.2

Unique biology Precision therapeutics Broad impact FHTX January 2026 NASDAQ LISTED
.2

Unique biology Precision therapeutics Broad impact FHTX January 2026 NASDAQ LISTED

2 | Forward Looking Statements This currently presentation available contains to management forward.- looking All statements statements other that than are statements based on of management’s historical facts beliefs contained and assumptions in this presentation and on are information forward-looking “anticipates,” statements “intends,” . In some “plans,” cases, “seeks,” you can “believes,” identify forward “estimates,” -looking “expects,” statements “continues,” by terms “projects” such as “could,” or the “may,” negative “might,” of these “will,” terms “likely,” or other are not similar limited expressions, to, statements although concerning: not all forward the potential -looking outcomes statements from contain our collaboration these words agreement . Forward- looking with Lilly; statements the initiation, include, timing, but Phase progress 1 dose and results escalation of our trial research of FHD —and 909 development with Lilly; our programs ability to advance and pre- clinical product studies candidates and clinical that we trials, may including develop and with to respect successfully to our complete Gene Traffic preclinical Control and Platform clinical ®; studies; the impact our of ability exogeneous to leverage factors, our initial including programs macroeconomic to develop additional and geopolitical product circumstances, candidates using on our our and related our collaborators’ business operations, including our research and development programs and pre-clinical studies; developments to our competitors and our industry; our ability to expand the target populations of our programs and the availability of patients regulatory for clinical authorities; testing; our our ability ability to to obtain identify regulatory and enter approval into future for license FHD-909 agreements and any future and collaborations; product candidates our ability from to the continue FDA and to rely other on our our CDMOs ability to and attract CROs and for retain our key manufacturing scientific and and management research needs; personnel; regulatory the scope developments of protection in the we United are able States to establish, and foreign maintain countries; and enforce proceeds for from intellectual capital- raising property transactions, rights covering estimates FHD- 909, of our our expenses, future products capital and requirements, our Gene Traffic and needs Control for Platform; additional and financing our use . You of should, presentation therefore, . Additional not rely important on these forward factors -looking to be considered statements in as connection representing with our views forward as -looking of any date statements subsequent are to described the date in of this the Annual Company’s Report filings on with Form the 10 Securities -K for the and fiscal Exchange year ended Commission, December including 31, 2024 .withing Any forward the section -looking entitled statements “Risk Factors” represent in the the Company’s Company’s views Company only explicitly as of the date disclaims of this any presentation obligation and to should update not any be forward relied upon -looking as representing statements. its The views Company’s as of any business subsequent is subject date. The to substantial risks and uncertainties.
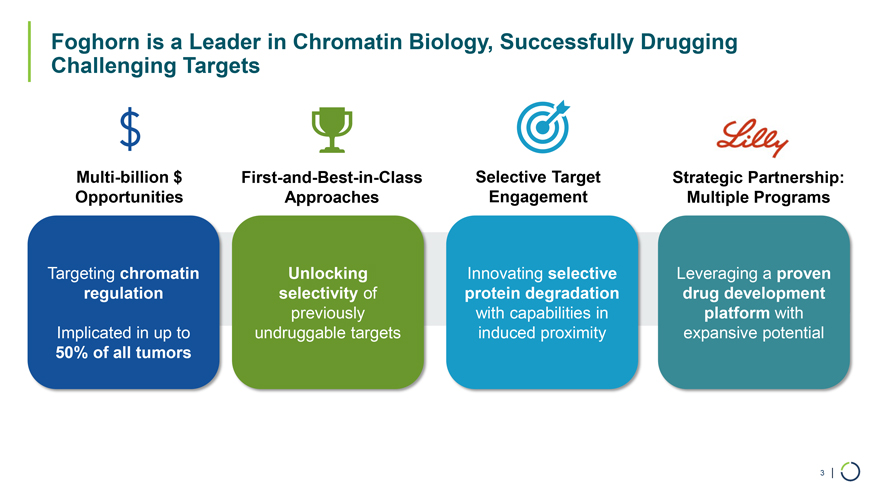
Foghorn is a Leader in Chromatin Biology, Successfully Drugging Challenging Targets Multi-billion $ First-and-Best-in-Class Selective Target Strategic Partnership: Opportunities Approaches Engagement Multiple Programs Targeting chromatin Unlocking Innovating selective Leveraging a proven regulation selectivity of protein degradation drug development previously with capabilities in platform with Implicated in up to undruggable targets induced proximity expansive potential 50% of all tumors 3 |
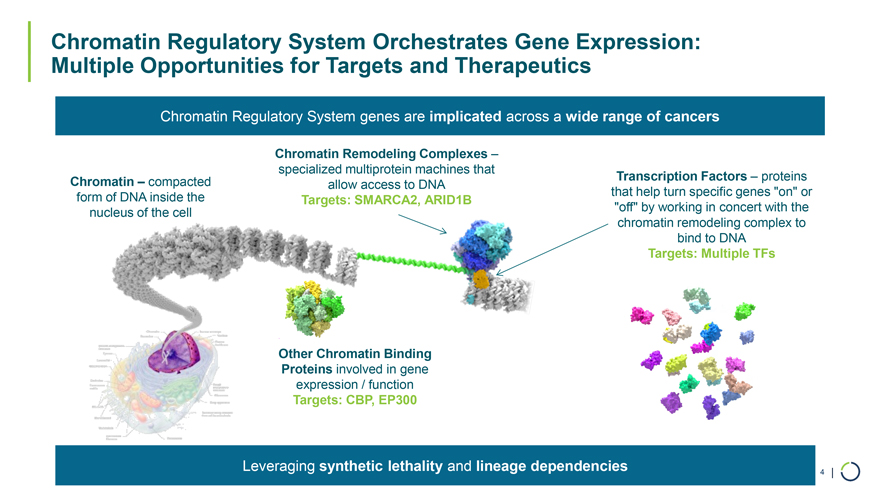
Chromatin Remodeling Complexes – specialized multiprotein machines that Chromatin – compacted Transcription Factors – proteins allow access to DNA form of DNA inside the that help turn specific genes “on” or Targets: SMARCA2, ARID1B nucleus of the cell “off” by working in concert with the chromatin remodeling complex to bind to DNA Targets: Multiple TFs Chromatin Regulatory System Orchestrates Gene Expression: Multiple Opportunities for Targets and Therapeutics Chromatin Regulatory System genes are implicated across a wide range of cancers Other Chromatin Binding Proteins involved in gene expression / function Targets: CBP, EP300 Leveraging synthetic lethality and lineage dependencies 4 |
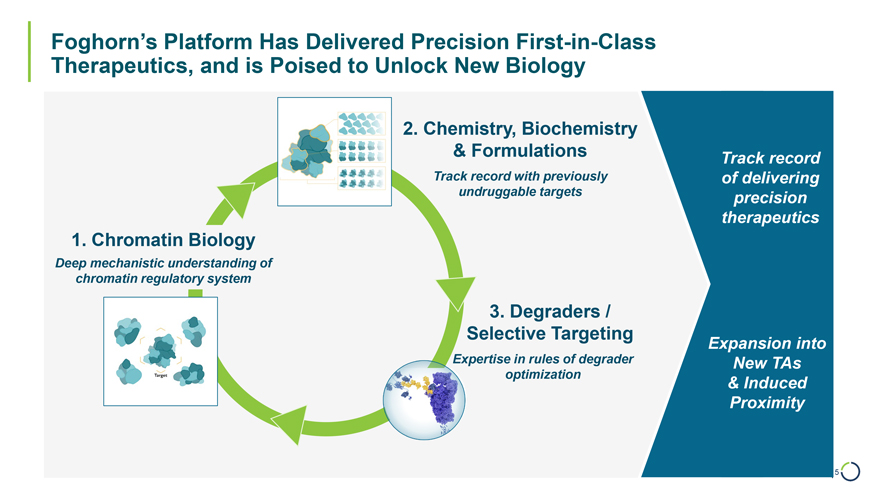
2. Chemistry, Biochemistry & Formulations Track record Track record with previously of delivering undruggable targets precision therapeutics Foghorn’s Platform Has Delivered Precision First-in-Class Therapeutics, and is Poised to Unlock New Biology 1. Chromatin Biology Deep mechanistic understanding of chromatin regulatory system 3. Degraders / Selective Targeting Expansion into Expertise in rules of degrader New TAs optimization & Induced Proximity 5
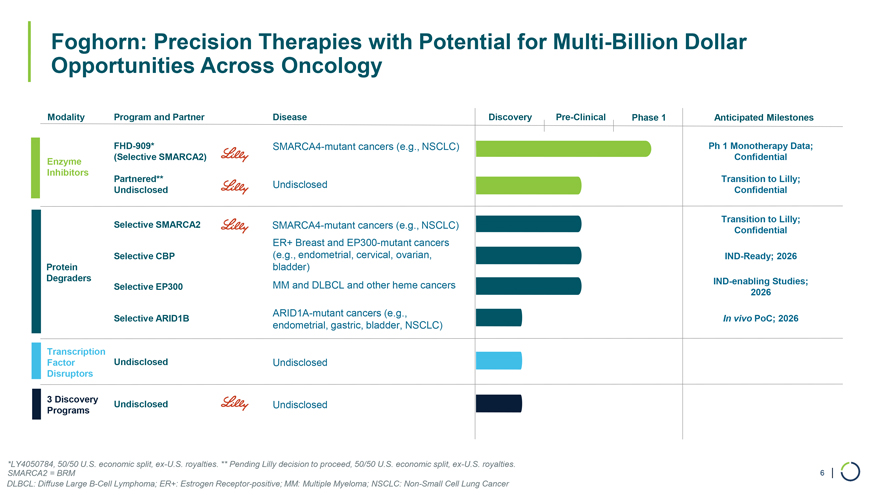
Modality Program and Partner Disease Discovery Pre-Clinical Phase 1 Anticipated Milestones FHD-909* SMARCA4-mutant cancers (e.g., NSCLC) Ph 1 Monotherapy Data; Enzyme (Selective SMARCA2) Confidential Inhibitors Partnered** Transition to Lilly; Undisclosed Undisclosed Confidential Transition to Lilly; Selective SMARCA2 SMARCA4-mutant cancers (e.g., NSCLC) Confidential ER+ Breast and EP300-mutant cancers Selective CBP (e.g., endometrial, cervical, ovarian, IND-Ready; 2026 Protein bladder) Degraders IND-enabling Studies; Selective EP300 MM and DLBCL and other heme cancers 2026 ARID1A-mutant cancers (e.g., Selective ARID1B In vivo PoC; 2026 endometrial, gastric, bladder, NSCLC) Transcription Factor Undisclosed Undisclosed Disruptors 3 Discovery Undisclosed Undisclosed Programs Foghorn: Precision Therapies with Potential for Multi-Billion Dollar Opportunities Across Oncology *LY4050784, 50/50 U.S. economic split, ex-U.S. royalties. ** Pending Lilly decision to proceed, 50/50 U.S. economic split, ex-U.S. royalties. SMARCA2 = BRM 6 | DLBCL: Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma; ER+: Estrogen Receptor-positive; MM: Multiple Myeloma; NSCLC: Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
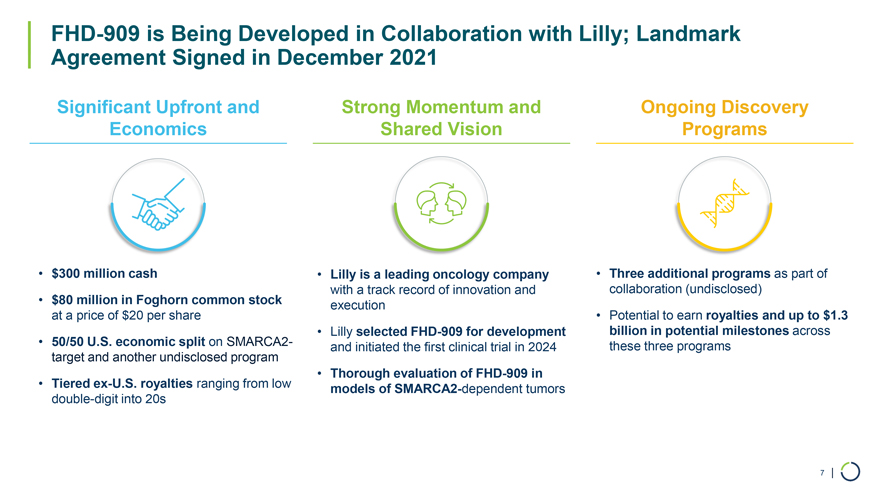
FHD-909 is Being Developed in Collaboration with Lilly; Landmark Agreement Signed in December 2021 Significant Upfront and Strong Momentum and Ongoing Discovery Economics Shared Vision Programs • $300 million cash • $80 million in Foghorn common stock at a price of $20 per share • 50/50 U.S. economic split on SMARCA2-target and another undisclosed program • Tiered ex-U.S. royalties ranging from low double-digit into 20s • Lilly is a leading oncology company with a track record of innovation and execution • Lilly selected FHD-909 for development and initiated the first clinical trial in 2024 • Thorough evaluation of FHD-909 in models of SMARCA2-dependent tumors • Three additional programs as part of collaboration (undisclosed) • Potential to earn royalties and up to $1.3 billion in potential milestones across these three programs 7 |
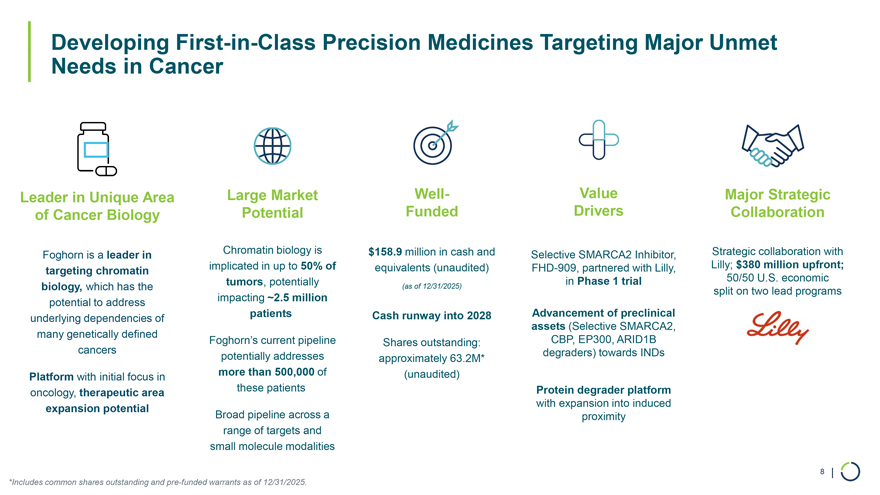
Large Market Well-Potential Funded Chromatin biology is $158.9 million in cash and implicated in up to 50% of equivalents (unaudited) tumors, potentially (as of 12/31/2025) impacting ~2.5 million patients Cash runway into 2028 Foghorn’s current pipeline Shares outstanding: potentially addresses approximately 63.2M* more than 500,000 of (unaudited) these patients Broad pipeline across a range of targets and small molecule modalities Developing First-in-Class Precision Medicines Targeting Major Unmet Needs in Cancer Leader in Unique Area of Cancer Biology Foghorn is a leader in targeting chromatin biology, which has the potential to address underlying dependencies of many genetically defined cancers Platform with initial focus in oncology, therapeutic area expansion potential Value Major Strategic Drivers Collaboration Selective SMARCA2 Inhibitor, Strategic collaboration with FHD-909, partnered with Lilly, Lilly; $380 million upfront; in Phase 1 trial 50/50 U.S. economic split on two lead programs Advancement of preclinical assets (Selective SMARCA2, CBP, EP300, ARID1B degraders) towards INDs Protein degrader platform with expansion into induced proximity 8 | *Includes common shares outstanding and pre-funded warrants as of 12/31/2025.
For SMARCA4-mutant Cancers Selective SMARCA2 Program • FHD-909 (LY4050784) – Selective SMARCA2 Inhibitor 9
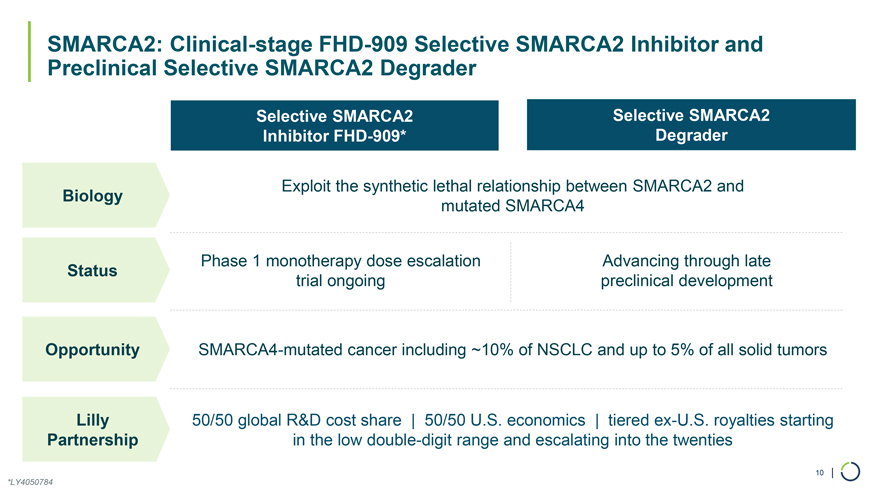
Selective SMARCA2 Selective SMARCA2 Inhibitor FHD-909* Degrader Exploit the synthetic lethal relationship between SMARCA2 and Biology mutated SMARCA4 SMARCA2: Clinical-stage FHD-909 Selective SMARCA2 Inhibitor and Preclinical Selective SMARCA2 Degrader Phase 1 monotherapy dose escalation Advancing through late Status trial ongoing preclinical development Opportunity SMARCA4-mutated cancer including ~10% of NSCLC and up to 5% of all solid tumors Lilly 50/50 global R&D cost share | 50/50 U.S. economics | tiered ex-U.S. royalties starting Partnership in the low double-digit range and escalating into the twenties 10 | *LY4050784
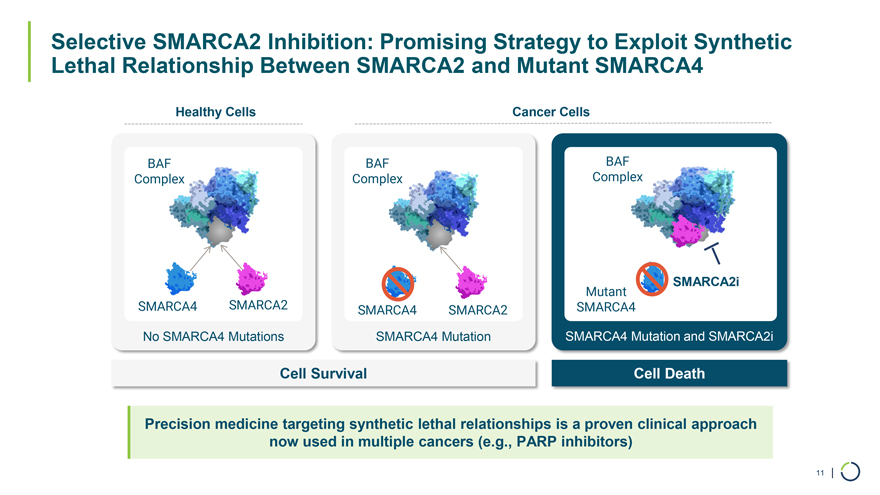
Selective SMARCA2 Selective SMARCA2 Inhibitor FHD-909* Degrader Exploit the synthetic lethal relationship between SMARCA2 and Biology mutated SMARCA4 SMARCA2: Clinical-stage FHD-909 Selective SMARCA2 Inhibitor and Preclinical Selective SMARCA2 Degrader Phase 1 monotherapy dose escalation Advancing through late Status trial ongoing preclinical development Opportunity SMARCA4-mutated cancer including ~10% of NSCLC and up to 5% of all solid tumors Lilly 50/50 global R&D cost share | 50/50 U.S. economics | tiered ex-U.S. royalties starting Partnership in the low double-digit range and escalating into the twenties 10 | *LY4050784 Selective SMARCA2 Inhibition: Promising Strategy to Exploit Synthetic Lethal Relationship Between SMARCA2 and Mutant SMARCA4 Healthy Cells Cancer Cells BAF BAF BAF Complex Complex Complex SMARCA2i SMARCA2 Mutant SMARCA4 SMARCA4 SMARCA2 SMARCA4 No SMARCA4 Mutations SMARCA4 Mutation SMARCA4 Mutation and SMARCA2i Cell Survival Cell Death Precision medicine targeting synthetic lethal relationships is a proven clinical approach now used in multiple cancers (e.g., PARP inhibitors) 11 |
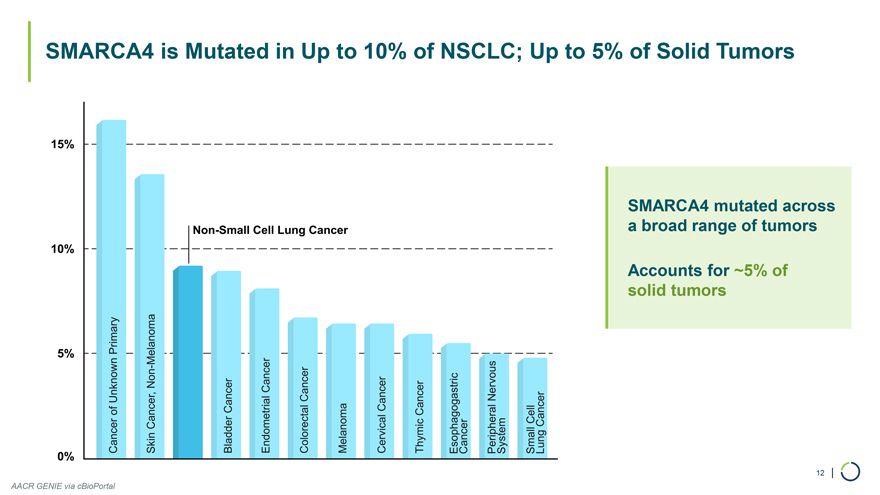
SMARCA4 mutated across a broad range of tumors Accounts for ~5% of solid tumors 12 | SMARCA4 is Mutated in Up to 10% of NSCLC; Up to 5% of Solid Tumors AACR GENIE via cBioPortal
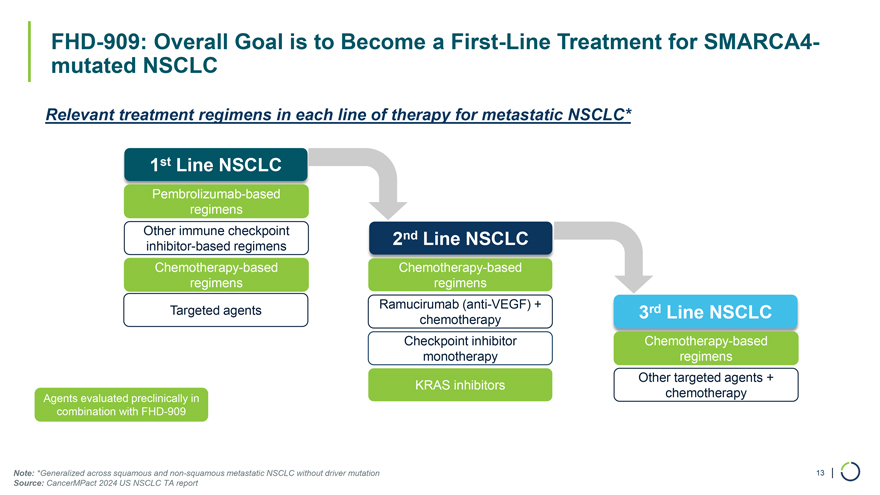
FHD-909: Overall Goal is to Become a First-Line Treatment for SMARCA4-mutated NSCLC Relevant treatment regimens in each line of therapy for metastatic NSCLC* 1st Line NSCLC Pembrolizumab-based regimens Other immune checkpoint 2nd Line NSCLC inhibitor-based regimens Chemotherapy-based Chemotherapy-based regimens regimens Targeted agents Ramucirumab (anti-VEGF) + 3rd Line NSCLC chemotherapy Checkpoint inhibitor Chemotherapy-based monotherapy regimens Other targeted agents + KRAS inhibitors Agents evaluated preclinically in chemotherapy combination with FHD-909 Note: *Generalized across squamous and non-squamous metastatic NSCLC without driver mutation 13 | Source: CancerMPact 2024 US NSCLC TA report
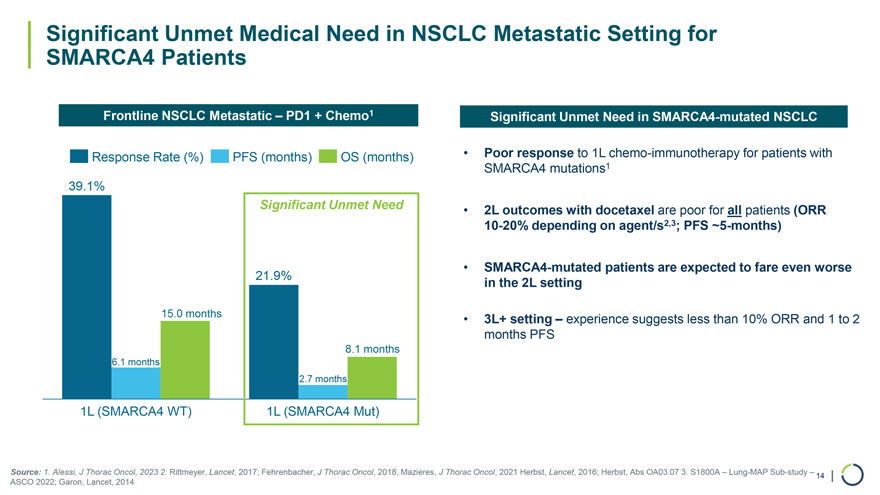
Significant Unmet Need 21.9% 15.0 months 8.1 months 6.1 months 2.7 months 1L (SMARCA4 WT) 1L (SMARCA4 Mut) Significant Unmet Medical Need in NSCLC Metastatic Setting for SMARCA4 Patients Frontline NSCLC Metastatic – PD1 + Chemo1 Response Rate (%) PFS (months) OS (months) 39.1% Significant Unmet Need in SMARCA4-mutated NSCLC • Poor response to 1L chemo-immunotherapy for patients with SMARCA4 mutations1 • 2L outcomes with docetaxel are poor for all patients (ORR 10-20% depending on agent/s2,3; PFS ~5-months) • SMARCA4-mutated patients are expected to fare even worse in the 2L setting • 3L+ setting – experience suggests less than 10% ORR and 1 to 2 months PFS Source: 1. Alessi, J Thorac Oncol, 2023 2. Rittmeyer, Lancet, 2017; Fehrenbacher, J Thorac Oncol, 2018; Mazieres, J Thorac Oncol, 2021 Herbst, Lancet, 2016; Herbst, Abs OA03.07 3. S1800A – Lung-MAP Sub-study – 14 | ASCO 2022; Garon, Lancet, 2014
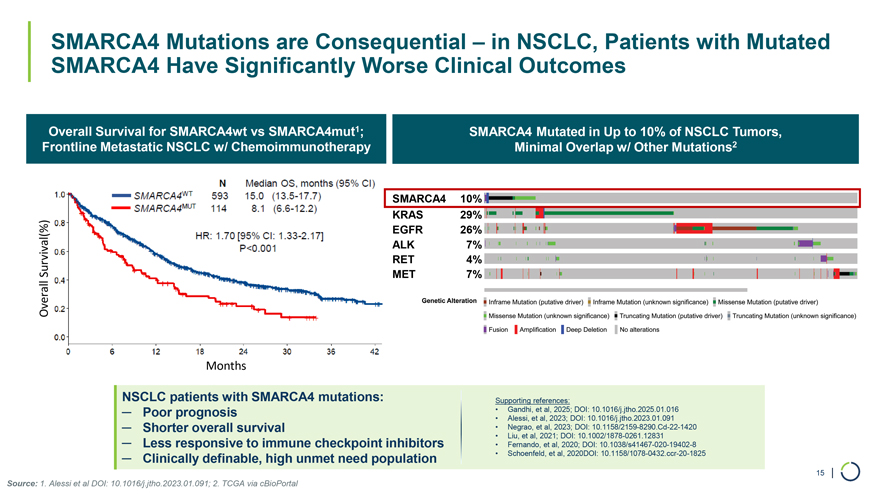
SMARCA4 10% KRAS 29% EGFR 26% ALK 7% Survival(%) RET 4% MET 7% Overall SMARCA4 Mutations are Consequential – in NSCLC, Patients with Mutated SMARCA4 Have Significantly Worse Clinical Outcomes Overall Survival for SMARCA4wt vs SMARCA4mut1; Frontline Metastatic NSCLC w/ Chemoimmunotherapy SMARCA4 Mutated in Up to 10% of NSCLC Tumors, Minimal Overlap w/ Other Mutations2 Months NSCLC patients with SMARCA4 mutations: — Poor prognosis — Shorter overall survival — Less responsive to immune checkpoint inhibitors — Clinically definable, high unmet need population Supporting references: • Gandhi, et al, 2025; DOI: 10.1016/j.jtho.2025.01.016 • Alessi, et al, 2023; DOI: 10.1016/j.jtho.2023.01.091 • Negrao, et al, 2023; DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-22-1420 • Liu, et al, 2021; DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.12831 • Fernando, et al, 2020; DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-19402-8 • Schoenfeld, et al, 2020DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-20-1825 15 | Source: 1. Alessi et al DOI: 10.1016/j.jtho.2023.01.091; 2. TCGA via cBioPortal
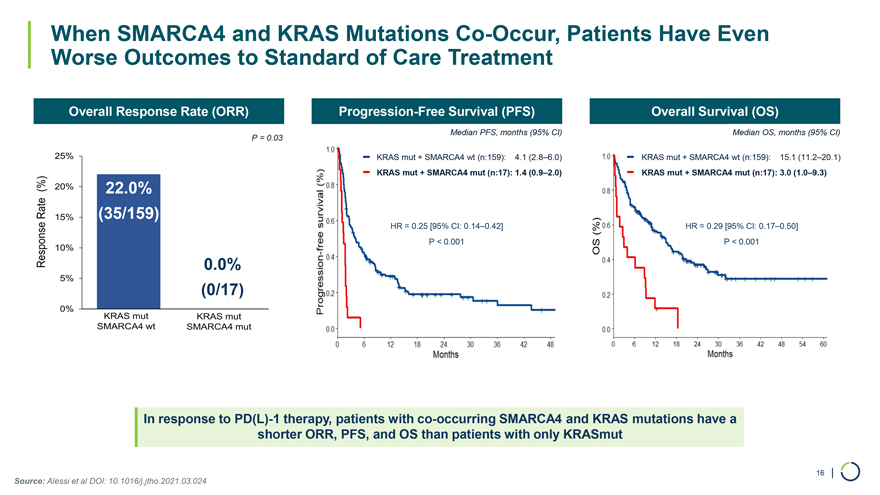
When SMARCA4 and KRAS Mutations Co-Occur, Patients Have Even Worse Outcomes to Standard of Care Treatment Overall Response Rate (ORR) Progression-Free Survival (PFS) Overall Survival (OS) Median PFS, months (95% CI) Median OS, months (95% CI) P = 0.03 KRAS mut + SMARCA4 wt (n:159): 4.1 (2.8–6.0) KRAS mut + SMARCA4 wt (n:159): 15.1 (11.2–20.1) KRAS mut + SMARCA4 mut (n:17): 1.4 (0.9–2.0) KRAS mut + SMARCA4 mut (n:17): 3.0 (1.0–9.3) 22.0% (35/159) HR = 0.25 [95% CI: 0.14–0.42] HR = 0.29 [95% CI: 0.17–0.50] P < 0.001 P < 0.001 0.0% (0/17) In response to PD(L)-1 therapy, patients with co-occurring SMARCA4 and KRAS mutations have a shorter ORR, PFS, and OS than patients with only KRASmut Source: Alessi et al DOI: 10.1016/j.jtho.2021.03.024 16 |
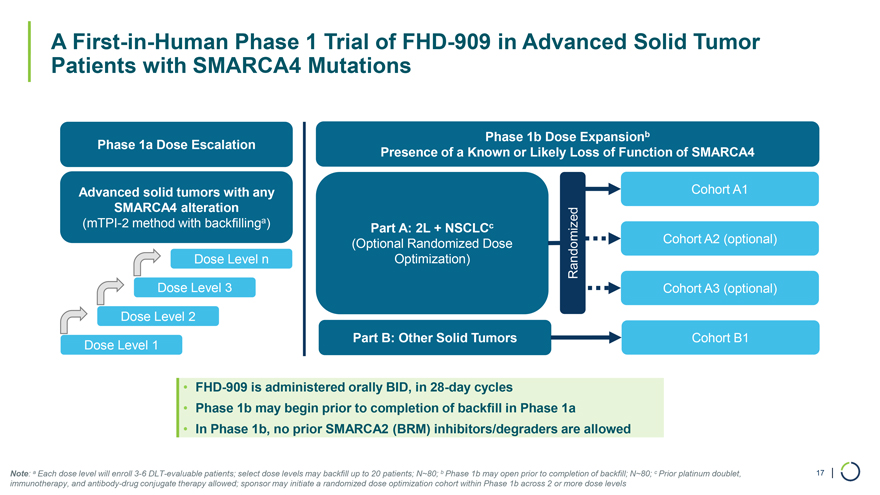
A First-in-Human Phase 1 Trial of FHD-909 in Advanced Solid Tumor Patients with SMARCA4 Mutations Phase 1b Dose Expansionb Phase 1a Dose Escalation Presence of a Known or Likely Loss of Function of SMARCA4 Advanced solid tumors with any Cohort A1 SMARCA4 alteration (mTPI-2 method with backfillinga) Part A: 2L + NSCLCc (Optional Randomized Dose Cohort A2 (optional) Dose Level n Optimization) Randomized Dose Level 3 Cohort A3 (optional) Dose Level 2 Part B: Other Solid Tumors Cohort B1 Dose Level 1 • FHD-909 is administered orally BID, in 28-day cycles • Phase 1b may begin prior to completion of backfill in Phase 1a • In Phase 1b, no prior SMARCA2 (BRM) inhibitors/degraders are allowed Note: a Each dose level will enroll 3-6 DLT-evaluable patients; select dose levels may backfill up to 20 patients; N~80; b Phase 1b may open prior to completion of backfill; N~80; c Prior platinum doublet, 17 | immunotherapy, and antibody-drug conjugate therapy allowed; sponsor may initiate a randomized dose optimization cohort within Phase 1b across 2 or more dose levels

Degrader Programs • Selective CBP Degrader • Selective EP300 Degrader • Selective ARID1B Degrader 18
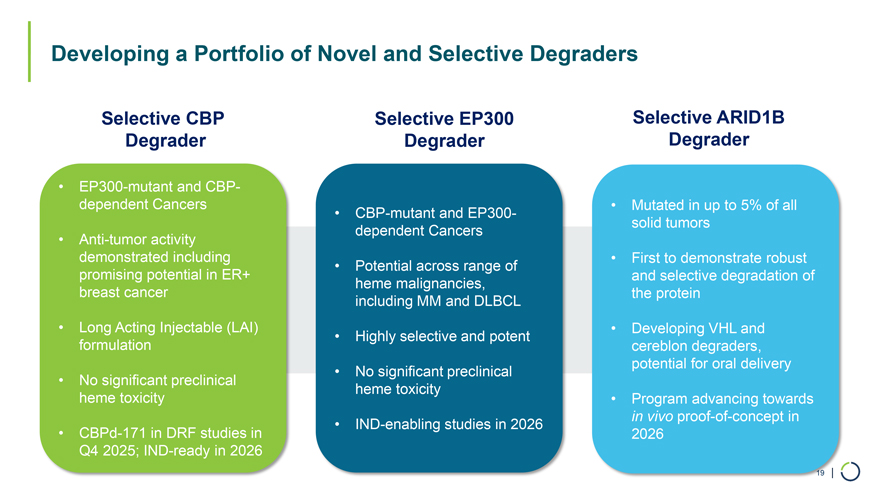
• EP300-mutant and CBP-dependent Cancers • Mutated in up to 5% of all • CBP-mutant and EP300-solid tumors dependent Cancers • Anti-tumor activity demonstrated including • First to demonstrate robust • Potential across range of promising potential in ER+ and selective degradation of heme malignancies, breast cancer the protein including MM and DLBCL • Long Acting Injectable (LAI) • Developing VHL and • Highly selective and potent formulation cereblon degraders, potential for oral delivery • No significant preclinical • No significant preclinical heme toxicity heme toxicity • Program advancing towards • IND-enabling studies in 2026 in vivo proof-of-concept in • CBPd-171 in DRF studies in 2026 Q4 2025; IND-ready in 2026 Developing a Portfolio of Novel and Selective Degraders Selective CBP Selective EP300 Selective ARID1B Degrader Degrader Degrader 19 |
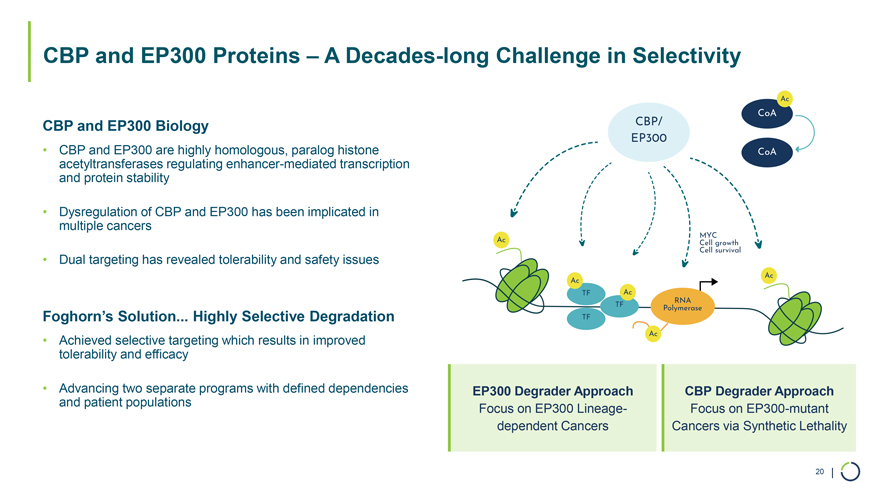
• Dysregulation of CBP and EP300 has been implicated in multiple cancers • Dual targeting has revealed tolerability and safety issues CBP and EP300 Proteins – A Decades-long Challenge in Selectivity CBP and EP300 Biology • CBP and EP300 are highly homologous, paralog histone acetyltransferases regulating enhancer-mediated transcription and protein stability Foghorn’s Solution... Highly Selective Degradation • Achieved selective targeting which results in improved tolerability and efficacy • Advancing two separate programs with defined dependencies and patient populations Ac CoA CBP/ EP300 CoA Ac MYC Cell growth Cell survival Ac Ac TF Ac TF RNA TF Polymerase Ac EP300 Degrader Approach CBP Degrader Approach Focus on EP300 Lineage- Focus on EP300-mutant dependent Cancers Cancers via Synthetic Lethality 20 |
Selective CBP Degrader, FHT-171 For EP300-mutant and CBP-dependent Cancers 21
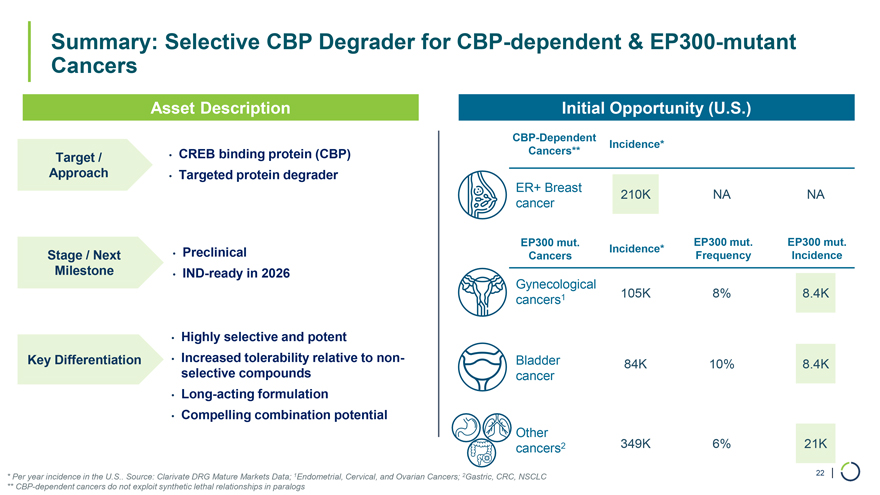
• CREB binding protein (CBP) • Targeted protein degrader • Preclinical • IND-ready in 2026 • Highly selective and potent • Increased tolerability relative to non-selective compounds • Long-acting formulation • Compelling combination potential Summary: Selective CBP Degrader for CBP-dependent & EP300-mutant Cancers Target / Approach Stage / Next Milestone Key Differentiation Asset Description Initial Opportunity (U.S.) CBP-Dependent Incidence* Cancers** ER+ Breast 210K NA NA cancer EP300 mut. EP300 mut. EP300 mut. Incidence* Cancers Frequency Incidence Gynecological cancers1 105K 8% 8.4K Bladder 84K 10% 8.4K cancer Other cancers2 349K 6% 21K * Per year incidence in the U.S.. Source: Clarivate DRG Mature Markets Data; 1Endometrial, Cervical, and Ovarian Cancers; 2Gastric, CRC, NSCLC 22 | ** CBP-dependent cancers do not exploit synthetic lethal relationships in paralogs
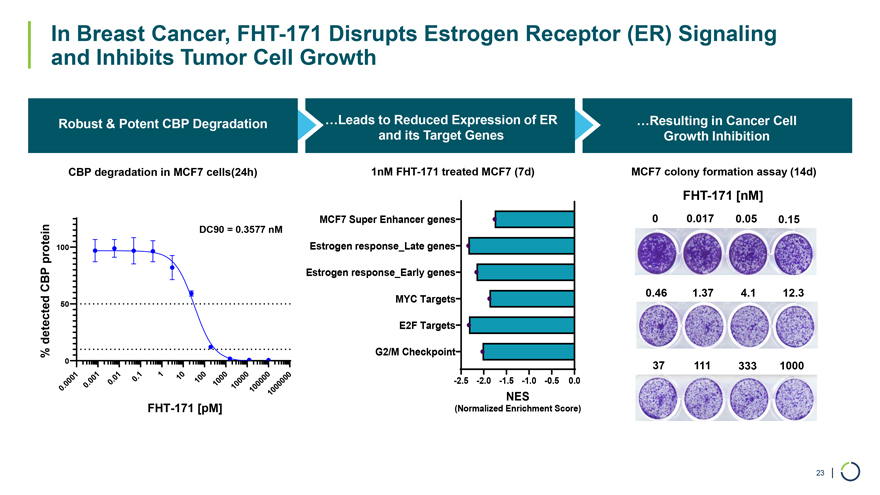
Robust & Potent CBP Degradation …Leads to Reduced Expression of ER …Resulting in Cancer Cell and its Target Genes Growth Inhibition CBP degradation in MCF7 cells(24h) 1nM FHT-171 treated MCF7 (7d) MCF7 colony formation assay (14d) FHT-171 [nM] DC90 = 0.3577 nM MCF7 Super Enhancer genes 0 0.017 0.05 0.15 protein 100 Estrogen response_Late genes CBP Estrogen response_Early genes MYC Targets 0.46 1.37 4.1 12.3 50 detected E2F Targets % G2/M Checkpoint 0 37 111 333 1000 1 . 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 01 . 01 0 10 0 0 0 00 . 00 0 1 0 0 -2.5 -2.0 -1.5 -1.0 -0.5 0.0 . 0 100 0 0 0 1000 0 0 1 0 1 NES FHT-171 [pM] (Normalized Enrichment Score) In Breast Cancer, FHT-171 Disrupts Estrogen Receptor (ER) Signaling and Inhibits Tumor Cell Growth 23 |
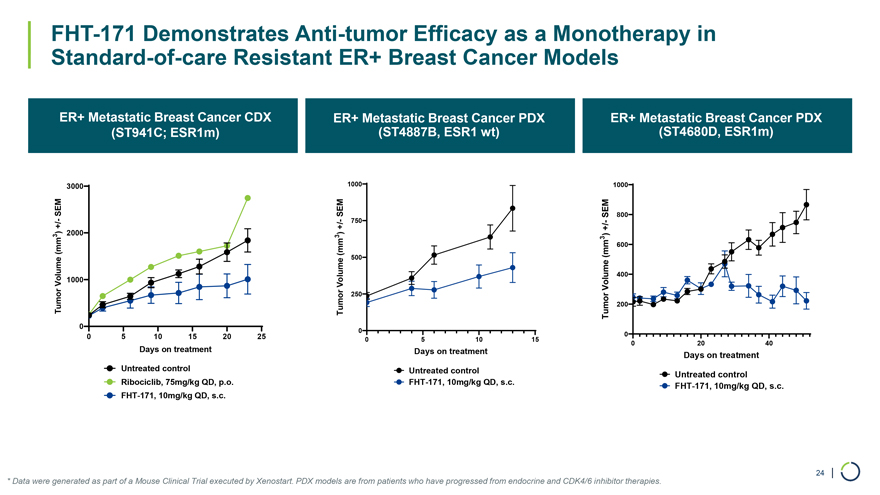
FHT-171 Demonstrates Anti-tumor Efficacy as a Monotherapy in Standard-of-care Resistant ER+ Breast Cancer Models ER+ Metastatic Breast Cancer CDX ER+ Metastatic Breast Cancer PDX ER+ Metastatic Breast Cancer PDX (ST941C; ESR1m) (ST4887B, ESR1 wt) (ST4680D, ESR1m) 3000 1000 1000 SEMSEM SEM 800——750—+/ +/ +/ ) 2000 ) ) 3 3 (mm 3 600 (mm 500 (mm 400 Volume 1000 Volume Volume 250 Tumor Tumor Tumor 200 0 0 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 0 5 10 15 0 20 40 Days on treatment Days on treatment Days on treatment Untreated control Untreated control Untreated control Ribociclib, 75mg/kg QD, p.o. FHT-171, 10mg/kg QD, s.c. FHT-171, 10mg/kg QD, s.c. FHT-171, 10mg/kg QD, s.c. 24 | * Data were generated as part of a Mouse Clinical Trial executed by Xenostart. PDX models are from patients who have progressed from endocrine and CDK4/6 inhibitor therapies.
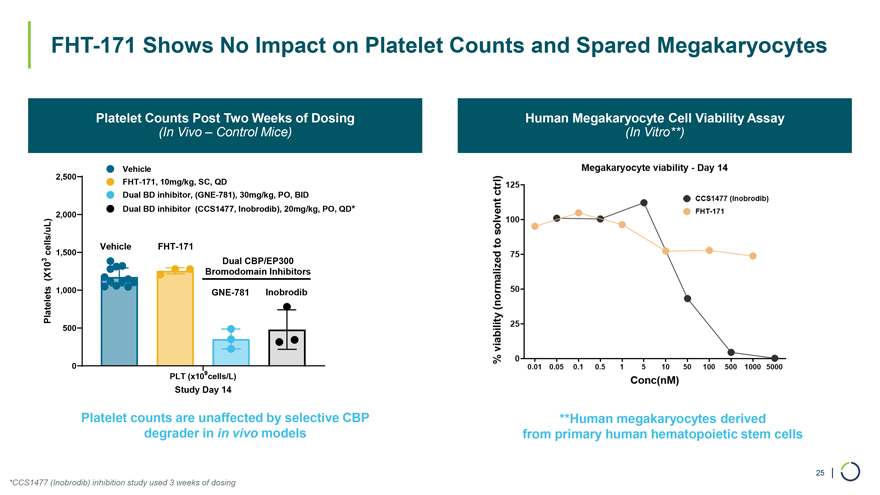
FHT-171 Shows No Impact on Platelet Counts and Spared Megakaryocytes Platelet Counts Post Two Weeks of Dosing Human Megakaryocyte Cell Viability Assay (In Vivo – Control Mice) (In Vitro**) Vehicle 2,500 FHT-171, 10mg/kg, SC, QD Dual BD inhibitor, (GNE-781), 30mg/kg, PO, BID Dual BD inhibitor (CCS1477, Inobrodib), 20mg/kg, PO, QD* 2,000 cells/uL) Vehicle FHT-171 1,500 3 Dual CBP/EP300 (X10 Bromodomain Inhibitors Platelets 1,000 GNE-781 Inobrodib 500 0 9 PLT (x10 cells/L) Study Day 14 Platelet counts are unaffected by selective CBP **Human megakaryocytes derived degrader in in vivo models from primary human hematopoietic stem cells *CCS1477 (Inobrodib) inhibition study used 3 weeks of dosing 25 |
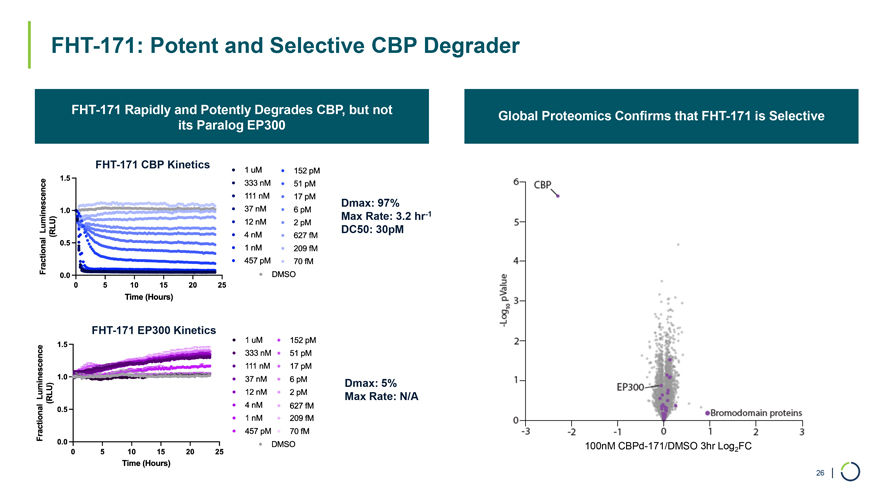
FHT-171 CBP Kinetics Dmax: 97% Max Rate: 3.2 hr-1 DC50: 30pM FHT-171 EP300 Kinetics Dmax: 5% Max Rate: N/A 100nM CBPd-171/DMSO 3hr Log2FC FHT-171: Potent and Selective CBP Degrader FHT-171 Rapidly and Potently Degrades CBP, but not its Paralog EP300 Global Proteomics Confirms that FHT-171 is Selective 26 |
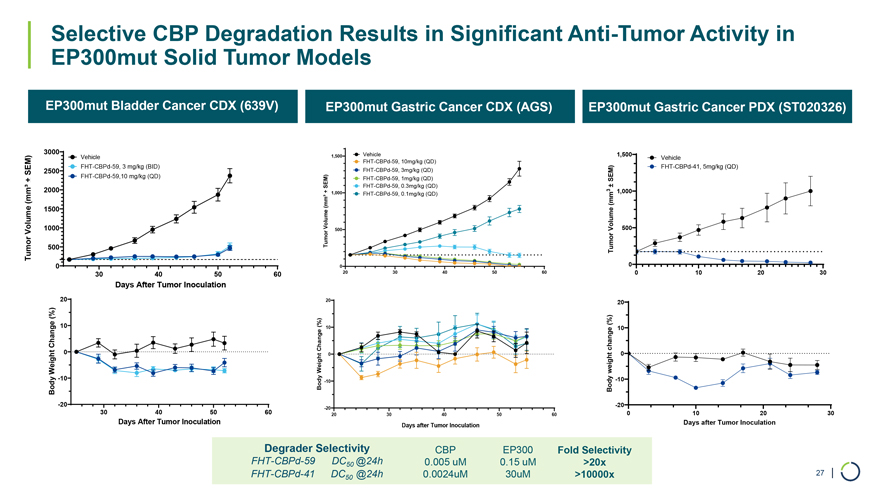
EP300mut Bladder Cancer CDX (639V) EP300mut Gastric Cancer CDX (AGS) EP300mut Gastric Cancer PDX (ST020326) 3000 Vehicle 1,500 Vehicle 1,500 FHT-CBPd-59, 10mg/kg (QD) Vehicle FHT-CBPd-59, 3 mg/kg (BID) FHT-CBPd-41, 5mg/kg (QD) SEM) 2500 FHT-CBPd-59, 3mg/kg (QD) + FHT-CBPd-59,10 mg/kg (QD) FHT-CBPd-59, 1mg/kg (QD) SEM) SEM) FHT-CBPd-59, 0.3mg/kg (QD)± (mm³ 2000+ 1,000 FHT-CBPd-59, 0.1mg/kg (QD) 3 1,000 (mm³(mm 1500 Volume 1000 500 Volume 500 Volume Tumor Tumor 500 Tumor 0 0 0 30 40 50 60 20 30 40 50 60 0 10 20 30 Days After Tumor Inoculation 20 20 20 (%) 10 (%)(%) Change 10 10 Change change 0 0 0 WeightWeightweight -10 -10 Body Body -10 Body -20 -20 -20 30 40 50 60 20 30 40 50 60 0 10 20 30 Days After Tumor Inoculation Days after Tumor Inoculation Days after Tumor Inoculation Degrader Selectivity CBP EP300 Fold Selectivity FHT-CBPd-59 DC50 @24h 0.005 uM 0.15 uM >20x FHT-CBPd-41 DC @24h 0.0024uM 30uM >10000x 27 | 50 Selective CBP Degradation Results in Significant Anti-Tumor Activity in EP300mut Solid Tumor Models
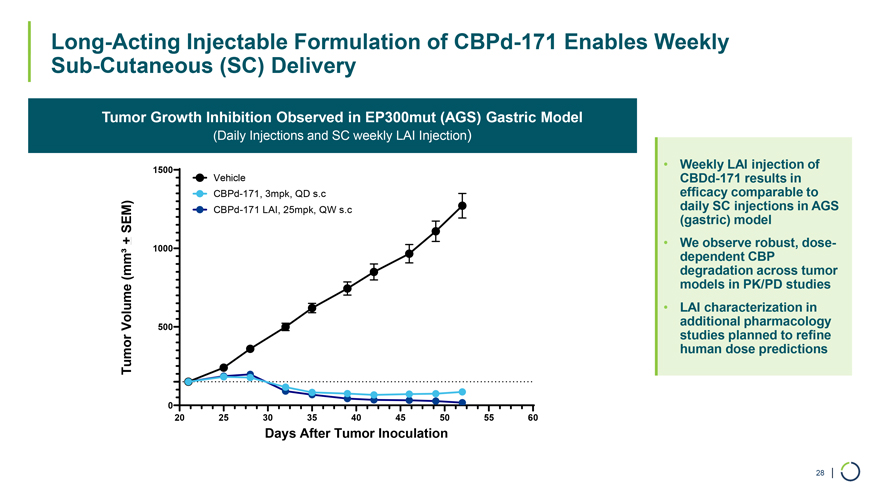
Long-Acting Injectable Formulation of CBPd-171 Enables Weekly Sub-Cutaneous (SC) Delivery Tumor Growth Inhibition Observed in EP300mut (AGS) Gastric Model (Daily Injections and SC weekly LAI Injection) 1500 Vehicle CBPd-171, 3mpk, QD s.c SEM) CBPd-171 LAI, 25mpk, QW s.c + 1000 (mm³ Volume 500 Tumor 0 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 Days After Tumor Inoculation • Weekly CBDd-171 LAI results injection in of daily efficacy SC comparable injections in to AGS (gastric) model • We dependent observe CBP robust, dose- degradation models in PK/PD across studies tumor • LAI additional characterization pharmacology in studies human dose planned predictions to refine 28 |

Selective EP300 Degrader For CBP-mutant and EP300-dependent Cancers 29
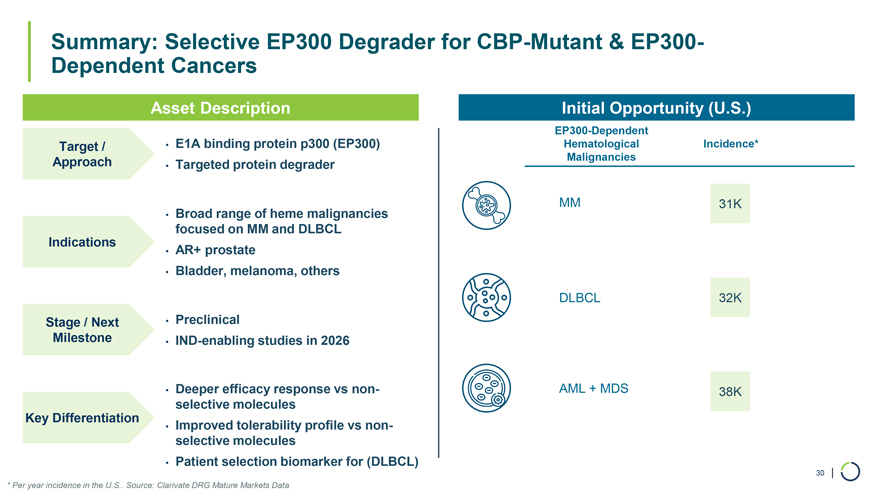
Asset Description Initial Opportunity (U.S.) EP300-Dependent Target / • E1A binding protein p300 (EP300) Hematological Incidence* Approach Malignancies • Targeted protein degrader MM 31K • Broad range of heme malignancies Indications focused on MM and DLBCL • AR+ prostate • Bladder, melanoma, others DLBCL 32K Stage / Next • Preclinical Milestone • IND-enabling studies in 2026 • Deeper efficacy response vs non- AML + MDS 38K Key Differentiation selective molecules • Improved tolerability profile vs non-selective molecules • Patient selection biomarker for (DLBCL) 30 | Summary: Selective EP300 Degrader for CBP-Mutant & EP300-Dependent Cancers * Per year incidence in the U.S.. Source: Clarivate DRG Mature Markets Data
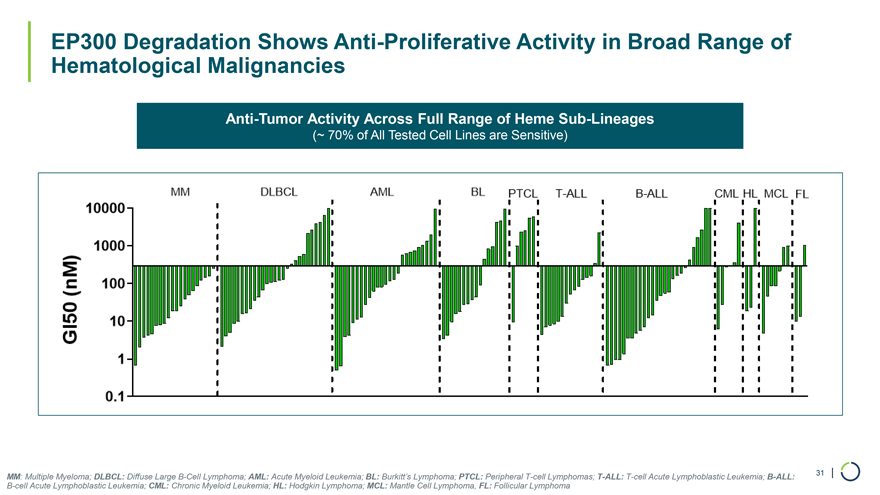
EP300 Degradation Shows Anti-Proliferative Activity in Broad Range of Hematological Malignancies Anti-Tumor Activity Across Full Range of Heme Sub-Lineages (~ 70% of All Tested Cell Lines are Sensitive) MM: Multiple Myeloma; DLBCL: Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma; AML: Acute Myeloid Leukemia; BL: Burkitt’s Lymphoma; PTCL: Peripheral T-cell Lymphomas; T-ALL: T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia; B-ALL: 31 | B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia; CML: Chronic Myeloid Leukemia; HL: Hodgkin Lymphoma; MCL: Mantle Cell Lymphoma, FL: Follicular Lymphoma
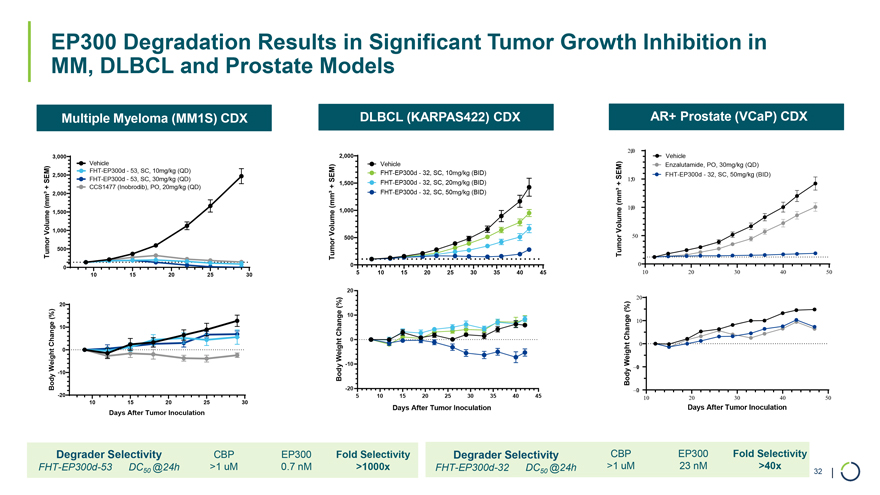
Multiple Myeloma (MM1S) CDX DLBCL (KARPAS422) CDX AR+ Prostate (VCaP) CDX 2,00 3,000 2,000 Vehicle Vehicle Vehicle Enzalutamide, PO, 30mg/kg (QD) FHT-EP300d—53, SC, 10mg/kg (QD) FHT-EP300d—32, SC, 10mg/kg (BID) 2,500 SEM) FHT-EP300d—32, SC, 50mg/kg (BID) SEM) FHT-EP300d—53, SC, 30mg/kg (QD) SEM) 1,50 1,500 FHT-EP300d—32, SC, 20mg/kg (BID) + CCS1477 (Inobrodib), PO, 20mg/kg (QD) + + 2,000 FHT-EP300d—32, SC, 50mg/kg (BID) (mm³ (mm³ (mm³ 1,00 1,500 1,000 Volume 1,000 VolumeVolume 500 50 Tumor 500 Tumor Tumor 0 0 0 10 15 20 25 30 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 10 20 30 40 50 Days After Tumor Inoculation Days After Tumor Inoculation Days After Tumor Inoculation 20 20 (%) (%) 10 10 Change Change 0 0 Weight Weight -0 1 Body -10 Body -2 0 -20 10 20 30 40 50 10 15 20 25 30 Days After Tumor Inoculation Days After Tumor Inoculation Degrader Selectivity CBP EP300 Fold Selectivity Degrader Selectivity CBP EP300 Fold Selectivity FHT-EP300d-53 DC @24h >1 uM 0.7 nM >1000x FHT-EP300d-32 DC @24h >1 uM 23 nM >40x 50 50 32 | EP300 Degradation Results in Significant Tumor Growth Inhibition in MM, DLBCL and Prostate Models
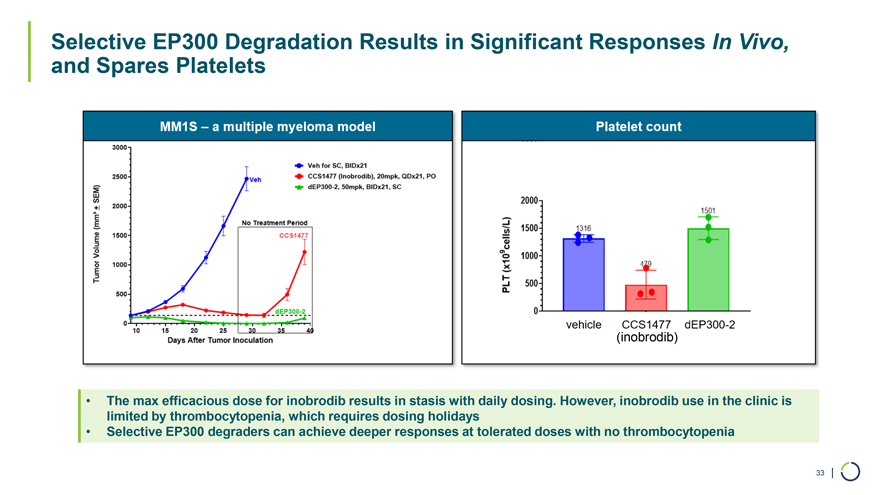
Selective EP300 Degradation Results in Significant Responses In Vivo, and Spares Platelets (inobrodib) • The max efficacious dose for inobrodib results in stasis with daily dosing. However, inobrodib use in the clinic is limited by thrombocytopenia, which requires dosing holidays • Selective EP300 degraders can achieve deeper responses at tolerated doses with no thrombocytopenia 33 |
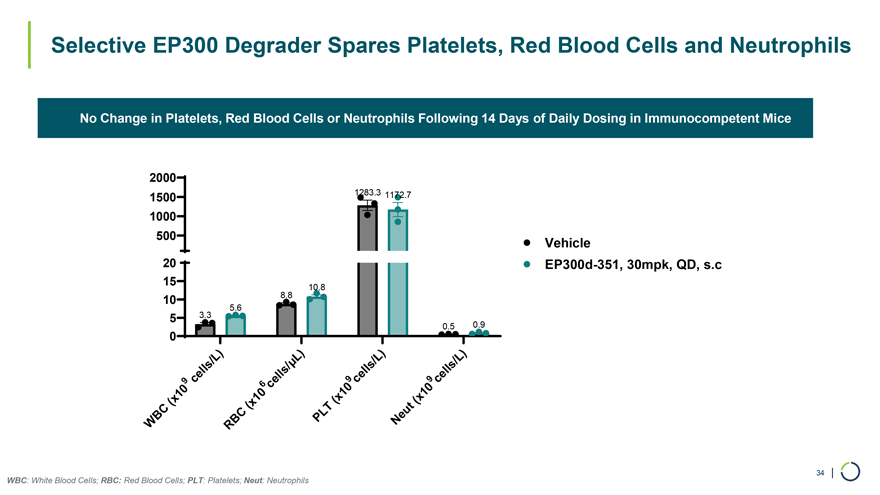
No Change in Platelets, Red Blood Cells or Neutrophils Following 14 Days of Daily Dosing in Immunocompetent Mice Selective EP300 Degrader Spares Platelets, Red Blood Cells and Neutrophils 2000 1500 1283.3 1172.7 1000 500 Vehicle 20 EP300d-351, 30mpk, QD, s.c 15 10.8 10 8.8 5.6 5 3.3 0 0.5 0.9 ) ) ) ) /L L /L /L ls ì ls ls l l s/ l l e e e 9c el 9 c 9 c 6 c 0 0 10 1 1 x x10 ( x x(( ( t BC C LT eu P N W RB WBC: White Blood Cells; RBC: Red Blood Cells; PLT: Platelets; Neut: Neutrophils 34 |
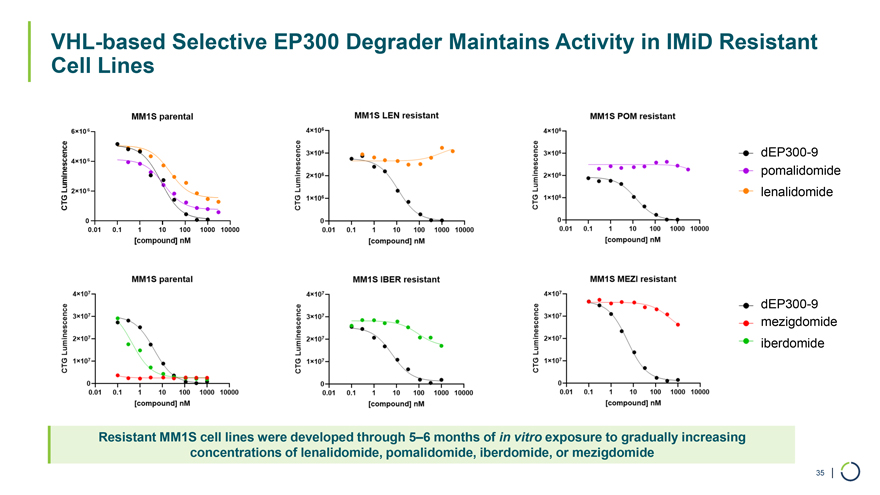
VHL-based Selective EP300 Degrader Maintains Activity in IMiD Resistant Cell Lines dEP300-9 pomalidomide lenalidomide dEP300-9 mezigdomide iberdomide Resistant MM1S cell lines were developed through 5–6 months of in vitro exposure to gradually increasing concentrations of lenalidomide, pomalidomide, iberdomide, or mezigdomide 35 |
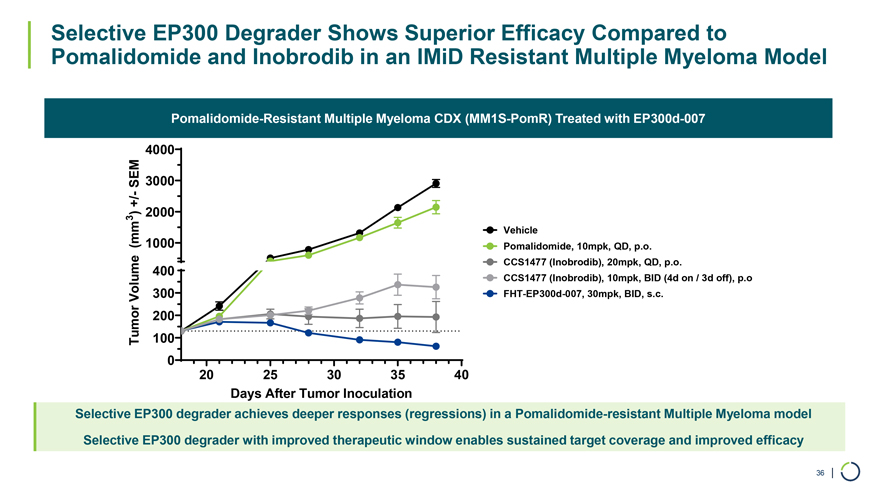
Pomalidomide-Resistant Multiple Myeloma CDX (MM1S-PomR) Treated with EP300d-007 Selective EP300 Degrader Shows Superior Efficacy Compared to Pomalidomide and Inobrodib in an IMiD Resistant Multiple Myeloma Model 4000 SEM 3000— +/ 3 ) 2000 (mm 1000 Vehicle Pomalidomide, 10mpk, QD, p.o. CCS1477 (Inobrodib), 20mpk, QD, p.o. 400 CCS1477 (Inobrodib), 10mpk, BID (4d on / 3d off), p.o Volume 300 FHT-EP300d-007, 30mpk, BID, s.c. 200 Tumor 100 0 20 25 30 35 40 Days After Tumor Inoculation Selective EP300 degrader achieves deeper responses (regressions) in a Pomalidomide-resistant Multiple Myeloma model Selective EP300 degrader with improved therapeutic window enables sustained target coverage and improved efficacy 36 |
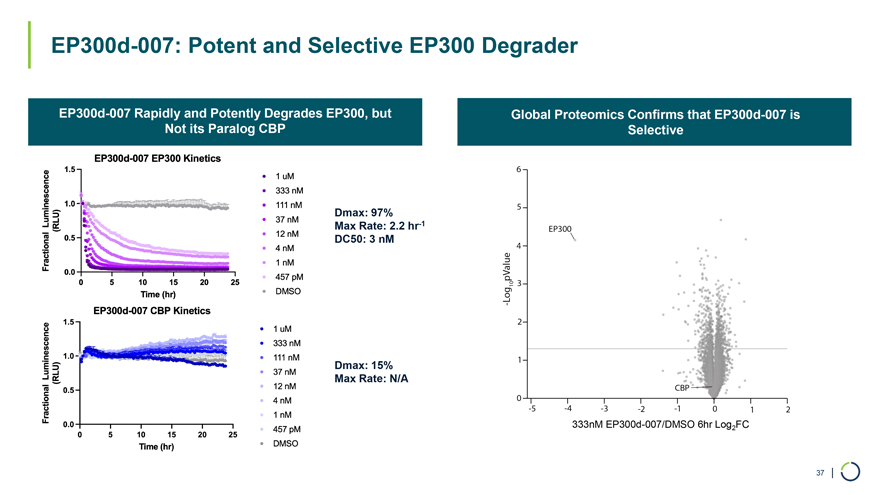
EP300d-007 Rapidly and Potently Degrades EP300, but Not its Paralog CBP EP300d-007: Potent and Selective EP300 Degrader Global Proteomics Confirms that EP300d-007 is Selective Dmax: 97% Max Rate: 2.2 hr-1 DC50: 3 nM Dmax: 15% Max Rate: N/A 333nM EP300d-007/DMSO 6hr Log2FC 37 |

Selective ARID1B Degrader For ARID1A-mutant Cancers 38
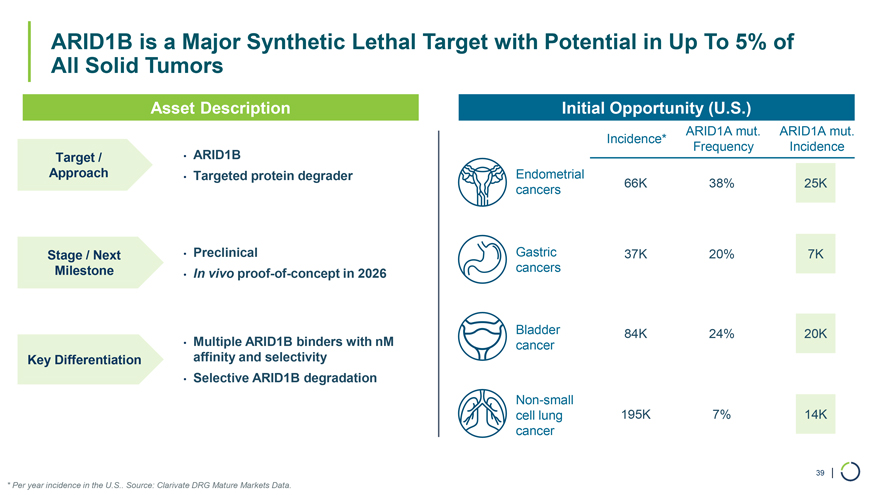
Asset Description Initial Opportunity (U.S.) ARID1A mut. ARID1A mut. Incidence* Frequency Incidence Target / • ARID1B Approach • Targeted protein degrader Endometrial cancers 66K 38% 25K ARID1B is a Major Synthetic Lethal Target with Potential in Up To 5% of All Solid Tumors Stage / Next • Preclinical Gastric 37K 20% 7K Milestone In vivo proof-of- in 2026 cancers • concept Bladder 84K 24% 20K • Multiple ARID1B binders with nM cancer Key Differentiation affinity and selectivity • Selective ARID1B degradation Non-small cell lung 195K 7% 14K cancer 39 | * Per year incidence in the U.S.. Source: Clarivate DRG Mature Markets Data.
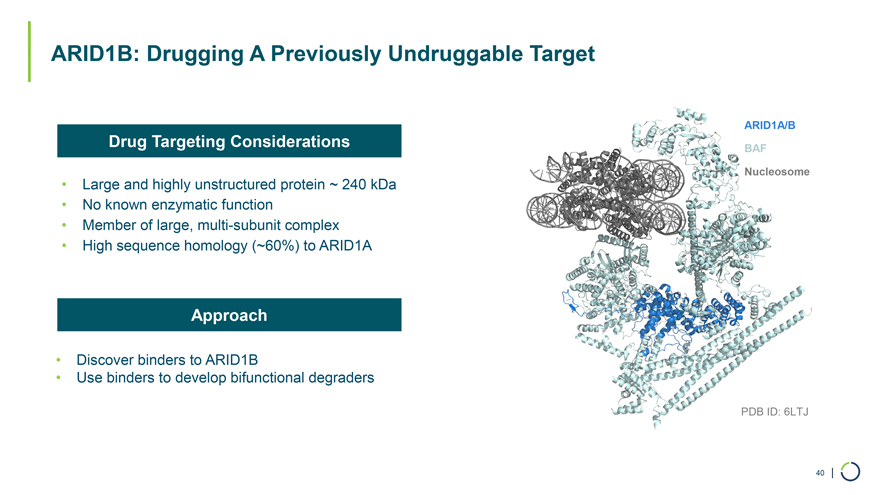
• Large and highly unstructured protein ~ 240 kDa • No known enzymatic function • Member of large, multi-subunit complex • High sequence homology (~60%) to ARID1A ARID1B: Drugging A Previously Undruggable Target Drug Targeting Considerations Approach • Discover binders to ARID1B • Use binders to develop bifunctional degraders ARID1A/B BAF Nucleosome PDB ID: 6LTJ 40 |
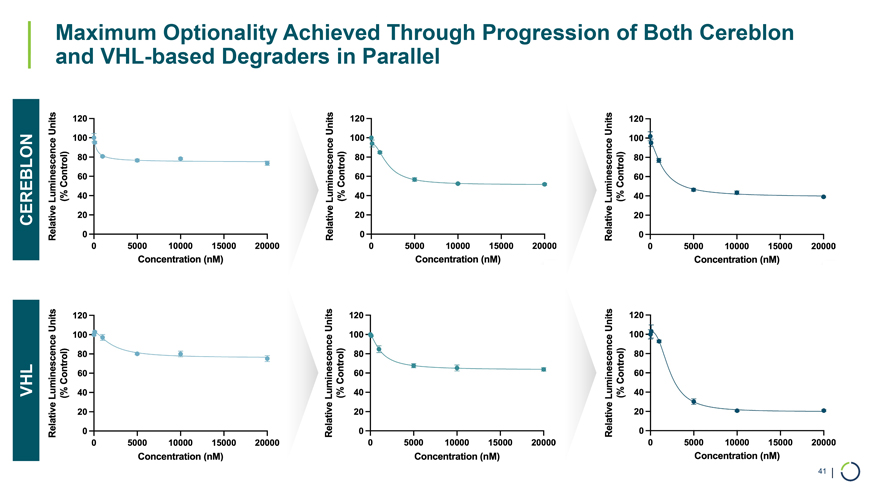
Maximum Optionality Achieved Through Progression of Both Cereblon and VHL-based Degraders in Parallel VHL CEREBLON 41 |
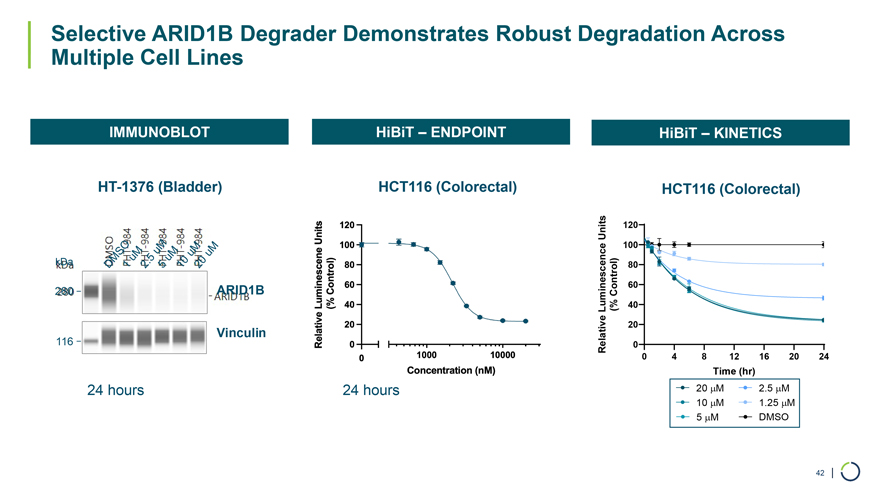
IMMUNOBLOT HiBiT – ENDPOINT HiBiT – KINETICS HT-1376 (Bladder) HCT116 (Colorectal) HCT116 (Colorectal) Units 120 100 kDa 80 ARID1B 60 280 Control) Luminescence(% 40 20 Vinculin 116 Relative 0 0 4 8 12 16 20 24 Time (hr) 24 hours 24 hours 20 µM 2.5 µM 10 µM 1.25 µM 5 µM DMSO Selective ARID1B Degrader Demonstrates Robust Degradation Across Multiple Cell Lines 42 |
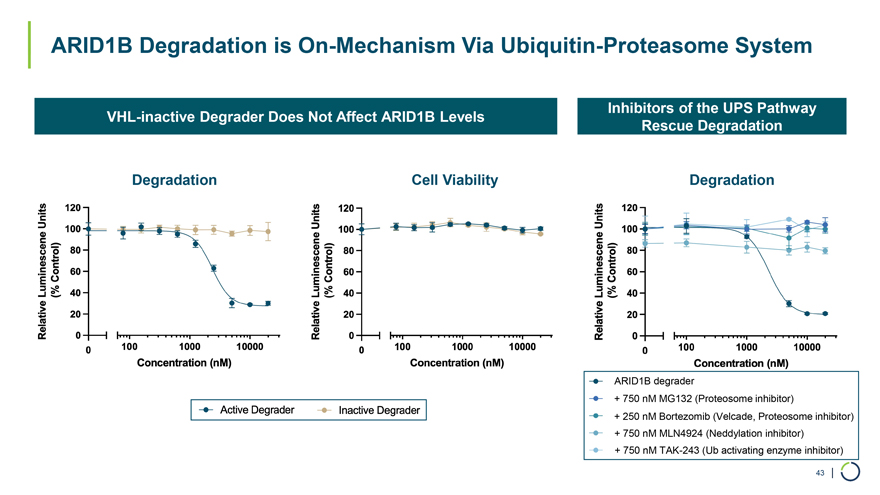
ARID1B Degradation is On-Mechanism Via Ubiquitin-Proteasome System Inhibitors of the UPS Pathway VHL-inactive Degrader Does Not Affect ARID1B Levels Rescue Degradation Degradation Cell Viability Degradation ARID1B degrader + 750 nM MG132 (Proteosome inhibitor) + 250 nM Bortezomib (Velcade, Proteosome inhibitor) + 750 nM MLN4924 (Neddylation inhibitor) + 750 nM TAK-243 (Ub activating enzyme inhibitor) 43 |
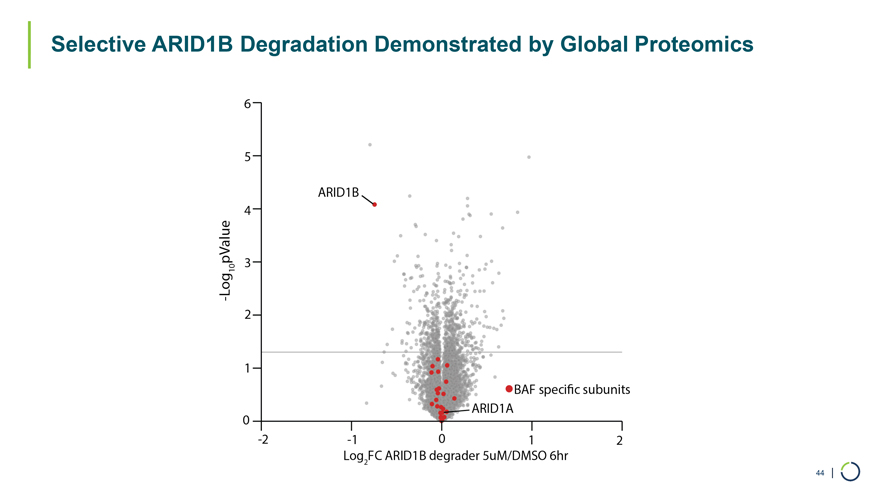
44 | Selective ARID1B Degradation Demonstrated by Global Proteomics
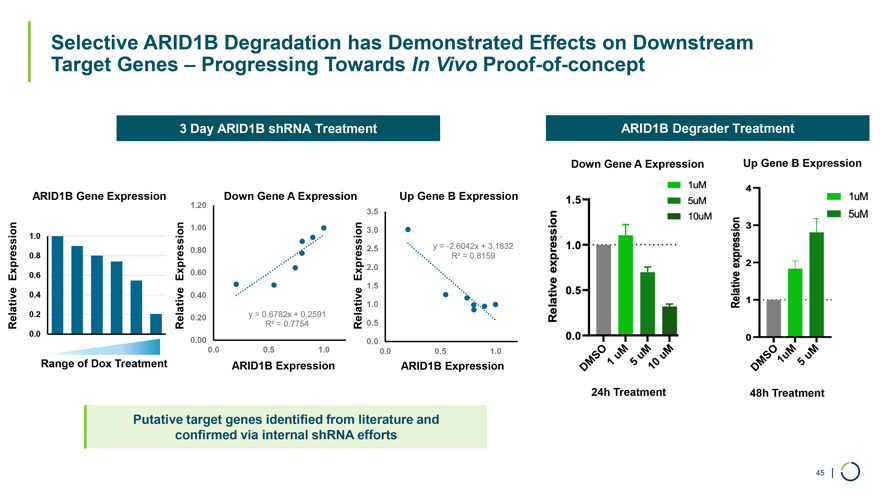
Selective ARID1B Degradation has Demonstrated Effects on Downstream Target Genes – Progressing Towards In Vivo Proof-of-concept 3 Day ARID1B shRNA Treatment ARID1B Degrader Treatment Down Gene A Expression Up Gene B Expression ARID1B Gene Expression 1.20 Down Gene A Expression Up Gene B Expression 3.5 1.0 1.00 3.0 0.80 2.5 y = -2.6042x + 3.1832 0.8 R² = 0.8159 2.0 Expression 0.6 Expression 0.60 Expression 1.5 0.4 0.40 1.0 0.2 0.20 y = 0.6782x + 0.2591 0.5 Relative Relative R² = 0.7754 Relative 0.0 6 0.00 0.0 0.0 0.5 1.0 0.0 0.5 1.0 Range of Dox Treatment ARID1B Expression ARID1B Expression 24h Treatment 48h Treatment Putative target genes identified from literature and confirmed via internal shRNA efforts 45 |
Developing First-in-Class Precision Medicines Targeting Major Unmet Needs in Cancer Leader in Unique Area of Cancer Biology Foghorn is a leader in targeting chromatin biology, which has the potential to address underlying dependencies of many genetically defined cancers Platform with initial focus in oncology, therapeutic area expansion potential Large Market Well-Potential Funded Chromatin biology is $158.9 million in cash and implicated in up to 50% of equivalents (unaudited) tumors, potentially (as of 12/31/2025) impacting ~2.5 million patients Cash runway into 2028 Foghorn’s current pipeline Shares outstanding: potentially addresses approximately 63.2M* more than 500,000 of (unaudited) these patients Broad pipeline across a range of targets and small molecule modalities Value Major Strategic Drivers Collaboration Selective SMARCA2 Inhibitor, Strategic collaboration with FHD-909, partnered with Lilly, Lilly; $380 million upfront; in Phase 1 trial 50/50 U.S. economic split on two lead programs Advancement of preclinical assets (Selective SMARCA2, CBP, EP300, ARID1B degraders) towards INDs Protein degrader platform with expansion into induced proximity 46 | *Includes common shares outstanding and pre-funded warrants as of 12/31/2025.

Unique biology Precision therapeutics Broad impact January 2026 47

Appendix 48

SMARCA2 Program 49
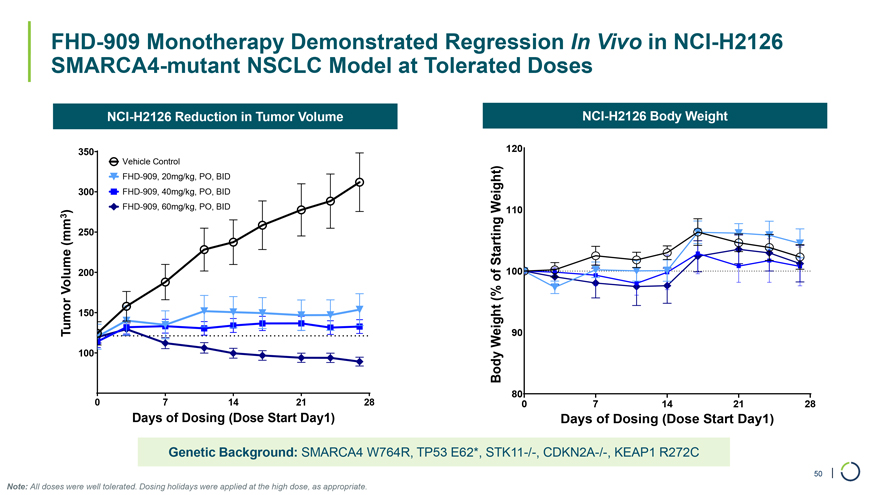
FHD-909 Monotherapy Demonstrated Regression In Vivo in NCI-H2126 SMARCA4-mutant NSCLC Model at Tolerated Doses NCI-H2126 Reduction in Tumor Volume NCI-H2126 Body Weight 350 120 Vehicle Control FHD-909, 20mg/kg, PO, BID 300 FHD-909, 40mg/kg, PO, BID ) FHD-909, 60mg/kg, PO, BID Weight) 110 3 (mm 250 Starting 200 of 100 Volume (% 150 Tumor Weight 90 100 Body 80 0 7 14 21 28 0 7 14 21 28 Days of Dosing (Dose Start Day1) Days of Dosing (Dose Start Day1) Genetic Background: SMARCA4 W764R, TP53 E62*, STK11-/-, CDKN2A-/-, KEAP1 R272C 50 | Note: All doses were well tolerated. Dosing holidays were applied at the high dose, as appropriate.
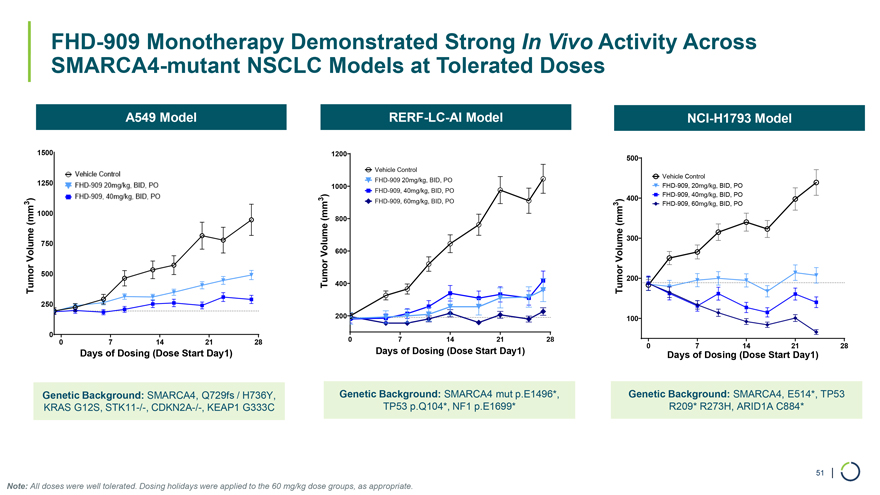
A549 Model RERF-LC-AI Model NCI-H1793 Model 1500 1200 500 Vehicle Control Vehicle Control 1250 FHD-909 20mg/kg, BID, PO 1000 FHD-909, 20mg/kg, BID, PO FHD-909, 40mg/kg, BID, PO ) 400 FHD-909, 40mg/kg, BID, PO 3 ) 3 FHD-909, 60mg/kg, BID, PO ) 3 FHD-909, 60mg/kg, BID, PO 1000 (mm 800 (mm (mm 300 750 Volume 600 Volume Volume 500 200 Tumor Tumor 400 Tumor FHD-909 Monotherapy Demonstrated Strong In Vivo Activity Across SMARCA4-mutant NSCLC Models at Tolerated Doses 250 200 100 0 0 7 14 21 28 0 7 14 21 28 Days of Dosing (Dose Start Day1) 0 7 14 21 28 Days of Dosing (Dose Start Day1) Days of Dosing (Dose Start Day1) Genetic Background: SMARCA4, Q729fs / H736Y, Genetic Background: SMARCA4 mut p.E1496*, Genetic Background: SMARCA4, E514*, TP53 KRAS G12S, STK11-/-, CDKN2A-/-, KEAP1 G333C TP53 p.Q104*, NF1 p.E1699* R209* R273H, ARID1A C884* 51 | Note: All doses were well tolerated. Dosing holidays were applied to the 60 mg/kg dose groups, as appropriate.
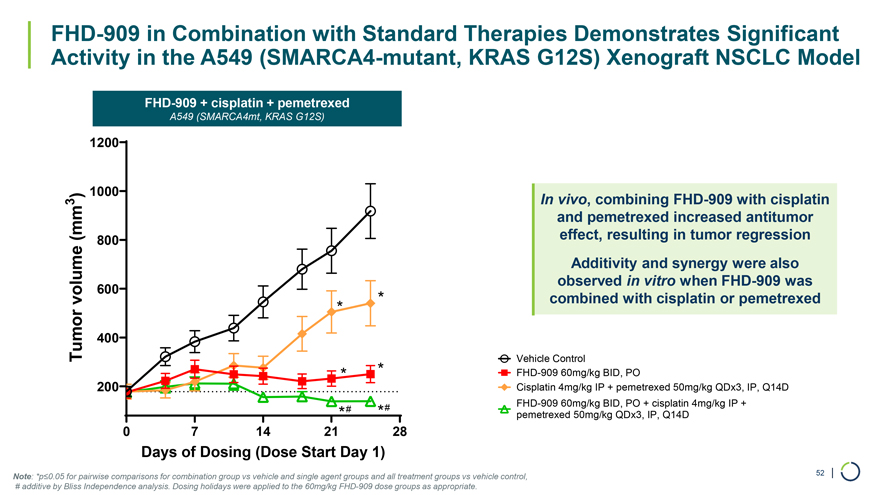
FHD-909 + cisplatin + pemetrexed A549 (SMARCA4mt, KRAS G12S) 1200 ) 1000 3 (mm 800 volume 600 * * Tumor 400 * * 200 *# *# 0 7 14 21 28 FHD-909 in Combination with Standard Therapies Demonstrates Significant Activity in the A549 (SMARCA4-mutant, KRAS G12S) Xenograft NSCLC Model In vivo, combining FHD-909 with cisplatin and pemetrexed increased antitumor effect, resulting in tumor regression Additivity and synergy were also observed in vitro when FHD-909 was combined with cisplatin or pemetrexed Vehicle Control FHD-909 60mg/kg BID, PO Cisplatin 4mg/kg IP + pemetrexed 50mg/kg QDx3, IP, Q14D FHD-909 60mg/kg BID, PO + cisplatin 4mg/kg IP + pemetrexed 50mg/kg QDx3, IP, Q14D Days of Dosing (Dose Start Day 1) Note: *p≤0.05 for pairwise comparisons for combination group vs vehicle and single agent groups and all treatment groups vs vehicle control, 52 | # additive by Bliss Independence analysis. Dosing holidays were applied to the 60mg/kg FHD-909 dose groups as appropriate.
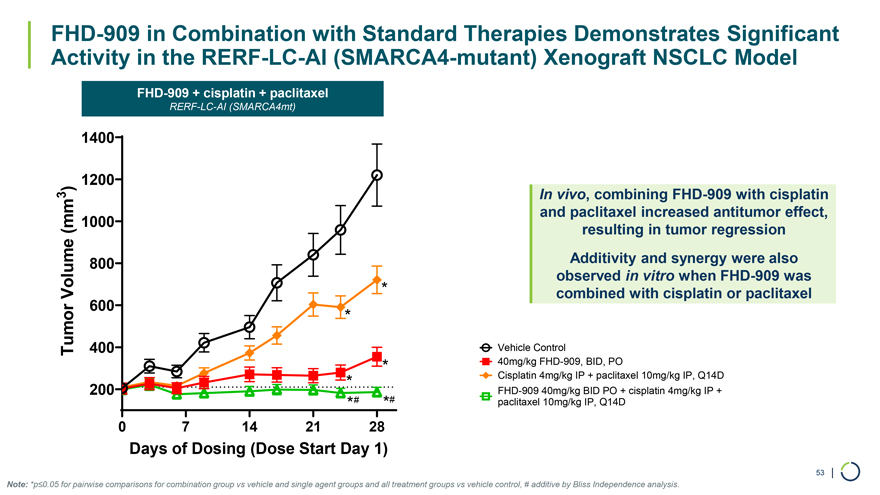
1400 1200 3 ) In vivo, combining FHD-909 with cisplatin and paclitaxel increased antitumor effect, (mm 1000 resulting in tumor regression 800 Additivity and synergy were also observed in vitro when FHD-909 was Volume * combined with cisplatin or paclitaxel 600 * Tumor 400 Vehicle Control * 40mg/kg FHD-909, BID, PO * Cisplatin 4mg/kg IP + paclitaxel 10mg/kg IP, Q14D 200 FHD-909 40mg/kg BID PO + cisplatin 4mg/kg IP + *# *# paclitaxel 10mg/kg IP, Q14D 0 7 14 21 28 Days of Dosing (Dose Start Day 1) 53 | FHD-909 in Combination with Standard Therapies Demonstrates Significant Activity in the RERF-LC-AI (SMARCA4-mutant) Xenograft NSCLC Model FHD-909 + cisplatin + paclitaxel RERF-LC-AI (SMARCA4mt) Note: *p≤0.05 for pairwise comparisons for combination group vs vehicle and single agent groups and all treatment groups vs vehicle control, # additive by Bliss Independence analysis.
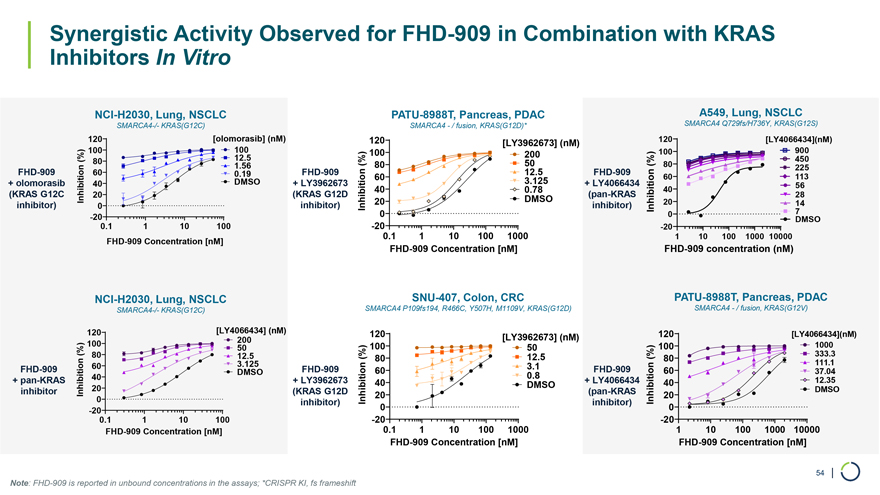
Synergistic Activity Observed for FHD-909 in Combination with KRAS Inhibitors In Vitro NCI-H2030, Lung, NSCLC PATU-8988T, Pancreas, PDAC A549, Lung, NSCLC SMARCA4-/- KRAS(G12C) SMARCA4—/ fusion, KRAS(G12D)* SMARCA4 Q729fs/H736Y, KRAS(G12S) 120 [olomorasib] (nM) 120 [LY3962673] (nM) 120 [LY4066434](nM) 100 100 100 200 100 900 (%) 80 12.5 450 (%) 80 50 (%) 80 FHD-909 60 1.56 FHD-909 12.5 FHD-909 225 0.19 60 60 113 + olomorasib 40 DMSO + LY3962673 3.125 + LY4066434 56 (KRAS G12C (KRAS G12D 40 0.78 (pan-KRAS 40 Inhibition 20 DMSO 28 inhibitor) 0 inhibitor) Inhibition 20 inhibitor) Inhibition 20 14 0 0 7 -20 DMSO 0.1 1 10 100 -200.1 1 10 100 1000 -20 1 10 100 1000 10000 FHD-909 Concentration [nM] FHD-909 Concentration [nM] FHD-909 concentration (nM) NCI-H2030, Lung, NSCLC SNU-407, Colon, CRC PATU-8988T, Pancreas, PDAC SMARCA4-/- KRAS(G12C) SMARCA4 P109fs194, R466C, Y507H, M1109V, KRAS(G12D) SMARCA4—/ fusion, KRAS(G12V) 120 [LY4066434] (nM) 120 120 [LY4066434](nM) 200 [LY3962673] (nM) 100 50 100 50 100 1000 (%) 80 12.5 (%) 12.5 (%) 333.3 80 80 111.1 60 3.125 3.1 FHD-909 DMSO FHD-909 60 FHD-909 60 37.04 + pan-KRAS 40 + LY3962673 0.8 + LY4066434 12.35 40 DMSO 40 inhibitor Inhibition 20 (KRAS G12D (pan-KRAS DMSO 0 Inhibition 20 Inhibition 20 inhibitor) 0 inhibitor) 0 -20 0.1 1 10 100 -200.1 1 10 100 1000 -20 1 10 100 1000 10000 FHD-909 Concentration [nM] FHD-909 Concentration [nM] FHD-909 Concentration [nM] 54 | Note: FHD-909 is reported in unbound concentrations in the assays; *CRISPR KI, fs frameshift
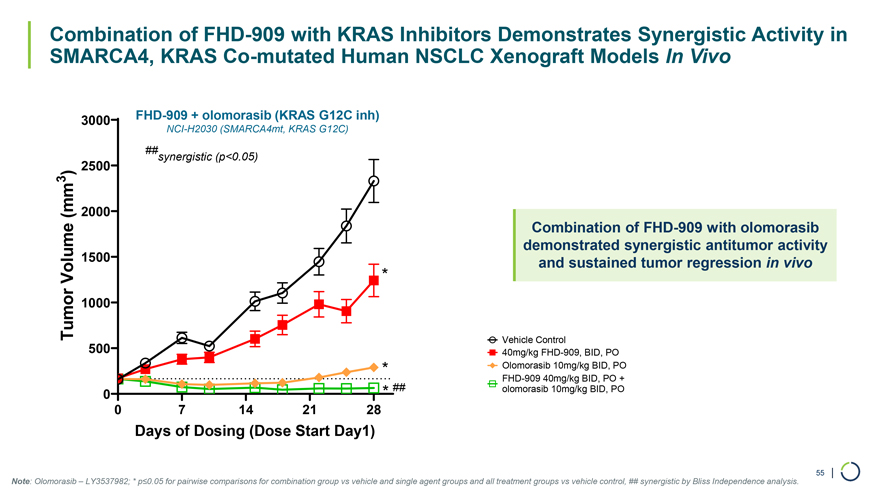
3000 FHD-909 + olomorasib (KRAS G12C inh) NCI-H2030 (SMARCA4mt, KRAS G12C) ## synergistic (p<0.05) 2500 3 ) (mm 2000 Combination of FHD-909 with olomorasib demonstrated synergistic antitumor activity 1500 and sustained tumor regression in vivo Volume * Tumor 1000 Vehicle Control 500 40mg/kg FHD-909, BID, PO * Olomorasib 10mg/kg BID, PO FHD-909 40mg/kg BID, PO + 0 * ## olomorasib 10mg/kg BID, PO 0 7 14 21 28 Days of Dosing (Dose Start Day1) 55 | Combination of FHD-909 with KRAS Inhibitors Demonstrates Synergistic Activity in SMARCA4, KRAS Co-mutated Human NSCLC Xenograft Models In Vivo Note: Olomorasib – LY3537982; * p≤0.05 for pairwise comparisons for combination group vs vehicle and single agent groups and all treatment groups vs vehicle control, ## synergistic by Bliss Independence analysis.
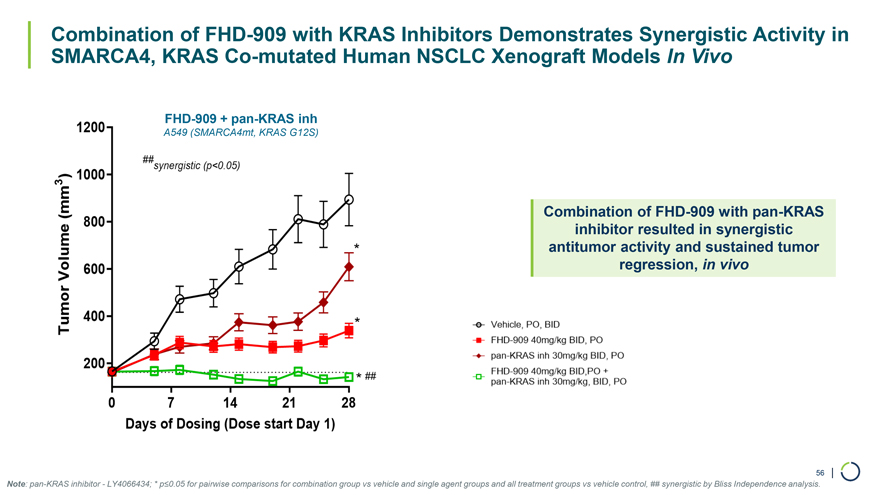
Combination of FHD-909 with KRAS Inhibitors Demonstrates Synergistic Activity in SMARCA4, KRAS Co-mutated Human NSCLC Xenograft Models In Vivo FHD-909 + pan-KRAS inh A549 (SMARCA4mt, KRAS G12S) Combination of FHD-909 with pan-KRAS inhibitor resulted in synergistic antitumor activity and sustained tumor regression, in vivo 56 | Note: pan-KRAS inhibitor—LY4066434; * p≤0.05 for pairwise comparisons for combination group vs vehicle and single agent groups and all treatment groups vs vehicle control, ## synergistic by Bliss Independence analysis.
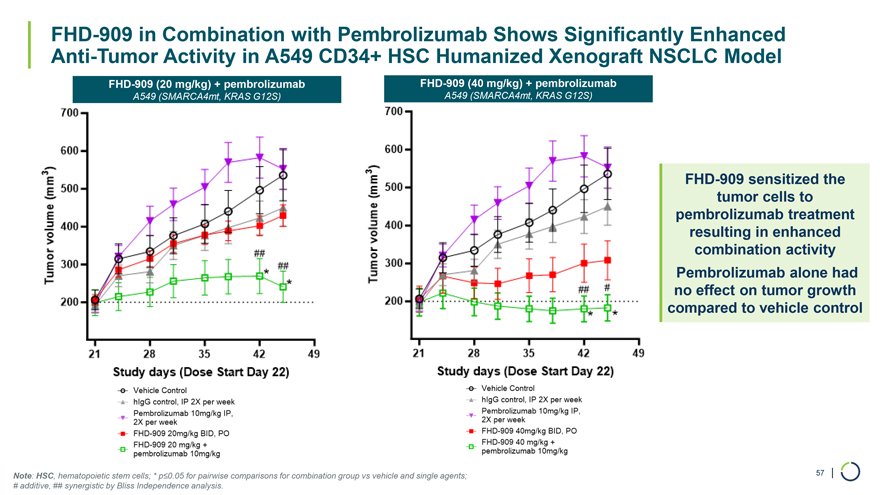
FHD-909 in Combination with Pembrolizumab Shows Significantly Enhanced Anti-Tumor Activity in A549 CD34+ HSC Humanized Xenograft NSCLC Model FHD-909 (20 mg/kg) + pembrolizumab FHD-909 (40 mg/kg) + pembrolizumab A549 (SMARCA4mt, KRAS G12S) A549 (SMARCA4mt, KRAS G12S) FHD-909 sensitized the tumor cells to pembrolizumab treatment resulting in enhanced combination activity Pembrolizumab alone had no effect on tumor growth compared to vehicle control Note: HSC, hematopoietic stem cells; * p≤0.05 for pairwise comparisons for combination group vs vehicle and single agents; 57 | # additive, ## synergistic by Bliss Independence analysis.
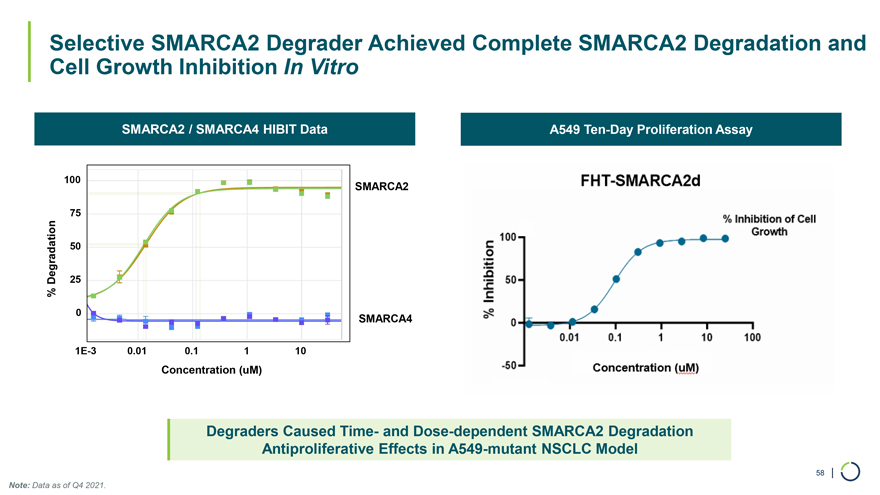
Selective SMARCA2 Degrader Achieved Complete SMARCA2 Degradation and Cell Growth Inhibition In Vitro SMARCA2 / SMARCA4 HIBIT Data A549 Ten-Day Proliferation Assay 100 SMARCA2 75 50 Degradation 25 % 0 SMARCA4 1E-3 0.01 0.1 1 10 Concentration (uM) Degraders Caused Time- and Dose-dependent SMARCA2 Degradation Antiproliferative Effects in A549-mutant NSCLC Model 58 | Note: Data as of Q4 2021.

Protein Degradation Importance of Rate Analysis FHD-609 is a Selective, Potent, Protein Degrader of the BRD9 component of the BAF complex 59
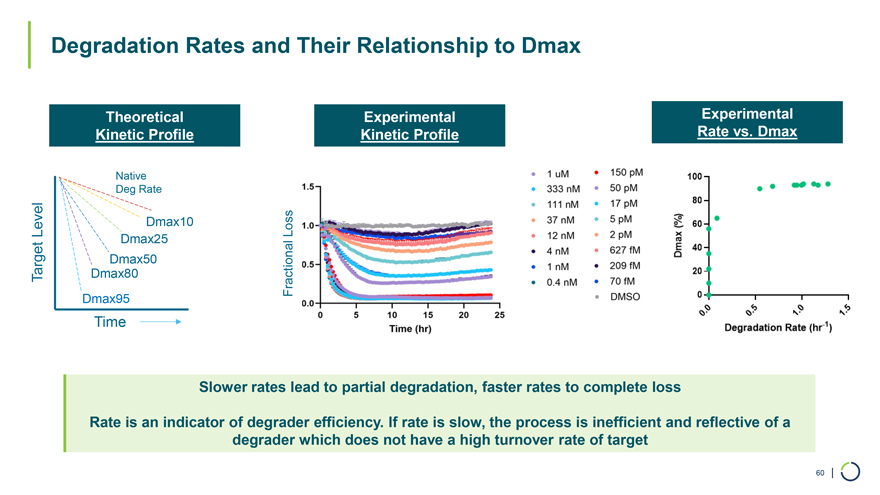
Theoretical Experimental Experimental Kinetic Profile Kinetic Profile Rate vs. Dmax Native Deg Rate Level Dmax10 Loss Dmax25 Dmax50 Target Dmax80 Fractional Dmax95 Time Degradation Rates and Their Relationship to Dmax Slower rates lead to partial degradation, faster rates to complete loss Rate is an indicator of degrader efficiency. If rate is slow, the process is inefficient and reflective of a degrader which does not have a high turnover rate of target 60 |
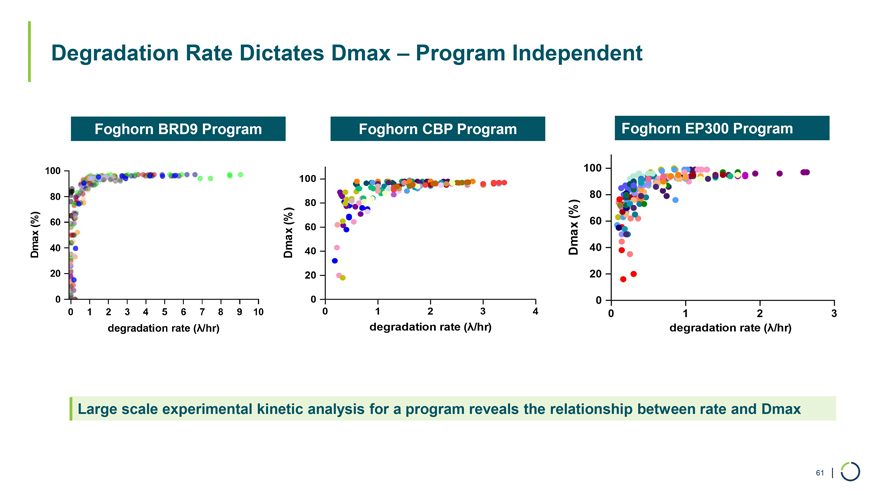
Foghorn BRD9 Program Foghorn CBP Program Foghorn EP300 Program Degradation Rate Dictates Dmax – Program Independent Large scale experimental kinetic analysis for a program reveals the relationship between rate and Dmax 61 |
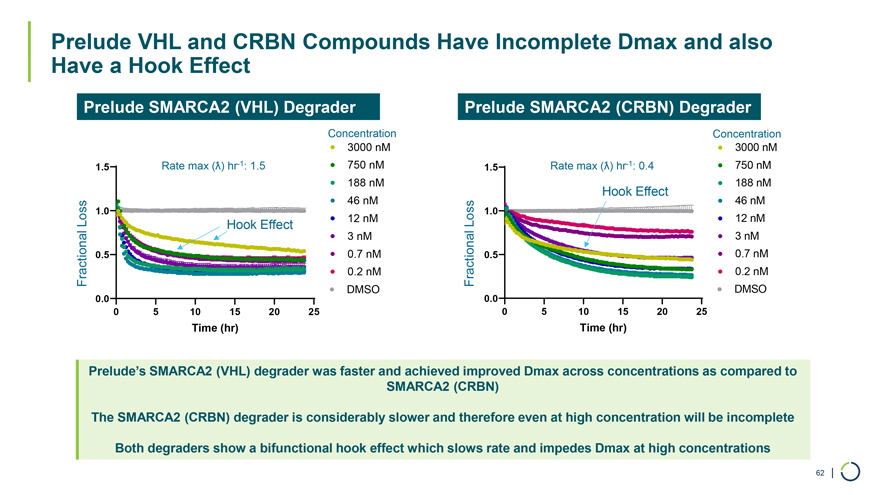
Prelude SMARCA2 (VHL) Degrader Prelude SMARCA2 (CRBN) Degrader Concentration Concentration 3000 nM 3000 nM 1.5 Rate max hr-1: 1.5 750 nM 1.5 Rate max hr-1: 0.4 750 nM 188 nM 188 nM Hook Effect 46 nM 46 nM 1.0 1.0 Loss Hook Effect 12 nM Loss 12 nM Luminescence 3 nM Luminescence 3 nM (RLU) 0.7 nM (RLU) 0.7 nM 0.5 0.5 Fractional 0.2 nM Fractional 0.2 nM Fractional DMSO Fractional DMSO 0.0 0.0 0 5 10 15 20 25 0 5 10 15 20 25 Time (hr) Time (hr) Prelude VHL and CRBN Compounds Have Incomplete Dmax and also Have a Hook Effect Prelude’s SMARCA2 (VHL) degrader was faster and achieved improved Dmax across concentrations as compared to SMARCA2 (CRBN) The SMARCA2 (CRBN) degrader is considerably slower and therefore even at high concentration will be incomplete Both degraders show a bifunctional hook effect which slows rate and impedes Dmax at high concentrations 62 |
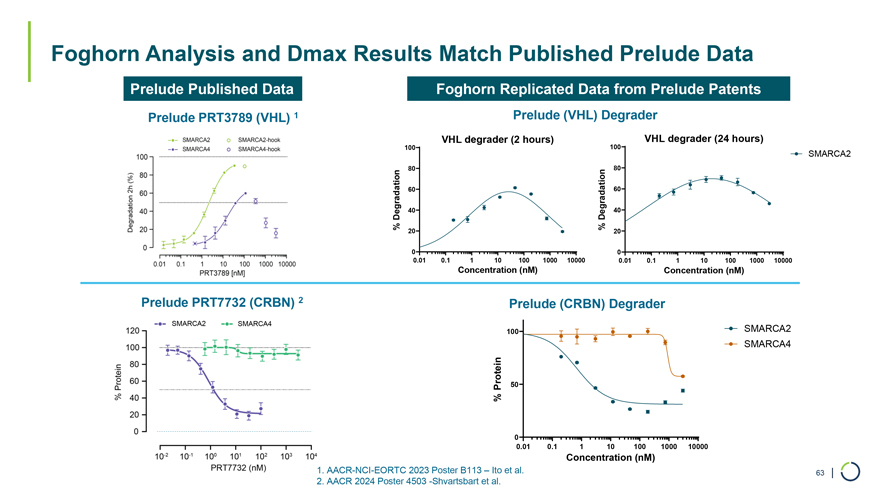
Foghorn Analysis and Dmax Results Match Published Prelude Data Prelude Published Data Foghorn Replicated Data from Prelude Patents Prelude PRT3789 (VHL) 1 Prelude (VHL) Degrader VHL degrader (2 hours) 100 VHL degrader (24 hours) 100 SMARCA2 80 80 60 60 Degradation 40 Degradation 40 % % 20 20 0 0 0.01 0.1 1 10 100 1000 10000 0.01 0.1 1 10 100 1000 10000 Concentration (nM) Concentration (nM) Prelude PRT7732 (CRBN) 2 Prelude (CRBN) Degrader 100 SMARCA2 SMARCA4 Protein 50 % 0 0.01 0.1 1 10 100 1000 10000 Concentration (nM) 1. AACR-NCI-EORTC 2023 Poster B113 – Ito et al. 63 | 2. AACR 2024 Poster 4503 -Shvartsbart et al.