

.2 1ST QUARTER 2026 Biomea Fusion Corporate Presentation

LEGAL DISCLAIMER & FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS Certain statements in this presentation and the accompanying oral commentary are forward-looking statements. These statements relate to future events or the future business and financial performance of Biomea Fusion, Inc. (the “Company”) and involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties, and other factors that may cause the actual results, levels of activity, performance or achievements of the Company or its industry to be materially different from those expressed or implied by any forward-looking statements. In some cases, forward-looking statements can be identified by terminology such as “may,” “will,” “could,” “would,” “should,” “expect,” “plan,” “anticipate,” “intend,” “believe,” “estimate,” “predict,” “potential” or other comparable terminology. All statements other than statements of historical fact could be deemed forward-looking, including any projections of financial information or profitability, the initiation, timing and results of pending or future preclinical studies and clinical trials, the actual or potential actions of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the status and timing of ongoing research, development and corporate partnering activities, any statements about historical results that may suggest trends for the Company's business; any statements of the plans, strategies, and objectives of management for future operations and any statements of expectation or belief regarding future events, potential markets or market size, or technology developments. The Company has based these forward-looking statements on its current expectations, assumptions, estimates, and projections. While the Company believes these expectations, assumptions, estimates and projections are reasonable, such forward-looking statements are only predictions and involve known and unknown risks and uncertainties, many of which are beyond the Company's control. For a discussion of these and other risks and uncertainties, and other important factors, any of which could cause our actual results to differ from those contained in the forward-looking statements, see the section entitled Risk Factors in our most recent annual report on Form 10-K filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the SEC), as well as discussions of potential risks, uncertainties, and other important factors in our other subsequent filings with the SEC. The forward-looking statements in this presentation are made only as of the date hereof. Except as required by law, the Company assumes no obligation and does not intend to update these forward- looking statements or to conform these statements to actual results or to changes in the Company's expectations. This presentation also contains estimates and other statistical data made by independent parties and by us relating to market size and growth and other data about our industry. This data involves a number of assumptions and limitations, and you are cautioned not to give undue weight to such estimates. In addition, projections, assumptions, and estimates of our future performance and the future performance of the markets in which we operate are necessarily subject to a high degree of uncertainty and risk.

Transformative Oral Therapies for Metabolic Disease ICOVAMENIB BMF-650 Biomea Fusion Potentially first-in-class Next-generation, (NASDAQ:BMEA) is a diabetes and investigational selective investigational oral GLP- obesity medicines company developing oral small menin inhibitor 1 receptor agonist molecules with the potential to restore beta cell • SMALL MOLECULE • SMALL MOLECULE function and reduce body weight while providing • ORAL • ORAL convenient, patient-friendly treatment options. • TARGET: DIABETES • TARGET: OBESITY 3
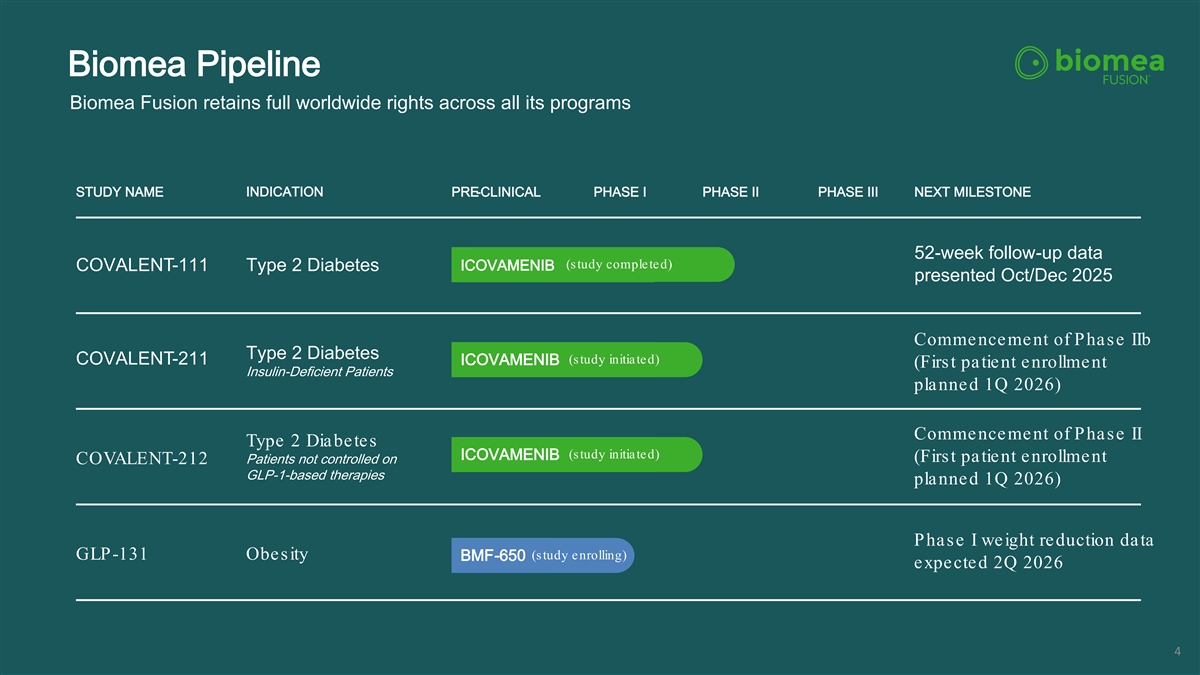
Biomea Pipeline Biomea Fusion retains full worldwide rights across all its programs STUDY NAME INDICATION PRE-CLINICAL PHASE I PHASE II PHASE III NEXT MILESTONE 52-week follow-up data (study completed) COVALENT-111 Type 2 Diabetes ICOVAMENIB presented Oct/Dec 2025 Commencement of Phase IIb Type 2 Diabetes (study initiated) COVALENT-211 ICOVAMENIB (First patient enrollment Insulin-Deficient Patients planned 1Q 2026) Commencement of Phase II Type 2 Diabetes (study initiated) ICOVAMENIB (First patient enrollment Patients not controlled on COVALENT-212 GLP-1-based therapies planned 1Q 2026) Phase I weight reduction data (study enrolling) GLP-131 Obesity BMF-650 expected 2Q 2026 4

ICOVAMENIB Potential First -in-Class Oral Menin Inhibitor Target: DIABETES
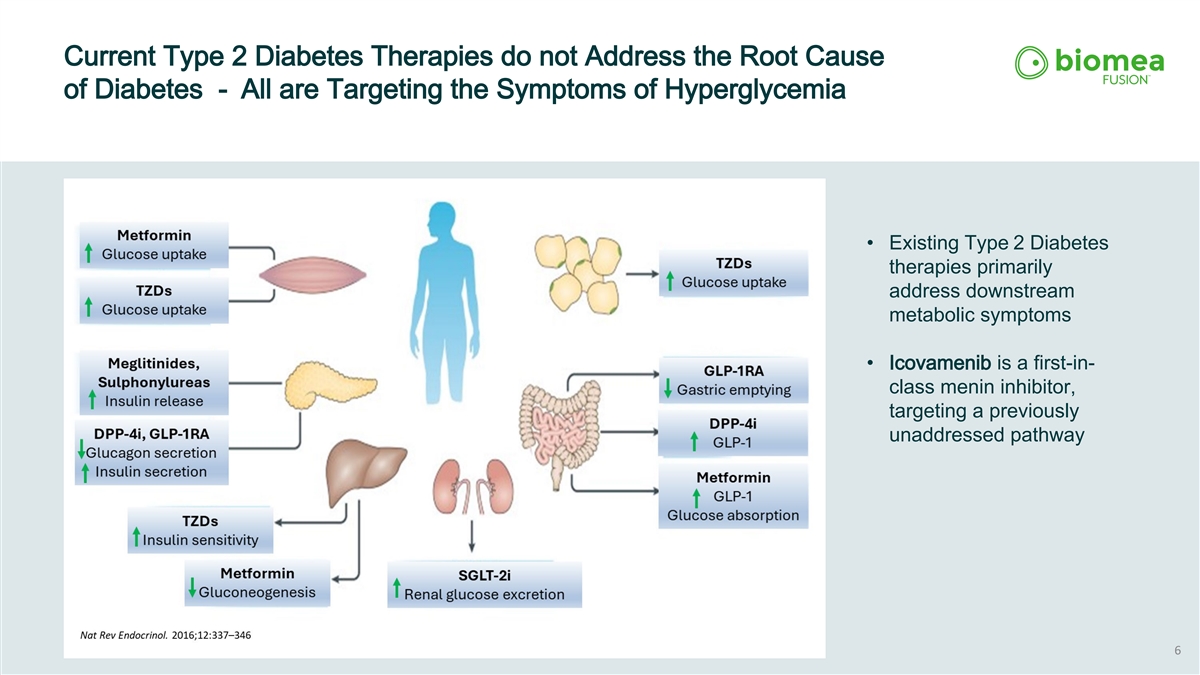
Current Type 2 Diabetes Therapies do not Address the Root Cause of Diabetes - All are Targeting the Symptoms of Hyperglycemia • Existing Type 2 Diabetes therapies primarily address downstream metabolic symptoms • Icovamenib is a first-in- class menin inhibitor, targeting a previously unaddressed pathway 6
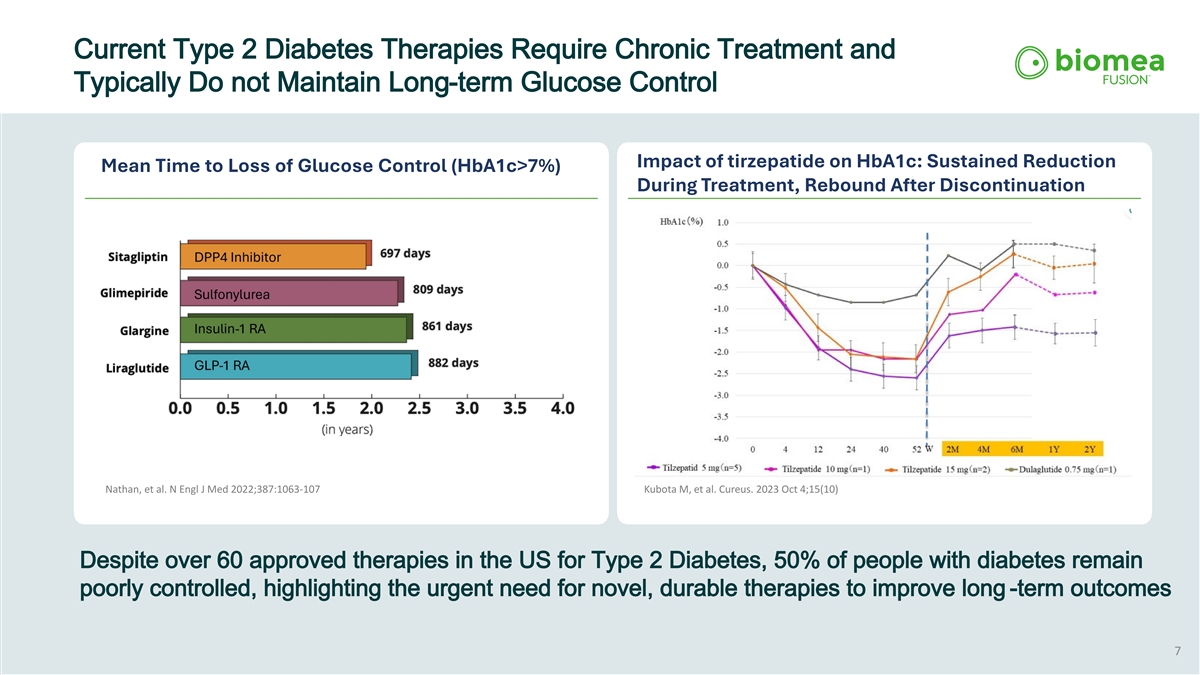
Current Type 2 Diabetes Therapies Require Chronic Treatment and Typically Do not Maintain Long-term Glucose Control Impact of tirzepatide on HbA1c: Sustained Reduction Mean Time to Loss of Glucose Control (HbA1c>7%) During Treatment, Rebound After Discontinuation Nathan, et al. N Engl J Med 2022;387:1063-107 Kubota M, et al. Cureus. 2023 Oct 4;15(10) Despite over 60 approved therapies in the US for Type 2 Diabetes, 50% of people with diabetes remain poorly controlled, highlighting the urgent need for novel, durable therapies to improve long -term outcomes 7
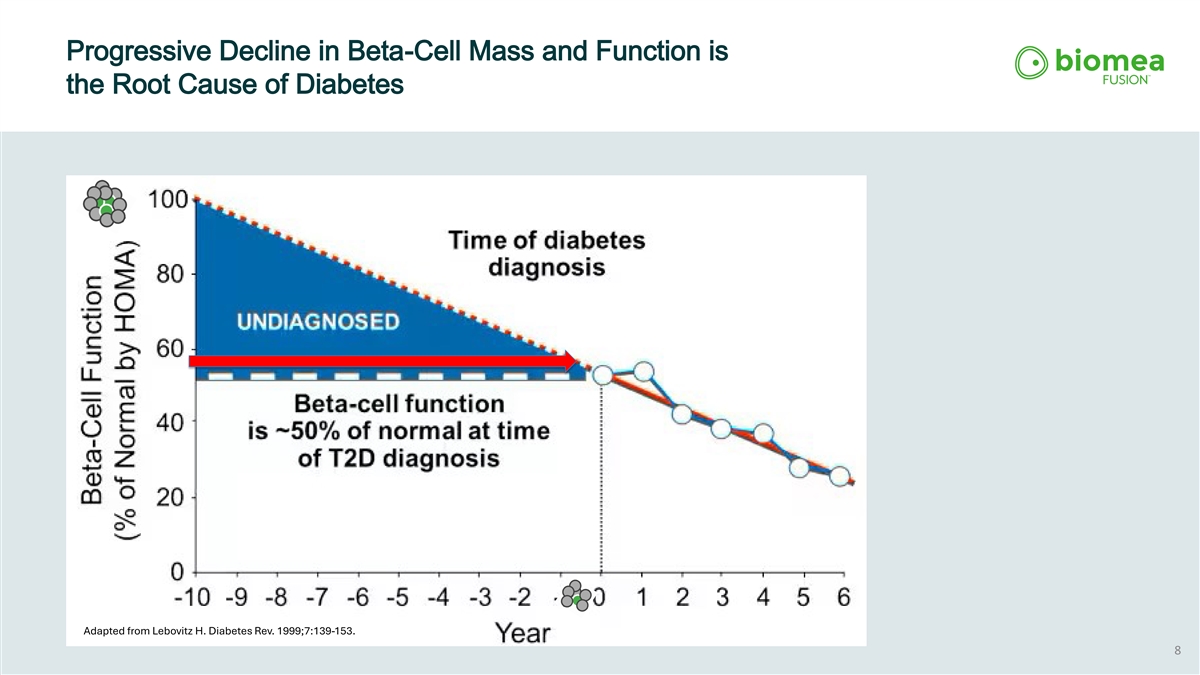
Progressive Decline in Beta-Cell Mass and Function is the Root Cause of Diabetes Adapted from Lebovitz H. Diabetes Rev. 1999;7:139-153. 8

ICOVAMENIB Addressing Diabetes at the Root Cause Level Icovamenib is a potentially first -in-class investigational oral therapy designed to be taken for 12 weeks to restore the body’s natural insulin production by regenerating beta cells - offering the potential for durable, disease-modifying benefits for diabetes patients. GENERALLY FAVORABLE ONCE-DAILY ORAL THERAPY NON-CHRONIC SAFETY-PROFILE OBSERVED TO DATE 9
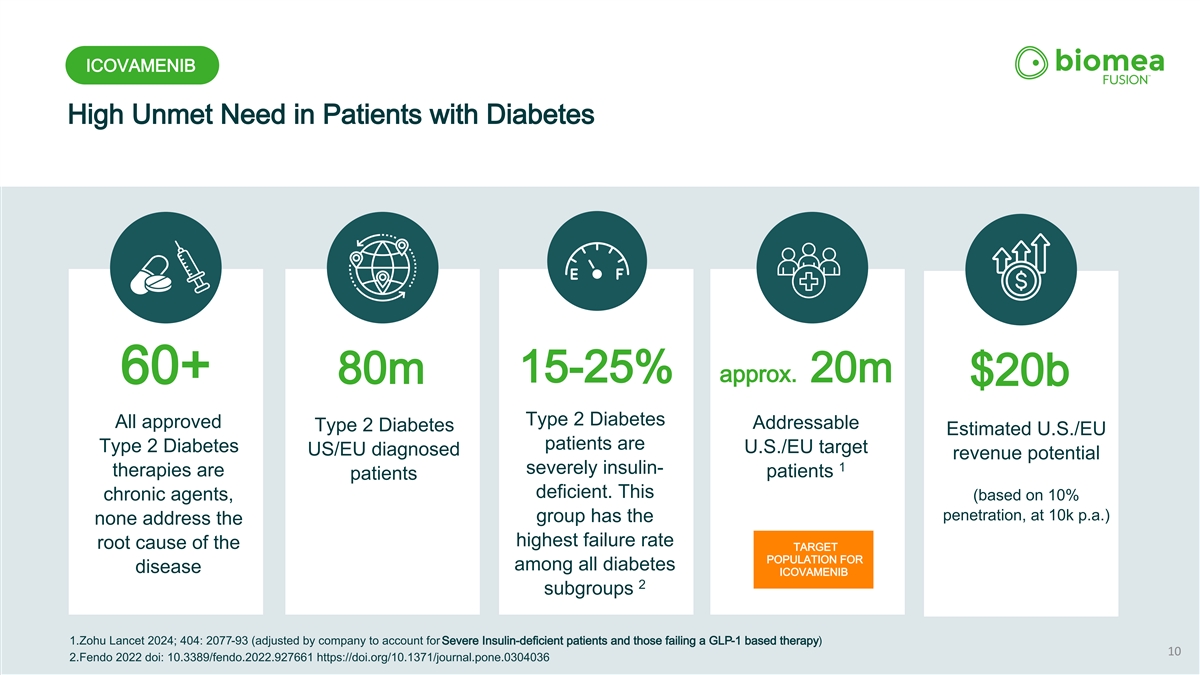
ICOVAMENIB High Unmet Need in Patients with Diabetes 15-25% approx. 20m 60+ 80m $20b Type 2 Diabetes All approved Addressable Type 2 Diabetes Estimated U.S./EU patients are Type 2 Diabetes U.S./EU target US/EU diagnosed revenue potential 1 severely insulin- therapies are patients patients deficient. This (based on 10% chronic agents, penetration, at 10k p.a.) group has the none address the highest failure rate root cause of the TARGET POPULATION FOR among all diabetes disease ICOVAMENIB 2 subgroups 1.Zohu Lancet 2024; 404: 2077-93 (adjusted by company to account for Severe Insulin-deficient patients and those failing a GLP-1 based therapy) 10 2.Fendo 2022 doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.927661 https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0304036

Menin is Naturally Inhibited During Pregnancy & Breastfeeding Allowing for Beta Cell Regeneration & Reduced Diabetes Risk Menin inhibition with icovamenib may phenocopy the marked reduction in Type 2 Diabetes incidence observed during pregnancy and after breastfeeding 1 • 2007 Stanford study found menin regulates islet growth during pregnancy • Elevated prolactin (during pregnancy and breastfeeding) lowers menin, 1 promoting beta cell growth • Nursing mice show higher beta cell mass than mice separated from their 2 offspring immediately postpartum Karnik SK, et al. Science. 2007;318:806-809 3-5 • In humans, lactation lowers the lifetime maternal T2D risk by up to 50% 5 • Reduced Type 2 Diabetes risk persists for up to 30 years postpartum 1. Karnik SK et al._2007_Science_Menin controls growth of pancreatic beta-cells in pregnant mice and promotes gestational diabetes mellitus. 2. Hens JR et al. Protective Effects Of Lactation On Maternal Metabolism. J Endocrine Soc, Volume 7, Issue Supplement_1, Abst ract citation ID: bvad114.737, Diabetes And Glucose Metabolism, THU302, October–November 2023. 3. Kim SY_2018_KJFM_Breastfeeding can reduce the risk of developing diabetes. 4. Pinho‐ Gomes A-C et al._2021_Diabetes Obes Metab_Association of lactation with maternal risk of type 2 diabetes - A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. 5. Gunderson EP et al._2018_JAMA Int Med_Lactation duration and progression to diabetes in women across the childbearing years - The 30-year CARDIA study 11
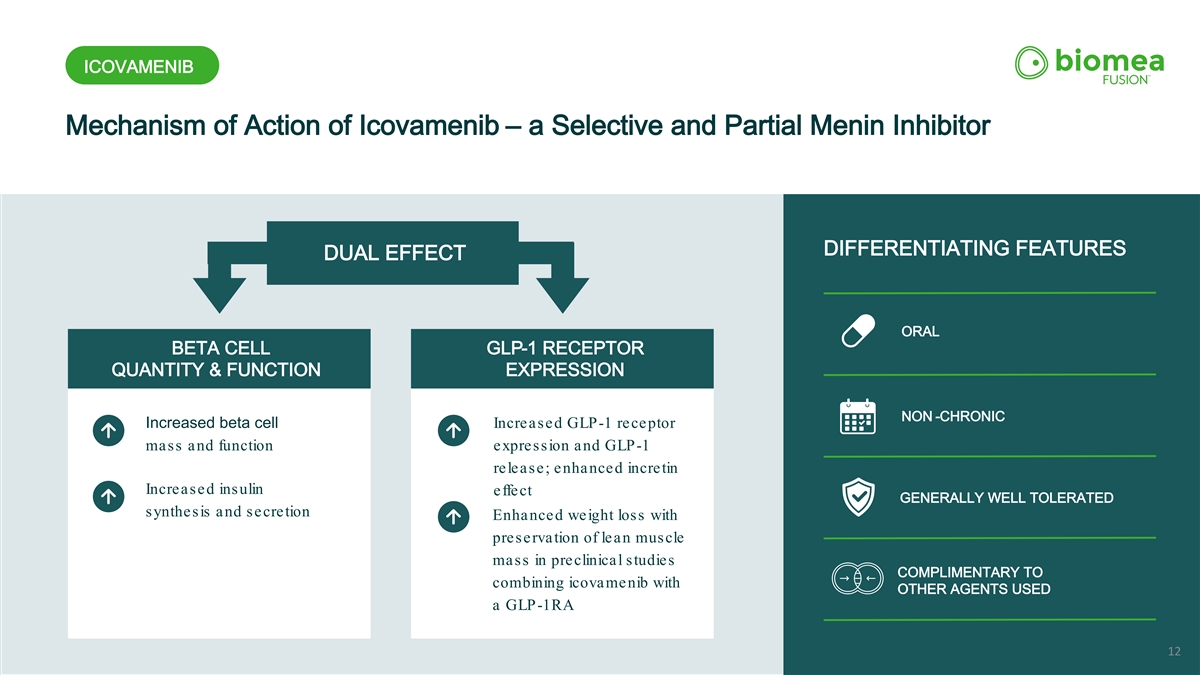
ICOVAMENIB Mechanism of Action of Icovamenib – a Selective and Partial Menin Inhibitor ORAL DIFFERENTIATING FEATURES DUAL EFFECT ORAL BETA CELL GLP-1 RECEPTOR QUANTITY & FUNCTION EXPRESSION NON -CHRONIC Increased beta cell Increased GLP-1 receptor mass and function expression and GLP-1 release; enhanced incretin Increased insulin effect GENERALLY WELL TOLERATED synthesis and secretion Enhanced weight loss with preservation of lean muscle mass in preclinical studies COMPLIMENTARY TO combining icovamenib with OTHER AGENTS USED a GLP-1RA 12

ICOVAMENIB 52-Week Results COVALENT-111 Phase II Study Icovamenib in Type 2 Diabetes – All Comers Reported in 4Q 2025
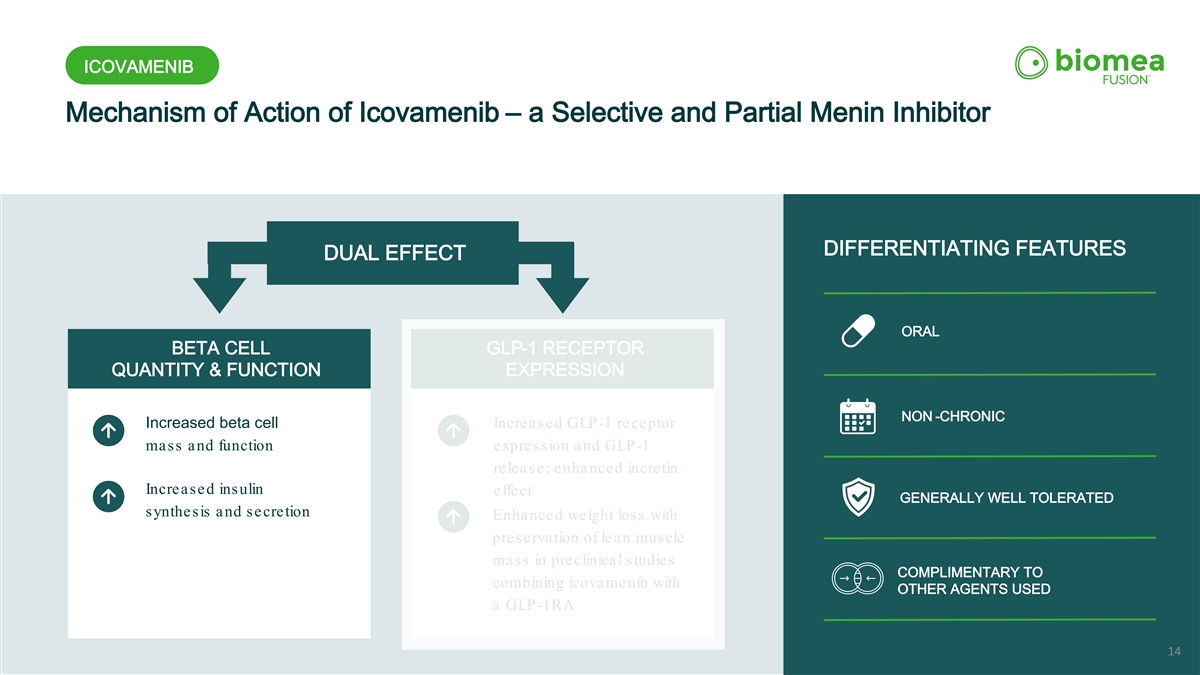
ICOVAMENIB Mechanism of Action of Icovamenib – a Selective and Partial Menin Inhibitor ORAL DIFFERENTIATING FEATURES DUAL EFFECT ORAL BETA CELL GLP-1 RECEPTOR QUANTITY & FUNCTION EXPRESSION NON -CHRONIC Increased beta cell Increased GLP-1 receptor mass and function expression and GLP-1 release; enhanced incretin Increased insulin effect GENERALLY WELL TOLERATED synthesis and secretion Enhanced weight loss with preservation of lean muscle mass in preclinical studies COMPLIMENTARY TO combining icovamenib with OTHER AGENTS USED a GLP-1RA 14
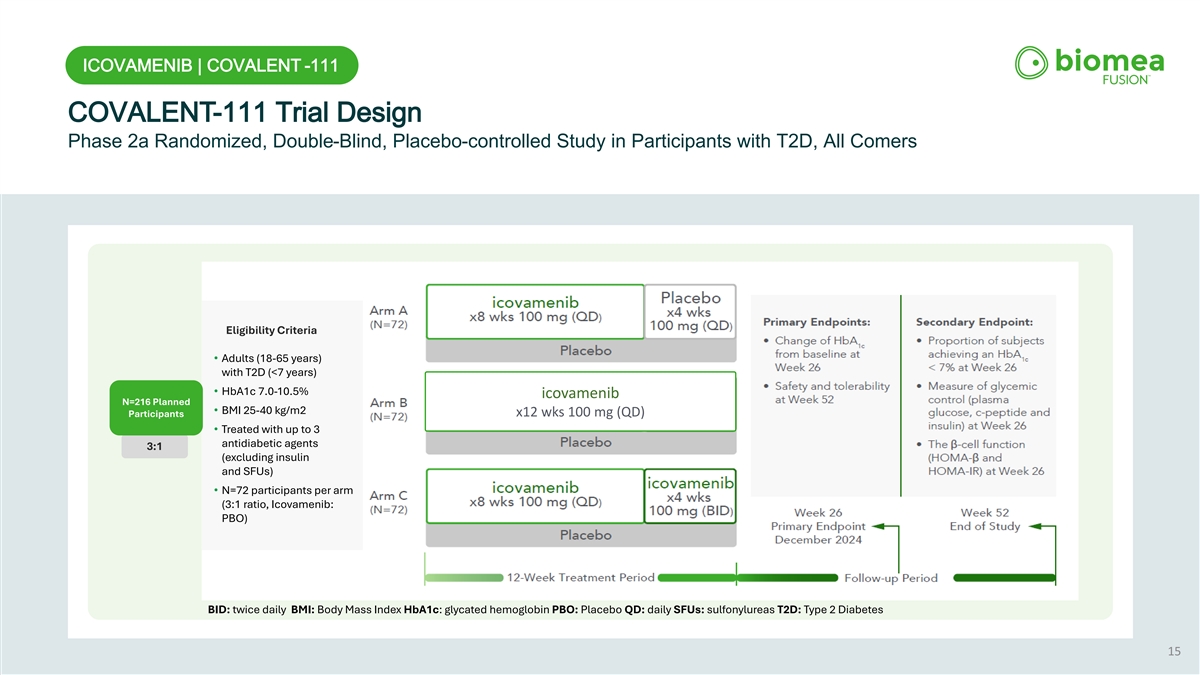
ICOVAMENIB | COVALENT -111 COVALENT-111 Trial Design Phase 2a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-controlled Study in Participants with T2D, All Comers Eligibility Criteria • Adults (18-65 years) with T2D (<7 years) • HbA1c 7.0-10.5% icovamenib N=216 Planned • BMI 25-40 kg/m2 Participants x12 wks 100 mg (QD) • Treated with up to 3 antidiabetic agents 3:1 (excluding insulin and SFUs) • N=72 participants per arm (3:1 ratio, Icovamenib: PBO) BID: twice daily BMI: Body Mass Index HbA1c: glycated hemoglobin PBO: Placebo QD: daily SFUs: sulfonylureas T2D: Type 2 Diabetes 15

ICOVAMENIB | COVALENT -111 COVALENT-111 Statistical Analysis Plan Read Out of Insulin-Deficient & Insulin Resistant Subgroups at Weeks 26 and 52 Arm A, B, and C primary analysis: Change in HbA1c Prespecified subgroup analysis to include assessment of HbA1c change within each T2D subgroup: • Severe Insulin Deficient Diabetes • Mild Age-Related Diabetes • Mild Obesity Diabetes • Severe Insulin Resistant Diabetes Subgroup analysis based on algorithm e s ta blis he d pe r Ahlqvis t e t a l. (Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6:361-369) 16
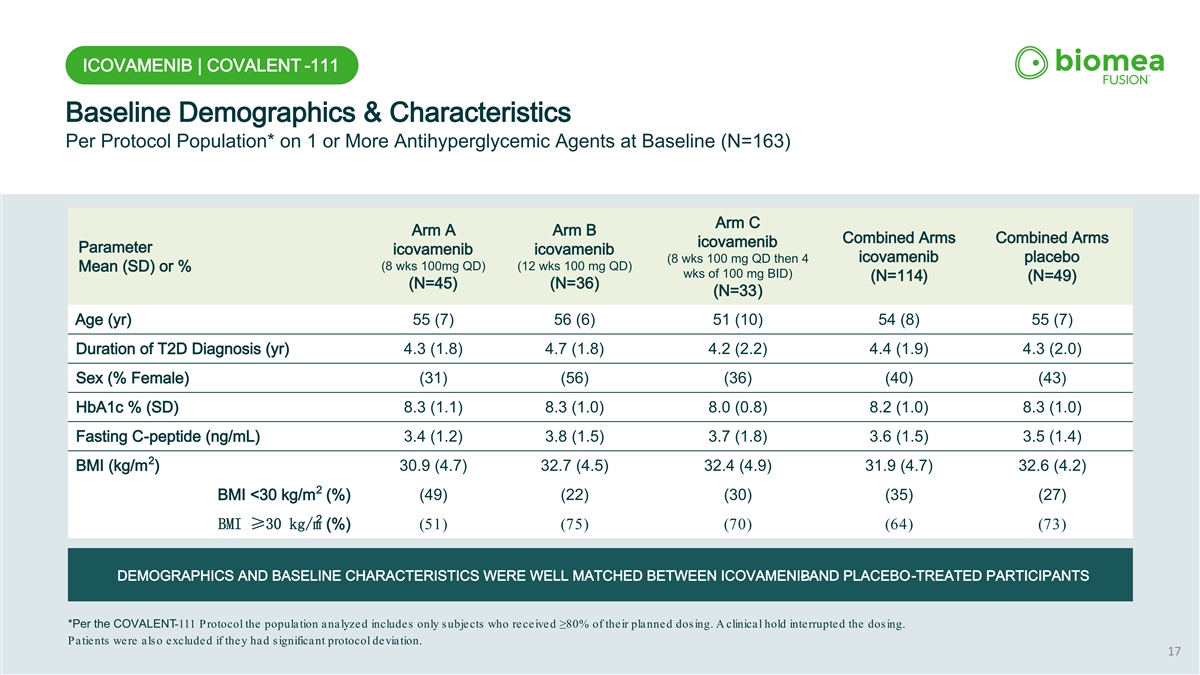
ICOVAMENIB | COVALENT -111 Baseline Demographics & Characteristics Per Protocol Population* on 1 or More Antihyperglycemic Agents at Baseline (N=163) Arm C Arm A Arm B Combined Arms Combined Arms icovamenib Parameter icovamenib icovamenib icovamenib placebo (8 wks 100 mg QD then 4 (8 wks 100mg QD) (12 wks 100 mg QD) Mean (SD) or % wks of 100 mg BID) (N=114) (N=49) (N=45) (N=36) (N=33) Age (yr) 55 (7) 56 (6) 51 (10) 54 (8) 55 (7) Duration of T2D Diagnosis (yr) 4.3 (1.8) 4.7 (1.8) 4.2 (2.2) 4.4 (1.9) 4.3 (2.0) Sex (% Female) (31) (56) (36) (40) (43) HbA1c % (SD) 8.3 (1.1) 8.3 (1.0) 8.0 (0.8) 8.2 (1.0) 8.3 (1.0) Fasting C-peptide (ng/mL) 3.4 (1.2) 3.8 (1.5) 3.7 (1.8) 3.6 (1.5) 3.5 (1.4) 2 BMI (kg/m ) 30.9 (4.7) 32.7 (4.5) 32.4 (4.9) 31.9 (4.7) 32.6 (4.2) 2 BMI <30 kg/m (%) (49) (22) (30) (35) (27) 2 BMI ≥30 kg/m (%) (51) (75) (70) (64) (73) DEMOGRAPHICS AND BASELINE CHARACTERISTICS WERE WELL MATCHED BETWEEN ICOVAMENIB - AND PLACEBO-TREATED PARTICIPANTS *Per the COVALENT-111 Protocol the population analyzed includes only subjects who received ≥80% of their planned dosing. A clini cal hold interrupted the dosing. Patients were also excluded if they had significant protocol deviation. 17
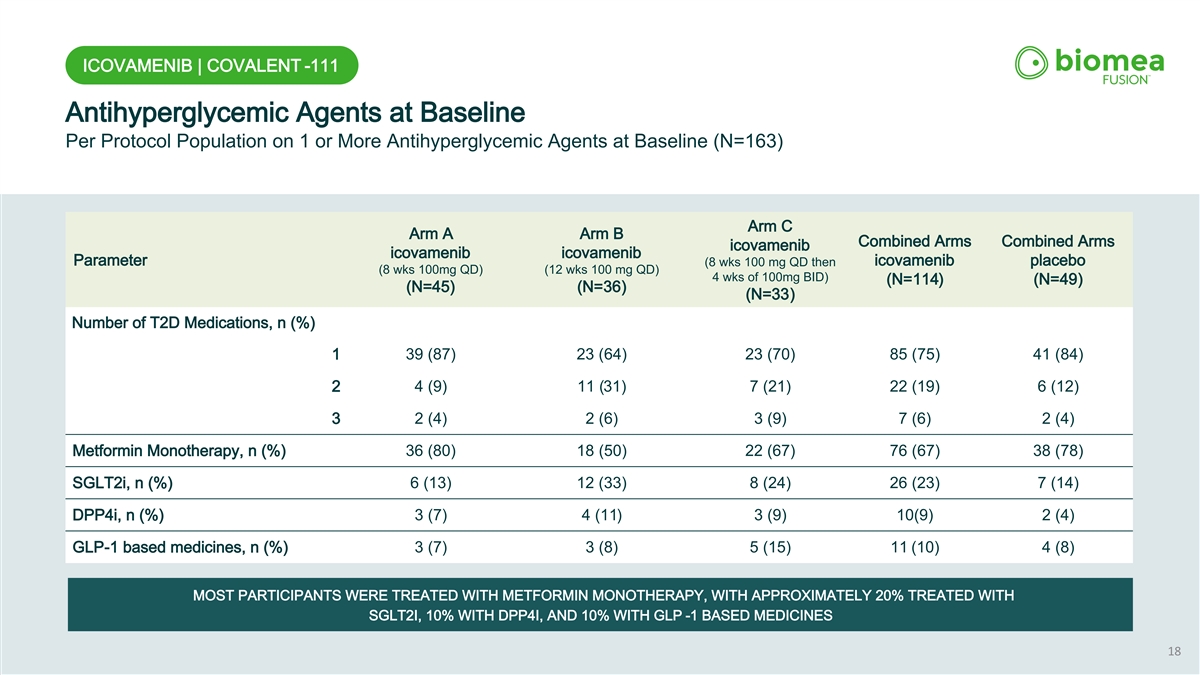
ICOVAMENIB | COVALENT -111 Antihyperglycemic Agents at Baseline Per Protocol Population on 1 or More Antihyperglycemic Agents at Baseline (N=163) Arm C Arm A Arm B Combined Arms Combined Arms icovamenib icovamenib icovamenib Parameter (8 wks 100 mg QD then icovamenib placebo (8 wks 100mg QD) (12 wks 100 mg QD) 4 wks of 100mg BID) (N=114) (N=49) (N=45) (N=36) (N=33) Number of T2D Medications, n (%) 1 39 (87) 23 (64) 23 (70) 85 (75) 41 (84) 2 4 (9) 11 (31) 7 (21) 22 (19) 6 (12) 3 2 (4) 2 (6) 3 (9) 7 (6) 2 (4) Metformin Monotherapy, n (%) 36 (80) 18 (50) 22 (67) 76 (67) 38 (78) SGLT2i, n (%) 6 (13) 12 (33) 8 (24) 26 (23) 7 (14) DPP4i, n (%) 3 (7) 4 (11) 3 (9) 10(9) 2 (4) GLP-1 based medicines, n (%) 3 (7) 3 (8) 5 (15) 11 (10) 4 (8) MOST PARTICIPANTS WERE TREATED WITH METFORMIN MONOTHERAPY, WITH APPROXIMATELY 20% TREATED WITH SGLT2I, 10% WITH DPP4I, AND 10% WITH GLP -1 BASED MEDICINES 18
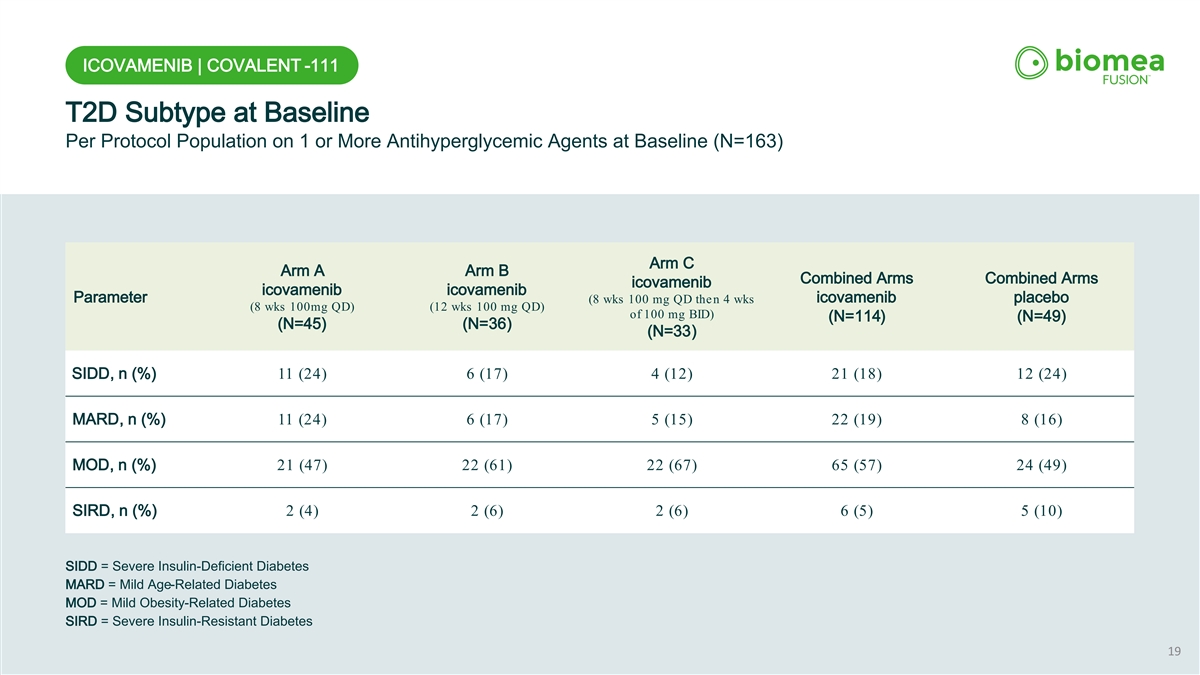
ICOVAMENIB | COVALENT -111 T2D Subtype at Baseline Per Protocol Population on 1 or More Antihyperglycemic Agents at Baseline (N=163) Arm C Arm A Arm B Combined Arms Combined Arms icovamenib icovamenib icovamenib Parameter icovamenib placebo (8 wks 100 mg QD then 4 wks (8 wks 100mg QD) (12 wks 100 mg QD) of 100 mg BID) (N=114) (N=49) (N=45) (N=36) (N=33) SIDD, n (%) 11 (24) 6 (17) 4 (12) 21 (18) 12 (24) MARD, n (%) 11 (24) 6 (17) 5 (15) 22 (19) 8 (16) MOD, n (%) 21 (47) 22 (61) 22 (67) 65 (57) 24 (49) SIRD, n (%) 2 (4) 2 (6) 2 (6) 6 (5) 5 (10) SIDD = Severe Insulin-Deficient Diabetes MARD = Mild Age-Related Diabetes MOD = Mild Obesity-Related Diabetes SIRD = Severe Insulin-Resistant Diabetes 19
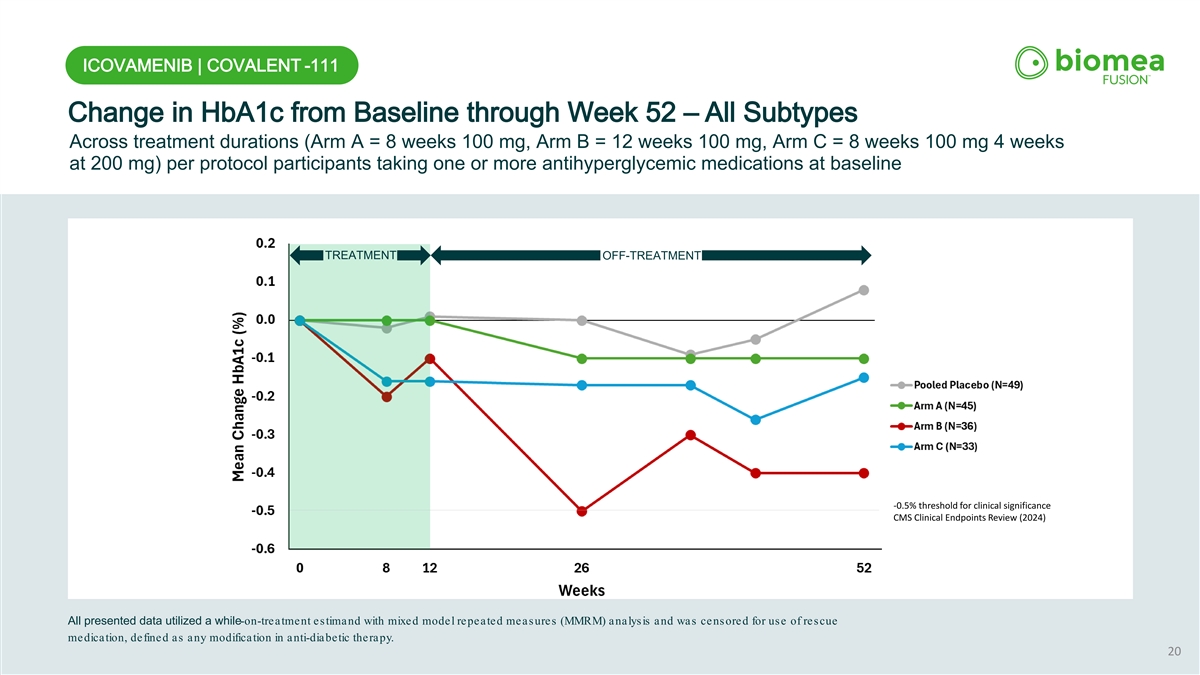
ICOVAMENIB | COVALENT -111 Change in HbA1c from Baseline through Week 52 – All Subtypes Across treatment durations (Arm A = 8 weeks 100 mg, Arm B = 12 weeks 100 mg, Arm C = 8 weeks 100 mg 4 weeks at 200 mg) per protocol participants taking one or more antihyperglycemic medications at baseline TREATMENT OFF-TREATMENT -0.5% threshold for clinical significance CMS Clinical Endpoints Review (2024) All presented data utilized a while-on-treatment estimand with mixed model repeated measures (MMRM) analysis and was censored for use of rescue medication, defined as any modification in anti-diabetic therapy. 20
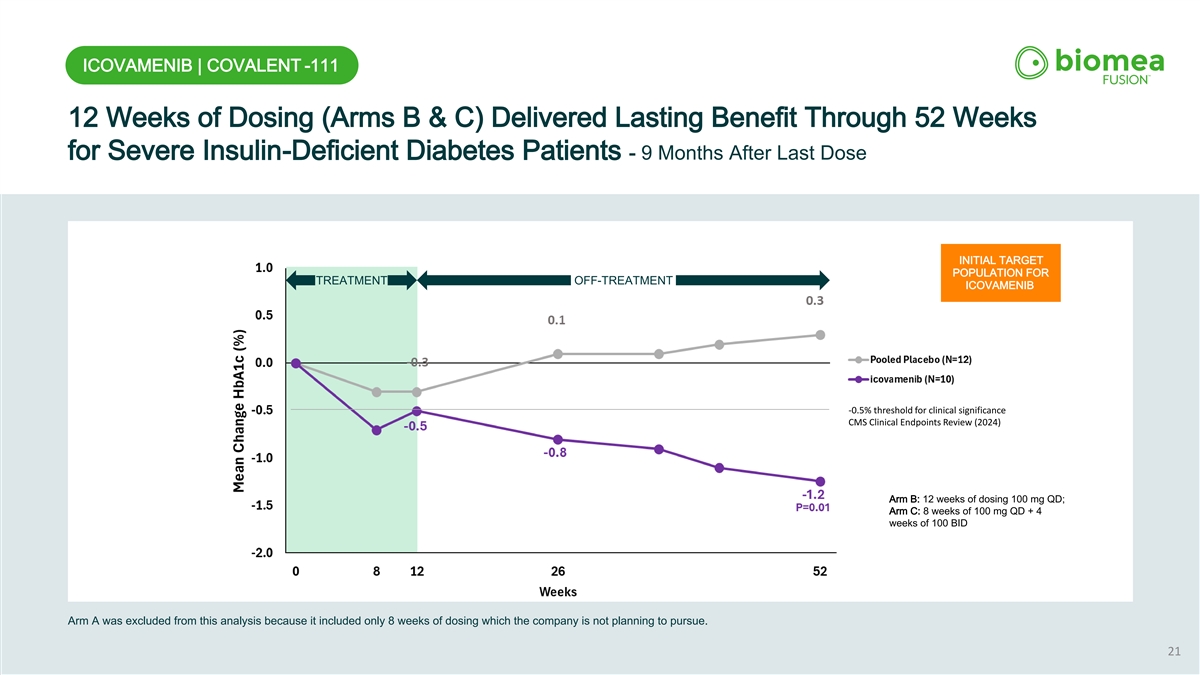
ICOVAMENIB | COVALENT -111 12 Weeks of Dosing (Arms B & C) Delivered Lasting Benefit Through 52 Weeks for Severe Insulin-Deficient Diabetes Patients - 9 Months After Last Dose INITIAL TARGET POPULATION FOR TREATMENT OFF-TREATMENT ICOVAMENIB -0.5% threshold for clinical significance CMS Clinical Endpoints Review (2024) Arm B: 12 weeks of dosing 100 mg QD; Arm C: 8 weeks of 100 mg QD + 4 PRIMARY TARGET weeks of 100 BID POPULATION FOR ICOVAMENIB Arm A was excluded from this analysis because it included only 8 weeks of dosing which the company is not planning to pursue. 21
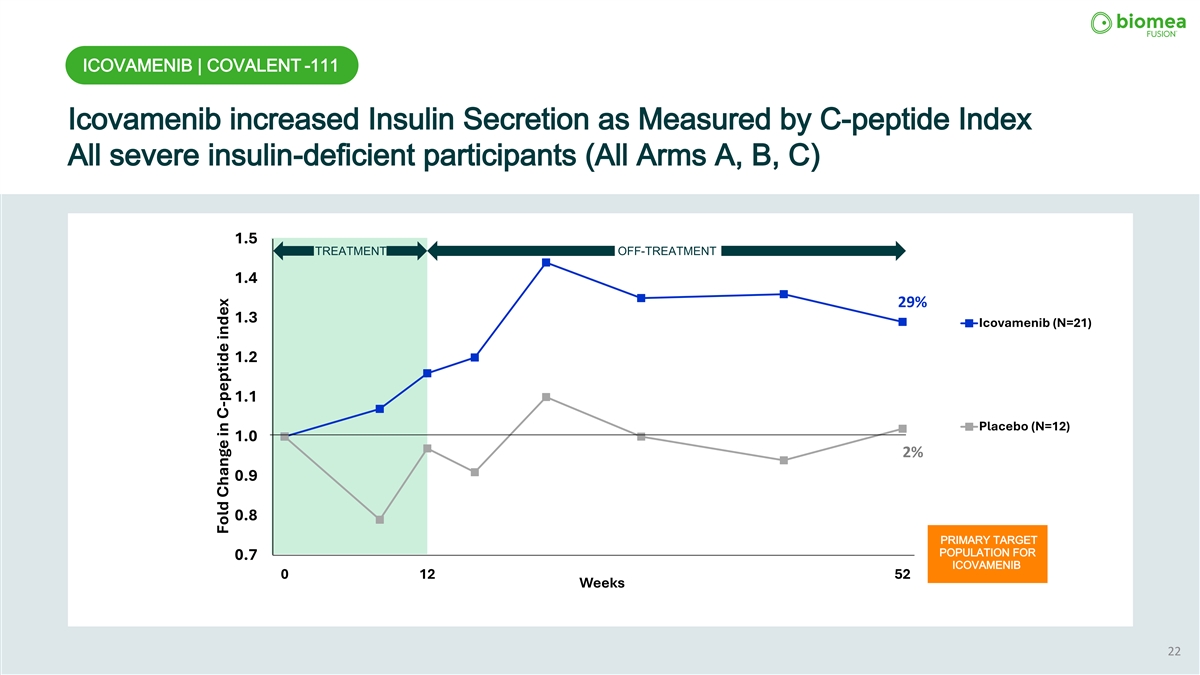
ICOVAMENIB | COVALENT -111 Icovamenib increased Insulin Secretion as Measured by C-peptide Index All severe insulin-deficient participants (All Arms A, B, C) 1.5 TREATMENT OFF-TREATMENT 1.4 29% 1.3 Icovamenib (N=21) 1.2 1.1 Placebo (N=12) 1.0 2% 0.9 0.8 PRIMARY TARGET POPULATION FOR 0.7 ICOVAMENIB 0 12 52 Weeks 22 Fold Change in C-peptide index
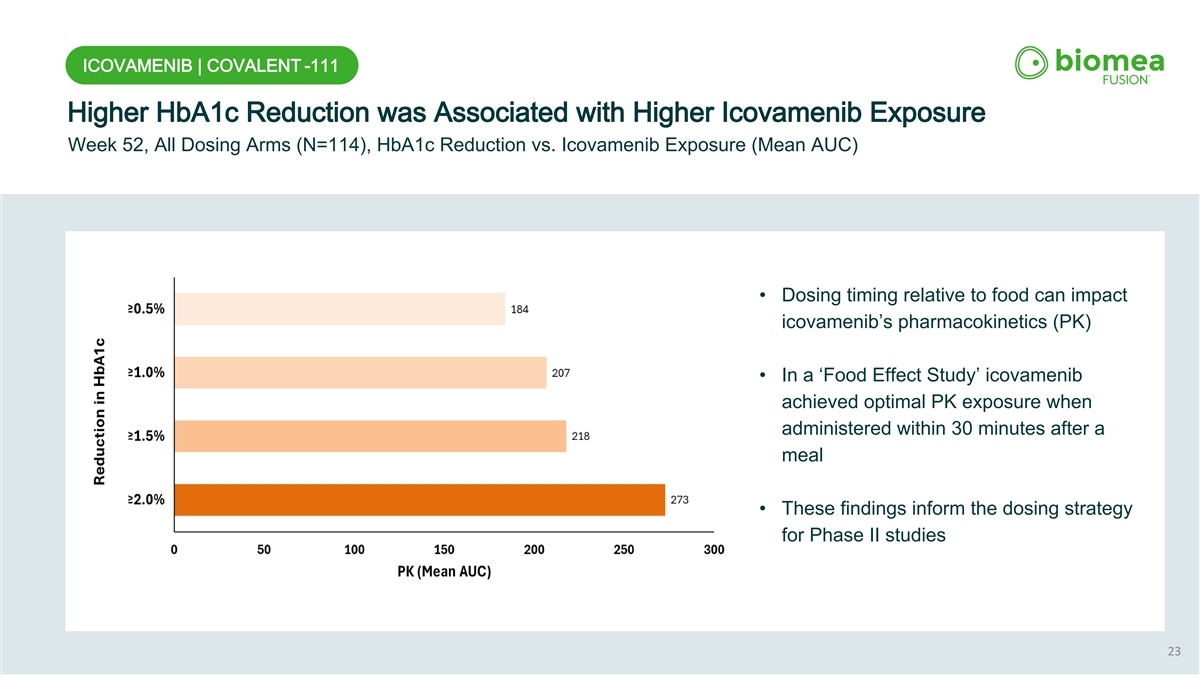
ICOVAMENIB | COVALENT -111 Higher HbA1c Reduction was Associated with Higher Icovamenib Exposure Week 52, All Dosing Arms (N=114), HbA1c Reduction vs. Icovamenib Exposure (Mean AUC) • Dosing timing relative to food can impact icovamenib’s pharmacokinetics (PK) • In a ‘Food Effect Study’ icovamenib achieved optimal PK exposure when administered within 30 minutes after a meal • These findings inform the dosing strategy for Phase II studies 23
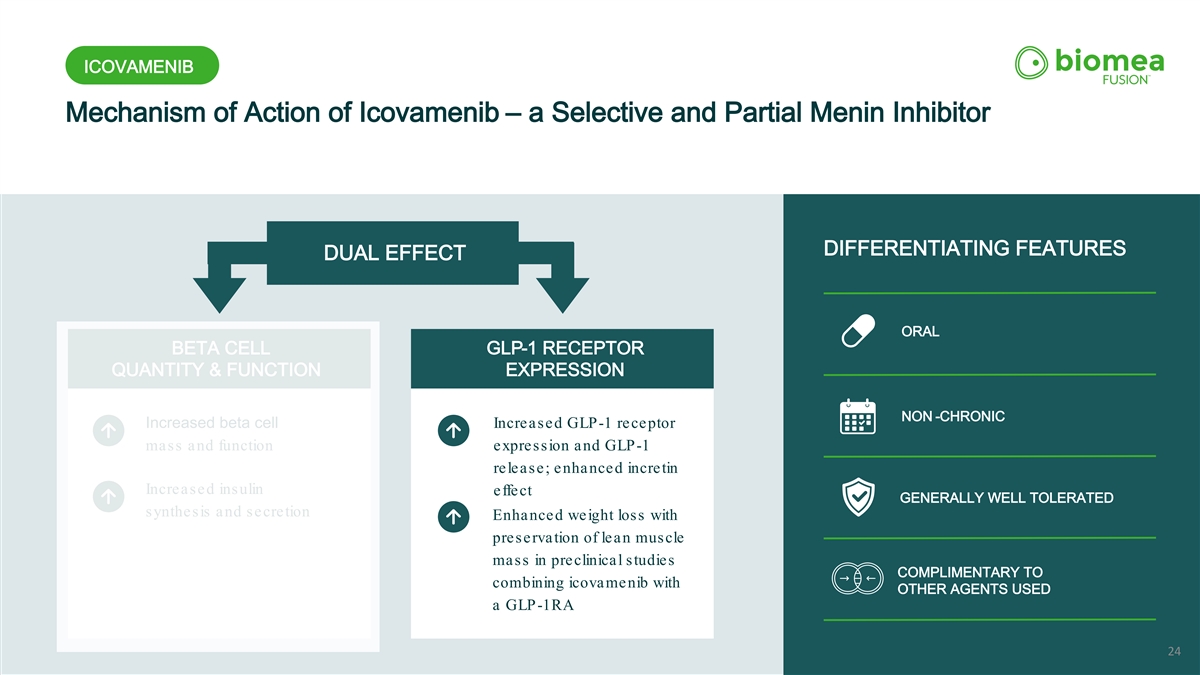
ICOVAMENIB Mechanism of Action of Icovamenib – a Selective and Partial Menin Inhibitor ORAL DIFFERENTIATING FEATURES DUAL EFFECT ORAL BETA CELL GLP-1 RECEPTOR QUANTITY & FUNCTION EXPRESSION NON -CHRONIC Increased beta cell Increased GLP-1 receptor mass and function expression and GLP-1 release; enhanced incretin Increased insulin effect GENERALLY WELL TOLERATED synthesis and secretion Enhanced weight loss with preservation of lean muscle mass in preclinical studies COMPLIMENTARY TO combining icovamenib with OTHER AGENTS USED a GLP-1RA 24
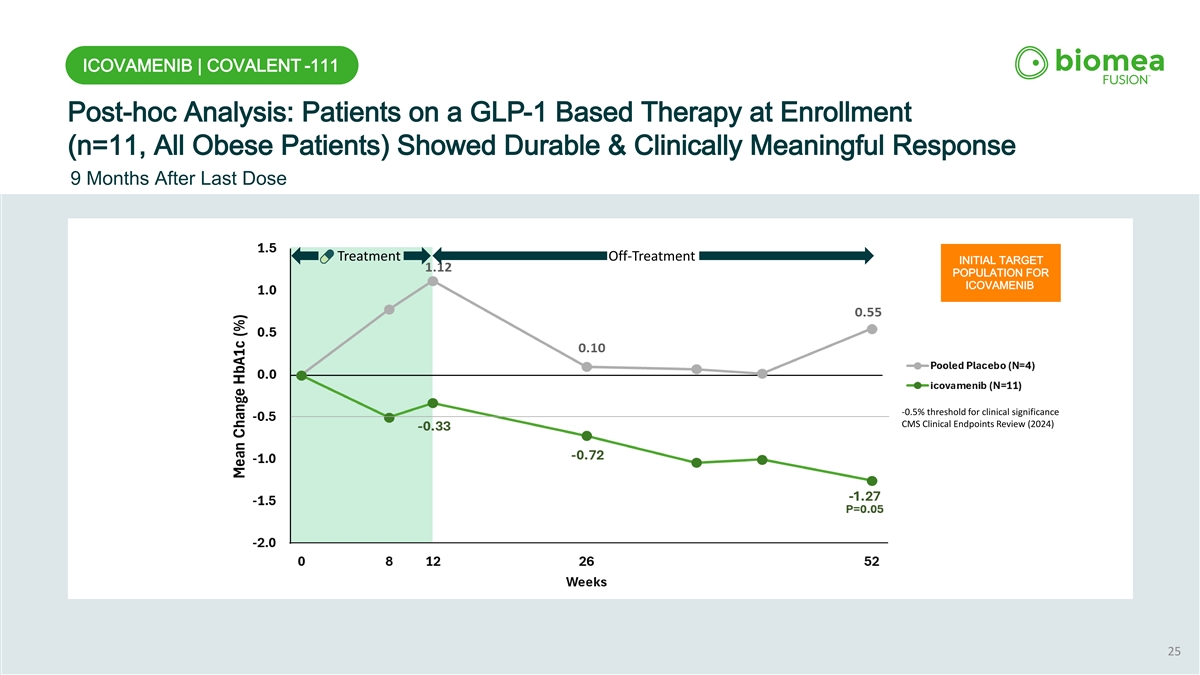
ICOVAMENIB | COVALENT -111 Post-hoc Analysis: Patients on a GLP-1 Based Therapy at Enrollment (n=11, All Obese Patients) Showed Durable & Clinically Meaningful Response 9 Months After Last Dose Treatment Off-Treatment INITIAL TARGET POPULATION FOR ICOVAMENIB -0.5% threshold for clinical significance CMS Clinical Endpoints Review (2024) 25
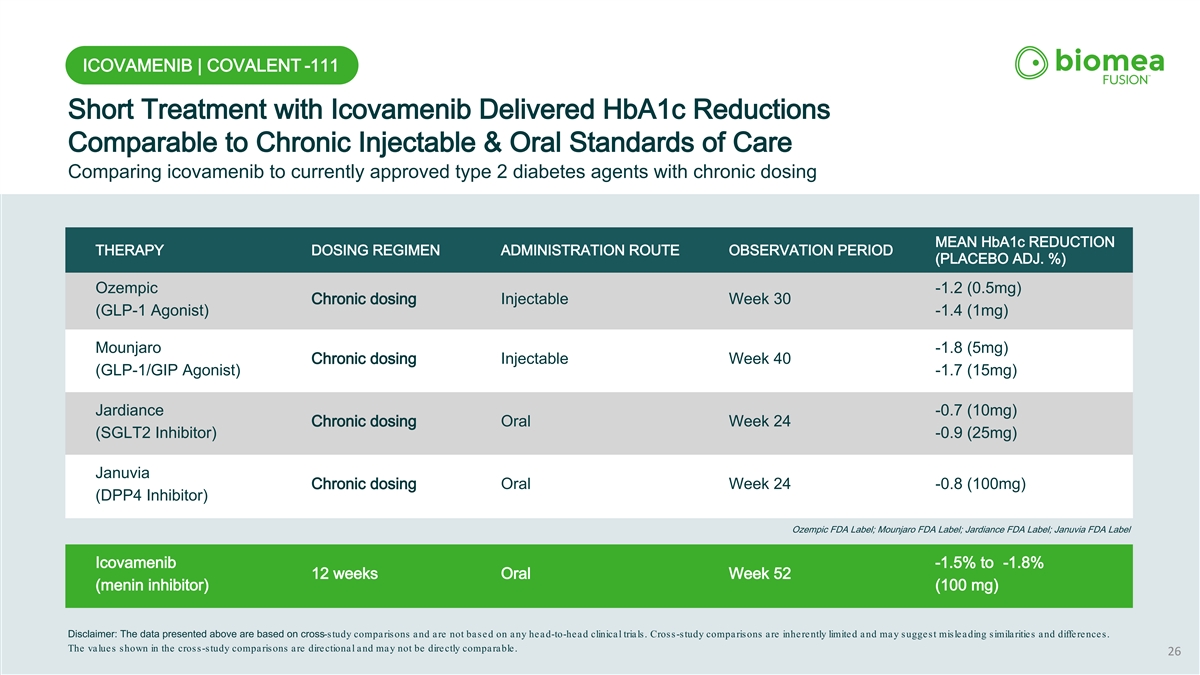
ICOVAMENIB | COVALENT -111 Short Treatment with Icovamenib Delivered HbA1c Reductions Comparable to Chronic Injectable & Oral Standards of Care Comparing icovamenib to currently approved type 2 diabetes agents with chronic dosing MEAN HbA1c REDUCTION THERAPY DOSING REGIMEN ADMINISTRATION ROUTE OBSERVATION PERIOD (PLACEBO ADJ. %) Ozempic -1.2 (0.5mg) Chronic dosing Injectable Week 30 (GLP-1 Agonist) -1.4 (1mg) Mounjaro -1.8 (5mg) Chronic dosing Injectable Week 40 (GLP-1/GIP Agonist) -1.7 (15mg) Jardiance -0.7 (10mg) Chronic dosing Oral Week 24 (SGLT2 Inhibitor) -0.9 (25mg) Januvia Chronic dosing Oral Week 24 -0.8 (100mg) (DPP4 Inhibitor) Ozempic FDA Label; Mounjaro FDA Label; Jardiance FDA Label; Januvia FDA Label Icovamenib -1.5% to -1.8% 12 weeks Oral Week 52 (menin inhibitor) (100 mg) Disclaimer: The data presented above are based on cross-study comparisons and are not based on any head-to-head clinical trials. Cross-study comparisons are inherently limited and may suggest misleading similarities and differences. The values shown in the cross-study comparisons are directional and may not be directly comparable. 26
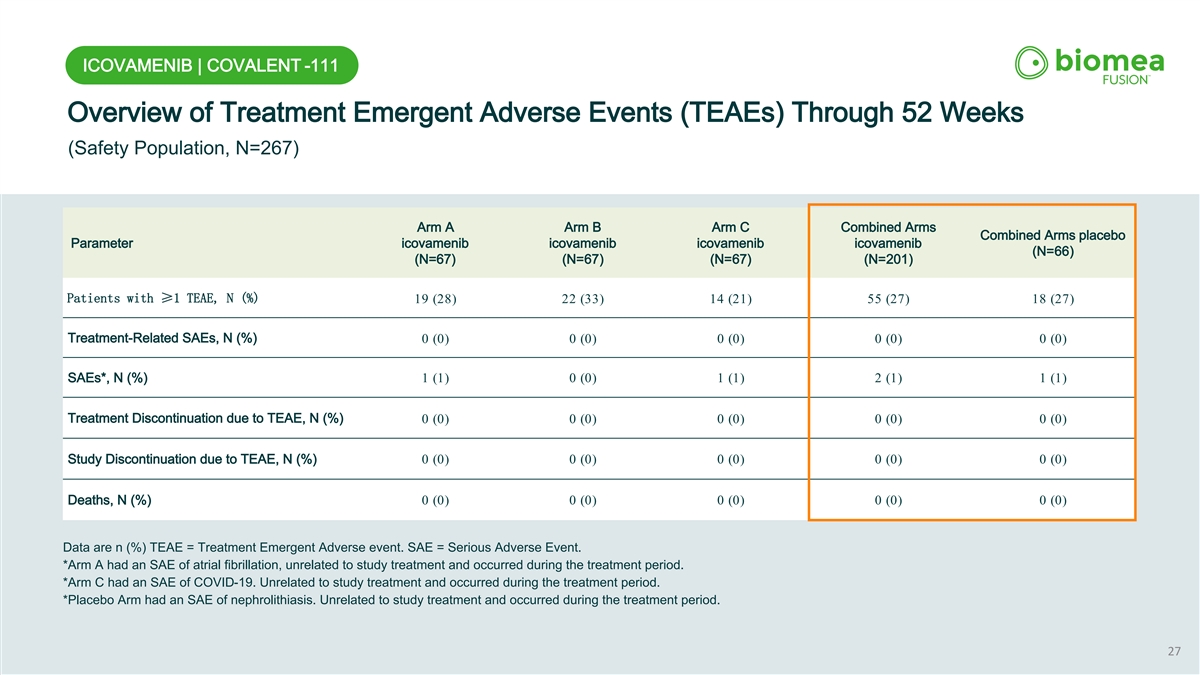
ICOVAMENIB | COVALENT -111 Overview of Treatment Emergent Adverse Events (TEAEs) Through 52 Weeks (Safety Population, N=267) Arm A Arm B Arm C Combined Arms Combined Arms placebo Parameter icovamenib icovamenib icovamenib icovamenib (N=66) (N=67) (N=67) (N=67) (N=201) Patients with ≥1 TEAE, N (%) 19 (28) 22 (33) 14 (21) 55 (27) 18 (27) Treatment-Related SAEs, N (%) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) SAEs*, N (%) 1 (1) 0 (0) 1 (1) 2 (1) 1 (1) Treatment Discontinuation due to TEAE, N (%) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) Study Discontinuation due to TEAE, N (%) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) Deaths, N (%) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) Data are n (%) TEAE = Treatment Emergent Adverse event. SAE = Serious Adverse Event. *Arm A had an SAE of atrial fibrillation, unrelated to study treatment and occurred during the treatment period. *Arm C had an SAE of COVID-19. Unrelated to study treatment and occurred during the treatment period. *Placebo Arm had an SAE of nephrolithiasis. Unrelated to study treatment and occurred during the treatment period. 27
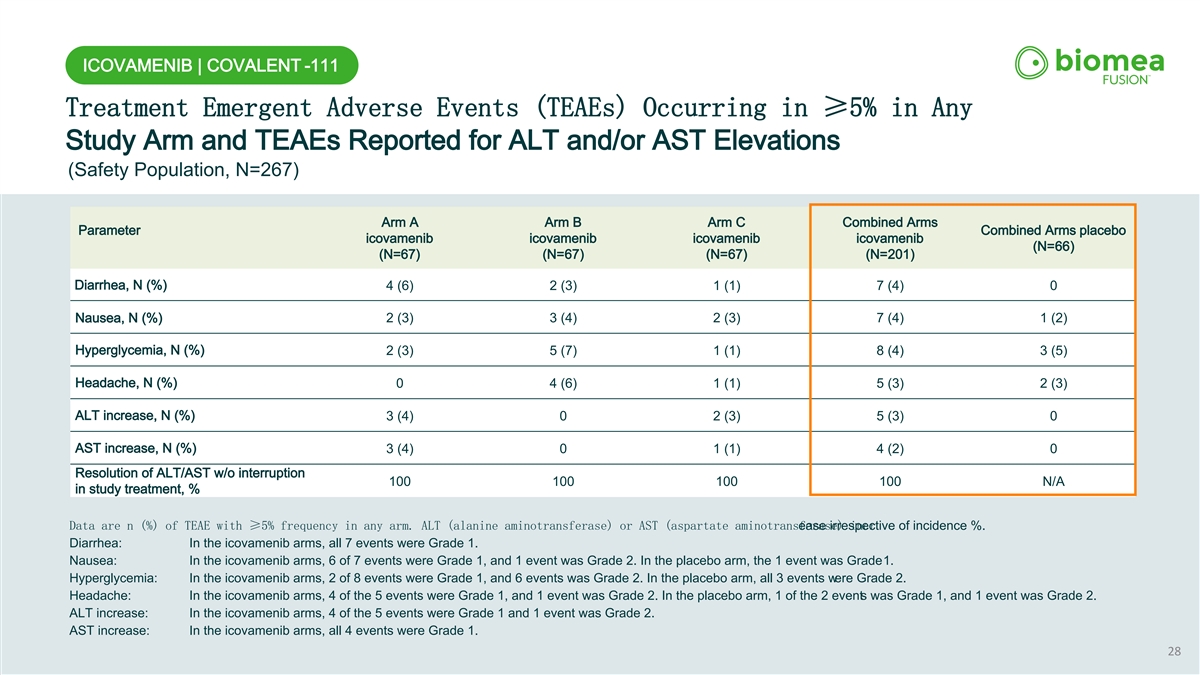
ICOVAMENIB | COVALENT -111 Treatment Emergent Adverse Events (TEAEs) Occurring in ≥5% in Any Study Arm and TEAEs Reported for ALT and/or AST Elevations (Safety Population, N=267) Arm A Arm B Arm C Combined Arms Parameter Combined Arms placebo icovamenib icovamenib icovamenib icovamenib (N=66) (N=67) (N=67) (N=67) (N=201) Diarrhea, N (%) 4 (6) 2 (3) 1 (1) 7 (4) 0 Nausea, N (%) 2 (3) 3 (4) 2 (3) 7 (4) 1 (2) Hyperglycemia, N (%) 2 (3) 5 (7) 1 (1) 8 (4) 3 (5) Headache, N (%) 0 4 (6) 1 (1) 5 (3) 2 (3) ALT increase, N (%) 3 (4) 0 2 (3) 5 (3) 0 AST increase, N (%) 3 (4) 0 1 (1) 4 (2) 0 Resolution of ALT/AST w/o interruption 100 100 100 100 N/A in study treatment, % Data are n (%) of TEAE with ≥5% frequency in any arm. ALT (alanine aminotransferase) or AST (aspartate aminotransferase) incr ease irrespective of incidence %. Diarrhea: In the icovamenib arms, all 7 events were Grade 1. Nausea: In the icovamenib arms, 6 of 7 events were Grade 1, and 1 event was Grade 2. In the placebo arm, the 1 event was Grade 1. Hyperglycemia: In the icovamenib arms, 2 of 8 events were Grade 1, and 6 events was Grade 2. In the placebo arm, all 3 events were Grade 2. Headache: In the icovamenib arms, 4 of the 5 events were Grade 1, and 1 event was Grade 2. In the placebo arm, 1 of the 2 events was Grade 1, and 1 event was Grade 2. ALT increase: In the icovamenib arms, 4 of the 5 events were Grade 1 and 1 event was Grade 2. AST increase: In the icovamenib arms, all 4 events were Grade 1. 28
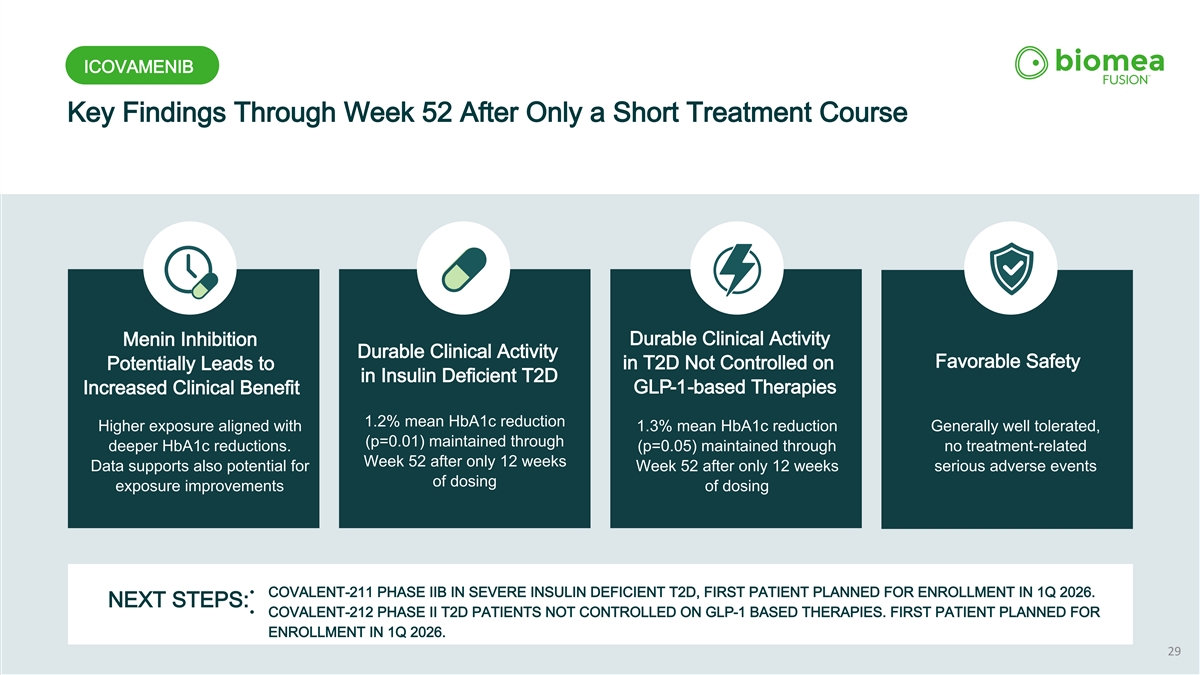
ICOVAMENIB Key Findings Through Week 52 After Only a Short Treatment Course Durable Clinical Activity Menin Inhibition Durable Clinical Activity Favorable Safety in T2D Not Controlled on Potentially Leads to in Insulin Deficient T2D GLP-1-based Therapies Increased Clinical Benefit 1.2% mean HbA1c reduction Higher exposure aligned with 1.3% mean HbA1c reduction Generally well tolerated, (p=0.01) maintained through deeper HbA1c reductions. (p=0.05) maintained through no treatment-related Week 52 after only 12 weeks Data supports also potential for Week 52 after only 12 weeks serious adverse events of dosing exposure improvements of dosing • COVALENT-211 PHASE IIB IN SEVERE INSULIN DEFICIENT T2D, FIRST PATIENT PLANNED FOR ENROLLMENT IN 1Q 2026. NEXT STEPS: • COVALENT-212 PHASE II T2D PATIENTS NOT CONTROLLED ON GLP-1 BASED THERAPIES. FIRST PATIENT PLANNED FOR ENROLLMENT IN 1Q 2026. 29
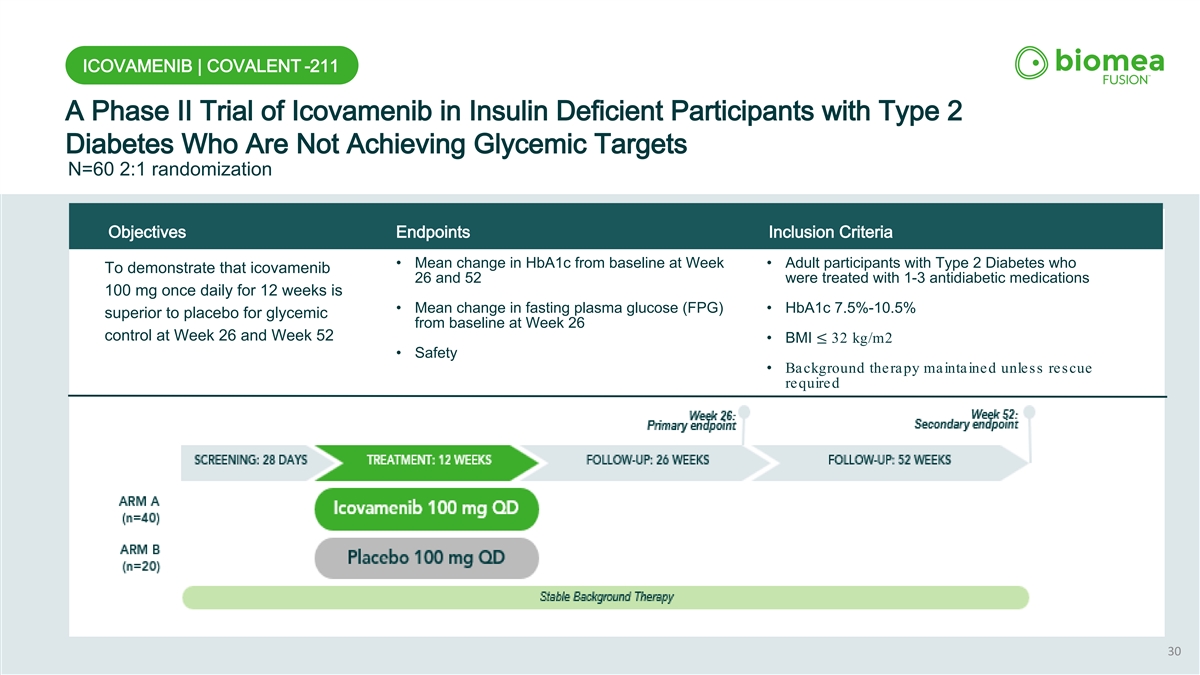
ICOVAMENIB | COVALENT -211 A Phase II Trial of Icovamenib in Insulin Deficient Participants with Type 2 Diabetes Who Are Not Achieving Glycemic Targets N=60 2:1 randomization Objectives Endpoints Inclusion Criteria • Mean change in HbA1c from baseline at Week • Adult participants with Type 2 Diabetes who To demonstrate that icovamenib 26 and 52 were treated with 1-3 antidiabetic medications 100 mg once daily for 12 weeks is • Mean change in fasting plasma glucose (FPG) • HbA1c 7.5%-10.5% superior to placebo for glycemic from baseline at Week 26 control at Week 26 and Week 52 • BMI ≤ 32 kg/m2 • Safety • Background therapy maintained unless rescue required 30

ICOVAMENIB | COVALENT -212 A Phase II Trial of Icovamenib in Participants with Type 2 Diabetes Who Are Not Achieving Glycemic Targets While Using GLP-1-Based Therapy N=60 2:1 randomization Objectives Inclusion Criteria Endpoints • Adult participants with T2D who are not achieving • Mean change in HbA1c from baseline at To demonstrate that icovamenib glycemic targets despite GLP-1-based therapy Week 26 and 52 100 mg once daily for 12 weeks • HbA1c ≥7.5% and ≤9.5% • Mean change in fasting plasma glucose is superior to placebo for (FPG) from baseline at Week 26 • BMI 25 to 40 kg/m2 glycemic control at Week 26 and • Safety Week 52 • Background therapy maintained unless rescue required 31

ICOVAMENIB Preclinical Study Results Icovamenib in Combination with GLP-1 Based Therapies
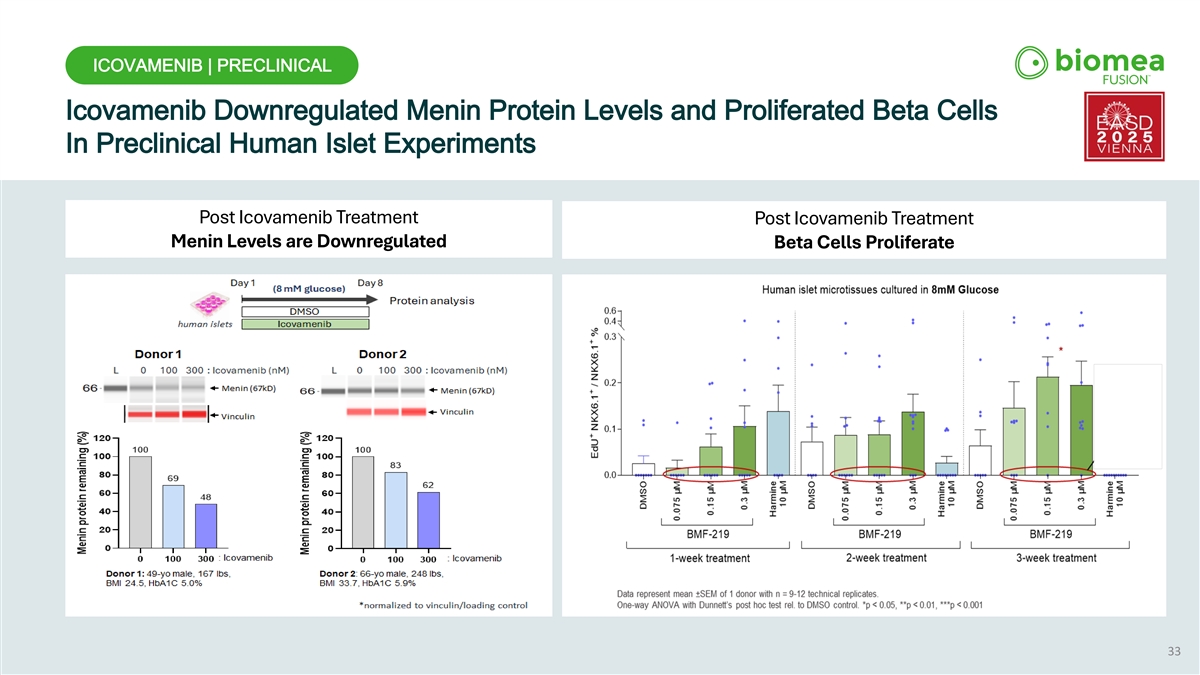
ICOVAMENIB | PRECLINICAL Icovamenib Downregulated Menin Protein Levels and Proliferated Beta Cells In Preclinical Human Islet Experiments Post Icovamenib Treatment Post Icovamenib Treatment Menin Levels are Downregulated Beta Cells Proliferate 33
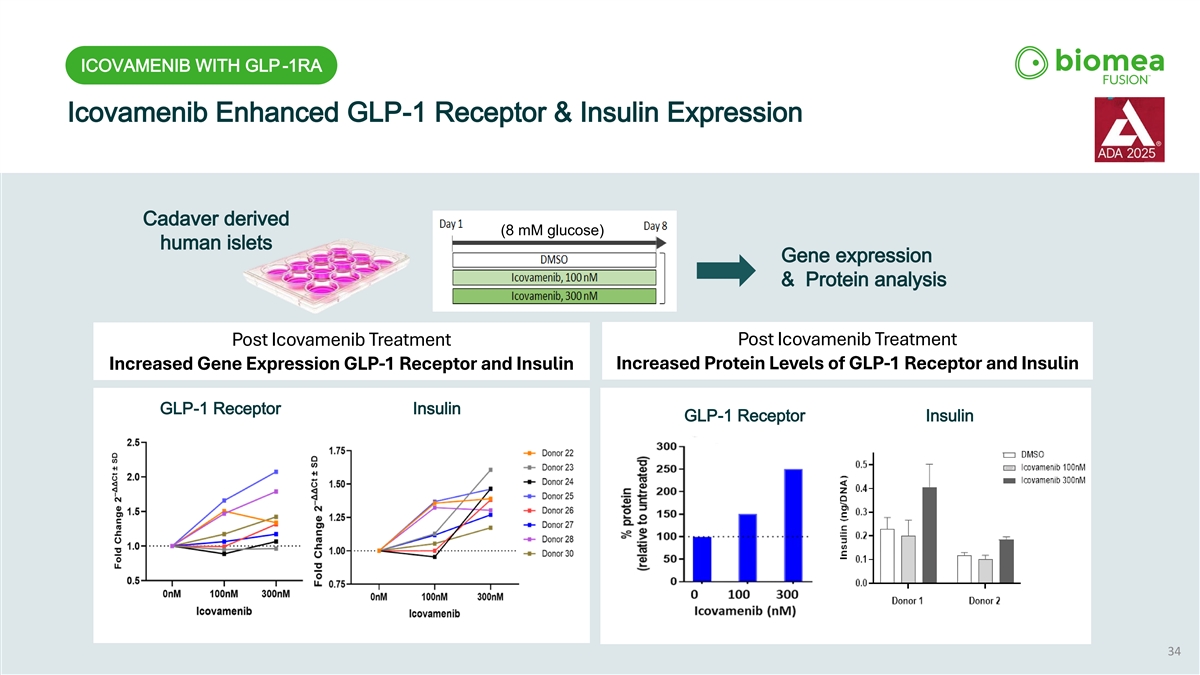
ICOVAMENIB WITH GLP-1RA Icovamenib Enhanced GLP-1 Receptor & Insulin Expression Cadaver derived (8 mM glucose) human islets Gene expression & Protein analysis Post Icovamenib Treatment Post Icovamenib Treatment Increased Protein Levels of GLP-1 Receptor and Insulin Increased Gene Expression GLP-1 Receptor and Insulin GLP-1 Receptor Insulin GLP-1 Receptor Insulin 34
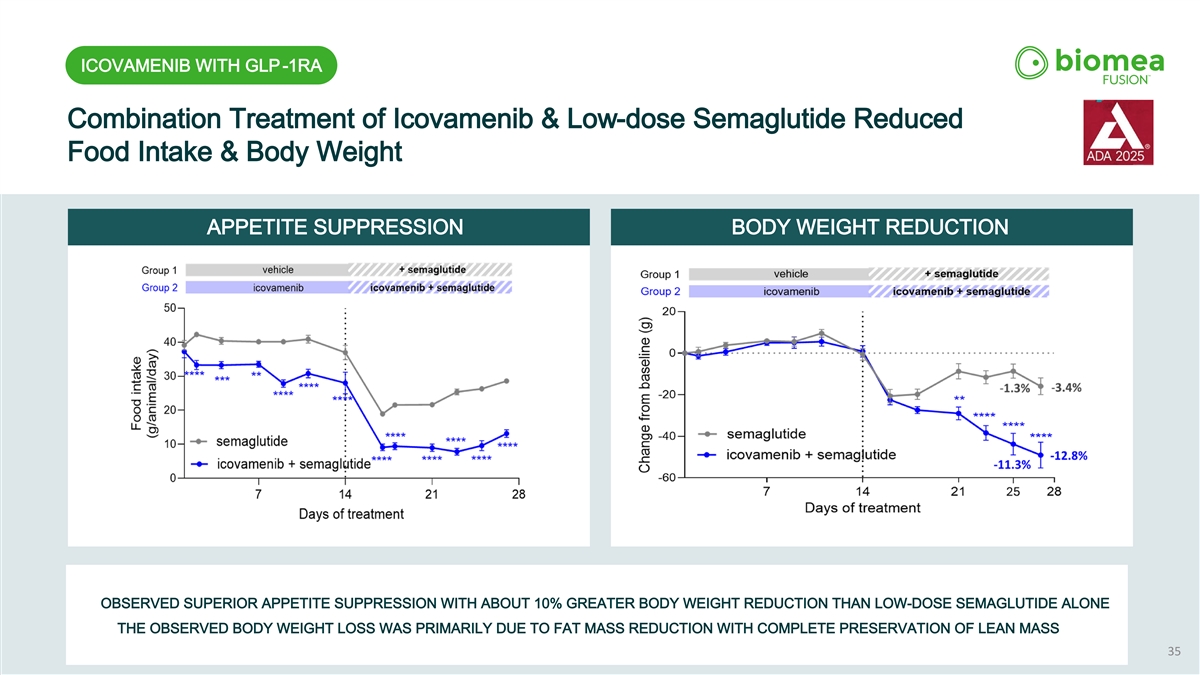
ICOVAMENIB WITH GLP-1RA Combination Treatment of Icovamenib & Low-dose Semaglutide Reduced Food Intake & Body Weight APPETITE SUPPRESSION BODY WEIGHT REDUCTION OBSERVED SUPERIOR APPETITE SUPPRESSION WITH ABOUT 10% GREATER BODY WEIGHT REDUCTION THAN LOW-DOSE SEMAGLUTIDE ALONE THE OBSERVED BODY WEIGHT LOSS WAS PRIMARILY DUE TO FAT MASS REDUCTION WITH COMPLETE PRESERVATION OF LEAN MASS 35
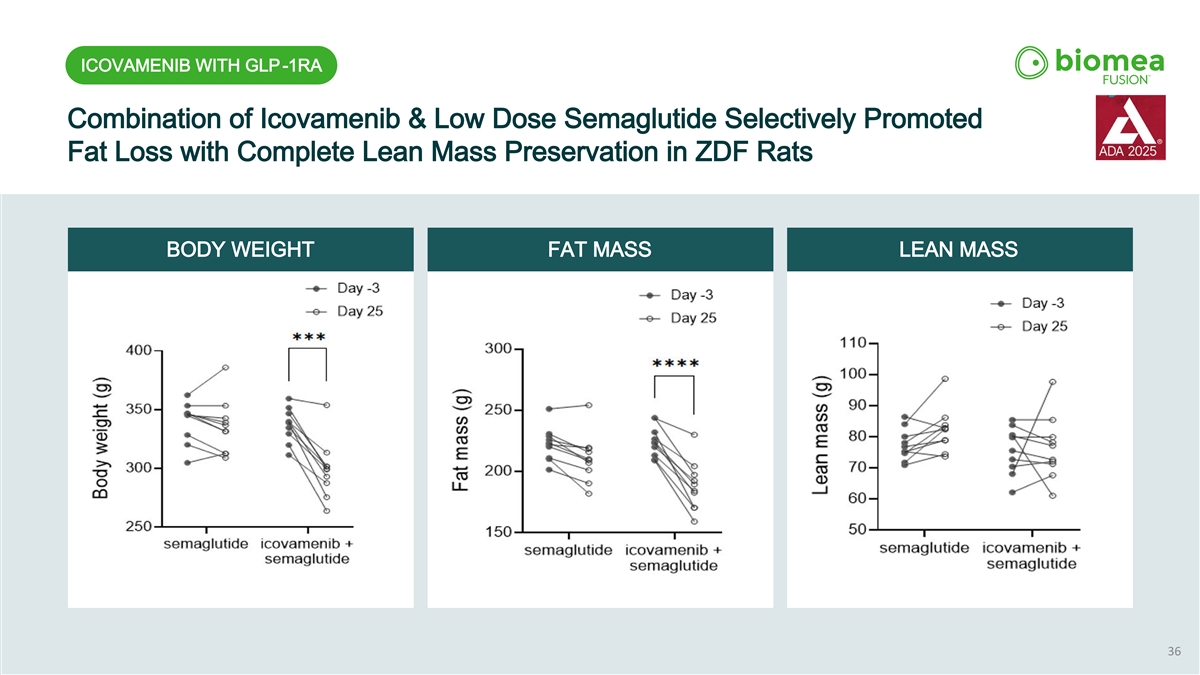
ICOVAMENIB WITH GLP-1RA Combination of Icovamenib & Low Dose Semaglutide Selectively Promoted Fat Loss with Complete Lean Mass Preservation in ZDF Rats BODY WEIGHT FAT MASS LEAN MASS 36

BMF-650 Next-Generation Oral GLP -1 Receptor Agonist Preclinical Results & Clinical Overview Target: OBESITY

BMF-650 Designed to Deliver Strong Efficacy with Improved Oral Tolerability A Next-Generation Oral GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Differentiated properties exhibited by BMF-650 “Why is a greater therapeutic window important?” Improved PK Generally Patient Friendly • Only 3 of 10 patients remain on GLP-1 therapy at one year due to tolerability, GI Profile Favorable Design 1 effects and complexity of use. Safety Profile Greater oral exposure with Oral delivery with the • A therapy with a greater therapeutic lower variability observed potential for simplified Better tolerability window can allow effective dosing with in preclinical studies dose escalation improved tolerability. associated with higher plasma protein binding in • An oral agent with improved tolerability preclinical models could potentially expand the long-term use. 38 1.Khan, et al. JAMA 2024 doi:10.1001/jama.2024.22284.
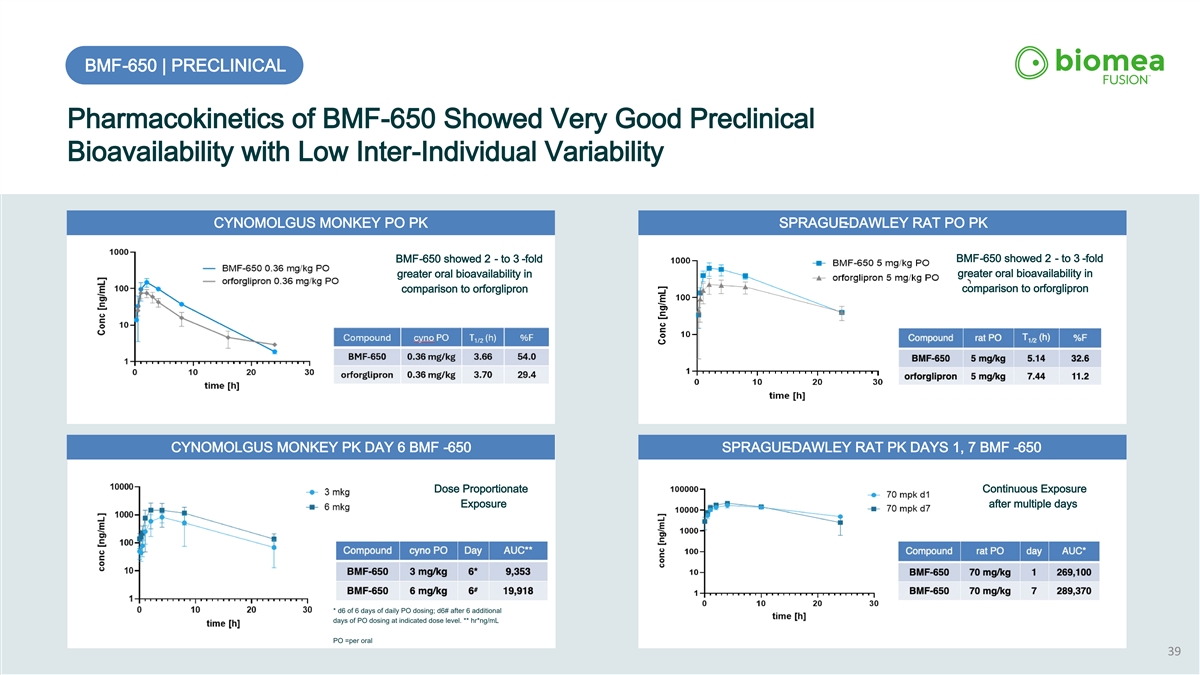
BMF-650 | PRECLINICAL Pharmacokinetics of BMF-650 Showed Very Good Preclinical Bioavailability with Low Inter-Individual Variability CYNOMOLGUS MONKEY PO PK SPRAGUE-DAWLEY RAT PO PK BMF-650 showed 2 - to 3 -fold BMF-650 showed 2 - to 3 -fold greater oral bioavailability in greater oral bioavailability in comparison to orforglipron comparison to orforglipron CYNOMOLGUS MONKEY PK DAY 6 BMF -650 SPRAGUE-DAWLEY RAT PK DAYS 1, 7 BMF -650 Dose Proportionate Continuous Exposure Exposure after multiple days * d6 of 6 days of daily PO dosing; d6# after 6 additional days of PO dosing at indicated dose level. ** hr*ng/mL PO =per oral 39

BMF-650 | PRECLINICAL Preclinical Weight-Loss Study in Obese Cynomolgus Monkeys STUDY OVERVIEW STUDY DESIGN PRE-STUDY: • 14-day acclimation; 3 groups (n=5) STUDY: 28 DAYS 14 DAYS • QD dosing via oral gavage for 28 days • BMF-650: 10 or 30 mg/kg, or vehicle GROUP 1 (n=5) VEHICLE ASSESSMENTS GROUP 2 (n=5) BMF-650, 10 mg/kg • Food provided as breakfast, fruit snack, and GROUP 3 (n=5) BMF-650, 30 mg/kg dinner; intake tracked • Body weight & physicals recorded daily • Lab values measured on days -5, 13, 20, 29 • Study captured daily food intake & weight change 40
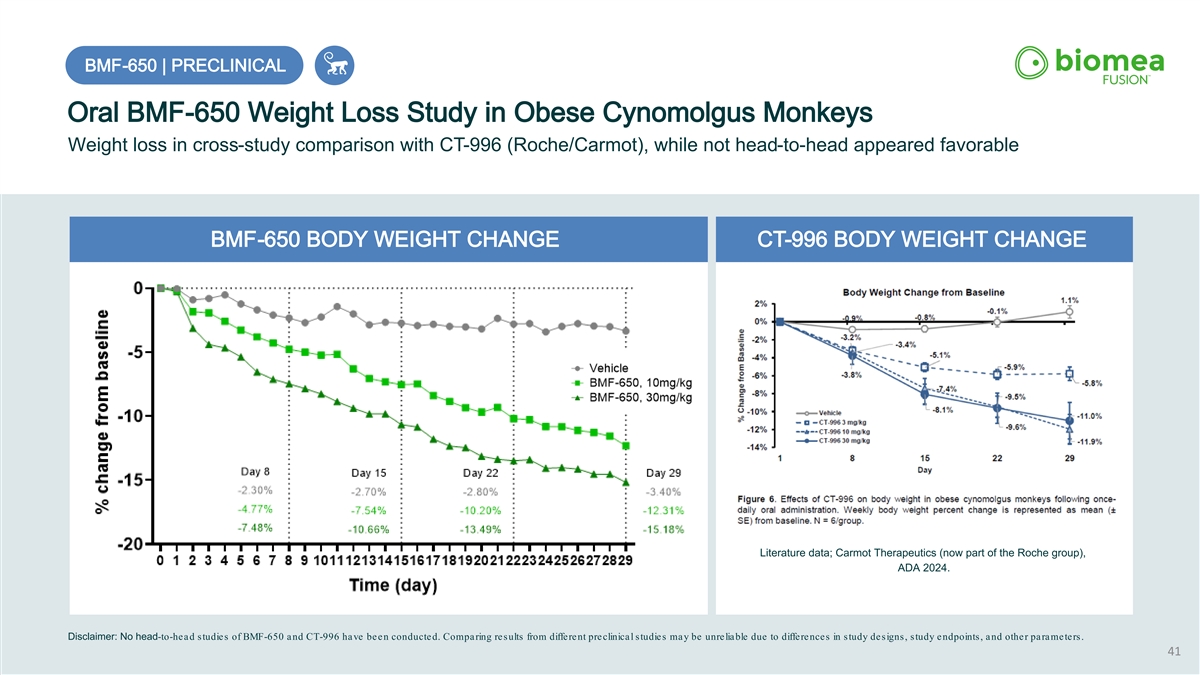
BMF BMF- -650 | PRECLINICAL 650 | PRECLINICAL Oral BMF-650 Weight Loss Study in Obese Cynomolgus Monkeys Weight loss in cross-study comparison with CT-996 (Roche/Carmot), while not head-to-head appeared favorable BMF-650 BODY WEIGHT CHANGE CT-996 BODY WEIGHT CHANGE Literature data; Carmot Therapeutics (now part of the Roche group), ADA 2024. Disclaimer: No head-to-head studies of BMF-650 and CT-996 have been conducted. Comparing results from different preclinical studies may be unreliable due to differences in study designs, study endpoints, and other parameters. 41
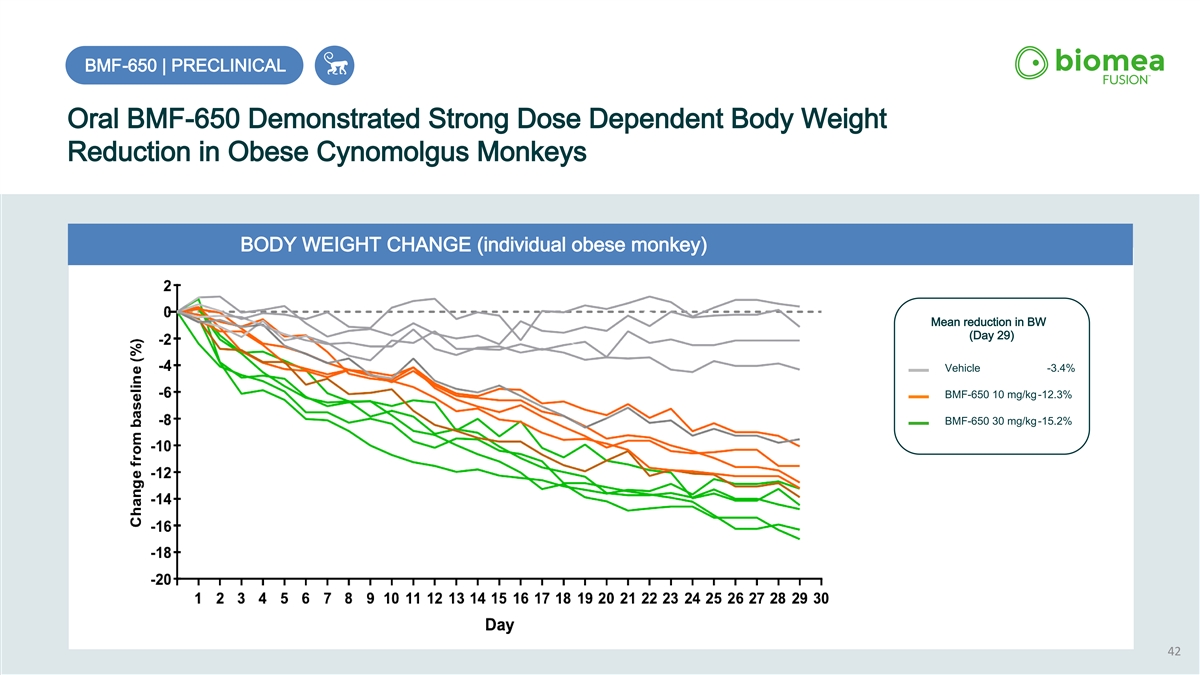
BMF-650 | PRECLINICAL Oral BMF-650 Demonstrated Strong Dose Dependent Body Weight Reduction in Obese Cynomolgus Monkeys BODY WEIGHT CHANGE (individual obese monkey) Mean reduction in BW (Day 29) Vehicle -3.4% BMF-650 10 mg/kg-12.3% BMF-650 30 mg/kg-15.2% 42

BMF-650 | PRECLINICAL Oral BMF-650 Generally Well Tolerated in 28 Day Preclinical Animal Study Low rate of emesis events, mostly in one animal, that decreased rapidly over time SAFETY SUMMARY • BMF-650 generally well tolerated with no elevations WEEK EMESIS of AST or ALT (Events per 70 weekly dosing occurrences) • With 420 dosing occurrences (280 active/140 1 16%* placebo) there were only a total of 18 (6.4%) events 2 4.2% of emesis in the active group 3 4.2% • Most events occurred early, with a marked decline after the first week 4 1.4% • Study was run without a titration scheme, once daily *One monkey (#3) accounted for 8 of the 18 total events dosing over 28 days 43
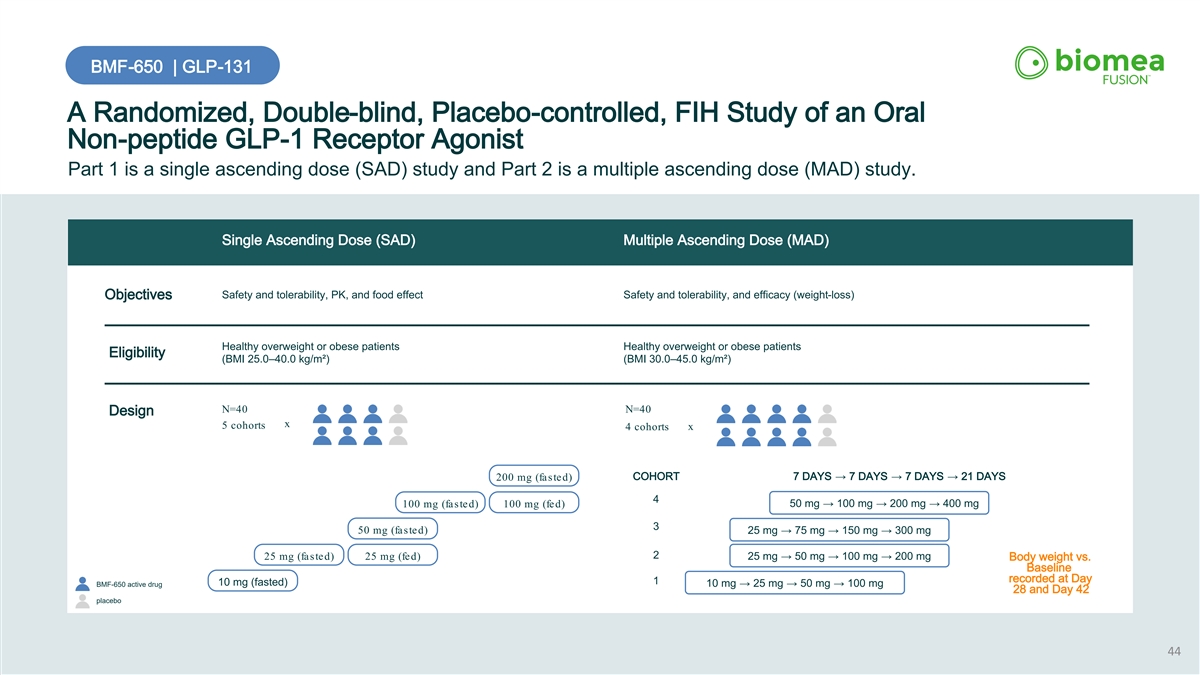
BMF-650 | GLP-131 A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled, FIH Study of an Oral Non-peptide GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Part 1 is a single ascending dose (SAD) study and Part 2 is a multiple ascending dose (MAD) study. Single Ascending Dose (SAD) Multiple Ascending Dose (MAD) Safety and tolerability, PK, and food effect Safety and tolerability, and efficacy (weight-loss) Objectives Healthy overweight or obese patients Healthy overweight or obese patients Eligibility (BMI 25.0–40.0 kg/m²) (BMI 30.0–45.0 kg/m²) N=40 N=40 Design x 5 cohorts 4 cohorts x COHORT 7 DAYS → 7 DAYS → 7 DAYS → 21 DAYS 200 mg (fasted) 4 50 mg → 100 mg → 200 mg → 400 mg 100 mg (fasted) 100 mg (fed) 3 50 mg (fasted) 25 mg → 75 mg → 150 mg → 300 mg 2 25 mg (fasted) 25 mg (fed) 25 mg → 50 mg → 100 mg → 200 mg Body weight vs. Baseline recorded at Day 1 10 mg (fasted) BMF-650 active drug 10 mg → 25 mg → 50 mg → 100 mg 28 and Day 42 placebo 44

BMF-650 Allowance for Intellectual Property of BMF-650 Received BMF-650 Intellectual Property: Our US and PCT applications for BMF-650 are published and proceeding through examination We received allowance in mid December 2025 for our US patent application covering BMF-650 Additional details, including the list of allowed claims, are available through the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO). 45
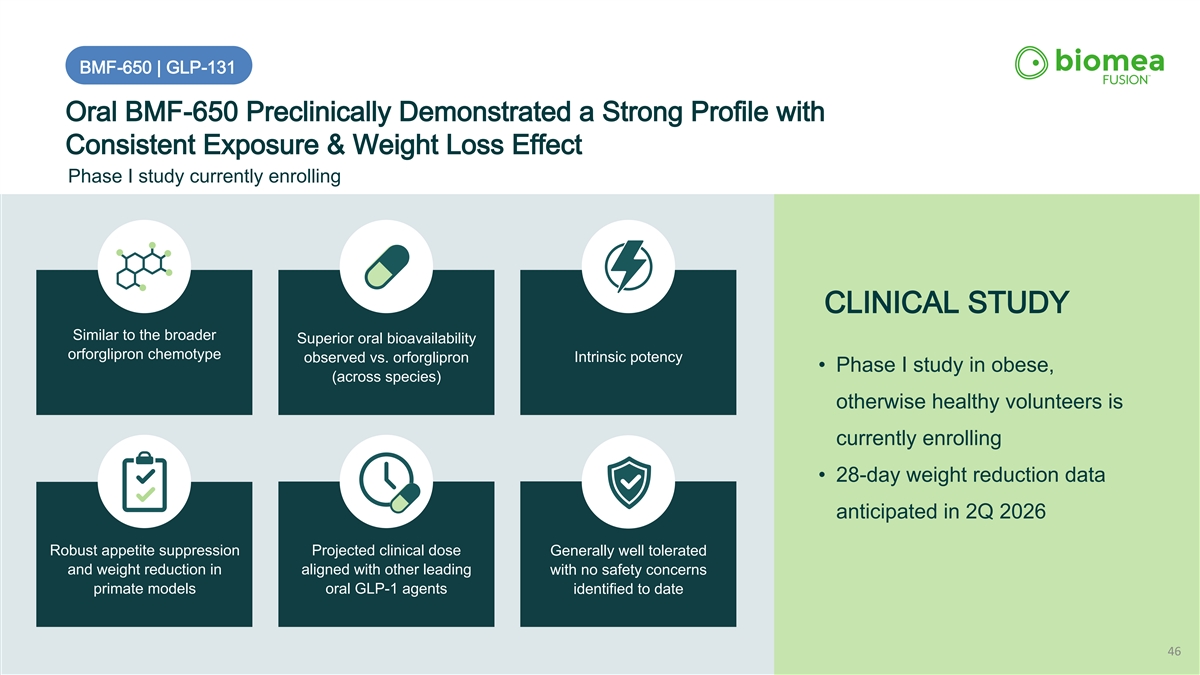
BMF-650 | GLP-131 Oral BMF-650 Preclinically Demonstrated a Strong Profile with Consistent Exposure & Weight Loss Effect Phase I study currently enrolling CLINICAL STUDY Similar to the broader Superior oral bioavailability orforglipron chemotype Intrinsic potency observed vs. orforglipron • Phase I study in obese, (across species) otherwise healthy volunteers is currently enrolling • 28-day weight reduction data anticipated in 2Q 2026 Robust appetite suppression Projected clinical dose Generally well tolerated and weight reduction in aligned with other leading with no safety concerns primate models oral GLP-1 agents identified to date 46

Advancing Multi Program Clinical Pipeline Through 2026 ICOVAMENIB ICOVAMENIB WITH GLP -1RA ICOVAMENIB BMF-650 COVALENT-121 COVALENT-211 COVALENT-212 GLP-131 Phase II T2D Patients not Food Effect Study Phase IIb Insulin Deficient Phase I Obesity Study controlled on GLP -1 based T2D Patients therapies Evaluate icovamenib Evaluate Safety of BMF- Evaluate icovamenib in Optimize Dosing + + + + added to GLP-1 based 650 and 28-Day Weight Insulin Deficient T2D Criteria Therapies in T2D Reduction in Obese Patients Started September + Patients 2025 + First Patient Enrollment + First Patient Enrollment Study Enrollment + Panned in 1Q 2026 Completed in Panned in 1Q 2026 Completion Expected + December 2025 2Q 2026 47
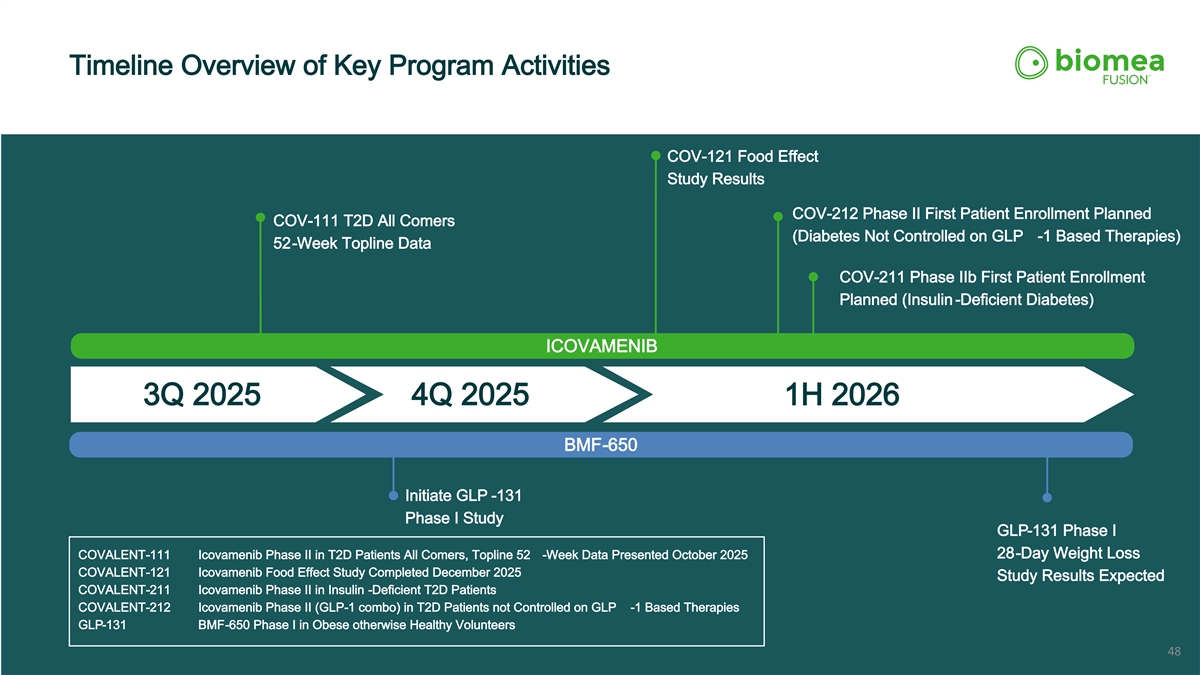
Timeline Overview of Key Program Activities COV-121 Food Effect Study Results COV-212 Phase II First Patient Enrollment Planned COV-111 T2D All Comers (Diabetes Not Controlled on GLP -1 Based Therapies) 52-Week Topline Data COV-211 Phase IIb First Patient Enrollment Planned (Insulin -Deficient Diabetes) ICOVAMENIB 3Q 2025 4Q 2025 1H 2026 BMF-650 Initiate GLP -131 Phase I Study GLP-131 Phase I 28-Day Weight Loss COVALENT-111 Icovamenib Phase II in T2D Patients All Comers, Topline 52 -Week Data Presented October 2025 COVALENT-121 Icovamenib Food Effect Study Completed December 2025 Study Results Expected COVALENT-211 Icovamenib Phase II in Insulin -Deficient T2D Patients COVALENT-212 Icovamenib Phase II (GLP-1 combo) in T2D Patients not Controlled on GLP -1 Based Therapies GLP-131 BMF-650 Phase I in Obese otherwise Healthy Volunteers 48

Key Opinion Leader Highlight Icovamenib’s Potential to Redefine Diabetes Care “Icovamenib's recent data has shown an “The icovamenib data looks exciting. The “Great foray into precision medicine. We impressive restoration of beta cell data presented today help to confirm need to be addressing patients in a much function as demonstrated by significant icovamenib’s mechanism of action. We more individualized manner. By elevations in C-peptide even after the have not previously seen data like this addressing insulin-deficient diabetes treatment period ended. with any antihyperglycemic agent. patients with icovamenib, we have seen post treatment that the beta cell pool is This data validates the mechanism of As more trials are conducted, I believe being restored and producing a higher action of this menin inhibitor as a disease that inhibition of menin may lead to level of insulin, as measured by C- modifying agent and helps address the benefits across all subtypes of diabetes. I peptide. poor adherence and persistence applaud Biomea for developing a potential commonly seen in type 2 diabetes.” new treatment option that may be disease This indicates a fundamental and modifying for patients with diabetes.” potentially lasting impact on the disease and validates the mechanism of action of Steve Edelman, M.D. menin inhibition.” ENDOCRINOLOGIST, PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE UCSD / VA SAN Ralph DeFronzo, M.D. Melanie Davies, M.D. DIEGO ENDOCRINOLOGIST, PROFESSOR DIABETOLOGIST, PROFESSOR OF OF MEDICINE UTHSCSA DIABETES MEDICINE AT THE UNIVERSITY OF LEICESTER 49

Key Opinion Leader Highlight Icovamenib’s Potential to Redefine Diabetes Care “We do not have an agent today that “The icovamenib data are quite “Icovamenib is a very interesting addresses one of the root cause of interesting because of the continued molecule that acts quite differently than diabetes - beta cell dysfunction - effects despite having stopped it. anything I have seen before. We are icovamenib would be the first. observing glucose controlled and beta Usually, one would expect to see the cell-specific proliferation and an increase Patients are achieving lasting benefits HbA1c levels climb towards baseline in stimulated C-peptide secretion leading without continuous chronic dosing, when the medication is stopped, but with to patient benefits that continued after the suggesting that icovamenib may be icovamenib, the HbA1c levels decreased, icovamenib dosage ended. disease modifying. I am very impressed.” which is quite intriguing and unprecedented.” I am very excited to further explore the many opportunities that the covalent Alice Cheng, M.D. inhibition of menin will provide to ENDOCRINOLOGIST, ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE patients.” Julio Rosenstock, M.D. UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO DIRECTOR VELOCITY CLINICAL RESEARCH AT MEDICAL CITY Rohit Kulkarni, DALLAS AND CLINICAL PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, UNIV. OF TEXAS M.D., Ph.D. SOUTHWESTERN MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE AT HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL 50

THANK YOU For questions or inquiries, please reach out to Meichiel Weiss at ir@biomeafusion.com www.biomeafusion.com