

Degrading Proteins, Making Medicines MRT-2359 Phase 1/2 Clinical Data Update December 16, 2025 .2

Forward-Looking Statements This communication includes express and implied “forward-looking statements,” including forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Forward-looking statements include all statements that are not historical facts and in some cases, can be identified by terms such as “may,” “might,” “will,” “could,” “would,” “should,” “expect,” “intend,” “plan,” “objective,” “anticipate,” “believe,” “estimate,” “predict,” “potential,” “continue,” “ongoing,” or the negative of these terms, or other comparable terminology intended to identify statements about the future. Forward-looking statements contained herein include, but are not limited to, statements about our ability to grow our product pipeline, our ability to successfully complete research and further development and commercialization of our drug candidates in current or future indications, including the timing and results of our clinical trials and our ability to conduct and complete clinical trials, statements regarding the promising interim results from our ongoing Phase 1/2 clinical study evaluating MRT-2359 in combination with enzalutamide in heavily pretreated patients with metastatic CRPC, our expectations regarding the clinical activity observed with MRT-2359 in combination with enzalutamide in heavily pretreated mCRPC patients and the significant opportunity for MRT-2359 in the rapidly evolving treatment landscape of prostate cancer, our plans to initiate a signal-confirming Phase 2 study evaluating MRT-2359 in combination with a second generation AR inhibitor in mCRPC patients with AR mutations and timing thereof, with potential to expand into additional patient subsets, the potential for the data from this study to confirm MRT-2359’s clinical activity and position the program for advancement into registrational studies, the clinical significance of the clinical data read-out at upcoming scientific meetings and timing thereof, our plans to present interim Phase 1 data on MRT-8102 in early 2026, statements around our ability to capitalize on and potential benefits resulting from our research and translational insights, among others. By their nature, these statements are subject to numerous risks and uncertainties, including those risks and uncertainties set forth in our most recent Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2024, filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission on March 20, 2025, and any subsequent filings, that could cause actual results, performance or achievement to differ materially and adversely from those anticipated or implied in the statements. You should not rely upon forward-looking statements as predictions of future events. Although our management believes that the expectations reflected in our statements are reasonable, we cannot guarantee that the future results, performance, or events and circumstances described in the forward-looking statements will be achieved or occur. Recipients are cautioned not to place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements, which speak only as of the date such statements are made and should not be construed as statements of fact. We undertake no obligation to publicly update any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, any future presentations, or otherwise, except as required by applicable law. Certain information contained in these materials and any statements made orally during any presentation of these materials that relate to the materials or are based on studies, publications, surveys and other data obtained from third-party sources and our own internal estimates and research. While we believe these third-party studies, publications, surveys and other data to be reliable as of the date of these materials, we have not independently verified, and make no representations as to the adequacy, fairness, accuracy or completeness of, any information obtained from third-party sources. In addition, no independent source has evaluated the reasonableness or accuracy of our internal estimates or research and no reliance should be made on any information or statements made in these materials relating to or based on such internal estimates and research. These materials remain the proprietary intellectual property of Monte Rosa Therapeutics and should not be distributed or reproduced in whole or in part without the prior written consent of Monte Rosa Therapeutics.

MRT-2359 in combination with enzalutamide achieved compelling clinical activity in a subset of heavily pre-treated metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) patients with androgen receptor (AR) mutations. Of the 4 patients with AR mutations: 4 patients showed a PSA response, including 2 patients with PSA90 and 2 patients with PSA50 responses 2 patients showed RECIST partial responses (1 confirmed, 1 unconfirmed) 2 patients had stable disease, leading to a 100% disease control rate in the AR mutant population 2 patients remained on therapy for 10 cycles or longer and 3 of 4 patients remained on drug as of data cut off on December 3rd 5 additional patients without AR mutations had stable disease per RECIST, several of which associated with tumor size reductions of target lesions, resulting in an overall disease control rate (DCR) of 64% in a total of 14 evaluable patients Combination of MRT-2359 and enzalutamide was well tolerated with mild or moderate manageable GI adverse events (AEs) being the most frequent toxicities Data support potential of combination of MRT-2359 with 2nd generation androgen receptor inhibitors for mCRPC patients with AR mutations (up to 30% of 2nd line+ mCRPC), with additional potential in earlier line settings or in combination with other agents Summary

Therapeutic Rationale in mCRPC
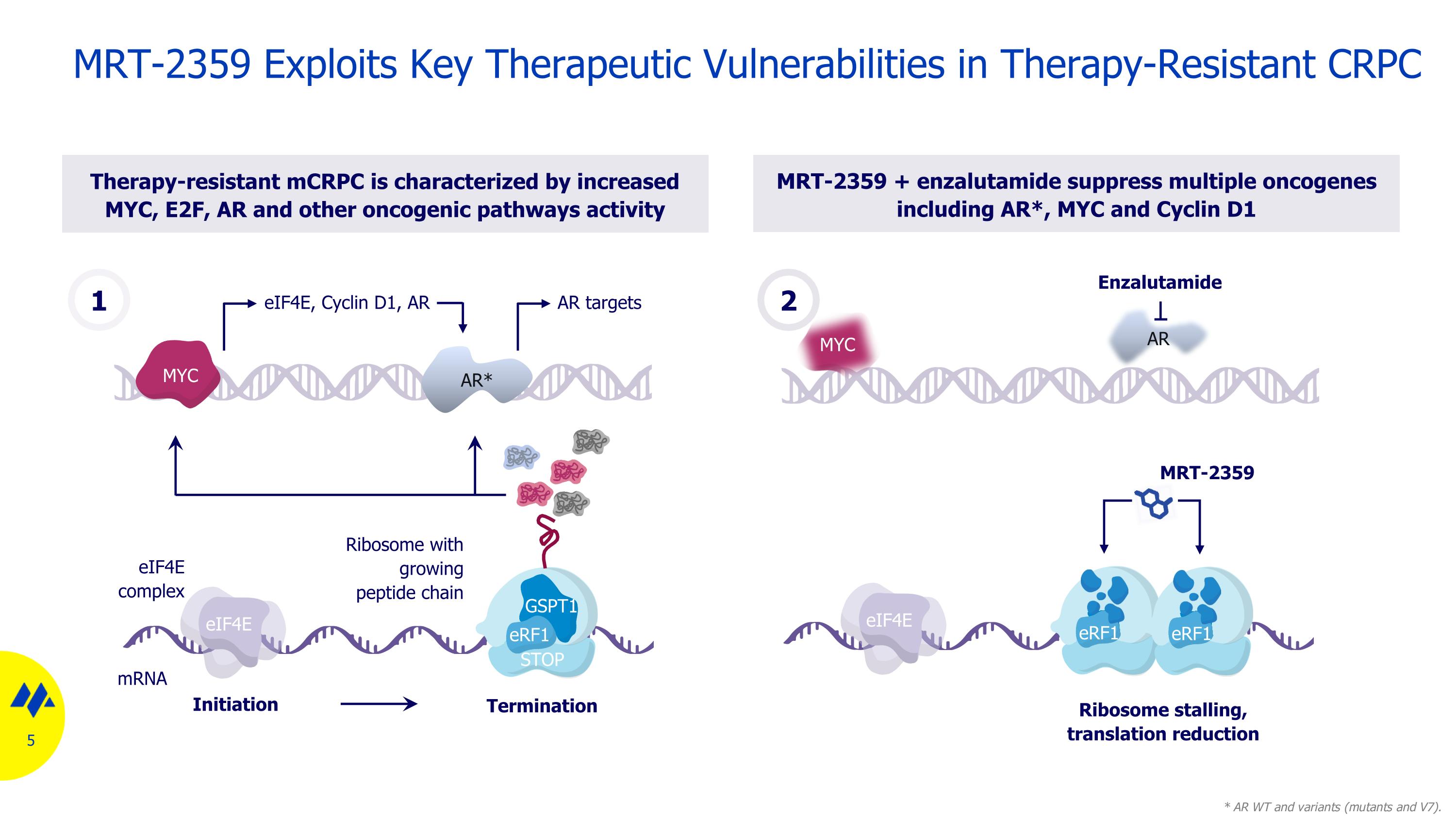
mRNA eIF4E eIF4E complex Initiation Termination GSPT1 STOP eRF1 Ribosome with growing peptide chain eIF4E Ribosome stalling, translation reduction MRT-2359 eRF1 eRF1 Therapy-resistant mCRPC is characterized by increased MYC, E2F, AR and other oncogenic pathways activity MRT-2359 + enzalutamide suppress multiple oncogenes including AR*, MYC and Cyclin D1 GSPT1 MRT-2359 Exploits Key Therapeutic Vulnerabilities in Therapy-Resistant CRPC 2 Enzalutamide AR MYC * AR WT and variants (mutants and V7). eIF4E, Cyclin D1, AR AR targets AR* MYC 1
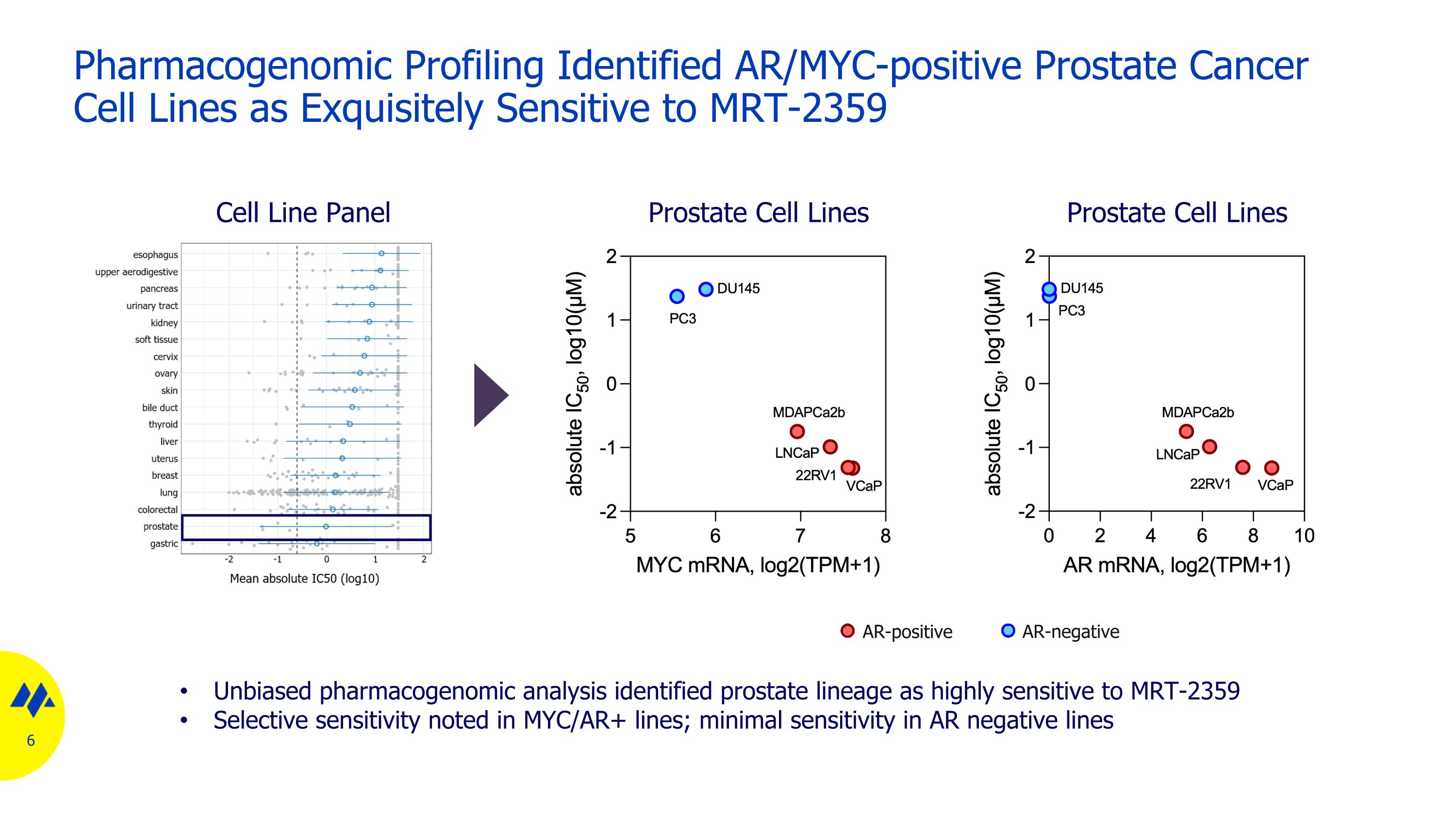
Pharmacogenomic Profiling Identified AR/MYC-positive Prostate Cancer Cell Lines as Exquisitely Sensitive to MRT-2359 Unbiased pharmacogenomic analysis identified prostate lineage as highly sensitive to MRT-2359 Selective sensitivity noted in MYC/AR+ lines; minimal sensitivity in AR negative lines AR-positive AR-negative Cell Line Panel Prostate Cell Lines Prostate Cell Lines
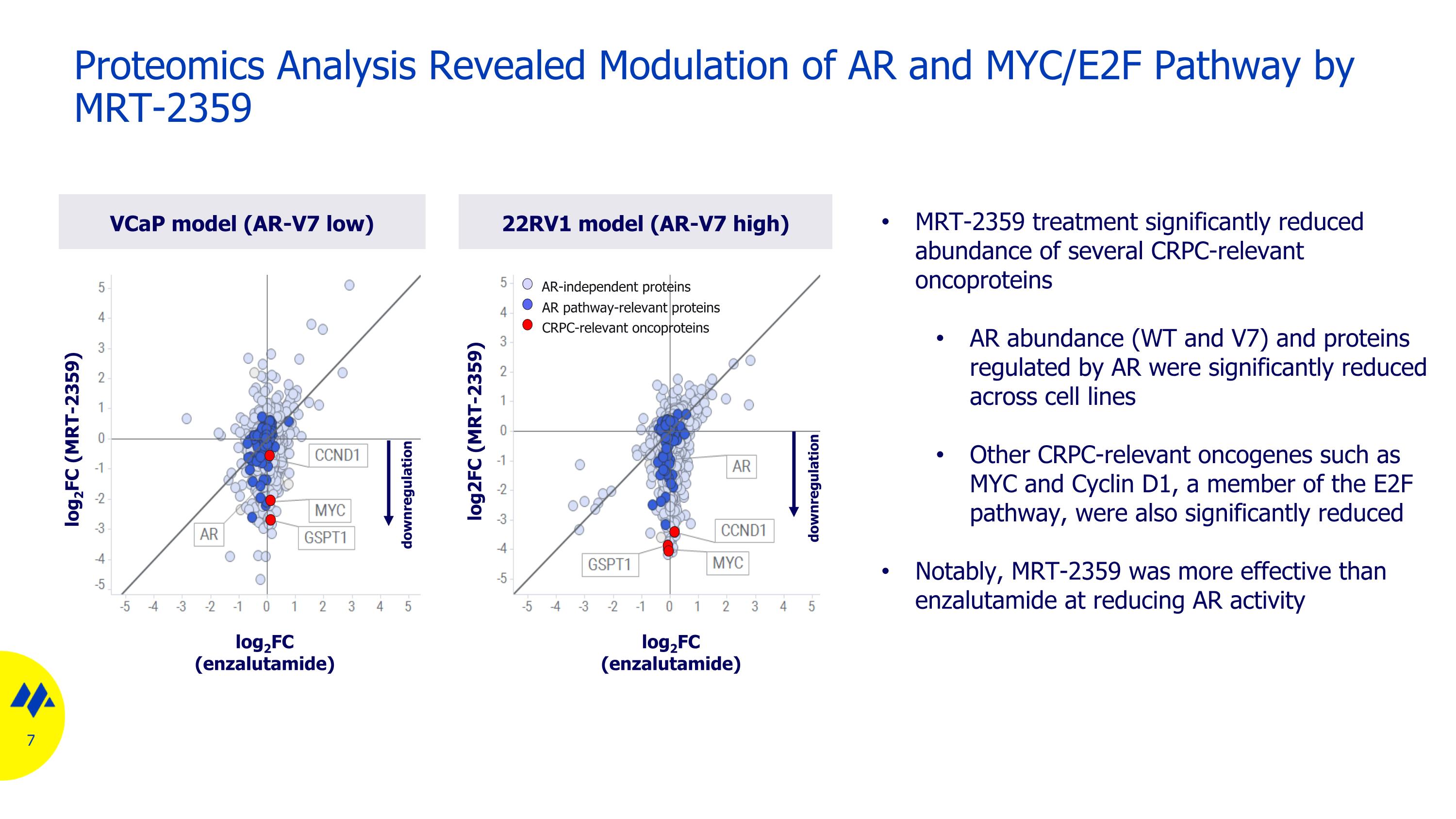
Proteomics Analysis Revealed Modulation of AR and MYC/E2F Pathway by MRT-2359 VCaP model (AR-V7 low) 22RV1 model (AR-V7 high) log2FC (MRT-2359) log2FC (enzalutamide) log2FC (MRT-2359) log2FC (enzalutamide) AR-independent proteins AR pathway-relevant proteins CRPC-relevant oncoproteins MRT-2359 treatment significantly reduced abundance of several CRPC-relevant oncoproteins AR abundance (WT and V7) and proteins regulated by AR were significantly reduced across cell lines Other CRPC-relevant oncogenes such as MYC and Cyclin D1, a member of the E2F pathway, were also significantly reduced Notably, MRT-2359 was more effective than enzalutamide at reducing AR activity downregulation downregulation
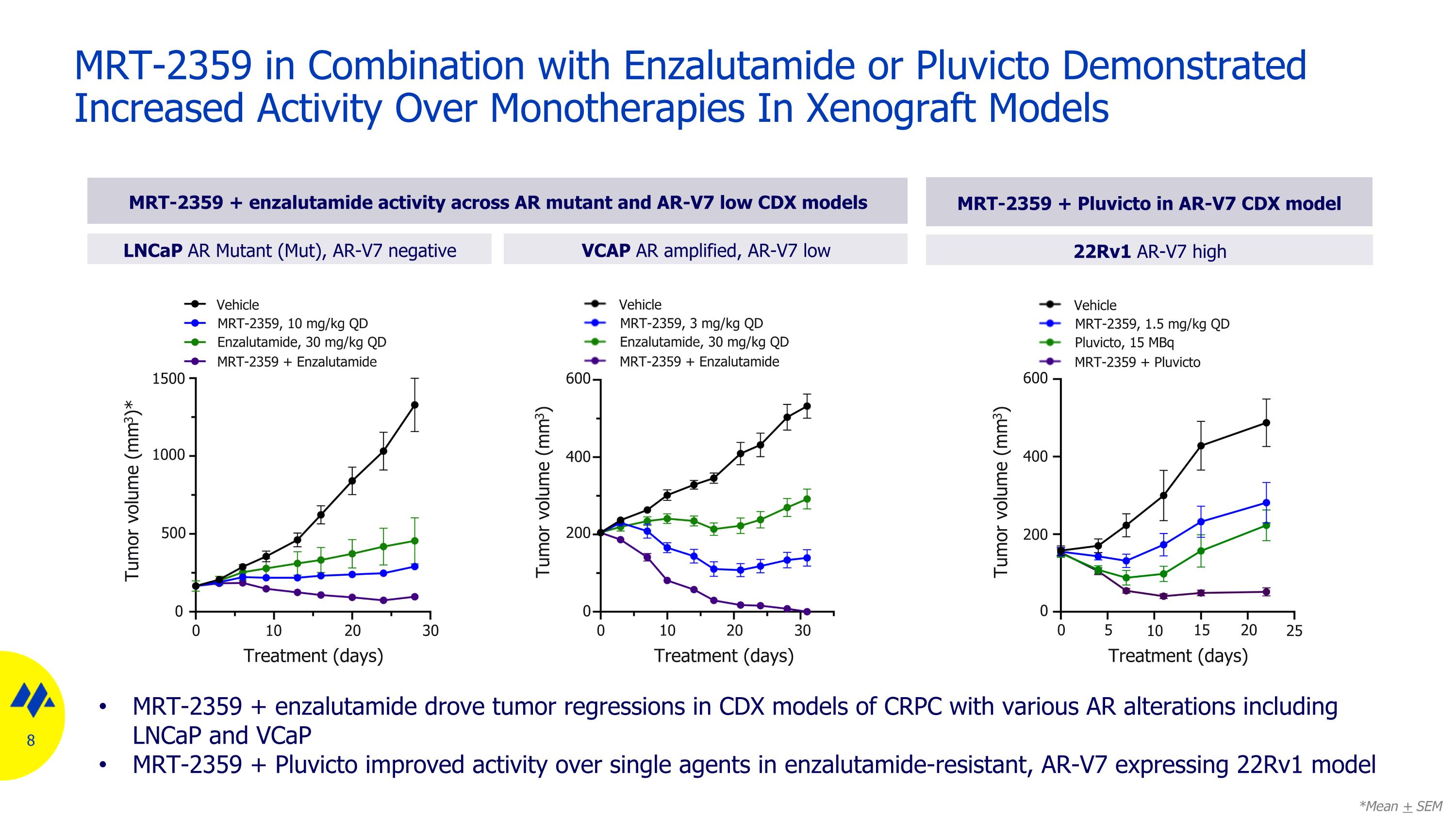
MRT-2359 in Combination with Enzalutamide or Pluvicto Demonstrated Increased Activity Over Monotherapies In Xenograft Models LNCaP AR Mutant (Mut), AR-V7 negative VCAP AR amplified, AR-V7 low MRT-2359 + enzalutamide drove tumor regressions in CDX models of CRPC with various AR alterations including LNCaP and VCaP MRT-2359 + Pluvicto improved activity over single agents in enzalutamide-resistant, AR-V7 expressing 22Rv1 model MRT-2359 + enzalutamide activity across AR mutant and AR-V7 low CDX models MRT-2359 + Pluvicto in AR-V7 CDX model Tumor volume (mm3)* 0 500 1000 1500 0 10 20 30 Treatment (days) Vehicle MRT-2359, 10 mg/kg QD Enzalutamide, 30 mg/kg QD MRT-2359 + Enzalutamide *Mean + SEM Tumor volume (mm3) 0 200 400 600 0 10 20 30 Treatment (days) Vehicle MRT-2359, 3 mg/kg QD Enzalutamide, 30 mg/kg QD MRT-2359 + Enzalutamide 22Rv1 AR-V7 high Tumor volume (mm3) Treatment (days) Vehicle MRT-2359, 1.5 mg/kg QD Pluvicto, 15 MBq MRT-2359 + Pluvicto 0 200 400 600 0 5 15 20 10 25

MRT-2359 Clinical Data Update
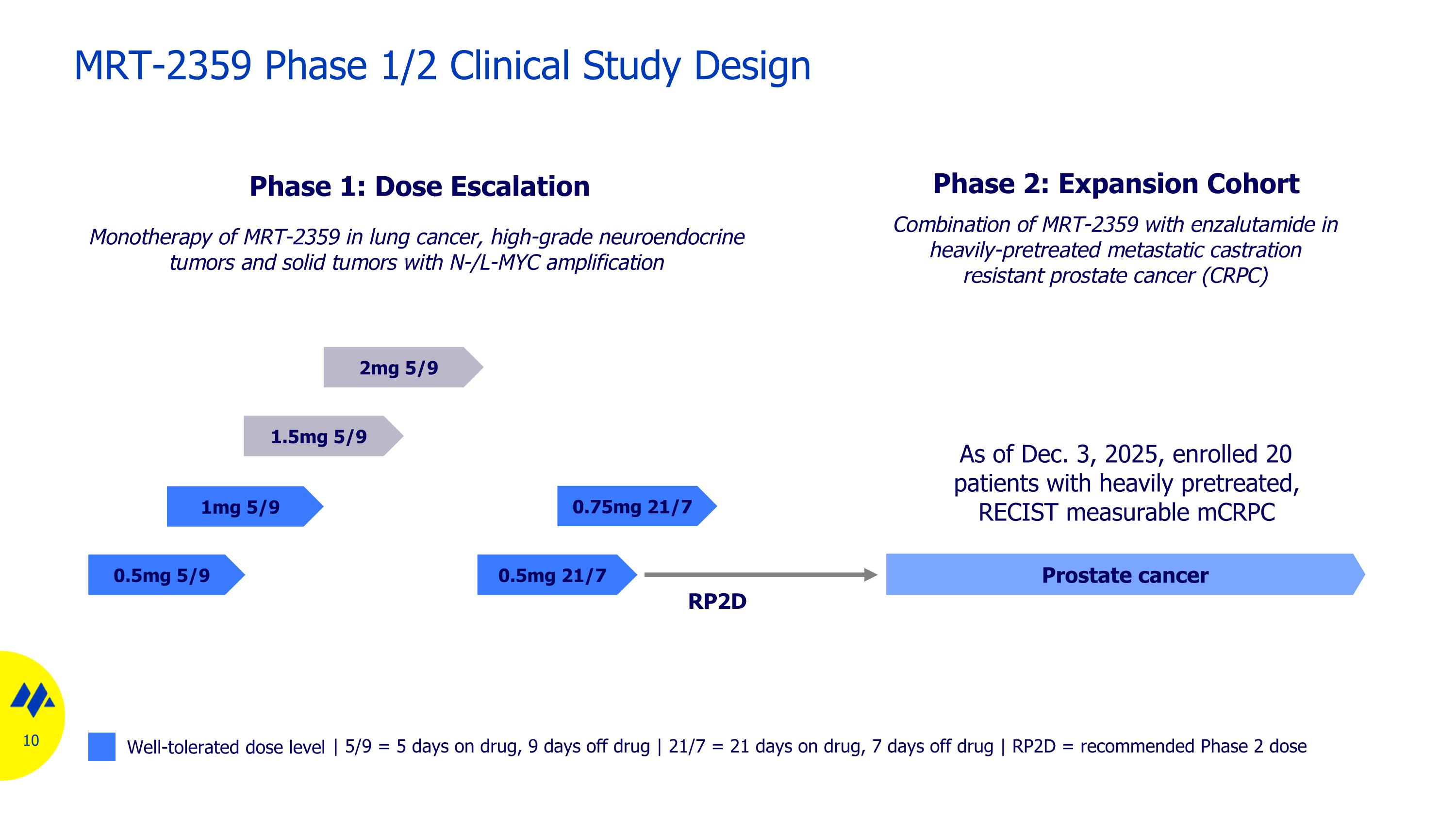
0.5mg 5/9 Phase 2: Expansion Cohort Phase 1: Dose Escalation 1.5mg 5/9 1mg 5/9 MRT-2359 Phase 1/2 Clinical Study Design Monotherapy of MRT-2359 in lung cancer, high-grade neuroendocrine tumors and solid tumors with N-/L-MYC amplification 2mg 5/9 | 5/9 = 5 days on drug, 9 days off drug | 21/7 = 21 days on drug, 7 days off drug | RP2D = recommended Phase 2 dose 0.5mg 21/7 0.75mg 21/7 RP2D Well-tolerated dose level Prostate cancer Combination of MRT-2359 with enzalutamide in heavily-pretreated metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) As of Dec. 3, 2025, enrolled 20 patients with heavily pretreated, RECIST measurable mCRPC
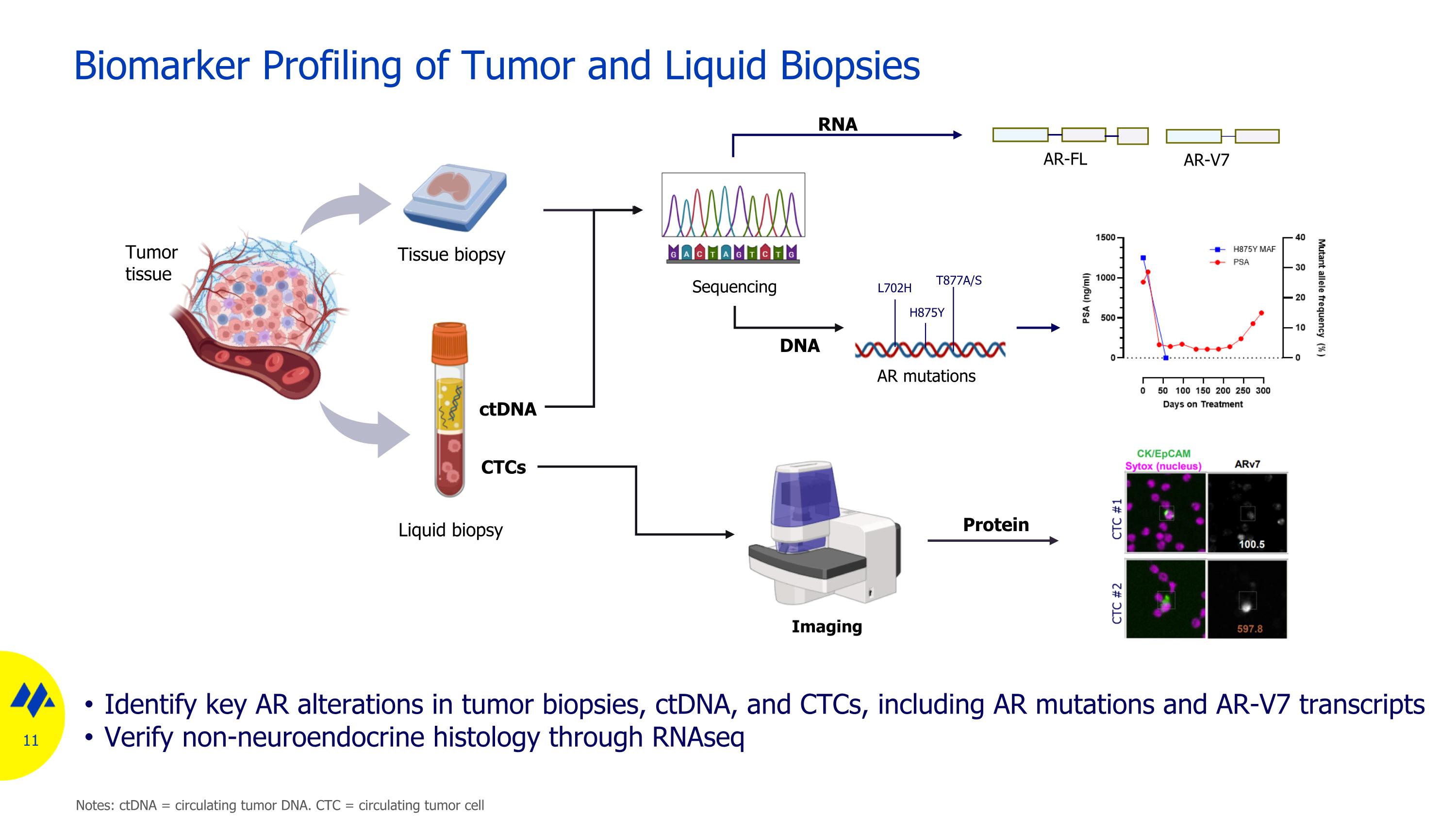
Biomarker Profiling of Tumor and Liquid Biopsies Identify key AR alterations in tumor biopsies, ctDNA, and CTCs, including AR mutations and AR-V7 transcripts Verify non-neuroendocrine histology through RNAseq Tissue biopsy L702H T877A/S H875Y AR mutations Tumor tissue CTCs ctDNA Liquid biopsy Sequencing Imaging DNA RNA Protein AR-V7 AR-FL Notes: ctDNA = circulating tumor DNA. CTC = circulating tumor cell
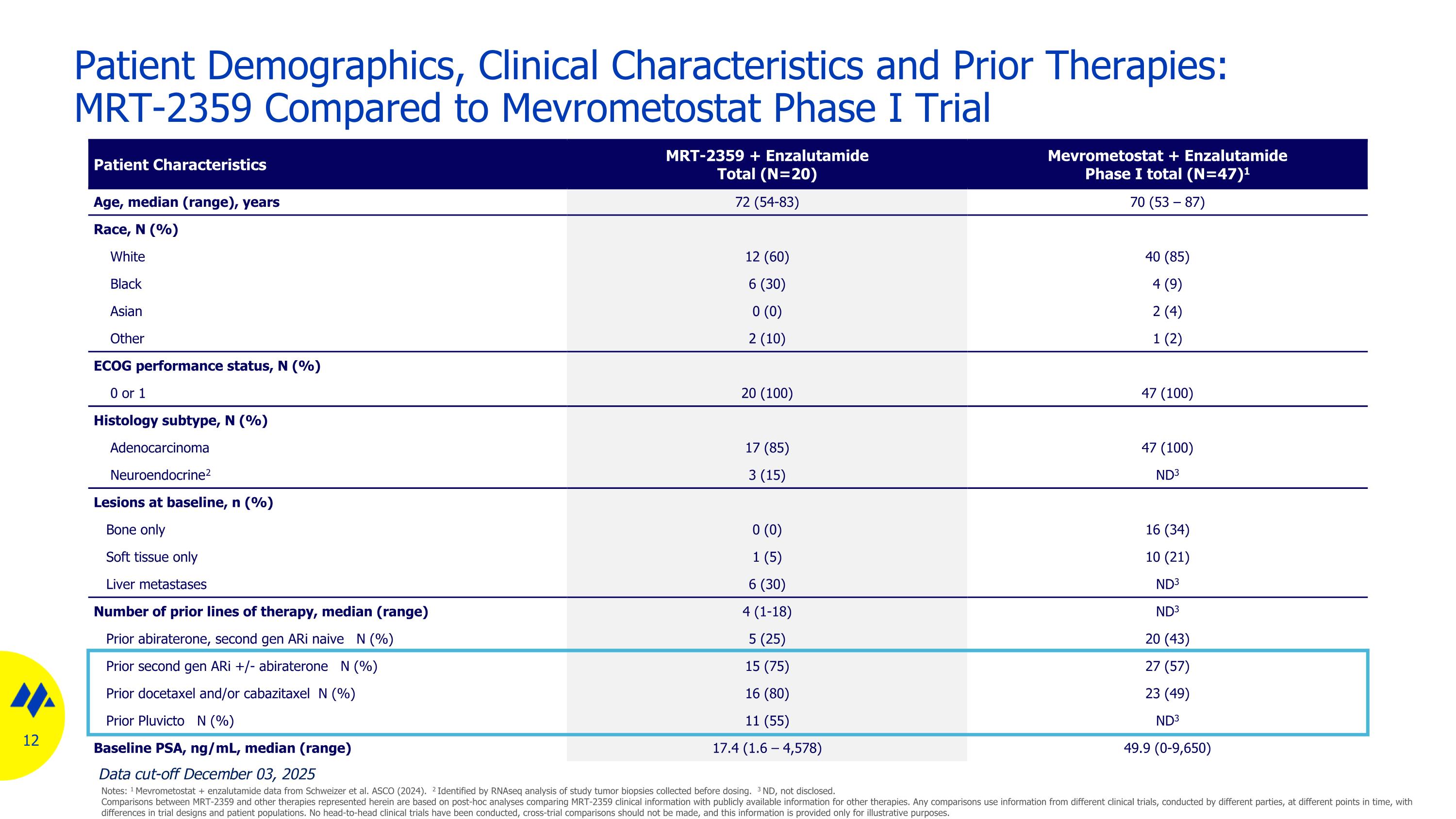
Patient Demographics, Clinical Characteristics and Prior Therapies: MRT-2359 Compared to Mevrometostat Phase I Trial Patient Characteristics MRT-2359 + Enzalutamide Total (N=20) Mevrometostat + Enzalutamide Phase I total (N=47)1 Age, median (range), years 72 (54-83) 70 (53 – 87) Race, N (%) White 12 (60) 40 (85) Black 6 (30) 4 (9) Asian 0 (0) 2 (4) Other 2 (10) 1 (2) ECOG performance status, N (%) 0 or 1 20 (100) 47 (100) Histology subtype, N (%) Adenocarcinoma 17 (85) 47 (100) Neuroendocrine2 3 (15) ND3 Lesions at baseline, n (%) Bone only 0 (0) 16 (34) Soft tissue only 1 (5) 10 (21) Liver metastases 6 (30) ND3 Number of prior lines of therapy, median (range) 4 (1-18) ND3 Prior abiraterone, second gen ARi naive N (%) 5 (25) 20 (43) Prior second gen ARi +/- abiraterone N (%) 15 (75) 27 (57) Prior docetaxel and/or cabazitaxel N (%) 16 (80) 23 (49) Prior Pluvicto N (%) 11 (55) ND3 Baseline PSA, ng/mL, median (range) 17.4 (1.6 – 4,578) 49.9 (0-9,650) Data cut-off December 03, 2025 Notes: 1 Mevrometostat + enzalutamide data from Schweizer et al. ASCO (2024). 2 Identified by RNAseq analysis of study tumor biopsies collected before dosing. 3 ND, not disclosed. Comparisons between MRT-2359 and other therapies represented herein are based on post-hoc analyses comparing MRT-2359 clinical information with publicly available information for other therapies. Any comparisons use information from different clinical trials, conducted by different parties, at different points in time, with differences in trial designs and patient populations. No head-to-head clinical trials have been conducted, cross-trial comparisons should not be made, and this information is provided only for illustrative purposes.
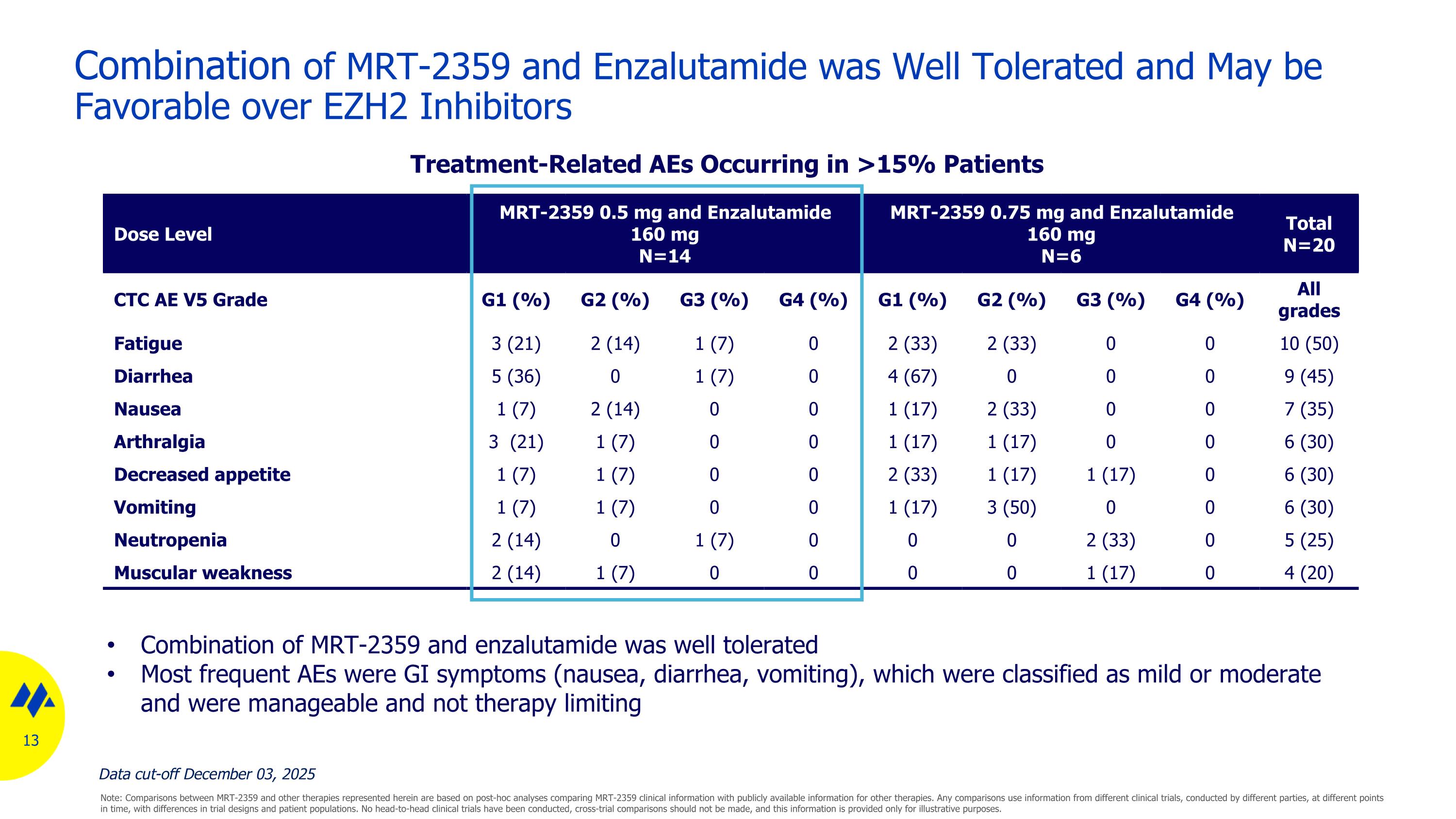
Combination of MRT-2359 and Enzalutamide was Well Tolerated and May be Favorable over EZH2 Inhibitors Dose Level MRT-2359 0.5 mg and Enzalutamide 160 mg N=14 MRT-2359 0.75 mg and Enzalutamide 160 mg N=6 Total N=20 CTC AE V5 Grade G1 (%) G2 (%) G3 (%) G4 (%) G1 (%) G2 (%) G3 (%) G4 (%) All grades Fatigue 3 (21) 2 (14) 1 (7) 0 2 (33) 2 (33) 0 0 10 (50) Diarrhea 5 (36) 0 1 (7) 0 4 (67) 0 0 0 9 (45) Nausea 1 (7) 2 (14) 0 0 1 (17) 2 (33) 0 0 7 (35) Arthralgia 3 (21) 1 (7) 0 0 1 (17) 1 (17) 0 0 6 (30) Decreased appetite 1 (7) 1 (7) 0 0 2 (33) 1 (17) 1 (17) 0 6 (30) Vomiting 1 (7) 1 (7) 0 0 1 (17) 3 (50) 0 0 6 (30) Neutropenia 2 (14) 0 1 (7) 0 0 0 2 (33) 0 5 (25) Muscular weakness 2 (14) 1 (7) 0 0 0 0 1 (17) 0 4 (20) Combination of MRT-2359 and enzalutamide was well tolerated Most frequent AEs were GI symptoms (nausea, diarrhea, vomiting), which were classified as mild or moderate and were manageable and not therapy limiting Treatment-Related AEs Occurring in >15% Patients Note: Comparisons between MRT-2359 and other therapies represented herein are based on post-hoc analyses comparing MRT-2359 clinical information with publicly available information for other therapies. Any comparisons use information from different clinical trials, conducted by different parties, at different points in time, with differences in trial designs and patient populations. No head-to-head clinical trials have been conducted, cross-trial comparisons should not be made, and this information is provided only for illustrative purposes. Data cut-off December 03, 2025
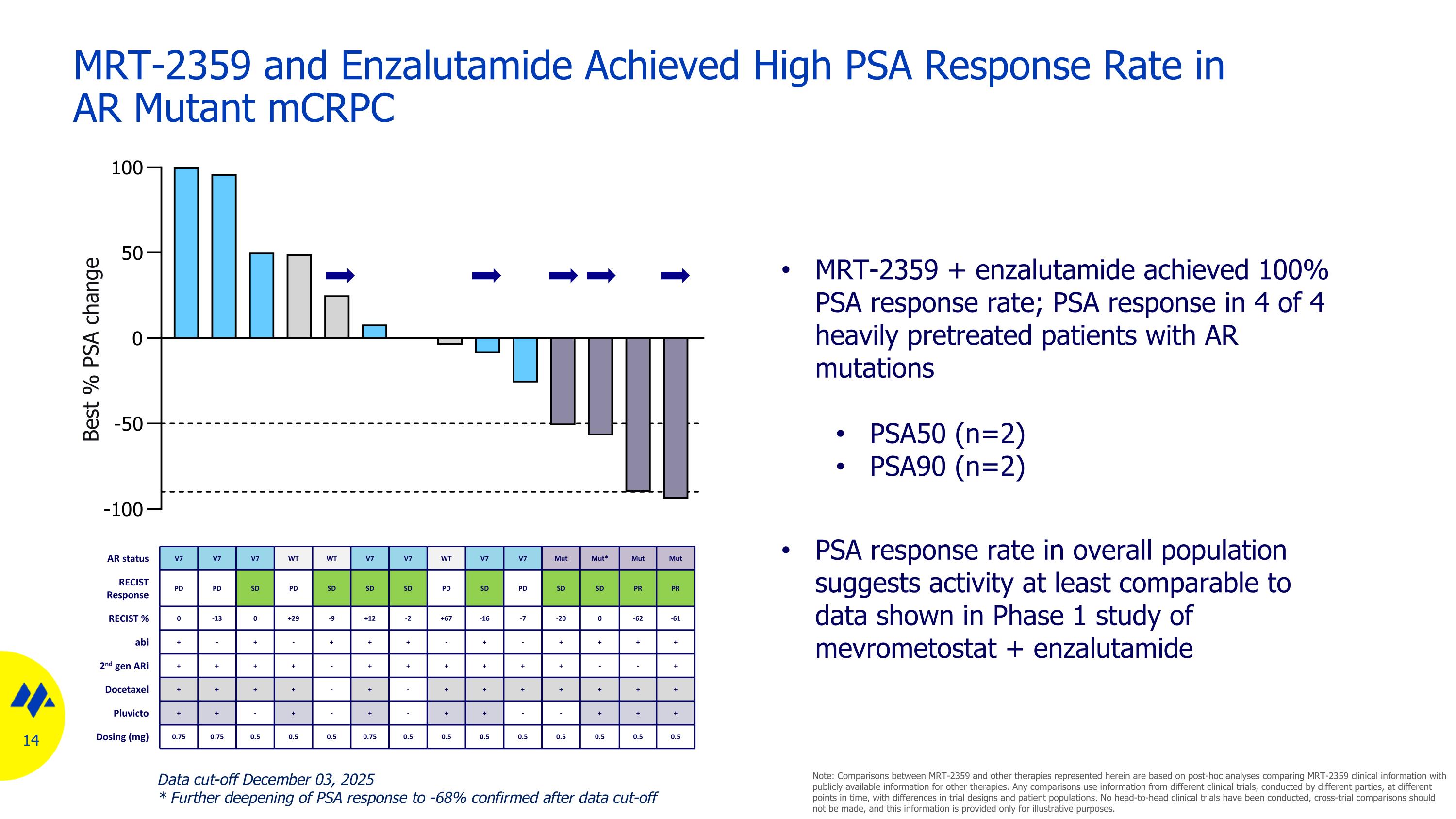
MRT-2359 and Enzalutamide Achieved High PSA Response Rate in AR Mutant mCRPC AR status V7 V7 V7 WT WT V7 V7 WT V7 V7 Mut Mut* Mut Mut RECIST Response PD PD SD PD SD SD SD PD SD PD SD SD PR PR RECIST % 0 -13 0 +29 -9 +12 -2 +67 -16 -7 -20 0 -62 -61 abi + - + - + + + - + - + + + + 2nd gen ARi + + + + - + + + + + + - - + Docetaxel + + + + - + - + + + + + + + Pluvicto + + - + - + - + + - - + + + Dosing (mg) 0.75 0.75 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.75 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 Best % PSA change MRT-2359 + enzalutamide achieved 100% PSA response rate; PSA response in 4 of 4 heavily pretreated patients with AR mutations PSA50 (n=2) PSA90 (n=2) PSA response rate in overall population suggests activity at least comparable to data shown in Phase 1 study of mevrometostat + enzalutamide Data cut-off December 03, 2025 * Further deepening of PSA response to -68% confirmed after data cut-off Note: Comparisons between MRT-2359 and other therapies represented herein are based on post-hoc analyses comparing MRT-2359 clinical information with publicly available information for other therapies. Any comparisons use information from different clinical trials, conducted by different parties, at different points in time, with differences in trial designs and patient populations. No head-to-head clinical trials have been conducted, cross-trial comparisons should not be made, and this information is provided only for illustrative purposes.
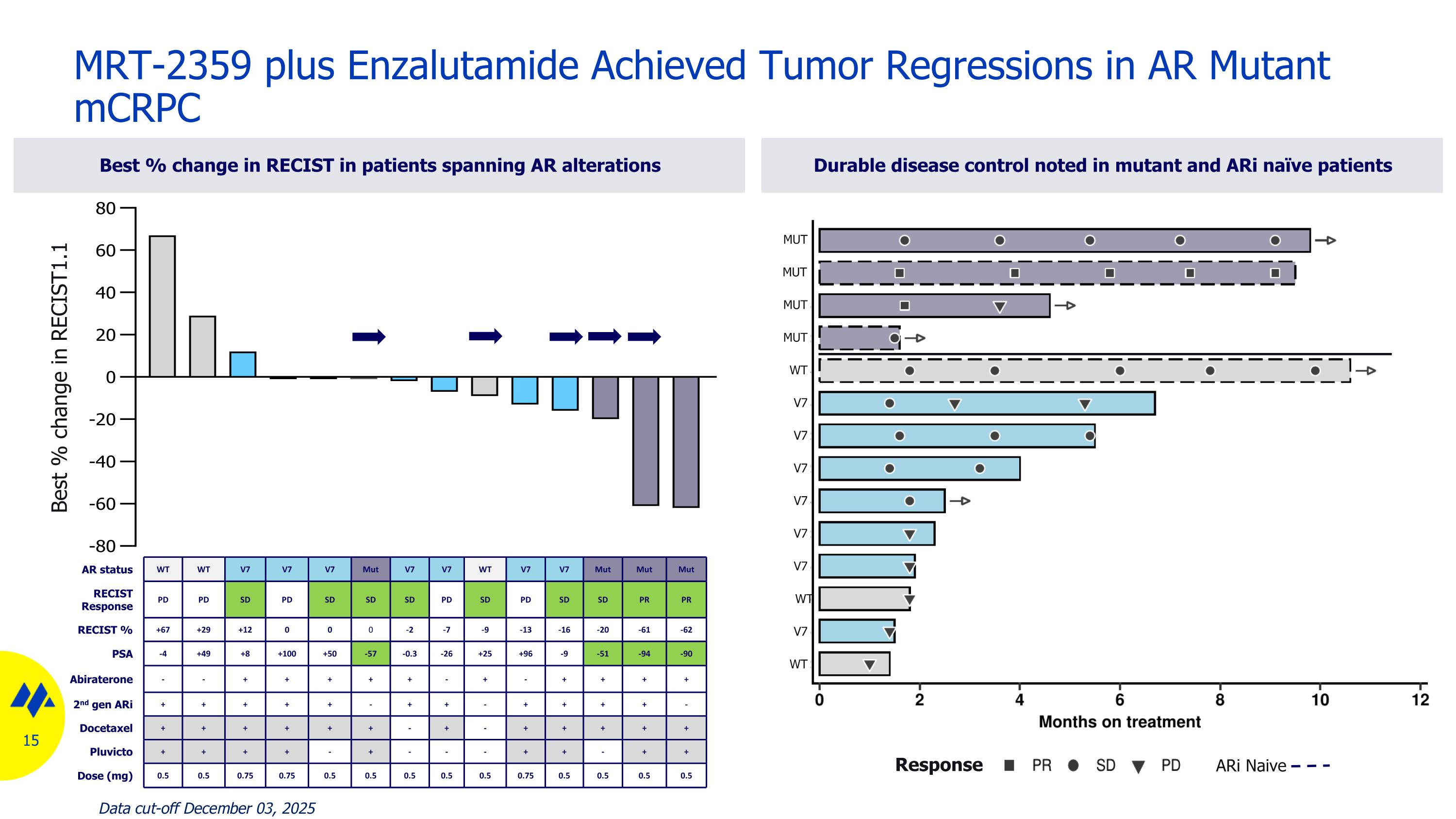
MRT-2359 plus Enzalutamide Achieved Tumor Regressions in AR Mutant mCRPC Best % change in RECIST in patients spanning AR alterations Durable disease control noted in mutant and ARi naïve patients AR status WT WT V7 V7 V7 Mut V7 V7 WT V7 V7 Mut Mut Mut RECIST Response PD PD SD PD SD SD SD PD SD PD SD SD PR PR RECIST % +67 +29 +12 0 0 0 -2 -7 -9 -13 -16 -20 -61 -62 PSA -4 +49 +8 +100 +50 -57 -0.3 -26 +25 +96 -9 -51 -94 -90 Abiraterone - - + + + + + - + - + + + + 2nd gen ARi + + + + + - + + - + + + + - Docetaxel + + + + + + - + - + + + + + Pluvicto + + + + - + - - - + + - + + Dose (mg) 0.5 0.5 0.75 0.75 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.75 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 Best % change in RECIST1.1 MUT MUT MUT MUT WT V7 V7 V7 V7 V7 V7 WT V7 WT ARi Naive Response Data cut-off December 03, 2025
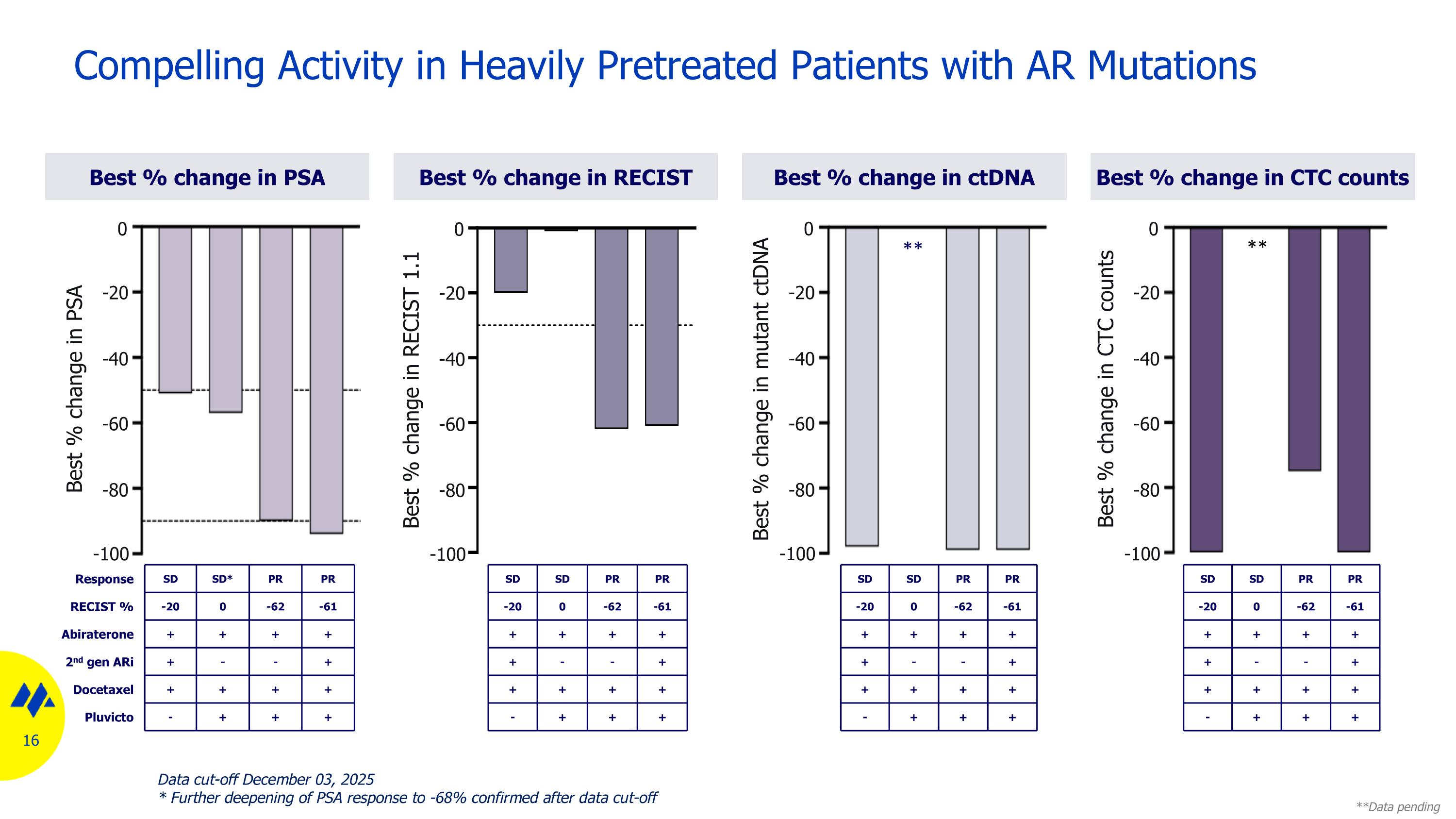
Compelling Activity in Heavily Pretreated Patients with AR Mutations Best % change in ctDNA Best % change in RECIST Best % change in CTC counts Best % change in PSA Response SD SD* PR PR RECIST % -20 0 -62 -61 Abiraterone + + + + 2nd gen ARi + - - + Docetaxel + + + + Pluvicto - + + + N/A N/D 0 -20 -40 -60 -80 -100 Best % change in PSA N/A SD SD PR PR -20 0 -62 -61 + + + + + - - + + + + + - + + + ** **Data pending SD SD PR PR -20 0 -62 -61 + + + + + - - + + + + + - + + + SD SD PR PR -20 0 -62 -61 + + + + + - - + + + + + - + + + ** 0 -20 -40 -60 -80 -100 Best % change in RECIST 1.1 0 -20 -40 -60 -80 -100 Best % change in mutant ctDNA 0 -20 -40 -60 -80 -100 Best % change in CTC counts Data cut-off December 03, 2025 * Further deepening of PSA response to -68% confirmed after data cut-off
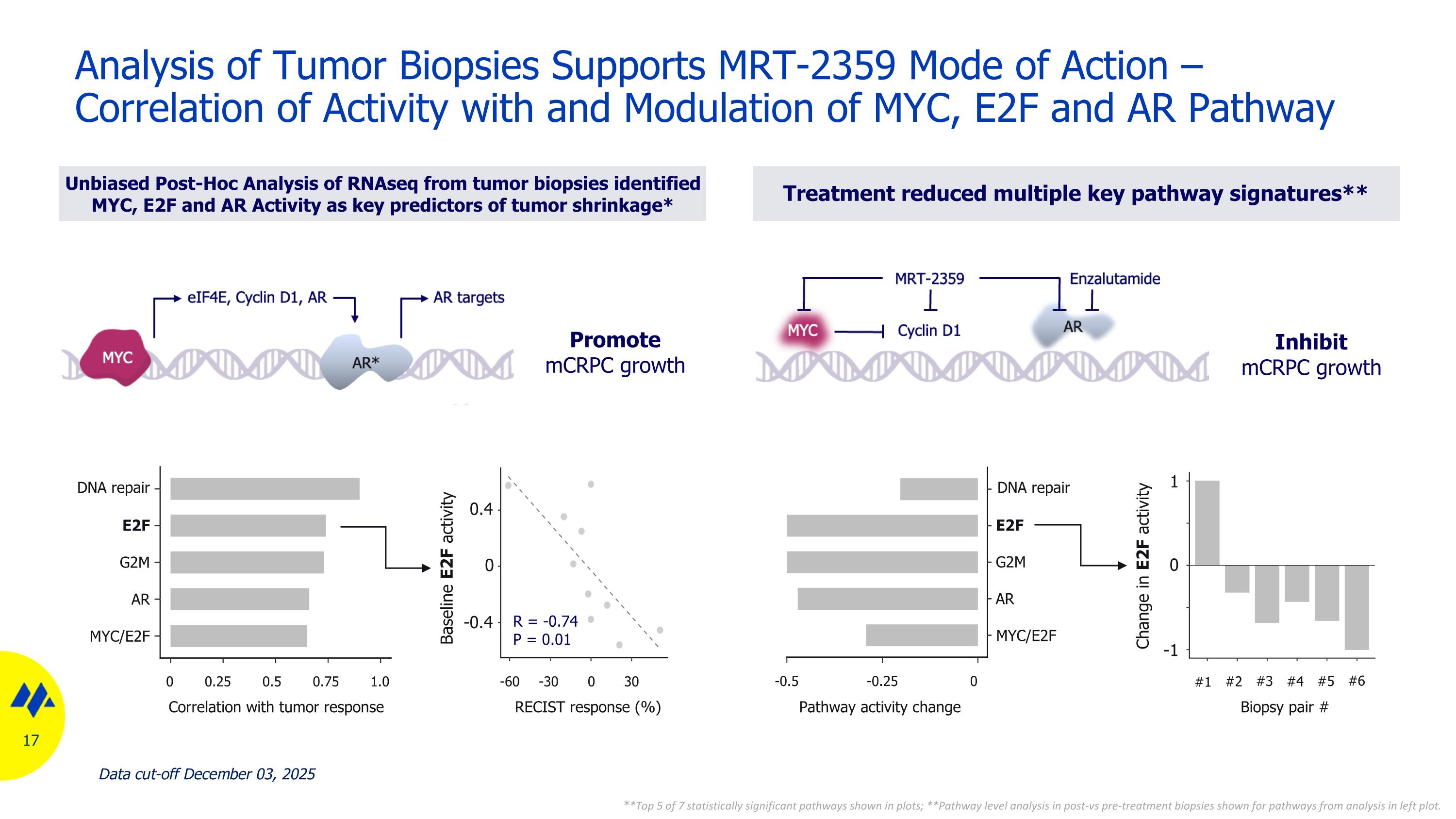
Analysis of Tumor Biopsies Supports MRT-2359 Mode of Action – Correlation of Activity with and Modulation of MYC, E2F and AR Pathway Unbiased Post-Hoc Analysis of RNAseq from tumor biopsies identified MYC, E2F and AR Activity as key predictors of tumor shrinkage* Treatment reduced multiple key pathway signatures** Baseline E2F activity 0 -1 DNA repair E2F G2M AR MYC/E2F Correlation with tumor response 1.0 0.75 0.5 0.25 0 30 0 -30 -60 RECIST response (%) 0 -0.4 0.4 DNA repair E2F G2M AR MYC/E2F Pathway activity change 0 -0.25 -0.5 #1 #2 #3 #4 #5 #6 Biopsy pair # **Top 5 of 7 statistically significant pathways shown in plots; **Pathway level analysis in post-vs pre-treatment biopsies shown for pathways from analysis in left plot. Change in E2F activity R = -0.74 P = 0.01 Promote mCRPC growth Inhibit mCRPC growth 1 Data cut-off December 03, 2025
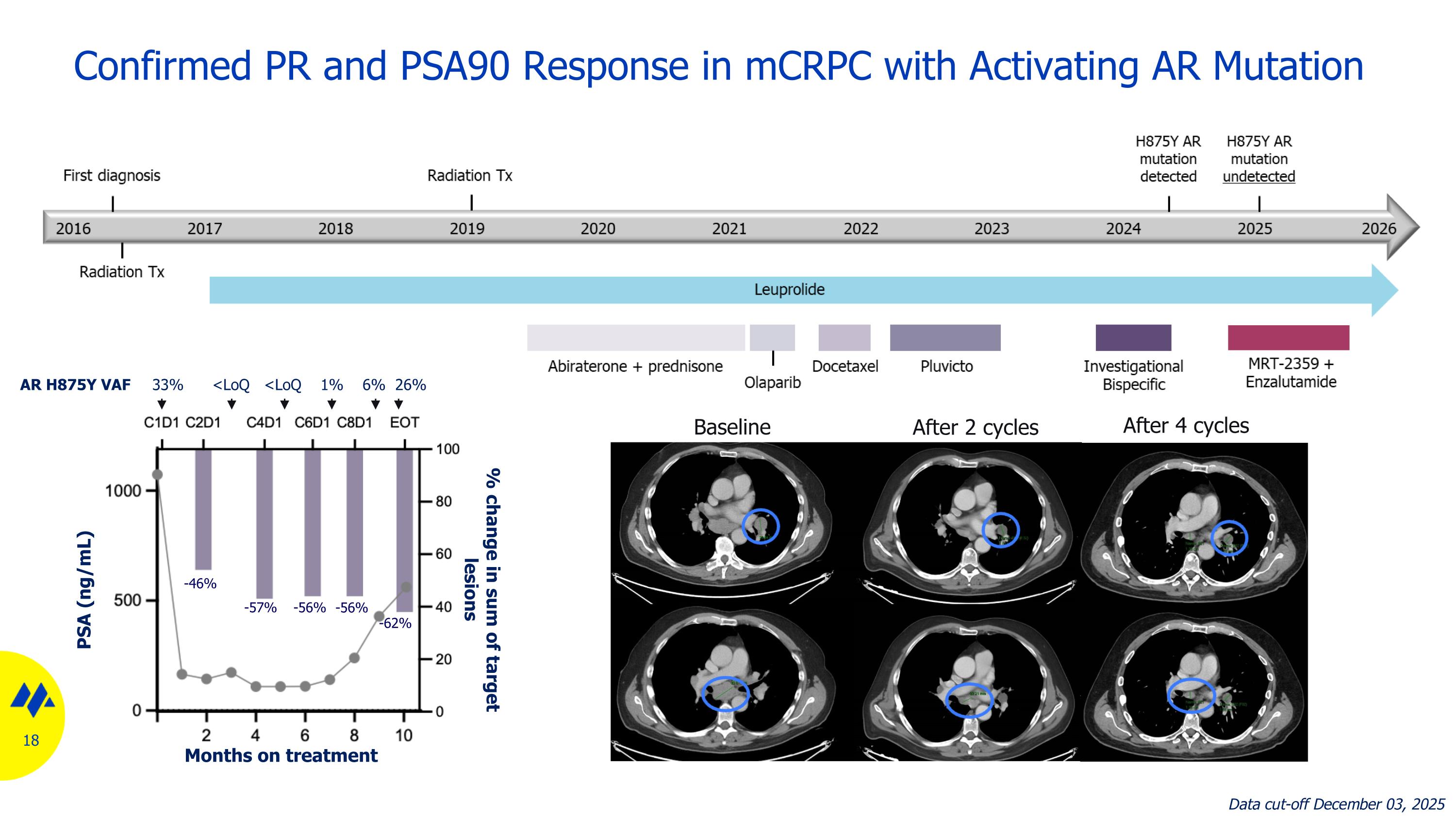
Confirmed PR and PSA90 Response in mCRPC with Activating AR Mutation Baseline After 2 cycles After 4 cycles Treatment cycle -46% -57% -56% -56% -62% AR H875Y VAF 33% <LoQ <LoQ 1% 6% 26% Months on treatment PSA (ng/mL) % change in sum of target lesions Data cut-off December 03, 2025
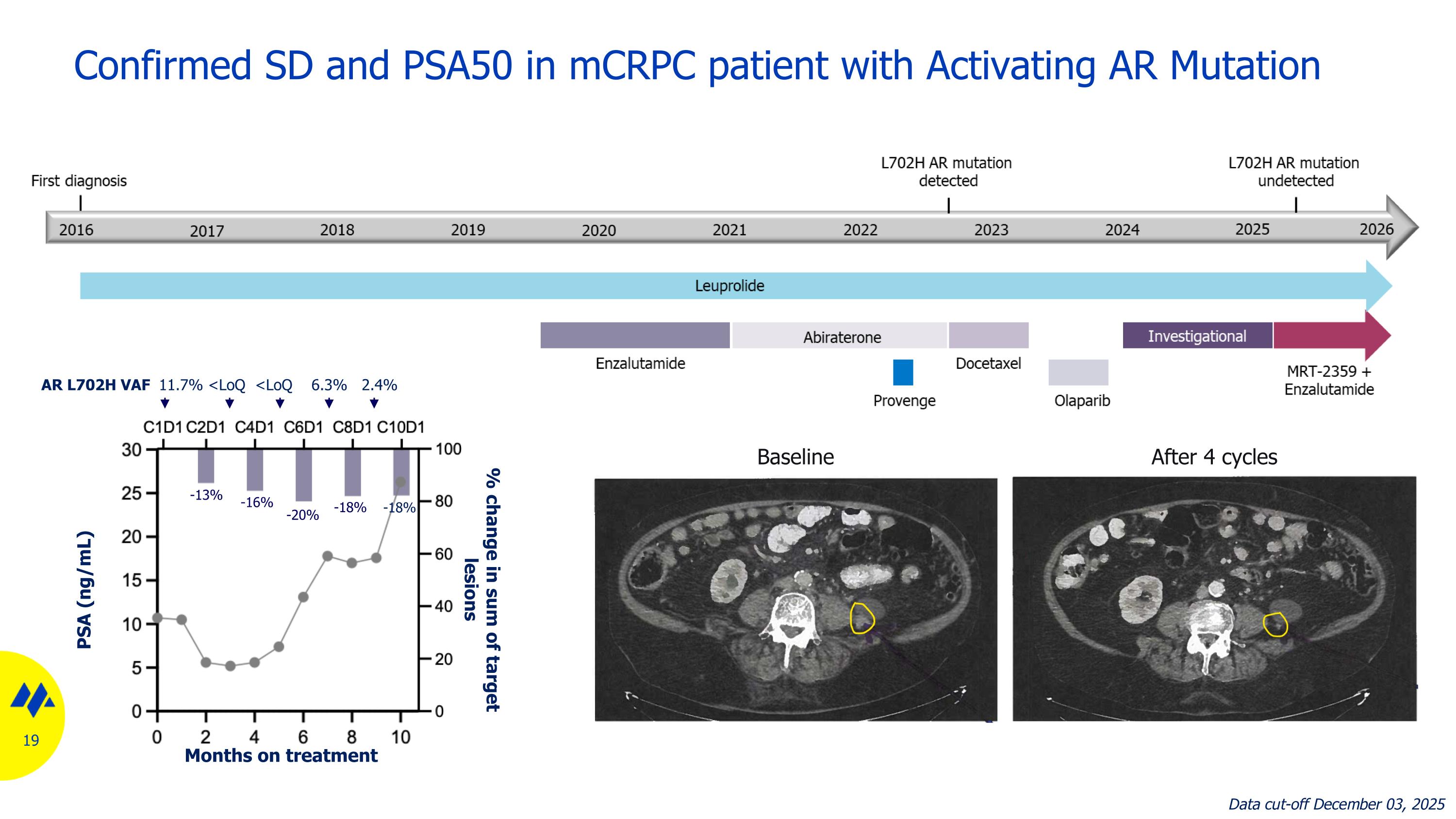
Confirmed SD and PSA50 in mCRPC patient with Activating AR Mutation AR L702H VAF 11.7% <LoQ <LoQ 6.3% 2.4% Baseline After 4 cycles -13% -16% -20% -18% -18% Data cut-off December 03, 2025 Months on treatment PSA (ng/mL) % change in sum of target lesions

Next Steps
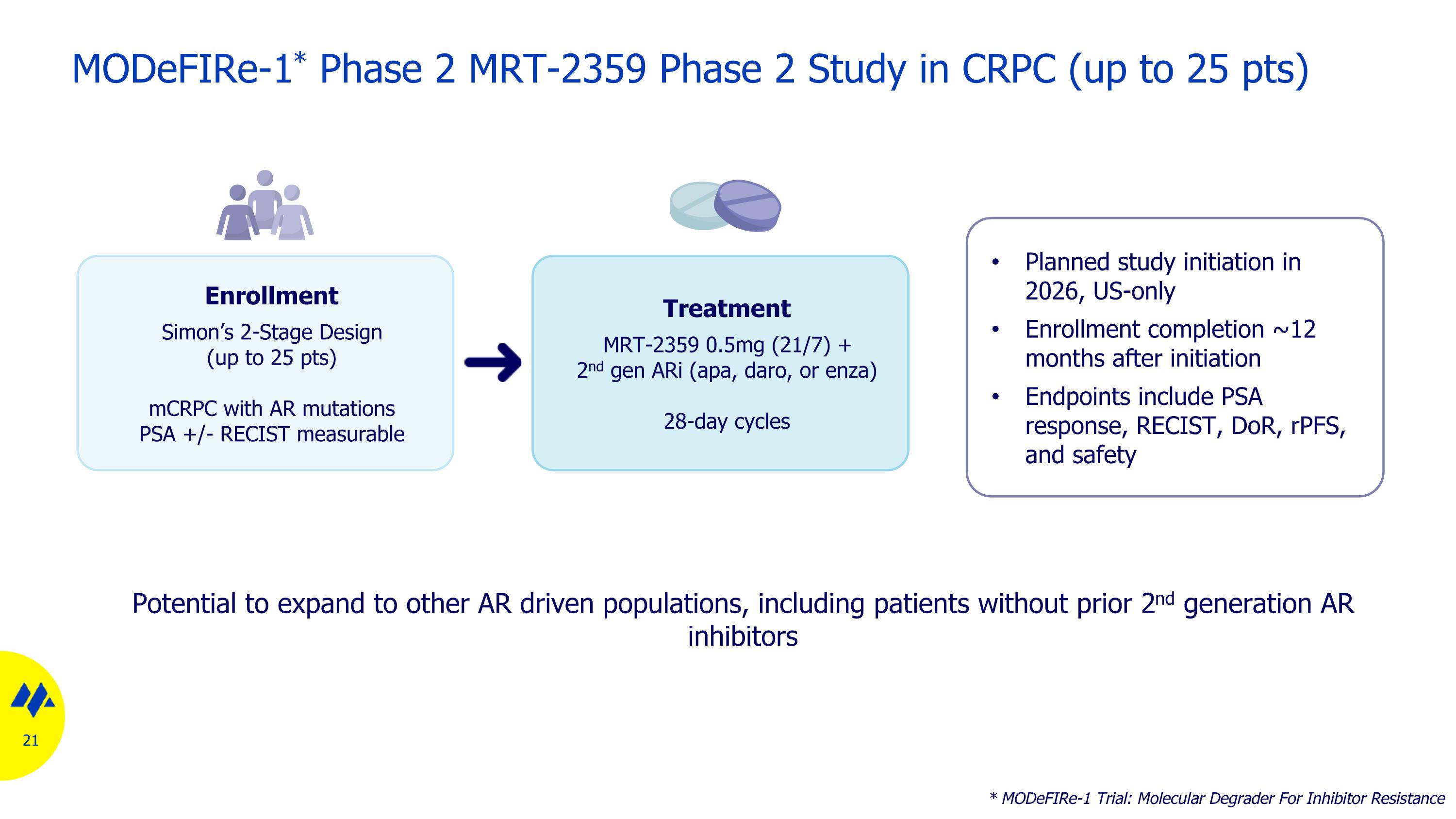
MODeFIRe-1* Phase 2 MRT-2359 Phase 2 Study in CRPC (up to 25 pts) * MODeFIRe-1 Trial: Molecular Degrader For Inhibitor Resistance Enrollment Simon’s 2-Stage Design (up to 25 pts) mCRPC with AR mutations PSA +/- RECIST measurable Treatment MRT-2359 0.5mg (21/7) + 2nd gen ARi (apa, daro, or enza) 28-day cycles Planned study initiation in 2026, US-only Enrollment completion ~12 months after initiation Endpoints include PSA response, RECIST, DoR, rPFS, and safety Potential to expand to other AR driven populations, including patients without prior 2nd generation AR inhibitors

Summary

MRT-2359 in combination with enzalutamide achieved compelling clinical activity (100% PSA response) in a subset of heavily pre-treated metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) patients with androgen receptor (AR) mutations. Overall disease control rate (DCR) of 64% in a total of 14 evaluable patients Combination of MRT-2359 and enzalutamide was well tolerated with mild or moderate manageable GI adverse events (AEs) being the most frequent toxicities Data support potential of combination of MRT-2359 with 2nd generation androgen receptor inhibitors for mCRPC patients with AR mutations (up to 30% of 2nd line+ mCRPC), with additional potential in earlier line settings or in combination with other agents Updated data from the Phase 1/2 study expected to be presented at ASCO Genitourinary Cancers Symposium in February 2026 Planning to initiate a signal-confirming 2-stage Phase 2 study of MRT-2359 in combination with 2nd generation AR inhibitor to target AR-mutated mCRPC in 2026 Summary and Next Steps
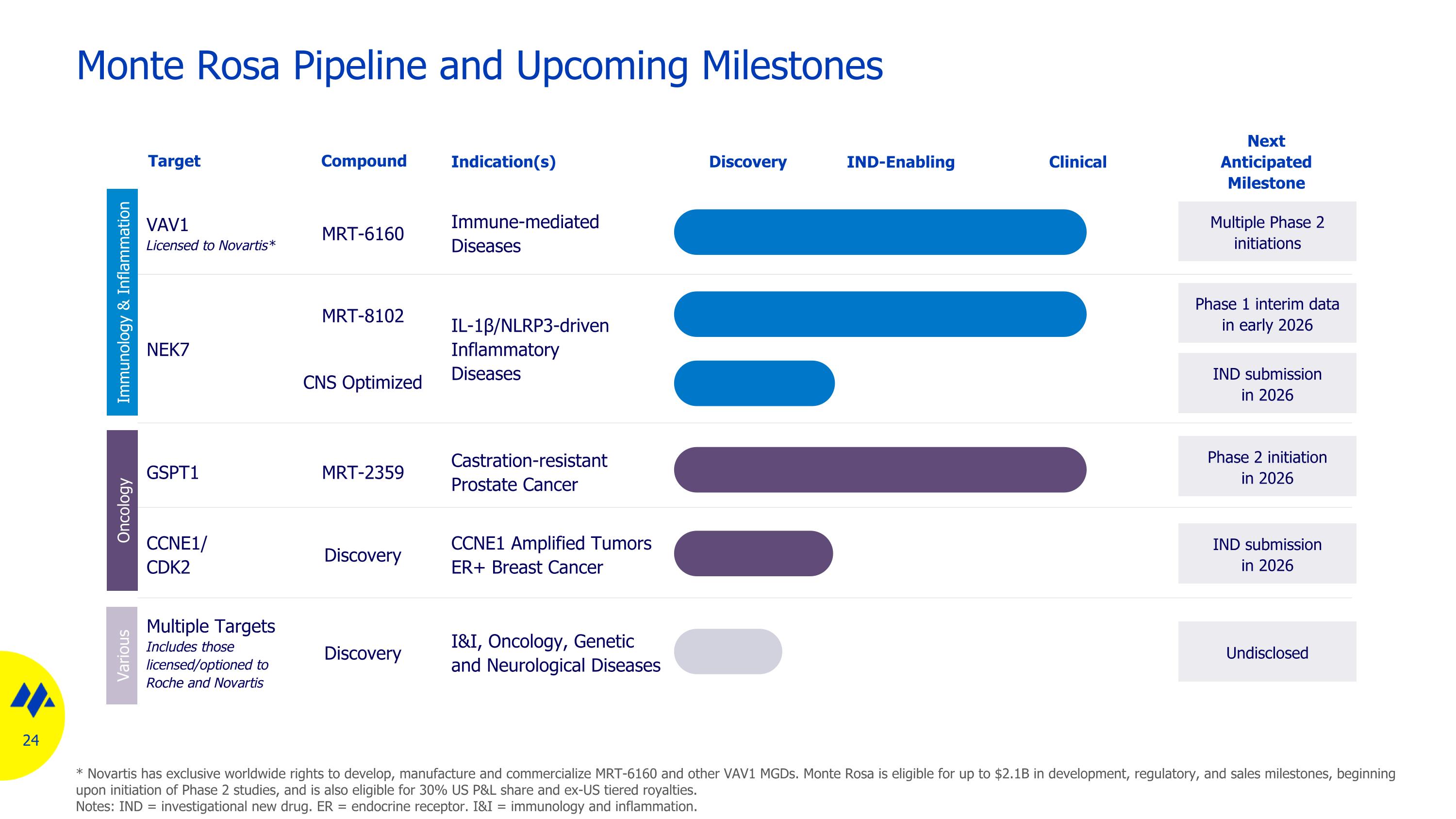
Monte Rosa Pipeline and Upcoming Milestones GSPT1 Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer IL-1β/NLRP3-driven Inflammatory Diseases VAV1 Licensed to Novartis* Immune-mediated Diseases Discovery Target Indication(s) Phase 2 initiation in 2026 Next Anticipated Milestone IND-Enabling Clinical Phase 1 interim data in early 2026 Multiple Phase 2 initiations Multiple Targets Includes those licensed/optioned to Roche and Novartis I&I, Oncology, Genetic and Neurological Diseases Undisclosed NEK7 Compound MRT-2359 MRT-6160 MRT-8102 Discovery IND submission in 2026 CNS Optimized CCNE1/ CDK2 CCNE1 Amplified Tumors ER+ Breast Cancer IND submission in 2026 Discovery Immunology & Inflammation Oncology Various * Novartis has exclusive worldwide rights to develop, manufacture and commercialize MRT-6160 and other VAV1 MGDs. Monte Rosa is eligible for up to $2.1B in development, regulatory, and sales milestones, beginning upon initiation of Phase 2 studies, and is also eligible for 30% US P&L share and ex-US tiered royalties. Notes: IND = investigational new drug. ER = endocrine receptor. I&I = immunology and inflammation.
Q&A

Thank you