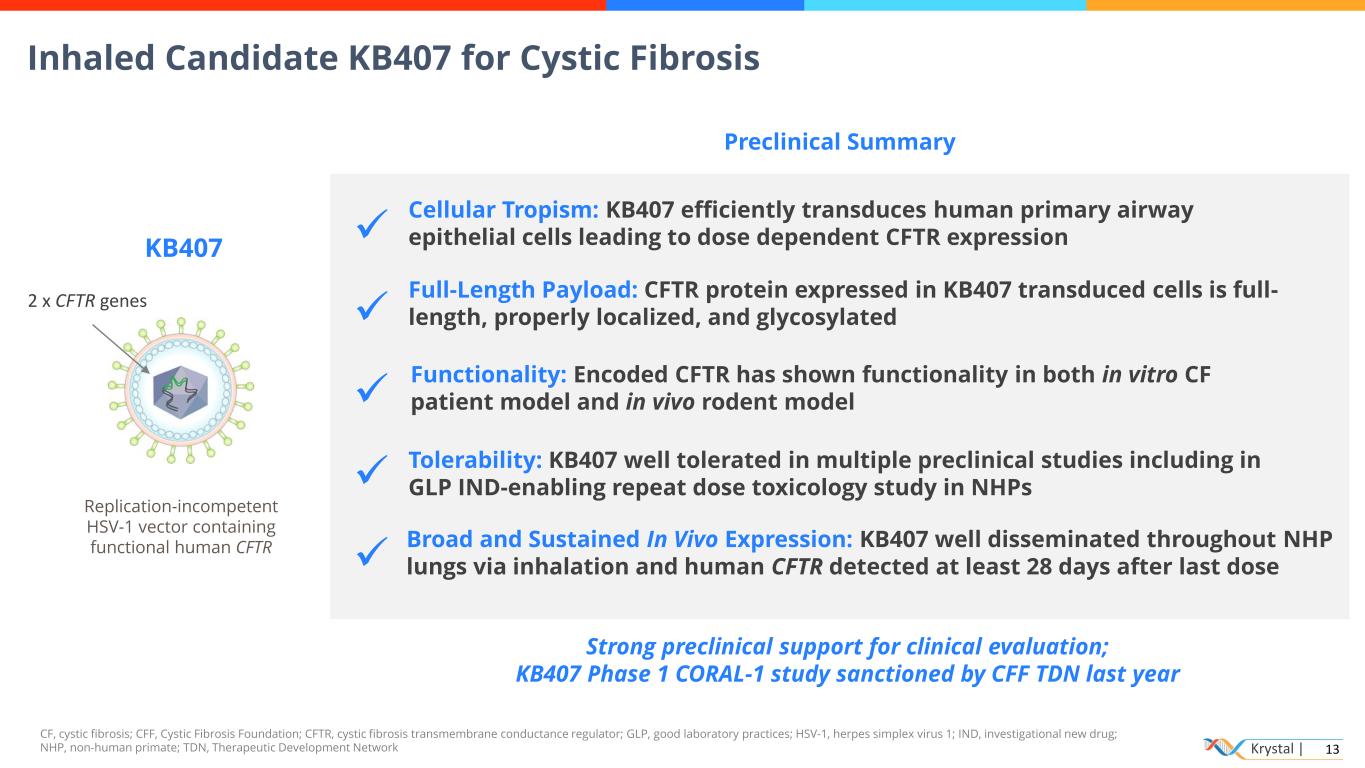
Krystal | 13 CF, cystic fibrosis; CFF, Cystic Fibrosis Foundation; CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; GLP, good laboratory practices; HSV-1, herpes simplex virus 1; IND, investigational new drug; NHP, non-human primate; TDN, Therapeutic Development Network KB407 Replication-incompetent HSV-1 vector containing functional human CFTR 2 x CFTR genes ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ Functionality: Encoded CFTR has shown functionality in both in vitro CF patient model and in vivo rodent model Broad and Sustained In Vivo Expression: KB407 well disseminated throughout NHP lungs via inhalation and human CFTR detected at least 28 days after last dose Strong preclinical support for clinical evaluation; KB407 Phase 1 CORAL-1 study sanctioned by CFF TDN last year Tolerability: KB407 well tolerated in multiple preclinical studies including in GLP IND-enabling repeat dose toxicology study in NHPs Preclinical Summary Cellular Tropism: KB407 efficiently transduces human primary airway epithelial cells leading to dose dependent CFTR expression Full-Length Payload: CFTR protein expressed in KB407 transduced cells is full- length, properly localized, and glycosylated Inhaled Candidate KB407 for Cystic Fibrosis
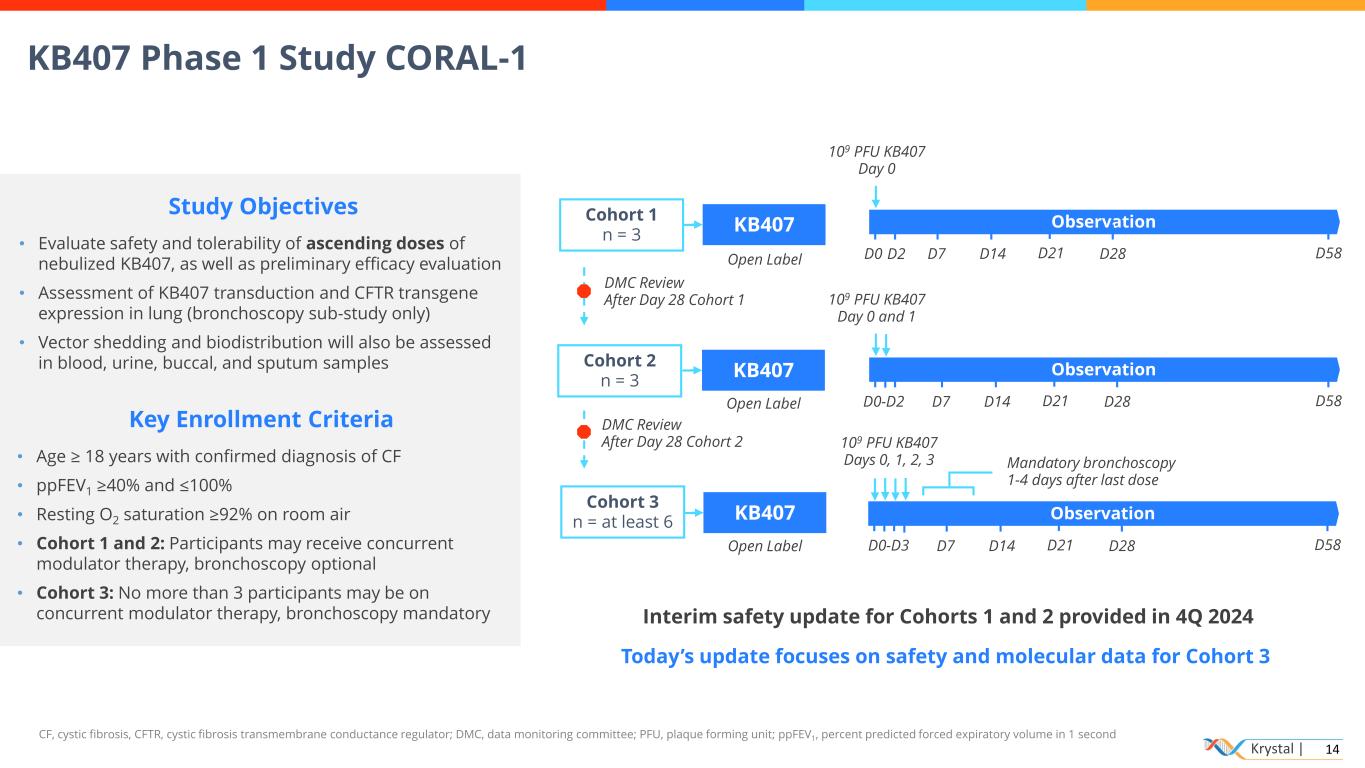
Krystal | 14 Observation Cohort 3 n = at least 6 Cohort 2 n = 3 KB407 Cohort 1 n = 3 KB407 Study Objectives • Evaluate safety and tolerability of ascending doses of nebulized KB407, as well as preliminary efficacy evaluation • Assessment of KB407 transduction and CFTR transgene expression in lung (bronchoscopy sub-study only) • Vector shedding and biodistribution will also be assessed in blood, urine, buccal, and sputum samples Key Enrollment Criteria • Age ≥ 18 years with confirmed diagnosis of CF • ppFEV1 ≥40% and ≤100% • Resting O2 saturation ≥92% on room air • Cohort 1 and 2: Participants may receive concurrent modulator therapy, bronchoscopy optional • Cohort 3: No more than 3 participants may be on concurrent modulator therapy, bronchoscopy mandatory CF, cystic fibrosis, CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; DMC, data monitoring committee; PFU, plaque forming unit; ppFEV1, percent predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 second Open Label Open Label 109 PFU KB407 Days 0, 1, 2, 3 DMC Review After Day 28 Cohort 1 DMC Review After Day 28 Cohort 2 109 PFU KB407 Day 0 D28D0 D2 D7 D14 D58D21 Observation 109 PFU KB407 Day 0 and 1 D0-D2 D58 Observation Mandatory bronchoscopy 1-4 days after last dose D0-D3 D58 D28D7 D14 D21 D28D7 D14 D21 KB407 Open Label Interim safety update for Cohorts 1 and 2 provided in 4Q 2024 KB407 Phase 1 Study CORAL-1 Today’s update focuses on safety and molecular data for Cohort 3
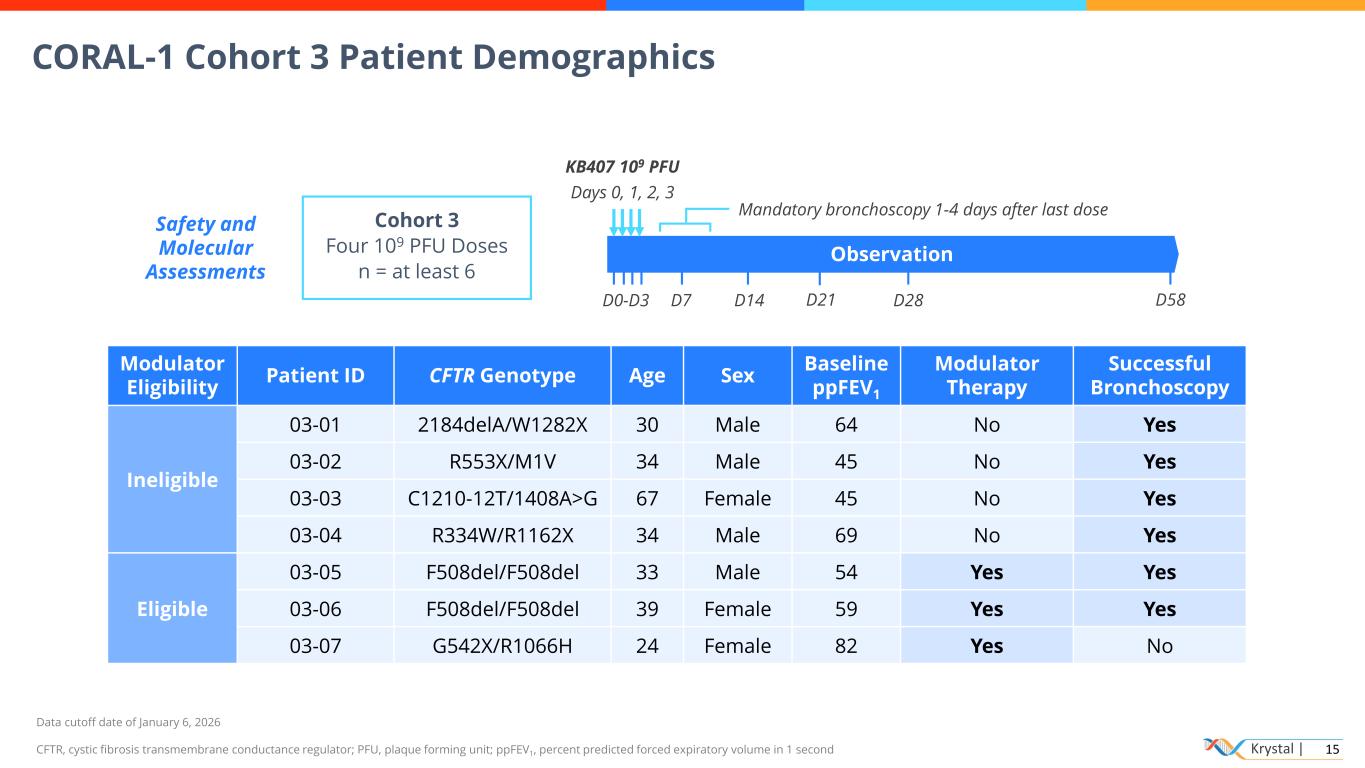
Krystal | 15 CORAL-1 Cohort 3 Patient Demographics Data cutoff date of January 6, 2026 CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; PFU, plaque forming unit; ppFEV1, percent predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 second Cohort 3 Four 109 PFU Doses n = at least 6 Observation KB407 109 PFU Days 0, 1, 2, 3 D28D0-D3 D7 D14 D58D21 Safety and Molecular Assessments Modulator Eligibility Patient ID CFTR Genotype Age Sex Baseline ppFEV1 Modulator Therapy Successful Bronchoscopy Ineligible 03-01 2184delA/W1282X 30 Male 64 No Yes 03-02 R553X/M1V 34 Male 45 No Yes 03-03 C1210-12T/1408A>G 67 Female 45 No Yes 03-04 R334W/R1162X 34 Male 69 No Yes Eligible 03-05 F508del/F508del 33 Male 54 Yes Yes 03-06 F508del/F508del 39 Female 59 Yes Yes 03-07 G542X/R1066H 24 Female 82 Yes No Mandatory bronchoscopy 1-4 days after last dose
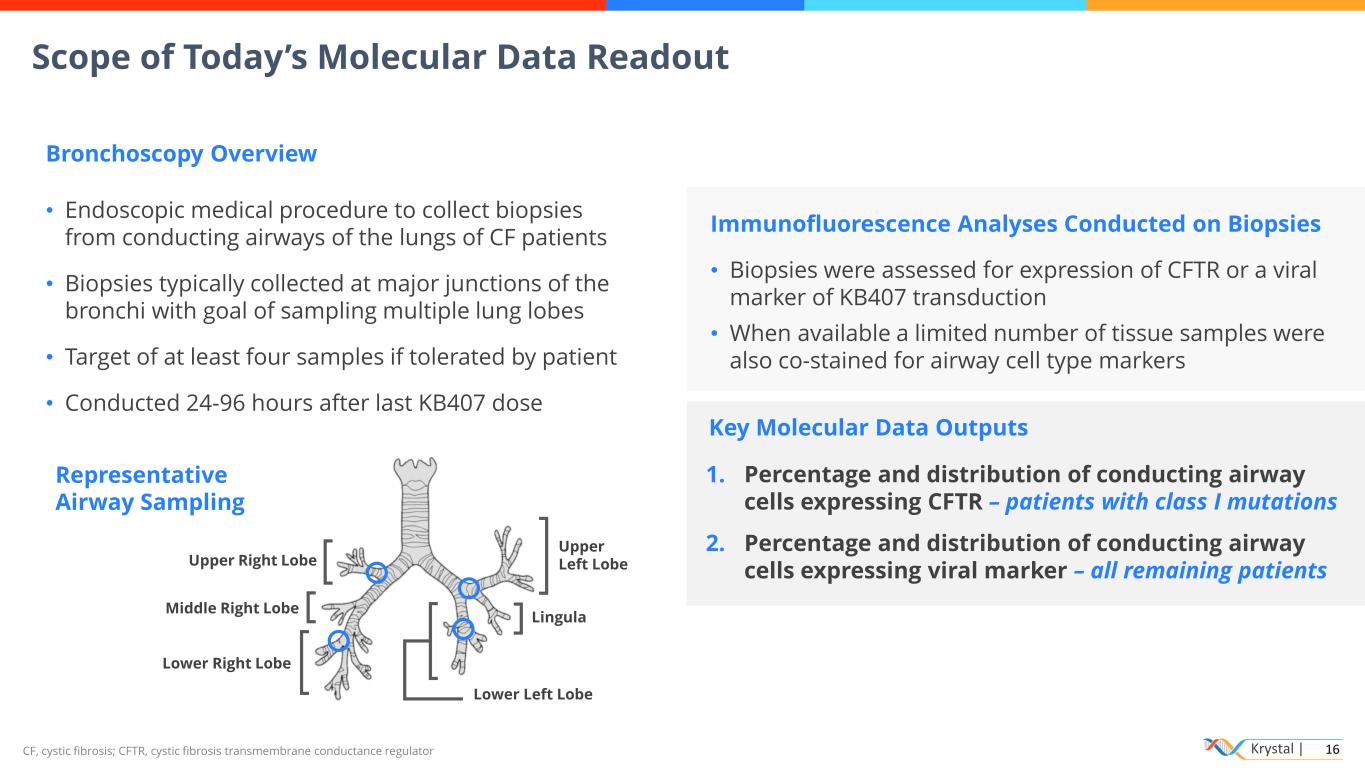
Krystal | 16 Representative Airway Sampling Key Molecular Data Outputs CF, cystic fibrosis; CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator Scope of Today’s Molecular Data Readout Bronchoscopy Overview • Endoscopic medical procedure to collect biopsies from conducting airways of the lungs of CF patients • Biopsies typically collected at major junctions of the bronchi with goal of sampling multiple lung lobes • Target of at least four samples if tolerated by patient • Conducted 24-96 hours after last KB407 dose Immunofluorescence Analyses Conducted on Biopsies • Biopsies were assessed for expression of CFTR or a viral marker of KB407 transduction • When available a limited number of tissue samples were also co-stained for airway cell type markers 1. Percentage and distribution of conducting airway cells expressing CFTR – patients with class I mutations 2. Percentage and distribution of conducting airway cells expressing viral marker – all remaining patients Upper Right Lobe Middle Right Lobe Lower Right Lobe Upper Left Lobe Lingula Lower Left Lobe
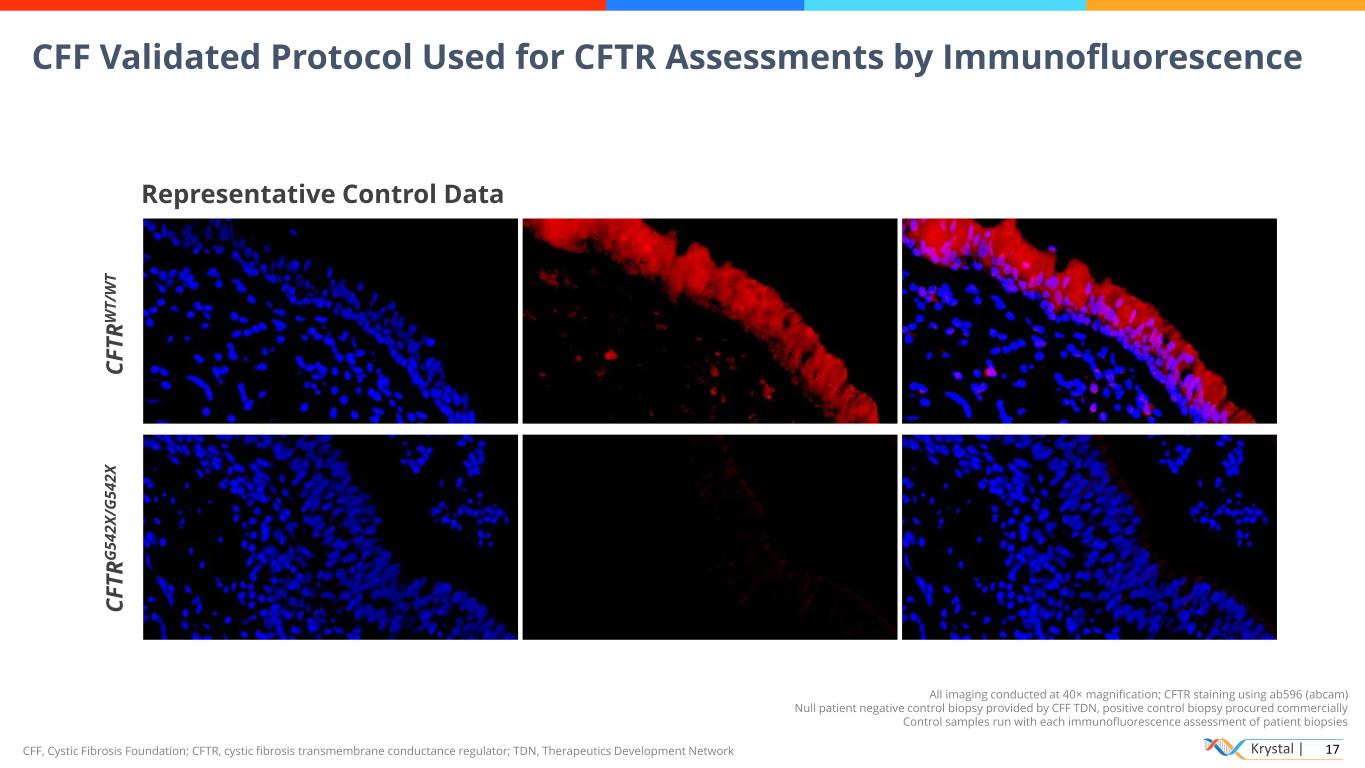
Krystal | 17CFF, Cystic Fibrosis Foundation; CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; TDN, Therapeutics Development Network CFF Validated Protocol Used for CFTR Assessments by Immunofluorescence Representative Control Data C F T R W T /W T C F T R G 5 4 2 X /G 5 4 2 X All imaging conducted at 40× magnification; CFTR staining using ab596 (abcam) Null patient negative control biopsy provided by CFF TDN, positive control biopsy procured commercially Control samples run with each immunofluorescence assessment of patient biopsies
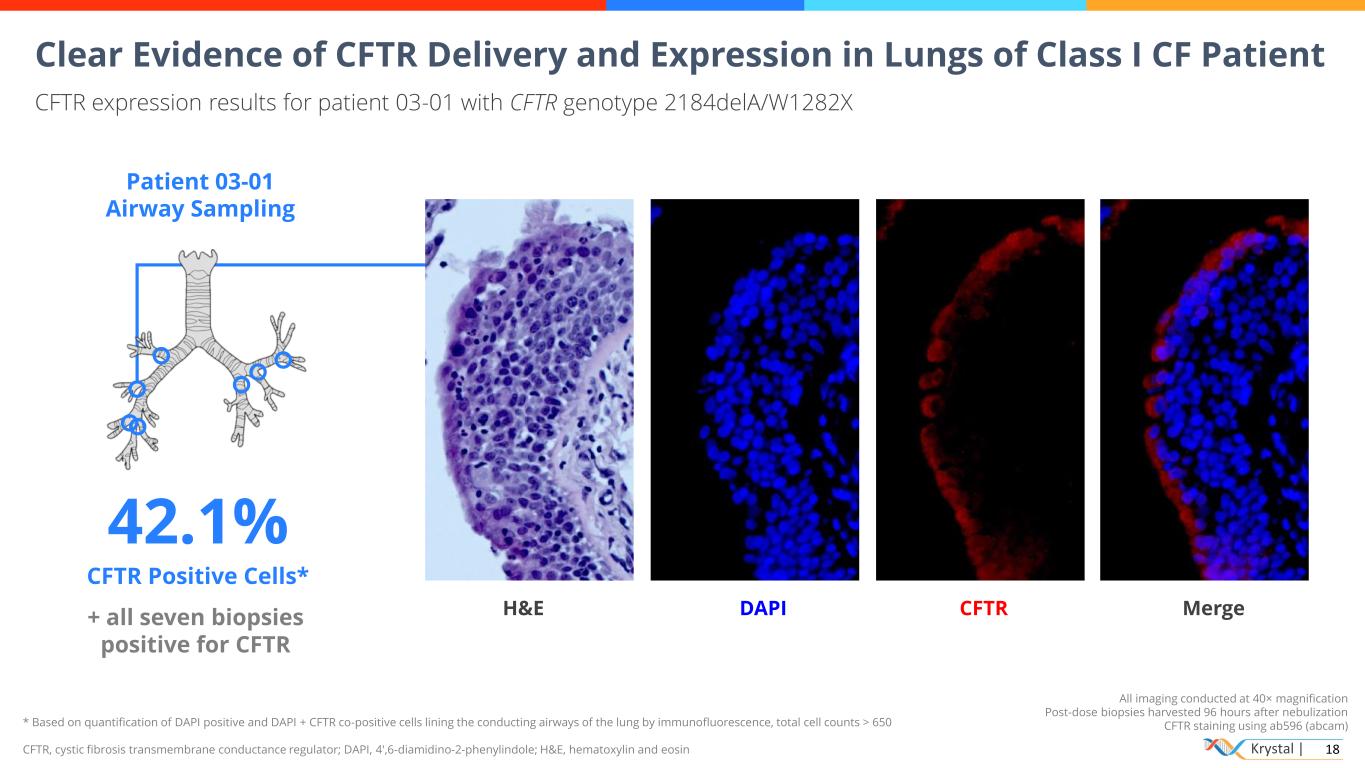
Krystal | 18 All imaging conducted at 40× magnification Post-dose biopsies harvested 96 hours after nebulization CFTR staining using ab596 (abcam) Clear Evidence of CFTR Delivery and Expression in Lungs of Class I CF Patient CFTR expression results for patient 03-01 with CFTR genotype 2184delA/W1282X Patient 03-01 Airway Sampling 42.1% CFTR Positive Cells* + all seven biopsies positive for CFTR H&E DAPI CFTR Merge * Based on quantification of DAPI positive and DAPI + CFTR co-positive cells lining the conducting airways of the lung by immunofluorescence, total cell counts > 650 CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin
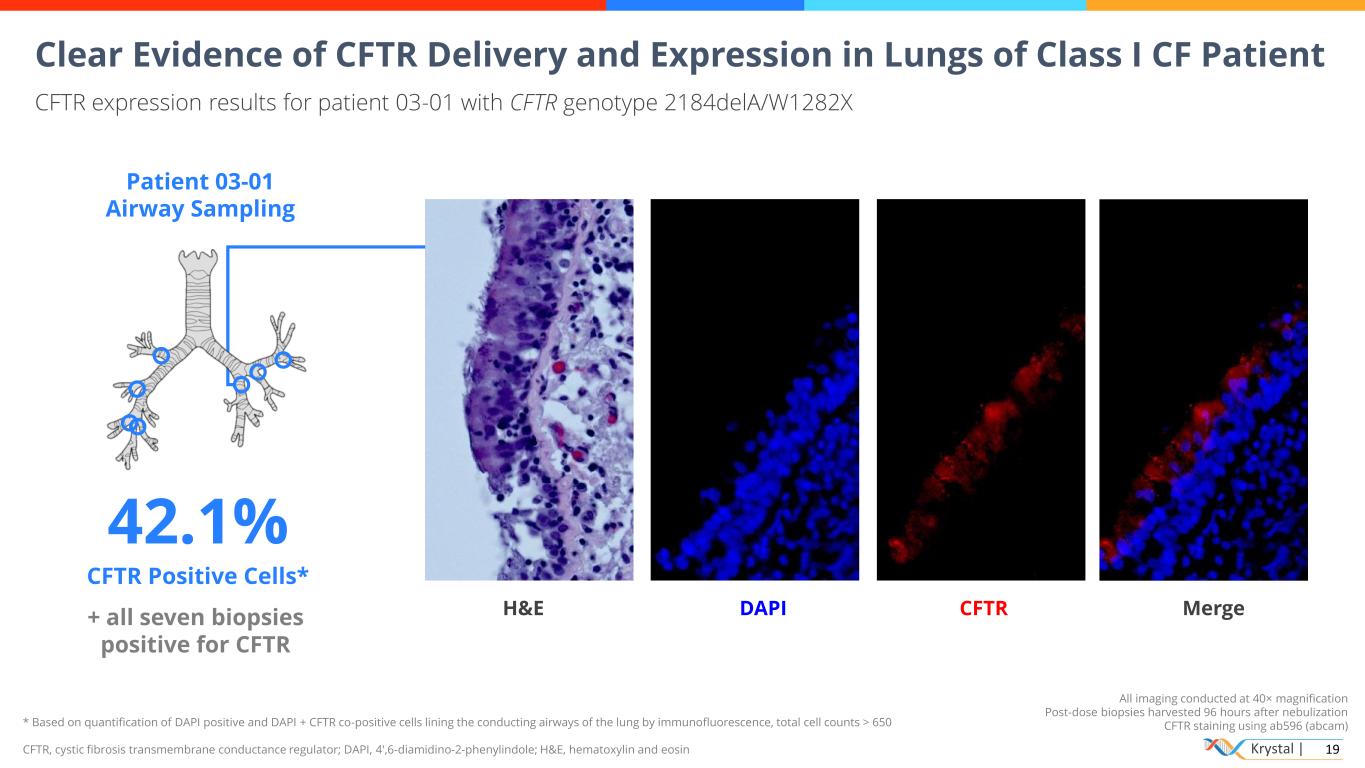
Krystal | 19 All imaging conducted at 40× magnification Post-dose biopsies harvested 96 hours after nebulization CFTR staining using ab596 (abcam) CFTR expression results for patient 03-01 with CFTR genotype 2184delA/W1282X Patient 03-01 Airway Sampling 42.1% CFTR Positive Cells* + all seven biopsies positive for CFTR H&E DAPI CFTR Merge Clear Evidence of CFTR Delivery and Expression in Lungs of Class I CF Patient * Based on quantification of DAPI positive and DAPI + CFTR co-positive cells lining the conducting airways of the lung by immunofluorescence, total cell counts > 650 CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin
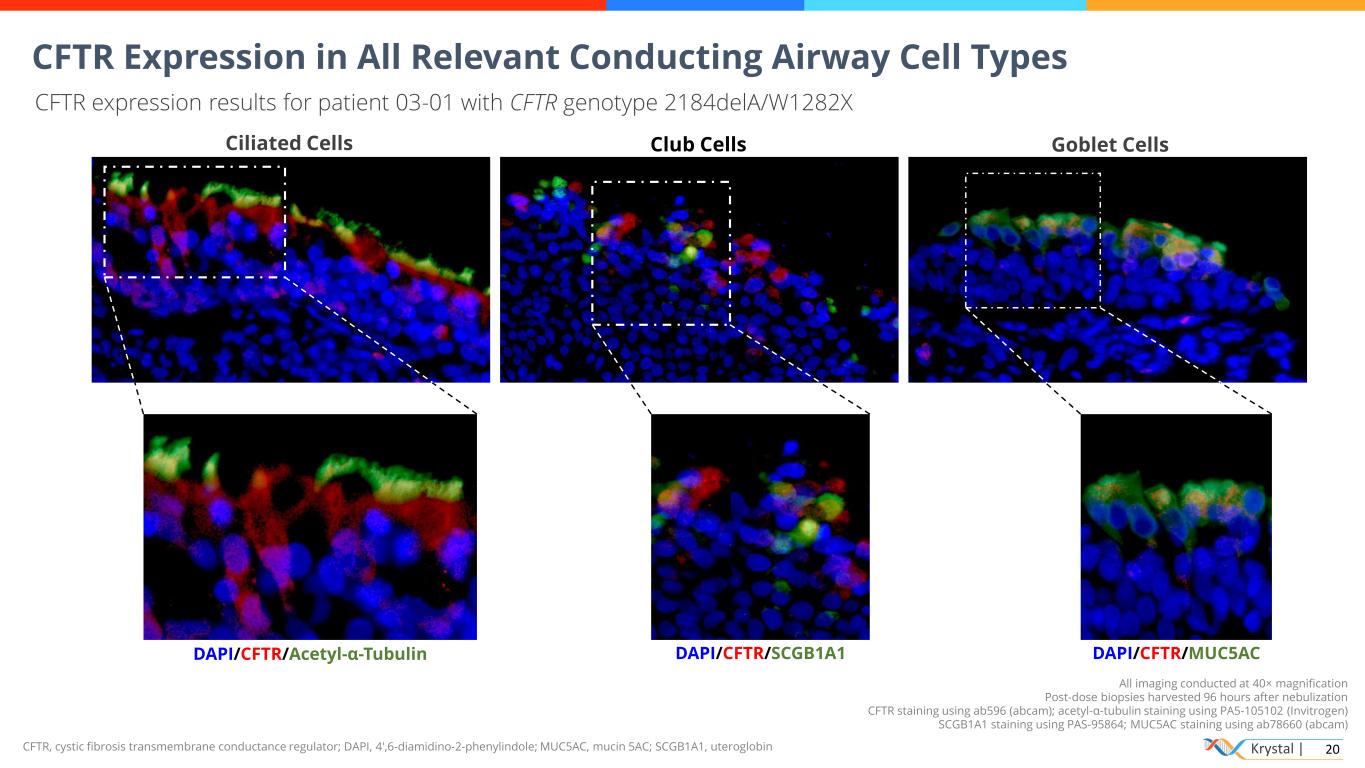
Krystal | 20CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; MUC5AC, mucin 5AC; SCGB1A1, uteroglobin All imaging conducted at 40× magnification Post-dose biopsies harvested 96 hours after nebulization CFTR staining using ab596 (abcam); acetyl-α-tubulin staining using PA5-105102 (Invitrogen) SCGB1A1 staining using PAS-95864; MUC5AC staining using ab78660 (abcam) CFTR Expression in All Relevant Conducting Airway Cell Types CFTR expression results for patient 03-01 with CFTR genotype 2184delA/W1282X DAPI/CFTR/Acetyl-α-Tubulin Ciliated Cells DAPI/CFTR/SCGB1A1 Club Cells DAPI/CFTR/MUC5AC Goblet Cells
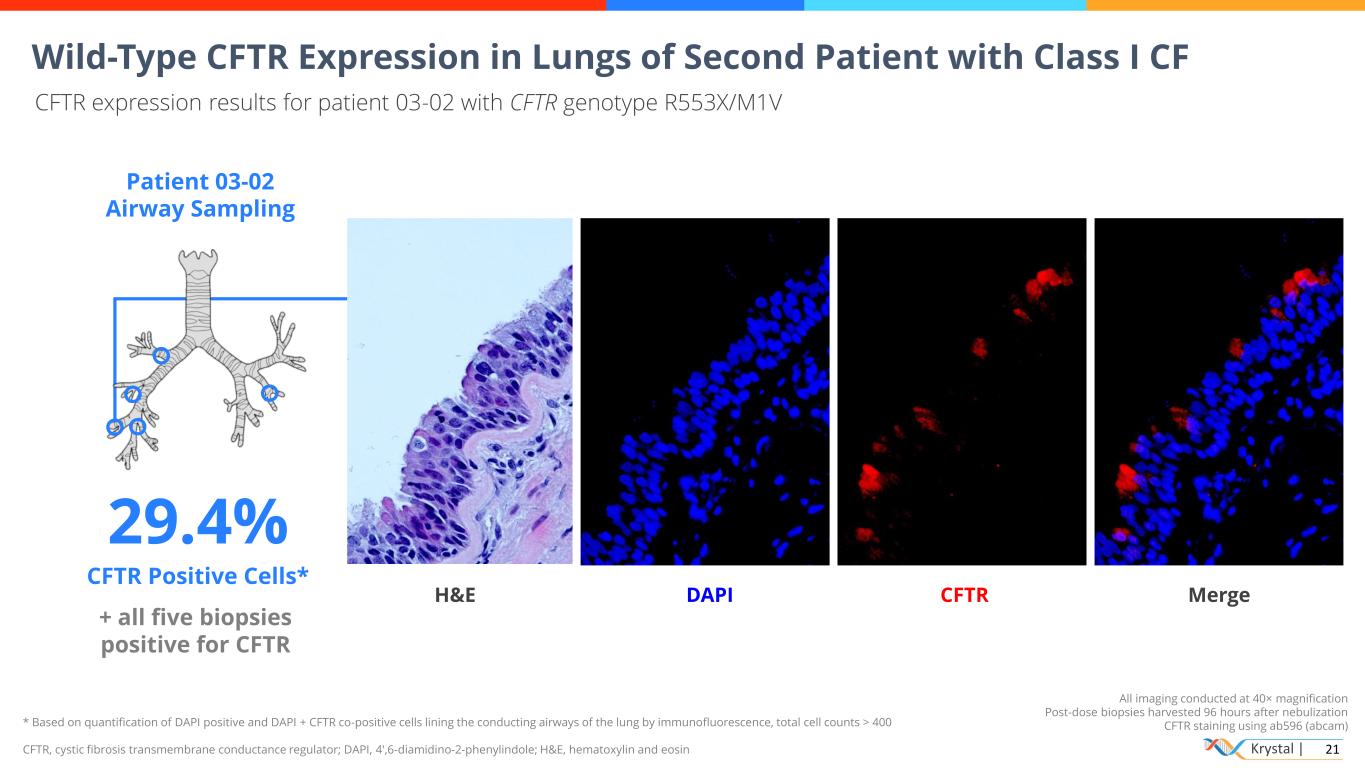
Krystal | 21 * Based on quantification of DAPI positive and DAPI + CFTR co-positive cells lining the conducting airways of the lung by immunofluorescence, total cell counts > 400 CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin All imaging conducted at 40× magnification Post-dose biopsies harvested 96 hours after nebulization CFTR staining using ab596 (abcam) Wild-Type CFTR Expression in Lungs of Second Patient with Class I CF CFTR expression results for patient 03-02 with CFTR genotype R553X/M1V Patient 03-02 Airway Sampling 29.4% CFTR Positive Cells* + all five biopsies positive for CFTR H&E DAPI CFTR Merge
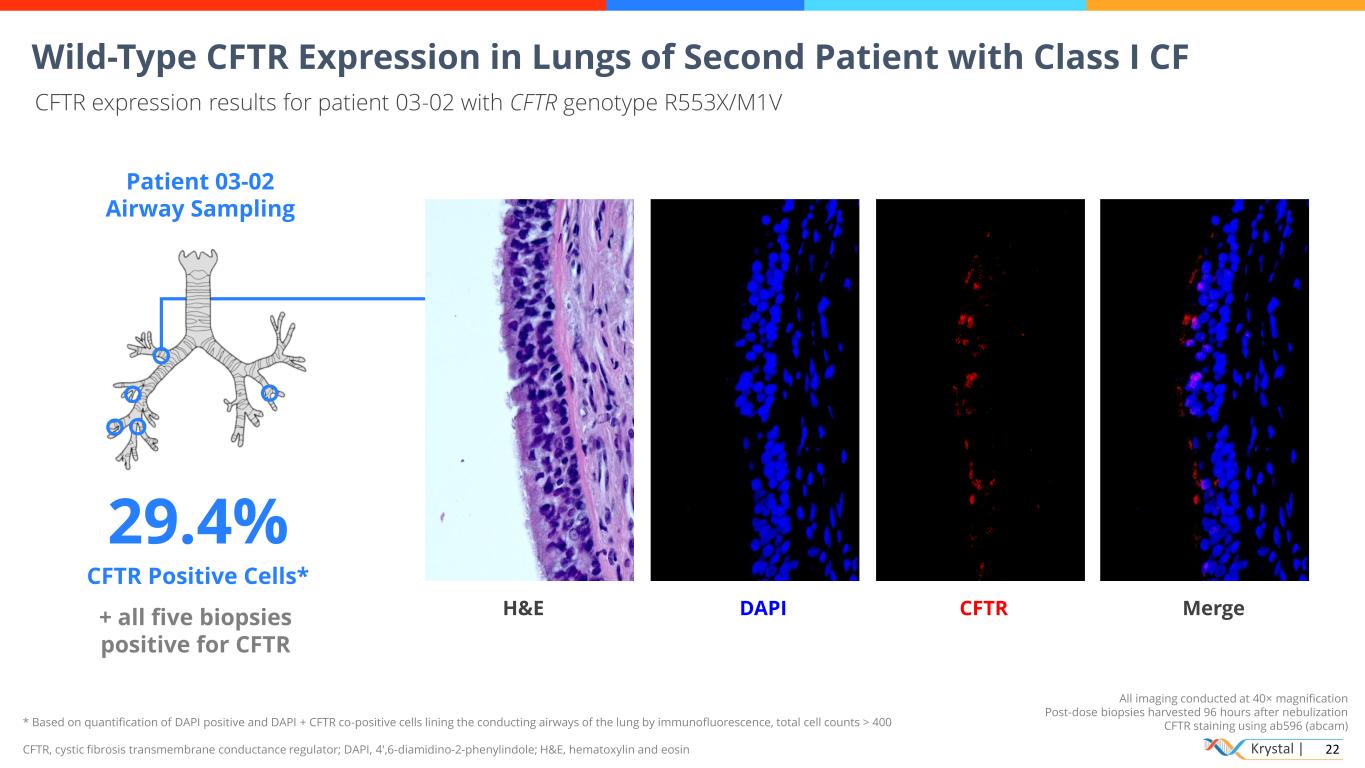
Krystal | 22 All imaging conducted at 40× magnification Post-dose biopsies harvested 96 hours after nebulization CFTR staining using ab596 (abcam) Wild-Type CFTR Expression in Lungs of Second Patient with Class I CF CFTR expression results for patient 03-02 with CFTR genotype R553X/M1V Patient 03-02 Airway Sampling 29.4% CFTR Positive Cells* + all five biopsies positive for CFTR H&E DAPI CFTR Merge * Based on quantification of DAPI positive and DAPI + CFTR co-positive cells lining the conducting airways of the lung by immunofluorescence, total cell counts > 400 CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin
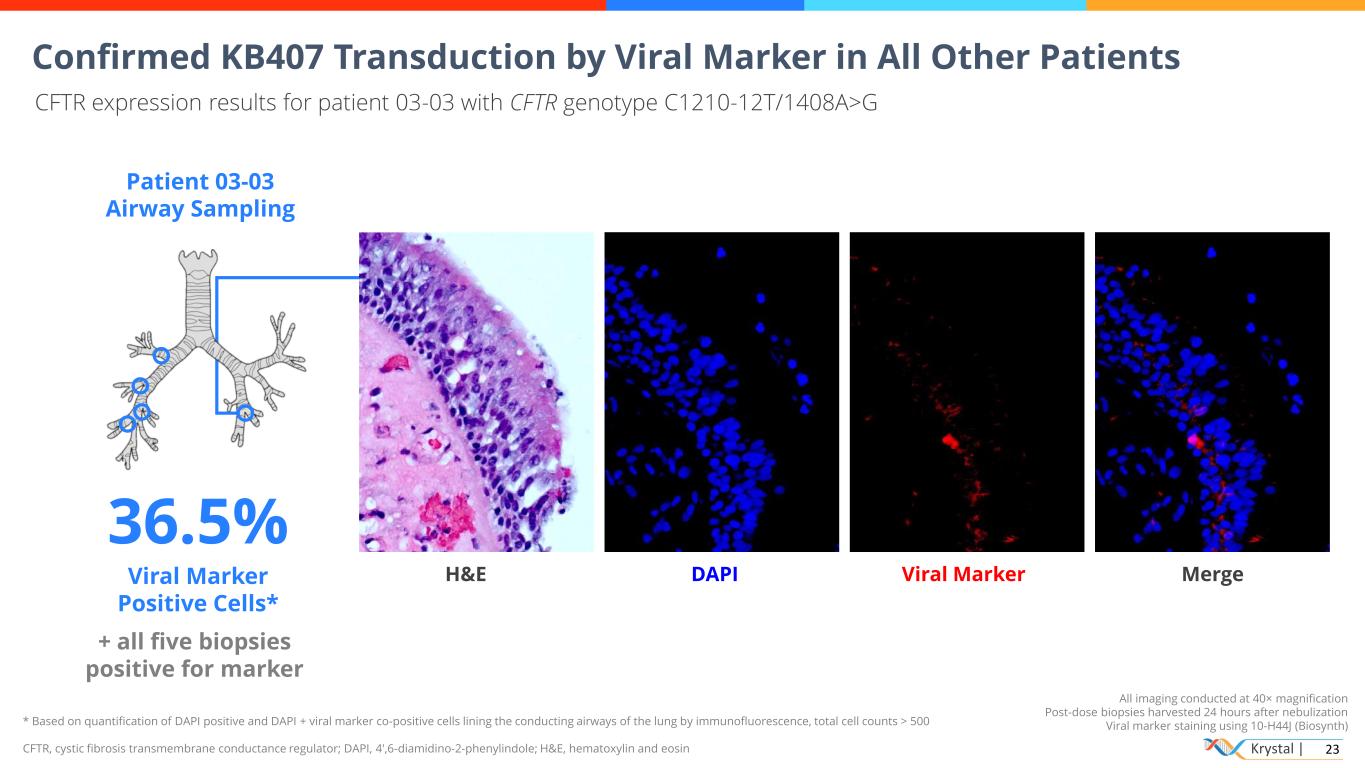
Krystal | 23 * Based on quantification of DAPI positive and DAPI + viral marker co-positive cells lining the conducting airways of the lung by immunofluorescence, total cell counts > 500 CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin All imaging conducted at 40× magnification Post-dose biopsies harvested 24 hours after nebulization Viral marker staining using 10-H44J (Biosynth) Confirmed KB407 Transduction by Viral Marker in All Other Patients CFTR expression results for patient 03-03 with CFTR genotype C1210-12T/1408A>G Patient 03-03 Airway Sampling 36.5% Viral Marker Positive Cells* + all five biopsies positive for marker H&E DAPI Viral Marker Merge
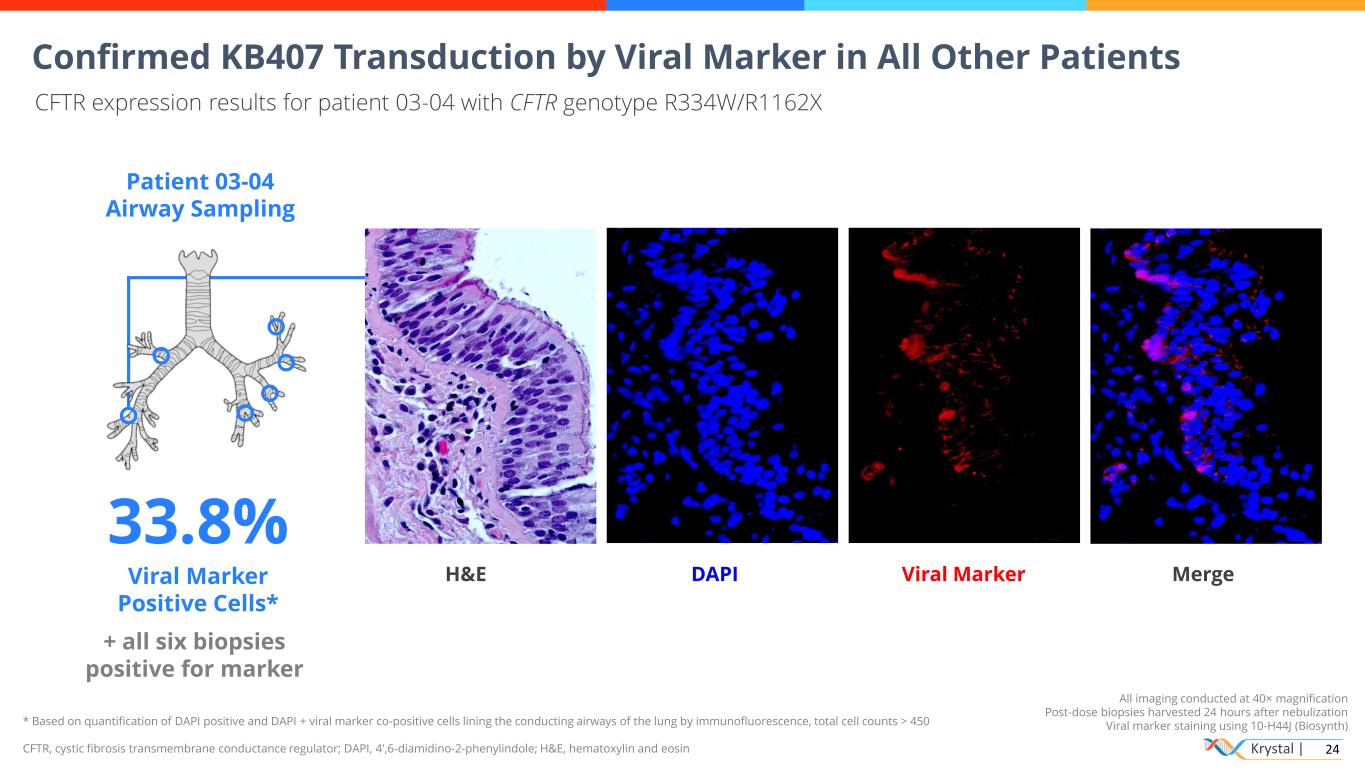
Krystal | 24 * Based on quantification of DAPI positive and DAPI + viral marker co-positive cells lining the conducting airways of the lung by immunofluorescence, total cell counts > 450 CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin All imaging conducted at 40× magnification Post-dose biopsies harvested 24 hours after nebulization Viral marker staining using 10-H44J (Biosynth) Confirmed KB407 Transduction by Viral Marker in All Other Patients CFTR expression results for patient 03-04 with CFTR genotype R334W/R1162X Patient 03-04 Airway Sampling 33.8% Viral Marker Positive Cells* + all six biopsies positive for marker H&E DAPI Viral Marker Merge
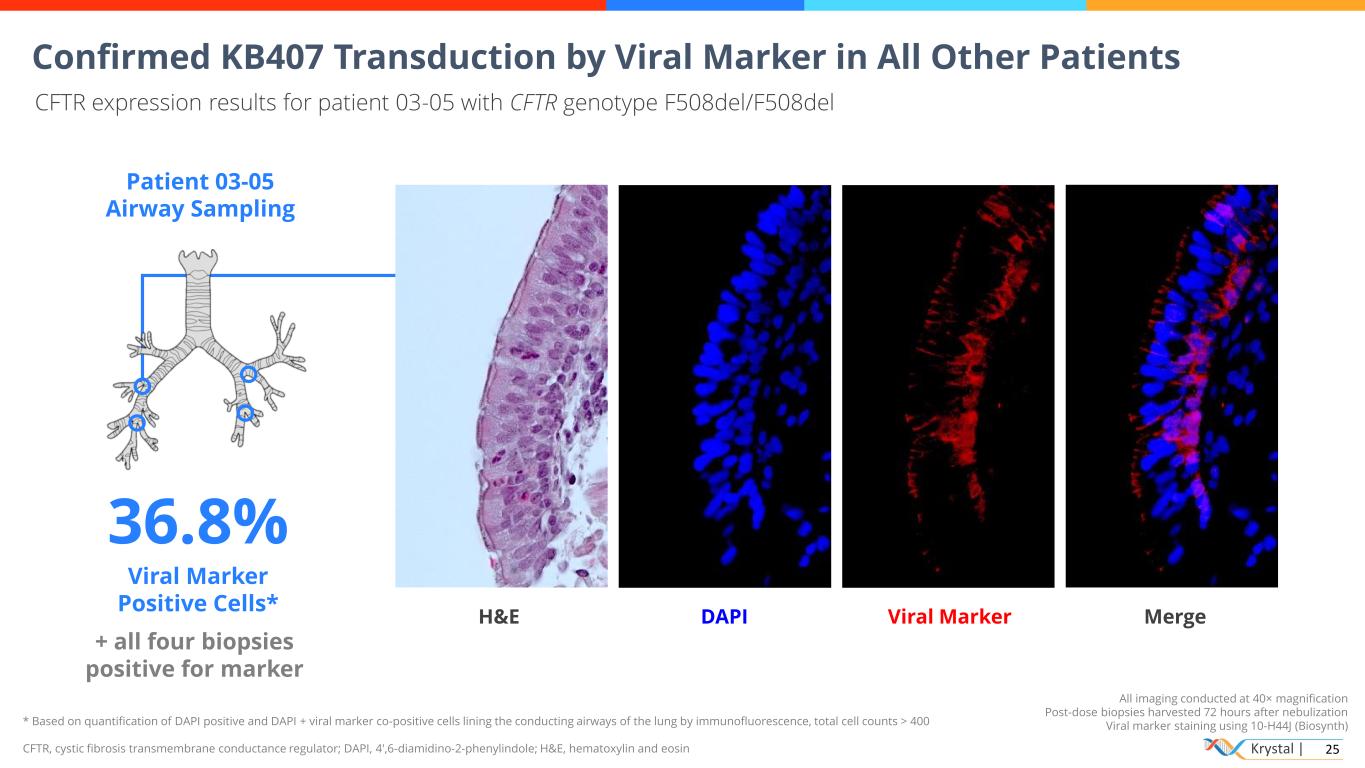
Krystal | 25 * Based on quantification of DAPI positive and DAPI + viral marker co-positive cells lining the conducting airways of the lung by immunofluorescence, total cell counts > 400 CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin All imaging conducted at 40× magnification Post-dose biopsies harvested 72 hours after nebulization Viral marker staining using 10-H44J (Biosynth) Confirmed KB407 Transduction by Viral Marker in All Other Patients CFTR expression results for patient 03-05 with CFTR genotype F508del/F508del Patient 03-05 Airway Sampling 36.8% Viral Marker Positive Cells* + all four biopsies positive for marker H&E DAPI Viral Marker Merge
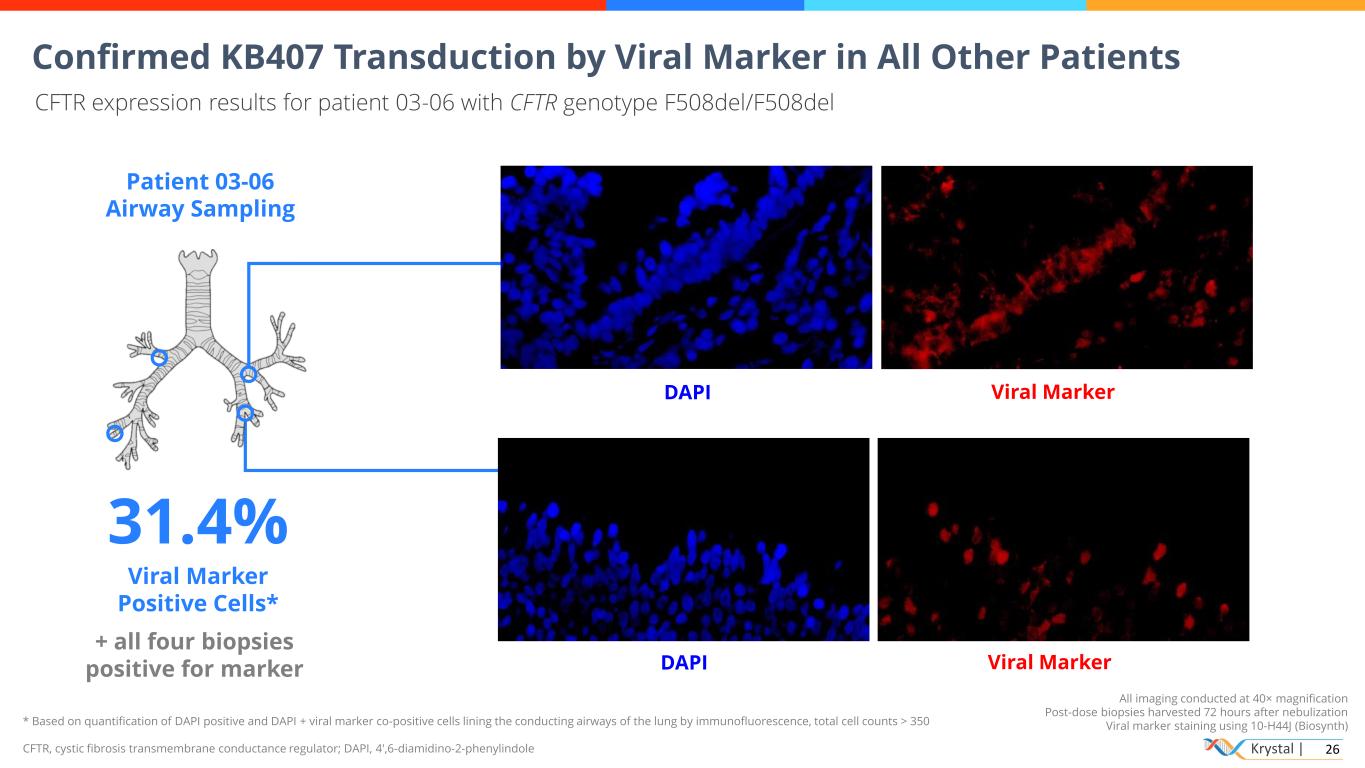
Krystal | 26 * Based on quantification of DAPI positive and DAPI + viral marker co-positive cells lining the conducting airways of the lung by immunofluorescence, total cell counts > 350 CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole All imaging conducted at 40× magnification Post-dose biopsies harvested 72 hours after nebulization Viral marker staining using 10-H44J (Biosynth) Confirmed KB407 Transduction by Viral Marker in All Other Patients CFTR expression results for patient 03-06 with CFTR genotype F508del/F508del Patient 03-06 Airway Sampling 31.4% Viral Marker Positive Cells* + all four biopsies positive for marker DAPI Viral Marker DAPI Viral Marker
Krystal | 27 KB407 Transduction Confirmed in All Cohort 3 Patients with Bronchoscopies Data cutoff date of January 6, 2026 * Based on CFTR protein expression for Patients 1 and 2, based on viral marker expression for Patients 3, 4, 5, and 6; conducting airway cells defined as airway-exposed epithelial cells lining the bronchi of the lung CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; PFU, plaque forming unit; ppFEV1, percent predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 second Patient Number 03-01 03-02 03-03 03-04 03-05 03-06 CFTR Variants 2184delA / W1282X R553X / M1V C1210-12T / 1408A>G R334W / R1162X F508del / F508del F508del / F508del Baseline ppFEV1 64 45 45 69 54 59 Total Number of Biopsies Suitable for Analysis 7 5 5 6 4 4 Percentage of Conducting Airway Cells Transduced with KB407* 42.1% 29.4% 36.5% 33.8% 36.8% 31.4% Molecular Data Summary ✓ Broad airway distribution: All usable biopsies were positive for CFTR and/or viral marker of KB407 transduction ✓ Exceeded transduction target: Over 29% of conducting airway cells transduced in all six patients ✓ Apical CFTR expression pattern: Suggestive of appropriate post-translational modification and CFTR localization ✓ CFTR protein expression for at least 96 hours: Positive indicator for potential weekly or better dosing

Krystal | 28 KB407 Continues To Be Well Tolerated in Highest Dose Cohort ▪ All but one KB407-related adverse events were mild-to-moderate; all were transient ▪ One serious adverse event of asthma exacerbation reported 24 hours after bronchoscopy ▪ Data monitoring committee considered the adverse event procedure related and not related to KB407 ▪ Event resolved in five days ▪ No evidence of significant neutralizing antibody response following KB407 administration ▪ No systemic vector distribution after inhalation, based on blood and urine analysis Advancing into repeat dosing study

Krystal | 29 Next Steps and Accelerating The Path to Potential Registration of KB407 Advancing Into Repeat Dosing ▪ Today’s data clearly demonstrate efficient vector delivery and expression of CFTR in patients treated with KB407 ▪ Already working with CFF TDN on repeat dosing CORAL-3 study design which has been submitted to the FDA ▪ Goal will be to assess safety of repeat KB407 treatment and potential impact on lung function by spirometry Upside: Making CORAL-3 Registrational ▪ Clear and urgent unmet need for patients that are either ineligible for or respond poorly to modulators ▪ Clinically-validated HSV-1 platform with demonstrated full-length gene delivery to lung across multiple programs ▪ Potential strategies to support registration with CORAL-3 under discussion with CFF TDN and the FDA Expecting to align with FDA and initiate potentially registrational CORAL-3 study in the first half of 2026 CF, cystic fibrosis; CFF, Cystic Fibrosis Foundation; CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; FDA, United States Food and Drug Administration; HSV-1, herpes simplex virus 1; TDN, Therapeutics Development Network
Krystal | 30 Building Momentum in Krystal’s Rare Disease Pipeline CF, cystic fibrosis; CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; DEB, dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa; HSV-1, herpes simplex virus type 1; NK, neurotrophic keratitis ▪ Confirmation of CFTR delivery sets KB407 on accelerated path towards $2B+ market ▪ Adds to potential registrational readouts for KB803 in ocular DEB and KB801 in NK ▪ Building a portfolio of rare disease medicines that Krystal can launch directly ▪ Gene delivery in CF also reinforces that potential of HSV-1 platform in the lung

Developing Genetic Medicines to Treat Diseases with High Unmet Medical Needs © Copyright 2026 Krystal Biotech, Inc. All rights reserved.