

RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT DAY Virtual Event | December 5, 2025 NASDAQ: CADL

Forward-looking statements This presentation contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. All statements other than statements of historical facts contained in this Presentation, including express or implied statements regarding our strategy, future financial condition, future operations, projected costs, prospects, plans, objectives of management and expected market size, are forward-looking statements. In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by terminology such as “may,” “will,” “should,” “expect,” “intend,” “plan,” “anticipate,” “believe,” “estimate,” “target,” “seek,” “predict,” “potential,” “continue” or the negative of these terms or other comparable terminology. Although we believe that the expectations reflected in these forward-looking statements are reasonable, these statements relate to our strategy, future operations, future financial position, future revenue, projected costs, prospects, plans, objectives of management and expected market size, and involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that may cause our actual results, performance or achievements to be materially different from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by these forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements in this Presentation include, but are not limited to, statements about: the initiation, timing, progress, results, and cost of our research and development programs and our current and future preclinical and clinical studies, including statements regarding the timing of initiation and completion of studies or trials and related preparatory work, the period during which the results of the trials will become available, and our research and development programs; the therapeutic benefit of our programs, including the potential for our programs to extend patient survival; our ability to efficiently discover and develop product candidates; our ability to initiate, recruit and enroll patients in and conduct our clinical trials at the pace that we project; our ability to obtain and maintain regulatory approval of our product candidates; our ability to compete with companies currently marketing or engaged in the development of treatments that our product candidates are designed to target; our reliance on third parties to conduct our clinical trials and to manufacture drug substance for use in our clinical trials; the size and growth potential of the markets for our product candidates and our ability to serve those markets; the ability and willingness of our third-party strategic collaborators to continue research and development activities relating to our development candidates and product candidates; our ability to obtain and maintain adequate intellectual property rights; our estimates of our future expenses, revenue, capital requirements or our need for or ability to obtain additional financing; our ability to continue as a going concern, the potential benefits of strategic collaboration agreements, our ability to enter into additional strategic collaborations or arrangements, and our ability to attract collaborators with development, regulatory and commercialization expertise; our financial performance; and developments and projections relating to our competitors or our industry. We caution the recipient not to place considerable reliance on the forward-looking statements contained in this Presentation. The forward-looking statements in this Presentation speak only as of the date of this document, and we undertake no obligation to update or revise any of these statements. Our business is subject to substantial risks and uncertainties, including those referenced above. Certain information contained in this Presentation relates to or is based on estimates, projections and other information concerning the Company’s industry, its business and the markets for its programs and product candidates and studies, publications, surveys and other data obtained from third-party sources and the Company's own internal estimates and research. While the Company believes these third-party sources to be reliable as of the date of this Presentation, it has not independently verified, and makes no representation as to the adequacy, fairness, accuracy or completeness of, any information obtained from third-party sources. In addition, all of the market data included in this Presentation involves a number of assumptions; there can be no guarantee as to the accuracy or reliability of such assumptions. Finally, while we believe our own internal research is reliable, such research has not been verified by any independent source. These forward-looking statements are based on the beliefs of our management as well as assumptions made by and information currently available to us. Although we believe the expectations reflected in such forward-looking statements are reasonable, we can give no assurance that such expectations will prove to be correct. If such assumptions do not fully materialize or prove incorrect, the events or circumstances referred to in the forward-looking statements may not occur. We undertake no obligation to update publicly any forward-looking statements for any reason after the date of this presentation to conform these statements to actual results or to changes in our expectations, except as required by law. Accordingly, readers are cautioned not to place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements. Additional risks and uncertainties that could affect our business are included under the caption “Risk Factors” in our most recent Form 10-Q filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on November 13, 2025.

Candel at a glance o CAN-2409 (aglitimagene besadenovec): Off-the-shelf pan-solid tumor therapy, individualized anticancer immune response • Positive phase 3 randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial in localized, intermediate- to high-risk prostate cancer • Positive overall survival data from randomized phase 2a clinical trial of CAN-2409 in borderline resectable pancreatic cancer • Positive overall survival data from randomized phase 2a clinical trial of CAN-2409 in therapy-resistant non-small cell lung cancer • FDA Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapy (RMAT) designation in prostate cancer, Fast Track designation in NSCLC, pancreatic cancer, and prostate cancer. Orphan Drug designation in pancreatic cancer • “Pipeline in a product” strategy advancing multiple programs in several large indications o CAN-3110 (linoserpaturev): Oncolytic HSV-1 designed for tumor-specific replication • Proof of concept in patients with recurrent high-grade glioma, published in Nature and Science Translational Medicine • Fast Track designation, Orphan Drug designation • Opportunity for creation of “pipeline in a product” by expansion into indications beyond brain cancers o Corporate highlights • Experienced Executive Team and strong scientific support from high-profile Research Advisory Board • Cash and cash equivalents of $87.0 million as of September 30, 2025; expected runway into Q1 2027 • Entered into a term loan facility of up to $130 million in October 2025 • IP protection: CAN-2409 (2034, method of use); CAN-3110 (2036, composition of matter); 12 years data exclusivity • Low-cost manufacturing • Precommercialization activities underway to support potential post approval commercial launch of CAN-2409
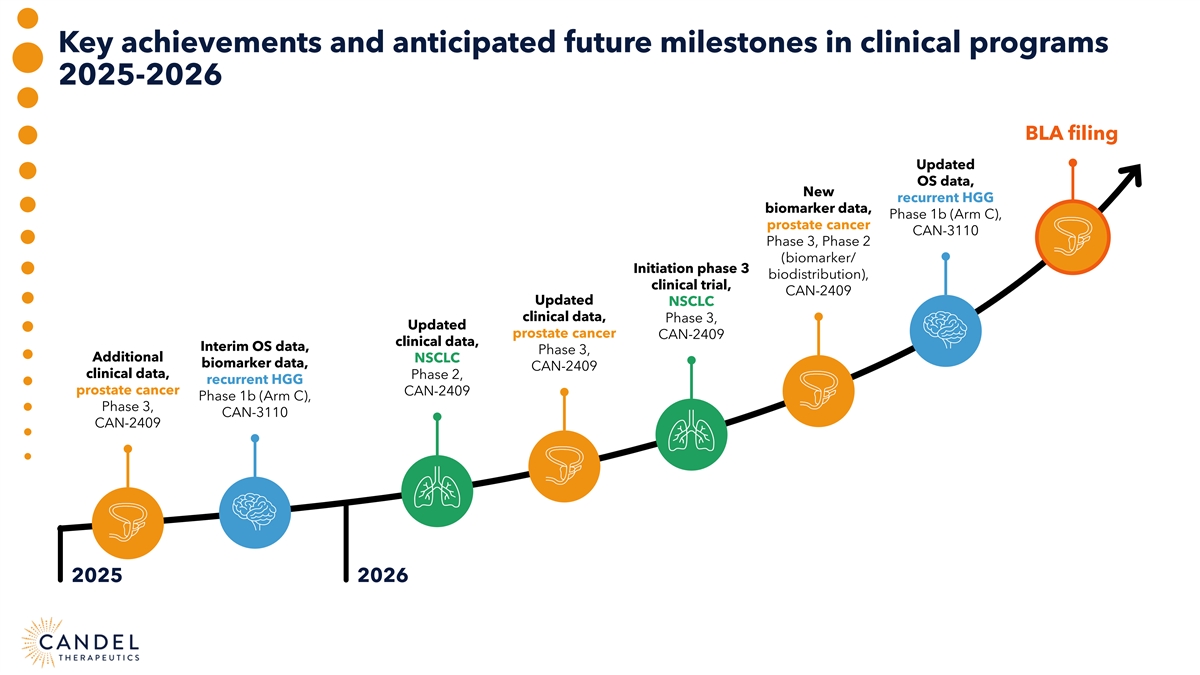
Key achievements and anticipated future milestones in clinical programs 2025-2026 BLA filing Updated OS data, New recurrent HGG biomarker data, Phase 1b (Arm C), prostate cancer CAN-3110 Phase 3, Phase 2 (biomarker/ Initiation phase 3 biodistribution), clinical trial, CAN-2409 Updated NSCLC clinical data, Phase 3, Updated prostate cancer CAN-2409 clinical data, Interim OS data, Phase 3, Additional NSCLC biomarker data, CAN-2409 clinical data, Phase 2, recurrent HGG prostate cancer CAN-2409 Phase 1b (Arm C), Phase 3, CAN-3110 CAN-2409 2025 2026

Leadership team with decades of experience in oncology, immunology, and drug development Paul Peter Tak, MD, PhD, FMedSci Charles Schoch, MBA, MSA President & Chief Executive Officer Chief Financial Officer Francesca Barone, MD, PhD Garrett Nichols, MD, MS Chief Scientific Officer Chief Medical Officer Seshu Tyagarajan, PhD, RAC Susan Stewart, JD Chief Technical and Development Officer Chief Regulatory Officer

Research Advisory Board of premier thought leaders James Allison, PhD Edward Benz, MD Henry Brem, MD Roy Herbst, MD, PhD Elizabeth M. Jaffee, MD Chair of the Department of President and CEO Emeritus Director, Department of Chief of Medical Oncology Deputy Director of the Sidney Immunology, MD Anderson Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Neurosurgery Yale Cancer Center Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Cancer Center Professor of Neurosurgery Center at Johns Hopkins and Johns Hopkins University Co-Director of the Gastrointestinal Director of the Parker Institute Cancers Program for Cancer Research 2018 Nobel Recipient Carl H. June, MD Philip Kantoff, MD Gary Nabel, MD, PhD Bali Pulendran, PhD Padmanee Sharma, MD, PhD Richard W. Vaque Professor Former Chair, Department of Chief Innovation Officer of OPKO Violetta L. Horton Professor at Professor of Genitourinary in Immunotherapy, Perelman Medicine, Memorial Sloan and President/CEO of ModeX Stanford University School of Medical Oncology and School of Medicine, Kettering Cancer Center Therapeutics Medicine and Director of the Immunology , MD Anderson University of Pennsylvania Institute for Immunity, Cancer Center Former CSO Sanofi Transplantation and Infection at Stanford University

R&D Day 2025: Agenda Introduction to Candel Therapeutics 11:00–11:10 AM 1 Immuno-oncology: The Next Wave of Innovation 11:10–11:40 AM 2 CAN-2409 for Newly Diagnosed Localized Prostate Cancer 11:40–12:10 PM 3 Road Map to Biologics License Application (BLA) 12:10–12:30 PM 4 12:30–12:50 PM 5 Pre-Commercialization Road Map CAN-2409 for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Refractory Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer 12:50–1:15 PM 6 CAN-3110 for Recurrent Glioblastoma 1:15–1:30 PM 7 Analyst | Management Q&A/Closing 1:30–2:00 PM 8

IMMUNO-ONCOLOGY: THE NEXT WAVE OF INNOVATION James P. Allison, PhD, Nobel Laureate, Regental Professor and Chair of Immunology, and Founding Director of Scientific Programs for the James P. Allison Institute at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Carl H. June, MD, Richard W. Vague Professor in Immunotherapy and Director, Center for Cellular Immunotherapies and Parker Institute for Cancer Therapy, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Padmanee Sharma, MD, PhD, Professor of Genitourinary Medical Oncology and Immunology, and Director of Scientific Programs for the James P. Allison Institute at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Moderator: Yigal Nochomovitz, PhD, Citi Group

CAN-2409 FOR NEWLY DIAGNOSED LOCALIZED PROSTATE CANCER Glen Gejerman, MD, Co-chief of Urologic Oncology, Hackensack University Medical Center Philip Kantoff, MD, Former Chair Department of Medicine, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, CEO, Convergent Therapeutics Garrett Nichols, MD, MS, Candel’s Chief Medical Officer Ron Tutrone, MD, National Director of Clinical Research, United Urology Moderator: Oliver McCammon, LifeSci Capital
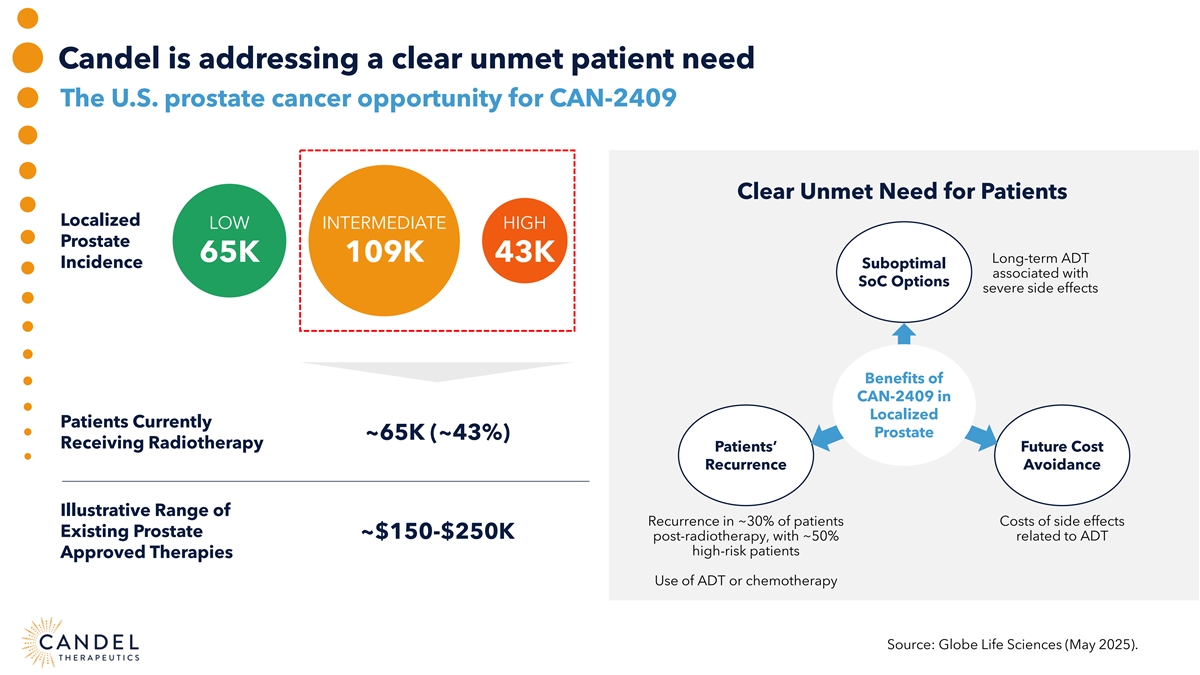
Candel is addressing a clear unmet patient need The U.S. prostate cancer opportunity for CAN-2409 Clear Unmet Need for Patients Localized LOW INTERMEDIATE HIGH Prostate 65K 109K 43K Long-term ADT Incidence Suboptimal associated with SoC Options severe side effects Benefits of CAN-2409 in Localized Patients Currently Prostate ~65K (~43%) Receiving Radiotherapy Patients’ Future Cost Recurrence Avoidance Illustrative Range of Recurrence in ~30% of patients Costs of side effects Existing Prostate ~$150-$250K post-radiotherapy, with ~50% related to ADT high-risk patients Approved Therapies Use of ADT or chemotherapy Source: Globe Life Sciences (May 2025).
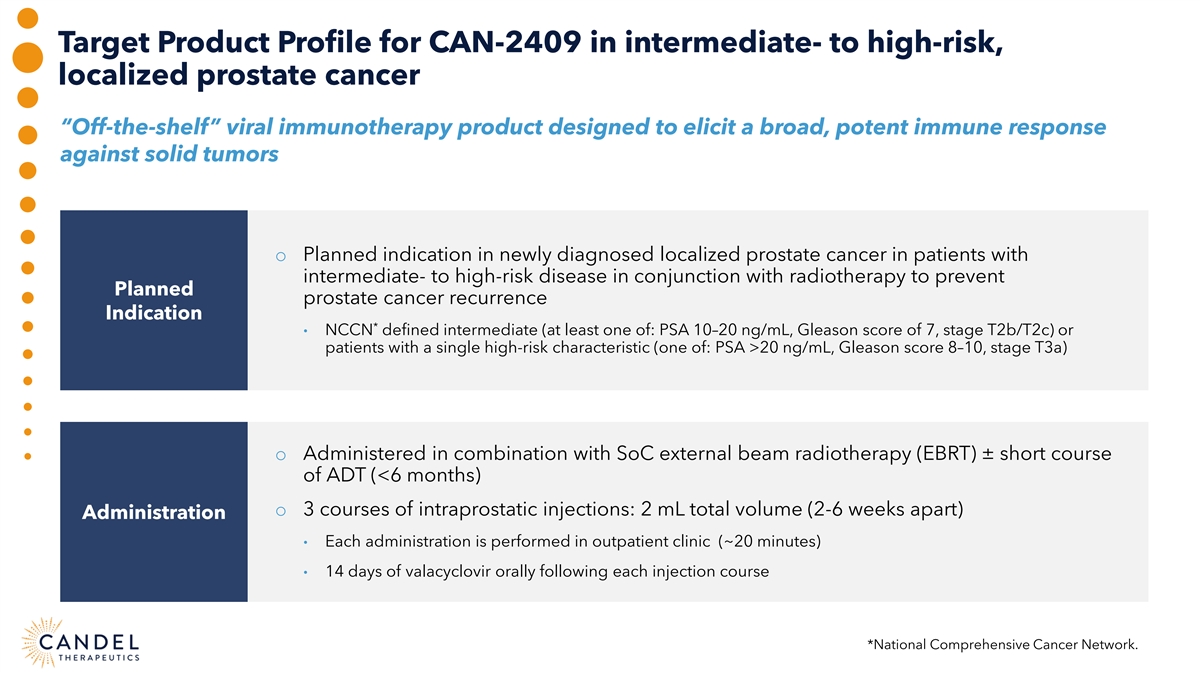
Target Product Profile for CAN-2409 in intermediate- to high-risk, localized prostate cancer “Off-the-shelf” viral immunotherapy product designed to elicit a broad, potent immune response against solid tumors o Planned indication in newly diagnosed localized prostate cancer in patients with intermediate- to high-risk disease in conjunction with radiotherapy to prevent Planned prostate cancer recurrence Indication * • NCCN defined intermediate (at least one of: PSA 10–20 ng/mL, Gleason score of 7, stage T2b/T2c) or patients with a single high-risk characteristic (one of: PSA >20 ng/mL, Gleason score 8–10, stage T3a) o Administered in combination with SoC external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) ± short course of ADT (<6 months) o 3 courses of intraprostatic injections: 2 mL total volume (2-6 weeks apart) Administration • Each administration is performed in outpatient clinic (~20 minutes) • 14 days of valacyclovir orally following each injection course *National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
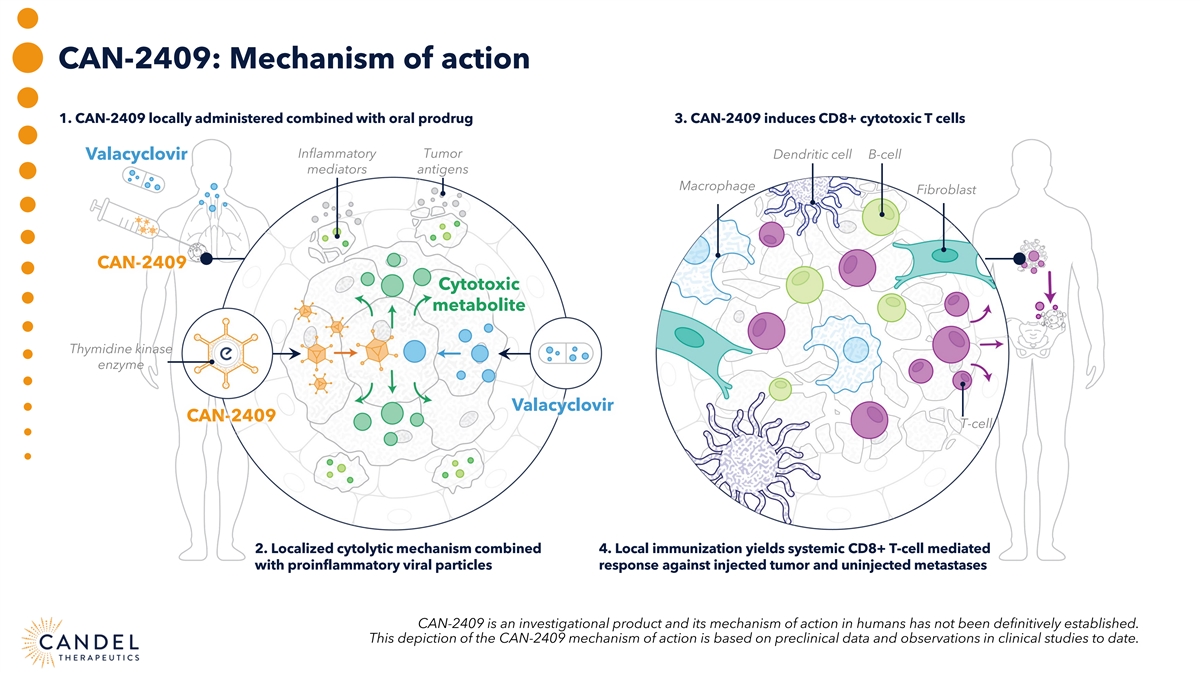
CAN-2409: Mechanism of action 1. CAN-2409 locally administered combined with oral prodrug 3. CAN-2409 induces CD8+ cytotoxic T cells Inflammatory Tumor Dendritic cell B-cell Valacyclovir mediators antigens Macrophage Fibroblast CAN-2409 Cytotoxic metabolite Thymidine kinase enzyme Valacyclovir CAN-2409 T-cell 2. Localized cytolytic mechanism combined 4. Local immunization yields systemic CD8+ T-cell mediated with proinflammatory viral particles response against injected tumor and uninjected metastases CAN-2409 is an investigational product and its mechanism of action in humans has not been definitively established. This depiction of the CAN-2409 mechanism of action is based on preclinical data and observations in clinical studies to date.
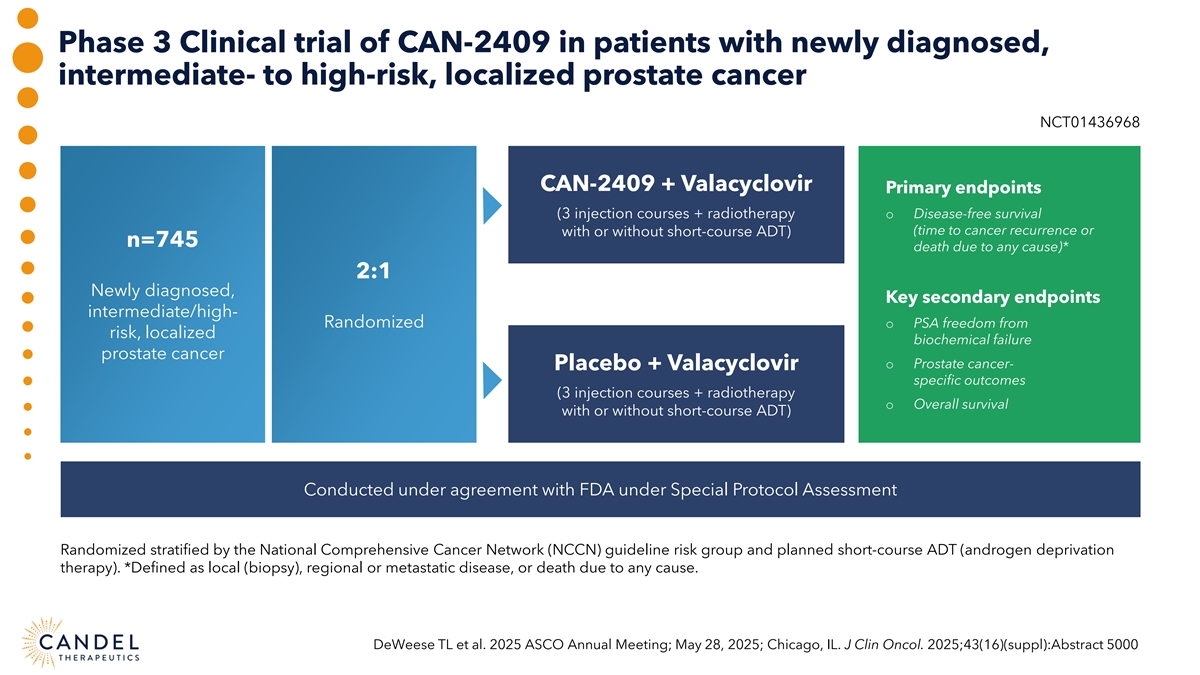
Phase 3 Clinical trial of CAN-2409 in patients with newly diagnosed, intermediate- to high-risk, localized prostate cancer NCT01436968 CAN-2409 + Valacyclovir Primary endpoints (3 injection courses + radiotherapy o Disease-free survival (time to cancer recurrence or with or without short-course ADT) n=745 death due to any cause)* 2:1 Newly diagnosed, Key secondary endpoints intermediate/high- Randomized o PSA freedom from risk, localized biochemical failure prostate cancer o Prostate cancer- Placebo + Valacyclovir specific outcomes (3 injection courses + radiotherapy o Overall survival with or without short-course ADT) Conducted under agreement with FDA under Special Protocol Assessment Randomized stratified by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guideline risk group and planned short-course ADT (androgen deprivation therapy). *Defined as local (biopsy), regional or metastatic disease, or death due to any cause. DeWeese TL et al. 2025 ASCO Annual Meeting; May 28, 2025; Chicago, IL. J Clin Oncol. 2025;43(16)(suppl):Abstract 5000
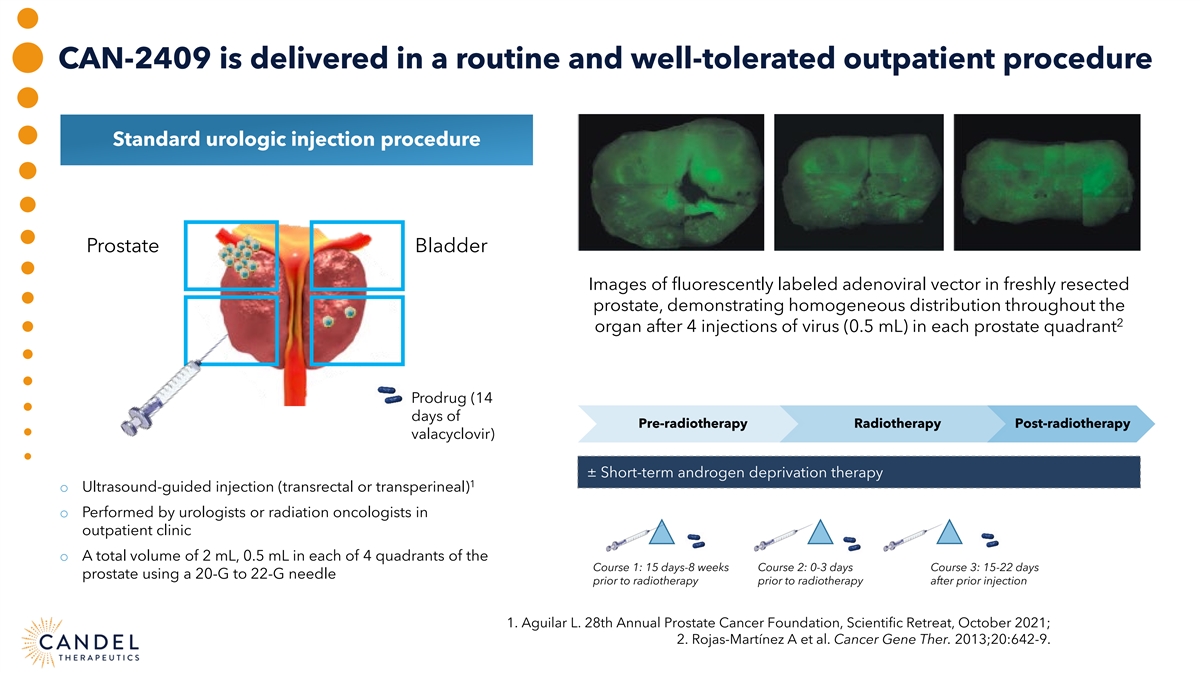
CAN-2409 is delivered in a routine and well-tolerated outpatient procedure Standard urologic injection procedure Prostate Bladder Images of fluorescently labeled adenoviral vector in freshly resected prostate, demonstrating homogeneous distribution throughout the 2 organ after 4 injections of virus (0.5 mL) in each prostate quadrant Prodrug (14 days of Pre-radiotherapy Radiotherapy Post-radiotherapy valacyclovir) ± Short-term androgen deprivation therapy 1 o Ultrasound-guided injection (transrectal or transperineal) o Performed by urologists or radiation oncologists in outpatient clinic o A total volume of 2 mL, 0.5 mL in each of 4 quadrants of the Course 1: 15 days-8 weeks Course 2: 0-3 days Course 3: 15-22 days prostate using a 20-G to 22-G needle prior to radiotherapy prior to radiotherapy after prior injection 1. Aguilar L. 28th Annual Prostate Cancer Foundation, Scientific Retreat, October 2021; 2. Rojas-Martínez A et al. Cancer Gene Ther. 2013;20:642-9.
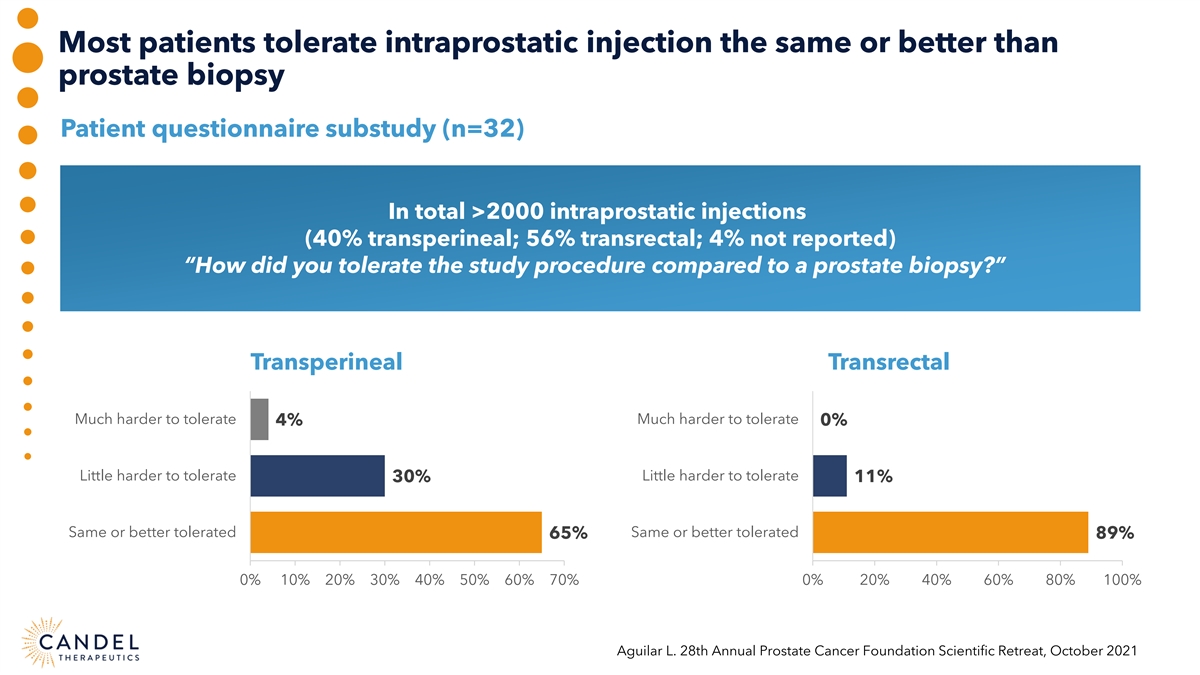
Most patients tolerate intraprostatic injection the same or better than prostate biopsy Patient questionnaire substudy (n=32) In total >2000 intraprostatic injections (40% transperineal; 56% transrectal; 4% not reported) “How did you tolerate the study procedure compared to a prostate biopsy?” Transperineal Transrectal Much harder to tolerate Much harder to tolerate 4% 0% Little harder to tolerate Little harder to tolerate 30% 11% Same or better tolerated Same or better tolerated 65% 89% 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% Aguilar L. 28th Annual Prostate Cancer Foundation Scientific Retreat, October 2021
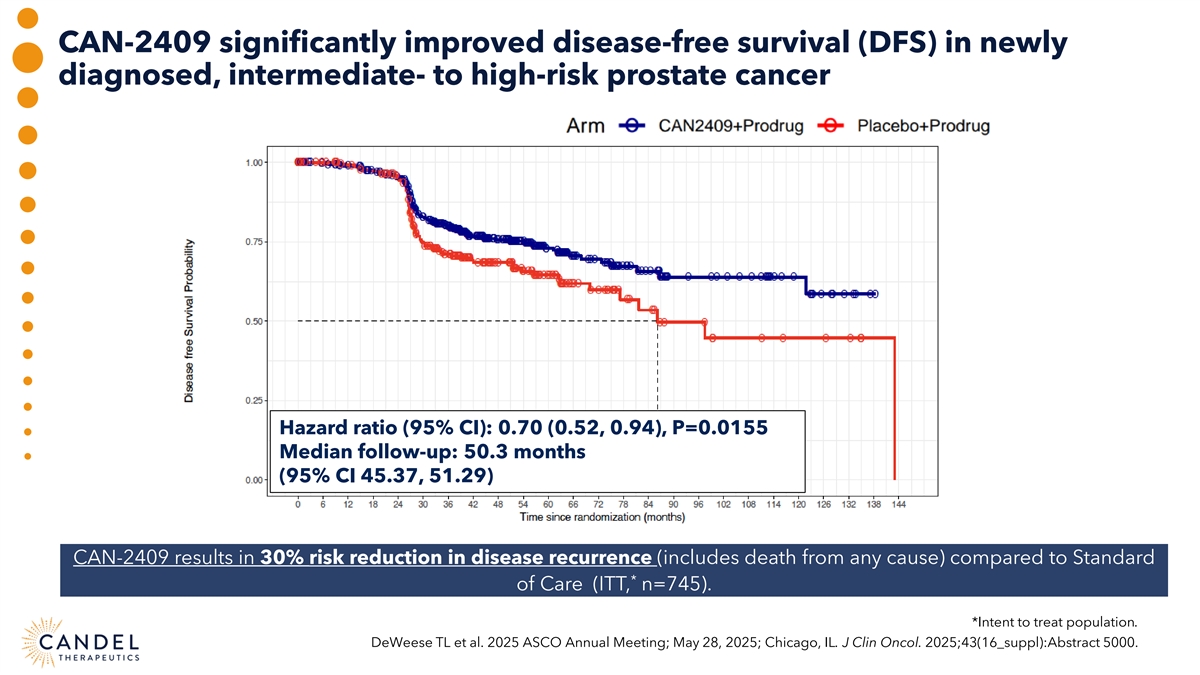
CAN-2409 significantly improved disease-free survival (DFS) in newly diagnosed, intermediate- to high-risk prostate cancer Hazard ratio (95% CI): 0.70 (0.52, 0.94), P=0.0155 Median follow-up: 50.3 months (95% CI 45.37, 51.29) CAN-2409 results in 30% risk reduction in disease recurrence (includes death from any cause) compared to Standard * of Care (ITT, n=745). *Intent to treat population. DeWeese TL et al. 2025 ASCO Annual Meeting; May 28, 2025; Chicago, IL. J Clin Oncol. 2025;43(16_suppl):Abstract 5000.
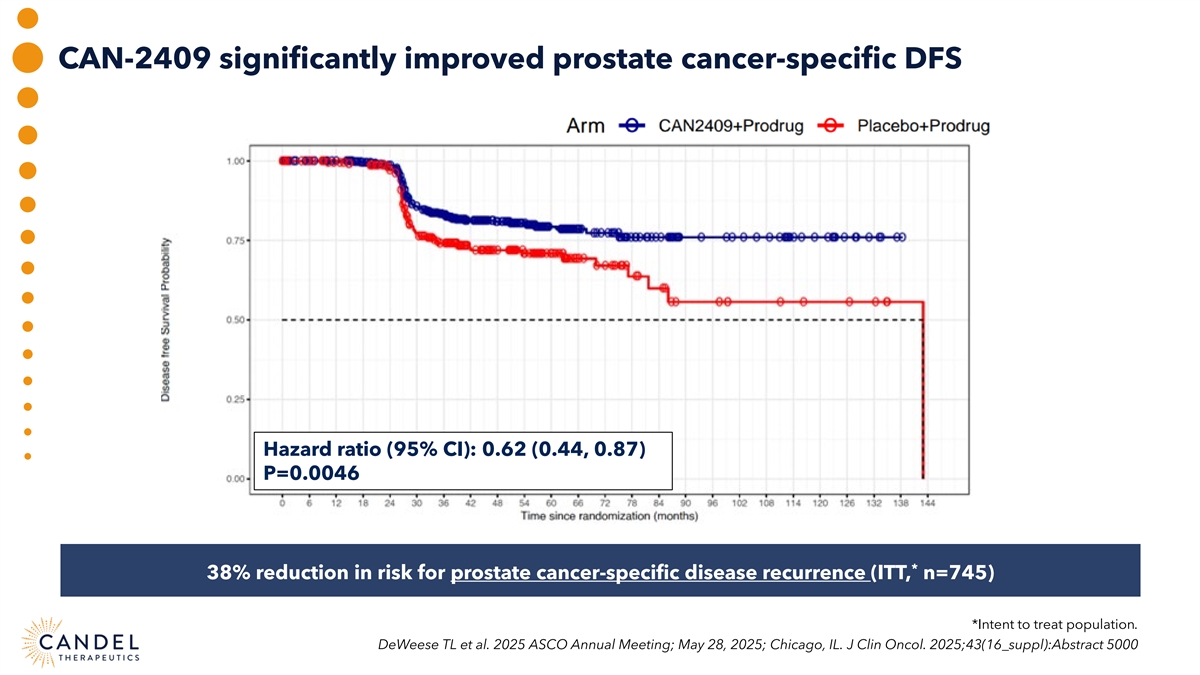
CAN-2409 significantly improved prostate cancer-specific DFS Hazard ratio (95% CI): 0.62 (0.44, 0.87) P=0.0046 * 38% reduction in risk for prostate cancer-specific disease recurrence (ITT, n=745) *Intent to treat population. DeWeese TL et al. 2025 ASCO Annual Meeting; May 28, 2025; Chicago, IL. J Clin Oncol. 2025;43(16_suppl):Abstract 5000
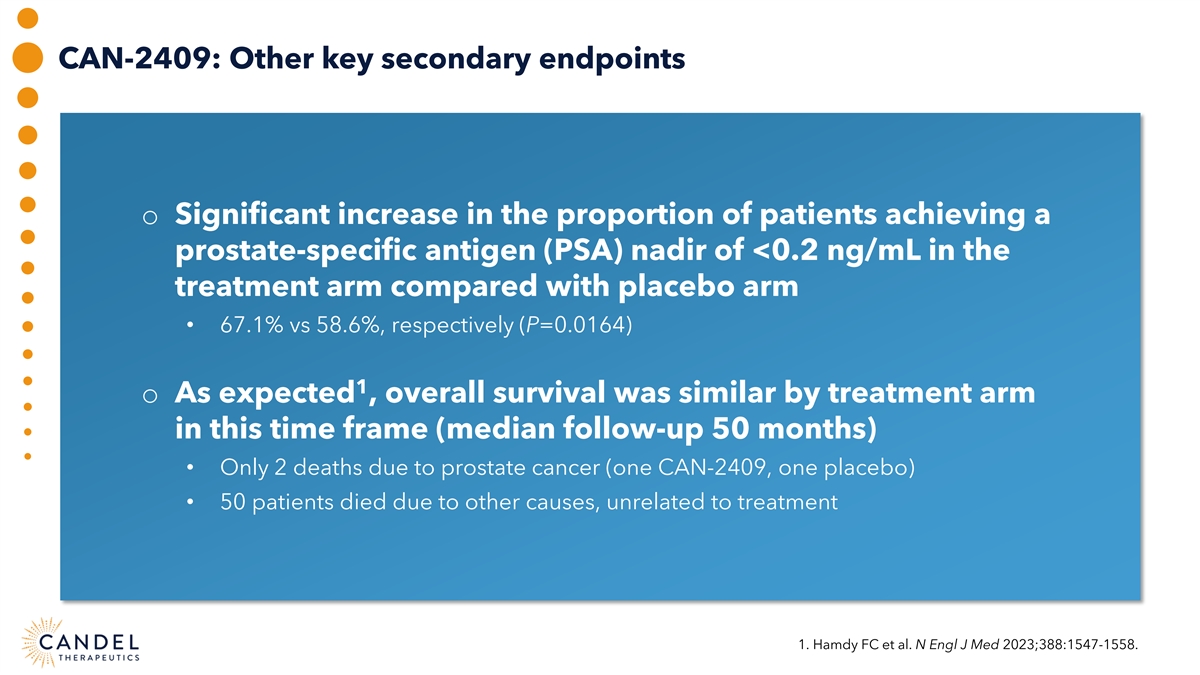
CAN-2409: Other key secondary endpoints o Significant increase in the proportion of patients achieving a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) nadir of <0.2 ng/mL in the treatment arm compared with placebo arm • 67.1% vs 58.6%, respectively (P=0.0164) 1 o As expected , overall survival was similar by treatment arm in this time frame (median follow-up 50 months) • Only 2 deaths due to prostate cancer (one CAN-2409, one placebo) • 50 patients died due to other causes, unrelated to treatment 1. Hamdy FC et al. N Engl J Med 2023;388:1547-1558.
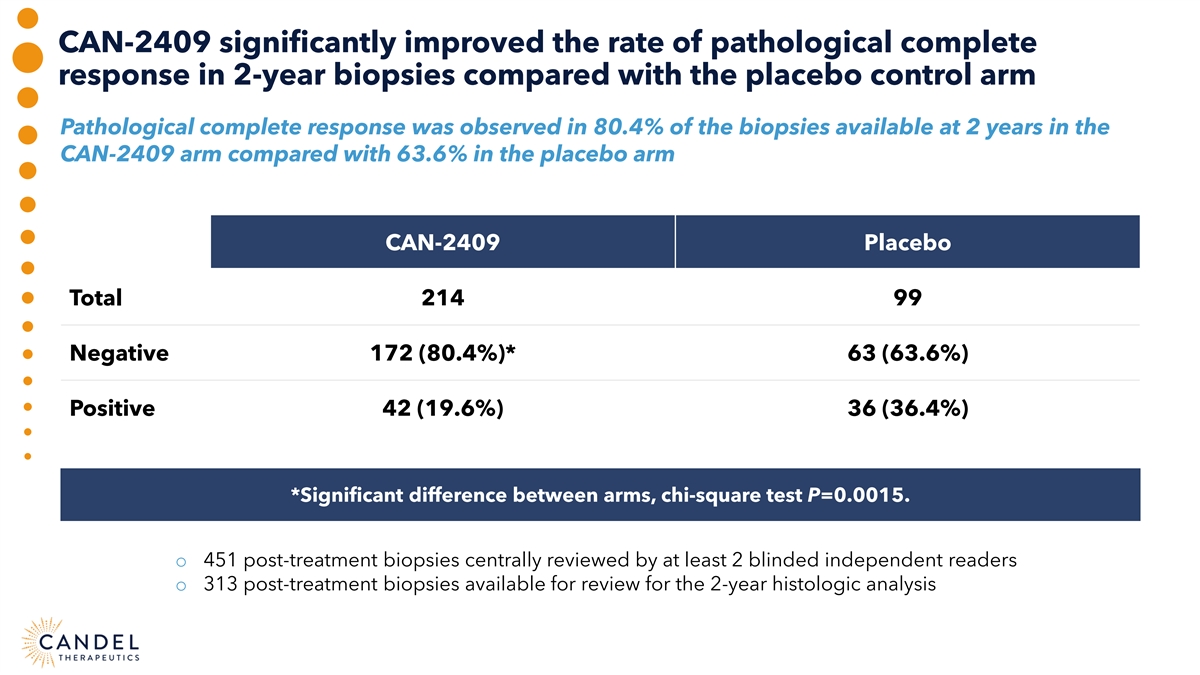
CAN-2409 significantly improved the rate of pathological complete response in 2-year biopsies compared with the placebo control arm Pathological complete response was observed in 80.4% of the biopsies available at 2 years in the CAN-2409 arm compared with 63.6% in the placebo arm CAN-2409 Placebo Total 214 99 Negative 172 (80.4%)* 63 (63.6%) Positive 42 (19.6%) 36 (36.4%) *Significant difference between arms, chi-square test P=0.0015. o 451 post-treatment biopsies centrally reviewed by at least 2 blinded independent readers o 313 post-treatment biopsies available for review for the 2-year histologic analysis
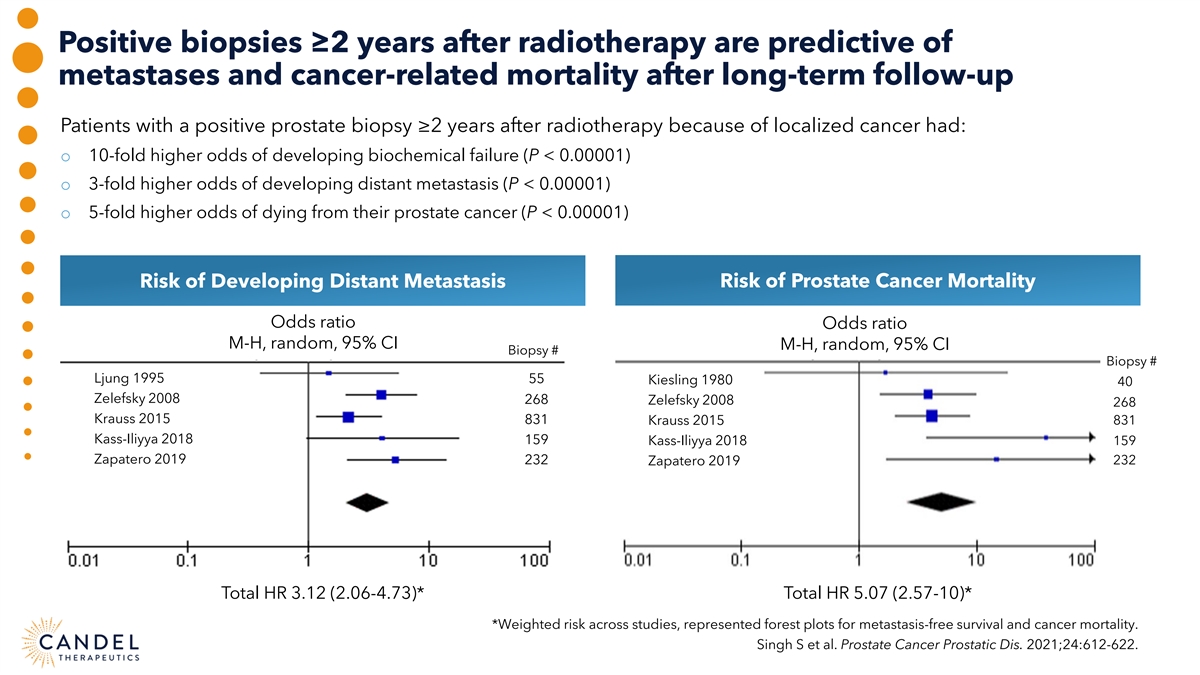
Positive biopsies ≥2 years after radiotherapy are predictive of metastases and cancer-related mortality after long-term follow-up Patients with a positive prostate biopsy ≥2 years after radiotherapy because of localized cancer had: o 10-fold higher odds of developing biochemical failure (P < 0.00001) o 3-fold higher odds of developing distant metastasis (P < 0.00001) o 5-fold higher odds of dying from their prostate cancer (P < 0.00001) Risk of Developing Distant Metastasis Risk of Prostate Cancer Mortality Odds ratio Odds ratio M-H, random, 95% CI M-H, random, 95% CI Biopsy # Biopsy # Ljung 1995 55 Kiesling 1980 40 Zelefsky 2008 268 Zelefsky 2008 268 Krauss 2015 831 Krauss 2015 831 Kass-Iliyya 2018 159 Kass-Iliyya 2018 159 Zapatero 2019 232 Zapatero 2019 232 Total HR 3.12 (2.06-4.73)* Total HR 5.07 (2.57-10)* *Weighted risk across studies, represented forest plots for metastasis-free survival and cancer mortality. Singh S et al. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2021;24:612-622.
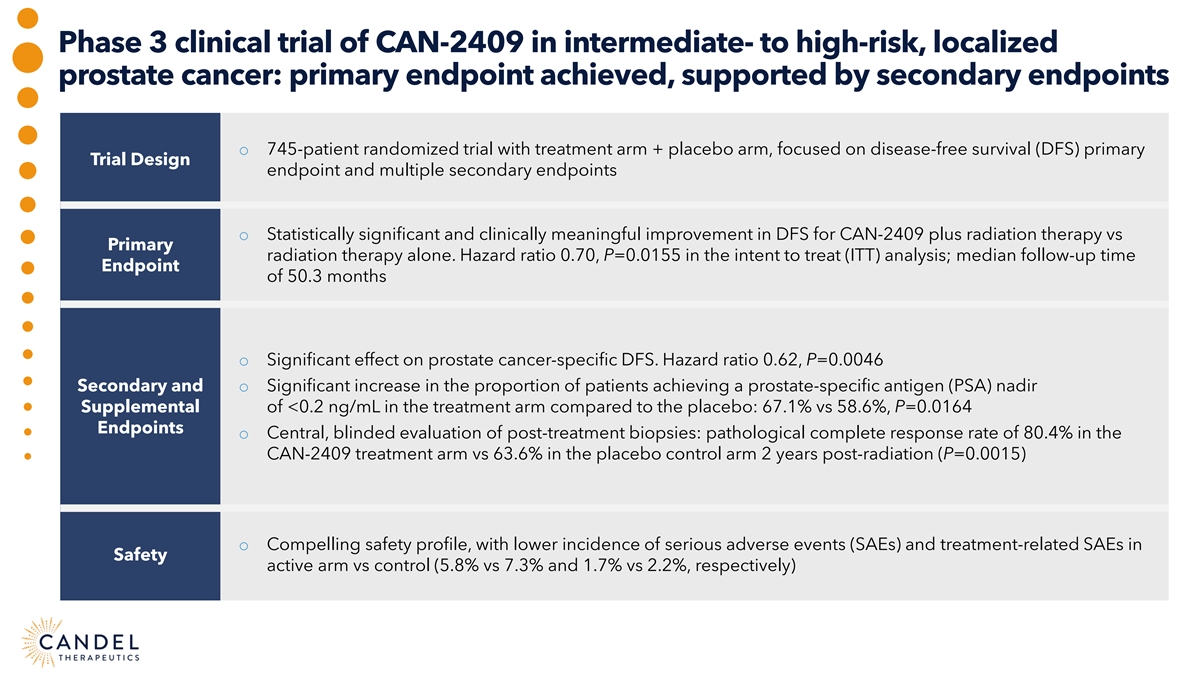
Phase 3 clinical trial of CAN-2409 in intermediate- to high-risk, localized prostate cancer: primary endpoint achieved, supported by secondary endpoints o 745-patient randomized trial with treatment arm + placebo arm, focused on disease-free survival (DFS) primary Trial Design endpoint and multiple secondary endpoints o Statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in DFS for CAN-2409 plus radiation therapy vs Primary radiation therapy alone. Hazard ratio 0.70, P=0.0155 in the intent to treat (ITT) analysis; median follow-up time Endpoint of 50.3 months o Significant effect on prostate cancer-specific DFS. Hazard ratio 0.62, P=0.0046 Secondary and o Significant increase in the proportion of patients achieving a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) nadir Supplemental of <0.2 ng/mL in the treatment arm compared to the placebo: 67.1% vs 58.6%, P=0.0164 Endpoints o Central, blinded evaluation of post-treatment biopsies: pathological complete response rate of 80.4% in the CAN-2409 treatment arm vs 63.6% in the placebo control arm 2 years post-radiation (P=0.0015) o Compelling safety profile, with lower incidence of serious adverse events (SAEs) and treatment-related SAEs in Safety active arm vs control (5.8% vs 7.3% and 1.7% vs 2.2%, respectively)

CAN-2409 FOR NEWLY DIAGNOSED LOCALIZED PROSTATE CANCER Glen Gejerman, MD, Co-chief of Urologic Oncology, Hackensack University Medical Center Philip Kantoff, MD, Former Chair Department of Medicine, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, CEO, Convergent Therapeutics Garrett Nichols, MD, MS, Candel's Chief Medical Officer Ron Tutrone, MD, National Director of Clinical Research, United Urology Moderator: Oliver McCammon, LifeSci Capital

ROAD MAP TO BIOLOGICS LICENSE APPLICATION (BLA) Susan Stewart, JD LLM, Candel’s Chief Regulatory Officer Seshu Tyagarajan, PhD, Candel’s Chief Technical and Development Officer Moderator: Andres Maldonado, PhD, H.C. Wainwright & Co.
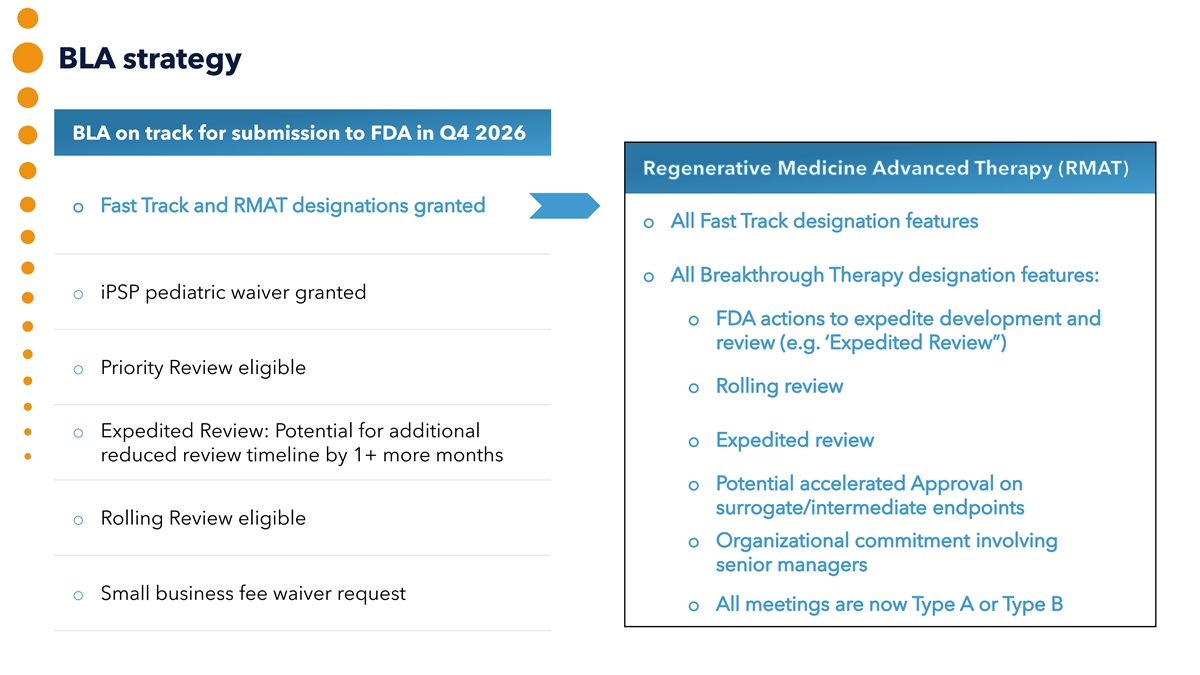
BLA strategy BLA on track for submission to FDA in Q4 2026 o iPSP pediatric waiver granted o Priority Review eligible o Expedited Review: Potential for additional reduced review timeline by 1+ more months o Rolling Review eligible o Small business fee waiver request
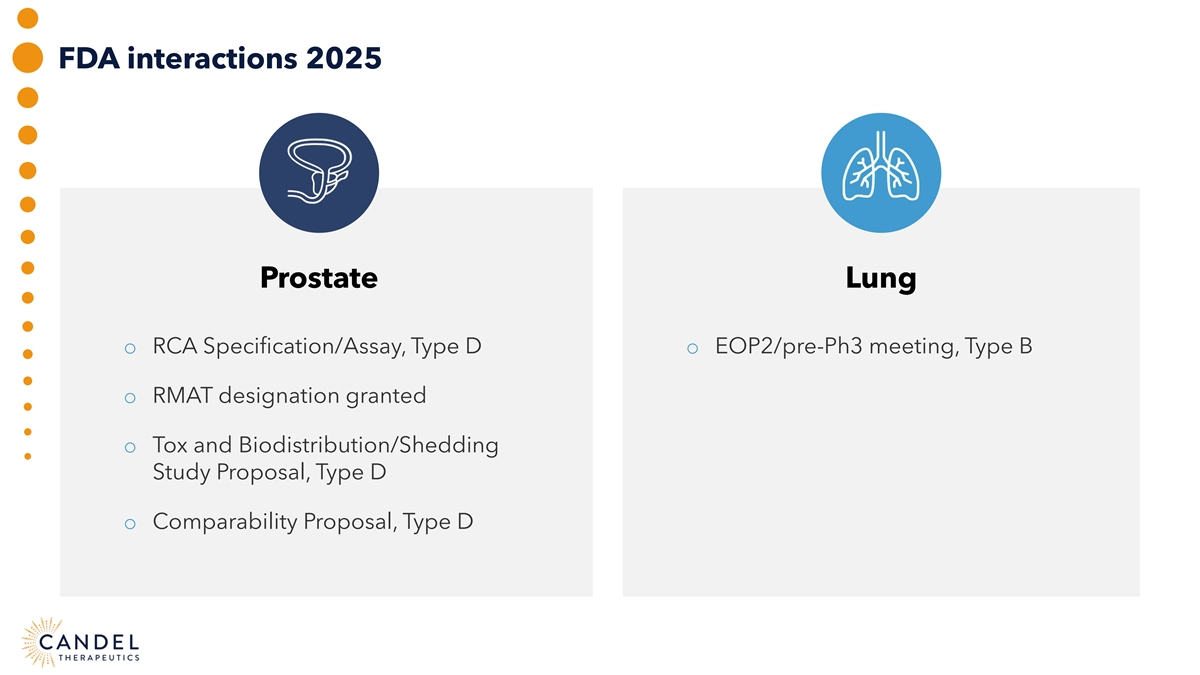
FDA interactions 2025 Prostate Lung o RCA Specification/Assay, Type D o EOP2/pre-Ph3 meeting, Type B o RMAT designation granted o Tox and Biodistribution/Shedding Study Proposal, Type D o Comparability Proposal, Type D
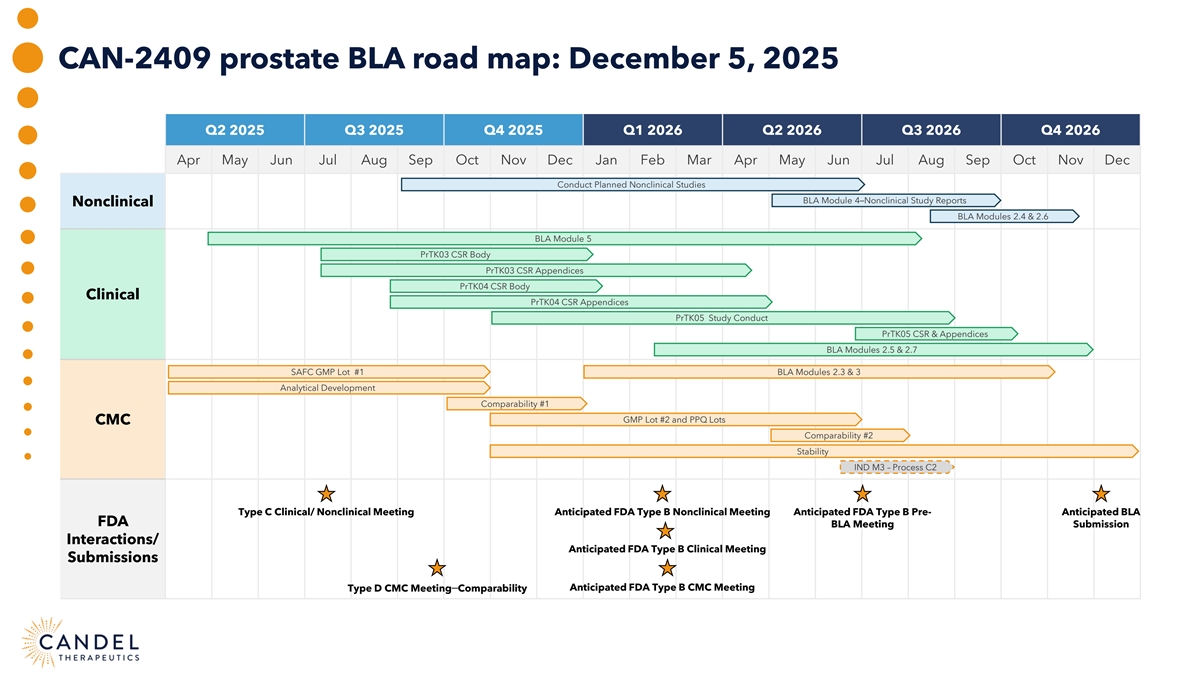
CAN-2409 prostate BLA road map: December 5, 2025 Q2 2025 Q3 2025 Q4 2025 Q1 2026 Q2 2026 Q3 2026 Q4 2026 Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Conduct Planned Nonclinical Studies BLA Module 4–Nonclinical Study Reports Nonclinical BLA Modules 2.4 & 2.6 BLA Module 5 PrTK03 CSR Body PrTK03 CSR Appendices PrTK04 CSR Body Clinical PrTK04 CSR Appendices PrTK05 Study Conduct PrTK05 CSR & Appendices BLA Modules 2.5 & 2.7 SAFC GMP Lot #1 BLA Modules 2.3 & 3 Analytical Development Comparability #1 GMP Lot #2 and PPQ Lots CMC Comparability #2 Stability IND M3 – Process C2 Type C Clinical/ Nonclinical Meeting Anticipated FDA Type B Nonclinical Meeting Anticipated FDA Type B Pre- Anticipated BLA FDA BLA Meeting Submission Interactions/ Anticipated FDA Type B Clinical Meeting Submissions Type D CMC Meeting–Comparability Anticipated FDA Type B CMC Meeting

Interactions with FDA about CAN-2409 in prostate cancer RMAT designation granted, allowing for frequent meetings FDA aligned with approach to setting RCA specification FDA aligned with proposed nonclinical toxicology package and clinical biodistribution/shedding study FDA aligned with the analytical approach for comparability Discussions regarding BLA submission ongoing (eg, data sets for rolling submission)

Interactions with FDA about CAN-2409 in NSCLC FDA alignment with: Proposed phase 3 Single preclinical registration study toxicology study: Clinical biodistribution Contribution of the agents and shedding plan Species (mouse); RoA (IV); requirement noted—July 2025 prodrug (ip ganciclovir) FDA Guidance issued “We tentatively agree that the primary evidence from the proposed phase 3 registrational study, if successful, when supported by confirmatory evidence from the phase 2 clinical trial, could demonstrate substantial evidence of effectiveness (SEE) to support a supplemental BLA submission and review.”

MANUFACTURING UPDATE
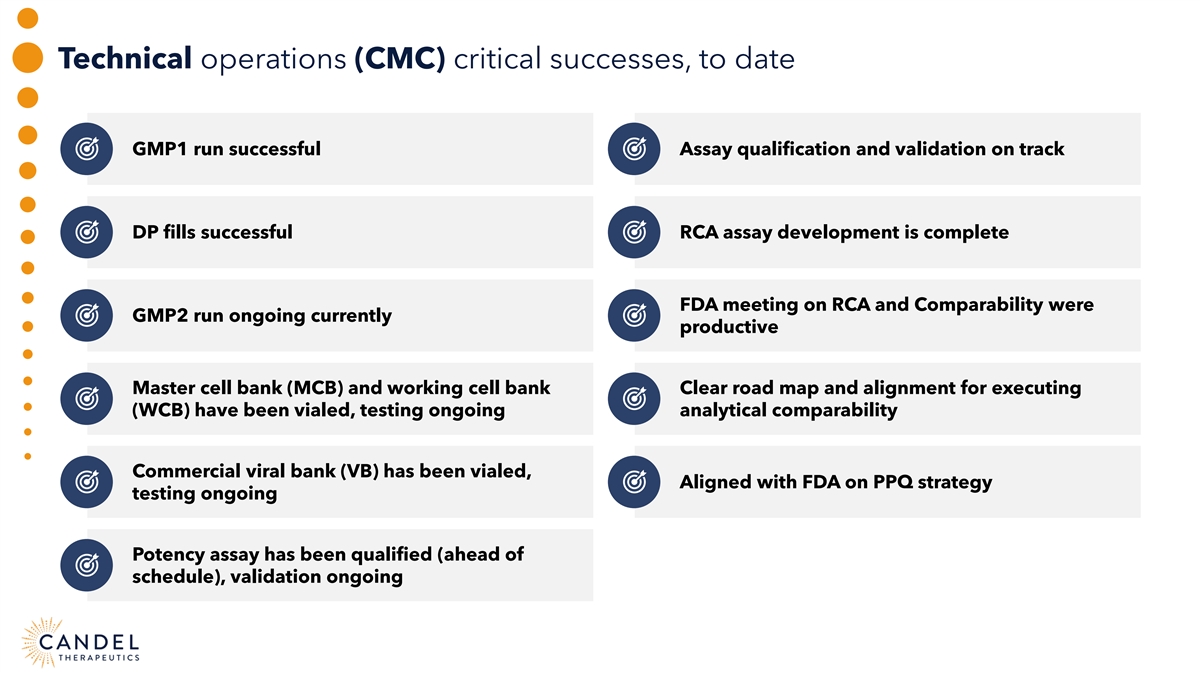
Technical operations (CMC) critical successes, to date GMP1 run successful Assay qualification and validation on track DP fills successful RCA assay development is complete FDA meeting on RCA and Comparability were GMP2 run ongoing currently productive Master cell bank (MCB) and working cell bank Clear road map and alignment for executing (WCB) have been vialed, testing ongoing analytical comparability Commercial viral bank (VB) has been vialed, Aligned with FDA on PPQ strategy testing ongoing Potency assay has been qualified (ahead of schedule), validation ongoing
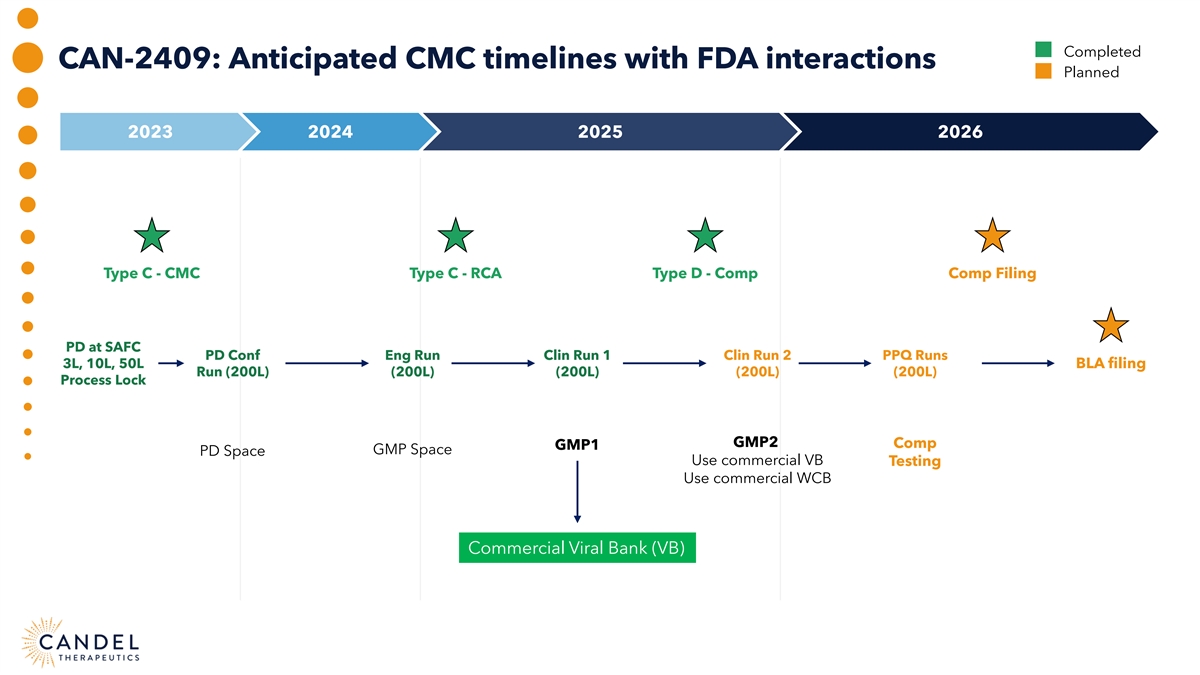
Completed CAN-2409: Anticipated CMC timelines with FDA interactions Planned 2023 2024 2025 2026 Type C - CMC Type C - RCA Type D - Comp Comp Filing PD at SAFC PD Conf Eng Run Clin Run 1 Clin Run 2 PPQ Runs 3L, 10L, 50L BLA filing Run (200L) (200L) (200L) (200L) (200L) Process Lock GMP2 Comp GMP1 GMP Space PD Space Use commercial VB Testing Use commercial WCB Commercial Viral Bank (VB)
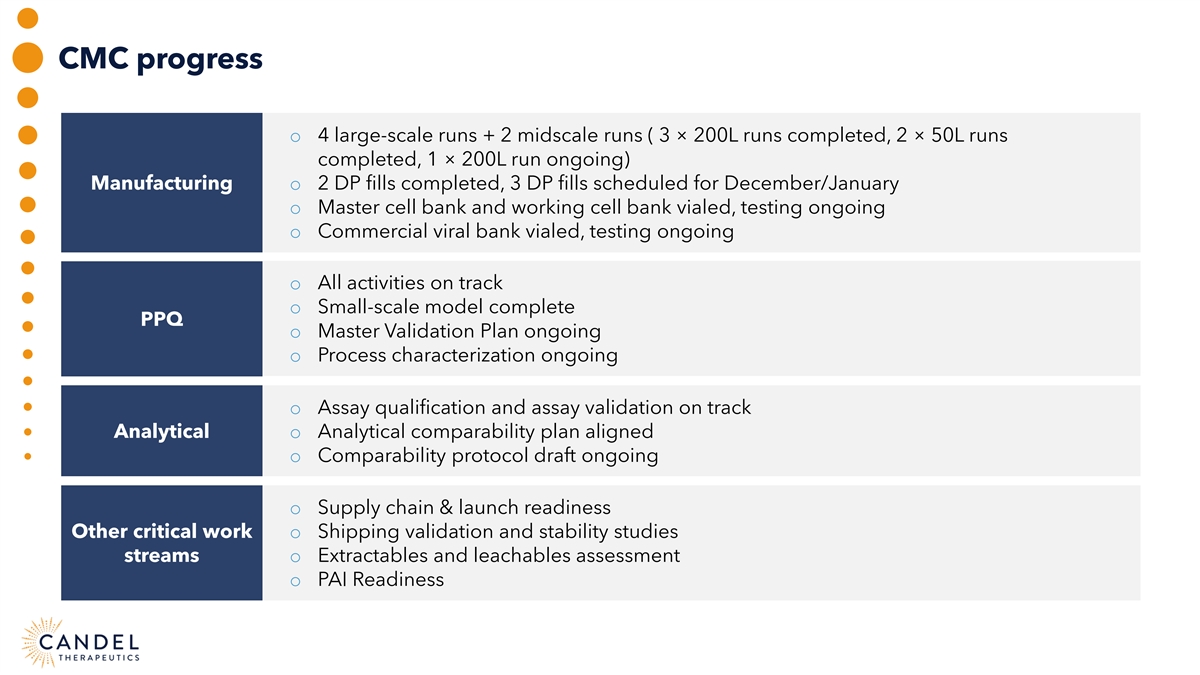
CMC progress o 4 large-scale runs + 2 midscale runs ( 3 × 200L runs completed, 2 × 50L runs completed, 1 × 200L run ongoing) Manufacturing o 2 DP fills completed, 3 DP fills scheduled for December/January o Master cell bank and working cell bank vialed, testing ongoing o Commercial viral bank vialed, testing ongoing o All activities on track o Small-scale model complete PPQ o Master Validation Plan ongoing o Process characterization ongoing o Assay qualification and assay validation on track Analytical o Analytical comparability plan aligned o Comparability protocol draft ongoing o Supply chain & launch readiness Other critical work o Shipping validation and stability studies streams o Extractables and leachables assessment o PAI Readiness
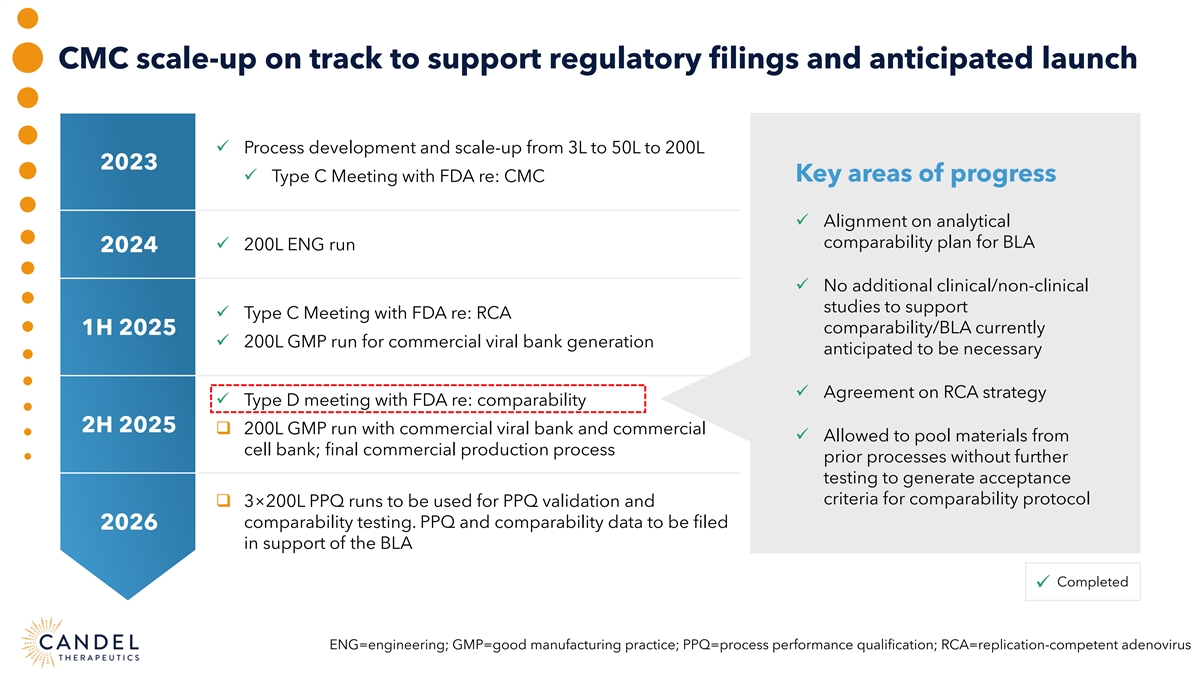
CMC scale-up on track to support regulatory filings and anticipated launch ü Process development and scale-up from 3L to 50L to 200L 2023 Key areas of progress ü Type C Meeting with FDA re: CMC ü Alignment on analytical comparability plan for BLA ü 200L ENG run 2024 ü No additional clinical/non-clinical studies to support ü Type C Meeting with FDA re: RCA comparability/BLA currently 1H 2025 ü 200L GMP run for commercial viral bank generation anticipated to be necessary ü Agreement on RCA strategy ü Type D meeting with FDA re: comparability 2H 2025 q 200L GMP run with commercial viral bank and commercial ü Allowed to pool materials from cell bank; final commercial production process prior processes without further testing to generate acceptance criteria for comparability protocol q 3×200L PPQ runs to be used for PPQ validation and comparability testing. PPQ and comparability data to be filed 2026 in support of the BLA Completed ü ENG=engineering; GMP=good manufacturing practice; PPQ=process performance qualification; RCA=replication-competent adenovirus
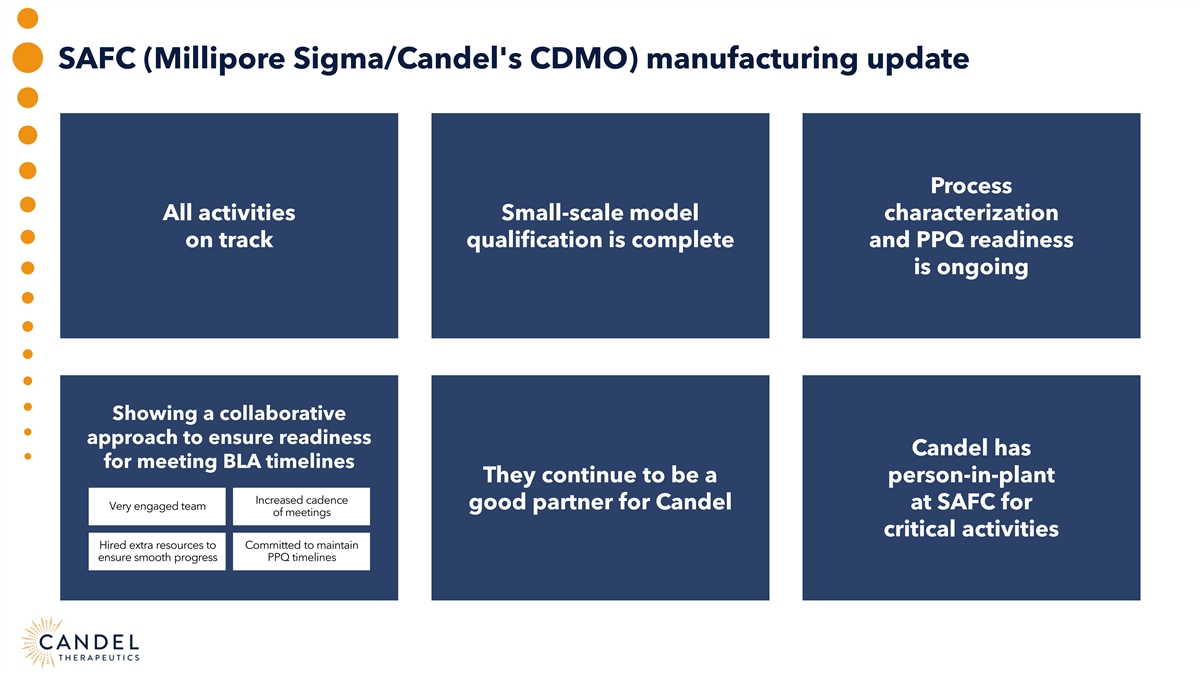
SAFC (Millipore Sigma/Candel's CDMO) manufacturing update Process All activities Small-scale model characterization on track qualification is complete and PPQ readiness is ongoing Showing a collaborative approach to ensure readiness Candel has for meeting BLA timelines They continue to be a person-in-plant Increased cadence Very engaged team good partner for Candel at SAFC for of meetings critical activities Hired extra resources to Committed to maintain ensure smooth progress PPQ timelines

ROAD MAP TO BIOLOGICS LICENSE APPLICATION (BLA) Susan Stewart, JD LLM, Candel’s Chief Regulatory Officer Seshu Tyagarajan, PhD, Candel’s Chief Technical and Development Officer Moderator: Andres Maldonado, PhD, H.C. Wainwright & Co.

PRE-COMMERCIALIZATION ROAD MAP Jonathon Mitchell, MSc, Partner, Globe Life Sciences Jacqueline Poot, President, IDEA Pharma Paul Peter Tak, MD, PhD, FMedSci, Candel’s President and CEO Moderator: Andres Maldonado, PhD, H.C. Wainwright & Co.
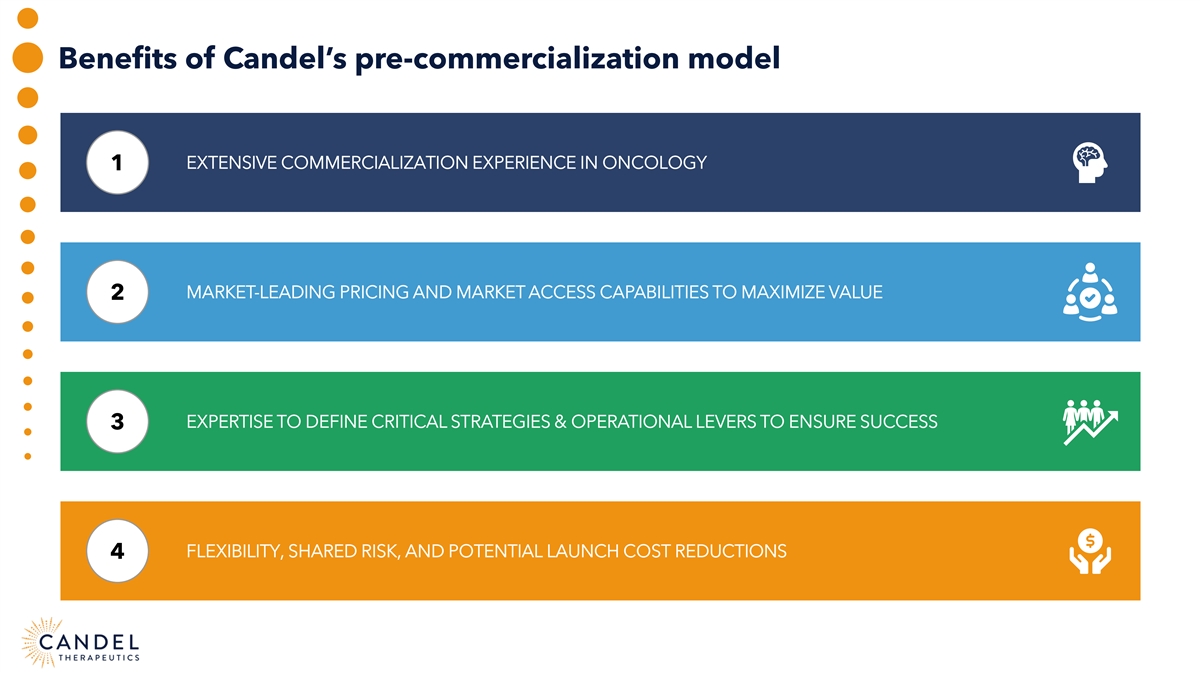
Benefits of Candel’s pre-commercialization model EXTENSIVE COMMERCIALIZATION EXPERIENCE IN ONCOLOGY 1 MARKET-LEADING PRICING AND MARKET ACCESS CAPABILITIES TO MAXIMIZE VALUE 2 EXPERTISE TO DEFINE CRITICAL STRATEGIES & OPERATIONAL LEVERS TO ENSURE SUCCESS 3 FLEXIBILITY, SHARED RISK, AND POTENTIAL LAUNCH COST REDUCTIONS 4
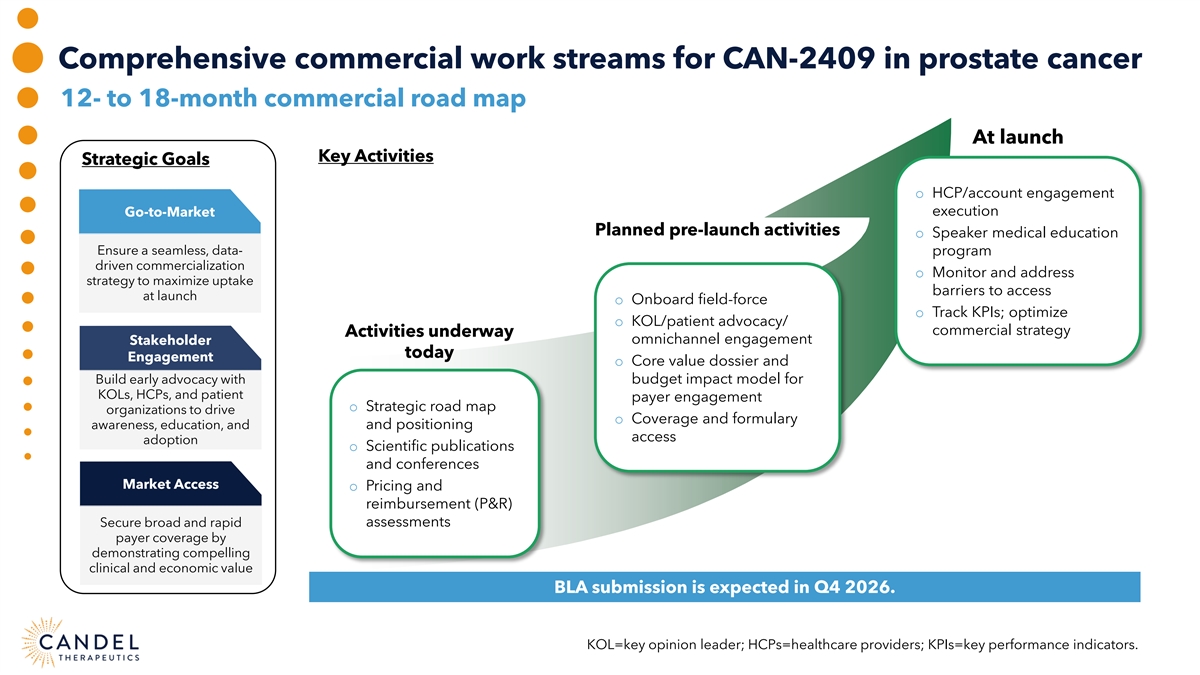
Comprehensive commercial work streams for CAN-2409 in prostate cancer 12- to 18-month commercial road map At launch Key Activities Strategic Goals o HCP/account engagement Go-to-Market execution Planned pre-launch activities o Speaker medical education Ensure a seamless, data- program driven commercialization o Monitor and address strategy to maximize uptake barriers to access at launch o Onboard field-force o Track KPIs; optimize o KOL/patient advocacy/ commercial strategy Activities underway omnichannel engagement Stakeholder today Engagement o Core value dossier and Build early advocacy with budget impact model for KOLs, HCPs, and patient payer engagement o Strategic road map organizations to drive o Coverage and formulary awareness, education, and and positioning access adoption o Scientific publications and conferences Market Access o Pricing and reimbursement (P&R) assessments Secure broad and rapid payer coverage by demonstrating compelling clinical and economic value BLA submission is expected in Q4 2026. KOL=key opinion leader; HCPs=healthcare providers; KPIs=key performance indicators.

For patients electing to undergo radical therapy, achieving cure was consistently identified as the primary goal of treatment Goals of Treatment If you were going to rank these, cure is probably the top, and it’s 1 going to be competing with quality of life … I want to live as long as I can, but I want that amount of time that I’m here to be as Cure high quality as possible. It’s the quality versus quantity argument. KOL – US, Rad Primary goal among >95% of physicians interviewed The goal is the same for surgery and for radiation, which is to control the disease and to have a PSA value which goes down to zero. The purpose if you undergo or undertake these kind of treatment modalities is to cure. KOL – FRA, Uro I think the top two goals patients have are cure and preserving quality Preservation of of life. Cure is usually number one. Preserving quality of life is a very quality of life close second. KOL – US, Rad Second priority Globe Life Sciences commercial evaluation of CAN-2409 in prostate cancer, March-May 2025. Methodology included secondary analysis and primary research with 30 KOLs/physicians and 20 payers across the US/Europe.
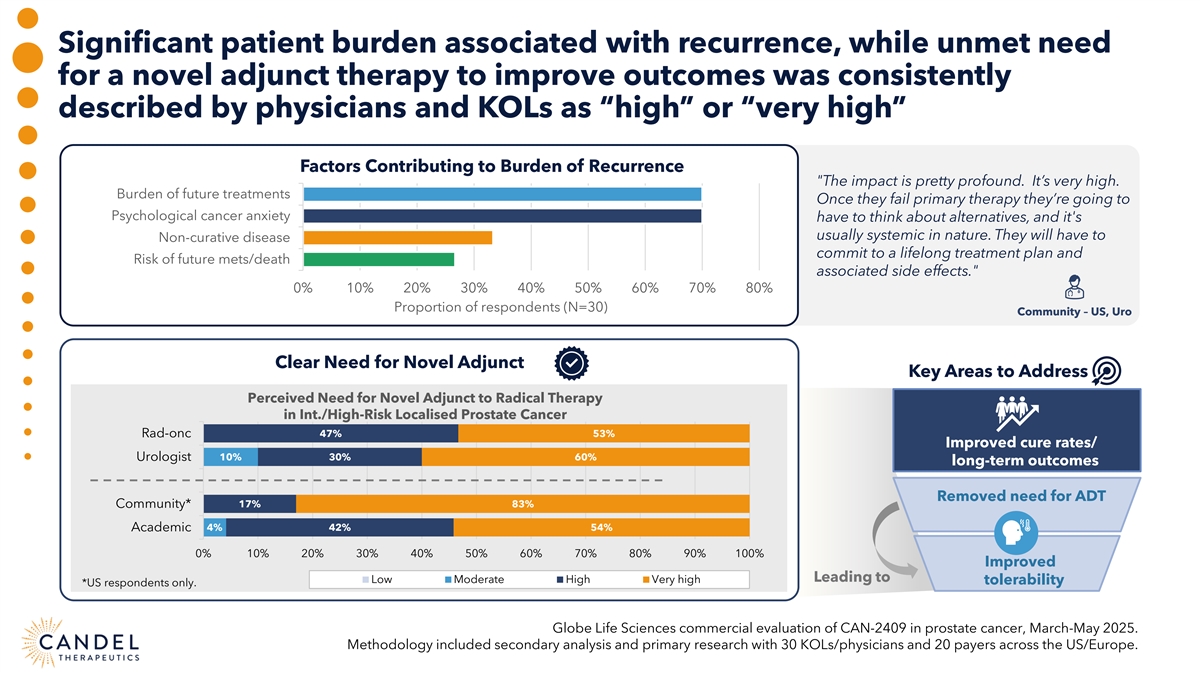
Significant patient burden associated with recurrence, while unmet need for a novel adjunct therapy to improve outcomes was consistently described by physicians and KOLs as “high” or “very high” Factors Contributing to Burden of Recurrence The impact is pretty profound. It’s very high. Burden of future treatments Once they fail primary therapy they’re going to Psychological cancer anxiety have to think about alternatives, and it's usually systemic in nature. They will have to Non-curative disease commit to a lifelong treatment plan and Risk of future mets/death associated side effects. 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% Proportion of respondents (N=30) Community – US, Uro Clear Need for Novel Adjunct Key Areas to Address Perceived Need for Novel Adjunct to Radical Therapy in Int./High-Risk Localised Prostate Cancer Rad-onc 47% 53% Improved cure rates/ Urologist 10% 30% 60% long-term outcomes Removed need for ADT Community* 17% 83% Academic 4% 42% 54% 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% Improved Leading to Low Moderate High Very high tolerability *US respondents only. Globe Life Sciences commercial evaluation of CAN-2409 in prostate cancer, March-May 2025. Methodology included secondary analysis and primary research with 30 KOLs/physicians and 20 payers across the US/Europe.
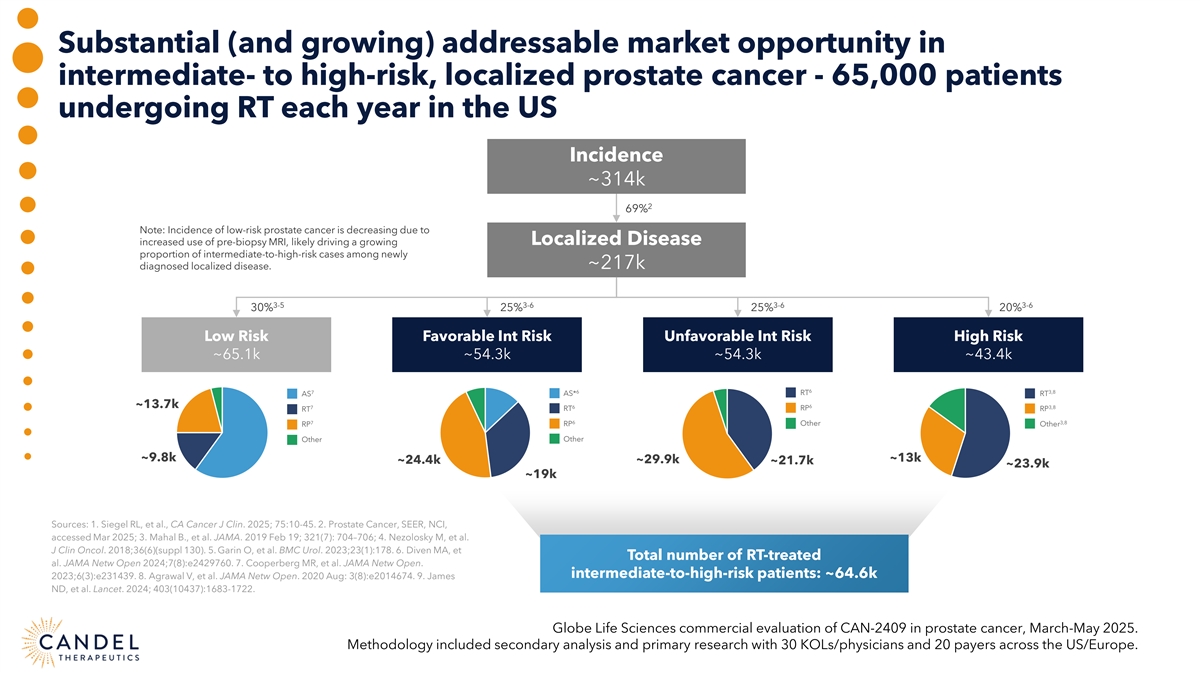
Substantial (and growing) addressable market opportunity in intermediate- to high-risk, localized prostate cancer - 65,000 patients undergoing RT each year in the US Incidence ~314k 2 69% Note: Incidence of low-risk prostate cancer is decreasing due to increased use of pre-biopsy MRI, likely driving a growing Localized Disease proportion of intermediate-to-high-risk cases among newly ~217k diagnosed localized disease. 3-5 3-6 3-6 3-6 30% 25% 25% 20% Low Risk Favorable Int Risk Unfavorable Int Risk High Risk ~65.1k ~54.3k ~54.3k ~43.4k 6 7 6 3,8 RT AS AS* RT ~13.7k 6 6 3,8 7 RP RT RT RP 6 7 3,8 RP Other Other RP Other Other ~9.8k ~13k ~24.4k ~29.9k ~21.7k ~23.9k ~19k Sources: 1. Siegel RL, et al., CA Cancer J Clin. 2025; 75:10-45. 2. Prostate Cancer, SEER, NCI, accessed Mar 2025; 3. Mahal B., et al. JAMA. 2019 Feb 19; 321(7): 704–706; 4. Nezolosky M, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(6)(suppl 130). 5. Garin O, et al. BMC Urol. 2023;23(1):178. 6. Diven MA, et Total number of RT-treated al. JAMA Netw Open 2024;7(8):e2429760. 7. Cooperberg MR, et al. JAMA Netw Open. intermediate-to-high-risk patients: ~64.6k 2023;6(3):e231439. 8. Agrawal V, et al. JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Aug: 3(8):e2014674. 9. James ND, et al. Lancet. 2024; 403(10437):1683-1722. Globe Life Sciences commercial evaluation of CAN-2409 in prostate cancer, March-May 2025. Methodology included secondary analysis and primary research with 30 KOLs/physicians and 20 payers across the US/Europe.
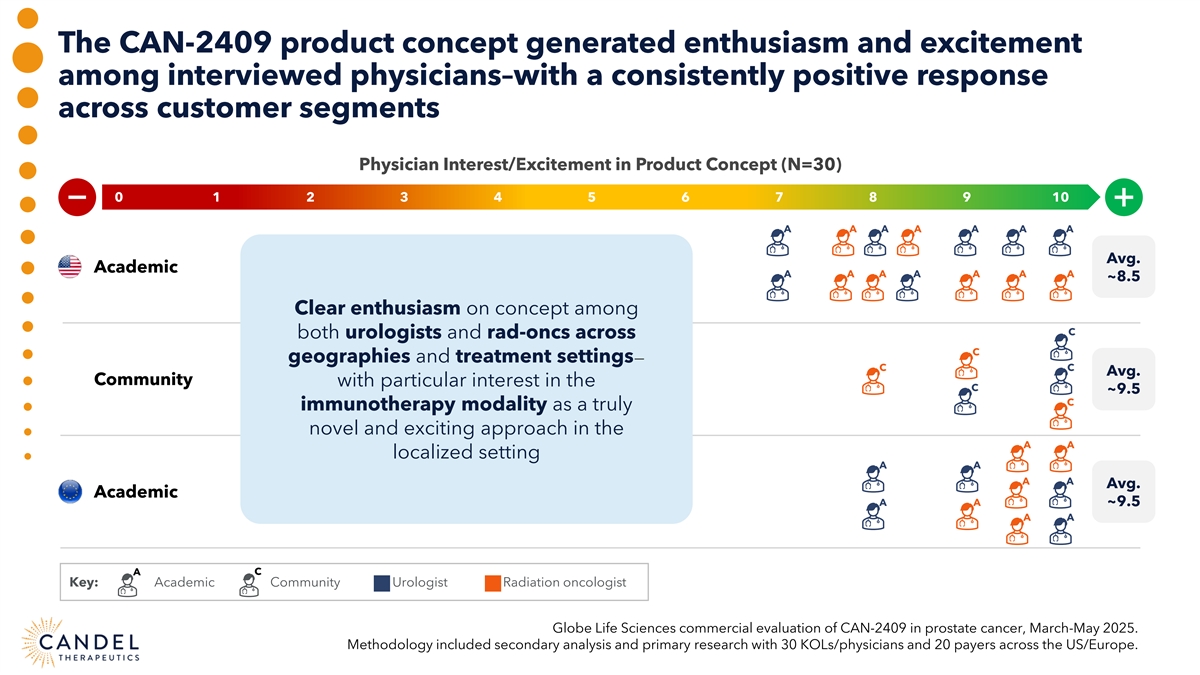
The CAN-2409 product concept generated enthusiasm and excitement among interviewed physicians–with a consistently positive response across customer segments Physician Interest/Excitement in Product Concept (N=30) 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 A A A A A A A Avg. Academic A A A A A A A ~8.5 Clear enthusiasm on concept among C both urologists and rad-oncs across C geographies and treatment settings— C C Avg. Community with particular interest in the C ~9.5 C immunotherapy modality as a truly novel and exciting approach in the A A localized setting A A A A Avg. Academic A A ~9.5 A A A C Key: Academic Community Urologist Radiation oncologist Globe Life Sciences commercial evaluation of CAN-2409 in prostate cancer, March-May 2025. Methodology included secondary analysis and primary research with 30 KOLs/physicians and 20 payers across the US/Europe.
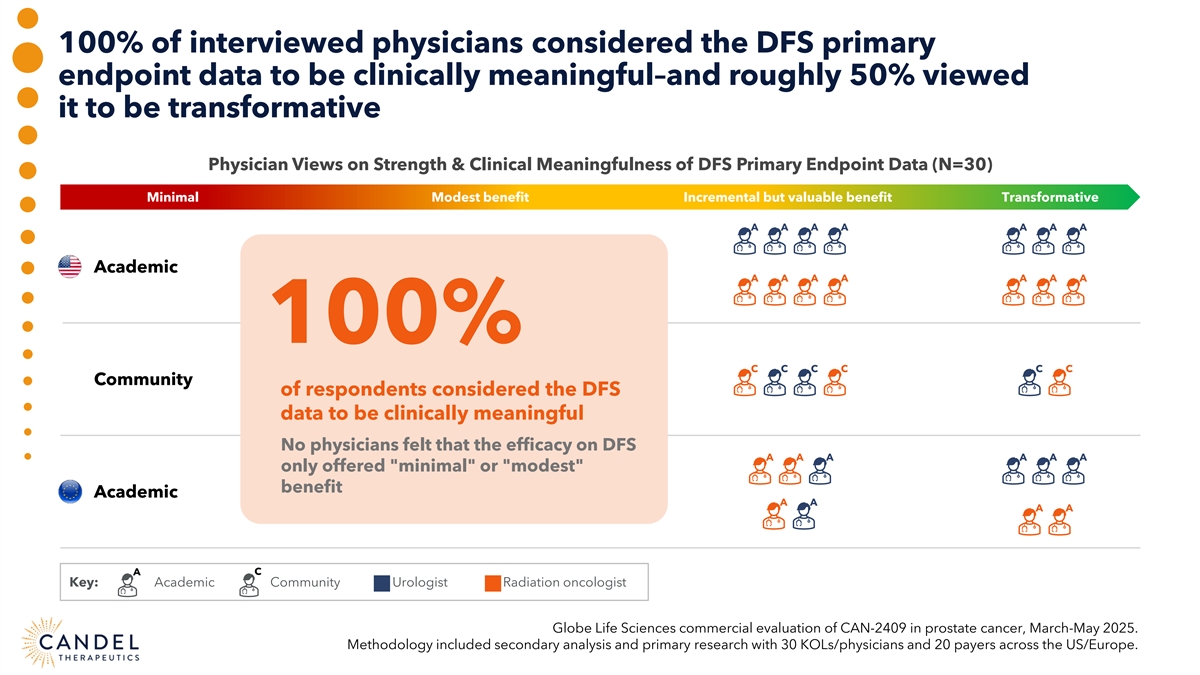
100% of interviewed physicians considered the DFS primary endpoint data to be clinically meaningful–and roughly 50% viewed it to be transformative Physician Views on Strength & Clinical Meaningfulness of DFS Primary Endpoint Data (N=30) Minimal Modest benefit Incremental but valuable benefit Transformative A A A A A A A Academic A A A A A A A 100% C C C C C C Community of respondents considered the DFS data to be clinically meaningful No physicians felt that the efficacy on DFS A A A A A A only offered minimal or modest benefit Academic A A A A A C Key: Academic Community Urologist Radiation oncologist Globe Life Sciences commercial evaluation of CAN-2409 in prostate cancer, March-May 2025. Methodology included secondary analysis and primary research with 30 KOLs/physicians and 20 payers across the US/Europe.
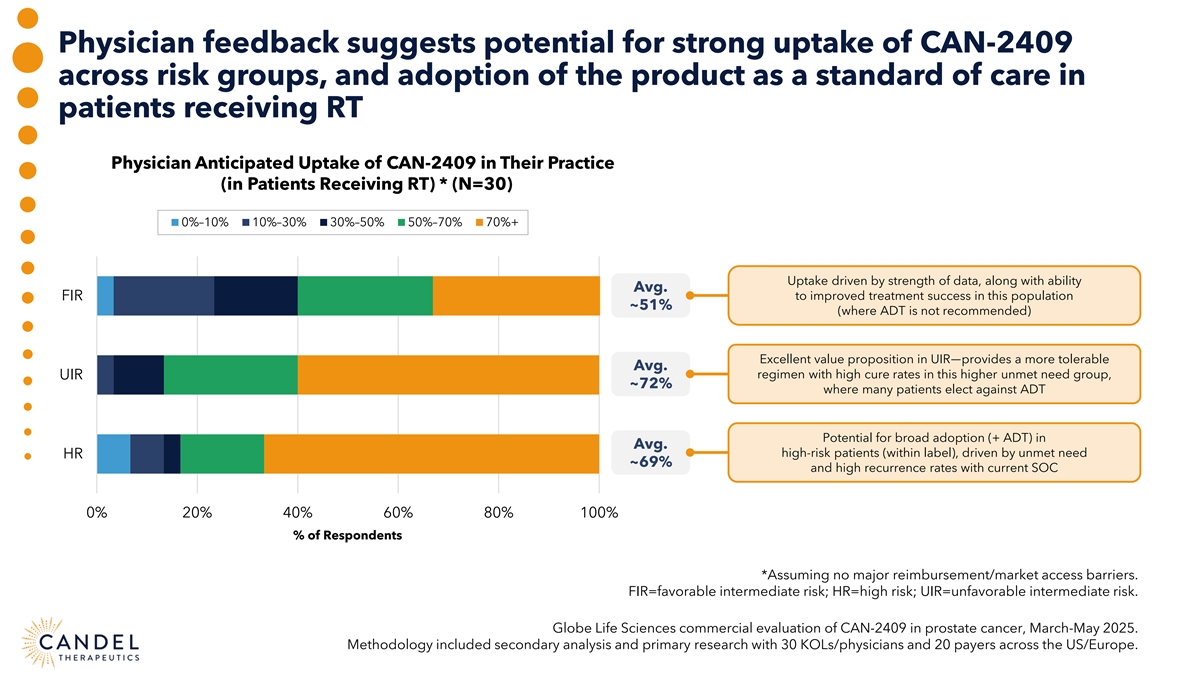
Physician feedback suggests potential for strong uptake of CAN-2409 across risk groups, and adoption of the product as a standard of care in patients receiving RT Physician Anticipated Uptake of CAN-2409 in Their Practice (in Patients Receiving RT) * (N=30) 0%–10% 10%–30% 30%–50% 50%–70% 70%+ Uptake driven by strength of data, along with ability Avg. FIR to improved treatment success in this population ~51% (where ADT is not recommended) Excellent value proposition in UIR—provides a more tolerable Avg. regimen with high cure rates in this higher unmet need group, UIR ~72% where many patients elect against ADT Potential for broad adoption (+ ADT) in Avg. high-risk patients (within label), driven by unmet need HR ~69% and high recurrence rates with current SOC 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% % of Respondents *Assuming no major reimbursement/market access barriers. FIR=favorable intermediate risk; HR=high risk; UIR=unfavorable intermediate risk. Globe Life Sciences commercial evaluation of CAN-2409 in prostate cancer, March-May 2025. Methodology included secondary analysis and primary research with 30 KOLs/physicians and 20 payers across the US/Europe.
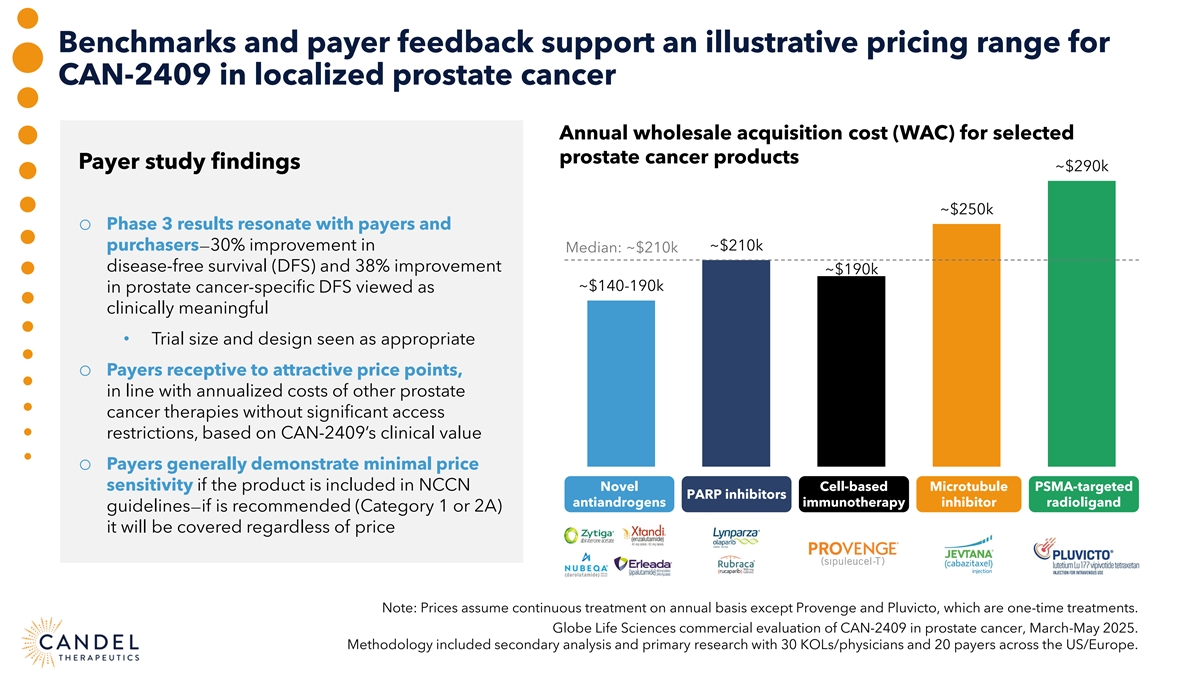
Benchmarks and payer feedback support an illustrative pricing range for CAN-2409 in localized prostate cancer Annual wholesale acquisition cost (WAC) for selected prostate cancer products Payer study findings ~$290k ~$250k o Phase 3 results resonate with payers and purchasers—30% improvement in ~$210k Median: ~$210k disease-free survival (DFS) and 38% improvement ~$190k ~$140-190k in prostate cancer-specific DFS viewed as clinically meaningful • Trial size and design seen as appropriate o Payers receptive to attractive price points, in line with annualized costs of other prostate cancer therapies without significant access restrictions, based on CAN-2409’s clinical value o Payers generally demonstrate minimal price sensitivity if the product is included in NCCN Novel Cell-based Microtubule PSMA-targeted PARP inhibitors antiandrogens immunotherapy inhibitor radioligand guidelines—if is recommended (Category 1 or 2A) it will be covered regardless of price Note: Prices assume continuous treatment on annual basis except Provenge and Pluvicto, which are one-time treatments. Globe Life Sciences commercial evaluation of CAN-2409 in prostate cancer, March-May 2025. Methodology included secondary analysis and primary research with 30 KOLs/physicians and 20 payers across the US/Europe.
CAN-2409 is positioned to succeed in early localized prostate cancer High Unmet Need Significant Market Opportunity Candel’s Unique Value Proposition CAN-2409: Off-the-shelf pan-solid tumor therapy, individualized anticancer immune response o Positive Phase 3 randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial in localized, intermediate-to-high-risk prostate cancer o Disease-free survival as primary endpoint was a key element of the Special Protocol Assessment (SPA) agreement with the FDA o FDA Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapy (RMAT) designation in prostate cancer, Fast Track designation in NSCLC, pancreatic cancer, and prostate cancer. Orphan Drug designation in pancreatic cancer o “Pipeline in a product” strategy advancing multiple programs in several large indications o IP protection: CAN-2409 (2034, method of use); 12 years data exclusivity o Low-cost manufacturing o Pre-commercialization activities underway to support potential post-approval commercial launch of CAN-2409

Our commercial strategy is anchored in aligned critical success factors Critical Success Factor 1 Critical Success Factor 2 Critical Success Factor 3 Establish stakeholder belief Optimize distribution, Maximize pricing by in CAN-2409 as a purchase, and reimbursement communicating strong value transformative new treatment of CAN-2409 proposition to payers and option that advances SoC providers Driving commercial success for CAN-2409 includes thoughtful medical communications, an optimized channel/distribution Go-to-Market approach, and a compelling pricing/market access strategy.
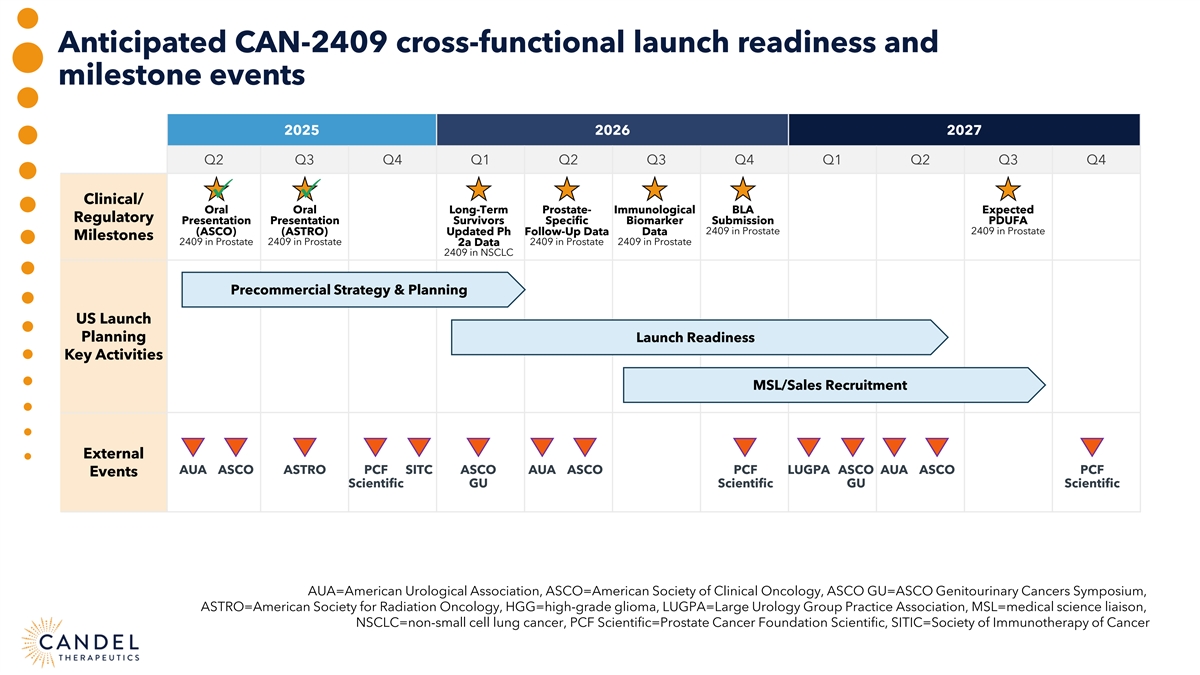
Anticipated CAN-2409 cross-functional launch readiness and milestone events 2025 2026 2027 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 ü ü Clinical/ Oral Oral Long-Term Prostate- Immunological BLA Expected Regulatory Presentation Presentation Survivors Specific Biomarker Submission PDUFA (ASCO) (ASTRO) Updated Ph Follow-Up Data Data 2409 in Prostate 2409 in Prostate Milestones 2409 in Prostate 2409 in Prostate 2409 in Prostate 2409 in Prostate 2a Data 2409 in NSCLC Precommercial Strategy & Planning US Launch Planning Launch Readiness Key Activities MSL/Sales Recruitment External AUA ASCO ASTRO PCF SITC ASCO AUA ASCO PCF LUGPA ASCO AUA ASCO PCF Events Scientific GU Scientific GU Scientific AUA=American Urological Association, ASCO=American Society of Clinical Oncology, ASCO GU=ASCO Genitourinary Cancers Symposium, ASTRO=American Society for Radiation Oncology, HGG=high-grade glioma, LUGPA=Large Urology Group Practice Association, MSL=medical science liaison, NSCLC=non-small cell lung cancer, PCF Scientific=Prostate Cancer Foundation Scientific, SITIC=Society of Immunotherapy of Cancer
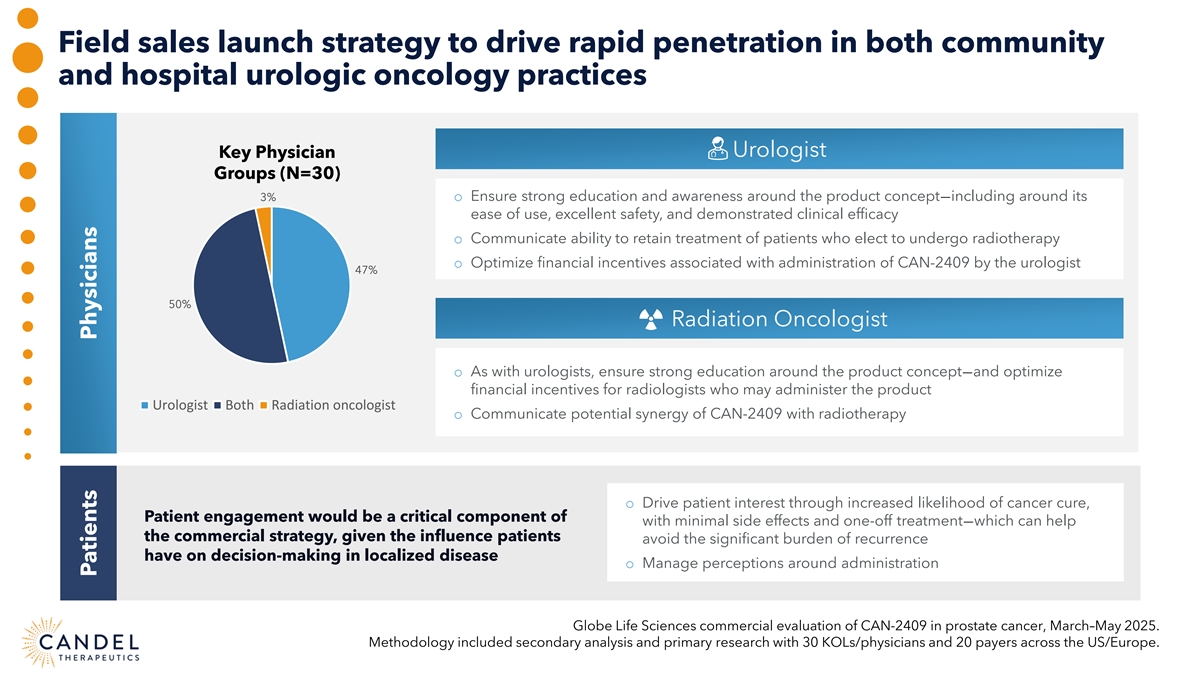
Field sales launch strategy to drive rapid penetration in both community and hospital urologic oncology practices Urologist Key Physician Groups (N=30) 3% o Ensure strong education and awareness around the product concept—including around its ease of use, excellent safety, and demonstrated clinical efficacy o Communicate ability to retain treatment of patients who elect to undergo radiotherapy o Optimize financial incentives associated with administration of CAN-2409 by the urologist 47% 50% Radiation Oncologist o As with urologists, ensure strong education around the product concept—and optimize financial incentives for radiologists who may administer the product Urologist Both Radiation oncologist o Communicate potential synergy of CAN-2409 with radiotherapy o Drive patient interest through increased likelihood of cancer cure, Patient engagement would be a critical component of with minimal side effects and one-off treatment—which can help the commercial strategy, given the influence patients avoid the significant burden of recurrence have on decision-making in localized disease o Manage perceptions around administration Globe Life Sciences commercial evaluation of CAN-2409 in prostate cancer, March–May 2025. Methodology included secondary analysis and primary research with 30 KOLs/physicians and 20 payers across the US/Europe. Patients Physicians
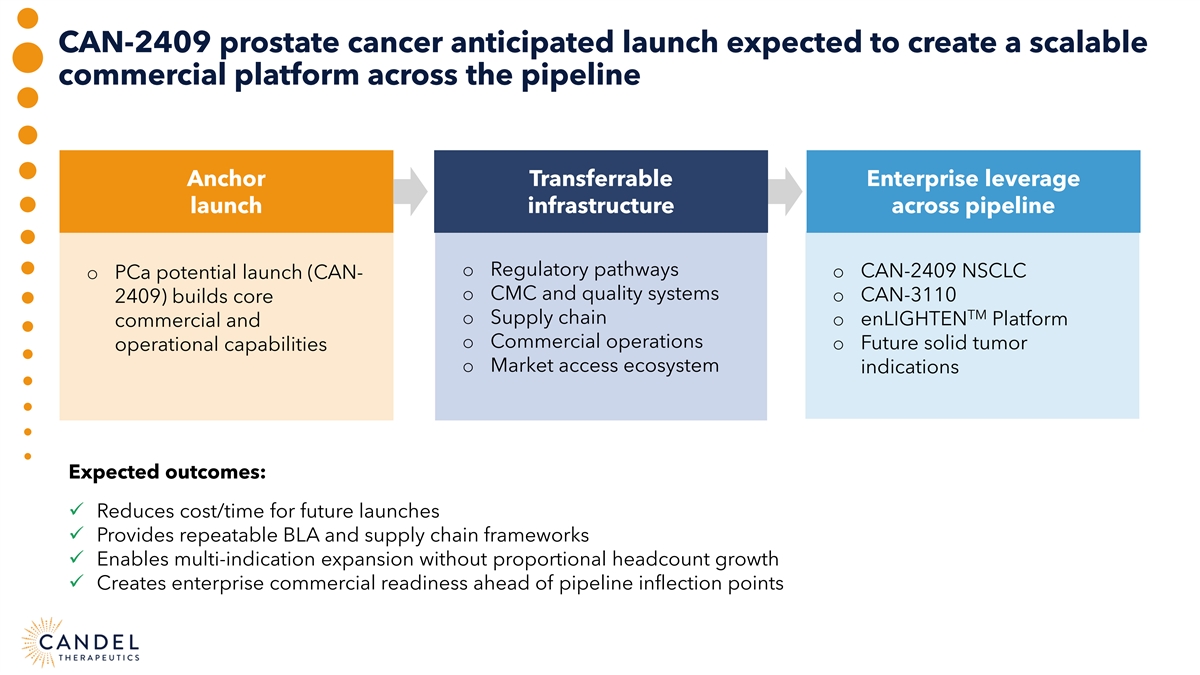
CAN-2409 prostate cancer anticipated launch expected to create a scalable commercial platform across the pipeline Anchor Transferrable Enterprise leverage launch infrastructure across pipeline o Regulatory pathways o CAN-2409 NSCLC o PCa potential launch (CAN- o CMC and quality systems o CAN-3110 2409) builds core TM o Supply chain o enLIGHTEN Platform commercial and o Commercial operations o Future solid tumor operational capabilities o Market access ecosystem indications Expected outcomes: ü Reduces cost/time for future launches ü Provides repeatable BLA and supply chain frameworks ü Enables multi-indication expansion without proportional headcount growth ü Creates enterprise commercial readiness ahead of pipeline inflection points

PRE-COMMERCIALIZATION ROAD MAP Jonathon Mitchell, MSc, Partner, Globe Life Sciences Jacqueline Poot, President, IDEA Pharma Paul Peter Tak, MD, PhD, FMedSci, Candel’s President and CEO Moderator: Andres Maldonado, PhD, H.C. Wainwright & Co.

CAN-2409 FOR IMMUNE CHECKPOINT INHIBITOR REFRACTORY NON-SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Charu Aggarwal, MD, Professor of Lung Cancer Excellence, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Roy Herbst, MD, PhD, Ensign Professor of Medicine (Medical Oncology) and Professor of Pharmacology, Yale Cancer Center Dan Sterman, MD, Thomas and Suzanne Murphy Professor of Medicine and Cardiothoracic Surgery, NYU Langone Health Moderator: John Newman, PhD, Canaccord Genuity
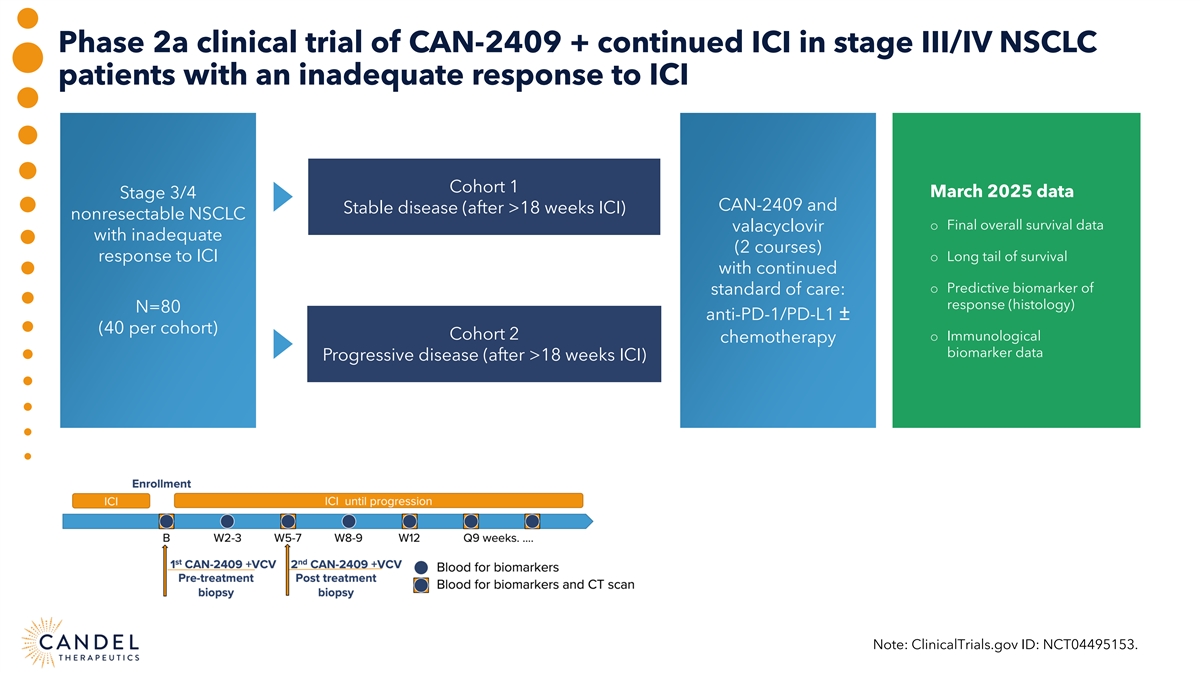
Phase 2a clinical trial of CAN-2409 + continued ICI in stage III/IV NSCLC patients with an inadequate response to ICI Cohort 1 March 2025 data Stage 3/4 CAN-2409 and Stable disease (after >18 weeks ICI) nonresectable NSCLC o Final overall survival data valacyclovir with inadequate (2 courses) response to ICI o Long tail of survival with continued o Predictive biomarker of standard of care: response (histology) N=80 anti-PD-1/PD-L1 ± (40 per cohort) Cohort 2 o Immunological chemotherapy biomarker data Progressive disease (after >18 weeks ICI) Note: ClinicalTrials.gov ID: NCT04495153.
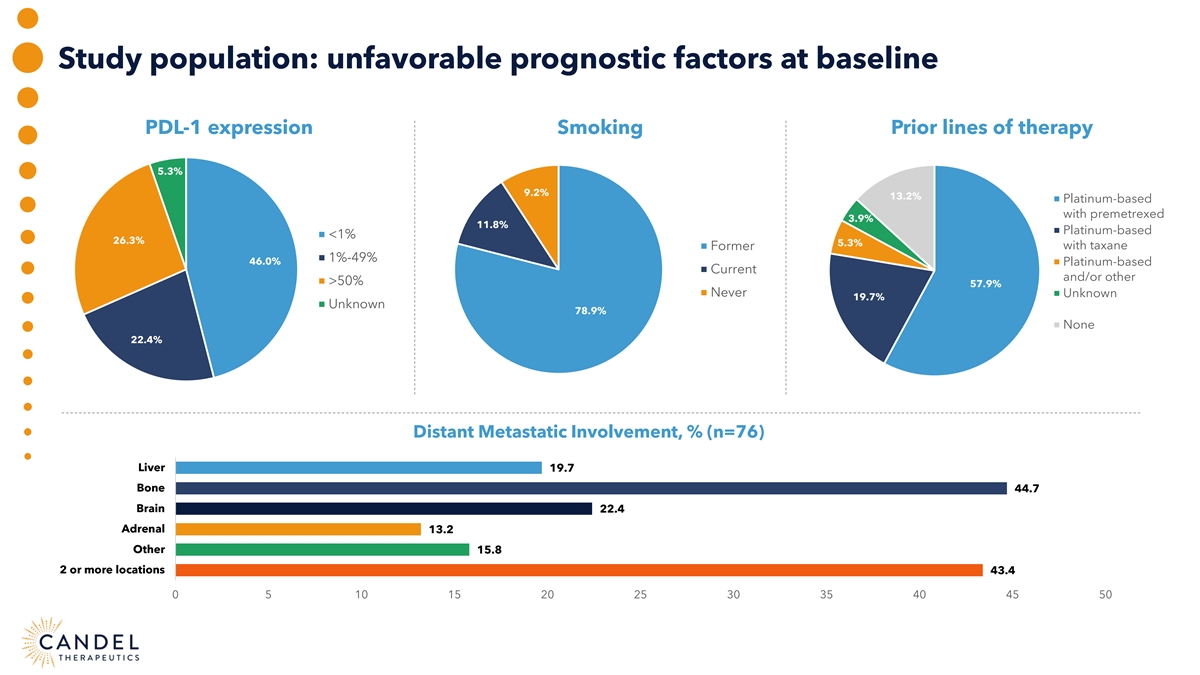
Study population: unfavorable prognostic factors at baseline PDL-1 expression Smoking Prior lines of therapy 5.3% 9.2% 13.2% Platinum-based with premetrexed 3.9% 11.8% Platinum-based <1% 26.3% 5.3% Former with taxane 1%-49% 46.0% Platinum-based Current and/or other >50% 57.9% Never Unknown 19.7% Unknown 78.9% None 22.4% Distant Metastatic Involvement, % (n=76) Liver 19.7 Bone 44.7 Brain 22.4 Adrenal 13.2 Other 15.8 2 or more locations 43.4 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
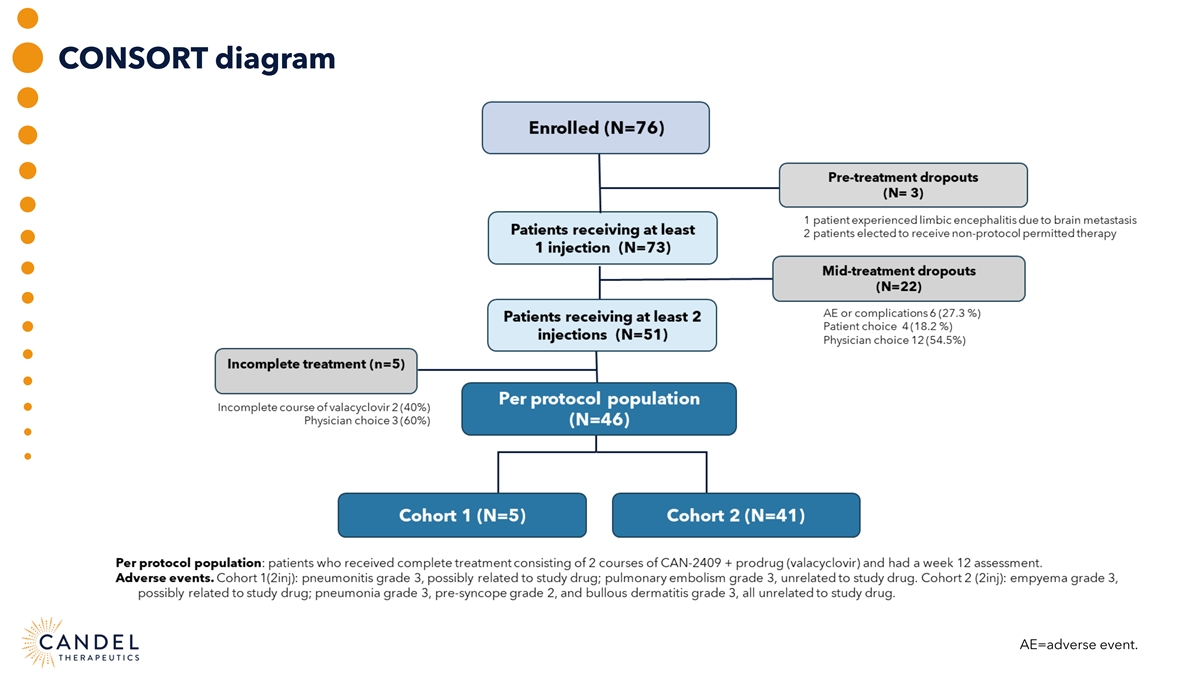
CONSORT diagram AE=adverse event.
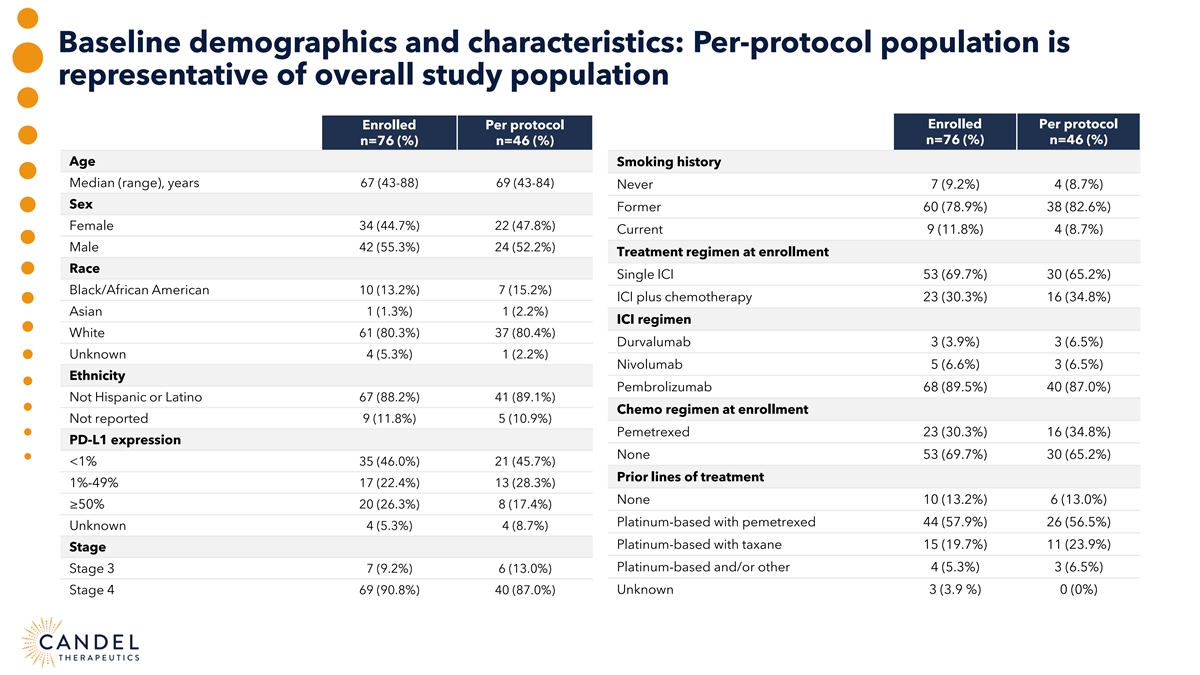
Baseline demographics and characteristics: Per-protocol population is representative of overall study population Enrolled Per protocol Enrolled Per protocol n=76 (%) n=46 (%) n=76 (%) n=46 (%) Age Smoking history Median (range), years 67 (43-88) 69 (43-84) Never 7 (9.2%) 4 (8.7%) Sex Former 60 (78.9%) 38 (82.6%) Female 34 (44.7%) 22 (47.8%) Current 9 (11.8%) 4 (8.7%) Male 42 (55.3%) 24 (52.2%) Treatment regimen at enrollment Race Single ICI 53 (69.7%) 30 (65.2%) Black/African American 10 (13.2%) 7 (15.2%) ICI plus chemotherapy 23 (30.3%) 16 (34.8%) Asian 1 (1.3%) 1 (2.2%) ICI regimen White 61 (80.3%) 37 (80.4%) Durvalumab 3 (3.9%) 3 (6.5%) Unknown 4 (5.3%) 1 (2.2%) Nivolumab 5 (6.6%) 3 (6.5%) Ethnicity Pembrolizumab 68 (89.5%) 40 (87.0%) Not Hispanic or Latino 67 (88.2%) 41 (89.1%) Chemo regimen at enrollment Not reported 9 (11.8%) 5 (10.9%) Pemetrexed 23 (30.3%) 16 (34.8%) PD-L1 expression None 53 (69.7%) 30 (65.2%) <1% 35 (46.0%) 21 (45.7%) Prior lines of treatment 1%-49% 17 (22.4%) 13 (28.3%) None 10 (13.2%) 6 (13.0%) ≥50% 20 (26.3%) 8 (17.4%) Platinum-based with pemetrexed 44 (57.9%) 26 (56.5%) Unknown 4 (5.3%) 4 (8.7%) Platinum-based with taxane 15 (19.7%) 11 (23.9%) Stage Platinum-based and/or other 4 (5.3%) 3 (6.5%) Stage 3 7 (9.2%) 6 (13.0%) Unknown 3 (3.9 %) 0 (0%) Stage 4 69 (90.8%) 40 (87.0%)
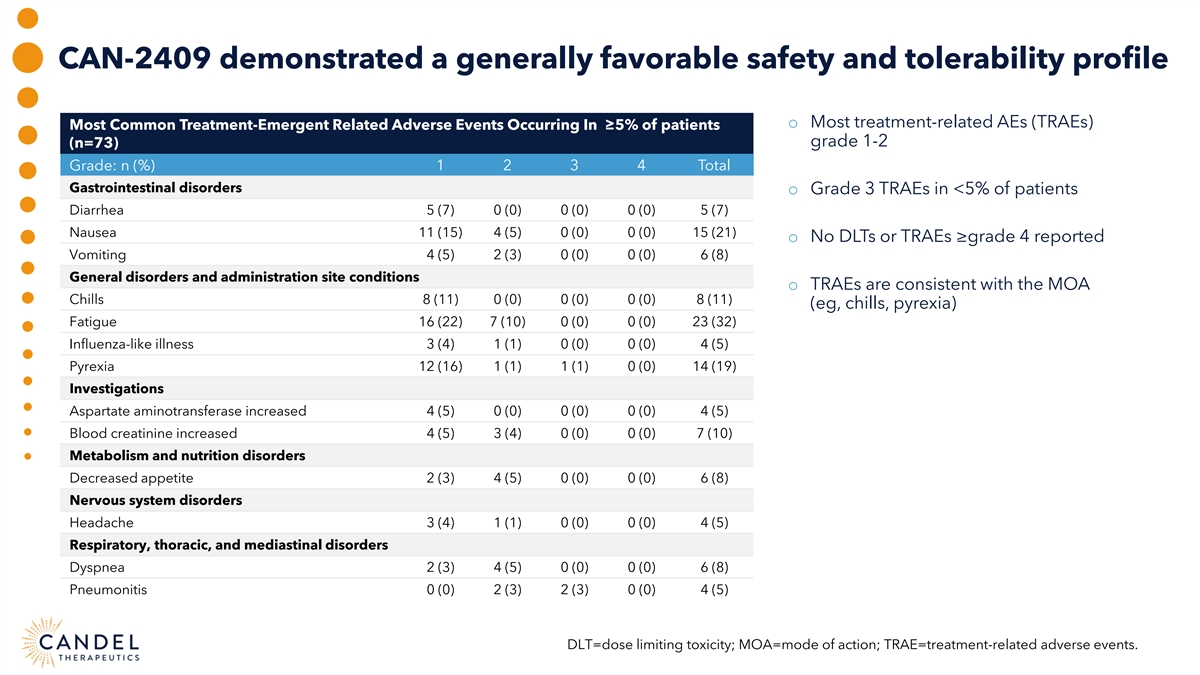
CAN-2409 demonstrated a generally favorable safety and tolerability profile o Most treatment-related AEs (TRAEs) Most Common Treatment-Emergent Related Adverse Events Occurring In ≥5% of patients grade 1-2 (n=73) 1 2 3 4 Total Grade: n (%) Gastrointestinal disorders o Grade 3 TRAEs in <5% of patients Diarrhea 5 (7) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 5 (7) Nausea 11 (15) 4 (5) 0 (0) 0 (0) 15 (21) o No DLTs or TRAEs ≥grade 4 reported Vomiting 4 (5) 2 (3) 0 (0) 0 (0) 6 (8) General disorders and administration site conditions o TRAEs are consistent with the MOA Chills 8 (11) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 8 (11) (eg, chills, pyrexia) Fatigue 16 (22) 7 (10) 0 (0) 0 (0) 23 (32) Influenza-like illness 3 (4) 1 (1) 0 (0) 0 (0) 4 (5) Pyrexia 12 (16) 1 (1) 1 (1) 0 (0) 14 (19) Investigations Aspartate aminotransferase increased 4 (5) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 4 (5) Blood creatinine increased 4 (5) 3 (4) 0 (0) 0 (0) 7 (10) Metabolism and nutrition disorders Decreased appetite 2 (3) 4 (5) 0 (0) 0 (0) 6 (8) Nervous system disorders Headache 3 (4) 1 (1) 0 (0) 0 (0) 4 (5) Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders Dyspnea 2 (3) 4 (5) 0 (0) 0 (0) 6 (8) Pneumonitis 0 (0) 2 (3) 2 (3) 0 (0) 4 (5) DLT=dose limiting toxicity; MOA=mode of action; TRAE=treatment-related adverse events.
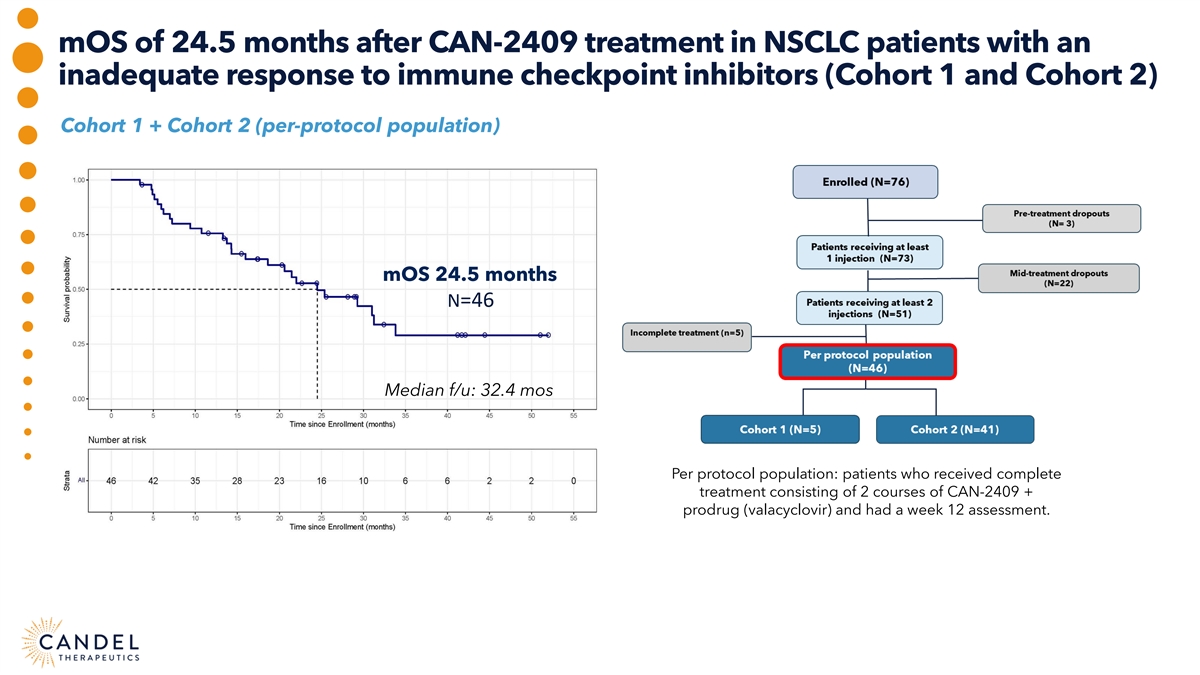
mOS of 24.5 months after CAN-2409 treatment in NSCLC patients with an inadequate response to immune checkpoint inhibitors (Cohort 1 and Cohort 2) Cohort 1 + Cohort 2 (per-protocol population) mOS 24.5 months N=46 Median f/u: 32.4 mos Per protocol population: patients who received complete treatment consisting of 2 courses of CAN-2409 + prodrug (valacyclovir) and had a week 12 assessment.
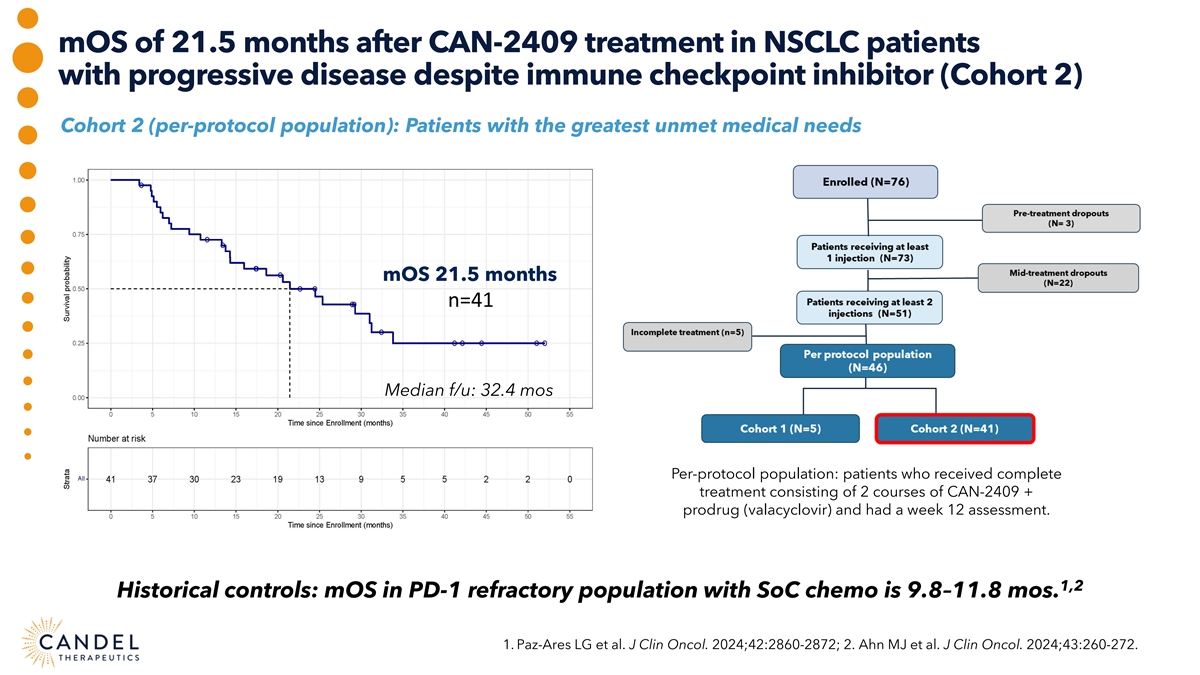
mOS of 21.5 months after CAN-2409 treatment in NSCLC patients with progressive disease despite immune checkpoint inhibitor (Cohort 2) Cohort 2 (per-protocol population): Patients with the greatest unmet medical needs mOS 21.5 months n=41 Median f/u: 32.4 mos Per-protocol population: patients who received complete treatment consisting of 2 courses of CAN-2409 + prodrug (valacyclovir) and had a week 12 assessment. 1,2 Historical controls: mOS in PD-1 refractory population with SoC chemo is 9.8–11.8 mos. 1. Paz-Ares LG et al. J Clin Oncol. 2024;42:2860-2872; 2. Ahn MJ et al. J Clin Oncol. 2024;43:260-272.
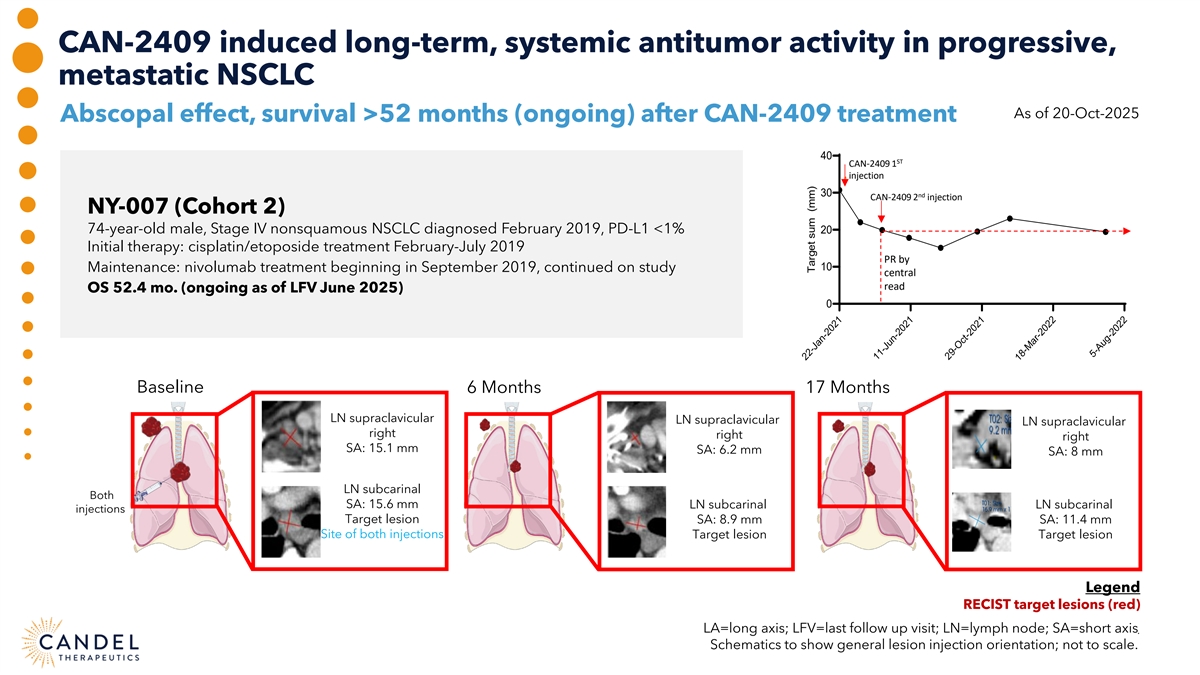
CAN-2409 induced long-term, systemic antitumor activity in progressive, metastatic NSCLC As of 20-Oct-2025 Abscopal effect, survival >52 months (ongoing) after CAN-2409 treatment 40 ST CAN-2409 1 injection 30 nd CAN-2409 2 injection NY-007 (Cohort 2) 74-year-old male, Stage IV nonsquamous NSCLC diagnosed February 2019, PD-L1 <1% 20 Initial therapy: cisplatin/etoposide treatment February-July 2019 PR by 10 Maintenance: nivolumab treatment beginning in September 2019, continued on study central read OS 52.4 mo. (ongoing as of LFV June 2025) 0 Baseline 6 Months 17 Months LN supraclavicular LN supraclavicular LN supraclavicular right right right SA: 15.1 mm SA: 6.2 mm SA: 8 mm LN subcarinal Both SA: 15.6 mm LN subcarinal LN subcarinal injections Target lesion SA: 8.9 mm SA: 11.4 mm Site of both injections Target lesion Target lesion Legend RECIST target lesions (red) LA=long axis; LFV=last follow up visit; LN=lymph node; SA=short axis . Schematics to show general lesion injection orientation; not to scale. 22-Jan-2021 11-Jun-2021 29-Oct-2021 18-Mar-2022 5-Aug-2022 Target sum (mm)
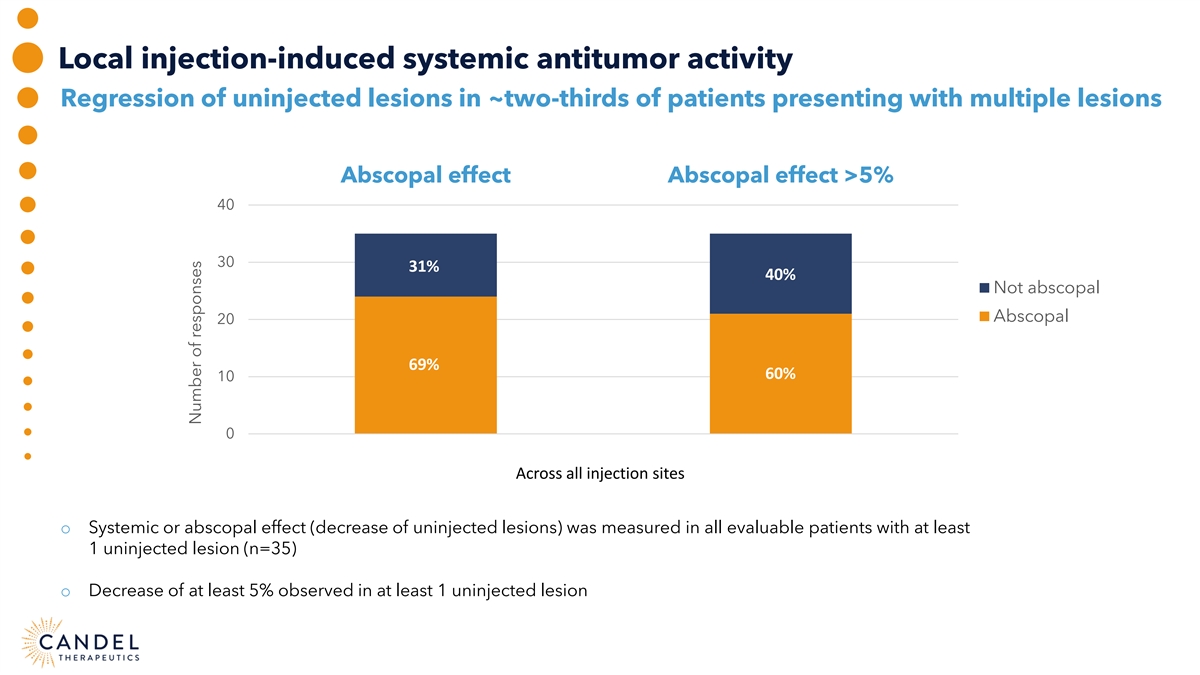
Local injection-induced systemic antitumor activity Regression of uninjected lesions in ~two-thirds of patients presenting with multiple lesions Abscopal effect Abscopal effect >5% 40 30 31% 40% Not abscopal Abscopal 20 69% 60% 10 0 Across all injection sites o Systemic or abscopal effect (decrease of uninjected lesions) was measured in all evaluable patients with at least 1 uninjected lesion (n=35) o Decrease of at least 5% observed in at least 1 uninjected lesion Number of responses
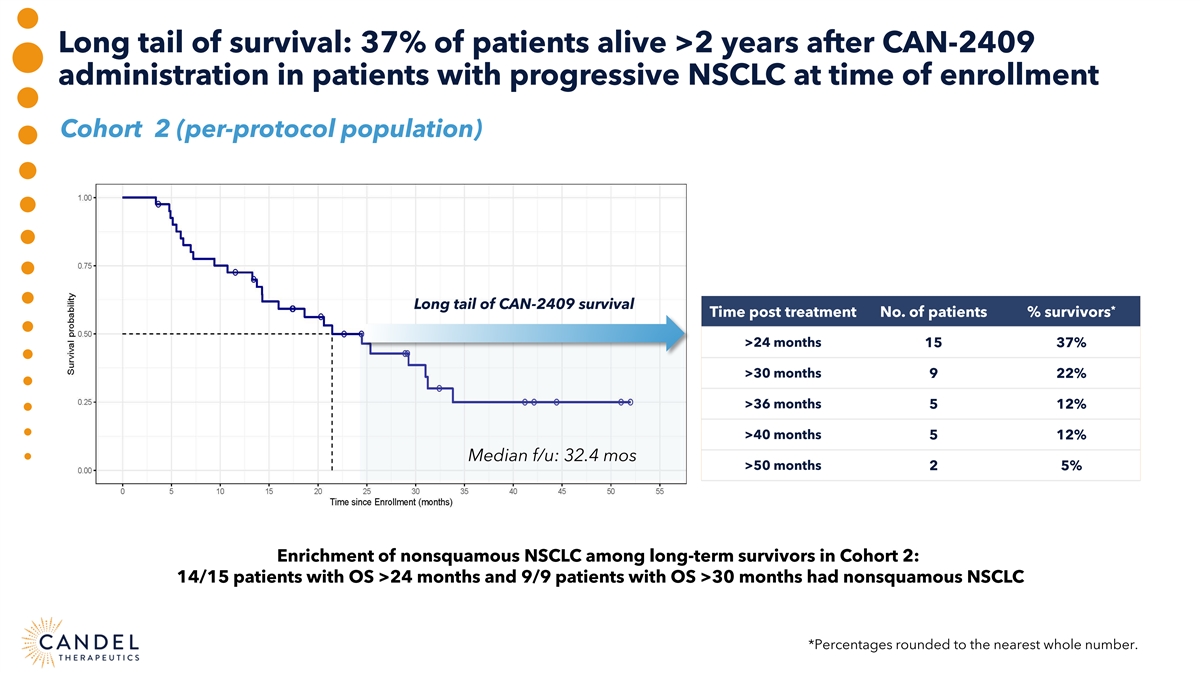
Long tail of survival: 37% of patients alive >2 years after CAN-2409 administration in patients with progressive NSCLC at time of enrollment Cohort 2 (per-protocol population) Long tail of CAN-2409 survival * Time post treatment No. of patients % survivors >24 months 15 37% >30 months 9 22% >36 months 5 12% >40 months 5 12% Median f/u: 32.4 mos >50 months 2 5% Enrichment of nonsquamous NSCLC among long-term survivors in Cohort 2: 14/15 patients with OS >24 months and 9/9 patients with OS >30 months had nonsquamous NSCLC *Percentages rounded to the nearest whole number.
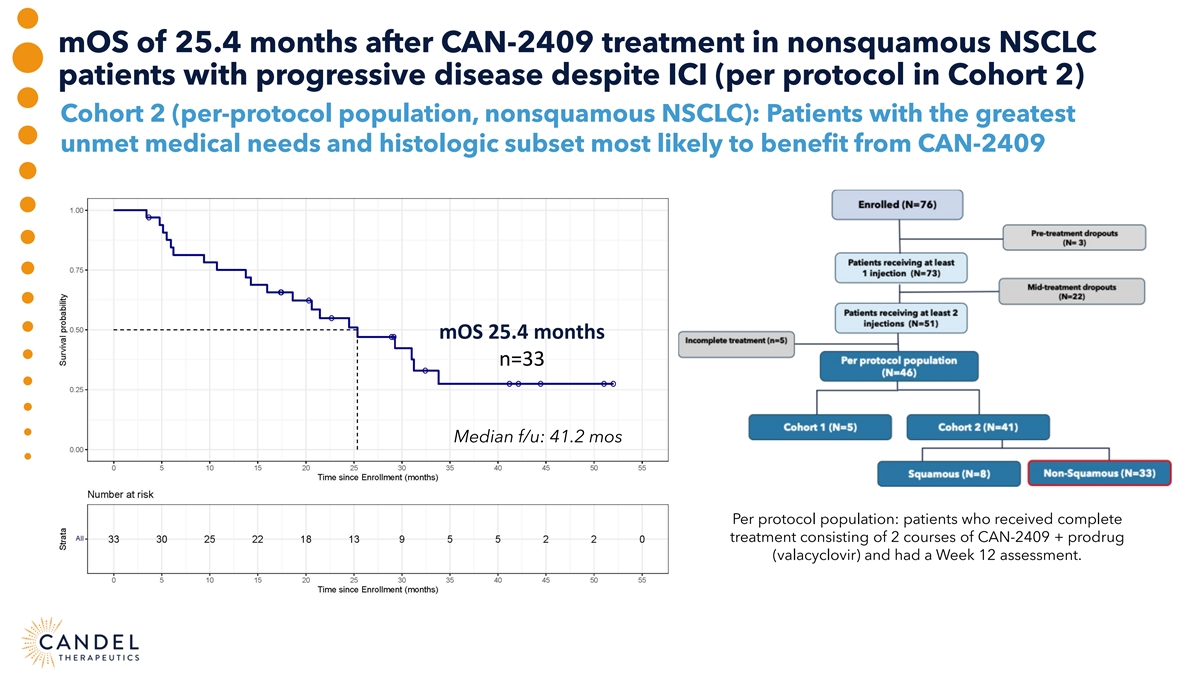
mOS of 25.4 months after CAN-2409 treatment in nonsquamous NSCLC patients with progressive disease despite ICI (per protocol in Cohort 2) Cohort 2 (per-protocol population, nonsquamous NSCLC): Patients with the greatest unmet medical needs and histologic subset most likely to benefit from CAN-2409 mOS 25.4 months n=33 Median f/u: 41.2 mos Per protocol population: patients who received complete treatment consisting of 2 courses of CAN-2409 + prodrug (valacyclovir) and had a Week 12 assessment.
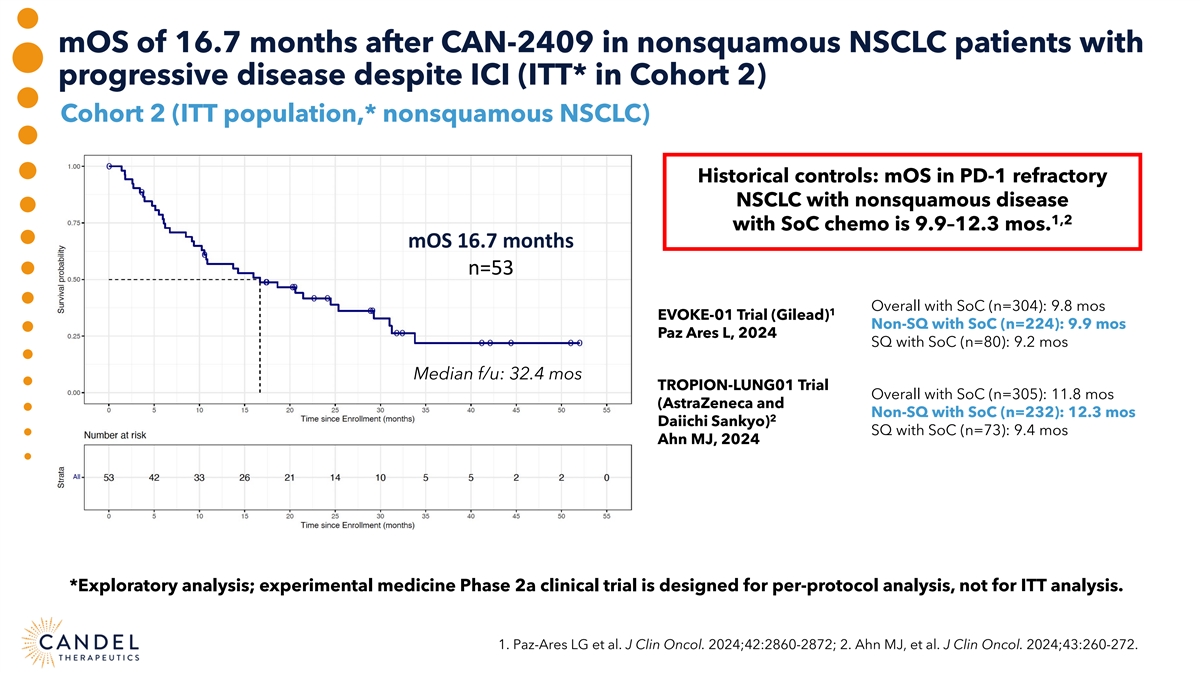
mOS of 16.7 months after CAN-2409 in nonsquamous NSCLC patients with progressive disease despite ICI (ITT* in Cohort 2) Cohort 2 (ITT population,* nonsquamous NSCLC) Historical controls: mOS in PD-1 refractory NSCLC with nonsquamous disease 1,2 with SoC chemo is 9.9–12.3 mos. mOS 16.7 months n=53 Overall with SoC (n=304): 9.8 mos 1 EVOKE-01 Trial (Gilead) Non-SQ with SoC (n=224): 9.9 mos Paz Ares L, 2024 SQ with SoC (n=80): 9.2 mos Median f/u: 32.4 mos TROPION-LUNG01 Trial Overall with SoC (n=305): 11.8 mos (AstraZeneca and Non-SQ with SoC (n=232): 12.3 mos 2 Daiichi Sankyo) SQ with SoC (n=73): 9.4 mos Ahn MJ, 2024 *Exploratory analysis; experimental medicine Phase 2a clinical trial is designed for per-protocol analysis, not for ITT analysis. 1. Paz-Ares LG et al. J Clin Oncol. 2024;42:2860-2872; 2. Ahn MJ, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2024;43:260-272.
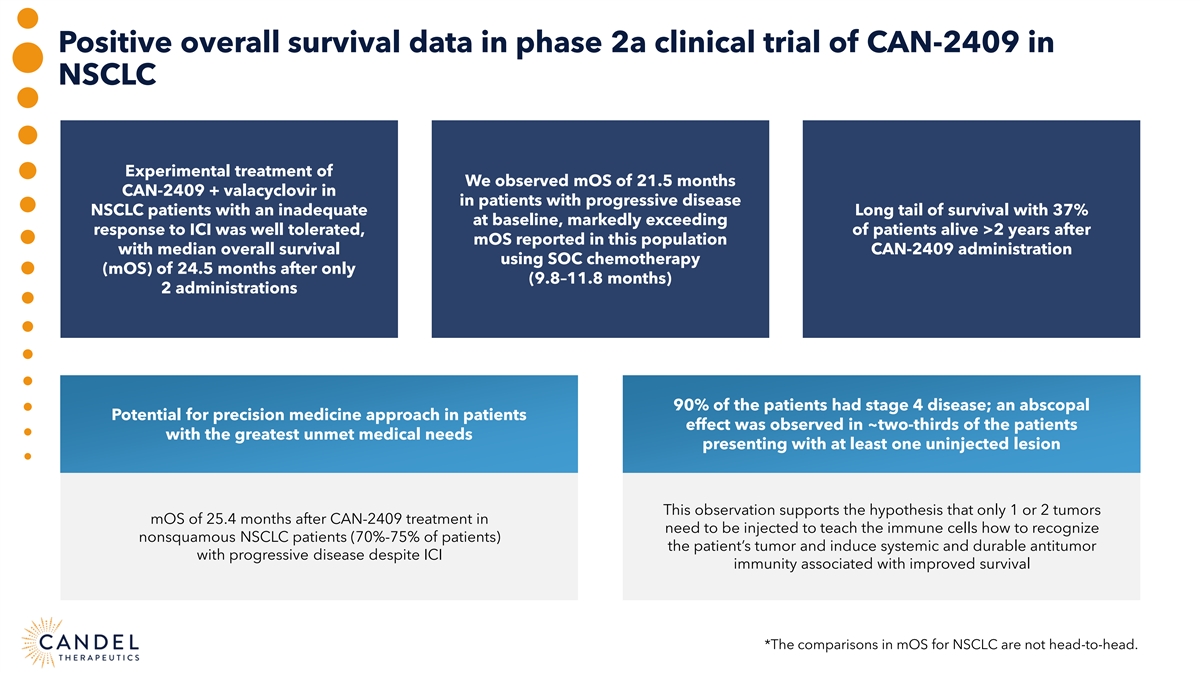
Positive overall survival data in phase 2a clinical trial of CAN-2409 in NSCLC Experimental treatment of We observed mOS of 21.5 months CAN-2409 + valacyclovir in in patients with progressive disease NSCLC patients with an inadequate Long tail of survival with 37% at baseline, markedly exceeding response to ICI was well tolerated, of patients alive >2 years after mOS reported in this population with median overall survival CAN-2409 administration using SOC chemotherapy (mOS) of 24.5 months after only (9.8–11.8 months) 2 administrations 90% of the patients had stage 4 disease; an abscopal Potential for precision medicine approach in patients effect was observed in ~two-thirds of the patients with the greatest unmet medical needs presenting with at least one uninjected lesion This observation supports the hypothesis that only 1 or 2 tumors mOS of 25.4 months after CAN-2409 treatment in need to be injected to teach the immune cells how to recognize nonsquamous NSCLC patients (70%-75% of patients) the patient’s tumor and induce systemic and durable antitumor with progressive disease despite ICI immunity associated with improved survival *The comparisons in mOS for NSCLC are not head-to-head.

CAN-2409 FOR IMMUNE CHECKPOINT INHIBITOR REFRACTORY NON-SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Charu Aggarwal, MD, Professor of Lung Cancer Excellence, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Roy Herbst, MD, PhD, Ensign Professor of Medicine (Medical Oncology) and Professor of Pharmacology, Yale Cancer Center Dan Sterman, MD, Thomas and Suzanne Murphy Professor of Medicine and Cardiothoracic Surgery, NYU Langone Health Moderator: John Newman, PhD, Canaccord Genuity

CAN-3110 FOR RECURRENT GLIOBLASTOMA Francesca Barone, MD, PhD, Candel’s Chief Scientific Officer Henry Brem, MD, Professor of Neurosurgery, Johns Hopkins University Moderator: Kemp Dolliver, Brookline Capital Markets
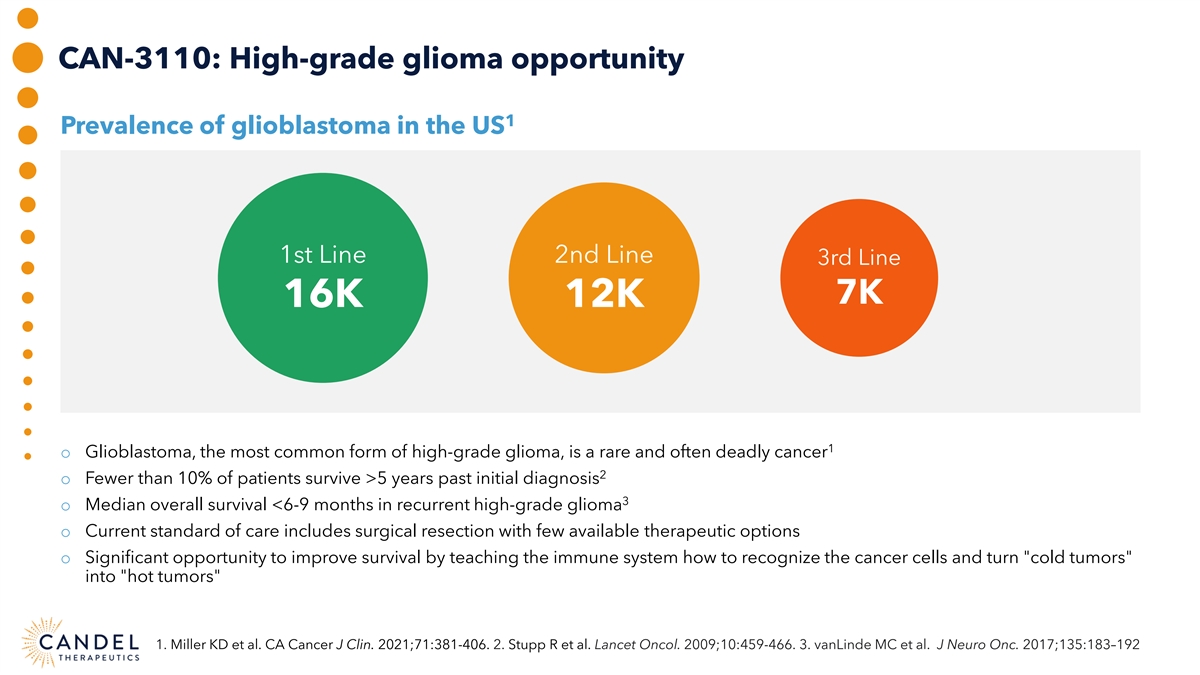
CAN-3110: High-grade glioma opportunity 1 Prevalence of glioblastoma in the US 1st Line 2nd Line 3rd Line 7K 16K 12K 1 o Glioblastoma, the most common form of high-grade glioma, is a rare and often deadly cancer 2 o Fewer than 10% of patients survive >5 years past initial diagnosis 3 o Median overall survival <6-9 months in recurrent high-grade glioma o Current standard of care includes surgical resection with few available therapeutic options o Significant opportunity to improve survival by teaching the immune system how to recognize the cancer cells and turn cold tumors into hot tumors 1. Miller KD et al. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:381-406. 2. Stupp R et al. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:459-466. 3. vanLinde MC et al. J Neuro Onc. 2017;135:183–192
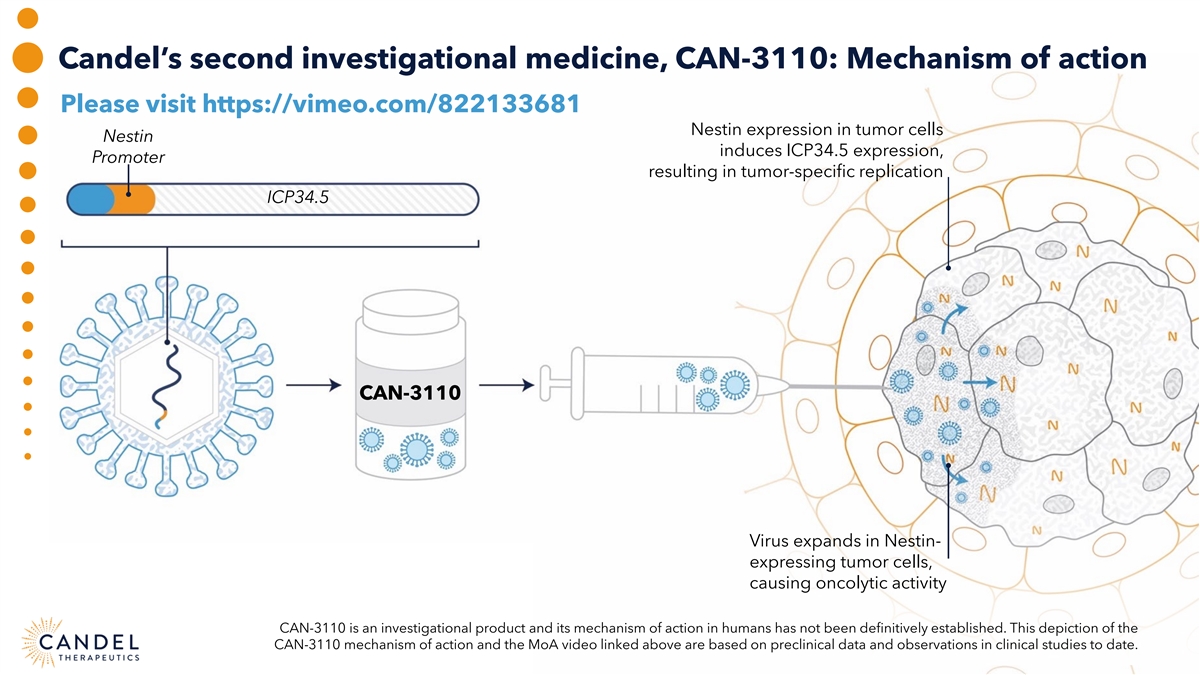
Candel’s second investigational medicine, CAN-3110: Mechanism of action Please visit https://vimeo.com/822133681 Nestin expression in tumor cells Nestin induces ICP34.5 expression, Promoter resulting in tumor-specific replication ICP34.5 CAN-3110 Virus expands in Nestin- expressing tumor cells, causing oncolytic activity CAN-3110 is an investigational product and its mechanism of action in humans has not been definitively established. This depiction of the CAN-3110 mechanism of action and the MoA video linked above are based on preclinical data and observations in clinical studies to date.
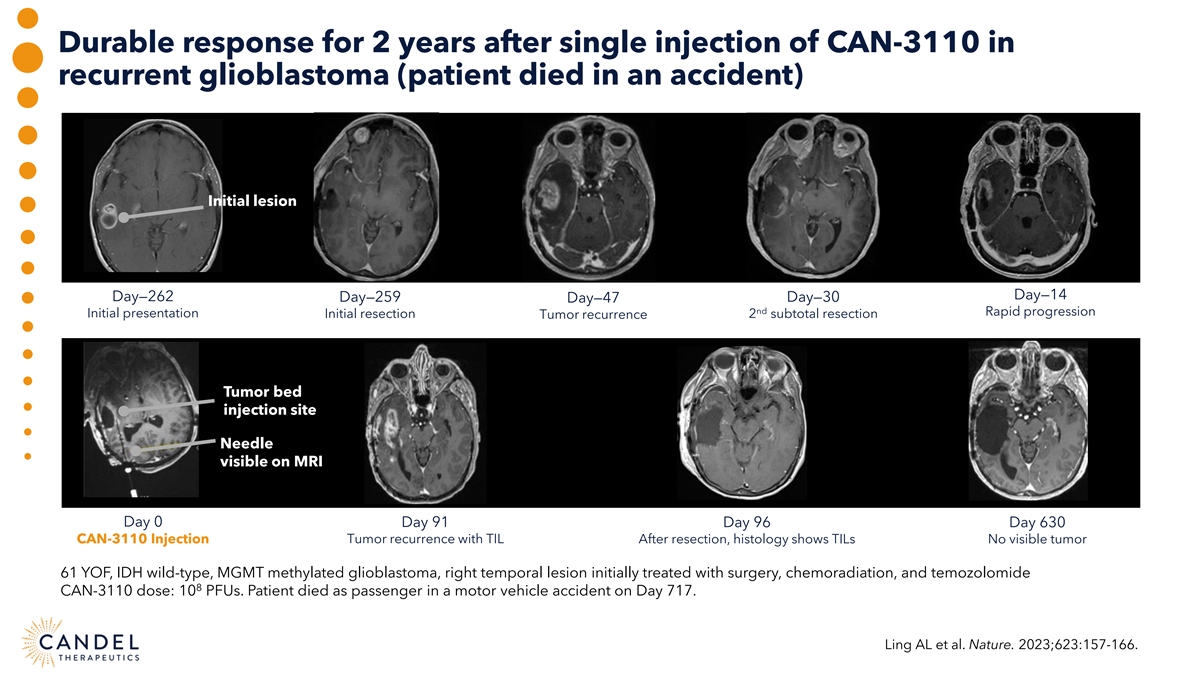
Durable response for 2 years after single injection of CAN-3110 in recurrent glioblastoma (patient died in an accident) Initial lesion Day—14 Day—262 Day—259 Day—47 Day—30 nd Rapid progression Initial presentation Initial resection Tumor recurrence 2 subtotal resection Tumor bed injection site Needle visible on MRI Day 0 Day 91 Day 96 Day 630 CAN-3110 Injection Tumor recurrence with TIL After resection, histology shows TILs No visible tumor 61 YOF, IDH wild-type, MGMT methylated glioblastoma, right temporal lesion initially treated with surgery, chemoradiation, and temozolomide 8 CAN-3110 dose: 10 PFUs. Patient died as passenger in a motor vehicle accident on Day 717. Ling AL et al. Nature. 2023;623:157-166.
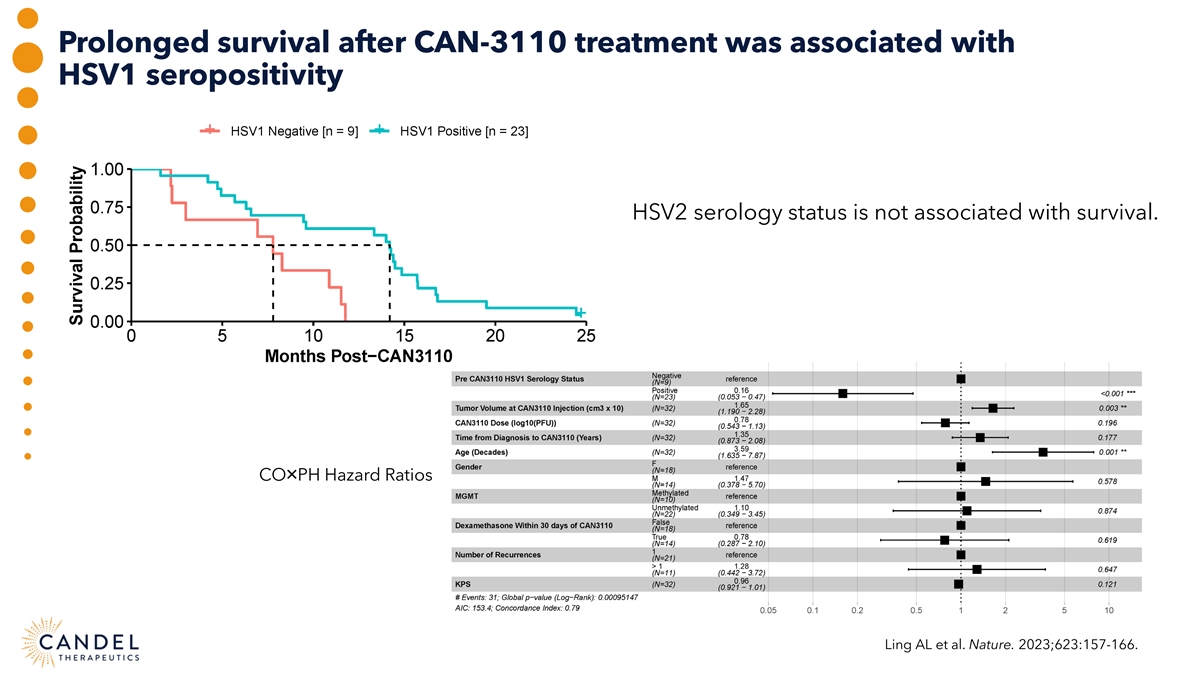
Prolonged survival after CAN-3110 treatment was associated with HSV1 seropositivity HSV2 serology status is not associated with survival. CO×PH Hazard Ratios Ling AL et al. Nature. 2023;623:157-166.
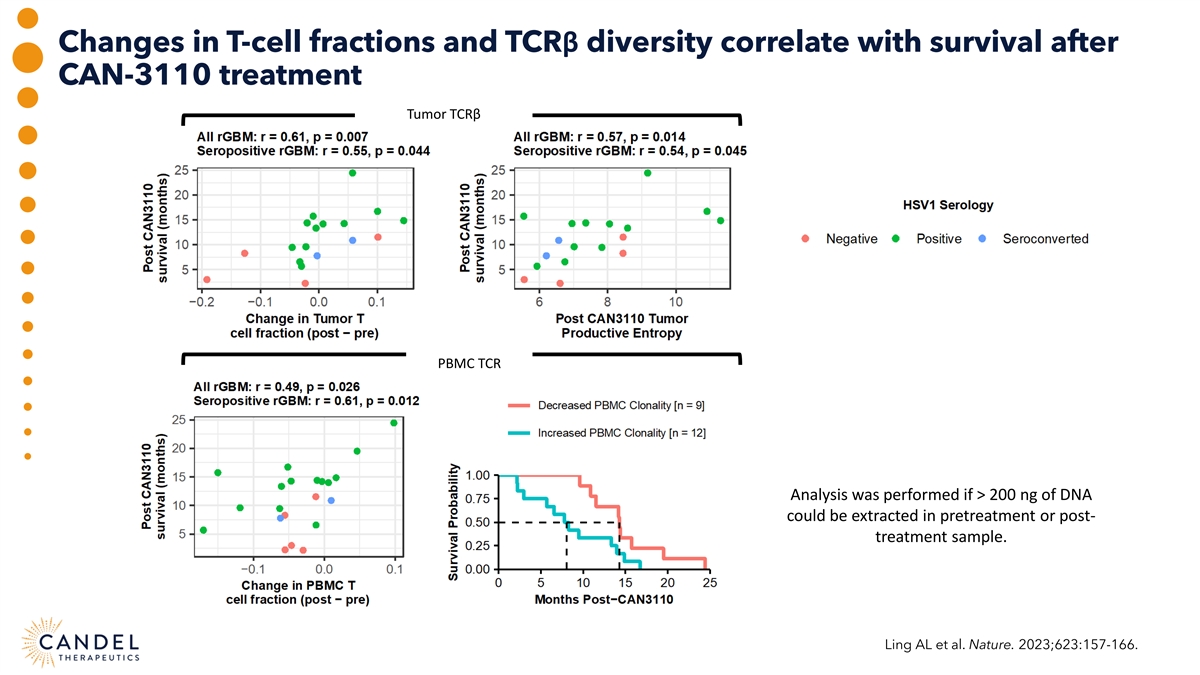
Changes in T-cell fractions and TCRβ diversity correlate with survival after CAN-3110 treatment Tumor TCRβ PBMC TCR Analysis was performed if > 200 ng of DNA could be extracted in pretreatment or post- treatment sample. Ling AL et al. Nature. 2023;623:157-166.
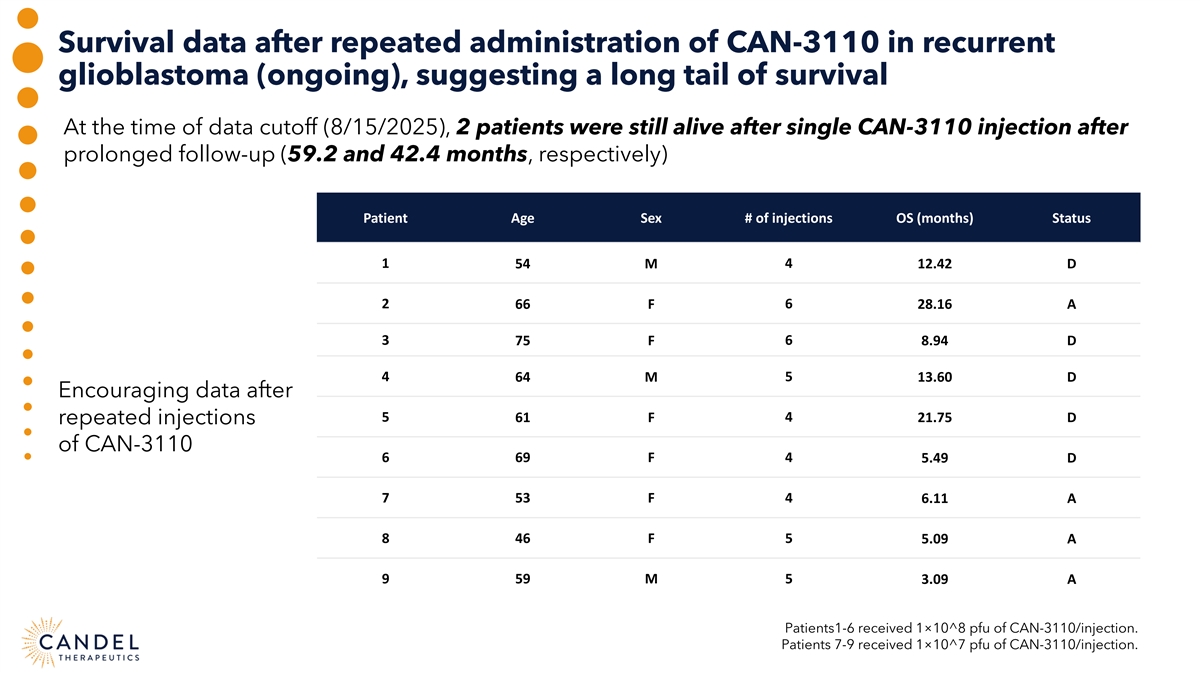
Survival data after repeated administration of CAN-3110 in recurrent glioblastoma (ongoing), suggesting a long tail of survival At the time of data cutoff (8/15/2025), 2 patients were still alive after single CAN-3110 injection after prolonged follow-up (59.2 and 42.4 months, respectively) Patient Age Sex # of injections OS (months) Status 1 54 M 4 12.42 D 2 66 F 6 28.16 A 3 75 F 6 8.94 D 4 5 64 M 13.60 D Encouraging data after 5 61 F 4 21.75 D repeated injections of CAN-3110 6 69 F 4 5.49 D 7 53 F 4 6.11 A 8 46 F 5 5.09 A 9 59 M 5 3.09 A Patients1-6 received 1×10^8 pfu of CAN-3110/injection. Patients 7-9 received 1×10^7 pfu of CAN-3110/injection.

CAN-3110 induced dynamic spatial and temporal remodeling of the tumor microenvironment, where tumor cells are replaced by immune cells Ling AL et al. Sci Transl Med. 2025;17:eadv2881.
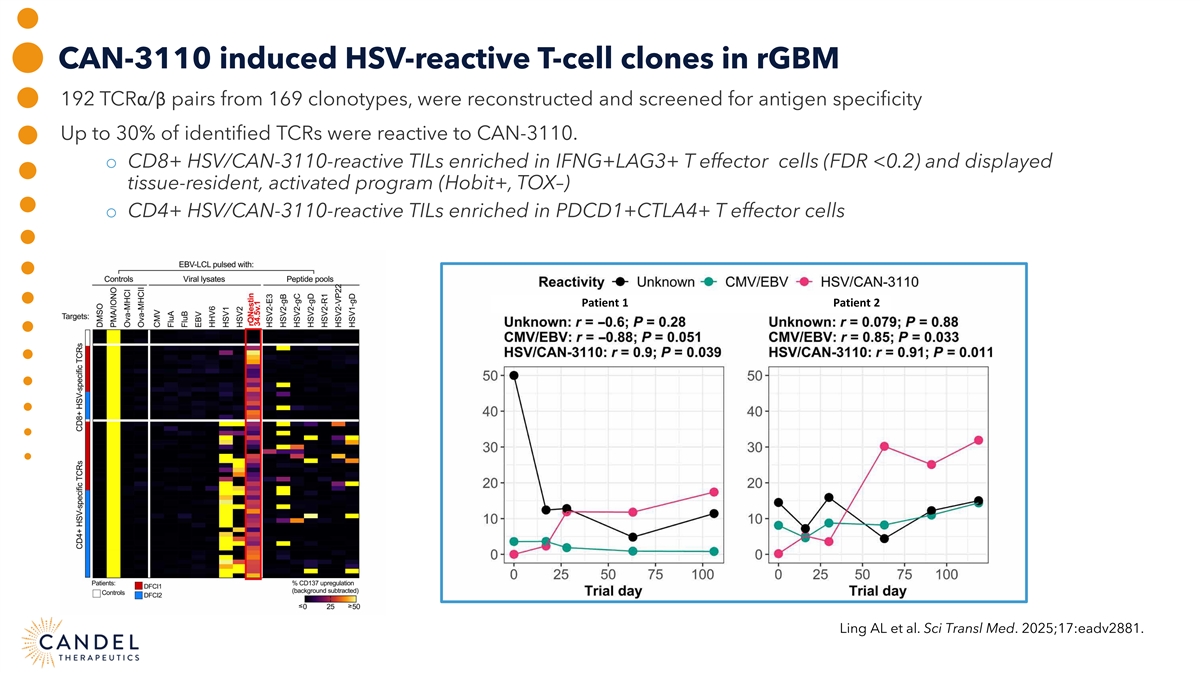
CAN-3110 induced HSV-reactive T-cell clones in rGBM 192 TCRα/β pairs from 169 clonotypes, were reconstructed and screened for antigen specificity Up to 30% of identified TCRs were reactive to CAN-3110. o CD8+ HSV/CAN-3110-reactive TILs enriched in IFNG+LAG3+ T effector cells (FDR <0.2) and displayed tissue-resident, activated program (Hobit+, TOX–) o CD4+ HSV/CAN-3110-reactive TILs enriched in PDCD1+CTLA4+ T effector cells Patient 1 Patient 2 Ling AL et al. Sci Transl Med. 2025;17:eadv2881.
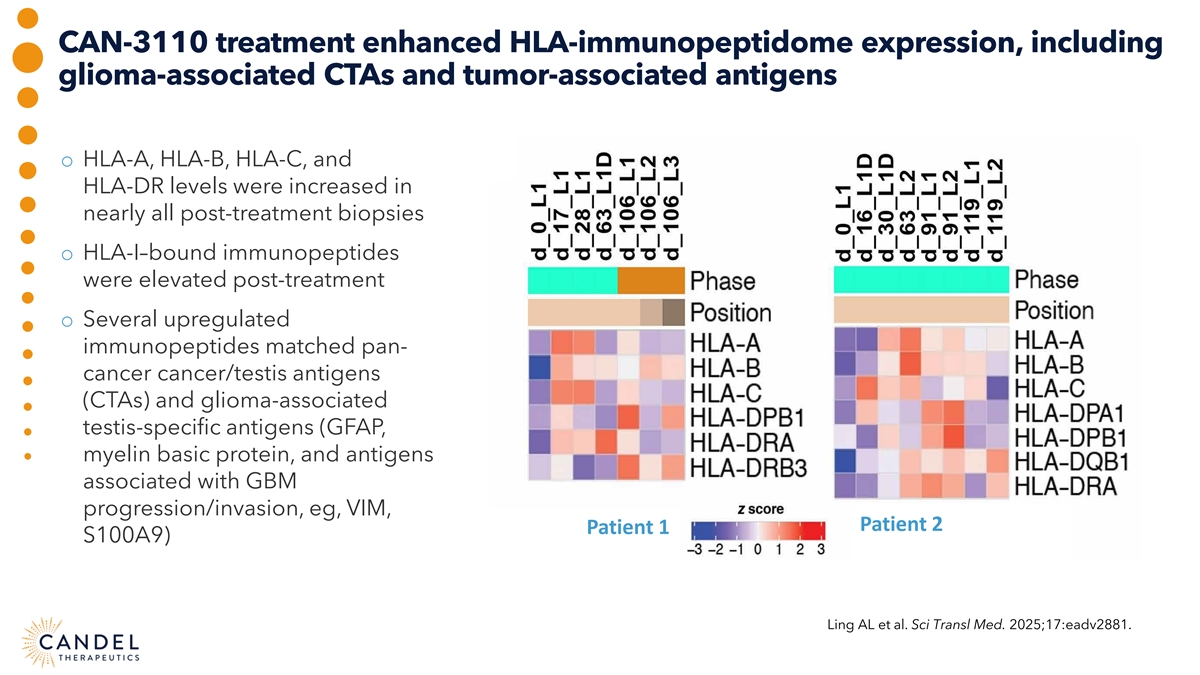
CAN-3110 treatment enhanced HLA-immunopeptidome expression, including glioma-associated CTAs and tumor-associated antigens o HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C, and HLA-DR levels were increased in nearly all post-treatment biopsies o HLA-I–bound immunopeptides were elevated post-treatment o Several upregulated immunopeptides matched pan- cancer cancer/testis antigens (CTAs) and glioma-associated testis-specific antigens (GFAP, myelin basic protein, and antigens associated with GBM progression/invasion, eg, VIM, Patient 2 Patient 1 S100A9) Ling AL et al. Sci Transl Med. 2025;17:eadv2881.

Encouraging safety data, clinical activity, and immunological changes after CAN-3110 in recurrent high-grade glioma (glioblastoma) Monotherapy treatment with CAN-3110 in rHGG is well tolerated and associated with doubling of expected median overall survival Immunological changes in the tumor microenvironment are associated with improved survival and HSV1 seropositivity First 9 patients have been dosed in Cohort C (fully funded by the Break Through Cancer foundation) Repeated injections of CAN-3110 (up to 6) feasible, well tolerated, and associated with encouraging survival data Near absence of tumor cells alongside dense lymphocyte infiltrates in biopsies obtained after repeated CAN-3110 administration Despite MRI-diagnosed tumor progression, multiomic analyses revealed therapeutic effects, including expansion of CAN-3110–reactive and other T-cell clonotypes, and induced expression of human leukocyte antigen (HLA)–presented immunopeptides

CAN-3110 FOR RECURRENT GLIOBLASTOMA Francesca Barone, MD, PhD, Candel’s Chief Scientific Officer Henry Brem, MD, Professor of Neurosurgery, Johns Hopkins University Moderator: Kemp Dolliver, Brookline Capital Markets

CANDEL THERAPEUTICS RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT DAY 2025: Q&A Kemp Dolliver, Brookline Capital Markets Sudan Loganathan, PhD, Stephens Andres Maldonado, PhD, H.C. Wainwright & Co. Imogen Mansfield, MA, MBA, Cantor Fitzgerald Oliver McCammon, LifeSci Capital John Newman, PhD, Canaccord Genuity Yigal Nochomovitz, PhD, Citi Group Alec Stranahan, PhD, Bank of America Moderator: Paul Peter Tak, MD, PhD, FMedSci, Candel’s CEO

THANK YOU Candel Research & Development Day December 5, 2025 NASDAQ: CADL