| Unlocking the Value of our Pipeline for T1D January 2026 |
| 2 Forward-looking statements This presentation contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of, and made pursuant to the safe harbor provisions of, The Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. All statements contained in this presentation, other than statements of historical facts or statements that relate to present facts or current conditions, including but not limited to, statements regarding our clinical development plans and timelines and the initial safety and efficacy profiles of our product candidates, and statements regarding our preclinical development programs, including initial preclinical data and development plans and timelines, and statements regarding cash runway and expected use of potential offering proceeds are forward-looking statements. These statements involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other important factors that may cause our actual results, performance, or achievements to be materially different from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements. In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by terms such as “may,” “might,” “will,” “should,” “expect,” “plan,” “aim,” “seek,” “anticipate,” “could,” “intend,” “target,” “project,” “contemplate,” “believe,” “estimate,” “predict,” “forecast,” “potential” or “continue” or the negative of these terms or other similar expressions. The forward-looking statements in this presentation are only predictions. We have based these forward-looking statements largely on our current expectations and projections about future events and financial trends that we believe may affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations. These forward-looking statements speak only as of the date of this presentation and are subject to a number of risks, uncertainties and assumptions, some of which cannot be predicted or quantified and some of which are beyond our control, including, among others: our ability to successfully advance our current and future product candidates through development activities, preclinical studies, and clinical trials; our ability to progress our product candidates through clinical development; our ability to meet development milestones on anticipated timelines; uncertainties inherent in the results of preliminary data, pre-clinical studies and earlier-stage clinical trials, which may not be predictive of final results or the results of later-stage clinical trials; our ability to obtain clearance of our future IND or CTA submissions and commence and complete clinical trials on expected timelines, or at all; our reliance on the maintenance of certain key collaborative relationships for the manufacturing and development of our product candidates; the timing, scope and likelihood of regulatory filings and approvals, including final regulatory approval of our product candidates; the impact of geopolitical issues, trade disputes and tariffs, banking instability and inflation on our business and operations, supply chain and labor force; the performance of third parties in connection with the development of our product candidates, including third parties conducting our clinical trials as well as third-party suppliers and manufacturers; our ability to successfully commercialize our product candidates and develop sales and marketing capabilities, if our product candidates are approved; our ability to recruit and maintain key members of management and our ability to maintain and successfully enforce adequate intellectual property protection. These and other risks and uncertainties are described more fully in the “Risk Factors” section of our most recent filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission and available at www.sec.gov. You should not rely on these forward-looking statements as predictions of future events. The events and circumstances reflected in our forward-looking statements may not be achieved or occur, and actual results could differ materially from those projected in the forward-looking statements. Moreover, we operate in a dynamic industry and economy. New risk factors and uncertainties may emerge from time to time, and it is not possible for management to predict all risk factors and uncertainties that we may face. Except as required by applicable law, we do not plan to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statements contained herein, whether as a result of any new information, future events, changed circumstances or otherwise. |
| Cell Foundry and Allo-Evasion Technology High Impact Programs Focused on Execution Century Therapeutics Today © 2025 3 Cell foundry generates fully functional cells at scale • Key developmental insights allow directed differentiation of cells that function like primary cells, such as beta Islet cells and CD4+/CD8+ αβ T cells Leaders in immune evasion engineering • Allo-Evasion allows cells to co-exist with a patient’s immune system • Enables enhanced persistence and potential for re-dosing of therapy Advancing lead iPSC derived cell therapies with Allo-Evasion 5.0 toward the clinic • CNTY-813 in IND-enabling studies with potential for functional cure in Type 1 Diabetes • CNTY-308 in IND-enabling studies for treatment of B-cell-mediated diseases • Patient enrollment ongoing for CNTY-101 in Phase 1/2 CARAMEL IST in autoimmune disease Cash runway extended beyond planned key clinical milestones • CNTY-813 IND submission planned for 2026 with initial clinical data expected 2027 • CNTY-308 αβ T cell program expected to enter the clinic in 2026 • CNTY-101 preliminary clinical data from Phase 1/2 CARAMEL IST expected in 2026 |
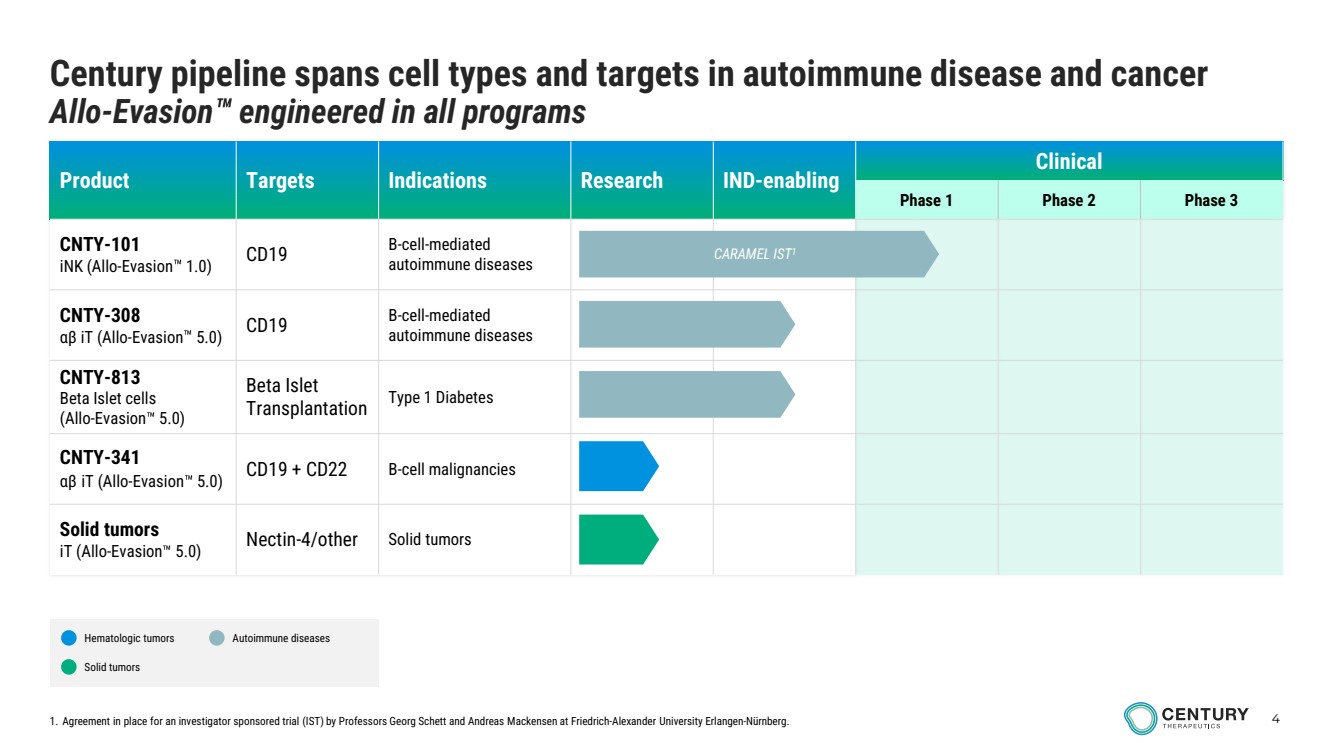
| 4 Product Targets Indications Research IND-enabling Clinical Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 CNTY-101 iNK (Allo-Evasion 1.0) CD19 B-cell-mediated autoimmune diseases CNTY-308 αβ iT (Allo-Evasion 5.0) CD19 B-cell-mediated autoimmune diseases CNTY-813 Beta Islet cells (Allo-Evasion 5.0) Beta Islet Transplantation Type 1 Diabetes CNTY-341 αβ iT (Allo-Evasion 5.0) CD19 + CD22 B-cell malignancies Solid tumors iT (Allo-Evasion 5.0) Nectin-4/other Solid tumors Century pipeline spans cell types and targets in autoimmune disease and cancer Allo-Evasion engineered in all programs CARAMEL IST1 Hematologic tumors Solid tumors Autoimmune diseases 1. Agreement in place for an investigator sponsored trial (IST) by Professors Georg Schett and Andreas Mackensen at Friedrich-Alexander University Erlangen-Nürnberg. |
| Allo-Evasion |
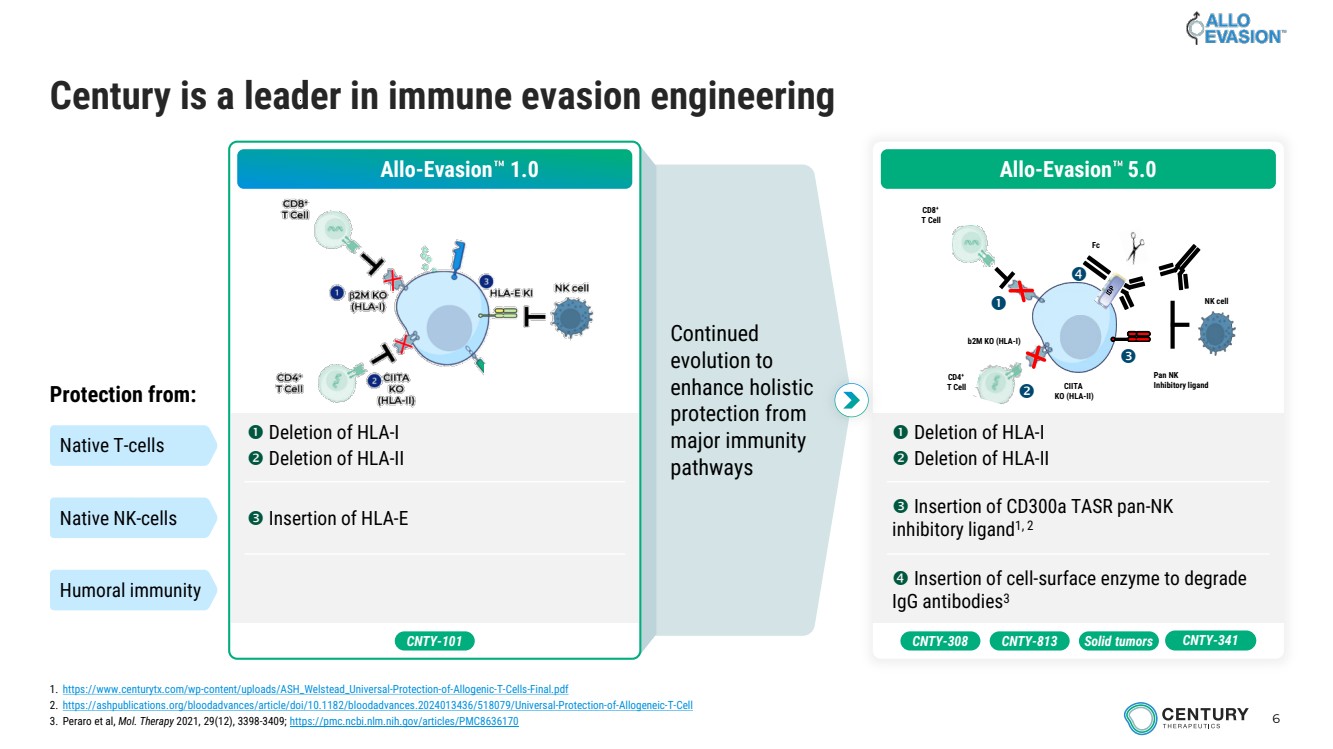
| 6 Continued evolution to enhance holistic protection from major immunity pathways Century is a leader in immune evasion engineering Allo-Evasion 1.0 Deletion of HLA-I Deletion of HLA-II Insertion of HLA-E Protection from: Native T-cells Native NK-cells Humoral immunity CNTY-101 Deletion of HLA-I Deletion of HLA-II Insertion of CD300a TASR pan-NK inhibitory ligand1, 2 Insertion of cell-surface enzyme to degrade IgG antibodies3 b2M KO (HLA-I) CIITA KO (HLA-II) CD8+ T Cell CD4+ T Cell Pan NK Inhibitory ligand Fc NK cell Allo-Evasion 5.0 CNTY-308 CNTY-813 Solid tumors CNTY-341 1. https://www.centurytx.com/wp-content/uploads/ASH_Welstead_Universal-Protection-of-Allogenic-T-Cells-Final.pdf 2. https://ashpublications.org/bloodadvances/article/doi/10.1182/bloodadvances.2024013436/518079/Universal-Protection-of-Allogeneic-T-Cell 3. Peraro et al, Mol. Therapy 2021, 29(12), 3398-3409; https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8636170 |
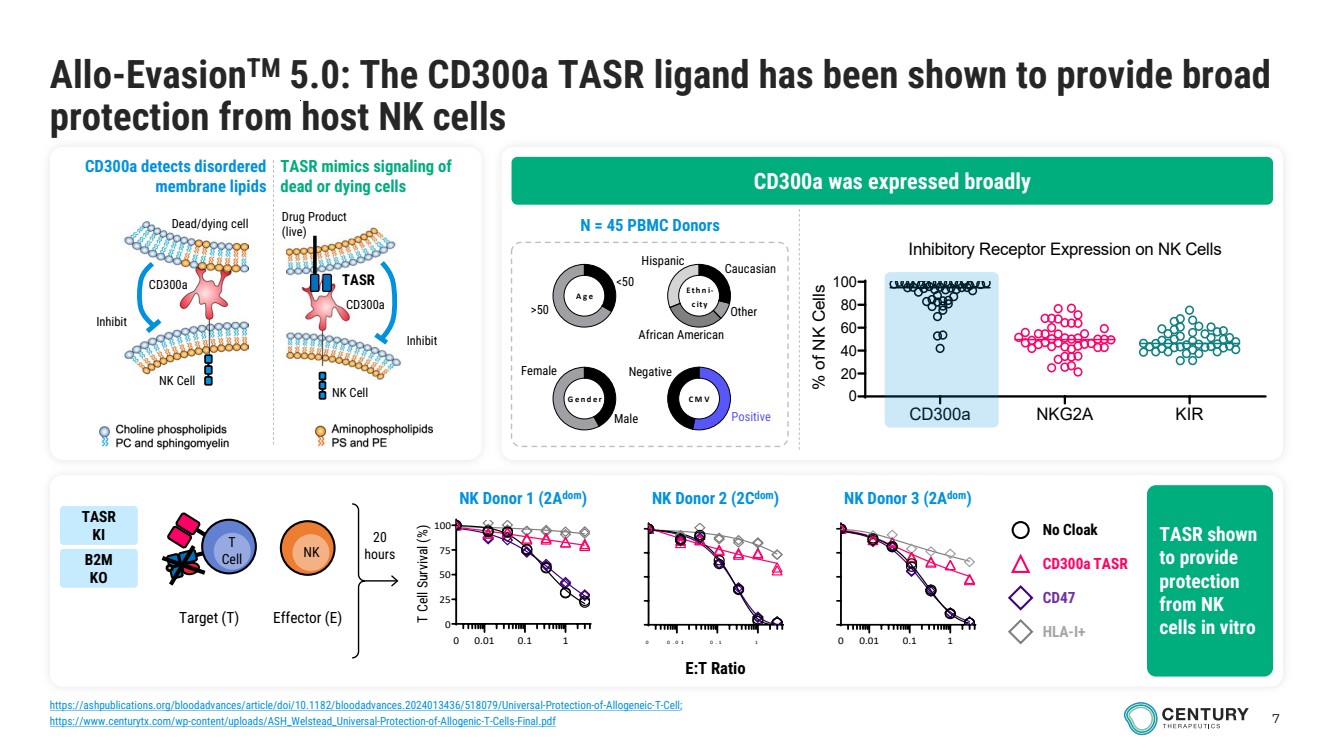
| 7 Allo-EvasionTM 5.0: The CD300a TASR ligand has been shown to provide broad protection from host NK cells Male Female <50 >50 Gender Age Ethni-city CMV Caucasian Other African American Hispanic Negative Positive N = 45 PBMC Donors 0.01 0.1 1 0 0 .0 1 0 .1 1 0 25 50 75 100 0 E:T Ratio T Cell Survival (%) 0 0.01 0.1 1 No Cloak CD300a TASR CD47 HLA-I+ 20 hours Target (T) T Cell NK Effector (E) CD300a was expressed broadly CD300a detects disordered membrane lipids TASR mimics signaling of dead or dying cells Drug Product (live) Inhibit NK Cell TASR CD300a Dead/dying cell NK Cell Inhibit CD300a TASR shown to provide protection from NK cells in vitro NK Donor 2 (2Cdom NK Donor 1 (2A ) dom) NK Donor 3 (2Adom) TASR KI B2M KO CD300a NKG2A KIR 0 20 40 60 80 100 Inhibitory Receptor Expression on NK Cells (n = 46 donors) % of NK Cells https://ashpublications.org/bloodadvances/article/doi/10.1182/bloodadvances.2024013436/518079/Universal-Protection-of-Allogeneic-T-Cell; https://www.centurytx.com/wp-content/uploads/ASH_Welstead_Universal-Protection-of-Allogenic-T-Cells-Final.pdf |
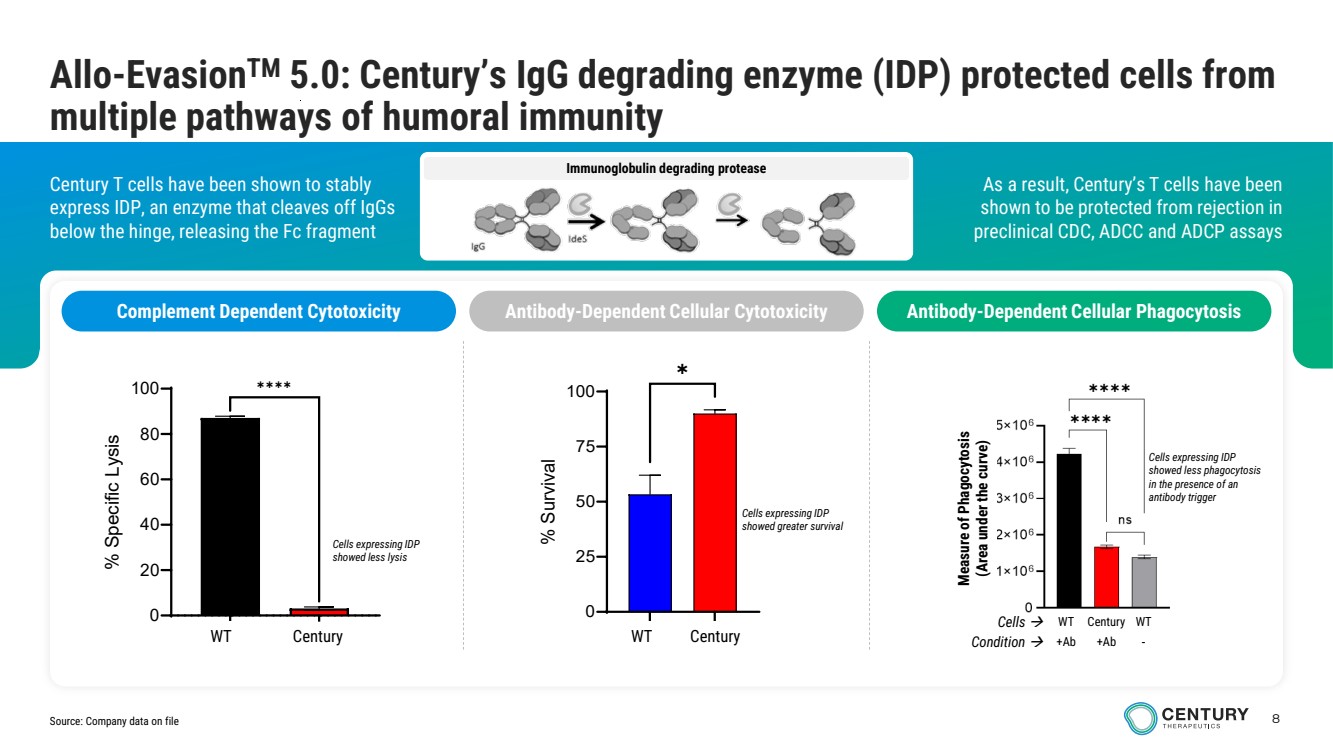
| 8 Immunoglobulin degrading protease As a result, Century’s T cells have been shown to be protected from rejection in preclinical CDC, ADCC and ADCP assays Century T cells have been shown to stably express IDP, an enzyme that cleaves off IgGs below the hinge, releasing the Fc fragment Allo-EvasionTM 5.0: Century’s IgG degrading enzyme (IDP) protected cells from multiple pathways of humoral immunity Complement Dependent Cytotoxicity Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity Antibody-Dependent Cellular Phagocytosis Measure of Phagocytosis (Area under the curve) Cells expressing IDP showed less phagocytosis in the presence of an antibody trigger Cells WT Century WT Condition +Ab +Ab - Cells expressing IDP showed greater survival GFP IdeStm 0 20 40 60 80 100 % Specific Lysis ✱✱✱✱ WT Century Cells expressing IDP showed less lysis WT Gen 2.3 0 25 50 75 100 % Survival ✱ WT Century Source: Company data on file |
| Type 1 Diabetes Program |
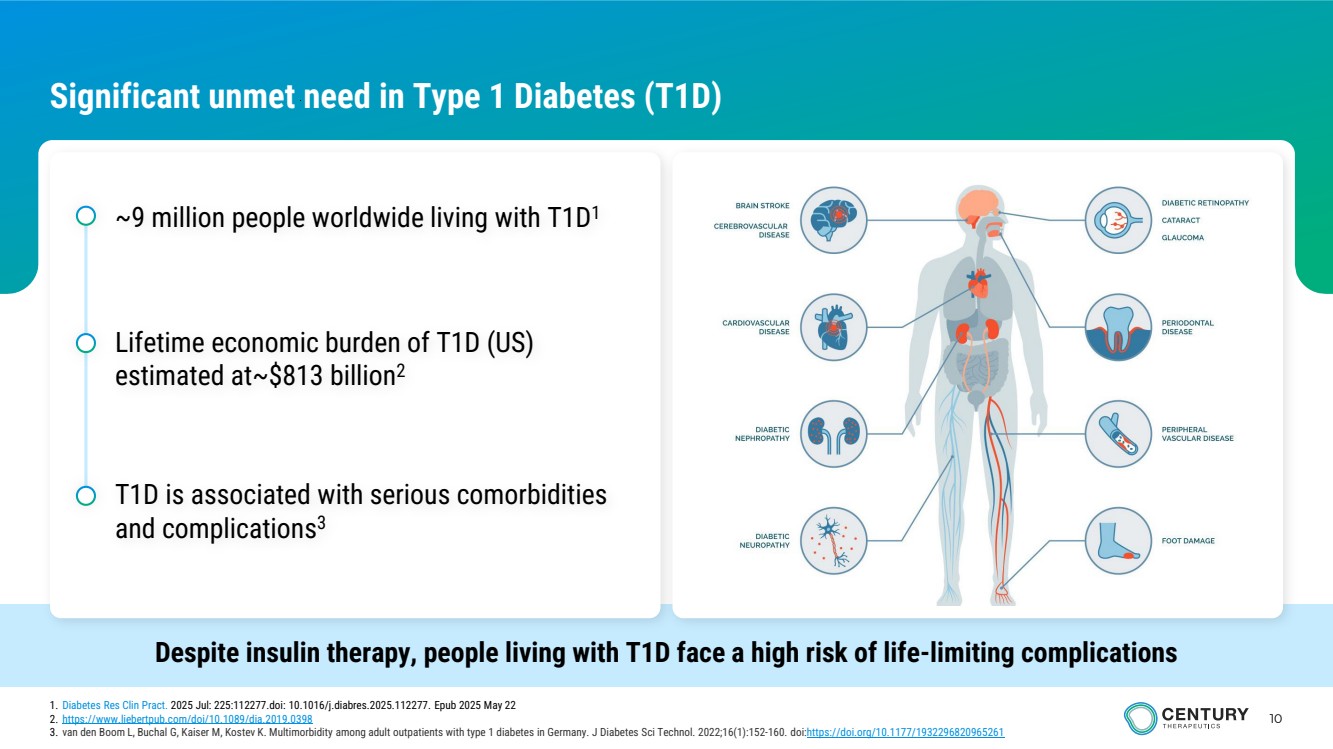
| 10 Significant unmet need in Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) Despite insulin therapy, people living with T1D face a high risk of life-limiting complications ~9 million people worldwide living with T1D1 Lifetime economic burden of T1D (US) estimated at~$813 billion2 T1D is associated with serious comorbidities and complications3 1. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2025 Jul: 225:112277.doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2025.112277. Epub 2025 May 22 2. https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/10.1089/dia.2019.0398 3. van den Boom L, Buchal G, Kaiser M, Kostev K. Multimorbidity among adult outpatients with type 1 diabetes in Germany. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2022;16(1):152-160. doi:https://doi.org/10.1177/1932296820965261 |
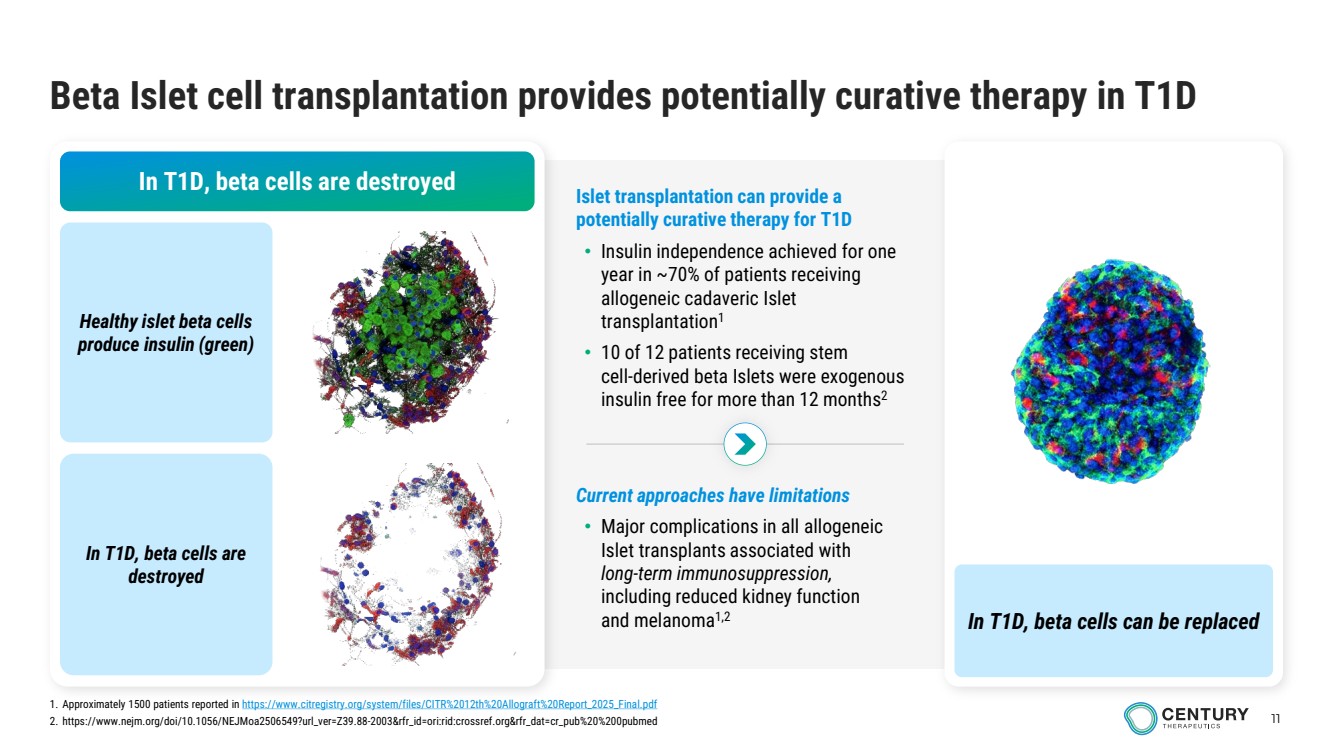
| 11 Beta Islet cell transplantation provides potentially curative therapy in T1D In T1D, beta cells are destroyed Healthy islet beta cells produce insulin (green) In T1D, beta cells are destroyed In T1D, beta cells can be replaced Current approaches have limitations • Major complications in all allogeneic Islet transplants associated with long-term immunosuppression, including reduced kidney function and melanoma1,2 Islet transplantation can provide a potentially curative therapy for T1D • Insulin independence achieved for one year in ~70% of patients receiving allogeneic cadaveric Islet transplantation1 • 10 of 12 patients receiving stem cell-derived beta Islets were exogenous insulin free for more than 12 months2 1. Approximately 1500 patients reported in https://www.citregistry.org/system/files/CITR%2012th%20Allograft%20Report_2025_Final.pdf 2. https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa2506549?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori:rid:crossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub%20%200pubmed |
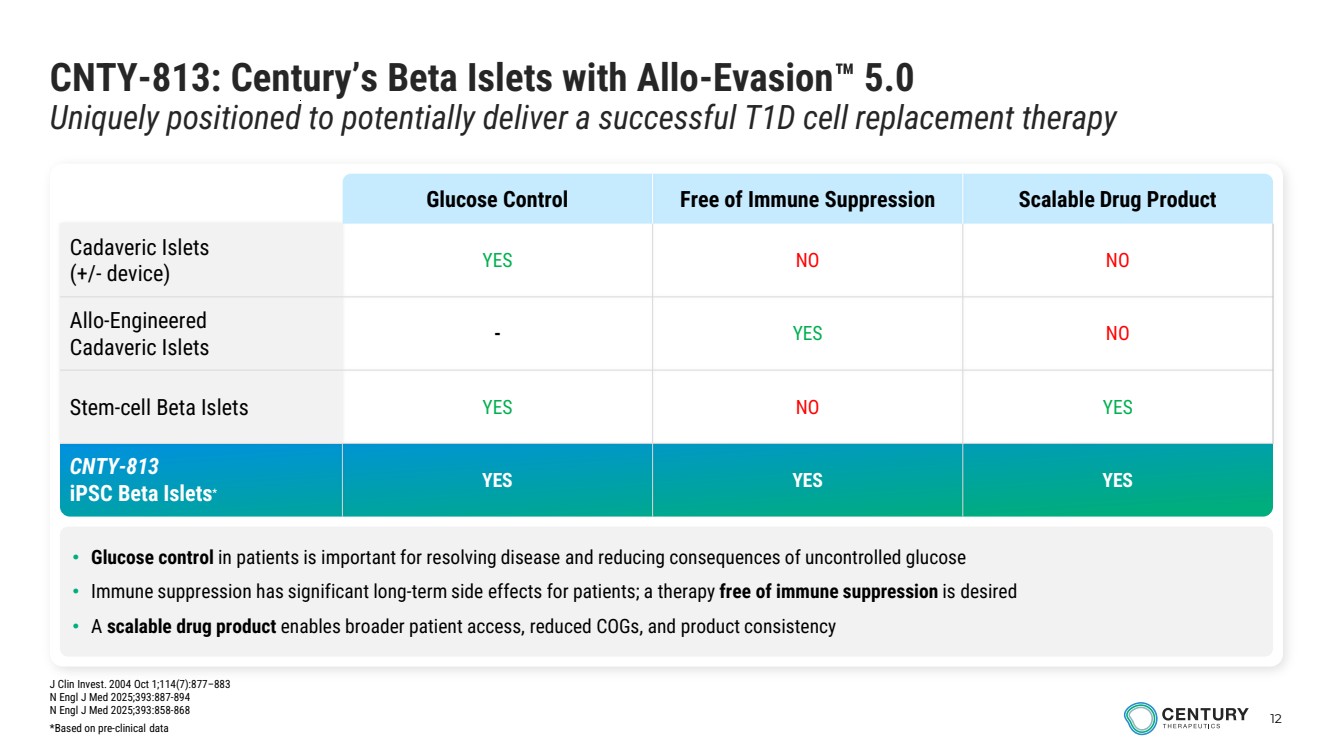
| 12 CNTY-813: Century’s Beta Islets with Allo-Evasion 5.0 Uniquely positioned to potentially deliver a successful T1D cell replacement therapy • Glucose control in patients is important for resolving disease and reducing consequences of uncontrolled glucose • Immune suppression has significant long-term side effects for patients; a therapy free of immune suppression is desired • A scalable drug product enables broader patient access, reduced COGs, and product consistency Glucose Control Free of Immune Suppression Scalable Drug Product Cadaveric Islets (+/- device) YES NO NO Allo-Engineered Cadaveric Islets - YES NO Stem-cell Beta Islets YES NO YES CNTY-813 iPSC Beta Islets* YES YES YES J Clin Invest. 2004 Oct 1;114(7):877–883 N Engl J Med 2025;393:887-894 N Engl J Med 2025;393:858-868 *Based on pre-clinical data |
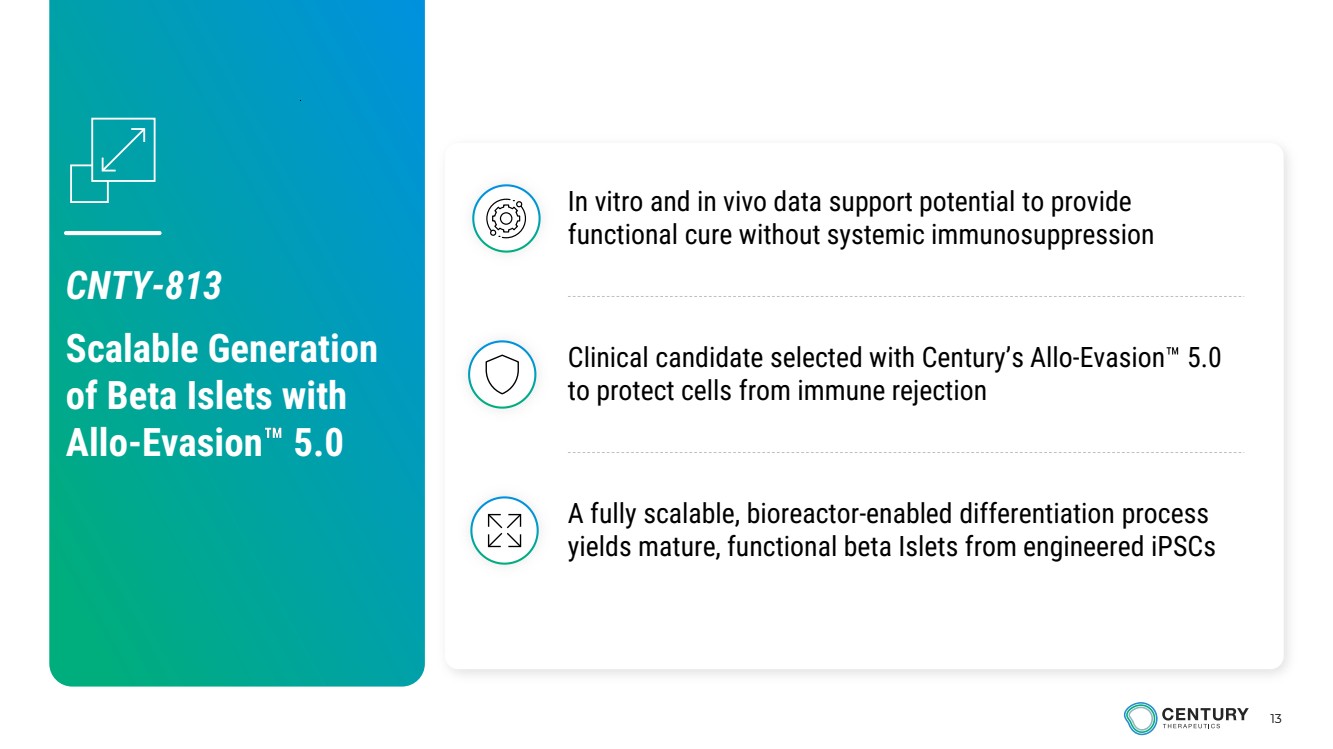
| 13 A fully scalable, bioreactor-enabled differentiation process yields mature, functional beta Islets from engineered iPSCs Clinical candidate selected with Century’s Allo-Evasion 5.0 to protect cells from immune rejection In vitro and in vivo data support potential to provide functional cure without systemic immunosuppression CNTY-813 Scalable Generation of Beta Islets with Allo-Evasion 5.0 |
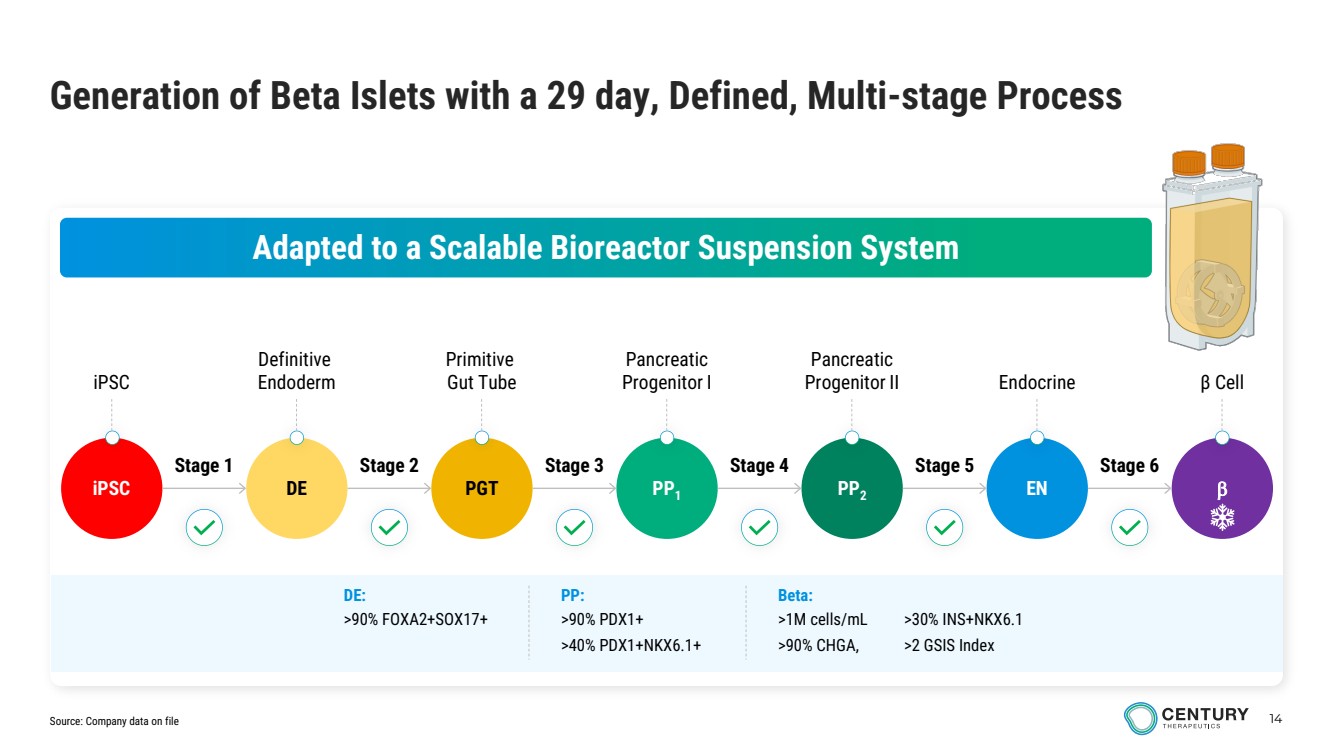
| 14 iPSC Definitive Endoderm Primitive Gut Tube Pancreatic Progenitor I Pancreatic Progenitor II Endocrine β Cell Generation of Beta Islets with a 29 day, Defined, Multi-stage Process Adapted to a Scalable Bioreactor Suspension System iPSC DE PGT PP1 PP2 EN β Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Stage 5 Stage 6 Beta: >1M cells/mL >90% CHGA, >30% INS+NKX6.1 >2 GSIS Index PP: >90% PDX1+ >40% PDX1+NKX6.1+ DE: >90% FOXA2+SOX17+ Source: Company data on file |
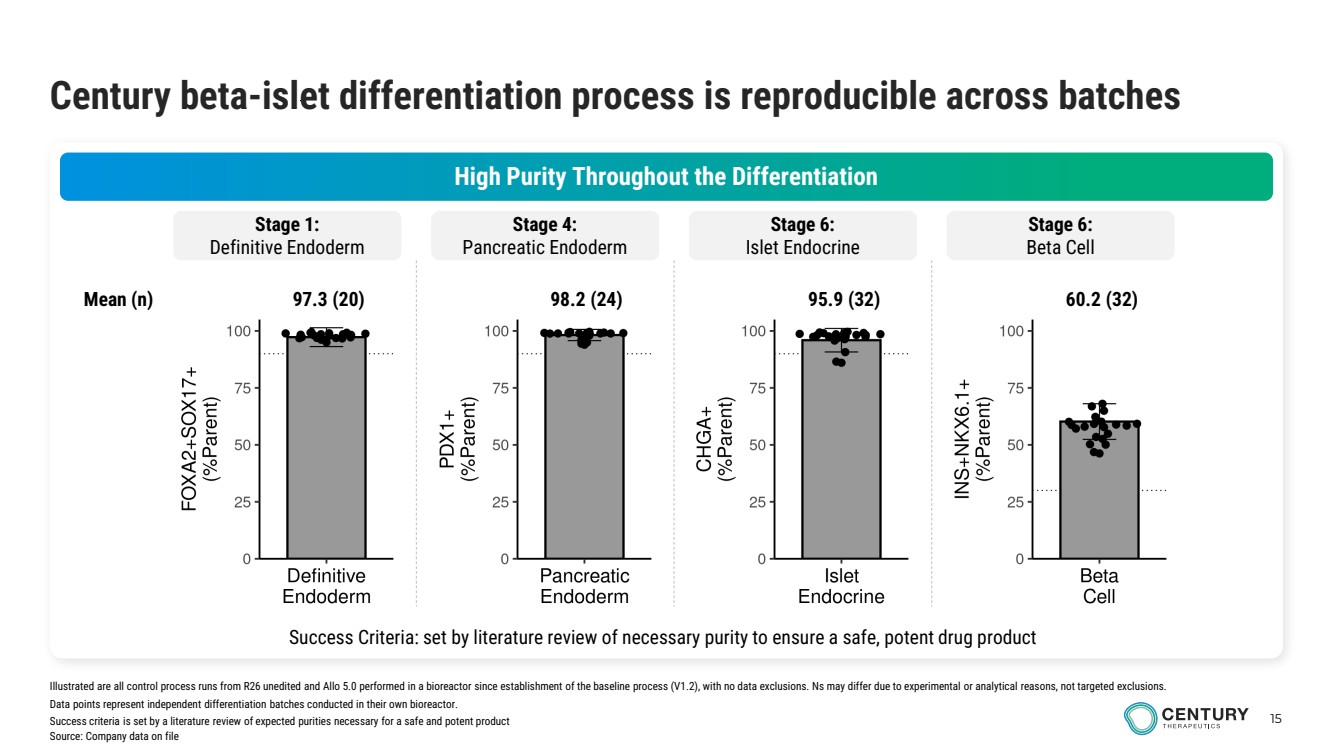
| 15 Century beta-islet differentiation process is reproducible across batches High Purity Throughout the Differentiation Stage 1: Definitive Endoderm Stage 4: Pancreatic Endoderm Stage 6: Islet Endocrine Stage 6: Beta Cell Success Criteria: set by literature review of necessary purity to ensure a safe, potent drug product Mean (n) 97.3 (20) 98.2 (24) 95.9 (32) 60.2 (32) Illustrated are all control process runs from R26 unedited and Allo 5.0 performed in a bioreactor since establishment of the baseline process (V1.2), with no data exclusions. Ns may differ due to experimental or analytical reasons, not targeted exclusions. Data points represent independent differentiation batches conducted in their own bioreactor. Success criteria is set by a literature review of expected purities necessary for a safe and potent product Source: Company data on file |
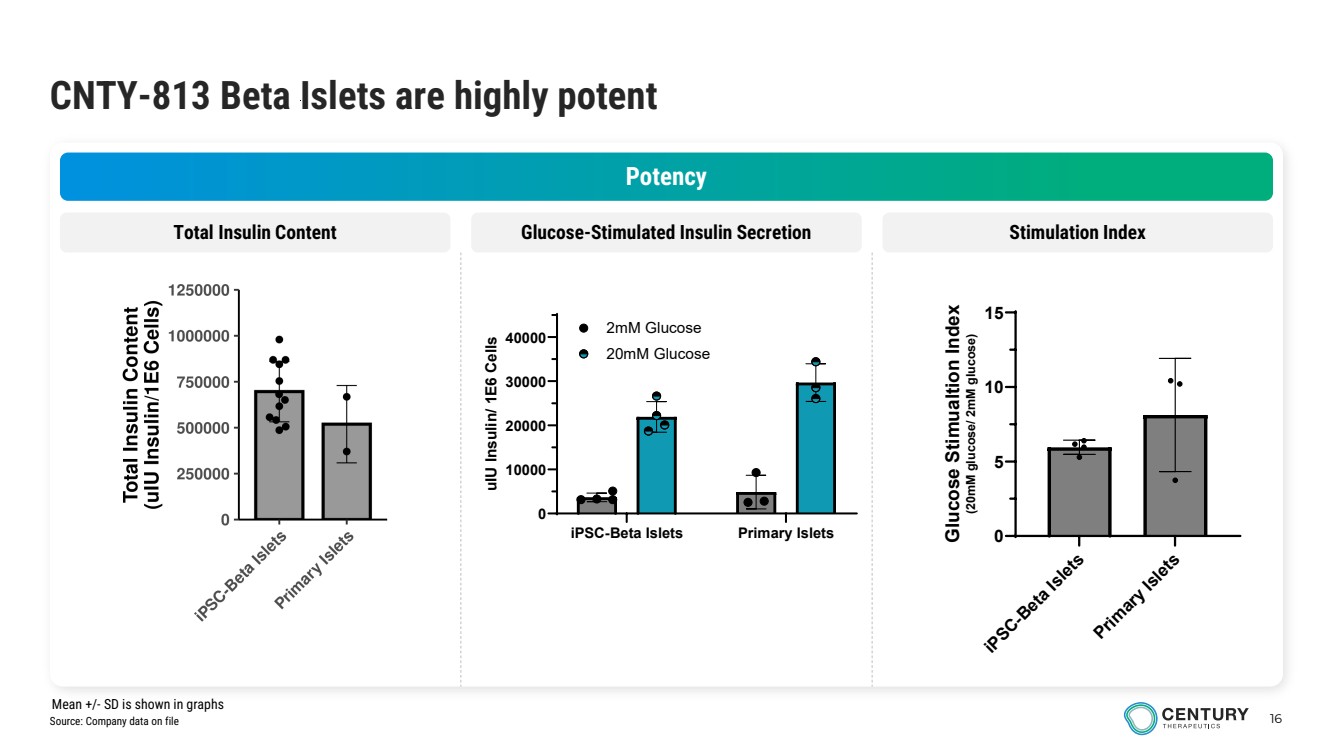
| 16 CNTY-813 Beta Islets are highly potent Potency Total Insulin Content Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion Stimulation Index iPSC-Beta Islets Primary Islets 0 10000 20000 30000 40000 uIU Insulin/ 1E6 Cells 2mM Glucose 20mM Glucose iPSC-Beta Islets Primary Islets 0 5 10 15 Glucose Stimualtion Index (20mM glucose/ 2mM glucose) Source: Company data on file Mean +/- SD is shown in graphs |
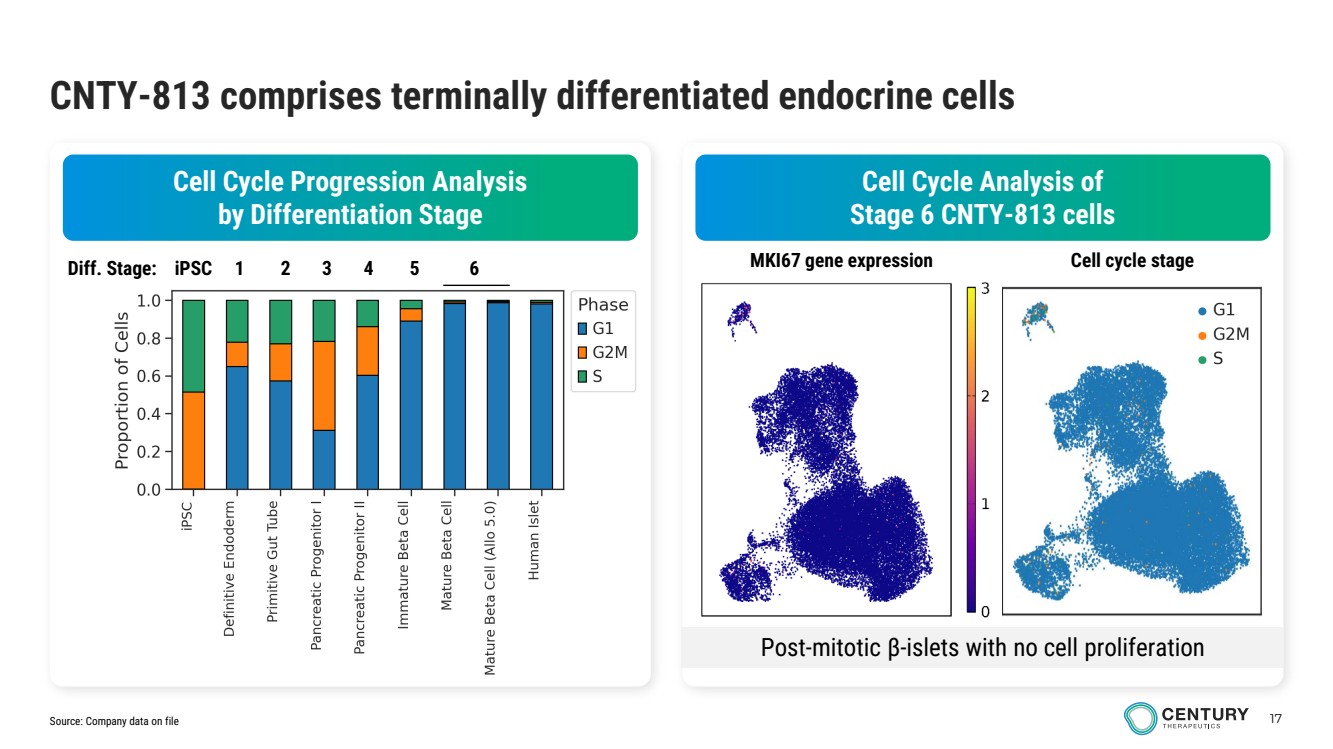
| 17 CNTY-813 comprises terminally differentiated endocrine cells Cell Cycle Analysis of Stage 6 CNTY-813 cells Cell Cycle Progression Analysis by Differentiation Stage Diff. Stage: iPSC 1 2 3 4 5 6 Post-mitotic β-islets with no cell proliferation MKI67 gene expression Cell cycle stage Source: Company data on file |
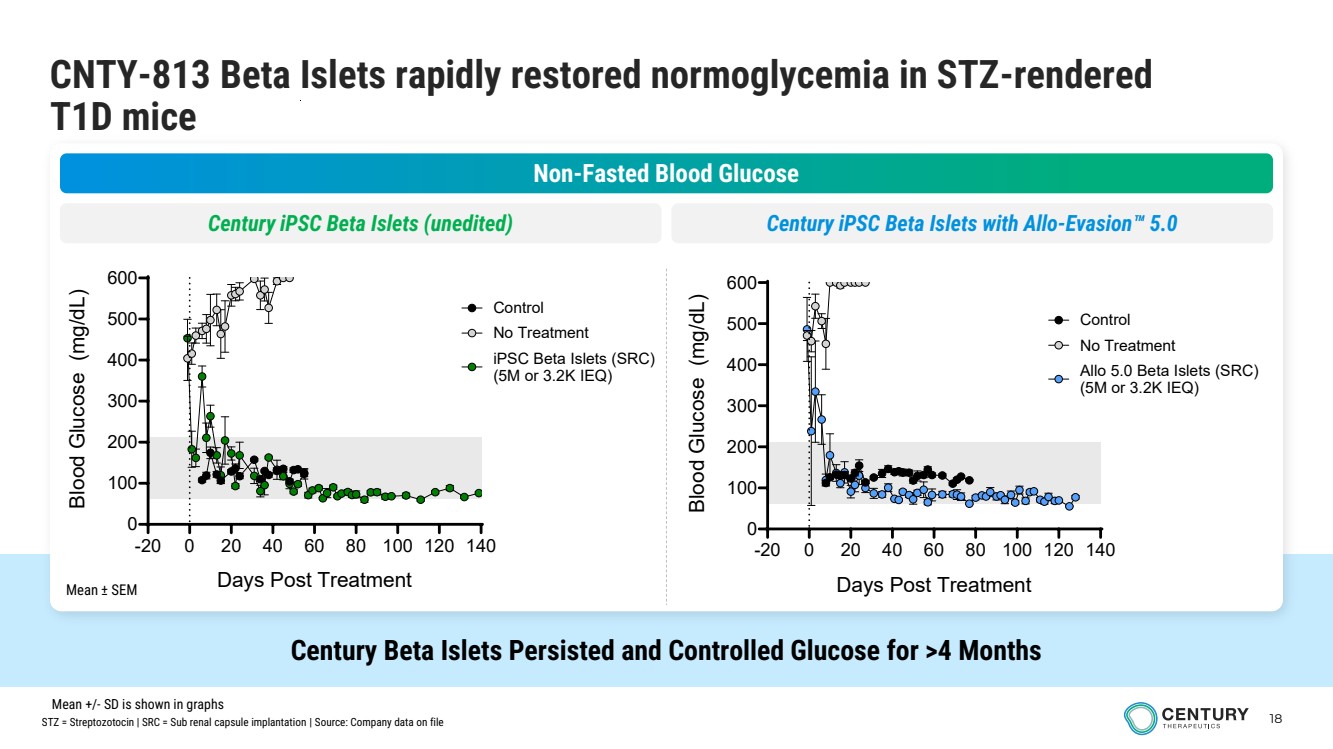
| 18 CNTY-813 Beta Islets rapidly restored normoglycemia in STZ-rendered T1D mice Century Beta Islets Persisted and Controlled Glucose for >4 Months Non-Fasted Blood Glucose Century iPSC Beta Islets (unedited) Century iPSC Beta Islets with Allo-Evasion 5.0 Mean ± SEM -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 Days Post Treatment Blood Glucose (mg/dL) No Treatment iPSC Beta Islets (SRC) (5M or 3.2K IEQ) Control -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 Days Post Treatment Blood Glucose (mg/dL) No Treatment Allo 5.0 Beta Islets (SRC) (5M or 3.2K IEQ) Control STZ = Streptozotocin | SRC = Sub renal capsule implantation | Source: Company data on file Mean +/- SD is shown in graphs |
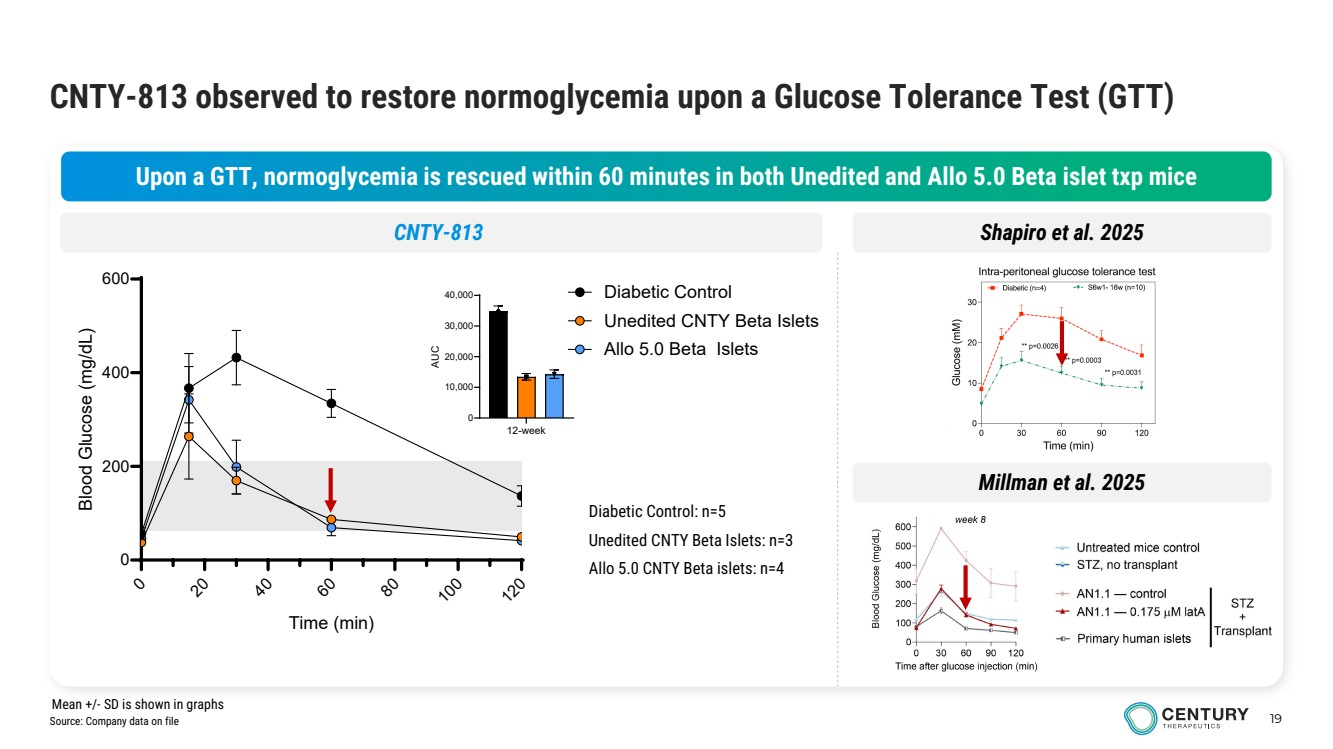
| 19 CNTY-813 observed to restore normoglycemia upon a Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT) Upon a GTT, normoglycemia is rescued within 60 minutes in both Unedited and Allo 5.0 Beta islet txp mice 12-week 0 10,000 20,000 30,000 40,000 AUC Diabetic Control: n=5 Unedited CNTY Beta Islets: n=3 Allo 5.0 CNTY Beta islets: n=4 CNTY-813 Shapiro et al. 2025 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 0 200 400 600 Time (min) Blood Glucose (mg/dL) Diabetic Control Unedited CNTY Beta Islets Allo 5.0 Beta Islets Millman et al. 2025 Source: Company data on file Mean +/- SD is shown in graphs |
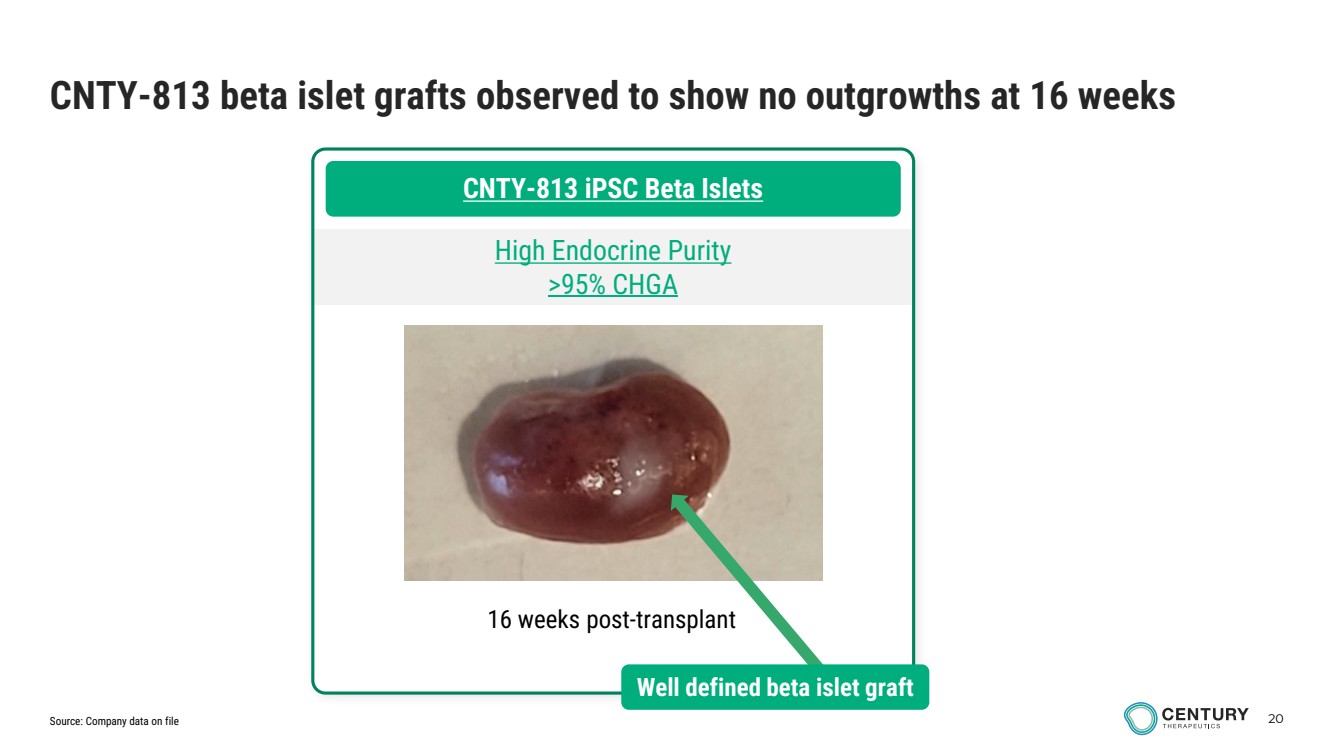
| 20 CNTY-813 beta islet grafts observed to show no outgrowths at 16 weeks CNTY-813 iPSC Beta Islets High Endocrine Purity >95% CHGA 16 weeks post-transplant Well defined beta islet graft Source: Company data on file |
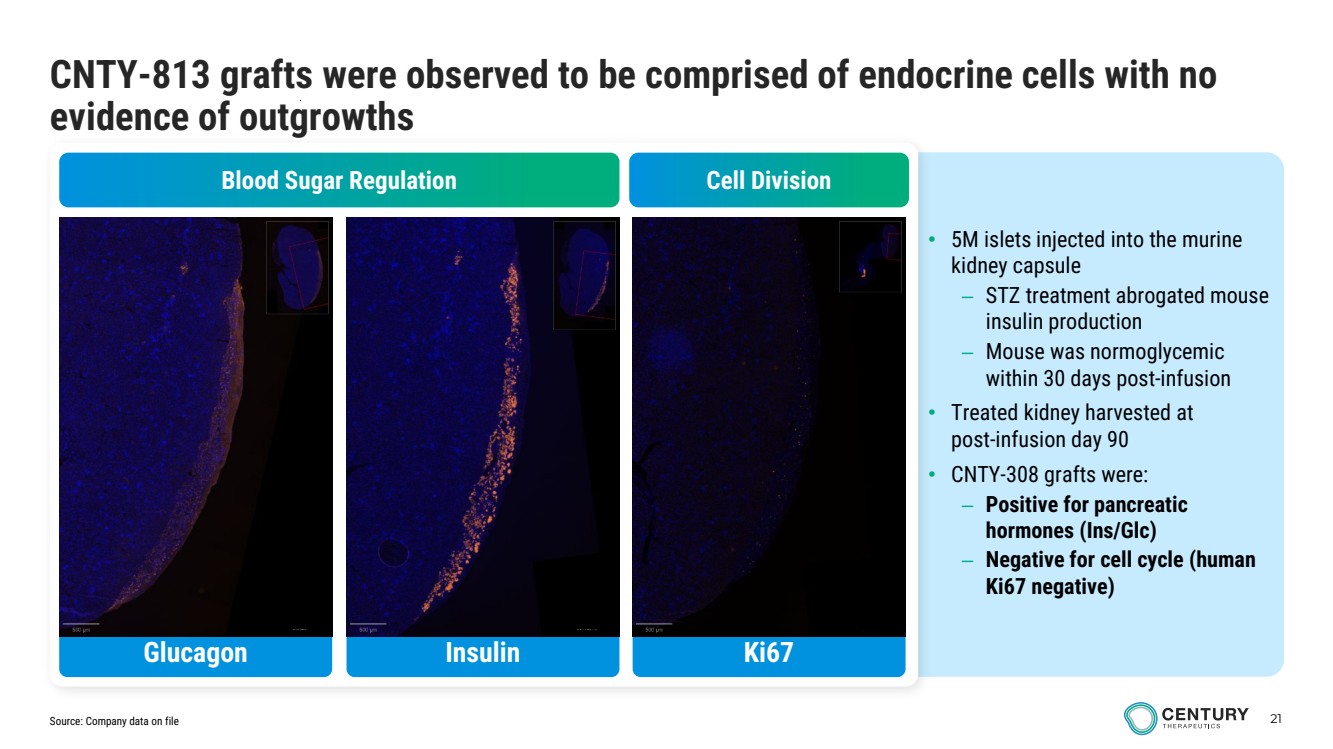
| 21 CNTY-813 grafts were observed to be comprised of endocrine cells with no evidence of outgrowths • 5M islets injected into the murine kidney capsule – STZ treatment abrogated mouse insulin production – Mouse was normoglycemic within 30 days post-infusion • Treated kidney harvested at post-infusion day 90 • CNTY-308 grafts were: – Positive for pancreatic hormones (Ins/Glc) – Negative for cell cycle (human Ki67 negative) Blood Sugar Regulation Cell Division Glucagon Insulin Ki67 Source: Company data on file |
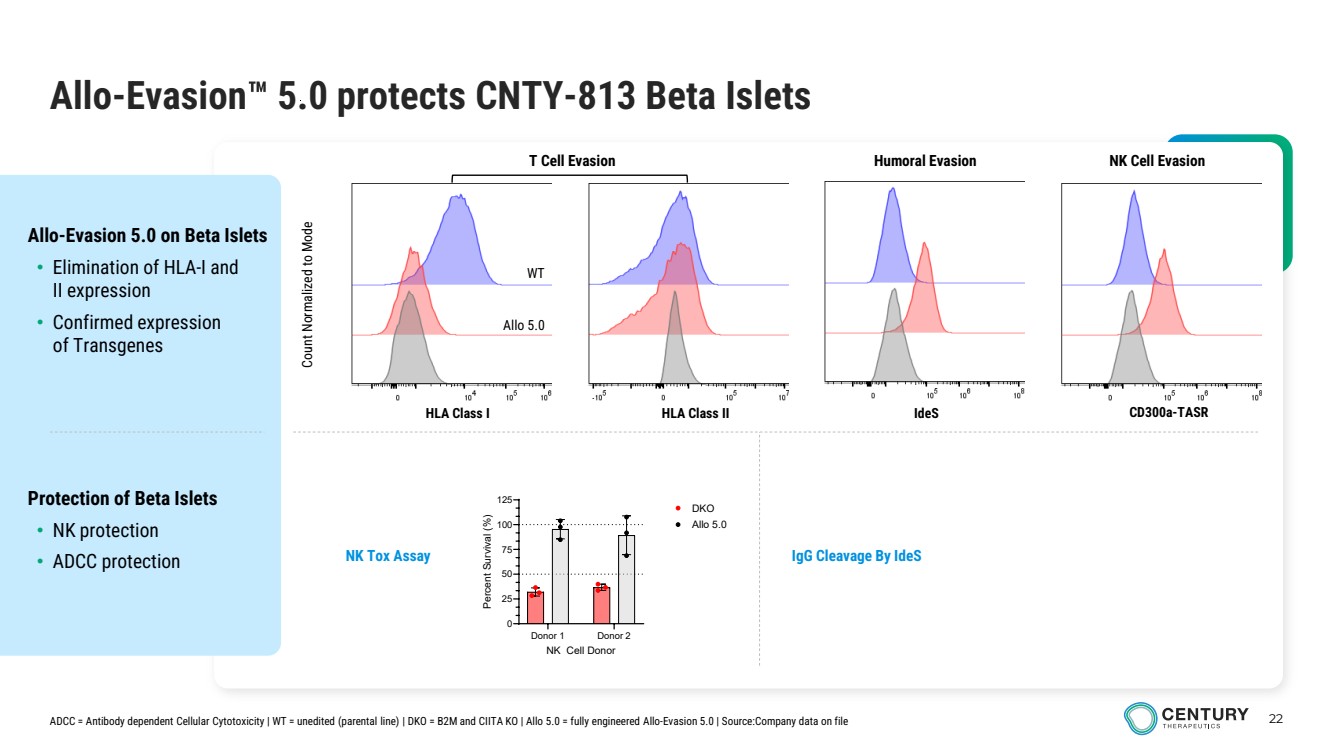
| 22 Allo-Evasion 5.0 protects CNTY-813 Beta Islets Protection of Beta Islets • NK protection • ADCC protection Allo-Evasion 5.0 on Beta Islets • Elimination of HLA-I and II expression • Confirmed expression of Transgenes Count Normalized to Mode HLA Class I HLA Class II IdeS CD300a-TASR T Cell Evasion Humoral Evasion NK Cell Evasion NK Tox Assay WT Allo 5.0 ADCC = Antibody dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity | WT = unedited (parental line) | DKO = B2M and CIITA KO | Allo 5.0 = fully engineered Allo-Evasion 5.0 | Source:Company data on file IgG Cleavage By IdeS Donor 1 Donor 2 0 25 50 75 100 125 NK Cell Donor Percent Survival (%) DKO Allo 5.0 |
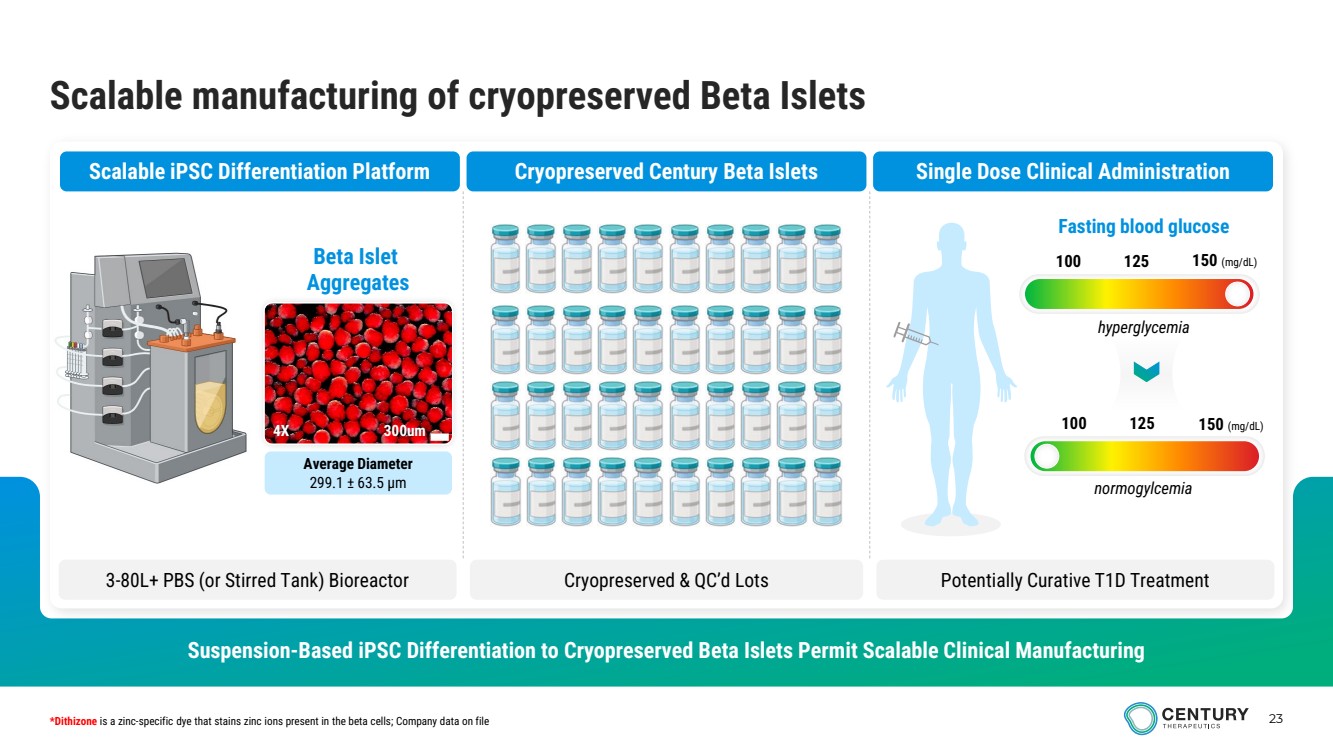
| 23 Scalable manufacturing of cryopreserved Beta Islets Suspension-Based iPSC Differentiation to Cryopreserved Beta Islets Permit Scalable Clinical Manufacturing Scalable iPSC Differentiation Platform Cryopreserved Century Beta Islets Single Dose Clinical Administration 3-80L+ PBS (or Stirred Tank) Bioreactor Cryopreserved & QC’d Lots Potentially Curative T1D Treatment Average Diameter 299.1 ± 63.5 μm Beta Islet Aggregates 4X 300um 100 125 150 (mg/dL) Fasting blood glucose 100 125 150 (mg/dL) *Dithizone is a zinc-specific dye that stains zinc ions present in the beta cells; Company data on file hyperglycemia normogylcemia |
| Autoimmune Disease Programs |
| 25 Addressing significant unmet need in autoimmunity with allogeneic CAR iT and CAR iNK cells • Limited but encouraging POC data2 with CAR-NK therapy support continued development in autoimmune disease • CARAMEL IST with CNTY-101 currently enrolling patients across four indications • Autologous CAR T cell therapies are showing compelling safety and efficacy across a broad range of autoimmune diseases1 • Emerging positive CAR-T data supports advancing the development of more accessible CAR iT cells • CNTY-308 expected to enter clinic in 2026 Clinical data from B-cell-targeted cell therapies in autoimmune disease support the MoA and development of CAR iT and CAR iNK therapies CNTY-308 (CAR iT) CNTY-101 (CAR iNK) 1. Muller 2024 doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2308917; Nordmann-Gomes 2025 doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2025.152786 2. Gao 2025 EULAR Abstract DOI: 10.1016/j.ard.2025.05.396; Wang 2025 doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2025.05.038 |
| CNTY-308 CD4+/CD8+ αβ iT-cell with Allo-Evasion 5.0 |
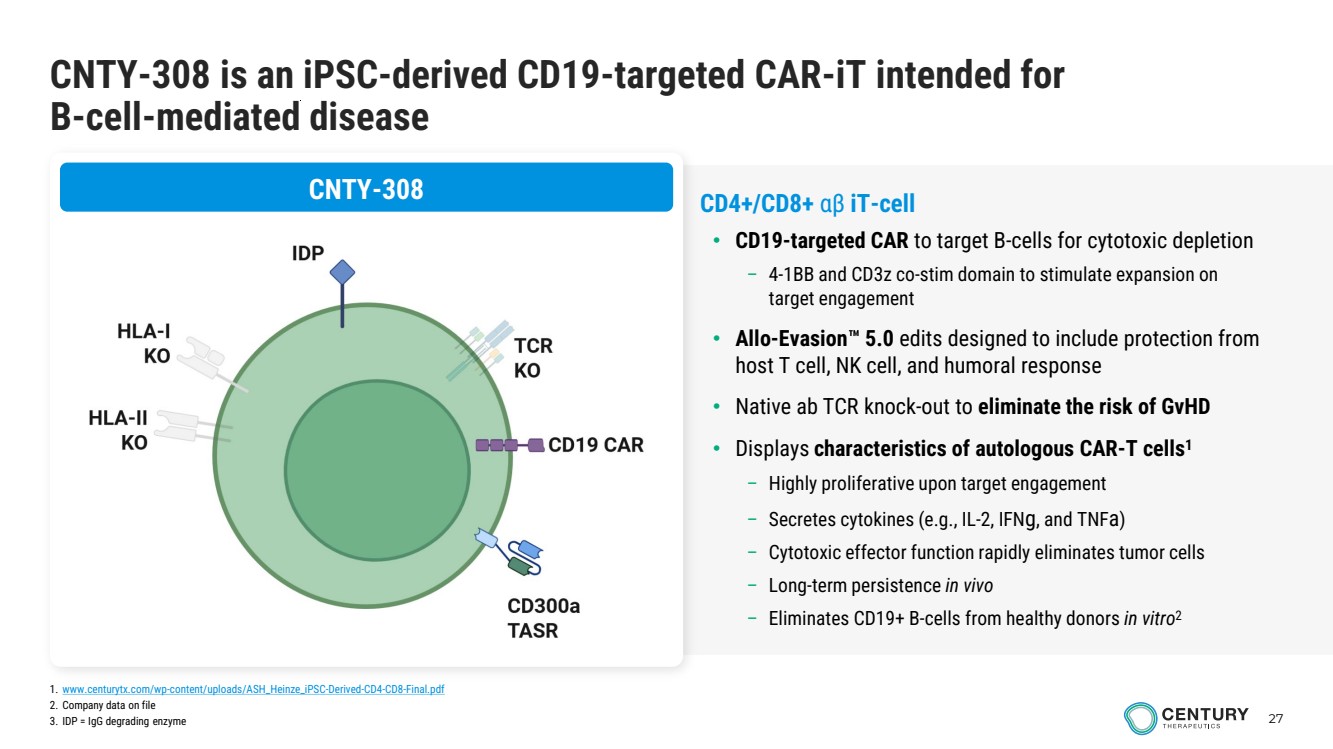
| 27 CNTY-308 is an iPSC-derived CD19-targeted CAR-iT intended for B-cell-mediated disease CNTY-308 CD4+/CD8+ αβ iT-cell • CD19-targeted CAR to target B-cells for cytotoxic depletion – 4-1BB and CD3z co-stim domain to stimulate expansion on target engagement • Allo-Evasion 5.0 edits designed to include protection from host T cell, NK cell, and humoral response • Native ab TCR knock-out to eliminate the risk of GvHD • Displays characteristics of autologous CAR-T cells1 – Highly proliferative upon target engagement – Secretes cytokines (e.g., IL-2, IFNg, and TNFa) – Cytotoxic effector function rapidly eliminates tumor cells – Long-term persistence in vivo – Eliminates CD19+ B-cells from healthy donors in vitro2 1. www.centurytx.com/wp-content/uploads/ASH_Heinze_iPSC-Derived-CD4-CD8-Final.pdf 2. Company data on file 3. IDP = IgG degrading enzyme |
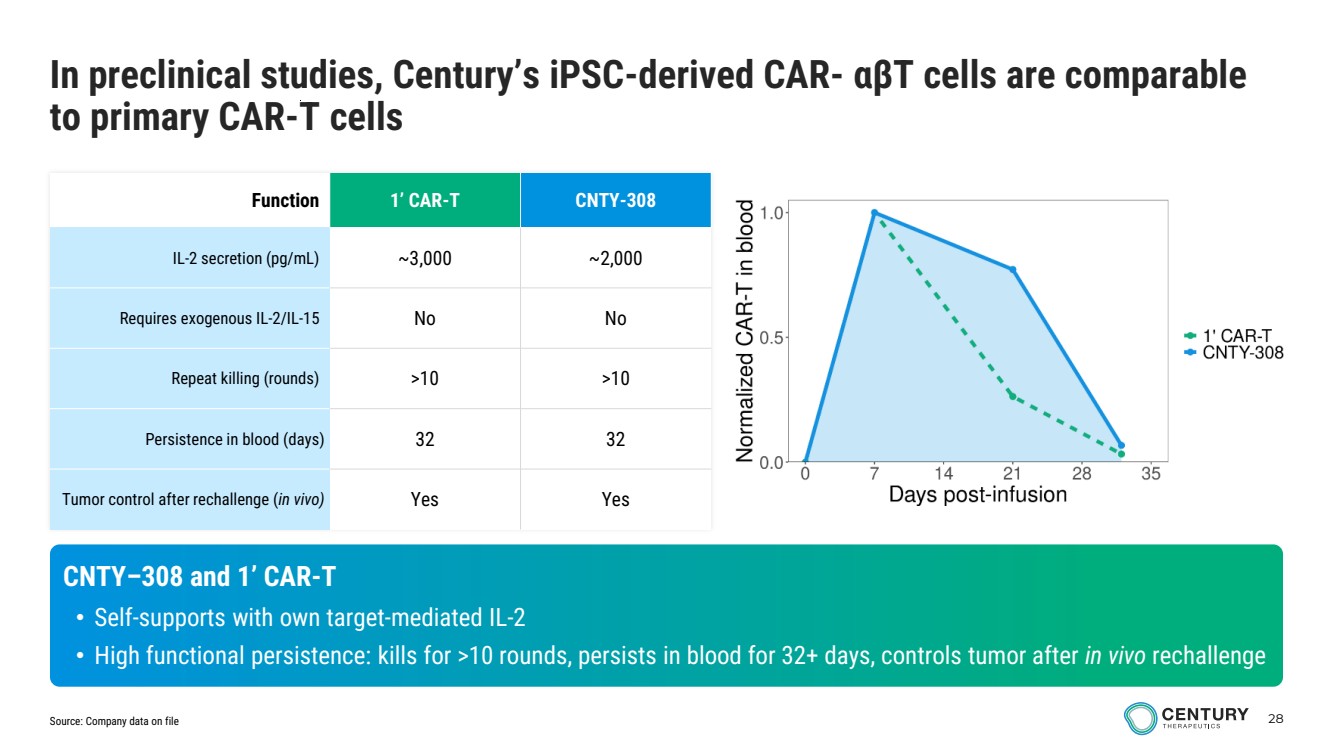
| 28 Function 1’ CAR-T CNTY-308 IL-2 secretion (pg/mL) ~3,000 ~2,000 Requires exogenous IL-2/IL-15 No No Repeat killing (rounds) >10 >10 Persistence in blood (days) 32 32 Tumor control after rechallenge (in vivo) Yes Yes CNTY–308 and 1’ CAR-T • Self-supports with own target-mediated IL-2 • High functional persistence: kills for >10 rounds, persists in blood for 32+ days, controls tumor after in vivo rechallenge In preclinical studies, Century’s iPSC-derived CAR- αβT cells are comparable to primary CAR-T cells Source: Company data on file |
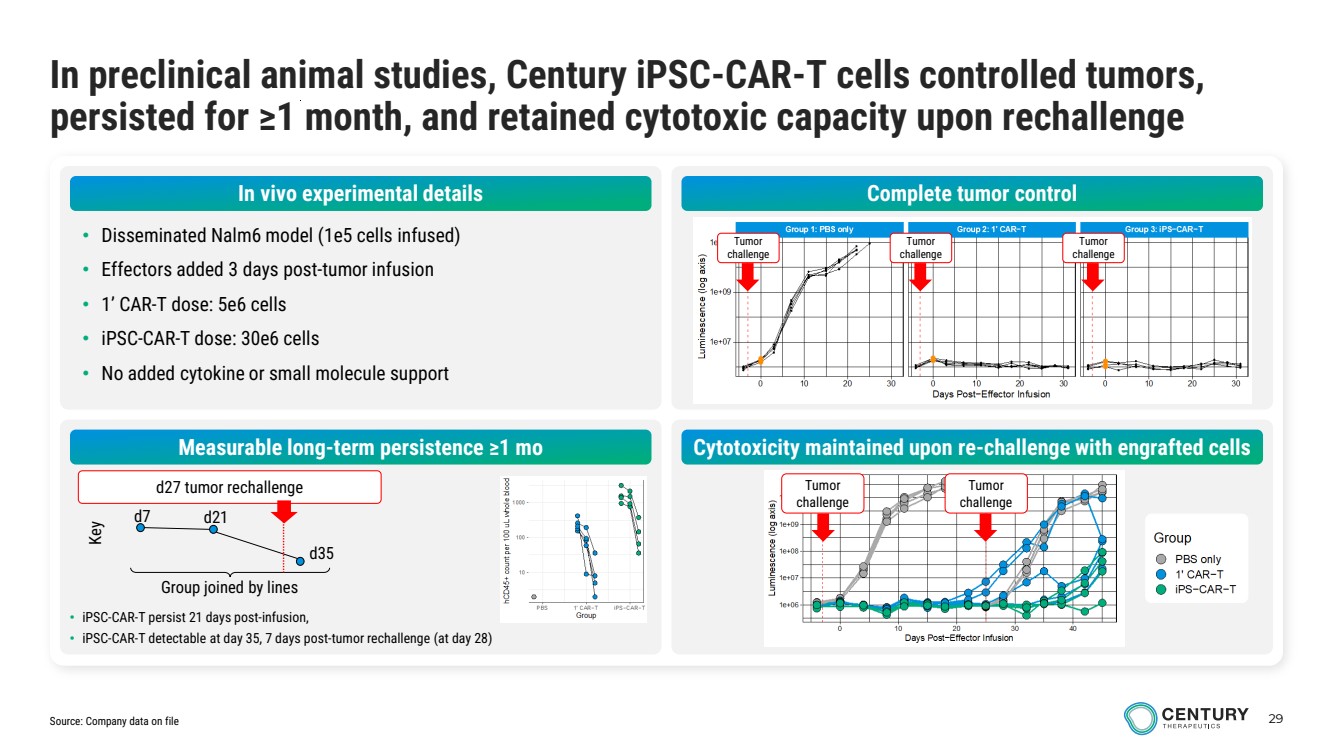
| 29 In preclinical animal studies, Century iPSC-CAR-T cells controlled tumors, persisted for ≥1 month, and retained cytotoxic capacity upon rechallenge • Disseminated Nalm6 model (1e5 cells infused) • Effectors added 3 days post-tumor infusion • 1’ CAR-T dose: 5e6 cells • iPSC-CAR-T dose: 30e6 cells • No added cytokine or small molecule support Complete tumor control Measurable long-term persistence ≥1 mo Cytotoxicity maintained upon re-challenge with engrafted cells Tumor challenge Tumor challenge Tumor challenge Tumor challenge Tumor challenge • iPSC-CAR-T persist 21 days post-infusion, • iPSC-CAR-T detectable at day 35, 7 days post-tumor rechallenge (at day 28) Group joined by lines d7 d21 d35 Key d27 tumor rechallenge Source: Company data on file In vivo experimental details |
| CNTY-101 CAR-iNK cell therapy with Allo-Evasion |
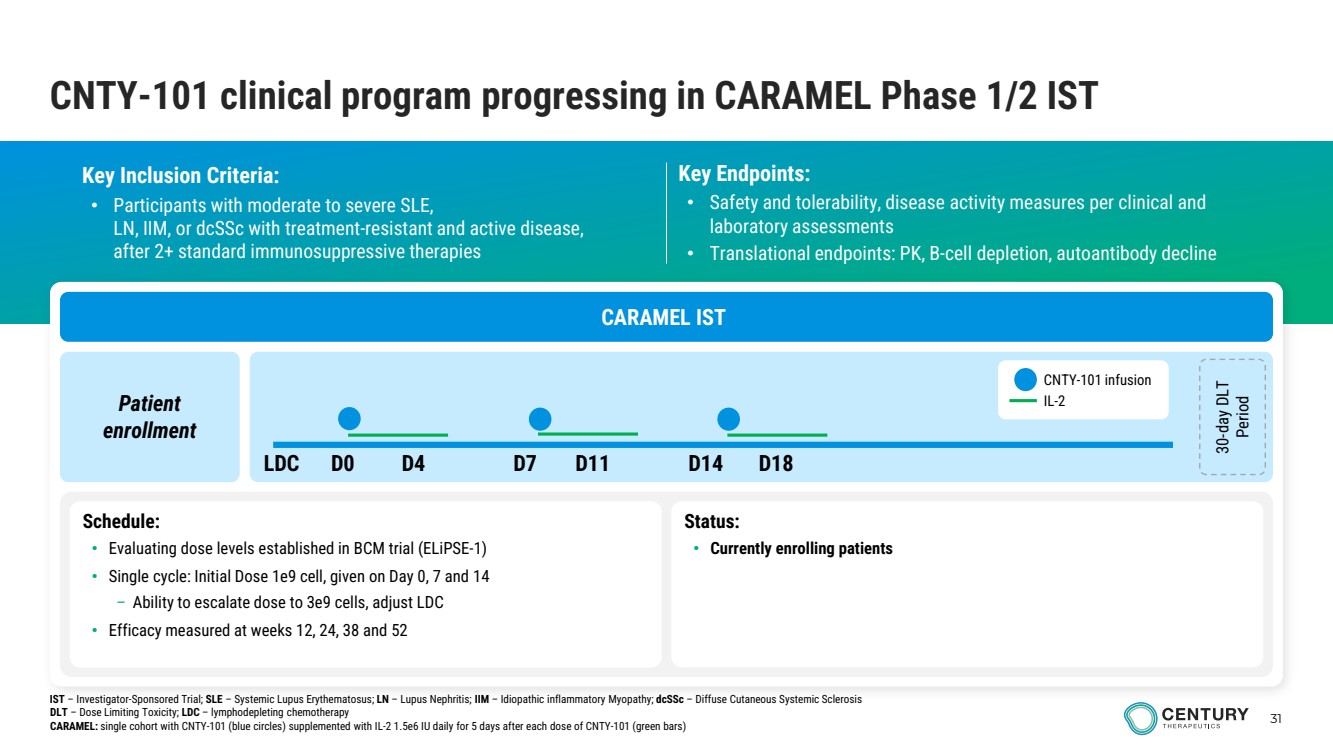
| 31 CNTY-101 clinical program progressing in CARAMEL Phase 1/2 IST Key Inclusion Criteria: • Participants with moderate to severe SLE, LN, IIM, or dcSSc with treatment-resistant and active disease, after 2+ standard immunosuppressive therapies Key Endpoints: • Safety and tolerability, disease activity measures per clinical and laboratory assessments • Translational endpoints: PK, B-cell depletion, autoantibody decline CARAMEL IST Patient enrollment 30-day DLT Period Schedule: • Evaluating dose levels established in BCM trial (ELiPSE-1) • Single cycle: Initial Dose 1e9 cell, given on Day 0, 7 and 14 – Ability to escalate dose to 3e9 cells, adjust LDC • Efficacy measured at weeks 12, 24, 38 and 52 Status: • Currently enrolling patients CNTY-101 infusion IL-2 LDC D0 D4 D7 D11 D14 D18 IST – Investigator-Sponsored Trial; SLE – Systemic Lupus Erythematosus; LN – Lupus Nephritis; IIM – Idiopathic inflammatory Myopathy; dcSSc – Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis DLT – Dose Limiting Toxicity; LDC – lymphodepleting chemotherapy CARAMEL: single cohort with CNTY-101 (blue circles) supplemented with IL-2 1.5e6 IU daily for 5 days after each dose of CNTY-101 (green bars) |
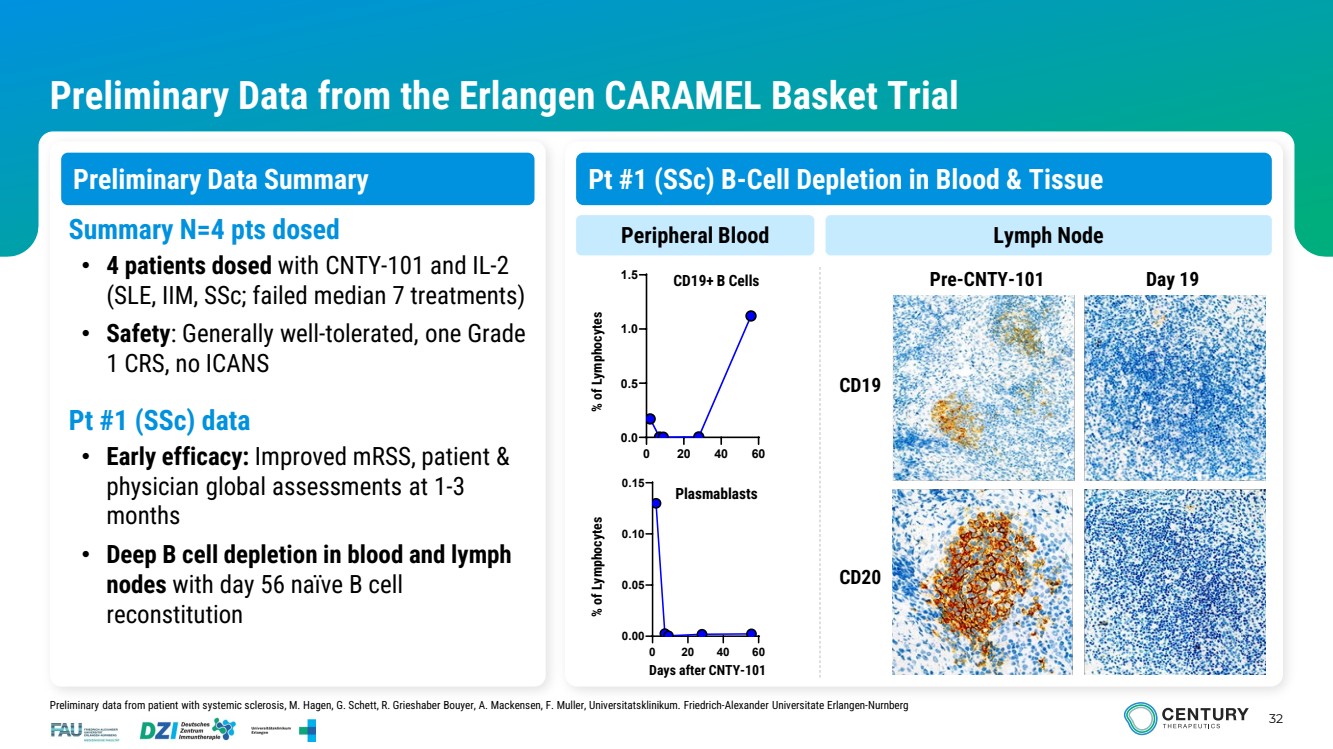
| 32 Preliminary Data from the Erlangen CARAMEL Basket Trial Preliminary Data Summary 0 20 40 60 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 0 20 40 60 0.00 0.05 0.10 0.15 CD19 Pre-CNTY-101 Day 19 Summary N=4 pts dosed Peripheral Blood Lymph Node • 4 patients dosed with CNTY-101 and IL-2 (SLE, IIM, SSc; failed median 7 treatments) • Safety: Generally well-tolerated, one Grade 1 CRS, no ICANS Pt #1 (SSc) data • Early efficacy: Improved mRSS, patient & physician global assessments at 1-3 months • Deep B cell depletion in blood and lymph nodes with day 56 naïve B cell reconstitution Plasmablasts CD19+ B Cells CD20 Days after CNTY-101 % of Lymphocytes % of Lymphocytes Preliminary data from patient with systemic sclerosis, M. Hagen, G. Schett, R. Grieshaber Bouyer, A. Mackensen, F. Muller, Universitatsklinikum. Friedrich-Alexander Universitate Erlangen-Nurnberg Pt #1 (SSc) B-Cell Depletion in Blood & Tissue |
| Corporate Summary |
| 34 Established in-house manufacturing from development to launch Quality product at disruptive scale and cost of goods • Built-for-purpose 53,000 ft2 cGMP facility • Produced and released clinical product for US and EU • Key leaders each with 1–2 decades of cell therapy manufacturing expertise, from leading commercial cell therapies • In-house team facilitates aligned priorities, learnings, faster product iteration for efficiency, speed, and product quality • Builds and protects proprietary know-how • Optionality with redundant sites (in-house, active CDMO) • Consistency: Control of manufacturing and single-donor master-cell-bank over product lifetime for batch-to-batch reproducibility • Increased cell fitness: Differentiated immune cells do not undergo excessive expansion cycles which often result in cell exhaustion • Product homogeneity: Clonal origin enables a well-characterized product • Potential to manufacture at antibody-like scale: Scalable platforms and optimized processes to maximize yield, reduce COGs, and meet demand Century platform and in-house manufacturing: Pathway to scalable, profitable cell therapy |
| Cell Foundry and Allo-Evasion Technology High Impact Programs Focused on Execution Century Therapeutics Today © 2025 35 Cell foundry generates fully functional cells at scale • Key developmental insights allow directed differentiation of cells that function like primary cells, such as beta Islet cells and CD4+/CD8+ αβ T cells Leaders in immune evasion engineering • Allo-Evasion allows cells to co-exist with a patient’s immune system • Enables enhanced persistence and potential for re-dosing of therapy Advancing lead iPSC derived cell therapies with Allo-Evasion 5.0 toward the clinic • CNTY-813 in IND-enabling studies with potential for functional cure in Type 1 Diabetes • CNTY-308 in IND-enabling studies for treatment of B-cell-mediated diseases • Patient enrollment ongoing for CNTY-101 in Phase 1/2 CARAMEL IST in autoimmune disease Cash runway extended beyond planned key clinical milestones • CNTY-813 IND submission planned for 2026 with initial clinical data expected 2027 • CNTY-308 αβ T cell program expected to enter the clinic in 2026 • CNTY-101 preliminary clinical data from Phase 1/2 CARAMEL IST expected in 2026 |
| www.centurytx.com |